-
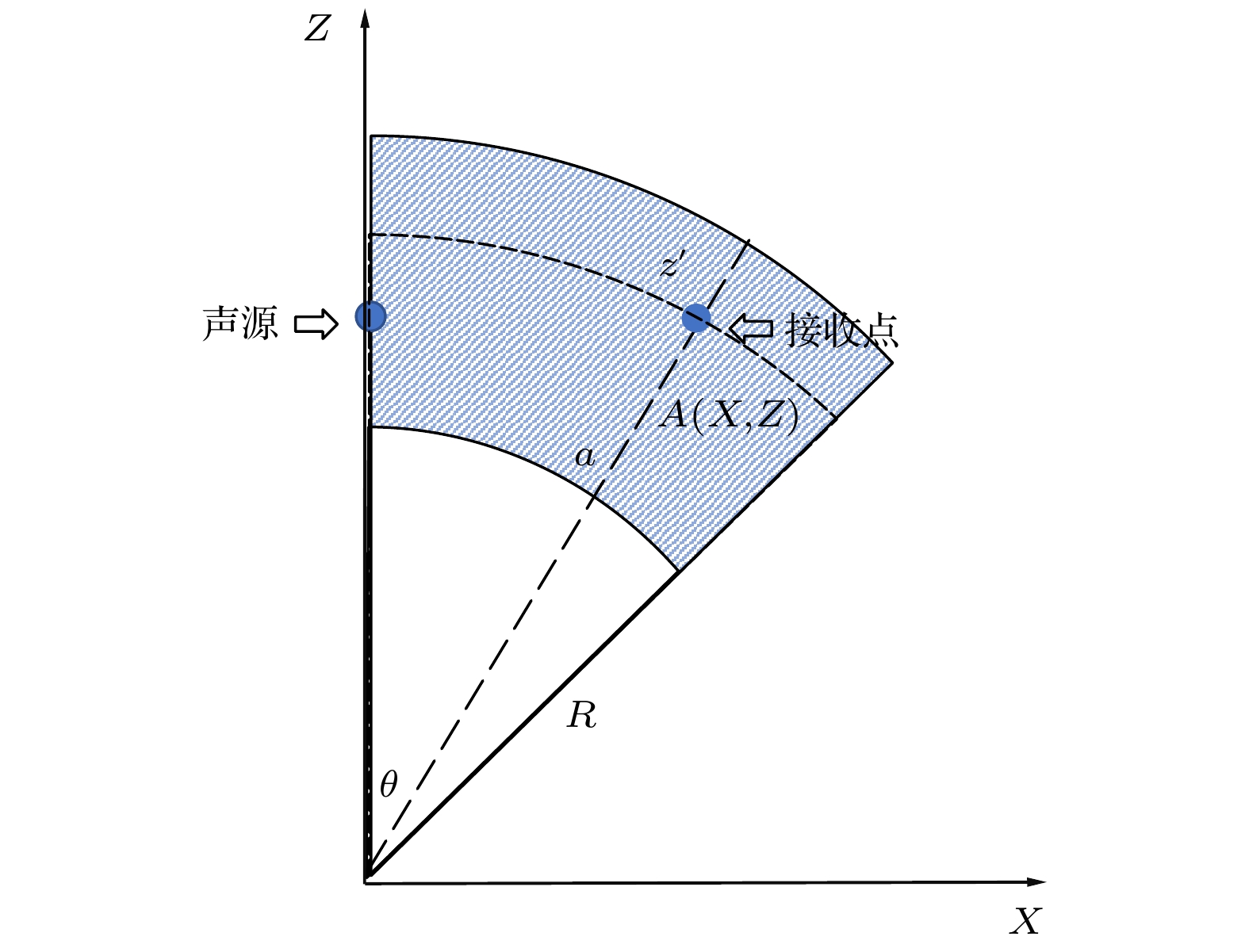
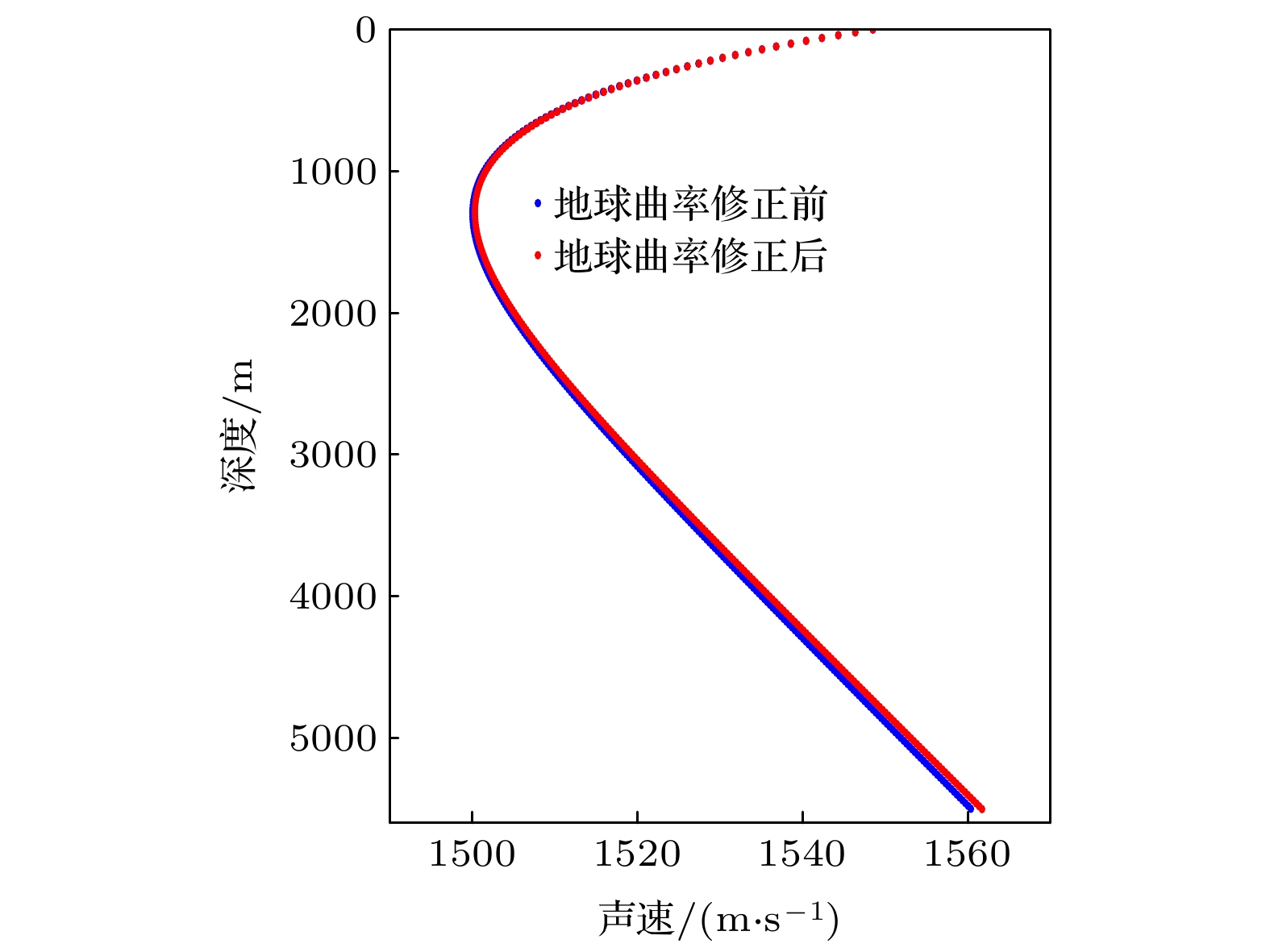
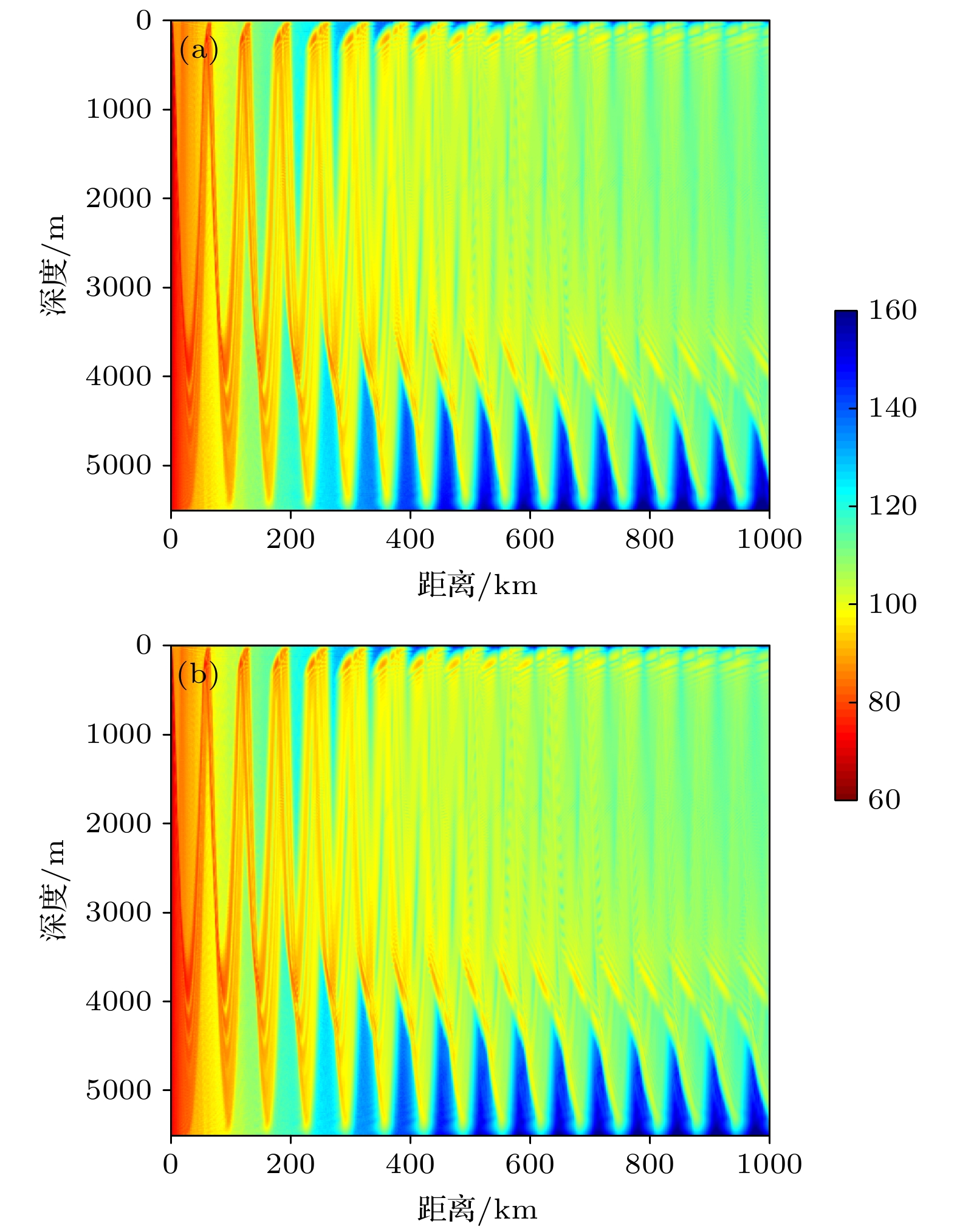
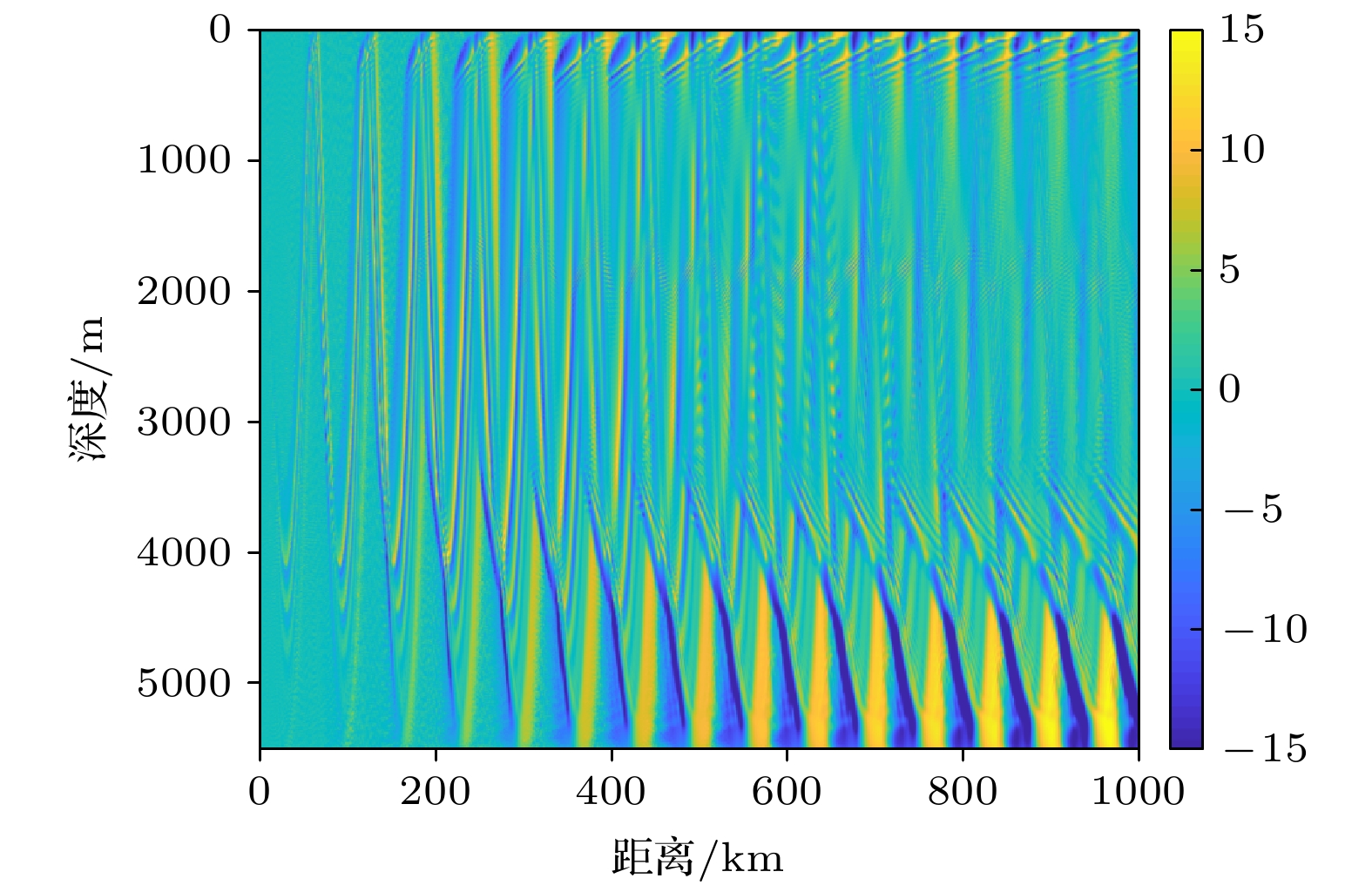
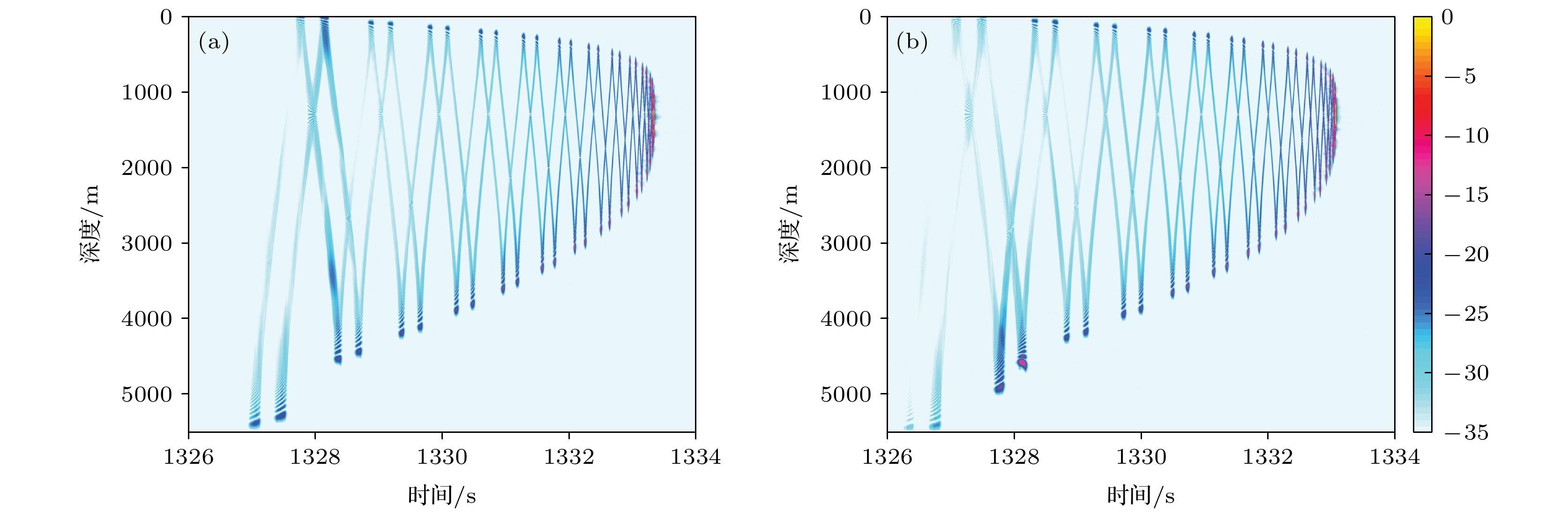
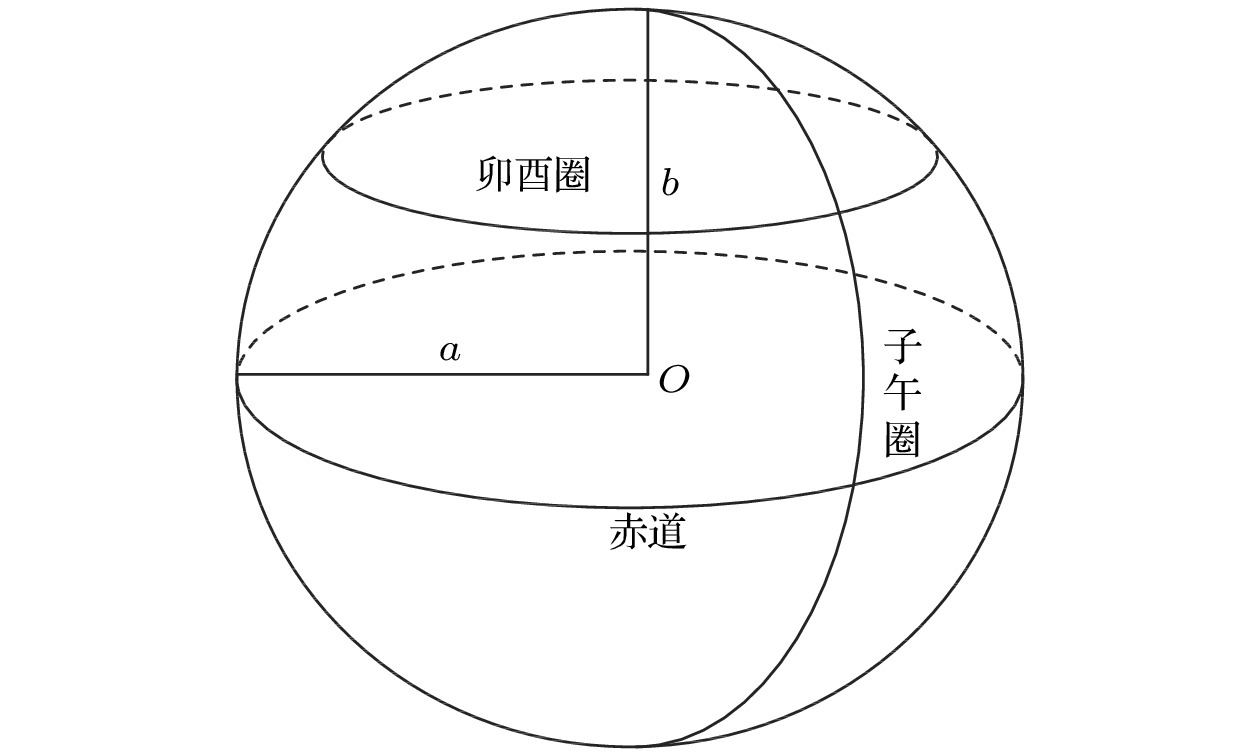
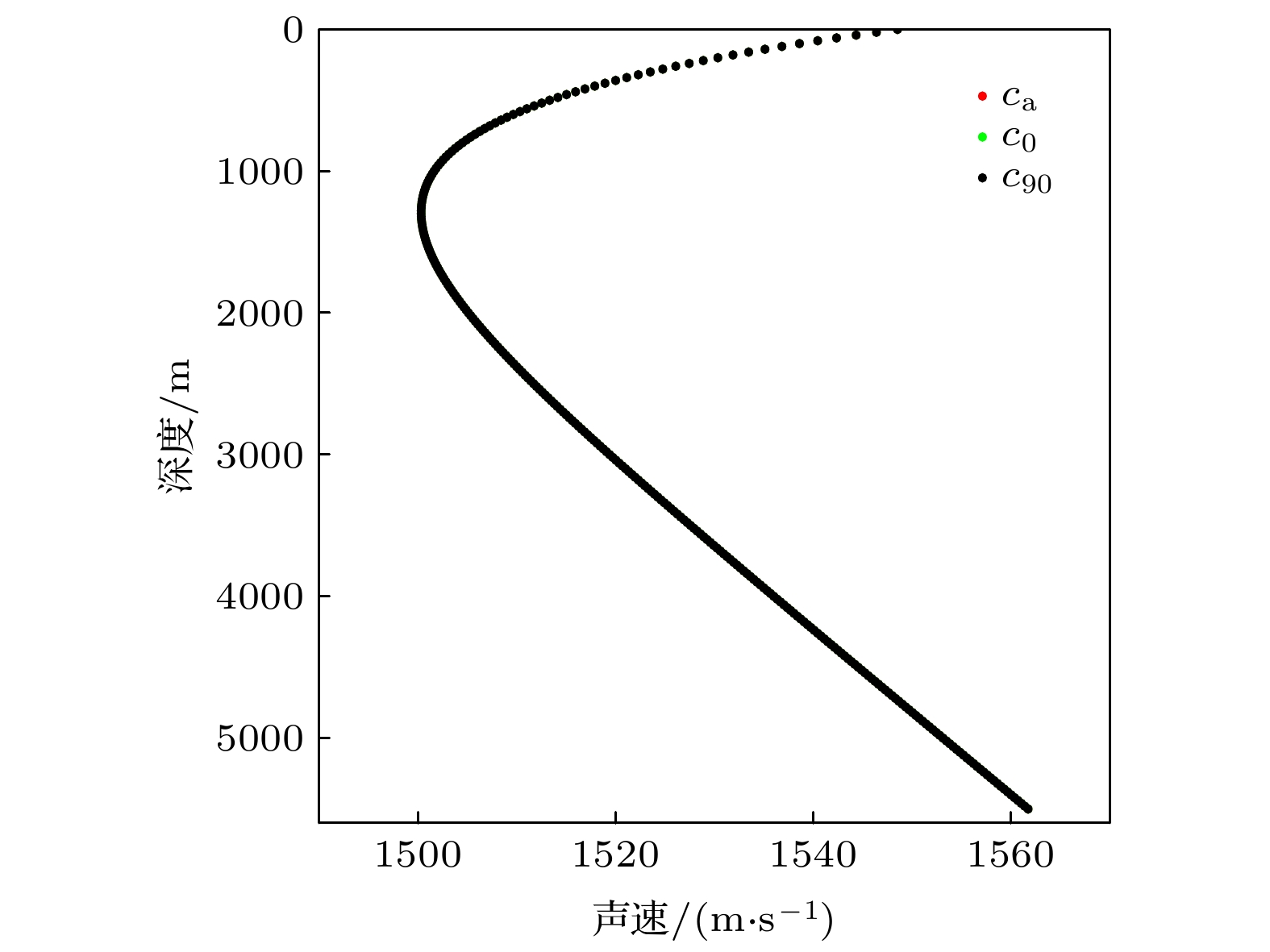
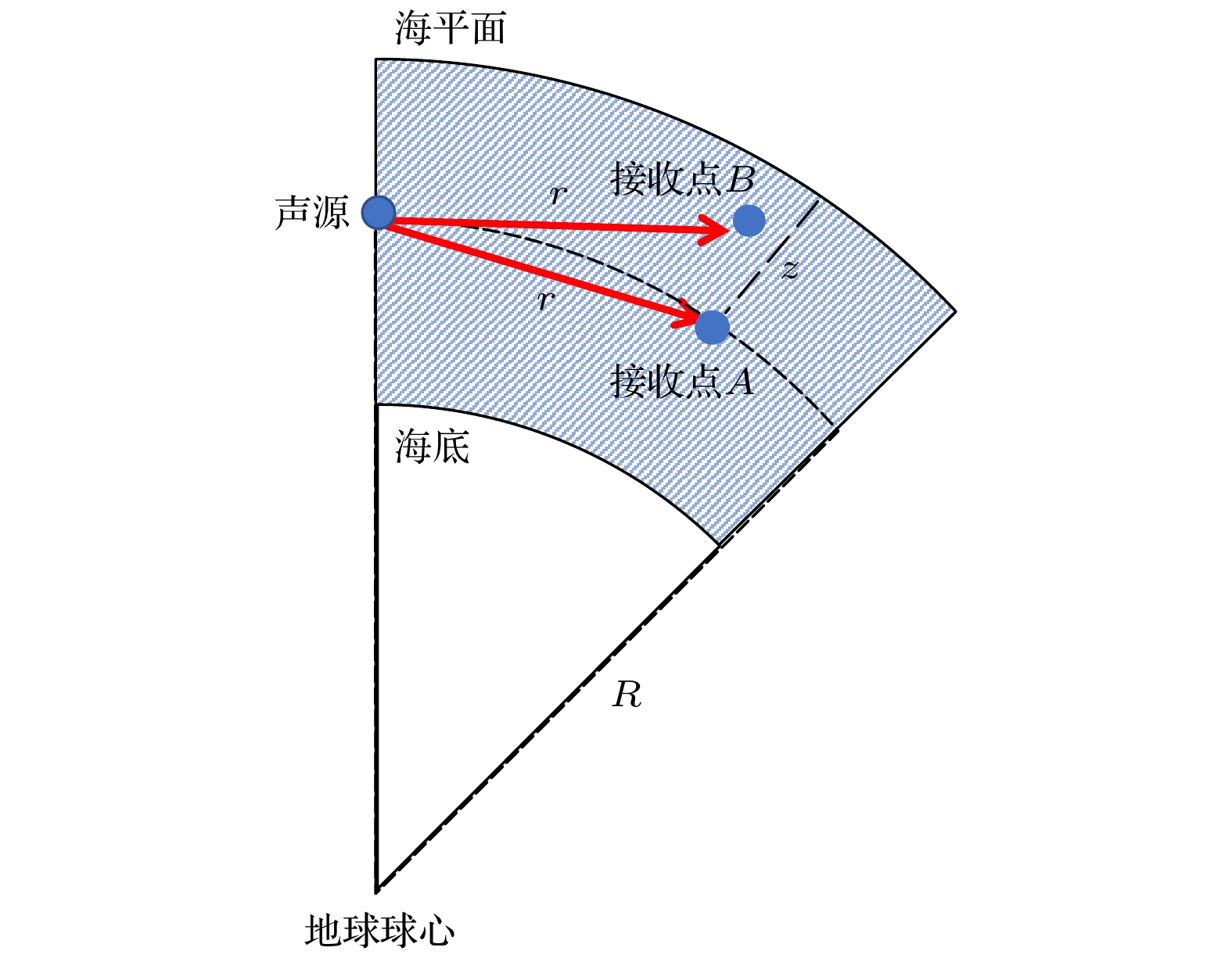
Since the earth is approximately a sphere, the sound speed equivalent surface on the range-depth plane is not a parallel plane, but a concentric sphere at a long distance. Therefore, for a long-range sound propagation, the effect of the curvature of the earth cannot be ignored. In this paper, conformal mapping is used to propose a method of earth curvature correction without changing the existing sound field calculation model, and has the characteristics of good portability and simple calculation. The simulation results in a typical environment show that because of the earth curvature, the location of the convergence zone moves toward the sound source, and its movement can reach 10 km at 1000 km in distance. Before and after the earth curvature correction, the transmission loss difference can reach up to 15 dB at a particular location. Through the analysis of the simulation results in four typical sound speed profiles in Northwest Pacific Ocean, it is found that the movement of the convergence zone and the distance change are approximately linear, and the movement of the convergence zone increases by about 1km for every increase of the propagation distance by 100 km. For deep-sea channel propagation, the earth curvature will cause the arrival structure to move forward as a whole on the time axis, and the degree of the forward motion will gradually increase with the distance increasing. At 1000 km, the amplitude of the forward motion can reach 136 ms. In addition, the earth curvature will also cause the depth and time extension of the arrival structure. For the received time-domain waveform at a certain depth, there is a big difference between before and after the earth curvature correction. The modified results from different earth approximation models show that the accuracy of the calculation can be satisfied by approximating the earth as a standard sphere.
-
Keywords:
- earth curvature /
- sound propagation /
- convergence zone /
- arrival structure
[1] Vadov R A 2005 Acoust. Phys. 51 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张鹏, 李整林, 吴立新, 张仁和, 秦继兴 2019 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang P, Li Z L, Wu L X, Zhang R H, Qin J X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 吴丽丽 2017 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院声学研究所)
Wu L L 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: The Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[4] Van L J, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Rudnick D L, Colosi J A 2010 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127 2169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Van L J, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Rudnick D L 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 3569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张燕, 李整林, 甘维明, 李文 2016 声学技术 35 2
Zhang Y, Li Z L, Gan V M, Li W 2016 Technical Acoustics 35 2
[7] Richer G H 1966 Radio Sci. 1 1435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Pekeris C L 1946 Phys. Rev. 70 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Muller G 1970 Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 21 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Muller G 1971 Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 23 435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Biswas N N 1972 Pure Appl. Geophys. 96 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Biswas N N, Knopoff L 1970 Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 60 1123
[13] 徐传秀, 朴胜春, 张红星, 杨士莪, 张海刚, 周建波 2015 声学技术 34 2
Xu C X, Piao S C, Zhang H X, Yang S E, Zhang H G, Zhou J B 2015 Technical Acoustics 34 2
[14] Yan J G 1999 Appl. Acoust. 57 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yan J G 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 1538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Etter P C 2018 Underwater Acoustic Modeling and Simulation (5th Ed.) (New York: CRC Press) p210
[17] 潘威炎 1981 30 661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan W Y 1981 Acta Phys. Sin. 30 661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 孔祥元, 郭际明, 刘宗泉 2005 大地测量学基础 (武汉: 武汉大学出版社) 第57页
Kong X Y, Guo J M, Liu Z Q 2005 Foundation of Geodesy (Wuhan: Wuhan University Press) p57 (in Chinese)
[19] 钟玉泉 2012 复变函数论(北京: 高等教育出版社) 第268页
Zhong Y Q 2012 Complex Analysis (Beijing: Higher Education Press) p268 (in Chinese)
[20] Ari B M, Jit S 1981 Seismic Waves and Sources (New York: Springer-Verlag) p469
[21] Peter H 1974 Applied and Computational Complex Analysis (Vol. 1) (New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons) p336
[22] Lynne D T, George L P, William J E, James H S 2011 Descriptive Physical Oceanography: An Introduction (6th Ed.) (London: Elsevier) p9
[23] Walter H M 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 55 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Collins M D 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 1736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 王彦磊, 高建华, 李杰, 张芳苒, 郑红莲 2013 海洋通报 32 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y L, Gao J H, Li J, Zhang F R, Zheng H L 2013 Marine Science Bulletin 32 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Locarnini R A, Mishonov A V, Baranova O K, Boyer T P, Zweng M M, Garcia H E, Reagan J R, Seidov D, Weathers K, Paver C R, Smolyar I 2018 World Ocean Atlas 2018, Volume 1: Temperature 81 52
[27] Zweng M M, Reagan J R, Seidov D, Boyer T P, Locarnini R A, Garcia H E, Mishonov A V, Baranova O K, Weathers K, Paver C R, Smolyar I 2018 World Ocean Atlas 2018, Volume 2: Salinity 82 50
[28] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (2nd Ed.) (New York: Springer) p638
-
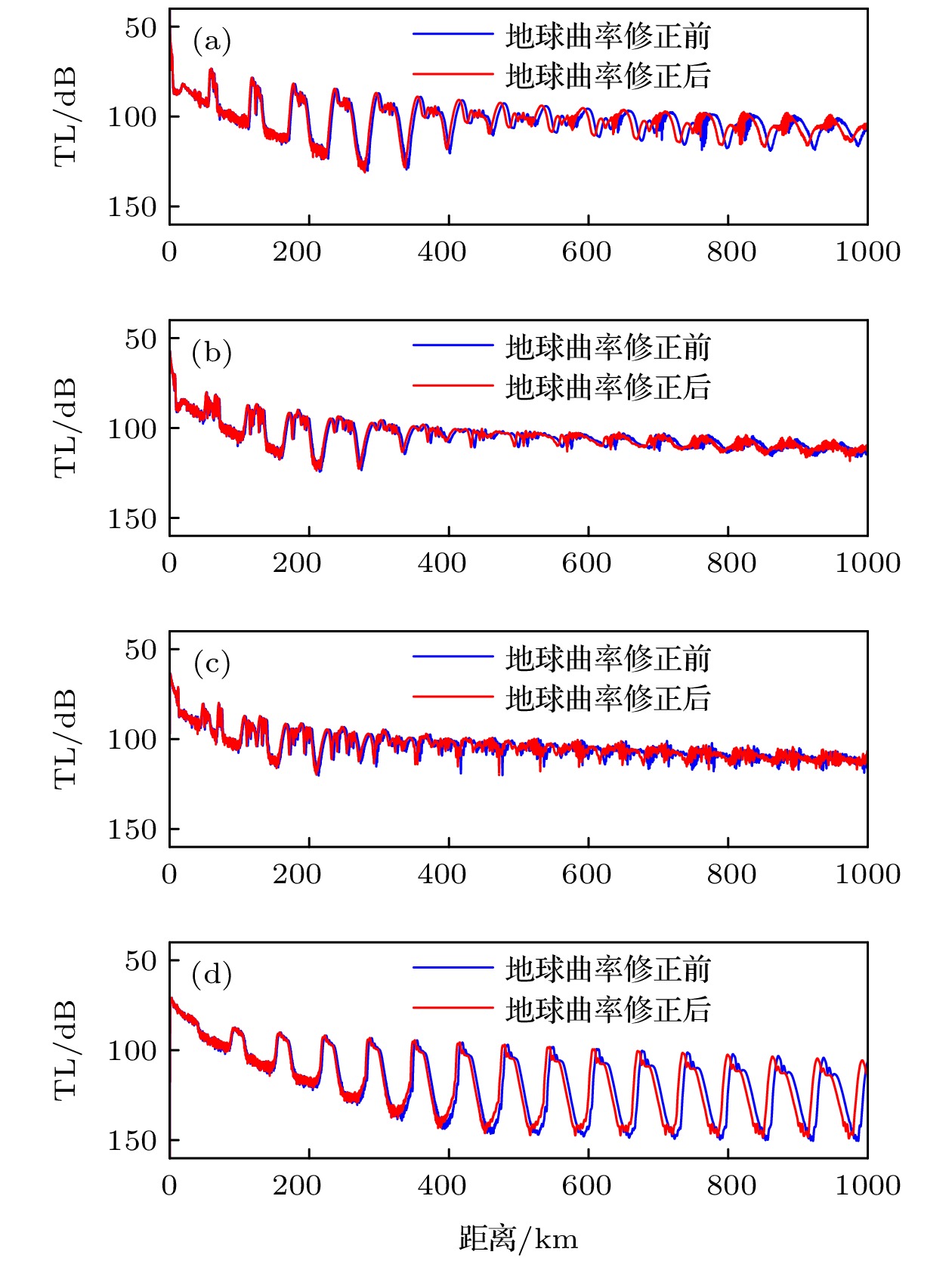
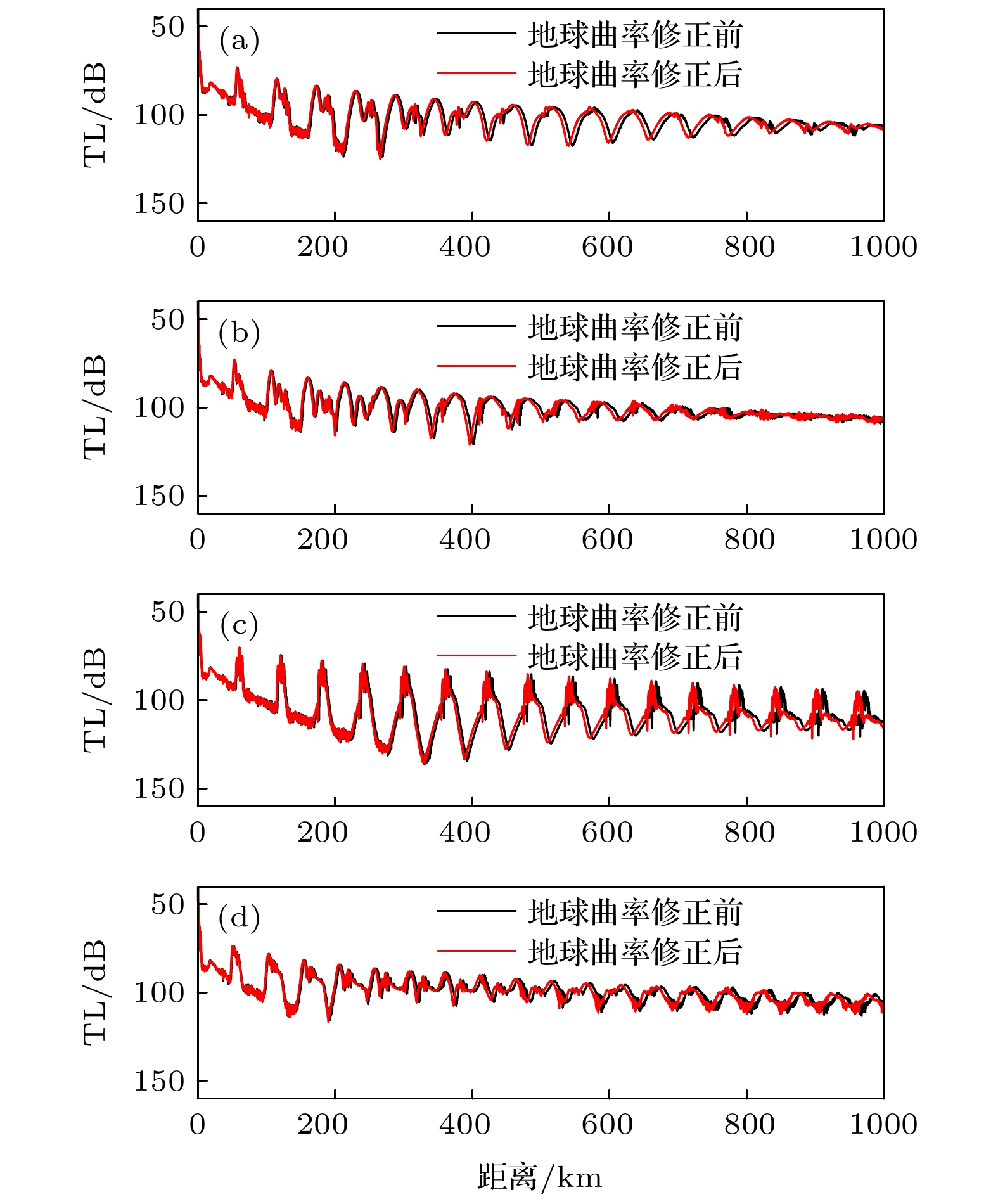
图 13 西北太平洋四类典型声速剖面的200 m深度的传播损失 (a)Ⅰ型声速剖面的传播损失; (b) Ⅱ型声速剖面的传播损失; (c) Ⅲ型声速剖面的传播损失; (d) Ⅳ型声速剖面的传播损失
Figure 13. TLs at a depth of 200 m in four types of typical sound speed profiles in the Northwest Pacific: (a) TLs of type Ⅰ sound speed profile; (b) TLs of type Ⅱ sound speed profile; (c) TLs of type Ⅲ sound speed profile; (d) TLs of type Ⅳ sound speed profile.
-
[1] Vadov R A 2005 Acoust. Phys. 51 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张鹏, 李整林, 吴立新, 张仁和, 秦继兴 2019 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang P, Li Z L, Wu L X, Zhang R H, Qin J X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 吴丽丽 2017 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院声学研究所)
Wu L L 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: The Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[4] Van L J, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Rudnick D L, Colosi J A 2010 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127 2169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Van L J, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Rudnick D L 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 3569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张燕, 李整林, 甘维明, 李文 2016 声学技术 35 2
Zhang Y, Li Z L, Gan V M, Li W 2016 Technical Acoustics 35 2
[7] Richer G H 1966 Radio Sci. 1 1435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Pekeris C L 1946 Phys. Rev. 70 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Muller G 1970 Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 21 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Muller G 1971 Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 23 435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Biswas N N 1972 Pure Appl. Geophys. 96 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Biswas N N, Knopoff L 1970 Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 60 1123
[13] 徐传秀, 朴胜春, 张红星, 杨士莪, 张海刚, 周建波 2015 声学技术 34 2
Xu C X, Piao S C, Zhang H X, Yang S E, Zhang H G, Zhou J B 2015 Technical Acoustics 34 2
[14] Yan J G 1999 Appl. Acoust. 57 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yan J G 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 1538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Etter P C 2018 Underwater Acoustic Modeling and Simulation (5th Ed.) (New York: CRC Press) p210
[17] 潘威炎 1981 30 661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan W Y 1981 Acta Phys. Sin. 30 661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 孔祥元, 郭际明, 刘宗泉 2005 大地测量学基础 (武汉: 武汉大学出版社) 第57页
Kong X Y, Guo J M, Liu Z Q 2005 Foundation of Geodesy (Wuhan: Wuhan University Press) p57 (in Chinese)
[19] 钟玉泉 2012 复变函数论(北京: 高等教育出版社) 第268页
Zhong Y Q 2012 Complex Analysis (Beijing: Higher Education Press) p268 (in Chinese)
[20] Ari B M, Jit S 1981 Seismic Waves and Sources (New York: Springer-Verlag) p469
[21] Peter H 1974 Applied and Computational Complex Analysis (Vol. 1) (New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons) p336
[22] Lynne D T, George L P, William J E, James H S 2011 Descriptive Physical Oceanography: An Introduction (6th Ed.) (London: Elsevier) p9
[23] Walter H M 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 55 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Collins M D 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 1736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 王彦磊, 高建华, 李杰, 张芳苒, 郑红莲 2013 海洋通报 32 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y L, Gao J H, Li J, Zhang F R, Zheng H L 2013 Marine Science Bulletin 32 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Locarnini R A, Mishonov A V, Baranova O K, Boyer T P, Zweng M M, Garcia H E, Reagan J R, Seidov D, Weathers K, Paver C R, Smolyar I 2018 World Ocean Atlas 2018, Volume 1: Temperature 81 52
[27] Zweng M M, Reagan J R, Seidov D, Boyer T P, Locarnini R A, Garcia H E, Mishonov A V, Baranova O K, Weathers K, Paver C R, Smolyar I 2018 World Ocean Atlas 2018, Volume 2: Salinity 82 50
[28] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (2nd Ed.) (New York: Springer) p638
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10945
- PDF Downloads: 108
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: