-
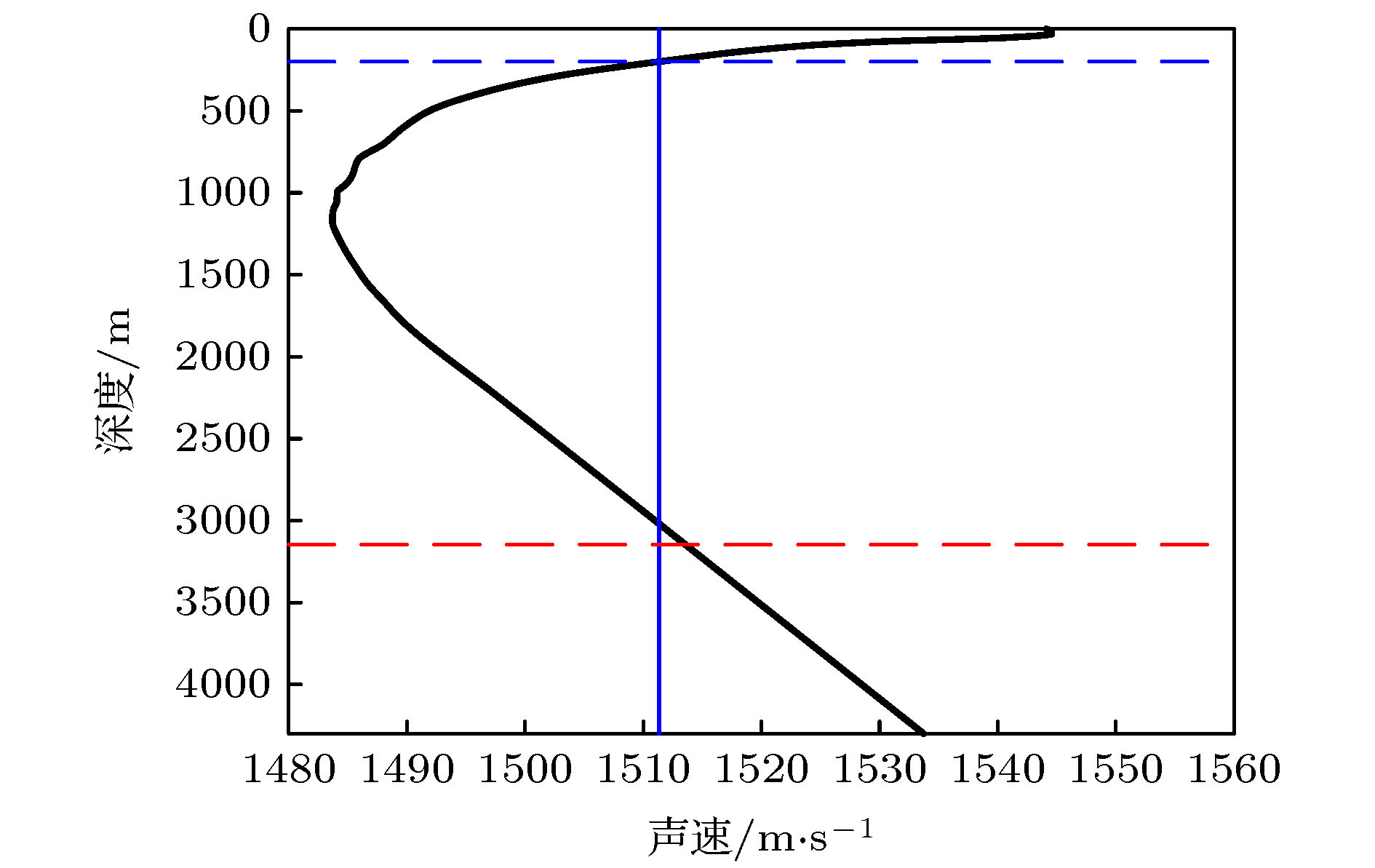
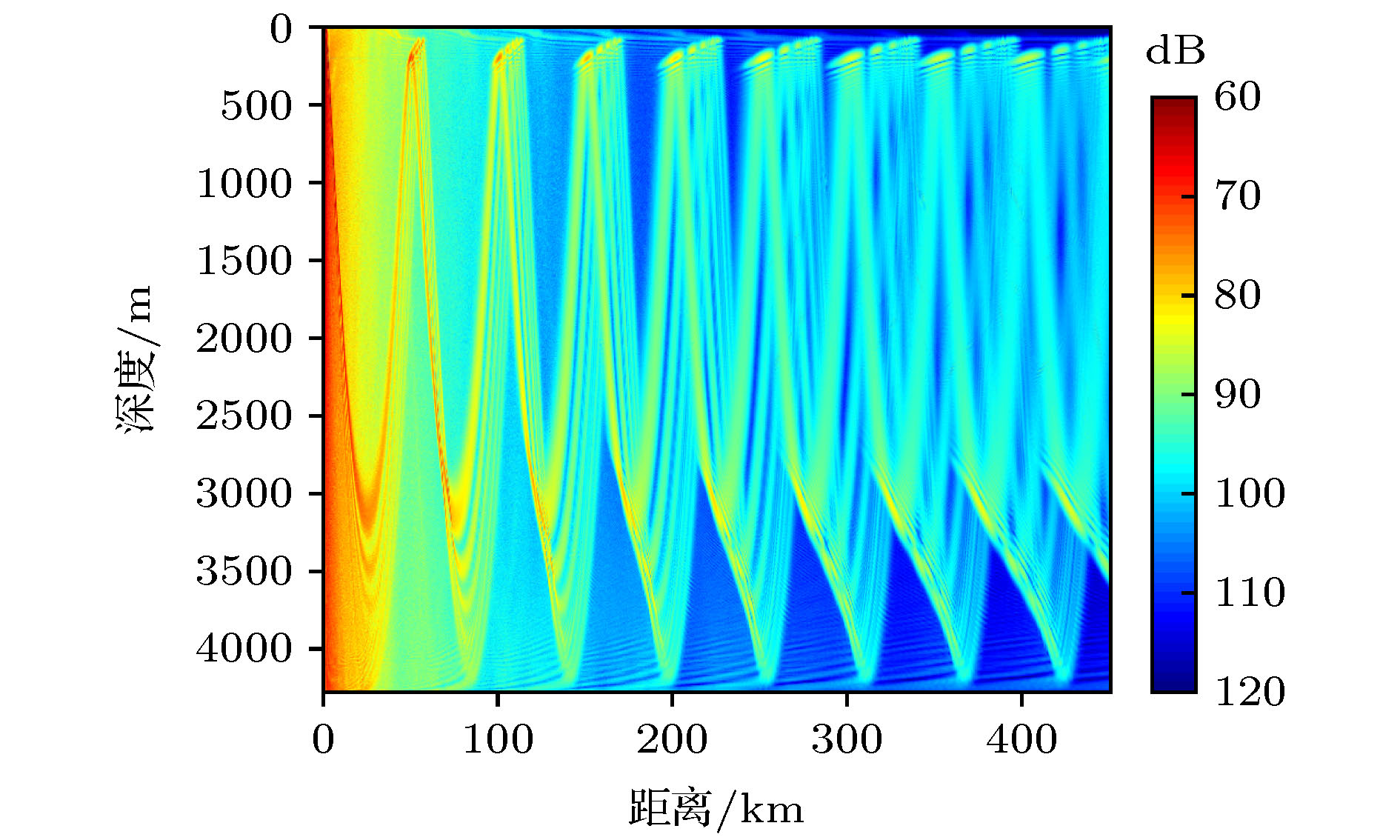
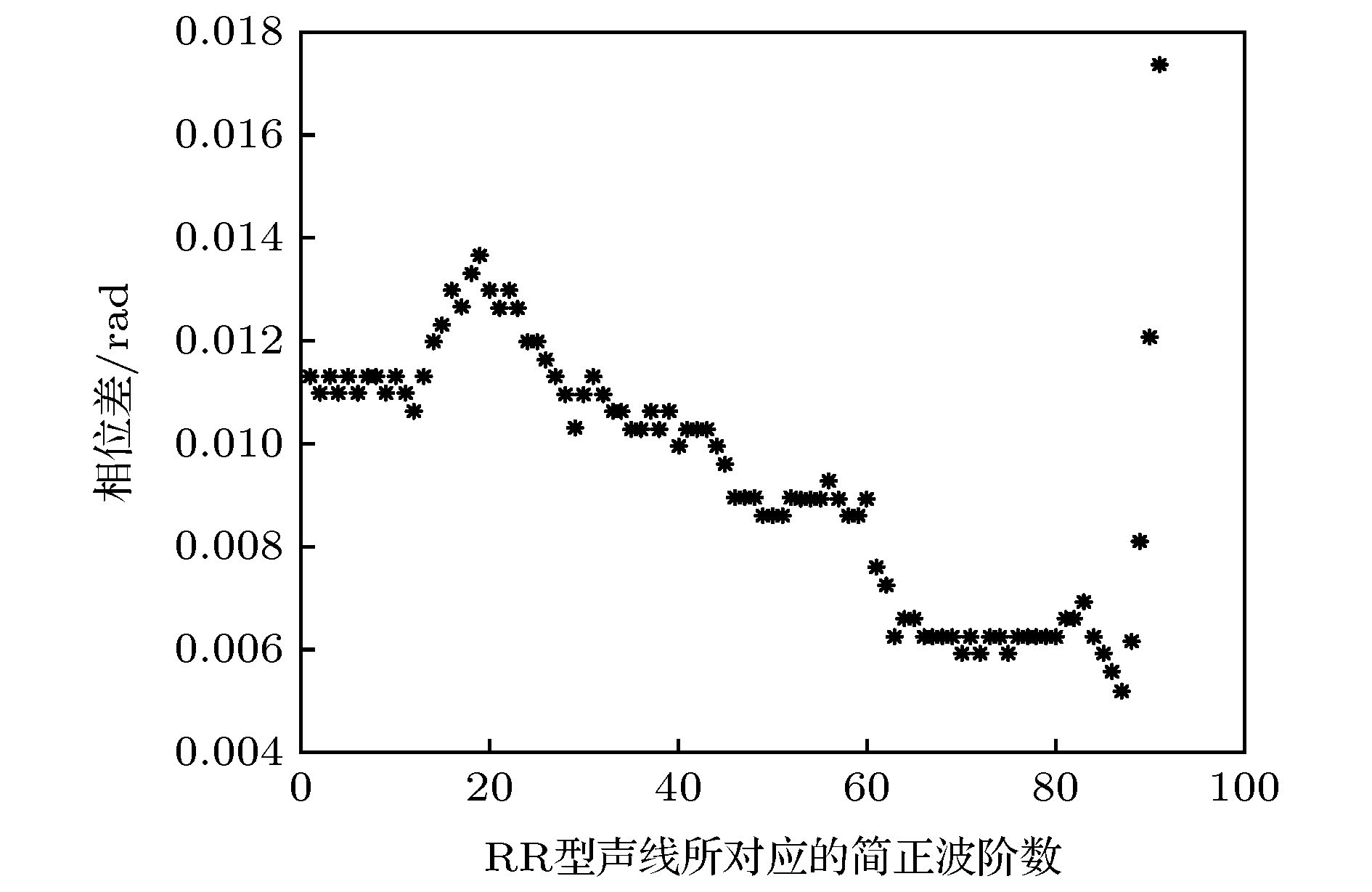
In a deep sea sound channel, rays will bend due to the sound speed profile, and convergence zone will occur when the rays are intensive. Transmission loss in the convergence zone is smaller and it is conducive to acoustic detection and communication. Therefore the study of acoustic characteristics in convergence zone is always the focus of deep-sea acoustics. A long-range sound propagation experiment is conducted in the South China Sea. An equivalent broadband explosive sound source of 1 kg is placed at a depth of 200 m, and the hydrophone receives the data at 3146 m far. The processing and analysis of the experimental data indicate that there is a convergence zone below the sound channel axis in the incomplete deep channel. Compared with the upper turning point convergence zone near the surface, this convergence zone has a high convergence gain at a long distance. The caustic lines of refracted type and refracted surface-refleted type are determined by means of ray-normal mode theory. It is found that the location of the deep convergence zone observed in the experiment is consistent with the position of the refracted caustic line. It is proved that the convergence zone is a lower turning point convergence zone formed by the superposition of a large number of normal modes in the same phase, and it has a convergence effect at a certain depth below the sound channel axis in the deep sea. The formation conditions of the convergence zone and the influence of sound source depth on the caustic structure of the convergence zone are studied. The comparisons of the transmission loss and the width between the upper and lower turning point convergence zone at a long distance aremade. The analysis shows that the convergence gain in the seventh lower turning point convergence zone is still no less than 10 dB. The influence of the vertical structure of sound velocity on the lower turning point convergence zone is studied. The theoretical analysis results are in good agreement with the experimental data.
-
Keywords:
- convergence effect /
- caustics /
- lower turning point /
- transmission loss
[1] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (2nd Ed.) (NewYork: Springer-Verlag) pp16, 175
[2] Woezel J L, Ewing M 1948 Geol. Soc. Amer. Memoirs 27 1
[3] Brekhovskikh L M 1948 Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 69 157
[4] Berman A, Clay C S, Frosch R A, Sherry H B 1959 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 31 838
[5] Hale F E 1961 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 33 456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Urick R J 1965 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 38 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张仁和 1980 声学学报 1 28
Zhang R H 1980 Acta Acust. 1 28
[8] 张仁和 1982 声学学报 2 75
Zhang R H 1982 Acta Acust. 2 75
[9] 龚敏, 肖金泉, 王孟新, 吴寅庚, 黄德华 1987 声学学报 6 417
Gong M, Xiao J Q, Wang M X, Wu Y G, Huang D H 1987 Acta Acust. 6 417
[10] 庄益夫, 张旭, 刘艳 2013 海洋通报 1 46
Zhuang Y F, Zhang X, Liu Y 2013 Marin Sci. Bull. 1 46
[11] 李文, 李整林 2016 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 46 094303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Li Z L 2016 Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 46 094303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张仁和, 孙庚辰, 雷良颖, 周坚力 1981 声学学报 3 198
Zhang R H, Sun G C, Lei L Y, Zhou J L 1981 Acta Acust. 3 198
[13] 胡治国, 李整林, 秦继兴, 任云, 张仁和 2016 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 46 094304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Z G, Li Z L, Qin J X, Ren Y, Zhang R H 2016 Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 46 094304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 范培勤, 笪良龙, 李玉阳 2012 海洋技术 4 23
Fan P Q, Da L L, Li Y Y 2012 Ocean Technol. 4 23
[15] 张鹏, 李整林, 吴立新, 张仁和, 秦继兴 2019 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang P, Li Z L, Wu L X, Zhang R H, Qin J X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Raphael D T 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 56 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sachs D A, Silbiger A 1971 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 49 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Blatstein I M 1971 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 49 1568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Duda T F, Bowlin J B 1994 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 96 1033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bongiovanni K P, Siegmann W L, Ko D S 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 3033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tindle C T 2002 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 112 464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ainslie M A, Robins A J, Simons D G 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115 1449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] White A W, Henyey F S, Andrew R K, Mercer J A, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Colosi J A 2016 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 140 3952
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Heaney K D, Baggeroer A B, D’Spain G L, Becker K M, Murray J J, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Mercer J, Andrew R 2009 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference & Exhibition on Underwater Acoustic Measurements: Technologies & Results (UAM’09) Napflion, Greece, June 21−26, 2009 p121
[25] Stephen R 2011 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Technical Report WHOI-2011-04.
[26] 徐传秀 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Xu C X 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
-
图 8 不同声速剖面传播损失对比图 (a) 完整声道; (b) 不完整声道声源深度声速小于海底声速; (c) 不完整声道声源深度声速大于海底声速
Figure 8. Comparisons of transmission losses at different sound speed profile: (a) Complete channel; (b) incomplete channel with source depth sound speed less than bottom sound speed; (c) incomplete channel with source depth sound speed greater than bottom sound speed.
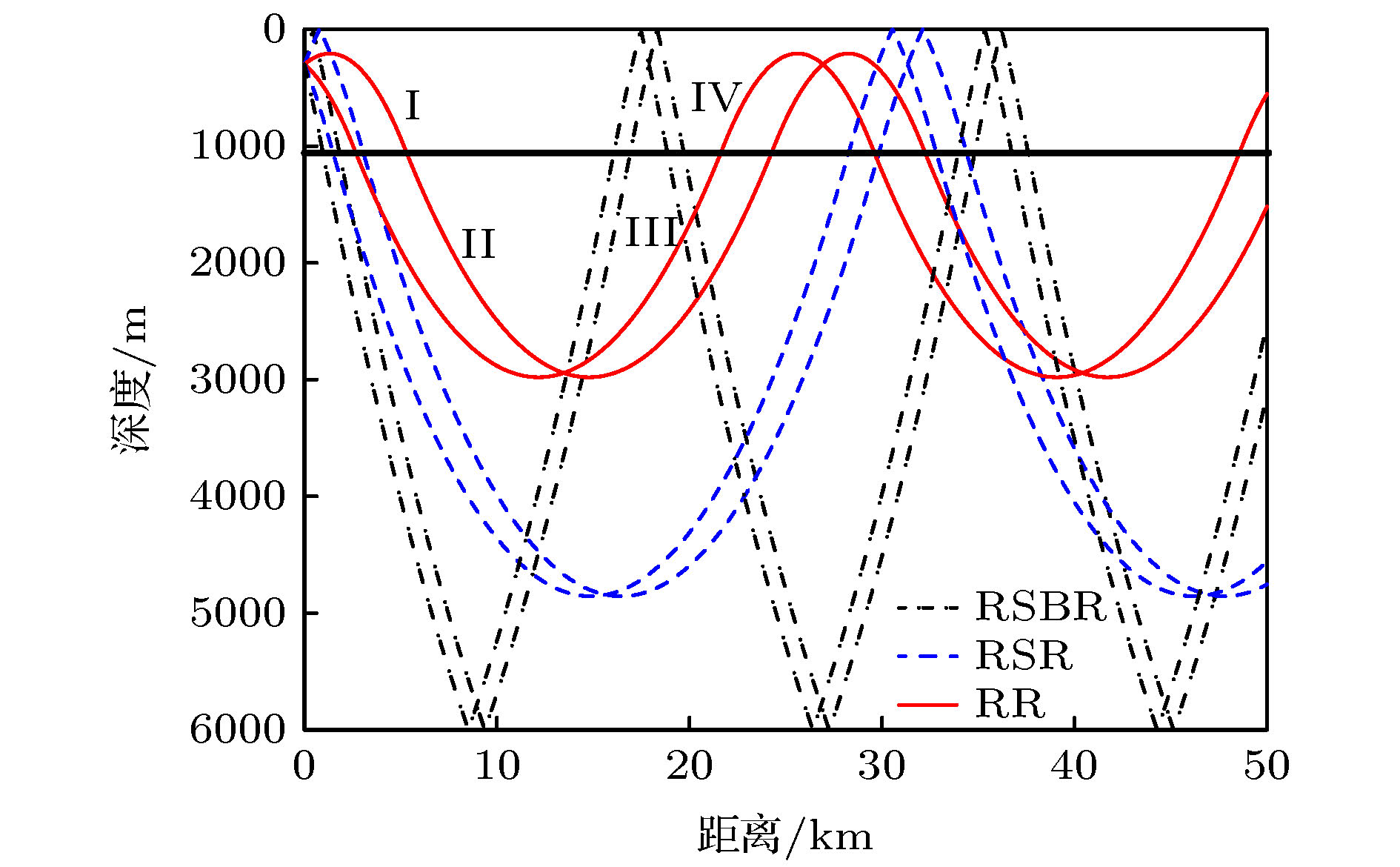
图 9 不同声源深度时RR型声线所形成的焦散线结构示意图, 实线为正角度出射声线所形成的焦散线, 虚线为负角度出射声线所形成的焦散线 (a) 声源深度100 m; (b) 声源深度200 m; (c) 声源深度500 m
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of the structure of caustic lines formed by RR type rays at different source depths. The full line is the caustic line formed by the positive angle of departure, and the imaginary line is the caustic line formed by the negative angle of departure: (a) 100 m; (b) 200 m; (c) 500 m.
-
[1] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (2nd Ed.) (NewYork: Springer-Verlag) pp16, 175
[2] Woezel J L, Ewing M 1948 Geol. Soc. Amer. Memoirs 27 1
[3] Brekhovskikh L M 1948 Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 69 157
[4] Berman A, Clay C S, Frosch R A, Sherry H B 1959 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 31 838
[5] Hale F E 1961 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 33 456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Urick R J 1965 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 38 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张仁和 1980 声学学报 1 28
Zhang R H 1980 Acta Acust. 1 28
[8] 张仁和 1982 声学学报 2 75
Zhang R H 1982 Acta Acust. 2 75
[9] 龚敏, 肖金泉, 王孟新, 吴寅庚, 黄德华 1987 声学学报 6 417
Gong M, Xiao J Q, Wang M X, Wu Y G, Huang D H 1987 Acta Acust. 6 417
[10] 庄益夫, 张旭, 刘艳 2013 海洋通报 1 46
Zhuang Y F, Zhang X, Liu Y 2013 Marin Sci. Bull. 1 46
[11] 李文, 李整林 2016 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 46 094303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Li Z L 2016 Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 46 094303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张仁和, 孙庚辰, 雷良颖, 周坚力 1981 声学学报 3 198
Zhang R H, Sun G C, Lei L Y, Zhou J L 1981 Acta Acust. 3 198
[13] 胡治国, 李整林, 秦继兴, 任云, 张仁和 2016 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 46 094304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Z G, Li Z L, Qin J X, Ren Y, Zhang R H 2016 Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 46 094304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 范培勤, 笪良龙, 李玉阳 2012 海洋技术 4 23
Fan P Q, Da L L, Li Y Y 2012 Ocean Technol. 4 23
[15] 张鹏, 李整林, 吴立新, 张仁和, 秦继兴 2019 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang P, Li Z L, Wu L X, Zhang R H, Qin J X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 014301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Raphael D T 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 56 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sachs D A, Silbiger A 1971 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 49 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Blatstein I M 1971 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 49 1568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Duda T F, Bowlin J B 1994 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 96 1033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bongiovanni K P, Siegmann W L, Ko D S 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 3033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tindle C T 2002 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 112 464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ainslie M A, Robins A J, Simons D G 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115 1449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] White A W, Henyey F S, Andrew R K, Mercer J A, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Colosi J A 2016 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 140 3952
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Heaney K D, Baggeroer A B, D’Spain G L, Becker K M, Murray J J, Worcester P F, Dzieciuch M A, Mercer J, Andrew R 2009 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference & Exhibition on Underwater Acoustic Measurements: Technologies & Results (UAM’09) Napflion, Greece, June 21−26, 2009 p121
[25] Stephen R 2011 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Technical Report WHOI-2011-04.
[26] 徐传秀 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Xu C X 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11954
- PDF Downloads: 209
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: