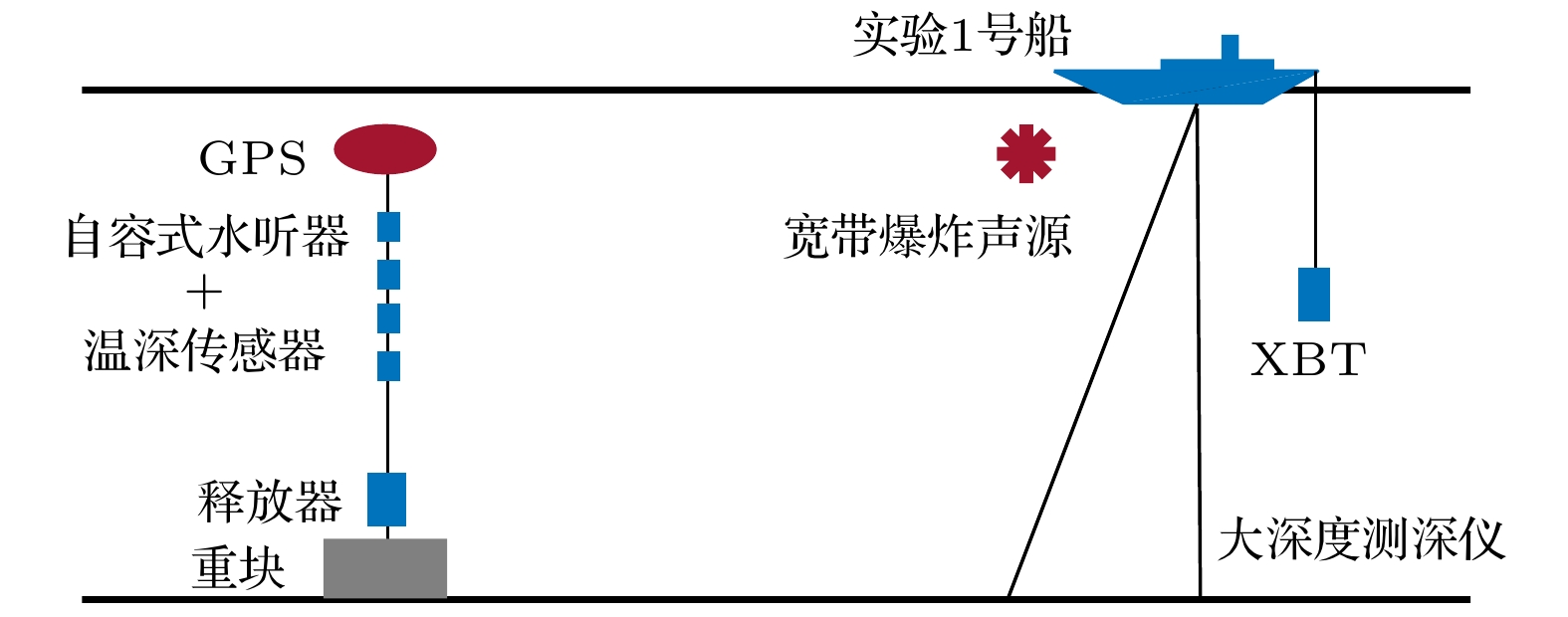
-
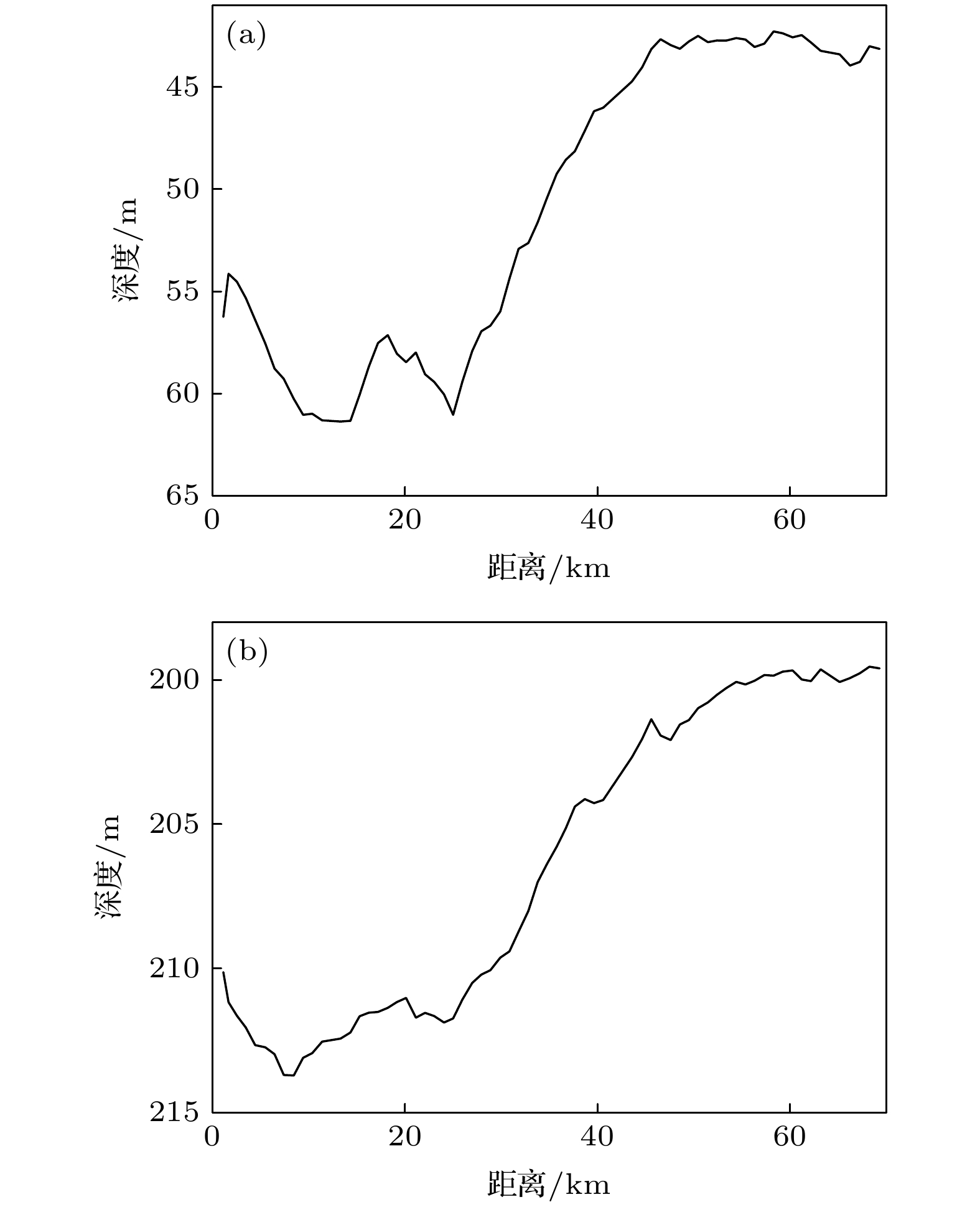
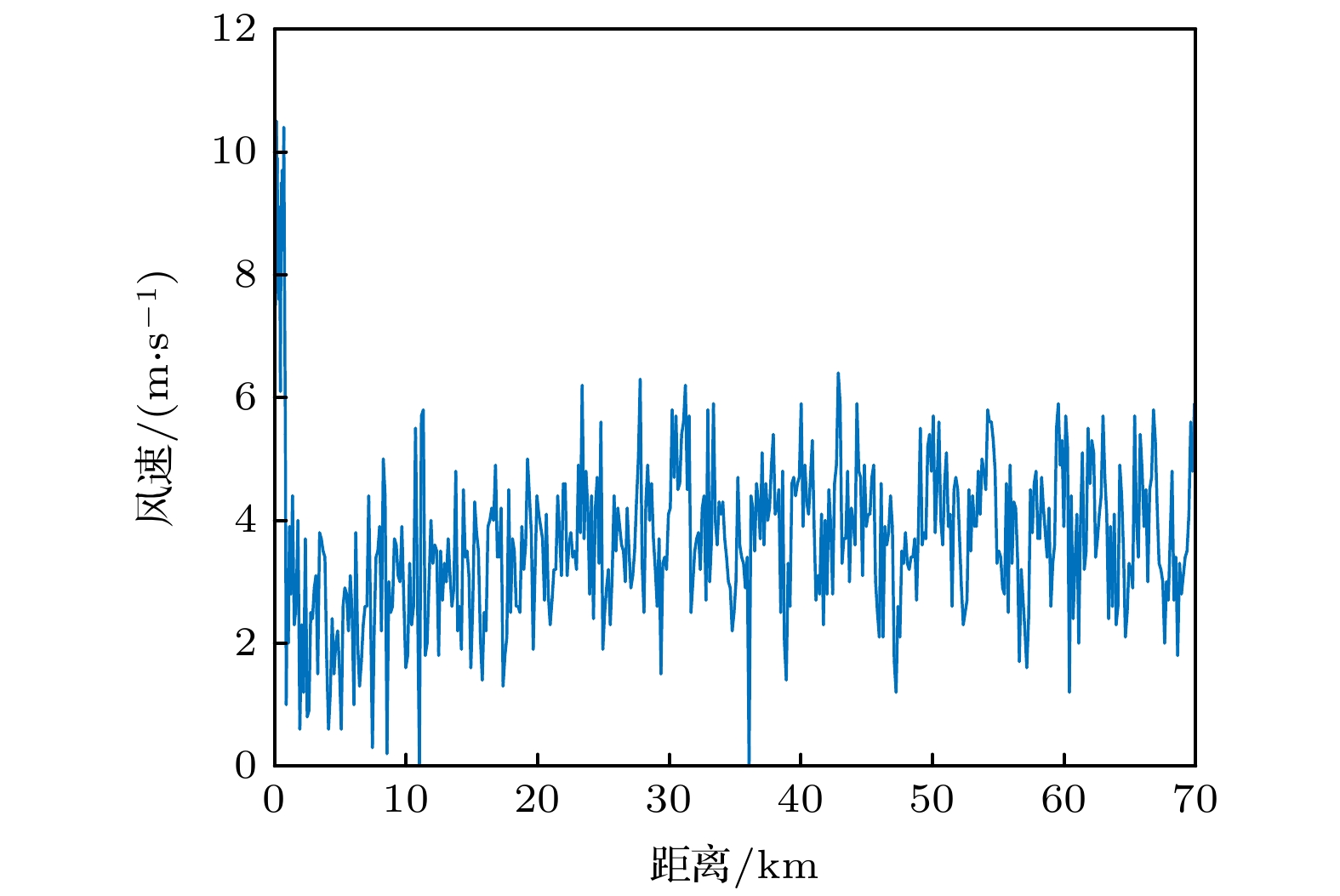
Surface duct is a common duct due to strong sea winds and sea-atmosphere interactions in winter and it is an excellent waveguide in which energy may propagate a long distance. However, the rough interface formed by sea surface waves will seriously damage this excellent performance. In this study, the experimental data of sound propagation over the continental slope in the South China Sea are used to analyze the characteristics of sound propagation in a surface duct. Modeling analyses based on the parabolic equation model RAM and ray trace theory BELLHOP are used to examine these characteristics. The parameters of sea bottom, source depth, wind-driven sea surface, and swell-containing sea surface are taken into consideration in the model. The results show that when the source is located in the surface duct, the parameters of the sea bottom have little influence on sound propagation, while the change of source depth exerts some effects on the sound propagation. By combining the Pierson Moscowitz (PM) spectrum with Monte Carlo method, the rough sea surface is investigated. Since the PM spectrum is related only to wind speed, the wind-driven sea surface is generated by using the actual wind speed measured by the shipborne anemometer. The swell-containing sea surface is defined as a superposition of a sinusoidal pressure-release surface and the wind-driven sea surface. By comparing the effects of two sea surfaces on sound propagation, it is found that when the wind speed is small, swells play an important role in the surface-duct propagation. Experimental data show that for the acoustic signal with a center frequency of
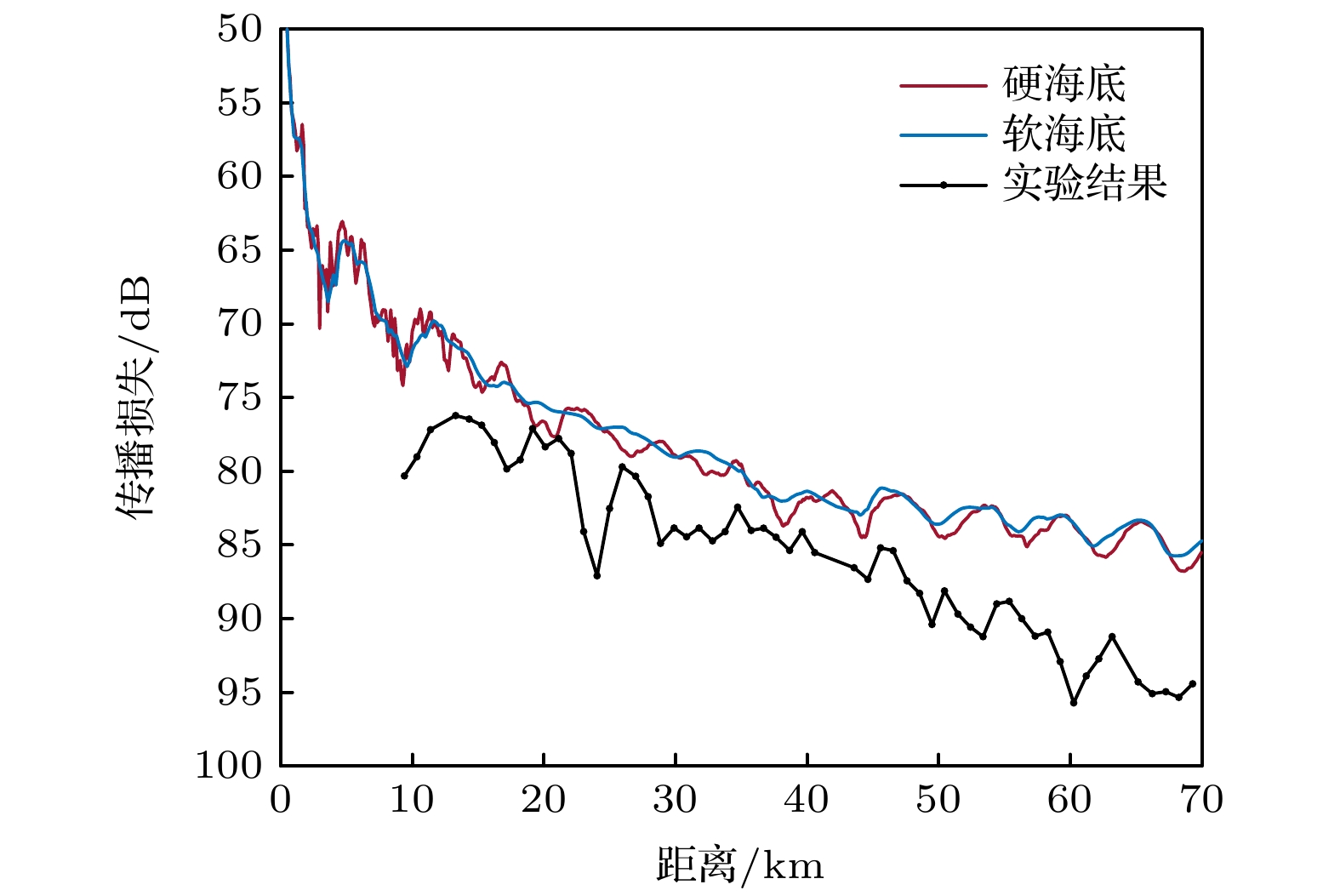
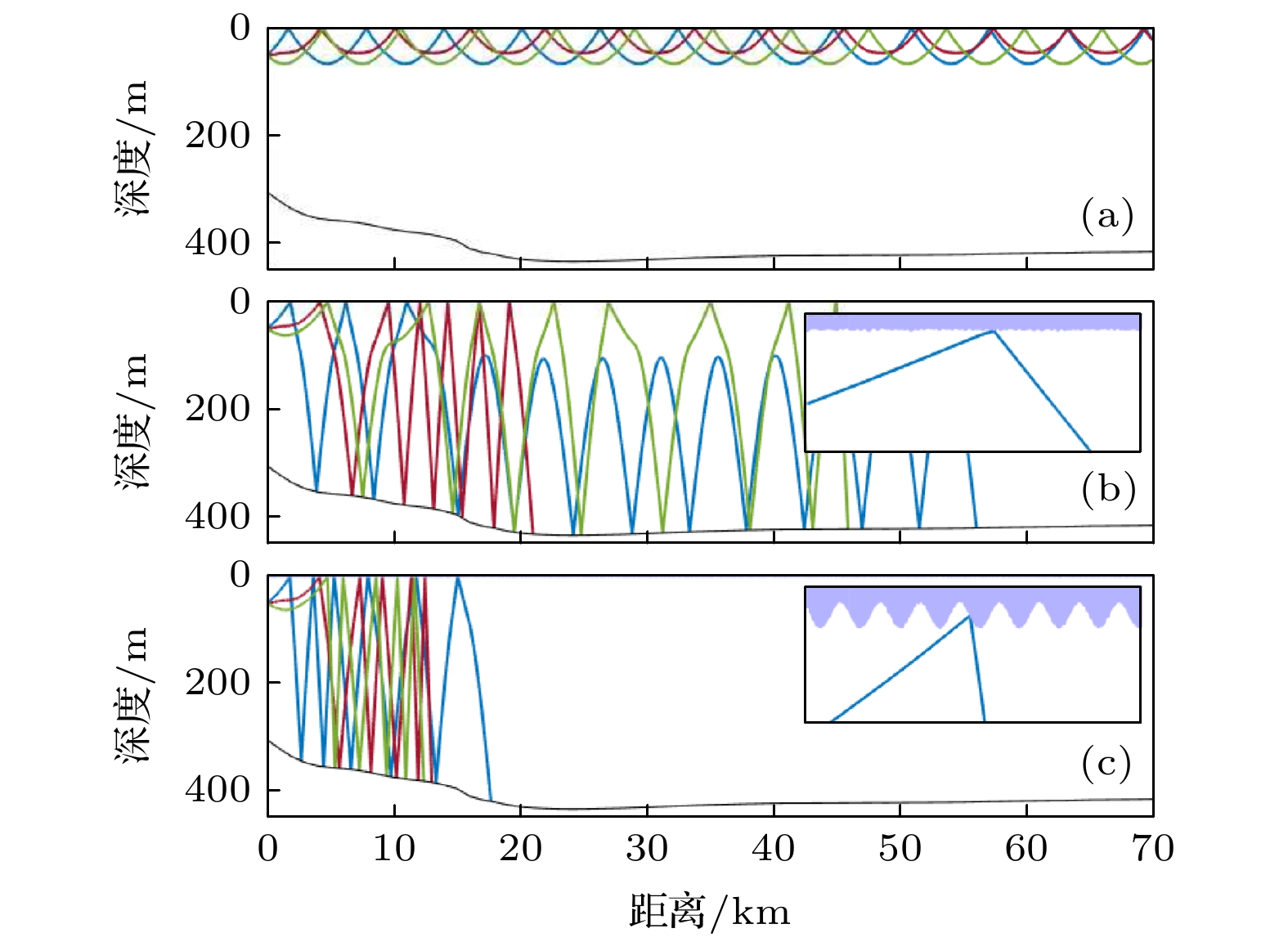
$1000\;{\rm{Hz}}$ , the swell-containing sea surface brings around$10 \;{\rm{dB}}$ loss to a distance of$70 \;{\rm{km}}$ . For the two kinds of rough sea surfaces, rays at launch angles of$\pm 1^{\circ}, 0^{\circ}$ are plotted to examine their effects on sound propagation. The results indicate that the swell-containing sea surface which has greater roughness makes rays go toward the sea bottom, thus resulting in larger loss. Therefore, in order to investigate the characteristics of the sound field in the northern South China Sea in winter, especially with high frequency sound signals, the influences of not only winds and waves, but also the swells from the surrounding sea should be taken into consideration. It is important to study the characteristics of sound propagation with swells for improving the performance of sonar equipment in poor sea conditions.-
Keywords:
- swell /
- rough sea surface /
- surface duct /
- sound propagation
[1] 张灵珊 2016 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang L S 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[2] 尹爽 2018 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Yin S 2018 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: The Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[3] 李整林 2002 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院研究生院)
Li Z L 2002 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[4] 王先华, 彭朝晖, 李整林 2007 声学技术 26 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X H, Peng Z H, Li Z L 2007 Technical Acoustics 26 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Thorsos E I, Broschat S L 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 2082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Broschat S L, Thorsos E I 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 2615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Collins M D 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 1097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Collins M D, Coury R A, Siegmann W L 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 2767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu R Y, Li Z L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 014302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zou Z G, Badiey M 2018 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 43 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Weston D E, Ching P A 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 1530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 王先华 2007 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Wang X H 2007 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[13] 姚美娟, 鹿力成, 郭圣明, 马力 2019 哈尔滨工程大学学报 40 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao M J, Lu L C, Guo S M, Ma L 2019 Journal of Harbin Engineering University 40 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Karjadi E A, Badiey M, Kirby J T, Bayindir C 2012 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 37 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tindle C T, Deane G B 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117 2783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Siderius M, Porter M B 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Badiey M, Mu Y K, Simmen J A, Forsythe S E 2000 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 25 492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Dahl P H 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mackenzie K V 1981 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer) pp1−794
[21] 段睿 2016 博士学位论文 (西安: 西北工业大学)
Duan R 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University) (in Chinese)
[22] 刘今, 彭朝晖 2019 中国声学学会水声学分会2019年学术会议论文集 南京 2019 第198页
Liu J, Peng Z H 2019 Proceedings of the Academic Conference of Underwater Acoustic Branch of Acoustics Society of China in 2019, Underwater Acoustic Branch Nanjing, China, May 25, 2019 p198 (in Chinese)
[23] 吴庚坤 2015 博士学位论文 (青岛: 中国海洋大学)
Wu G K 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Qingdao: Ocean University of China) (in Chinese)
[24] 欧家明 2011 硕士学位论文 (广州: 广东工业大学)
Ou J M 2011 M. S. Thesis (Guangzhou: School of information Engineering Guangdong University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[25] 林风 2007 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Lin F 2007 M. S. Thesis (Xi’an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[26] Japan Meteorological Agency, https://www.data.jma.go.jp/gmd/kaiyou/data/db/wave/chart/daily/pdf/pn/17/12/17121100 pn.pdf [2020-7-28]
[27] Japan Meteorological Agency, https://www.data.jma.go.jp/gmd/kaiyou/data/db/wave/chart/daily/pdf/pn/17/12/17121112 pn.pdf [2020-7-28]
[28] Vadov R A 2006 Acoust. Phys. 52 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 廖菲, 邓华, 曾琳, Chan Pak-wai 2018 海洋学报 40 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao F, Deng H, Zeng L, Chan P W 2018 Haiyang Xuebao 40 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 郭佩芳, 施平, 王华, 王正林 1997 青岛海洋大学学报 27 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo P F, Shi P, Wang H, Wang Z L 1997 Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao 27 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 李波 2010 博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Li B 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[32] Richards E L, Song H C, Hodgkiss W S 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 144 1296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 11 涌浪海面应用于不同频率和不同水听器的传播损失检验 (a)
$400\; {\rm{Hz}}$ , 第1个水听器; (b)$400\; {\rm{Hz}}$ , 第11个水听器; (c)$1000\; {\rm{Hz}}$ , 第11个水听器Figure 11. Examinations of transmission loss of two hydrophones with the swell surface under different frequencies: (a)
$400\; {\rm{Hz}}$ , the first hydrophone; (b)$400\; {\rm{Hz}}$ , the eleventh hydrophone; (c)$1000\; {\rm{Hz}}$ , the eleventh hydrophone. -
[1] 张灵珊 2016 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang L S 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[2] 尹爽 2018 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Yin S 2018 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: The Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[3] 李整林 2002 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院研究生院)
Li Z L 2002 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[4] 王先华, 彭朝晖, 李整林 2007 声学技术 26 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X H, Peng Z H, Li Z L 2007 Technical Acoustics 26 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Thorsos E I, Broschat S L 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 2082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Broschat S L, Thorsos E I 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 2615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Collins M D 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 1097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Collins M D, Coury R A, Siegmann W L 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 2767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu R Y, Li Z L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 014302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zou Z G, Badiey M 2018 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 43 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Weston D E, Ching P A 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 1530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 王先华 2007 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Wang X H 2007 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[13] 姚美娟, 鹿力成, 郭圣明, 马力 2019 哈尔滨工程大学学报 40 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao M J, Lu L C, Guo S M, Ma L 2019 Journal of Harbin Engineering University 40 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Karjadi E A, Badiey M, Kirby J T, Bayindir C 2012 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 37 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tindle C T, Deane G B 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117 2783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Siderius M, Porter M B 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Badiey M, Mu Y K, Simmen J A, Forsythe S E 2000 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 25 492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Dahl P H 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mackenzie K V 1981 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer) pp1−794
[21] 段睿 2016 博士学位论文 (西安: 西北工业大学)
Duan R 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University) (in Chinese)
[22] 刘今, 彭朝晖 2019 中国声学学会水声学分会2019年学术会议论文集 南京 2019 第198页
Liu J, Peng Z H 2019 Proceedings of the Academic Conference of Underwater Acoustic Branch of Acoustics Society of China in 2019, Underwater Acoustic Branch Nanjing, China, May 25, 2019 p198 (in Chinese)
[23] 吴庚坤 2015 博士学位论文 (青岛: 中国海洋大学)
Wu G K 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Qingdao: Ocean University of China) (in Chinese)
[24] 欧家明 2011 硕士学位论文 (广州: 广东工业大学)
Ou J M 2011 M. S. Thesis (Guangzhou: School of information Engineering Guangdong University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[25] 林风 2007 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Lin F 2007 M. S. Thesis (Xi’an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[26] Japan Meteorological Agency, https://www.data.jma.go.jp/gmd/kaiyou/data/db/wave/chart/daily/pdf/pn/17/12/17121100 pn.pdf [2020-7-28]
[27] Japan Meteorological Agency, https://www.data.jma.go.jp/gmd/kaiyou/data/db/wave/chart/daily/pdf/pn/17/12/17121112 pn.pdf [2020-7-28]
[28] Vadov R A 2006 Acoust. Phys. 52 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 廖菲, 邓华, 曾琳, Chan Pak-wai 2018 海洋学报 40 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao F, Deng H, Zeng L, Chan P W 2018 Haiyang Xuebao 40 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 郭佩芳, 施平, 王华, 王正林 1997 青岛海洋大学学报 27 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo P F, Shi P, Wang H, Wang Z L 1997 Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao 27 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 李波 2010 博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Li B 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[32] Richards E L, Song H C, Hodgkiss W S 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 144 1296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7426
- PDF Downloads: 122
- Cited By: 0


















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: