-
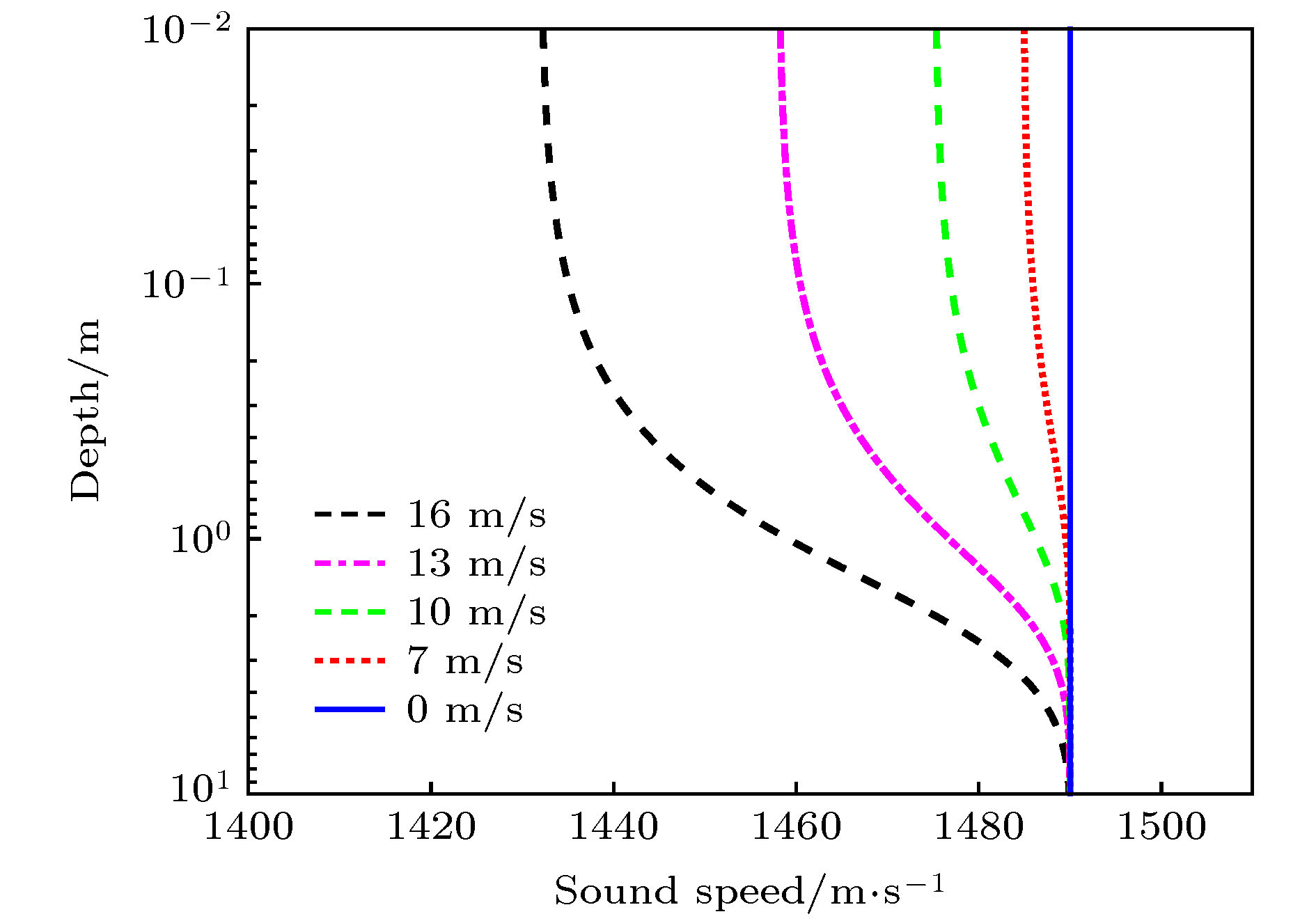
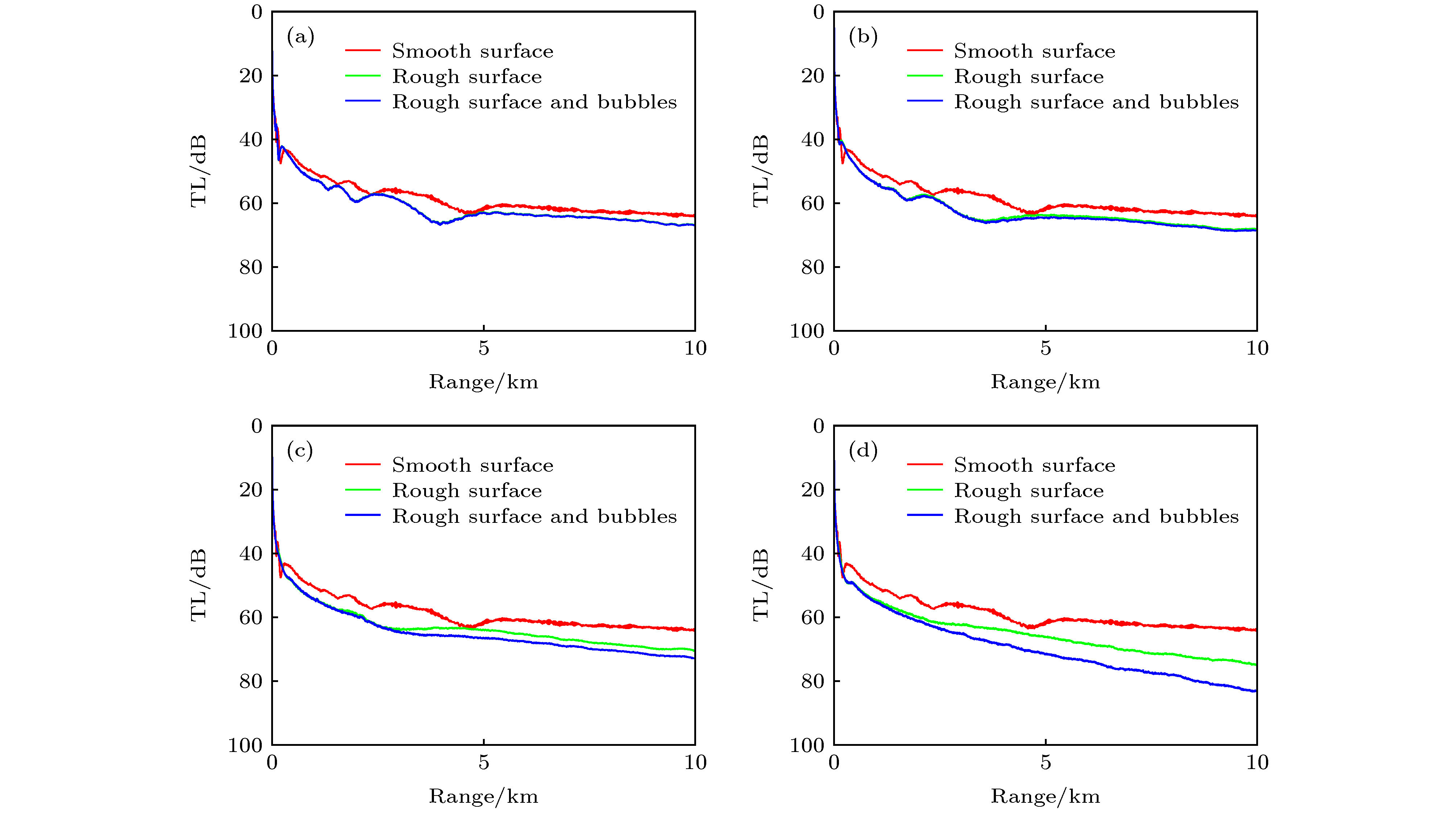
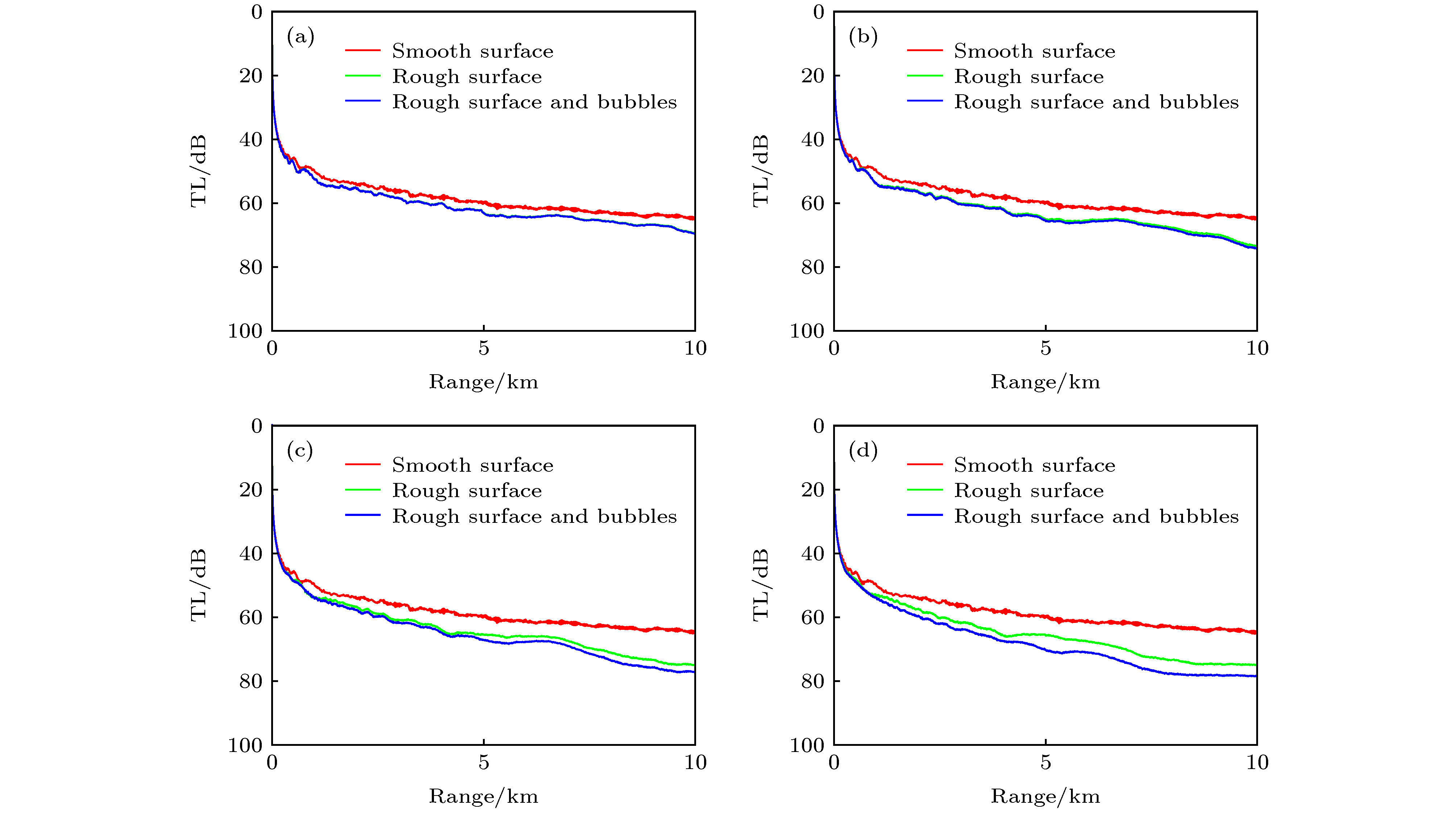
分析了起伏海面下风浪引起的气泡层对海面反射损失和对声传播的影响. 一方面, 气泡层会改变原来水中的声速剖面; 另一方面, 气泡层会对声波产生散射和吸收作用. 考虑以上两方面的因素, 分析了不同风速下气泡层对海面反射损失和声传播损失的影响, 仿真发现, 在风速大于10 m/s时, 对于2 kHz以上频率时气泡层对小掠射角下海面反射损失的影响不可忽视. 在给定的水声环境中, 当声源深度和接收深度都为7 m时, 风速为16 m/s的风浪下生成的气泡层, 在10 km处对3 kHz的声传播损失的影响达到8.1 dB. 当声源深度和接收深度都为18 m时, 风速为16 m/s的风浪下生成的气泡层, 在10 km处对3 kHz的声传播损失的影响达到4 dB.The reflection coefficient of the flat sea surface in the ideal condition to the incident sound wave is –1. The perfect reflection effect does not introduce reflection loss. However, the sea surface is usually rough due to the wind. The wind-generated rough sea surface has not only reflection effect, but also scattering effect on the sound wave. At the same time, the wind-generated bubbles layer also has significant effect on the sound propagation. On the one hand, the bubbles layer can change the sound speed profile and result in the refraction of the incident sound wave. On the other hand, the bubbles layer has scattering effect and absorption effect on the incident sound wave and leads to the sound wave to attenuate. In fact, the rough sea surface and the bubbles layer are two main factors affecting the sound propagation in the windy weather at sea. Many researchers have paid much attention to the effect of the wind-generated rough sea surface on the sound propagation, but few of them have considered the effect of the wind-generated bubbles layer on the sound propagation. Based on the Ramsurf sound propagation model under the rough sea surface, the effects of wind-generated bubbles layer underneath rough sea surface on reflection loss and sound propagation with different wind speeds are analyzed. Based on the Hall-Novarini bubbles population model, the sound speed profile in the bubbles layer is modified and the attenuation coefficient due to scattering and absorption of the bubbles layer is calculated. The simulation results shows that when the wind speed is 10 m/s, the effect of the bubbles layer is significant on reflection loss with the frequencies higher than 2 kHz. In the given underwater acoustic environment, for a frequency of 3 kHz, when the source depth and the receiver depth are both 7 m, the enhancement of the transmission loss due to the bubbles layer is 2.6 dB for a wind speed of 13 m/s, and the enhancement is 8.1 dB for a wind speed of 16 m/s. And when the source depth and the receiver depth are both 18 m, the enhancement of the transmission loss due to the bubbles layer is 2.5 dB for a wind speed of 13 m/s and the enhancement is 4 dB for a wind speed of 16 m/s.
-
Keywords:
- rough sea surface /
- bubbles layer /
- sound propagation
[1] Martin S, Michael B P 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tindle C T, Deane G B 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117 2783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tindle C T, Deane G B, Preisig J C 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Preisig J C, Deane G B 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 116 2067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chapman D M F 1983 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73 520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Williams K L, Thorsos E I, Elam W T 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 116 1975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhou J X, Zhang X Z, Peng Z H, Martin J S 2007 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Keiffer R S, Novarini J C, Norton G V 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vossen R V, Ainslie M A 2011 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130 3413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dahl P H, Choi J W, Williams N J, Graber H C 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 EL163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang T C 2006 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120 2595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Park C, Seong W, Gerstoft P, Hodgkiss W S 2011 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 129 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Karjadi E A, Badiey M, Kirby J T, Bayindir C 2012 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 37 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Jones A D, Duncan A J, Maggi A 2016 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 41 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zou Z G, Badiey M 2018 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 43 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu R Y, Li Z L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 014302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ainslie M A 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 118 3513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Thorsos E I, Broschat S L 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 2082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Broschat S L, Thorsos E I 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 2615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Persion W J, Moskowitz L 1964 J. Geophys. Res. 69 5181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Thorsos E I 1990 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 88 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hall M V 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 1103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer Business Media) p50
[24] 郭立新, 王蕊, 吴振森 2009 随机粗糙面散射的基本理论与方法 (北京: 科学出版社) 第4页
Guo L X, Wang R, Wu Z S 2009 Basic Theory and Method of Random Rough Surface Scattering (Beijing: Science Press) p4 (in Chinese)
-
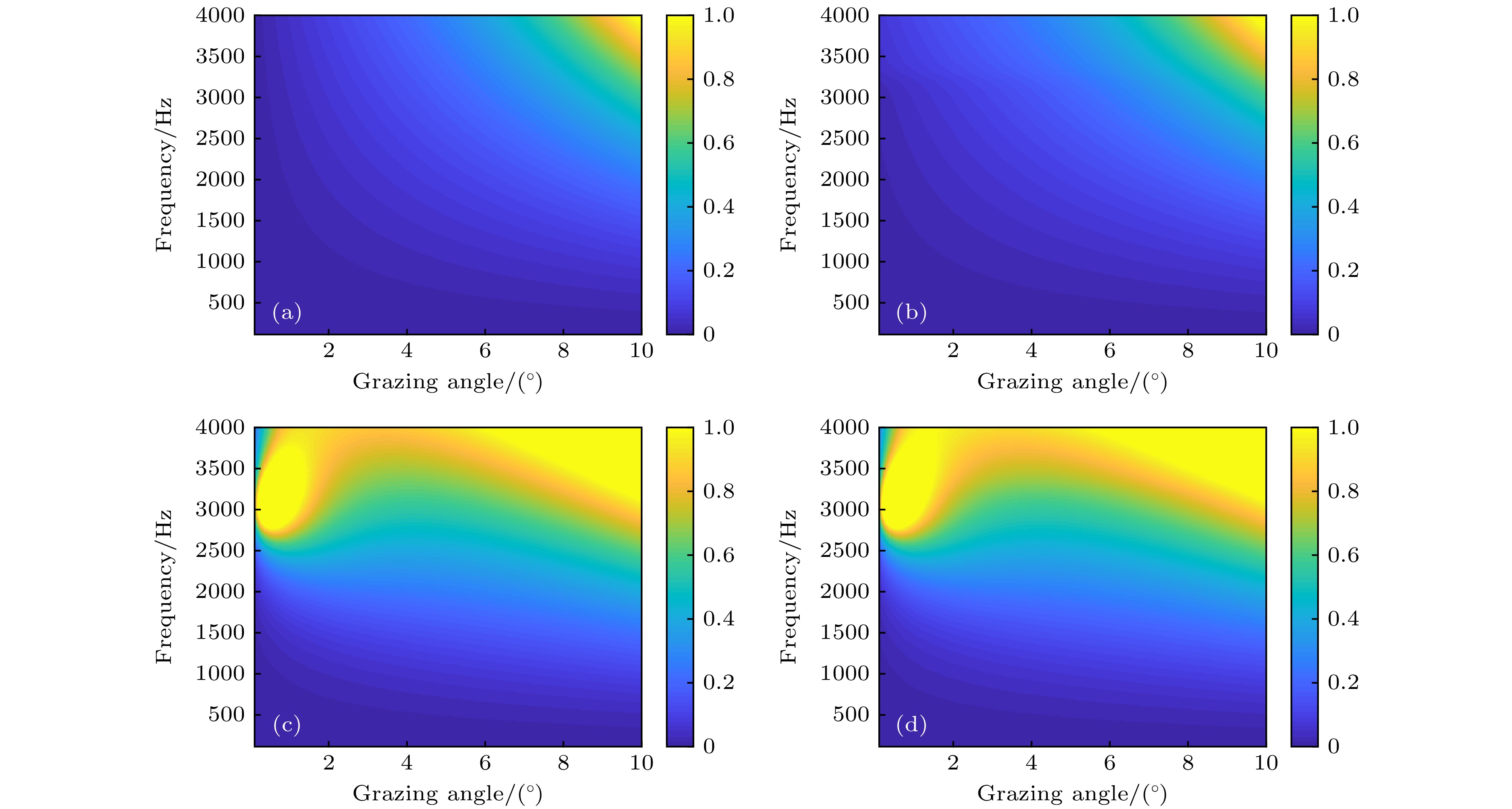
图 5 风速为7 m/s时起伏海面下气泡层对海面反射损失的影响 (a) 无气泡层; (b) 考虑气泡层对声波的消减效应; (c) 考虑气泡层对声波的折射效应; (d) 同时考虑气泡层对声波的折射效应和消减效应
Fig. 5. Effects of the bubbles layer underneath the rough sea surface on reflection loss in nepers with a wind speed of 7 m/s: (a) Rough sea surface; (b) rough sea surface + scattering and absorption effect of the bubbles layer; (c) rough sea surface + refraction effect of the bubbles layer; (d) rough sea surface + scattering and absorption effect of the bubbles layer + refraction effect of the bubbles layer.
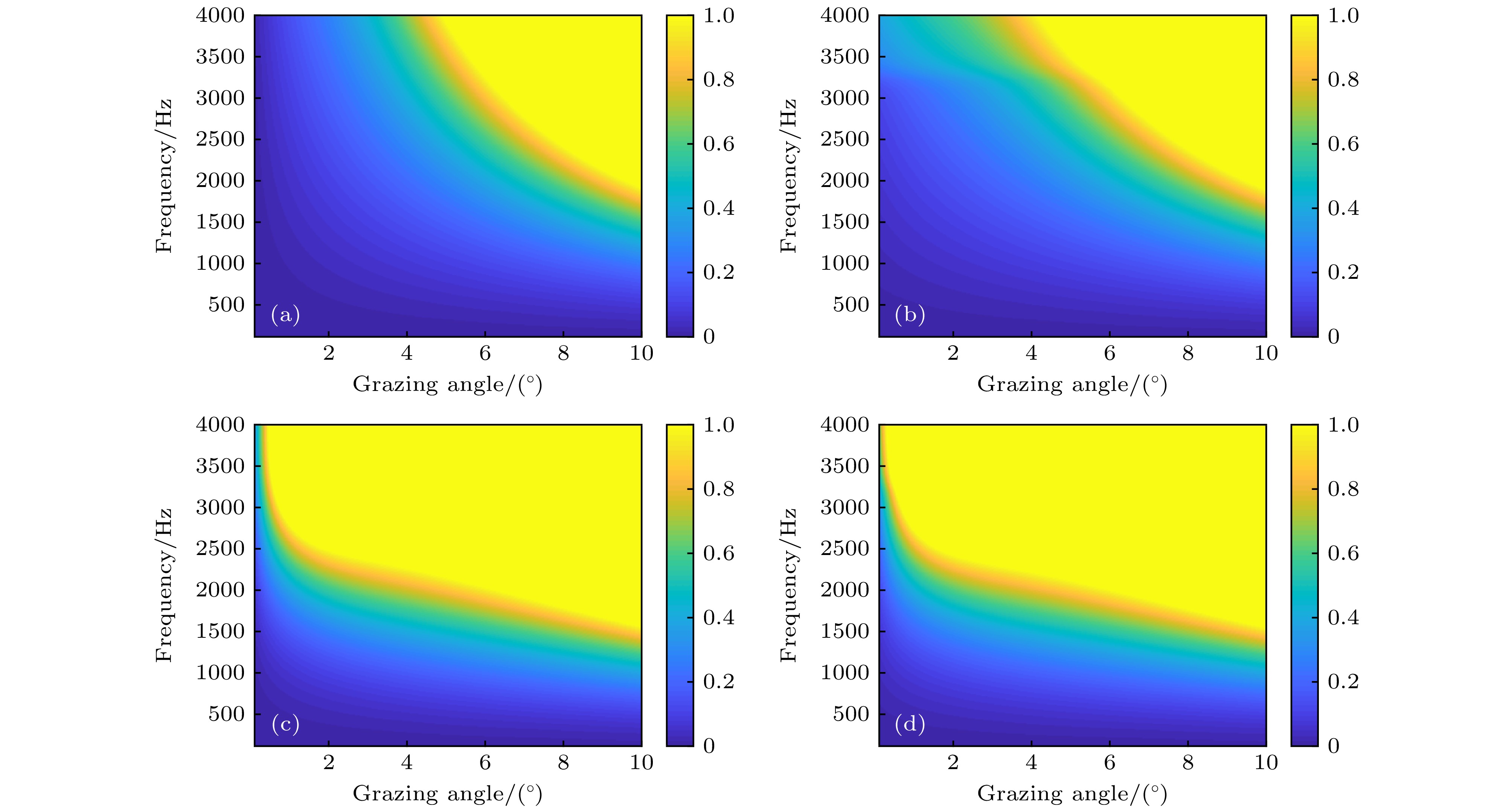
图 6 风速为10 m/s时起伏海面以及气泡层对海面反射损失的影响 (a) 无气泡层; (b) 考虑气泡层对声波的消减效应; (c) 考虑气泡层对声波的折射效应; (d) 同时考虑气泡层对声波的折射效应和消减效应
Fig. 6. Effects of the bubbles layer underneath the rough sea surface on reflection loss in nepers with a wind speed of 10 m/s: (a) Rough sea surface; (b) rough sea surface + scattering and absorption effect of the bubbles layer; (c) rough sea surface + refraction effect of the bubbles layer; (d) rough sea surface + scattering and absorption effect of the bubbles layer + refraction effect of the bubbles layer.
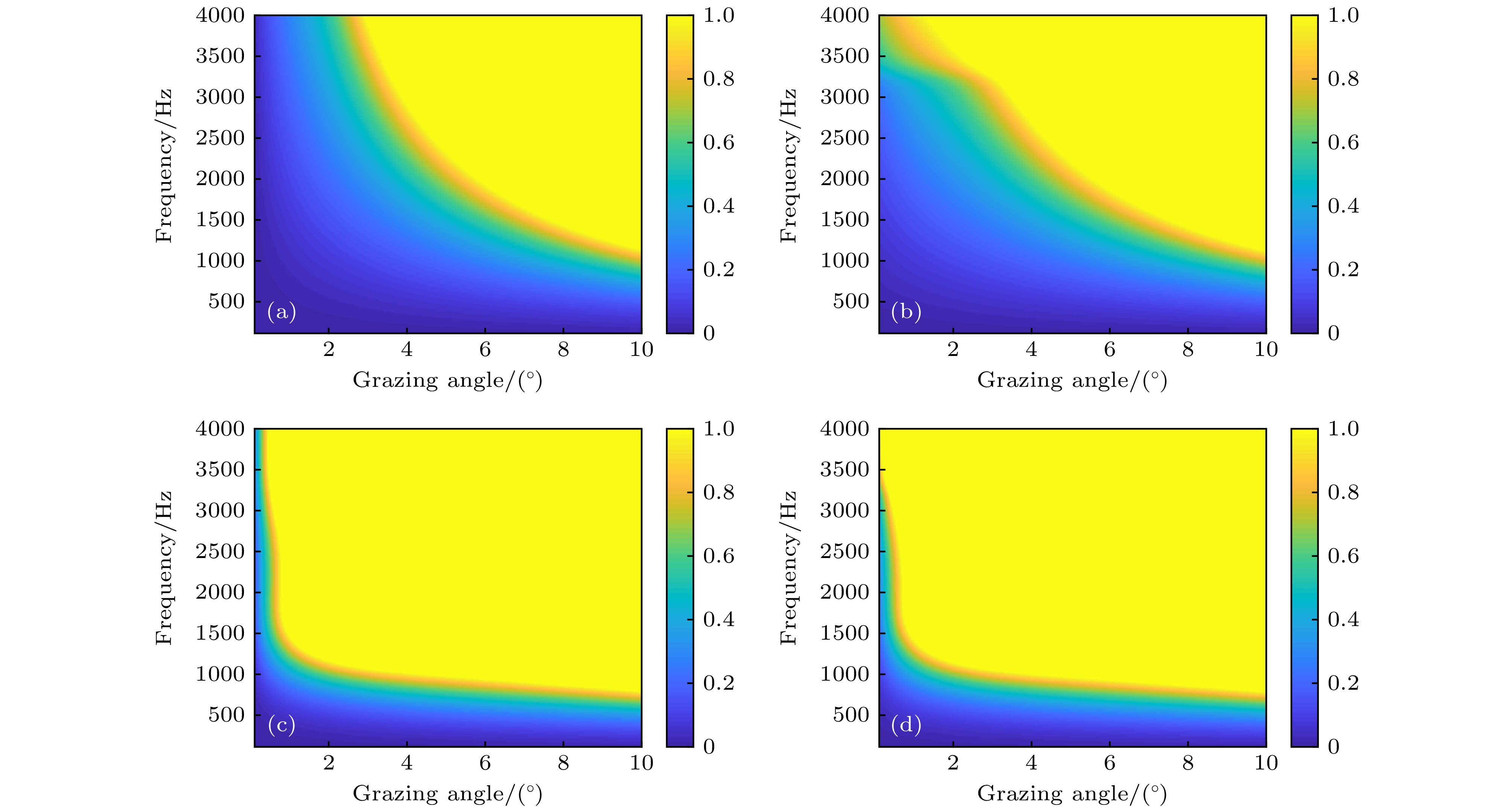
图 7 风速为13 m/s时起伏海面以及气泡层对海面反射损失的影响 (a) 无气泡层; (b) 考虑气泡层对声波的消减效应; (c) 考虑气泡层对声波的折射效应; (d) 同时考虑气泡层对声波的折射效应和消减效应
Fig. 7. Effects of the bubbles layer underneath the rough sea surface on reflection loss in nepers with a wind speed of 13 m/s: (a) Rough sea surface; (b) rough sea surface + scattering and absorption effect of the bubbles layer; (c) rough sea surface + refraction effect of the bubbles layer; (d) rough sea surface + scattering and absorption effect of the bubbles layer + refraction effect of the bubbles layer.
-
[1] Martin S, Michael B P 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tindle C T, Deane G B 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117 2783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tindle C T, Deane G B, Preisig J C 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Preisig J C, Deane G B 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 116 2067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chapman D M F 1983 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73 520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Williams K L, Thorsos E I, Elam W T 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 116 1975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhou J X, Zhang X Z, Peng Z H, Martin J S 2007 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Keiffer R S, Novarini J C, Norton G V 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vossen R V, Ainslie M A 2011 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130 3413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dahl P H, Choi J W, Williams N J, Graber H C 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 EL163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang T C 2006 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120 2595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Park C, Seong W, Gerstoft P, Hodgkiss W S 2011 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 129 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Karjadi E A, Badiey M, Kirby J T, Bayindir C 2012 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 37 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Jones A D, Duncan A J, Maggi A 2016 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 41 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zou Z G, Badiey M 2018 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 43 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu R Y, Li Z L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 014302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ainslie M A 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 118 3513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Thorsos E I, Broschat S L 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 2082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Broschat S L, Thorsos E I 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 2615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Persion W J, Moskowitz L 1964 J. Geophys. Res. 69 5181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Thorsos E I 1990 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 88 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hall M V 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 1103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer Business Media) p50
[24] 郭立新, 王蕊, 吴振森 2009 随机粗糙面散射的基本理论与方法 (北京: 科学出版社) 第4页
Guo L X, Wang R, Wu Z S 2009 Basic Theory and Method of Random Rough Surface Scattering (Beijing: Science Press) p4 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 15891
- PDF下载量: 199
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: