VIEWS AND PERSPECTIVES
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 077403.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20250313
Abstract +
High-temperature superconductivity, a fundamental topic in condensed matter physics, presents one of the critical scientific challenges of this century. The potential for breakthroughs in this field not only promises to reveal numerous novel quantum phenomena and deepen our understanding of quantum many-body physics but also to significantly drive advancements in experimental techniques, theories, and methodologies in probing correlated quantum systems. More importantly, as a non-perturbative quantum system, high-temperature superconductivity offers an ideal platform and a crucial driving force for systematically establishing non-perturbative quantum field theory. Currently, research on high-temperature superconductivity stands at a critical turning point. Achieving significant breakthroughs requires the development of cutting-edge detection technologies built upon novel concepts, the establishment of innovative theoretical frameworks and methodologies, and insightful elucidation of the physical pictures revealed by experimental findings. Such extensive exploration is vital for unveiling fundamental relationships and identifying the governing principles. By integrating these efforts, we can gain profound insights into the mechanisms of high-temperature superconductivity and significantly expand the horizons of quantum many-body theory.
SPECIAL TOPIC—Technology of magnetic resonance
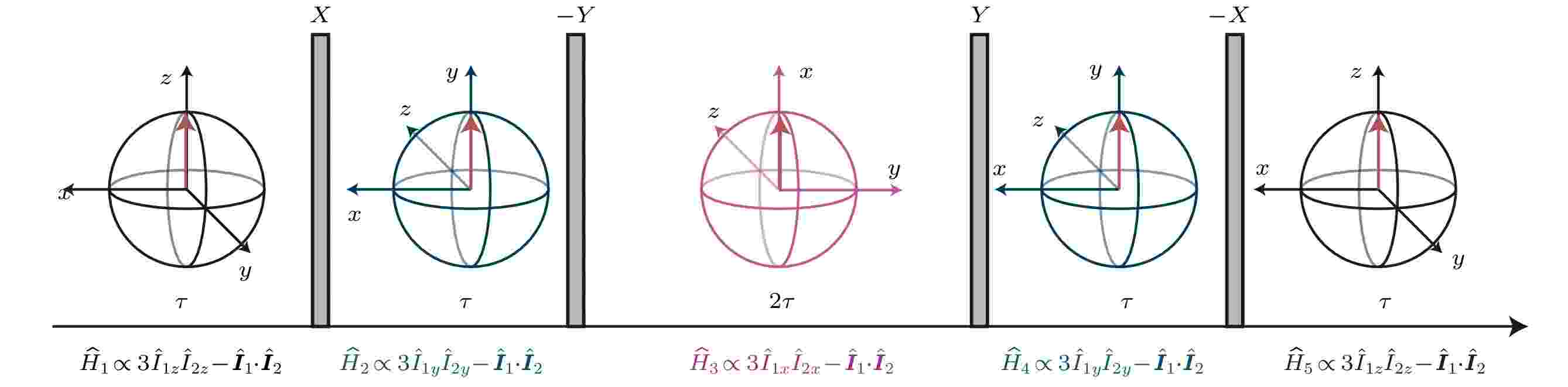
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 077402.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241709
Abstract +
Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) has emerged as an important technique for material characterization, finding extensive applications across a diverse range of disciplines including physics, materials science, chemistry, and biology. Its utility stems from the ability to probe the local atomic environments and molecular dynamics within solid materials, which provides information on the composition of the material. In recent years, the scope of solid-state NMR has expanded into the realm of quantum information science and technology, where its abundant many-body interactions pulse control methodologies make it have significant research value and application potential. This paper offers a comprehensive overview of the research objects and theoretical underpinnings of solid-state NMR, delving into the critical nuclear spin interaction mechanisms and their corresponding Hamiltonian forms. These interactions, which include dipolar coupling, chemical shift anisotropy, and quadrupolar interactions, are fundamental to the interpretation of NMR spectra and the understanding of material properties at the atomic level. Moreover, the paper introduces typical dynamical control methods employed in the manipulation of solid-state nuclear spins. Techniques such as dynamical decoupling, which mitigates the effects of spin-spin interactions to extend coherence times, and magic-angle spinning, which averages out anisotropic interactions to yield high-resolution spectra. These methods are essential for enhancing the sensitivity and resolution of NMR experiments, enabling the extraction of detailed structural and dynamic information from complex materials. Then we introduce some recent advancements in quantum control based on solid-state NMR, such as nuclear spin polarization enhancement techniques, which include dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) and cross polarization (CP), significantly boost the sensitivity of NMR measurements. Additionally, the control techniques of Floquet average Hamiltonians are mentioned, showcasing their role in the precise manipulation of quantum states and the realization of quantum dynamics. Finally, the paper presents a series of seminal research works that illustrate the application of solid-state NMR quantum control technologies in the field of quantum simulation. These studies demonstrate how solid-state NMR can be leveraged to simulate and investigate quantum many-body systems, providing valuable insights into quantum phase transitions, entanglement dynamics, and other phenomena relevant to quantum information science. By bridging the gap between fundamental research and practical applications, solid-state NMR continues to play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of quantum materials and technologies.
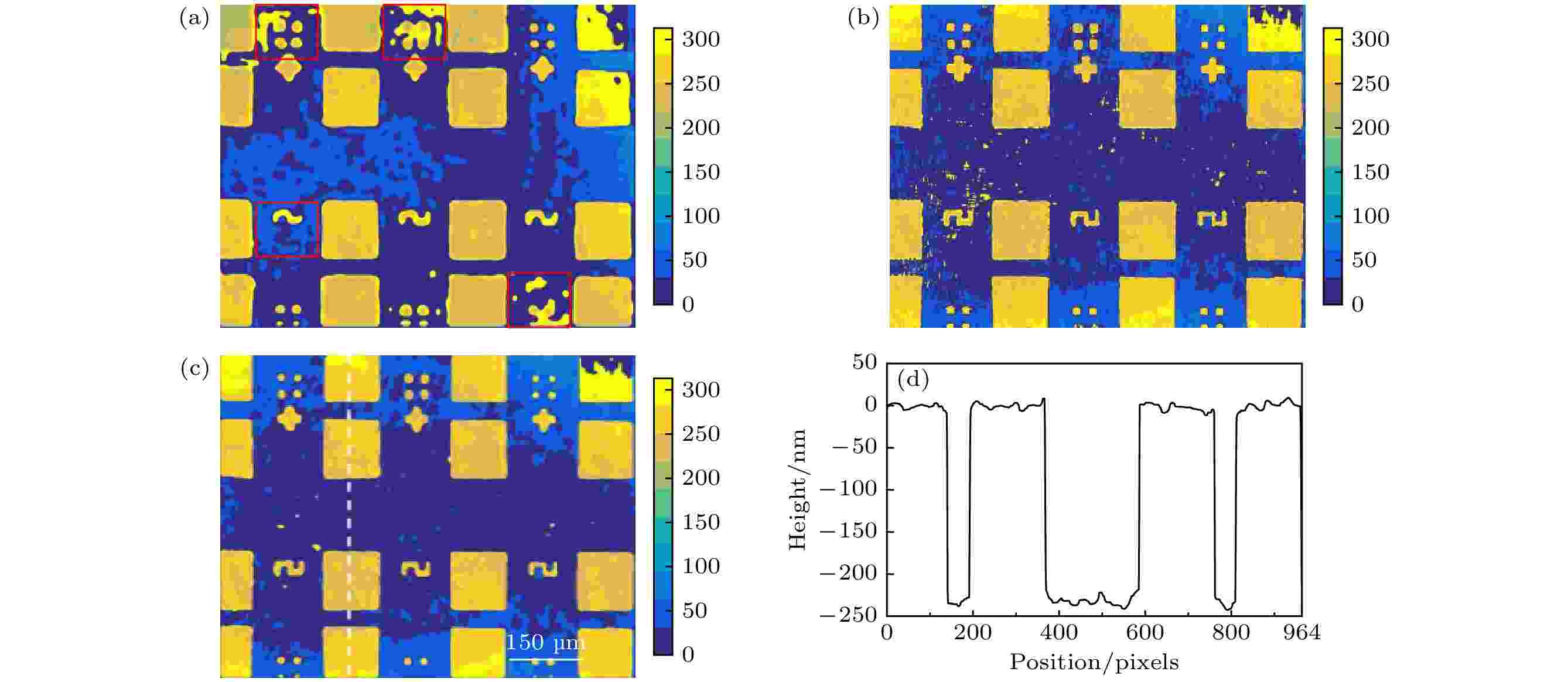
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 078701.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241759
Abstract +
SPECIAL TOPIC—Quantum information processing
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 070301.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20250029
Abstract +
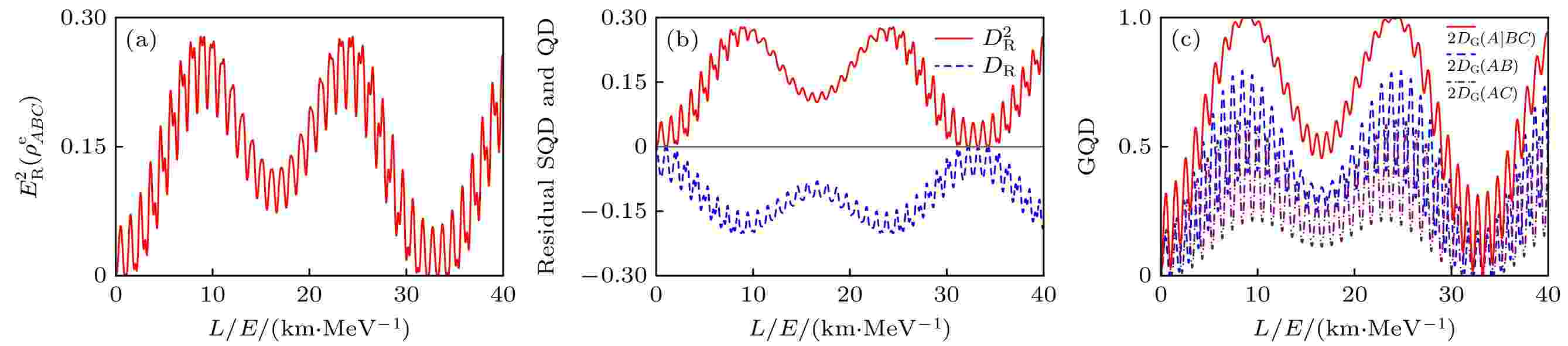
Studying the quantum resources of neutrino oscillations is a topic worth exploring. This review mainly introduces the use of quantum resource theory to characterize the quantum resource characteristics of three-flavor neutrino oscillations, and the specific evolutionary patterns of different entanglement measures in three-flavor neutrino oscillations. In addition, by comparing the cases of different entanglement evolutions, the optimal method of quantifying entanglement in three-flavor neutrino oscillations can be obtained. Moreover, this review also focuses on the quantifying the quantumness of neutrino oscillation observed experimentally by using the l1-norm of coherence. The maximal coherence is observed in the neutrino source from the KamLAND reactor. Furthermore, we examine the violation of the Mermin inequality and Svetlichny inequality to study the nonlocality in three-flavor neutrino oscillations. It is shown that even though the genuine tripartite nonlocal correlation is usually existent, it can disappear within specific time regions. In addition, this review also presents the trade-off relations in the quantum resource theory of three-flavor neutrino oscillations, mainly based on monogamy relations and complete complementarity relations. It is hoped that this review can bring inspiration to the development of this field.
SPECIAL TOPIC—Quantum transport in topological materials and devices
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 076401.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20250122
Abstract +
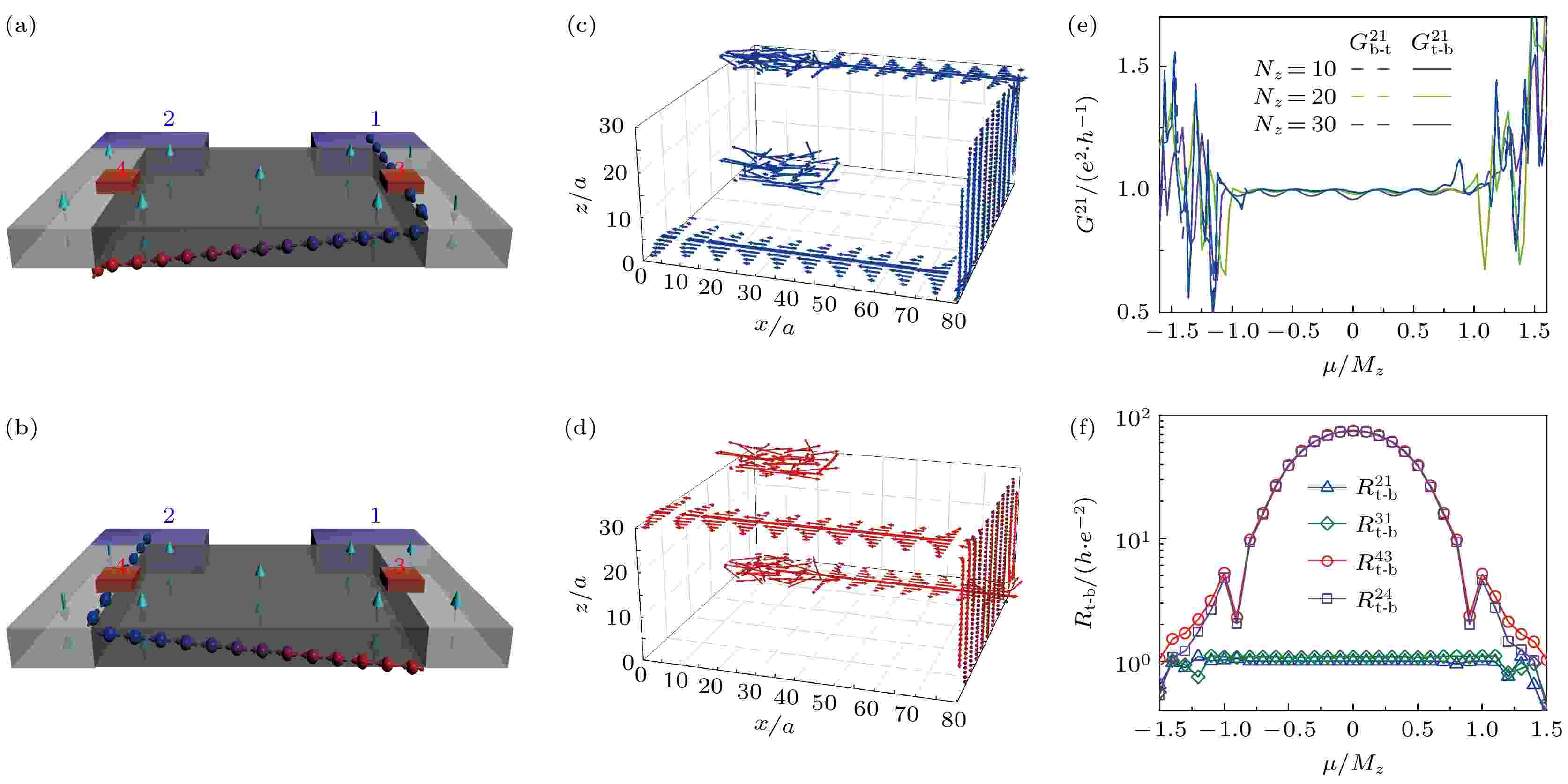
With the development of the topological theory, it is believed that topological states originate from topologically protected interfaces in condensed matter systems. Significantly, by adjusting the topological interfaces, one can manipulate the transport properties of a sample, thereby possessing distinct features. This paper briefly reviews recent progresses about topological interfaces and their potential applications in quantum devices. In the first part, we expound the fundamental ideas about topological interfaces in disordered Chern insulators. Based on their transport properties, the designs of programmable circuits and logical gates are also clarified. These designs significantly improve the utilization of sample compared with topological surface devices. The second part focuses on the topological interfaces in three-dimensional systems, which exhibits the layertronics of the interfaces. We present axion insulator MnBi2Te4 as a typical example, and the realization of the basic layertronics devices is proposed. Finally, this work summarizes the advantages of topological interface devices and proposes some potential breakthroughs to be achieved in this field.
SPECIAL TOPIC——Quantum transport in topological materials and devices

COVER ARTICLE
2025, 74 (7): 077401.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241672
Abstract +
The hybrid system of low-dimensional electronic materials and superconducting materials has always been an attractive structure for studying mesoscopic transport and low-dimensional superconducting properties. Low-dimensional structures with strong spin-orbit coupling exhibit rich quantum phenomena combined with superconducting macroscopic quantum states. Therefore it has become an important platform for exploring novel physical properties and developing new topological quantum devices. The construction of hybrid superconducting devices based on high-quality one-dimensional electronic materials and the exploration of interfacial quantum transport phenomena have become the research frontiers. It is crucial to understand the characteristic scattering mechanisms and quantum transport processes in these hybrid systems on a nanoscale. The study of the coupling mechanism between the charge state and the topological localized state, and the experimental probe of the intrinsic transport properties of the topological states are the key issues, which enable the development of the new principles and methods for novel superconducting nano electronic devices and topological quantum devices. Due to the competition of multiple energy scales and complex bound states in these hybrid structures, the device physics and measurement schemes are facing unprecedented challenges. This paper reviews recent research progress of hybrid superconducting devices based on one-dimensional electronic systems, focusing on the material systems based on semiconducting nanowires and carbon nanotubes. Semiconducting nanowires with strong spin-orbit coupling and large Landau g-factor are expected to support Majorana bound states, and further improvements are needed in the material quality, interface between superconductors and nanowires, understanding of the transport mechanism, and detection scheme. The construction strategies of extending topological phase space, including broken symmetry, helical modes, semiconducting characteristics, and attenuation of the external magnetic field, are proposed and discussed in hybrid superconducting devices based on carbon nanotubes. The main phenomena and experimental challenges, ranging from material to device physics, are introduced briefly. Finally, this paper summarizes and prospects the development and transport studies of topological quantum devices based on one-dimensional systems.
INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 070302.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241621
Abstract +
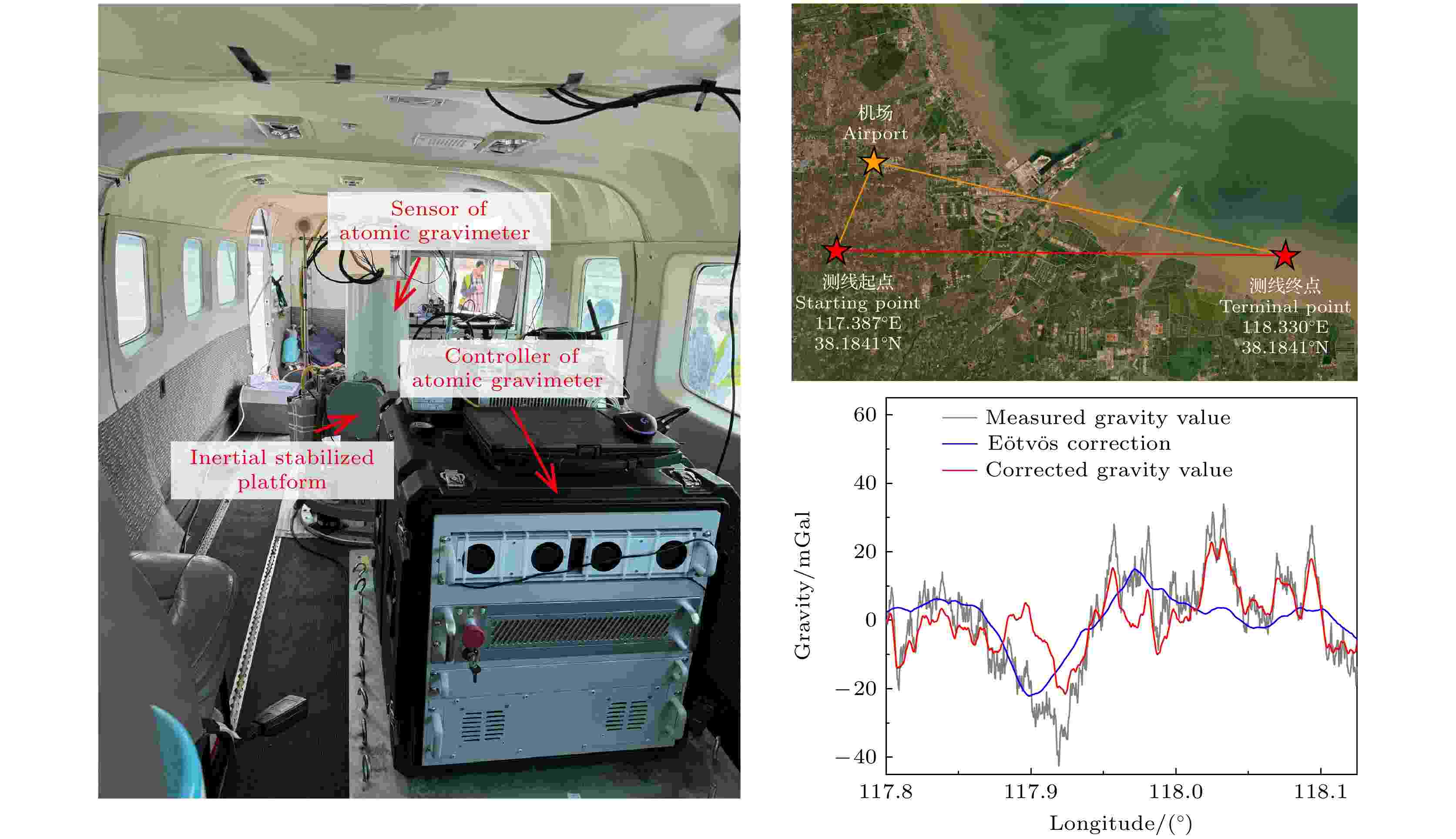
High-precision gravity field mapping plays a critical role in geological survey, resource exploration, and geoid modeling. The traditional ground-based static absolute gravity measurements possess high accuracy, but they are fundamentally constrained by low operational efficiency and inability to survey complex terrains such as river networks, lakes, and mountainous regions. This study tries to address these limitations through the development of an airborne absolute gravity measurement system based on quantum gravimeters. At a flight altitude of 1022 m and a speed of 240 km/h of the airplane, after a filtering process of 3 km, the measured gravity value shows a standard deviation of approximately 8.86 mGal. Furthermore, a comparative analysis with the EGM2008 gravity model shows a residual standard deviation of 8.16 mGal, validating the consistency of the system with established geophysical references. The experimental results confirm the operational feasibility of quantum gravimeters in scenarios of airborne dynamic measurement, demonstrating the viability of this technological framework for high-resolution gravity field mapping.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 074203.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241652
Abstract +
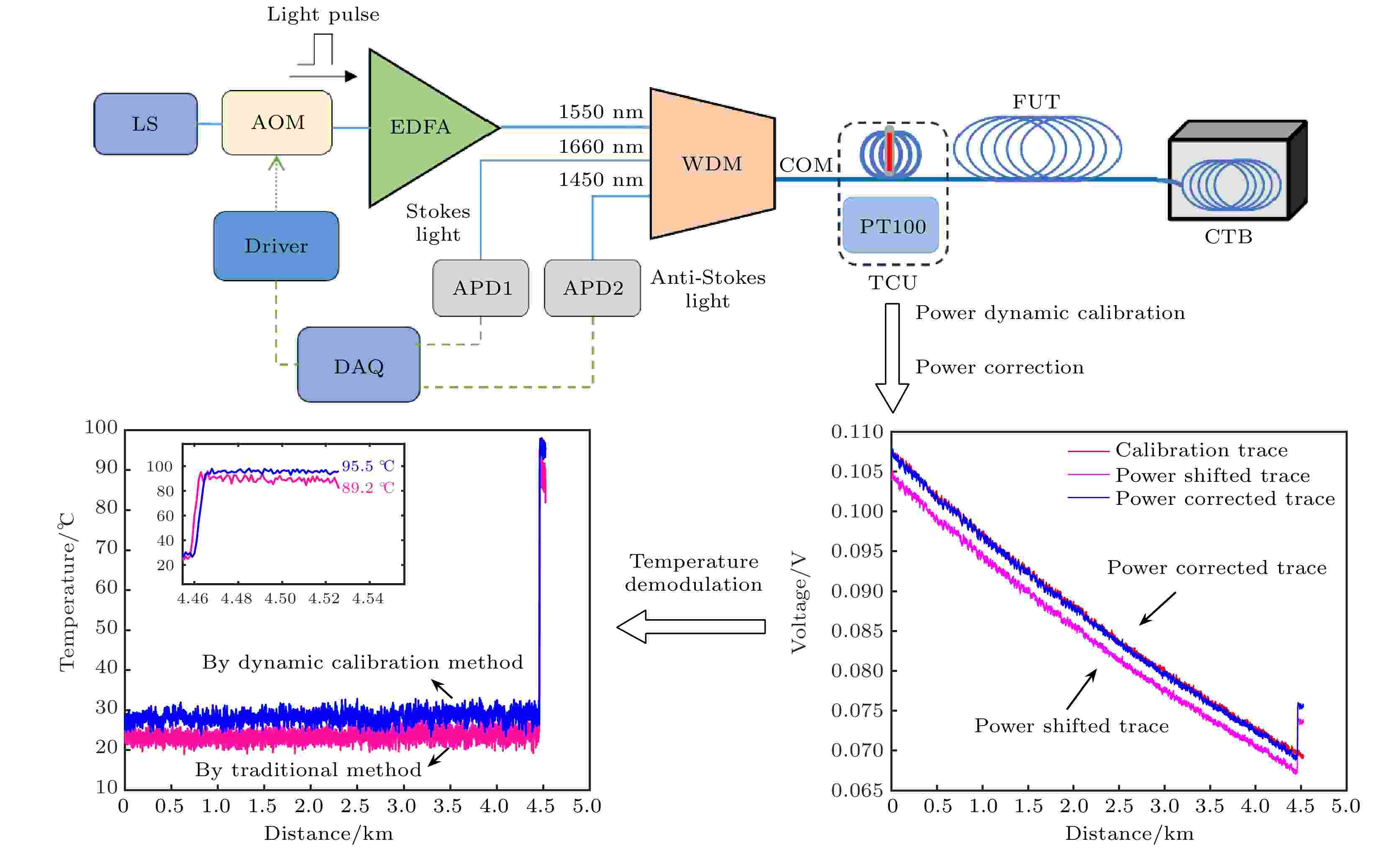
Distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system is widely used in the fields of substation, power cable, natural gas transmission pipeline and other temperature measurement systems. It can continuously measure the temperature information at each location along the sensing direction. Raman distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system demodulates the temperature information based on Raman Stokes scattered light and anti-Stokes scattered light power, and the Raman scattering light power directly affects the temperature measurement accuracy. So, it is a challenging task to control the hardware of the system to ensure the feasiblity of the Raman sacttering signals. The laser pulse power, and the gain of avalanche photodetector may vary randomly in the system, resulting in fluctuations in the acquired Raman scattered light power data. Therefore, a scheme of Raman distributed fiber temperature measurement system based on dynamic calibration is proposed in this work, and by setting up the temperature calibration unit and combining the proposed power correction algorithm and previous calibration data, the Raman Stokes scattering light and Raman anti-Stokes scattering light power are calibrated at the same laser pulse power level and avalanche photodetector gain, thereby improving the temperature measurement accuracy of the system. For the performance demonstration of the new scheme, the experimental system adopts 50-ns laser pulse to carry out temperature measurement experiments with a 4.6-km long single-mode fiber. The results show that in the temperature measurement range from 35 ℃ to 95 ℃, based on the traditional temperature demodulation algorithm, the temperature deviation measured is in the range from –5.8 ℃ to 1.0 ℃, and the root mean square error is 4.0 ℃, and by the dynamic calibration algorithm, the deviation of deviation measured is within –0.8 ℃ to 0.9 ℃ and the root mean square error is 0.5 ℃. Therefore, the novel Raman-type distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system proposed in this work has the function to dynamically correct the Raman-type scattered light power to suppress the influence caused by instability of the key devices such as pulsed laser and avalanche photodetector and improve the temperature measurement accuracy, which is valuable in practical engineering applications.
GENERAL
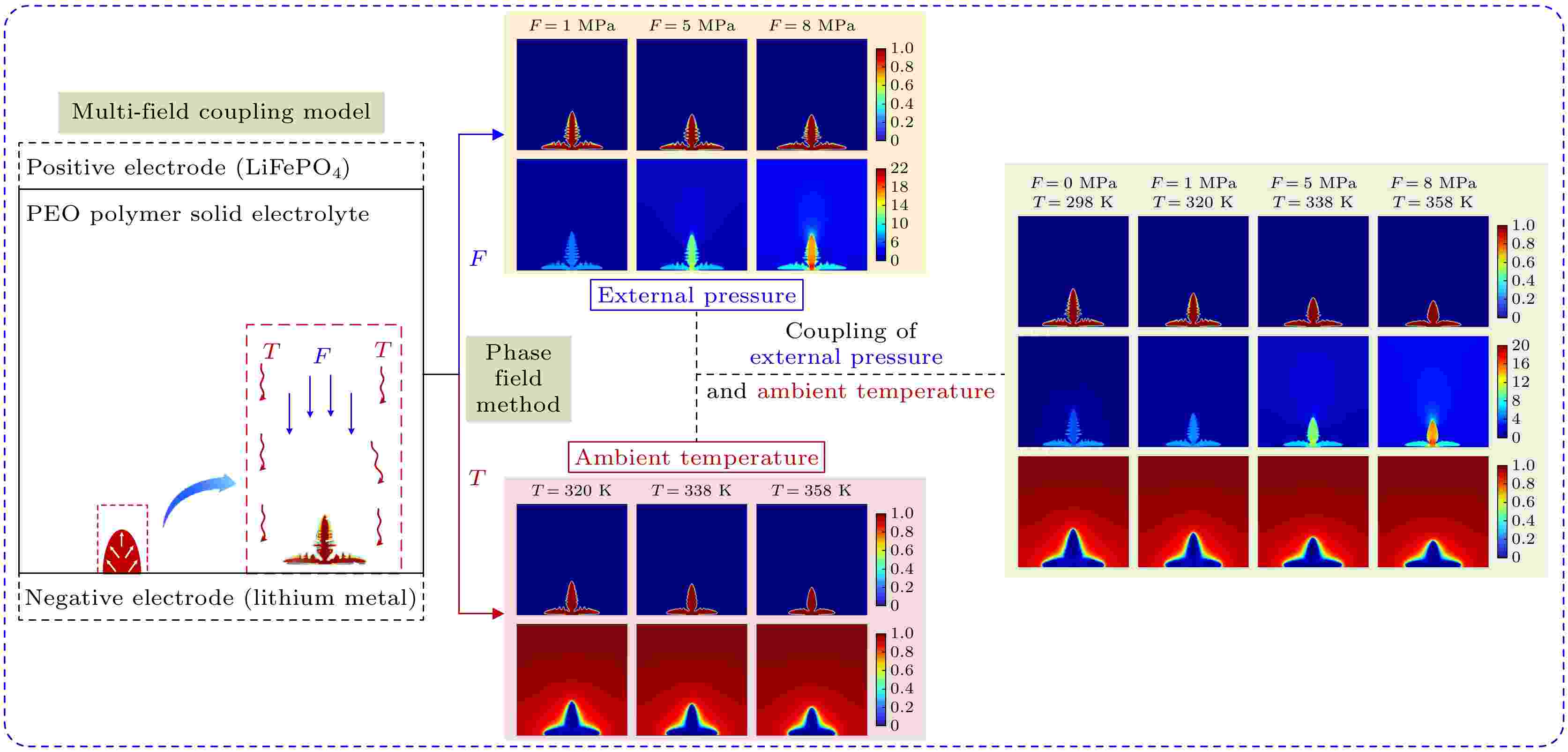
2025, 74 (7): 070201.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241727
Abstract +
Solid-state lithium batteries possess numerous advantages, such as high energy density, excellent cycle stability, superior mechanical strength, non-flammability, enhanced safety, and extended service life. These characteristics make them highly suitable for applications in aerospace, new energy vehicles, and portable electronic devices. However, the growth of lithium dendrite at the electrode/electrolyte interface remains a critical challenge, limiting both performance and safety. The growth of lithium dendrites in the electrolyte not only reduces the Coulombic efficiency of the battery but also poses a risk of puncturing the electrolyte, leading to internal short circuits between the anode and cathode. This study is to solve the problem of lithium dendrite growth in solid-state lithium batteries by employing phase-field theory for numerical simulations. A phase-field model is developed by coupling the mechanical stress field, thermal field, and electrochemical field, to investigate the morphology and evolution of lithium dendrites under the condition of different ambient temperatures, external pressures, and their combined effects. The results indicate that higher temperature and greater external pressure significantly suppress lithium dendrite growth, leading to fewer side branches, smoother surfaces, and more uniform electrochemical deposition. Increased external pressure inhibits longitudinal dendrite growth, resulting in a compressed morphology with higher compactness, but at the cost of increased mechanical instability. Similarly, elevated ambient temperature enhances lithium-ion diffusion and reaction rate, which further suppress dendrite growth rate and size. The combined effect of temperature and pressure exhibits a pronounced inhibitory influence on dendrite growth, with stress concentrating at the dendrite roots. This stress distribution promotes lateral growth, facilitating the formation of flatter and denser lithium deposits.
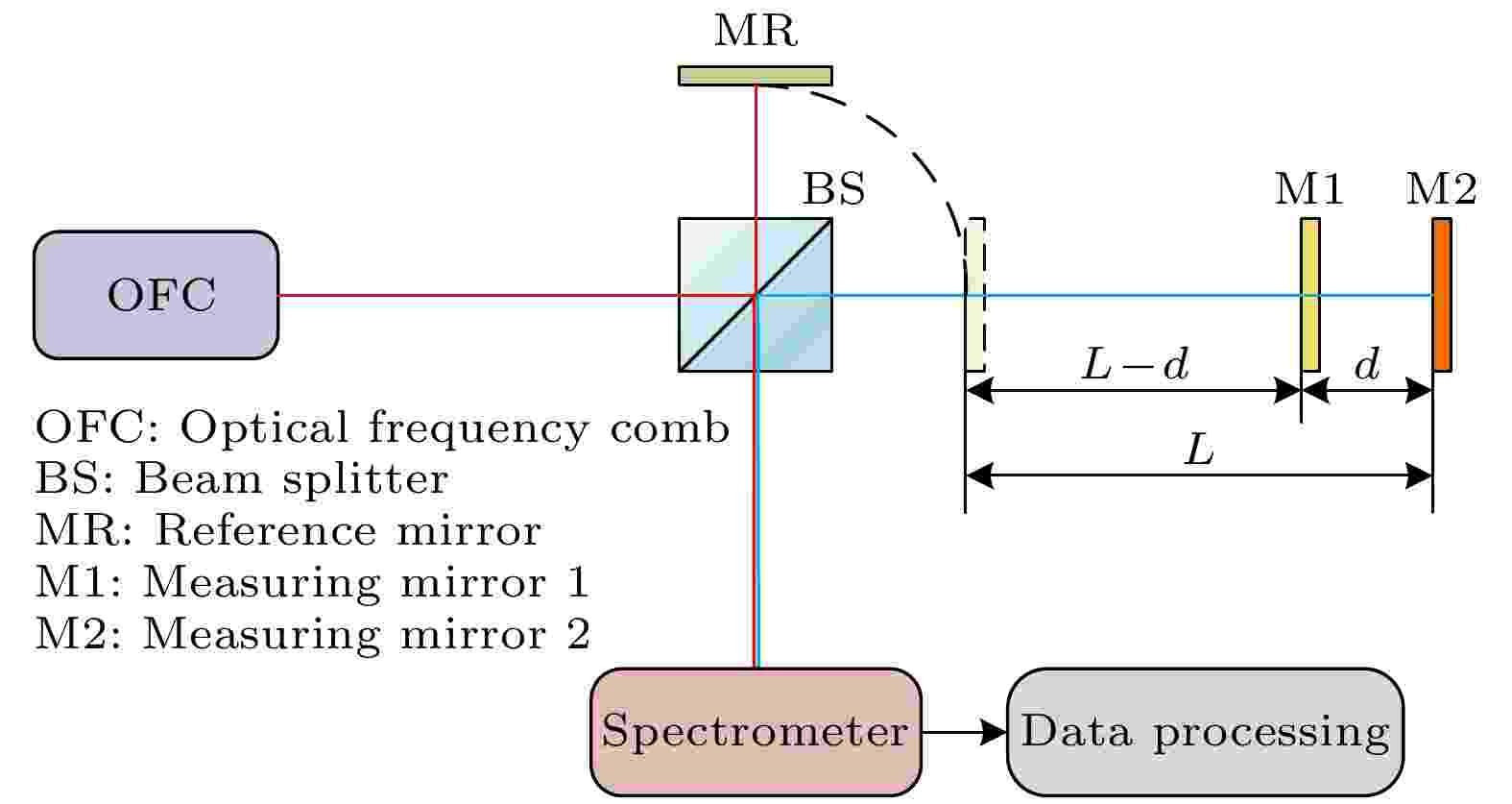
2025, 74 (7): 070601.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20250024
Abstract +
In industrial sites and outdoor long-distance measurements, the difficulty in accurately measuring and correcting the refractive index of air is a critical factor affecting precise distance measurement. In order to develop a simple, long-range, and high-precision absolute distance measurement technique, in this work an absolute distance measurement method is presented based on multi-pulse spectral interferometry by using an optical frequency comb. This method can dynamically correct the measurement errors introduced by group refractive index fluctuations. Firstly, a mathematical model for multi-pulse spectral interferometry is established. By performing a single Fourier transform on the multi-pulse spectral interference signal, the time delay measured in the pseudo-time domain can be used to simultaneously determine the group refractive index of the measurement path and the measured distance. Secondly, by fine-tuning the repetition frequency and using difference computation, the measurement range can be extended from the non-ambiguity range of traditional spectral interferometry to arbitrary lengths. Finally, extensive numerical simulations and analyses are conducted to validate the performance of the proposed method. The simulation results demonstrate that with a reference distance of 0.1 m, the maximum absolute error in group refractive index measurement is 0.12×10–6, and the maximum distance measurement error is 33 nm in a range of 0—200 m. In order to measure the group refractive index in real time under changing atmospheric conditions and compensate for ranging errors caused by changes in air refractive index, even under changing atmospheric conditions, the maximum distance measurement error is 38 nm, ensuring sub-micron-level measurement accuracy over long distances. The research results indicate that this method can be applied to large-scale and high-precision absolute distance measurement.
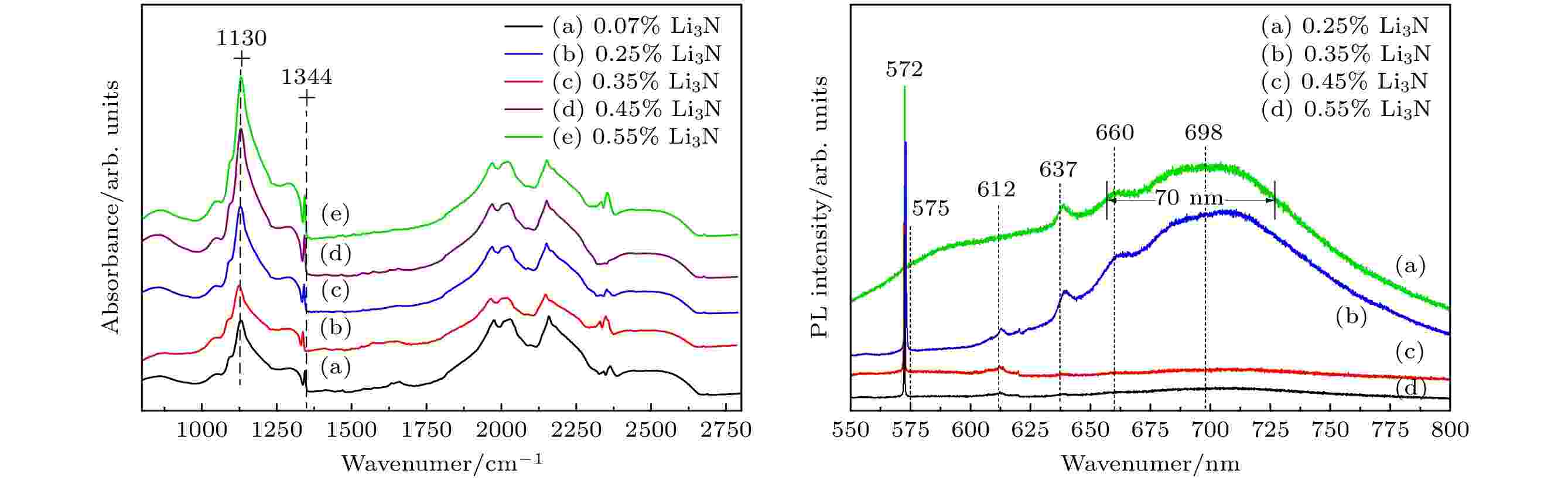
2025, 74 (7): 070701.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241769
Abstract +
In the paper, under 5.8 GPa and 1300 ℃, the Li3N doped diamond single crystals were synthesized in a cubic anvil high pressure and high temperature apparatus. Firstly, Fe59Ni25Co16 alloy was used as the catalyst, high-purity Li3N powder was used as the additive, industrial high-purity graphite powder was used as the carbon source, and the (100) crystal orientation of industrial grade diamond single crystal with good crystalline quality was used as the growth direction of diamond single crystal, the effect of Li3N addition ratio on the growth of diamond single crystals was systematically investigated with a growth time of 20 h. The research results indicate that with the increase of Li3N addition ratio, the color of diamond single crystals gradually transitions from yellow green, green, and dark green to dark green, and their morphology gradually transitions from hexahedron, hexahedron to octahedron. Moreover, the growth rate of single crystals decreases with the gradual increase of Li3N addition ratio, which can be attributed to the phenomenon of upward movement in the “V-shaped region” of diamond single crystal growth with the gradual increase of Li3N addition ratio in the P-T phase diagram of carbon. Secondly, using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, it was revealed that the nitrogen content of diamond single crystals increases with the increase of Li3N addition ratio, and increasing the diamond growth pressure can achieve the increase in the nitrogen content of diamond single crystals. Figure 5 shows FTIR spectra of diamond crystals synthesized under different Li3N addition ratios. When the weight percent of Li3N added to the catalyst is 0.55%, the nitrogen content of the grown diamond single crystal is 8.92×10–4. Thirdly, Raman spectroscopy testing revealed that the Raman characteristic peak of diamond single crystals gradually shifts towards the low-energy end with the increase of Li3N addition ratio, which is related to the increase of internal stress in diamond single crystals. Finally, the PL spectroscopy test results showed that this study achieved high temperature and high pressure preparation of diamond single crystals with NV– color centers, and the zero phonon line intensity of NV– color centers in the single crystals significantly decreased with the increase of crystal nitrogen content. Figure 7 shows PL spectra of diamond crystals synthesized under different Li3N addition ratios.
NUCLEAR PHYSICS
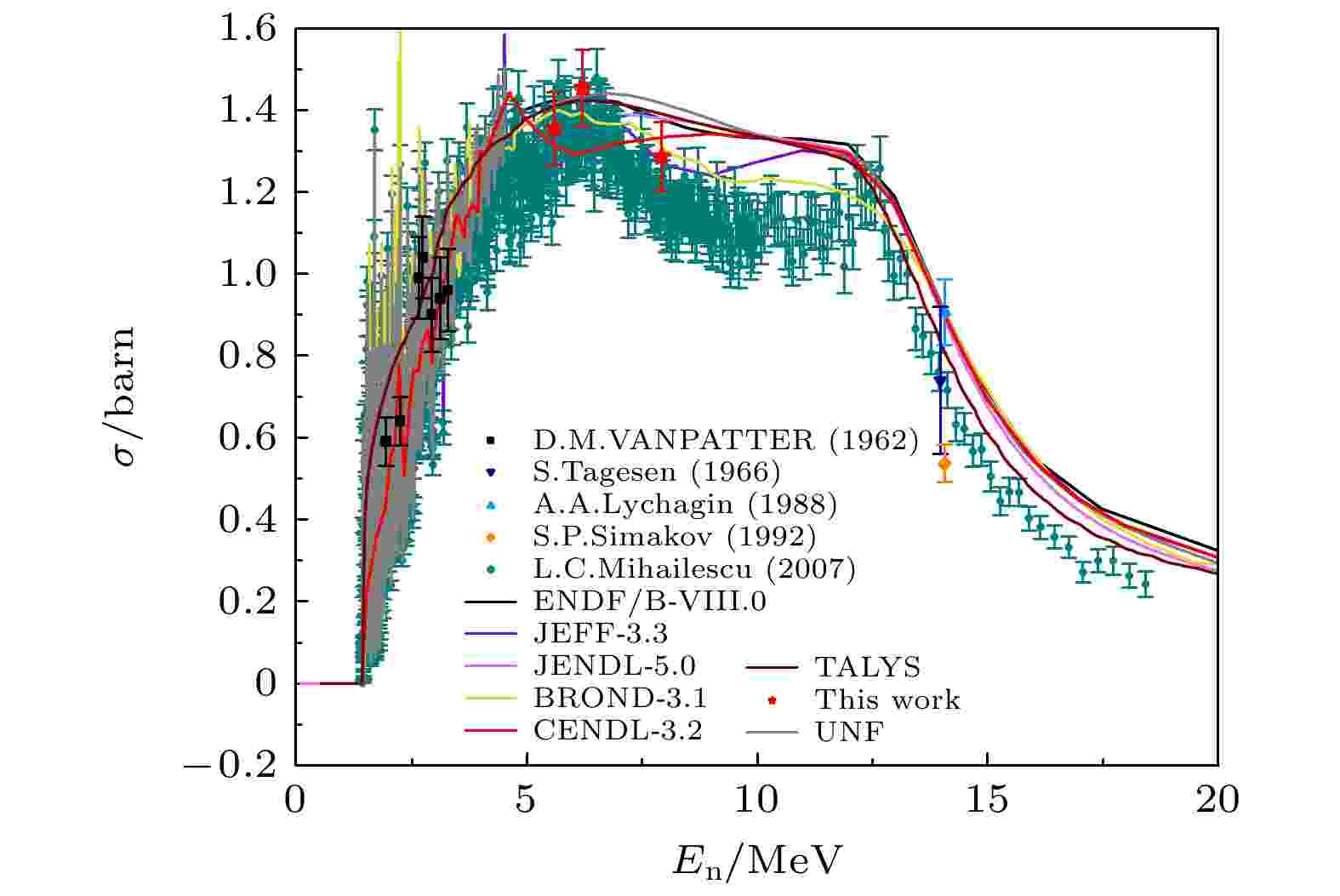
2025, 74 (7): 072901.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241660
Abstract +
With the development of next-generation reactors, the demand for higher precision in nuclear data has increased significantly to ensure operational efficiency and safety. Especially, inelastic scattering cross-section is one of the key parameters in nuclear reactor physics calculations, which directly affects neutron economy, thermal-hydraulic design, and safety analysis. Stainless steel is widely used in the nuclear industry. Chromium (Cr) is one of the main alloying elements in stainless steel, and 52Cr is the most abundant isotope in nature. However, the measurement of the inelastic scattering cross-section of 52Cr has not been explored in China, so the study of the 52Cr(n, n′ γ) reaction cross-section is crucial for nuclear reactor calculations. In this study, the neutron beams with energies of 5.62, 6.24, and 7.95 MeV via the D(d, n) 3He reaction are generated from the HI-13 tandem accelerator at the Institute of Atomic Energy in China. These neutrons are used to bombard a 52Cr target. Four CLOVER detectors are located at 30°, 70°, 110° and 150° relative to the beam direction in the horizontal plane. The prompt γ-ray method is used to measure the inelastic scattering cross-section by using an HPGe detector array. This is the first time that the cross-sections of five inelastic γ-rays with energies of 647.47 keV, 935.54 keV, 1333.65 keV, 1434.07 keV and 1530.67 keV have been obtained experimentally in China. Additionally, theoretical model calculations are performed to determine the inelastic scattering cross-sections of neutrons with energies below 20 MeV interacting with 52Cr. In the analysis of the experimental data, γ-ray self-absorption correction, neutron flux attenuation and multiple scattering correction are considered. The total experimental uncertainty includes the measurement uncertainty, correction term uncertainty, and standard cross-section uncertainty. The results show that the γ-ray production cross-sections obtained at the three neutron energy points are in good agreement with the data measured by Mihailescu et al. [Mihailescu L C, Borcea C, Koning A J, Plompen A J M 2007 Nucl. Phys. A 786 1 ] within the error margins, and the uncertainties are smaller. However, significant discrepancies are observed between the theoretical model calculations and the experimental data, which may be attributed to the lack of experimental information about the high-excitation-energy levels in the 52Cr level scheme. This study not only fills a gap in the measurement of the 52Cr inelastic scattering cross-section but also provides important nuclear data for designing and optimizing the next-generation reactors.
ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
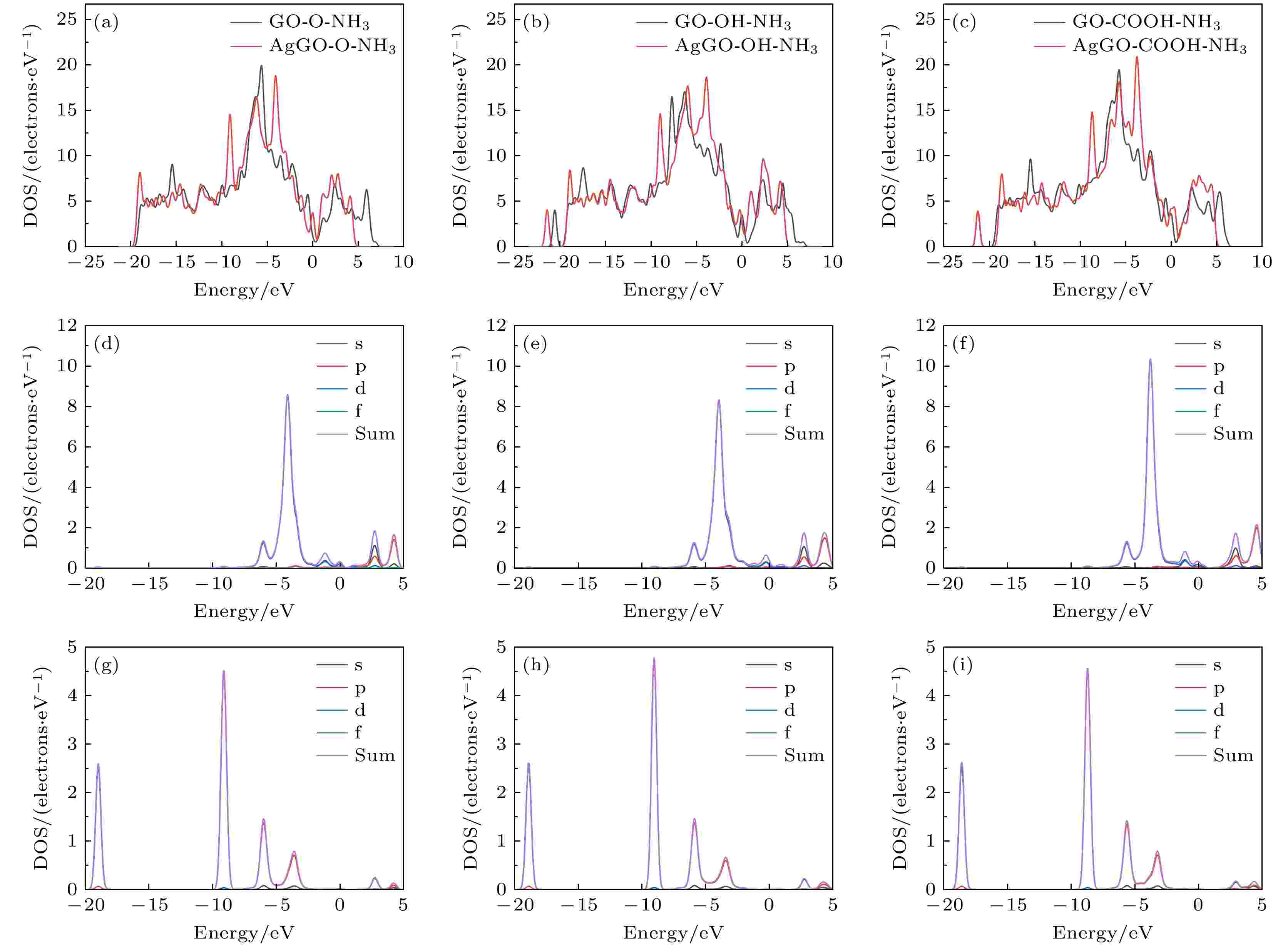
2025, 74 (7): 073101.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241737
Abstract +
Graphene has attracted great attention due to its large specific surface area, high charge carrier mobility, and excellent electrical conductivity. However, the inherent structural integrity and zero bandgap characteristics of graphene limit its gas sensing properties. Consequently, researchers have embarked on exploring avenues such as doping graphene or using graphene oxide as a gas-sensitive material to design gas sensors that respond optimally to ammonia. This work, based on first-principle density functional theory, focuses on the field of ammonia gas sensors, investigating in detail the adsorption characteristics of ammonia molecules on graphene oxide (GO) and graphene oxide doped with Ag and Cu (AgGO, CuGO). By calculating parameters including charge distribution, density of states, band structures, and adsorption energy, this work delves into the influences of diverse oxygen-containing groups and metal doping on the gas sensing properties of graphene oxide. The research results show that there is a substantial charge density overlap between the density of states of hydroxyl groups in graphene oxide and NH3 molecules, indicating a clear tendency towards chemical adsorption. It is particularly noteworthy that after NH3 adsorption, the graphene oxide containing hydroxyl shows the highest charge transfer (0.078e) and adsorption energy (0.60 eV), which indicates that the adsorption efficacy of NH3 is higher, followed by carboxyl groups and epoxy groups, which mainly participate in physical adsorption. Furthermore, this work delves into the influence of metal doping on graphene oxide, demonstrating that the adsorption capability of doped graphene oxide hinges upon the synergistic influence of oxygen-containing groups and metal atoms, with Ag-doped graphene oxide showing a several-fold increase in adsorption energy. Through the analysis of density of states, it is found that Ag atoms resonate with s, p, and d orbitals of the N atom in NH3, proving the formation of a chemical bond between Ag atom and N atom. Moreover, a comparative analysis shows that Cu-doped graphene oxide (CuGO) has an increased charge transfer of about 0.020e and slightly higher adsorption energy than Ag-doped graphene oxide (AgGO) when adsorbing NH3. Intriguingly, under the same doping concentration, CuGO exhibits superior adsorption performance to NH3. It is worth noting that in graphene oxide doped with Ag or Cu, the adsorption mechanism of carboxyl and epoxy groups transforms from physical adsorption into chemical adsorption, while the hydroxyl groups maintain consistent chemical adsorption properties before and after doping. This indicates that doping with Ag or Cu atoms can significantly enhance the adsorption capability of graphene oxide to NH3.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 073102.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241797
Abstract +
ELECTROMAGNETISM, OPTICS, ACOUSTICS, HEAT TRANSFER, CLASSICAL MECHANICS, AND FLUID DYNAMICS
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 074101.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241677
Abstract +
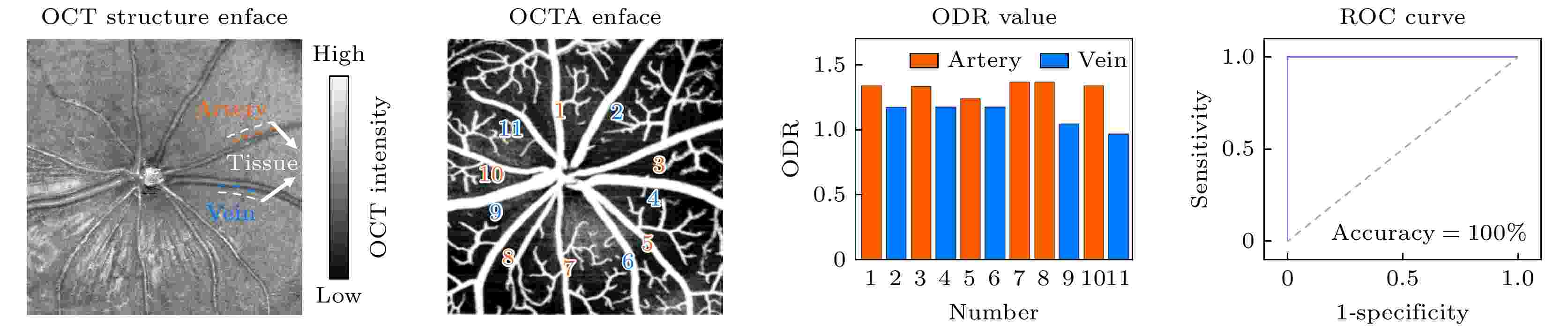
2025, 74 (7): 074201.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241686
Abstract +
Accurate measurement of retinal blood oxygen saturation (SO2) provides valuable early insights into the pathophysiology of ocular diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and retinal vein occlusion. Visible-light optical coherence tomography (OCT) can directly measure SO2 through spectral fitting, but its application is limited due to the irritability of visible light and its influence on the physiological state of the retina. Near-infrared band I (NIR-I) causes less ocular stimulation. Even though the hemoglobin absorption effect is weaker in this region, its scattering property is also related to SO2. According to this principle, we propose a novel optical coherence tomography (OCTA) guided NIR-I technique for retinal blood oxygen saturation measurement. This method is used to calculate SO2 through calibrating the optical density ratio (ODR) of oxygen-sensitive wavelength (855 nm) to isosbestic wavelength (805 nm). By utilizing the three-dimensional (3D) blood flow maps generated by the OCTA, this technique can automatically identify retinal vessels and surrounding tissue regions, thereby minimizing the errors caused by manual selection. Consequently, the classification accuracy of arteries and veins increases from 82.1% to 96.7%. The calibrated average retinal blood oxygen saturation is 94%±21% for arteries and 56%±13% for veins, which aligns with normal physiological range. The representative result of artery-vein classification is presented in the following figure. This method greatly improves the accuracy and efficiency of measurement, and provides a reliable tool for early diagnosis, disease assessment, and treatment monitoring of ophthalmic diseases, which has broad application prospects.
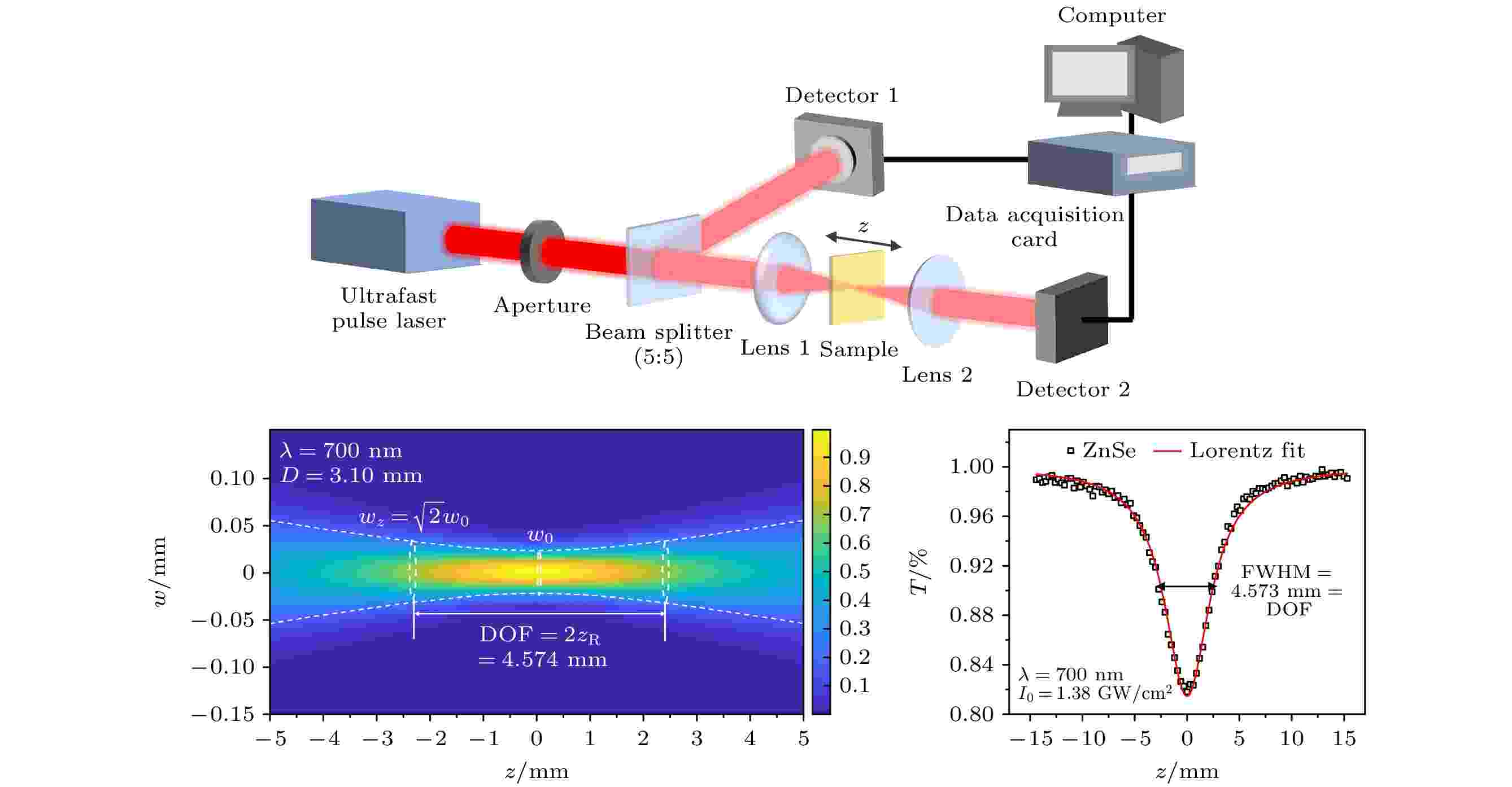
2025, 74 (7): 074202.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241658
Abstract +
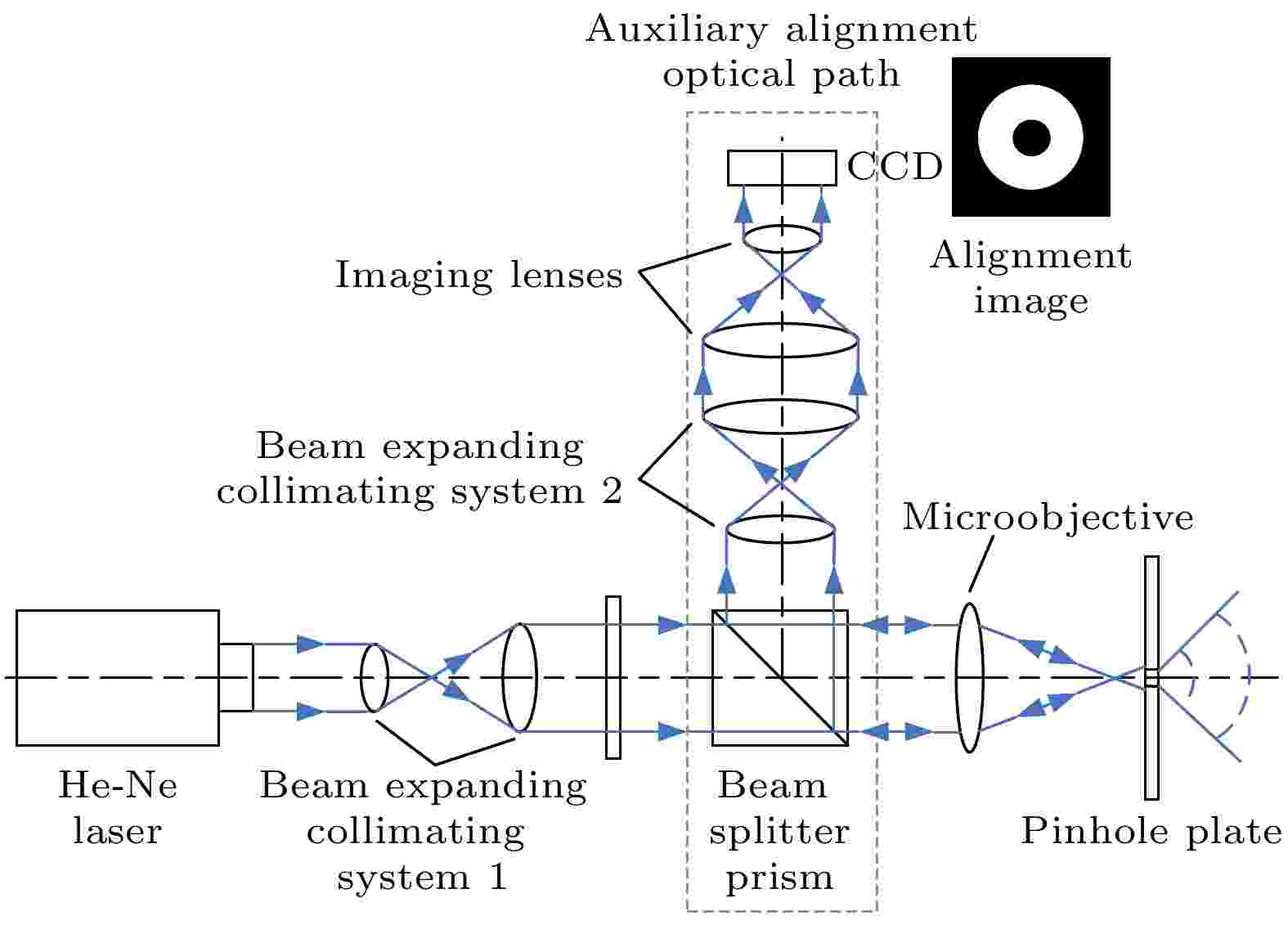
2025, 74 (7): 074204.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241180
Abstract +
In the construction of the pinhole point diffraction interferometer, the alignment error between the convergent spot of the microscopic objective lens and the diffraction hole in the front end of the pinhole diffraction will lead to problems such as diffraction wavefront error, diffraction intensity reduction, and interference fringe contrast reduction, which will affect the actual measurement accuracy. In order to solve the problem of inaccurate alignment between the convergent spot of the microscopic objective lens and the diffraction hole, a diffraction hole visual alignment method based on the auxiliary optical path is proposed in this work. An auxiliary alignment optical path is built at the front end of the pinhole diffraction, and the beam reflected by the pinhole diffraction plate is mainly reflected by the beam splitter prism, and then received by a charge coupled device (CCD). By collecting and processing the spot image reflected by the small hole diffraction plate, the alignment state of the small hole is monitored and the alignment error is calculated. In this work, a visual-precision optical path alignment scheme is designed, and the visual performance of the alignment image under three typical alignment deviations of translation, tilt and defocus is simulated and analyzed. The mathematical model of the object-image relationship between the alignment image and the alignment error is constructed, and the alignment image error measurement and processing algorithm is studied. The experimental results show that the auxiliary optical path alignment method and the alignment image processing algorithm proposed in this work are feasible, and the alignment accuracy can reach 0.05 μm. The research results are helpful in improving the alignment efficiency and accuracy of point diffraction interferometer, and can lay a certain technical foundation for the development of practical point diffraction interferometer.

EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 074301.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241747
Abstract +
As an important and promising experimental method of simulating the containerless state in outer space, acoustic levitation provides excellent contact-free condition for investigating solidification process. Meanwhile, the radiation pressure and acoustic streaming caused by nonlinear effects bring various kinds of novel phenomena to crystallization kinetics. In this work, high-speed charge coupled device (CCD), low-speed camera and infrared thermal imager are used simultaneously to observe the crystallization process of acoustically levitated SCN-DC transparent alloys. The undercooling ability and solidification process of alloy droplets with different aspect ratios are explored in acoustic levitation state. For hypoeutectic SCN-10%DC, eutectic SCN-23.6%DC and hypereutectic SCN-40%DC alloys, the experimental maximum undercoolings reach 22.5 K (0.07TL), 16 K (0.05TE) and 32.5 K (0.1TL) and the corresponding crystal growth velocities are 27.91, 0.21 and 0.45 mm/s, respectively. In SCN-10%DC hypoeutectic alloy, the nucleation mode of SCN dendrite changes from edge nucleation into random nucleation with the increase of undercooling. For SCN-23.6%DC eutectic alloy, when the undercooling exceeds 12.6 K, DC dendrites preferentially nucleate and grow, and then the (SCN+DC) eutectic adheres to and grows on DC dendrites. Moreover, the growth interface of DC dendrites gradually changes from sharp into smooth within SCN-40%DC hypereutectic alloy as the undercooling degree rises. The undercooling distribution curve and nucleation probability variation trend versus aspect ratio are analyzed. It is found that as the aspect ratio increases, undercooling of alloy droplet first increases, then decreases, and finally remains almost unchanged. Further analysis shows that with the increase of aspect ratio, the cooling rate will rise and thus enhance the undercooling. However, the increase in surface nucleation rate and the droplet oscillation inhibits deep undercooling of alloy droplet. Therefore, the coupled effects of cooling rate, surface nucleation rate, and droplet oscillation determine the undercooling of the alloy. In the case of SCN-40% DC hypereutectic alloy, the acoustic streaming and surface oscillation arising from acoustic field are the main factors intensifying surface nucleation.

EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 074401.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241731
Abstract +
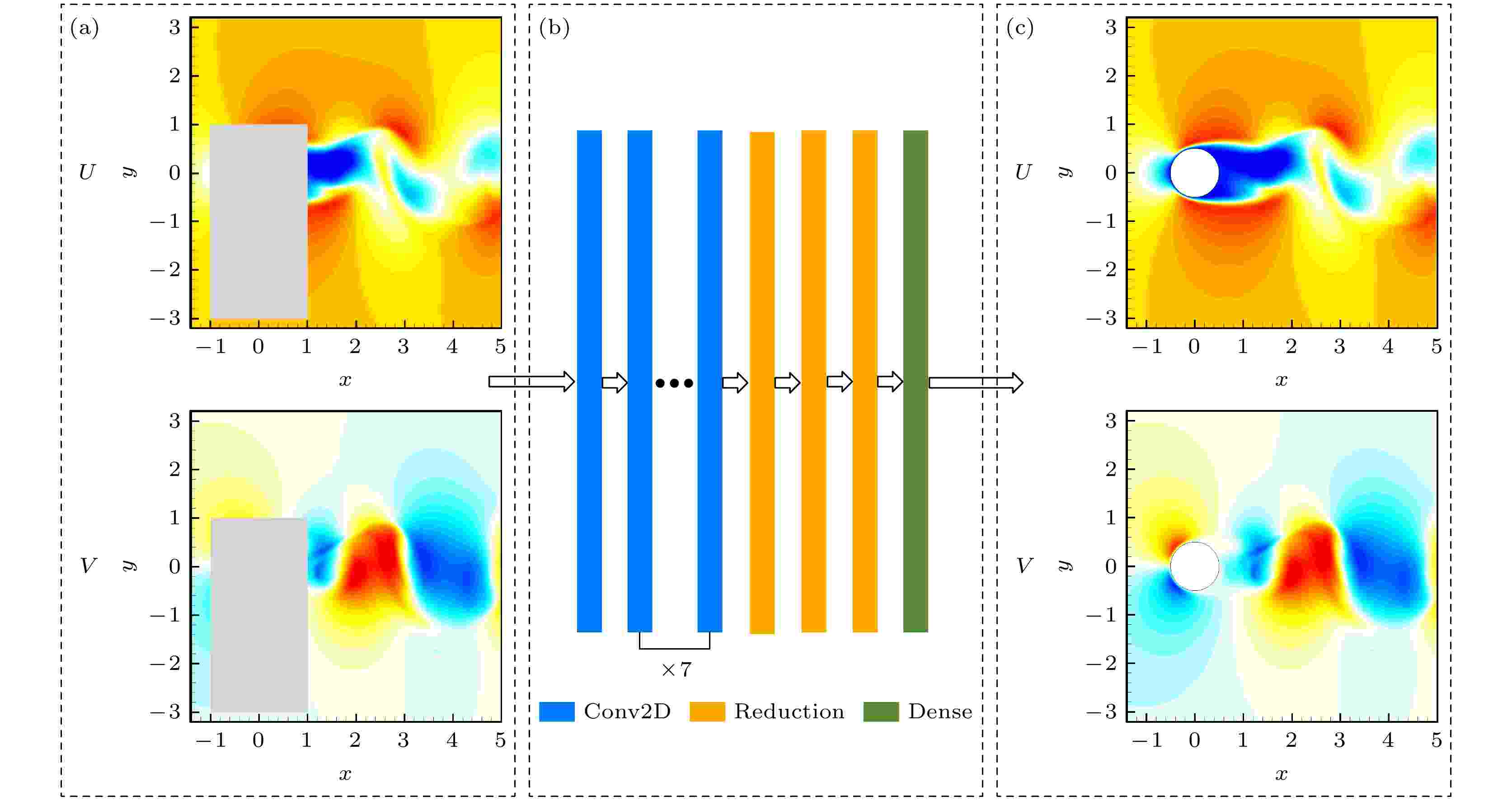
2025, 74 (7): 074701.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241689
Abstract +
The prerequisite for accurate prediction and effective control of flow phenomena lies in the understanding of flow dynamics, and experimental studies provide essential data to support this process. Particle image velocimetry (PIV), as one of the important methods of measuring flow fields, plays a critical role in experimental investigations such as flow passing through a circular cylinder. PIV is a non-contact laser-optical measurement technique, however, it often faces challenges in obtaining complete and accurate flow field data when the optical path is obstructed. Particularly in PIV experiments involving flow passing through a circular cylinder, the presence of the cylinder itself and the supporting structure can significantly obscure the optical path, making it highly challenging to acquire complete PIV data. To solve this problem, we propose a deep learning-based flow field data reconstruction method, in which a deep learning framework centered on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is used. The method aims to solve the reconstruction problem of gappy regions in flow field data by establishing a mapping relationship between flow fields with gappy regions and complete flow fields. First, the influence of gappy regions with different characteristics on the reconstruction accuracy of numerically simulated flow fields is investigated. The reconstructed flow fields are carefully compared with ground truth data through multi-dimensional assessments of instantaneous flow fields and velocity time statistics. The results indicate that the maximum L2 error between the reconstructed flow field and the ground truth is still about 0.02. Furthermore, it is observed that as the size of the gappy region increases along the flow direction, the difficulty in reconstructing flow field increases significantly. In contrast, changes in the size of the gappy region perpendicular to the flow direction have minimum influence on the accuracy of flow field reconstruction. Additionally, the robustness of the proposed deep neural network against noise is systematically evaluated. When clean numerical simulation data are used for training, test data are generated by artificially introducing varying levels of Gaussian noise to assess the network performance under noisy conditions. The results demonstrate that the error between the reconstructed data and the ground truth increases exponentially as the noise level rises. Finally, the proposed deep neural network model is applied to real PIV experimental data, with the training data remaining clean and numerically simulated. Both instantaneous flow fields and time-averaged statistics are analyzed and compared. The results show that the network model successfully reconstructs velocity information in the missing regions and effectively corrects data errors caused by measurement inaccuracies in the backflow zones. The reconstructed experimental results show closer statistical agreement with numerical simulation data, demonstrating that the model proposed in this work, when trained solely on numerical simulation data, is capable of reconstructing missing physical information in PIV experiments. This method provides a novel approach for addressing the challenge of data reconstructionin PIV experiments.
PHYSICS OF GASES, PLASMAS, AND ELECTRIC DISCHARGES
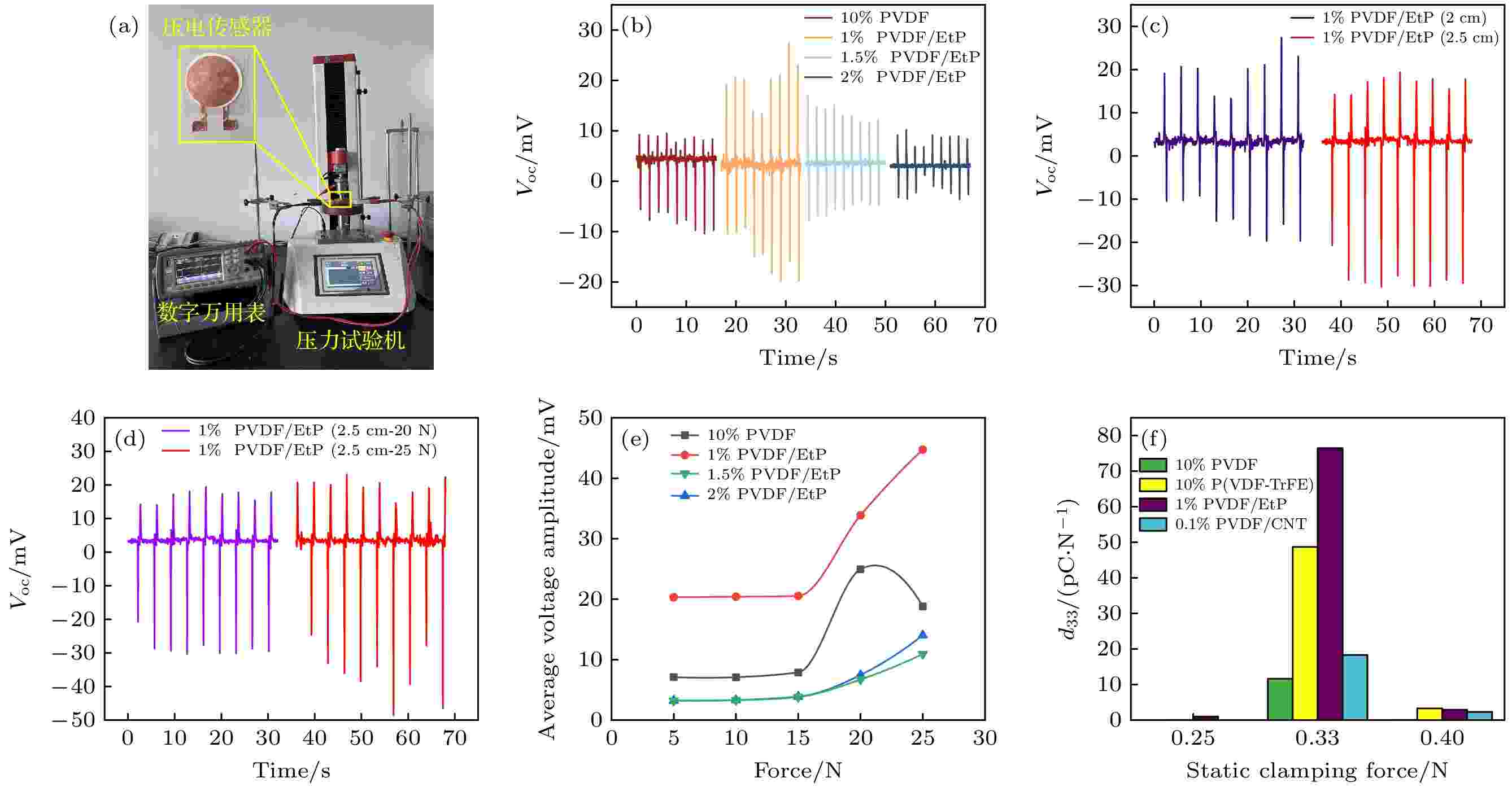
2025, 74 (7): 075201.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241680
Abstract +
In recent years, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)-based nanofiber membranes, as key materials for applications in sensors, energy harvesters, and flexible electronics, have received significant attention due to their excellent piezoelectric properties. However, the research on the piezoelectric performance of PVDF membranes is still limited because of their intrinsic structure and material characteristics. Therefore, in this work, the effects of filler doping on the properties of PVDF nanofiber membranes are investigated to enhance their piezoelectric performance and stability. Using electrospinning technology, electret particles are incorporated into PVDF nanofiber membranes at different concentrations (e.g. 1%, 1.5%, and 2%). Characterization tests of the composite nanofiber membranes, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), reveal that the doping of electret particles can increase the average fiber diameter and enhance the β-phase content. In the piezoelectric performance tests, the piezoelectric sensors made of nanofiber membranes doped with electric particles show significant improvement in electrical output at a test pressure of 20 N. Furthermore, increasing the membrane area and using higher pressure can further enhance the electrical output. These results show that the piezoelectric properties of PVDF membranes can be effectively improved by appropriately doping electric particles. Stability tests carried out three months after sensor was fabricated shows that the electrical output stability of the piezoelectric sensors containing electric particles has been significantly improved. Additionally, an efficient signal processing method is proposed, with an FIR digital low-pass filter used to remove high-frequency noise. This method is not only a smoothing prior method to eliminate baseline drift, but also an improved AMPD algorithm to accurately detect the peak position and features of the piezoelectric signal. This method can significantly enhance the stability and accuracy of signal feature extraction. All in all, this study presents a simple and effective approach to improving the piezoelectric performance and electrical output stability of PVDF nanofiber membranes through the combination of filler doping and electrospinning technology. This method not only optimizes the performance of PVDF-based composites but also provides new insights into and technical support for their broad applications in energy collection, smart sensors, flexible electronic devices, and other fields.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 075202.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241740
Abstract +
Using Feynman ratchet principle, it is possible to rectify the random motion into directed flow of particles in a nonequilibrium environment. In this work, an experimental setup for a dusty plasma metal straight ratchet is designed to create an asymmetric plasma environment along the ratchet channel, achieving controllable rectification of micron-sized dust particles. Monodispersed dust particles can form a directional flow in the ratchet channel, and the transport direction can be precisely controlled by adjusting the discharge power and the gas pressure. Research on the transport of dust particles with varying sizes proves that the rectification effect is universal. To reveal the rectification mechanism of dust particles, a fluid model of plasma is adopted to calculate the two-dimensional distribution of plasma parameters within the ratchet channel. Further research through Langevin simulation shows that dust particles experience ratchet potentials with different asymmetric orientations at different suspension heights within the ratchet channel, leading to different transport directions. The results of this work lays a theoretical and experimental foundation for further realizing the separation of bi-disperse particles in dusty plasma metal straight ratchets.
CONDENSED MATTER: STRUCTURAL, MECHANICAL, AND THERMAL PROPERTIES
2025, 74 (7): 076101.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241794
Abstract +
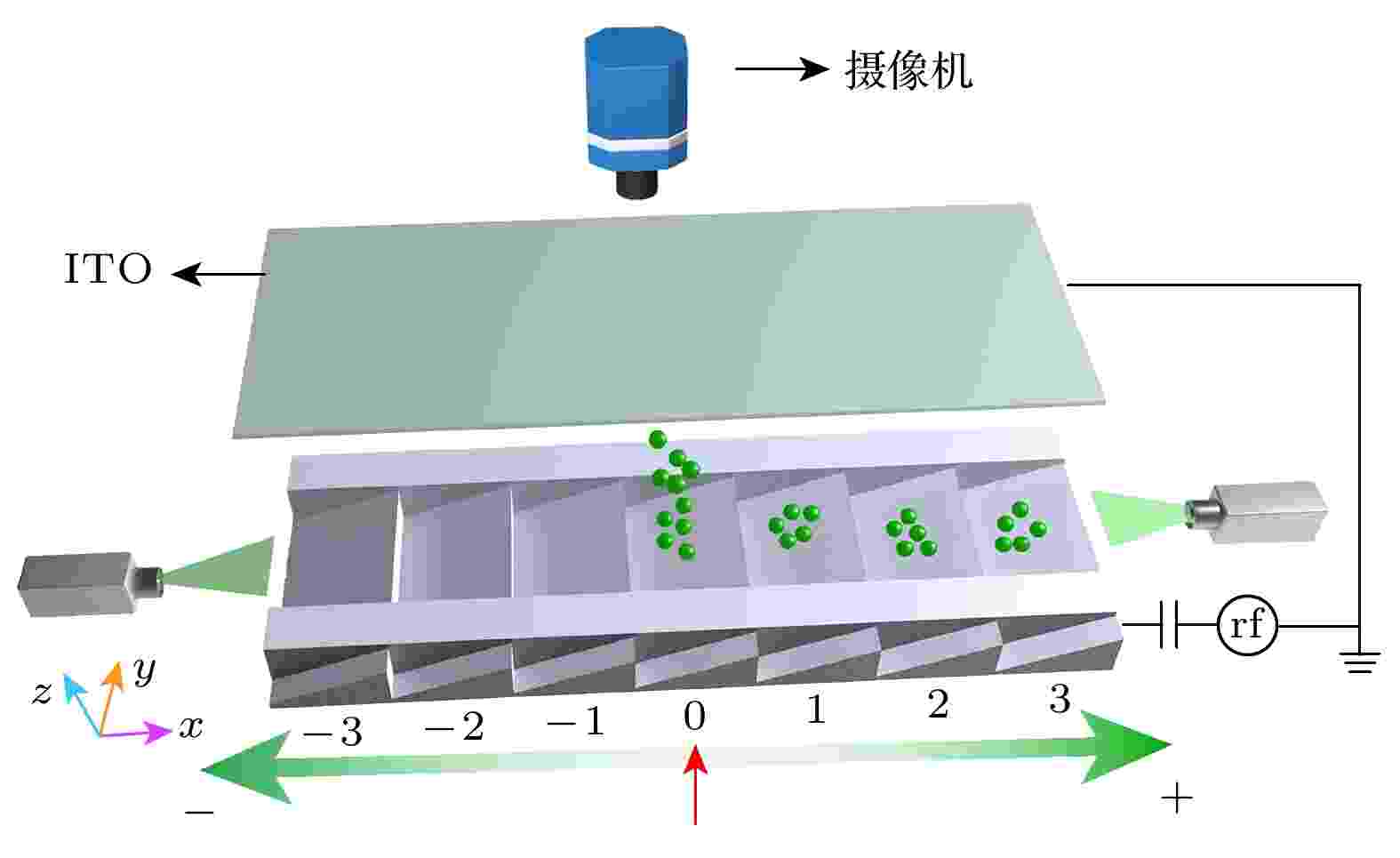
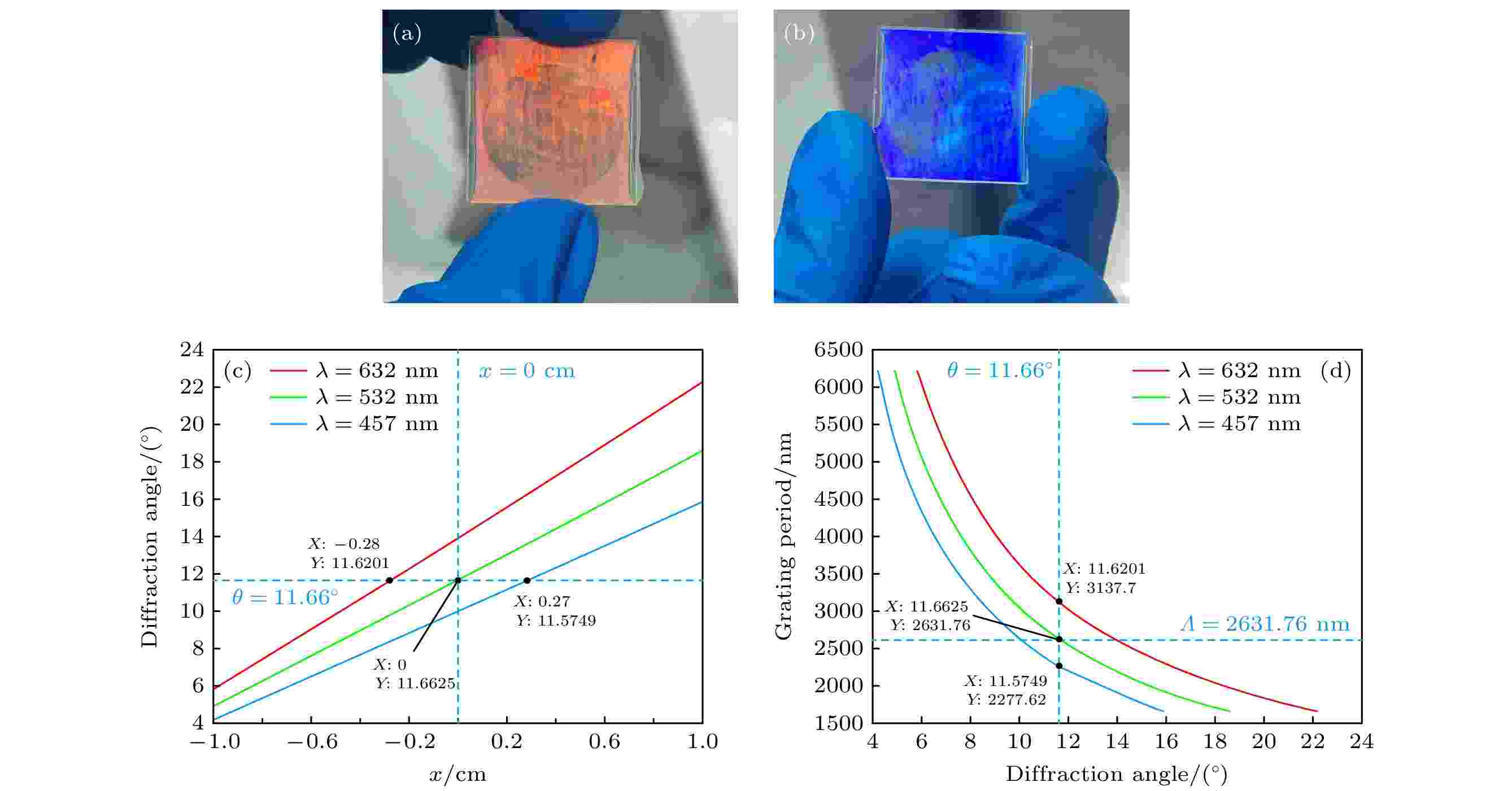
Photo-oriented liquid crystal technology utilizes polarized light illumination to achieve the directional alignment of liquid crystal molecules. This technology can be developed into polarization volume gratings (PVGs), which possess polarization and volume holographic selectivity characteristics, and also have a broad application prospect as an optical coupling element in optical waveguides and for pupil expansion output. This paper reports on the fabrication of a liquid crystal polarization volume holographic cylindrical lens (PVLS) with a beam diameter of 2 cm by using photo-oriented technology combined with a polarization off-axis holographic optical path. During the experiment, the exposure angle can be controlled to achieve the desired grating period variation range, enabling the diffraction angles of red, green, and blue light incident on different grating periods to be the same. The experimental results show that within the grating period variation range from 1721.2 to 5346.5 nm, when the red, the green, and the blue light are incident on grating with periods of 3147 nm, 2649.1 nm, and 2275.6 nm respectively, the measured diffraction angles are all 11.59°, with an error between the actual and theoretical diffraction angles within ±0.5°; under 532-nm right-handed circularly polarized light, the diffraction efficiency for 18 normal incidence reaches 90.6%, and the diffraction efficiency for oblique incidence satisfying the Bragg condition is 84.4%; simultaneously, beam expansion in one-dimensional direction is achieved, preliminarily verifying the feasibility of PVLS application in the field of color waveguides.
2025, 74 (7): 076102.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241720
Abstract +
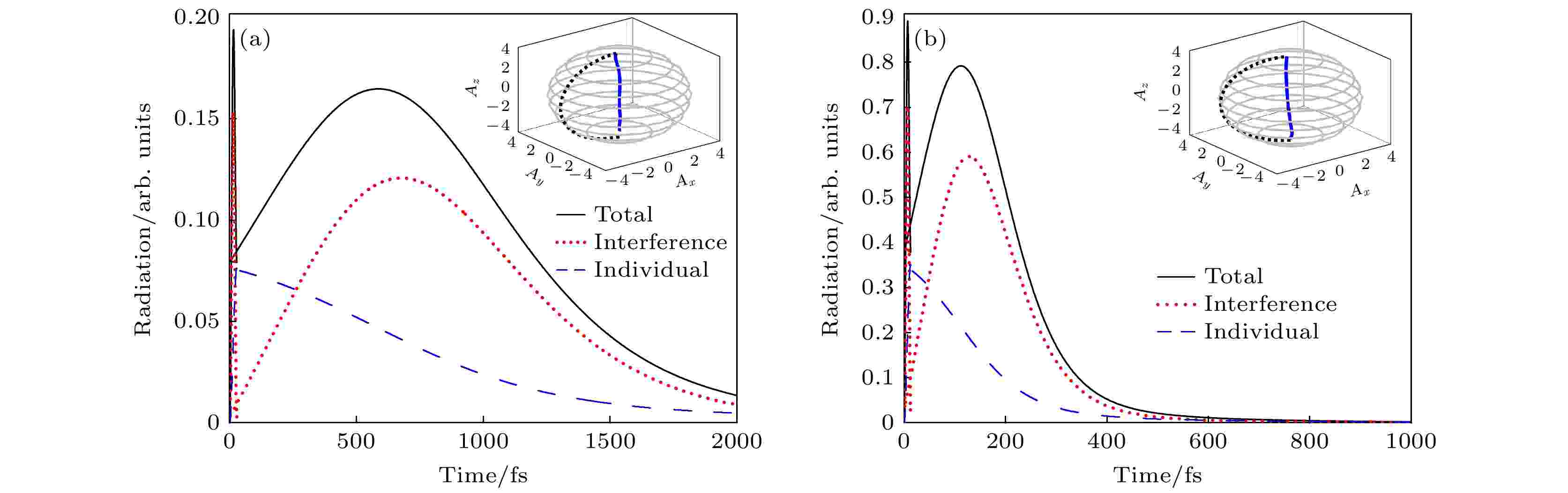
The plasmon cavity system composed of a scanning tunneling microscope tip and a substrate has attracted much attention due to its ability to break through the diffraction limit, enhance the electromagnetic field by hundreds of times, and localize it on a nanometer or even sub-nanometer scale. This plasmon cavity system can serve as an advanced platform for studying superradiance phenomena on an ultrafast scale. Methylene blue molecules have many applications in the field of optics due to their significant light absorption and fluorescence emission characteristics. In this work, macroscopic quantum electrodynamics and open quantum system theory are used to explore the radiation dynamics of methylene blue molecular clusters with three different configurations: cyclic, two-dimensional planar, and one-dimensional chain, in specific scanning tunneling microscope nanocavity and picocavity. Taking the cyclic molecular clusters for example, the radiation effects of different external field excitations on the molecular clusters in the cavity are studied. The research results indicate that for the same molecular cluster configuration, the scanning tunneling microscope picocavity has a more significant superradiance intensity, while the scanning tunneling microscope nanocavity has a longer duration of superradiance. From the perspective of symmetry, the one-dimensional chain molecular clusters only have axial symmetry, while the two-dimensional planar and cyclic molecular clusters have both axial symmetry and central symmetry. The cyclic molecular clusters also have multiple rotational symmetries. Therefore, within the same scanning tunneling microscope cavity, the higher the symmetry of the arrangement of molecular clusters, the easier it is to generate significant superradiance pulses. In addition, because of its higher spatial resolution and stronger local field enhancement effect, the picocavity of scanning tunneling microscope is more sensitive to changes of external conditions such as excitation wavelength. These results indicate that the occurrence and enhancement of superradiance can be effectively controlled by reasonably designing the cavity structure and geometric configuration of molecular clusters, and the time scale of superradiance pulses can be extended to the picosecond order, which provides new ideas and methods for practical applications in the fields of optics and nanotechnology in the future.
EDITOR'S SUGGESTION
2025, 74 (7): 076103.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241481
Abstract +
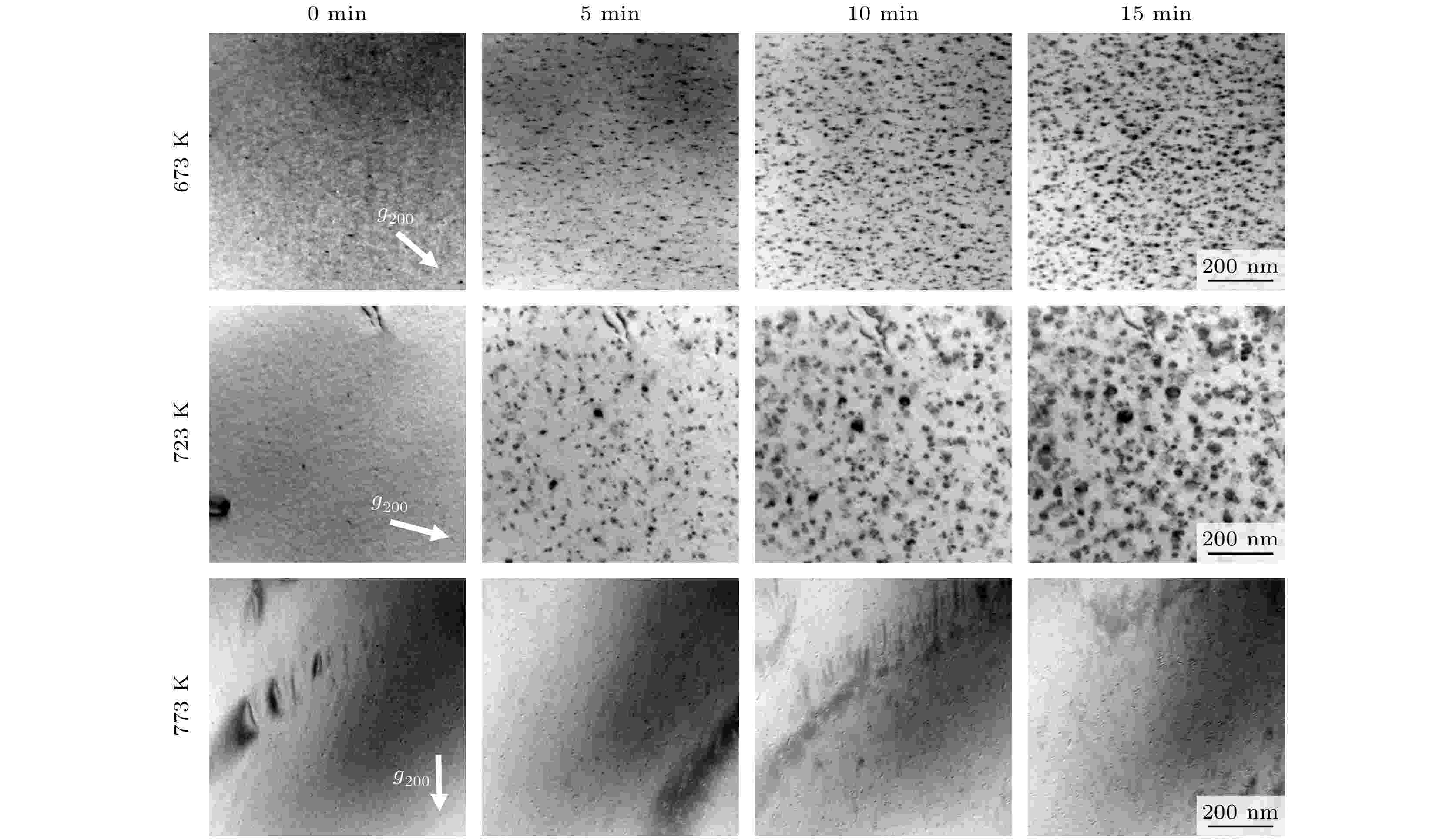
The sluggish diffusion and severe lattice distortion effects in high-entropy alloys (HEAs) theoretically impede the movement of radiation-induced point defects, thereby effectively suppressing the formation of larger defect clusters and ultimately enhancing the radiation resistance of materials. Current research on the radiation resistance of HEAs primarily concentrates on the qualitative analysis of the migration behaviors of radiation-induced defects, while the quantitative research on the energy barriers of the migration behavior of point defects is still limited. As a representative HEA system, FeCoCrNiAl-based alloy exhibits exceptional properties, including enhanced ductility, remarkable shear resistance, high tensile yield strength, and excellent oxidation resistance. In this study, FeCoCrNiAl0.3 alloy is selected as a model material and in-situ observations are conducted by using a 1.25-MV high-voltage electron microscope (HVEM) to systematically investigate the temporal evolution of irradiation-induced defects and precipitates at different temperatures. Based on the statistical data of saturated defect number density and defect growth rates under three irradiation temperatures, two intrinsic parameters of the alloy, i.e. interstitial atom migration energy and vacancy migration energy, are determined to be 1.09 eV and 1.47 eV, respectively. The higher interstitial atomic migration energy may be related to the incorporation of Al that has a smaller threshold energy and exhibits a larger atomic radius difference than the other elements in the alloy. In addition, the morphology and distribution of dislocation loops formed at 723 K and high-energy electron irradiation are characterized in detail, demonstrating the coexistence of perfect dislocation loops and Frank dislocation loops, both of which grow along different crystal planes. No systematic difference in growth process between the two types of loops is observed.
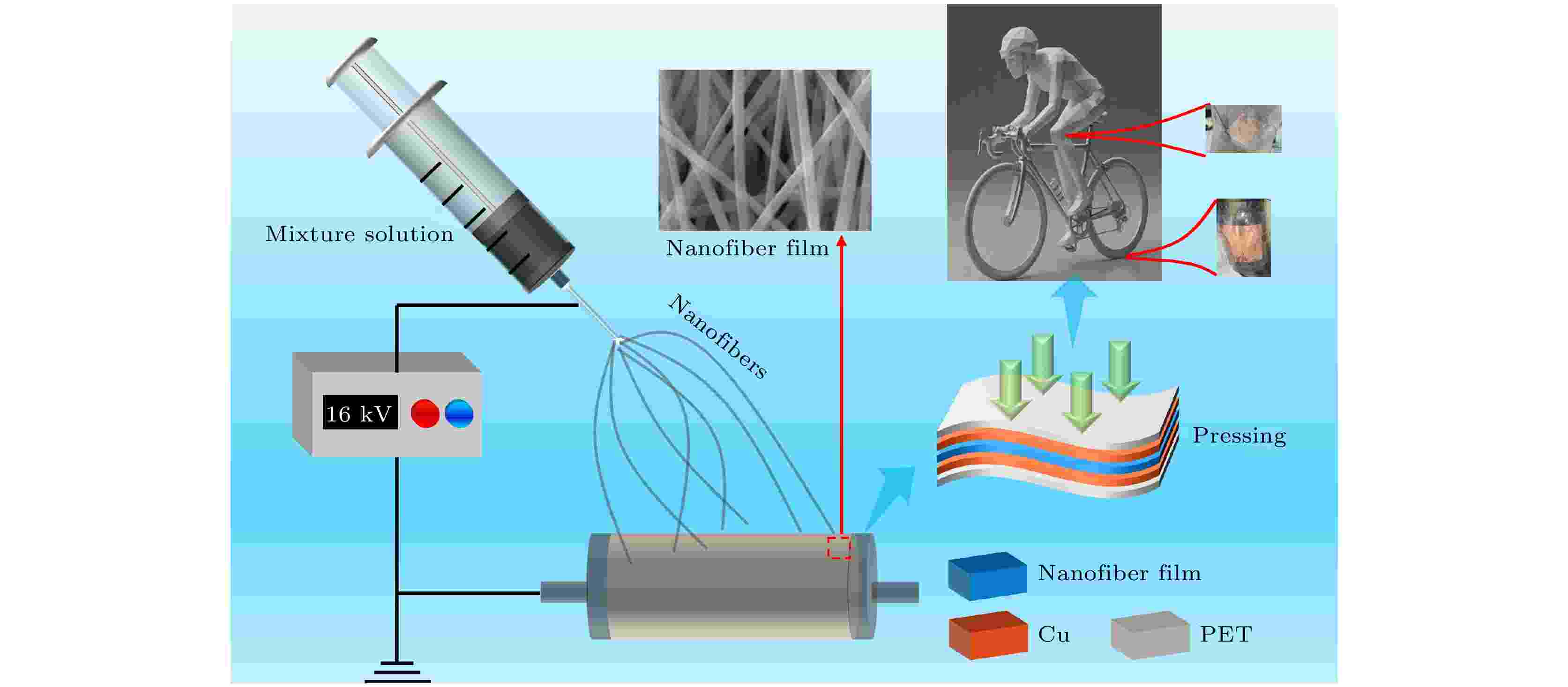
2025, 74 (7): 076801.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241676
Abstract +
Flexible piezoelectric materials can convert mechanical energy into electrical energy to power micro/nano electronic devices. In recent years, research into piezoelectric technologies has revealed that molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) can improve the piezoelectric properties of composite materials. In this research the fabrication of a PAN/MoS2 flexible composite nanofiber film piezoelectric sensor via electrospinning is presented. The influence of MoS2 nanosheet content on the piezoelectric performance of the PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber films is systematically investigated, and the morphology and structure of the composite nanofiber films are characterized. The results show that MoS2 is uniformly distributed in the composite nanofiber films, and the zigzag conformation of the PAN molecular is enhanced by adding MoS2. As the MoS2 doping content increases, the performance of the PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber film sensor shows a first-increasing-and-then-decreasing trend, and ultimately reaching a maximum value when the MoS2 weight content is 3.0%. When the MoS2 doping content increases from 0% to 3.0%, the open-circuit output voltage of the PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber film sensor increases from 1.92 V to 4.64 V, and the short-circuit output current increases from 1.03 μA to 2.69 μA. At 3.0% MoS2 doping, the maximum output power of the PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber film sensor reaches 3.46 μW, with an internal resistance of approximately 10 MΩ. The output voltage of the composite nanofiber film sensor increases with the applied external force increasing. At a frequency of 10 Hz, when external forces of 2 N, 3 N, 4 N, 5 N, and 6 N are applied, the sensor output voltages are 2 V, 3.4 V, 5.9 V, 8.7 V, and 10.3 V, respectively. Compared with pure PAN film, the PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber film has a piezoelectric constant d33 increases by 4.86 times. The PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber film sensor can efficiently charge commercial capacitors, and the discharging of capacitors can successfully power a green LED. Additionally, it can monitor in real-time, under passive conditions, the bending state of the knee and the forward movement of the bicycle wheel during cycling. After 10000 impact cycles, the PAN/MoS2 composite nanofiber film sensor shows stable voltage output with no obvious fluctuations, demonstrating excellent stability. All in all, the PAN/MoS2 flexible composite nanofiber film sensor exhibits outstanding flexibility, low cost, and self-powered capabilities, showing promising potential for applications in wearable/portable electronics, smart devices, and intelligent robotics.
CONDENSED MATTER: ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRICAL, MAGNETIC, AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES
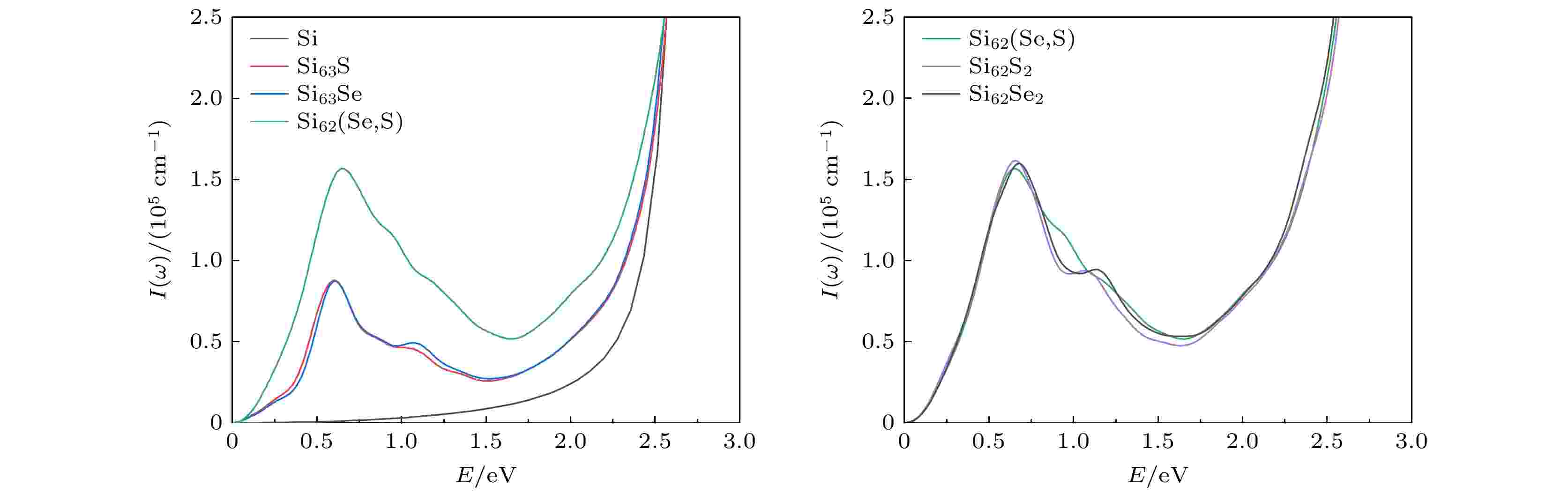
2025, 74 (7): 077101.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241434
Abstract +
In order to provide more accurate theoretical guidance for improving photoelectric properties of chalcogens doped silicon, the lattice structure, stability, band structure, density of state and optical properties of (S, Se) co-doped silicon are systematically investigated based on the first principles, and the related properties are compared with those of S-doped and Se-doped silicon. The calculated results show that the photoelectric characteristics of S-doped Si and Se-doped Si are extremely similar to each other, with a new impurity band appearing in their bandgap. This new impurity band primarily results from the contributions of the 3s state electrons of S and the 4s state electrons of Se, promoting the absorption of low-energy photons and increasing the optical absorptivity of doped Si in the near infrared region. Compared with monocrystalline silicon, the S-doped Si and Se-doped Si have the optical absorption spectra, each with a new peak at 0.6 eV, which is caused by the transition of electrons from the impurity band to the conduction band. The (S, Se) co-doped Si exhibits good stability at operating temperature, and two impurity bands appear between the valence band and conduction band, which are formed by electrons from the 3s state of S and the 4s state of Se, respectively. The optical absorptivity of (S, Se) co-doped Si is greatly improved in the low energy region compared with that of single doped Si, with a new absorption peak appearing at 0.65 eV, similar to the formation observed in singly doped Si. However, due to the indirect transition process between two impurity energy bands, the absorption peak of (S, Se) co-doped Si is larger in the low energy region. Compared with S-doped silicon and Se-doped silicon with the same concentration, the (S, Se) co-doped Si has optical absorptivity that is significantly improved in the range from 0.81 eV to 1.06 eV. This study provides theoretical guidance for applying the (S, Se) co-doped Si to the field of photoelectron such as infrared photodetectors and solar cells.
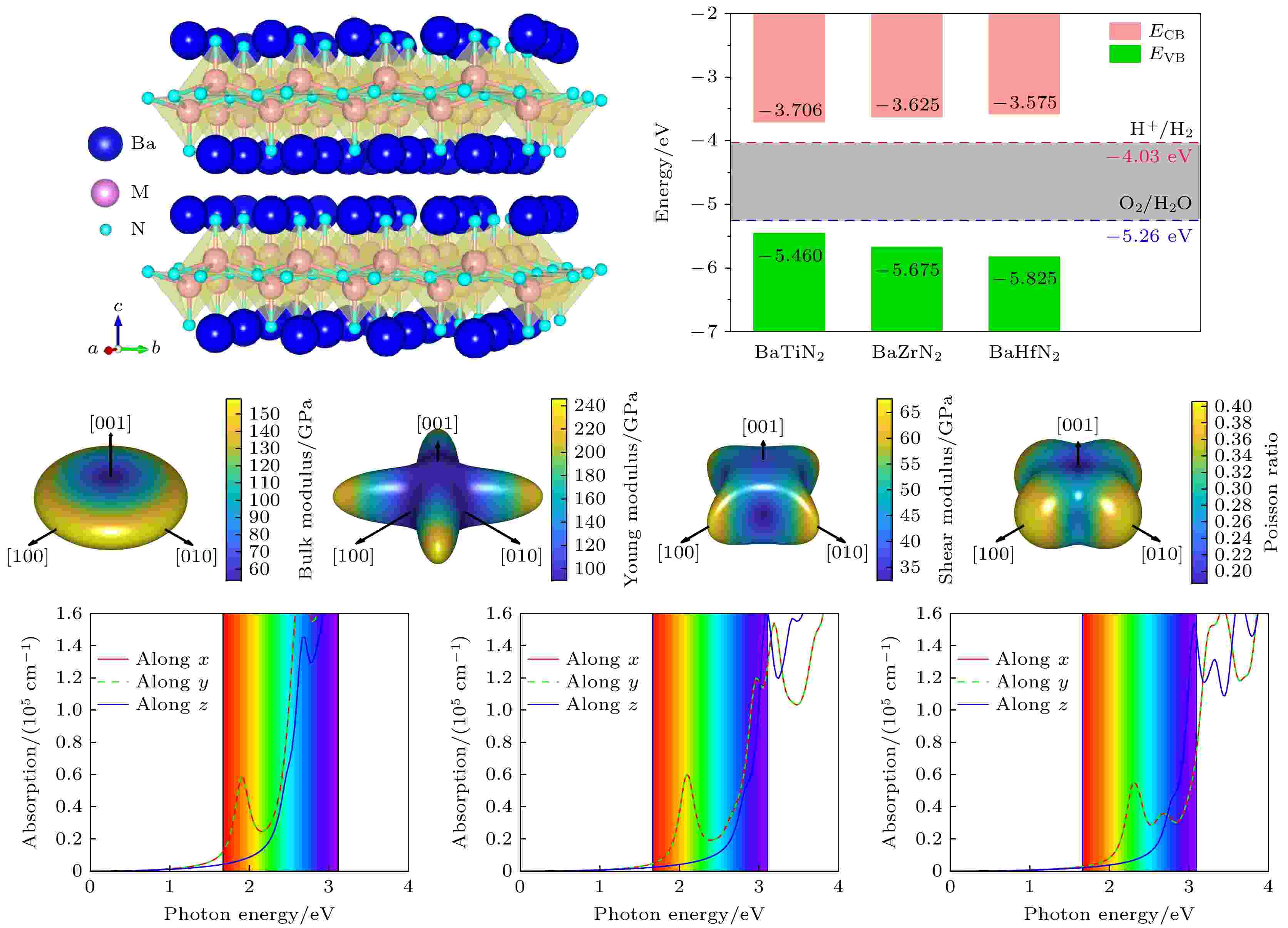
2025, 74 (7): 077102.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241665
Abstract +
Ternary layered nitrides have received widespread attention due to their unique electrical, optical and optoelectronic properties, which are promising for the fabrication of low-cost and high-efficiency optoelectronic materials, solar cell materials and photocatalysts. Although there is a lack of experimental reports on BaTiN2 so far, BaZrN2 and BaHfN2 have been synthesized experimentally by solid state methods. However, their optical and electrical transport properties have not been investigated systematically. This work is to systematically investigates the mechanical, electronic, optical absorption, carrier transport, and dielectric response properties of BaMN2 (M = Ti, Zr, Hf) nitrides through first-principles calculations based on density functional theory. Due to the quasi-two-dimensional layered arrangement of [MN2]2– slabs, the ionic bonds between Ba2+ and N3–, and the weak interactions between the slabs, the deformation along this direction is most likely to occur under the action of external stress. BaMN2 nitrides exhibit significant anisotropic physical properties. Firstly, the mechanical properties of BaMN2, such as bulk modulus, shear modulus, Young’s modulus, and Poisson’s ratio, show prominent anisotropy. The lower modulus, higher Poisson’s ratios and Pugh’s modulus ratios indicate good flexibility of the BaMN2 nitrides. In addition, BaMN2 has indirect bandgap values (1.75–2.25 eV) within the visible-light energy range, which meets the basic requirement for the band gap of a photocatalyst for water splitting (greater than 1.23 eV). Moreover, BaMN2 has suitable band-edge positions. The appropriate bandgap values and band-edge positions indicate their broad application prospects in the absorber layer of solar cells and photocatalytic water decomposition. Due to the significant difference in the effective mass of its charge carriers between different directions, BaMN2 exhibits ultrahigh anisotropic carrier mobility (on the order of 103 cm2⋅s–1⋅v–1) and lower exciton binding energy. At the same time, there are significant differences in atomic arrangement and bonding interactions between the in-plane direction and out of plane direction, resulting in high anisotropic visible-light absorption coefficient (on the order of 105 cm–1) in the low energy region. In contrast, the increase of the opportunity for electrons to transition from occupied to unoccupied states leads to more complex light absorption and relatively reduced anisotropy in higher energy region. Furthermore, the special layered structure has lower polarizability and higher vibration frequency along the vertical direction perpendicular to the [MN2]2– layers, rendering BaMN2 nitrides show high dielectric constants. These excellent anisotropic mechanical, optoelectronic, and transport properties allow BaMN2 layered nitrides to be used as promising semiconductor materials in the fields of optoelectronics, photovoltaics, and photocatalysis.
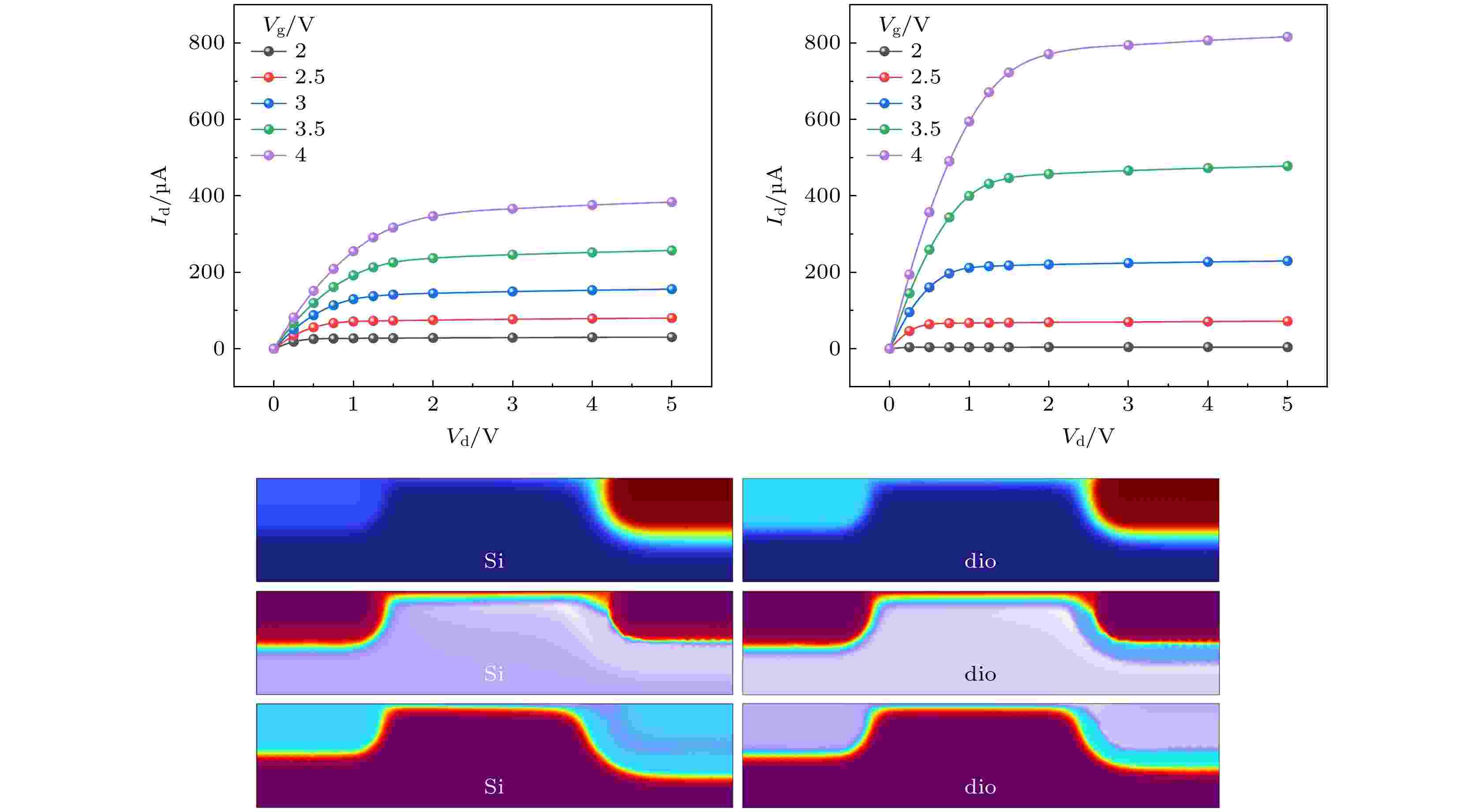
2025, 74 (7): 077201.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20250009
Abstract +
The new generation of detection equipment urgently requires high-sensitivity detectors. Traditional silicon-based detectors cannot meet the requirements for sensitivity and channel size. Diamondene has excellent performance such as high carrier mobility and wide band gap. Its excellent electronic characteristics are expected to effectively improve the sensitivity of the detector and provide a new way for developing the next generation of detectors. However, the detection mechanism based on diamondene is still unclear. Based on the above problems, the analytical model and mechanism of the transistor channel are first studied. By analyzing the relationship between the surface potential distribution of the current channel and the effective channel size in the working state and the sensitive characteristics of the two-dimensional material electrons of the channel, a theoretical model of the transistor detector is constructed based on the electronic characteristics of the channel material, and the working characteristics of the detector are investigated. The finite element simulation of the working mechanism, potential and electron distribution of the transistor detector is carried out. The simulation results show that the mobility level of the diamondene-based detector is 2.5 times that of the traditional silicon-based detector, which theoretically verifies the hypersensitive detection characteristics of the diamondene-based detector. This study is of great significance in designing and applying a new generation of carbon-based ultra-sensitive detection devices.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PHYSICS AND RELATED AREAS OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
2025, 74 (7): 078101.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241757
Abstract +
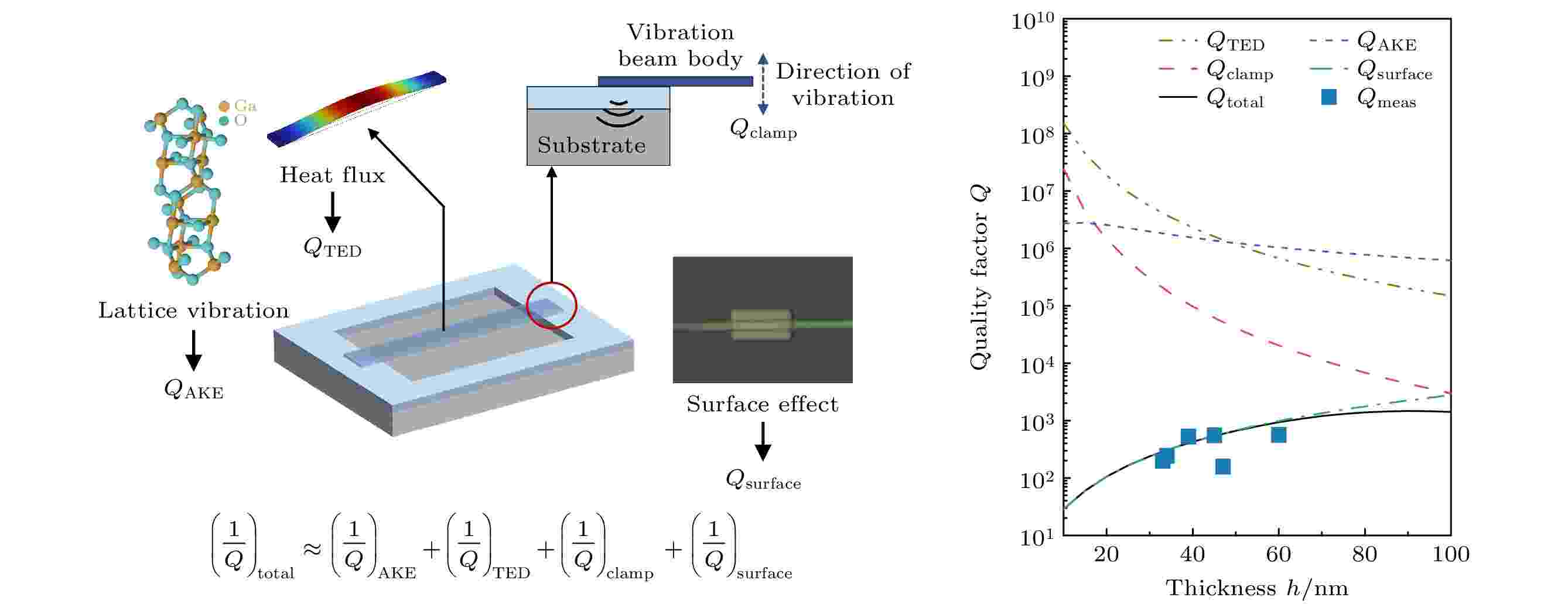
2025, 74 (7): 078501.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241706
Abstract +
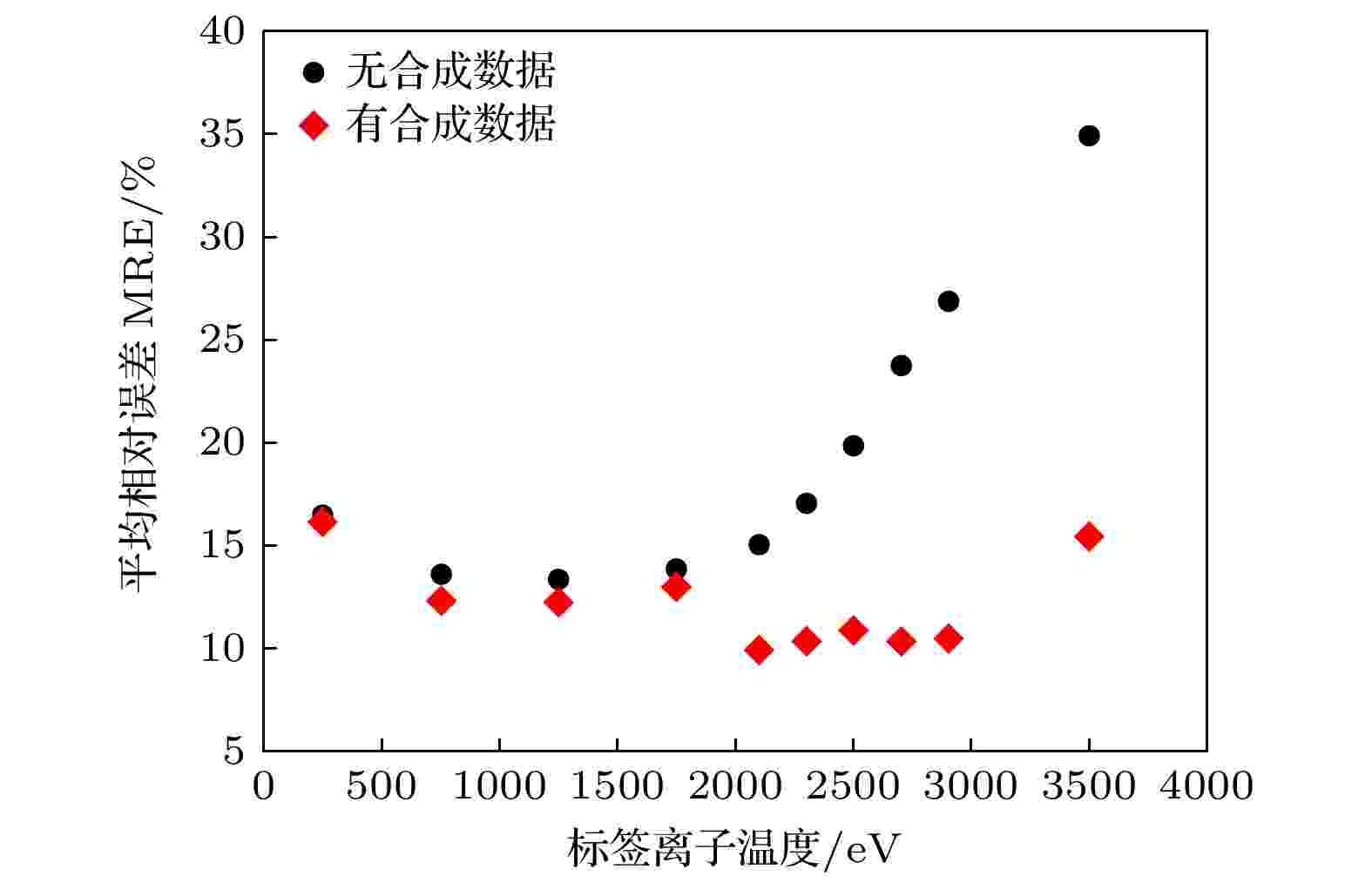
2025, 74 (7): 078901.
doi: 10.7498/aps.74.20241739
Abstract +
ERRATA