-
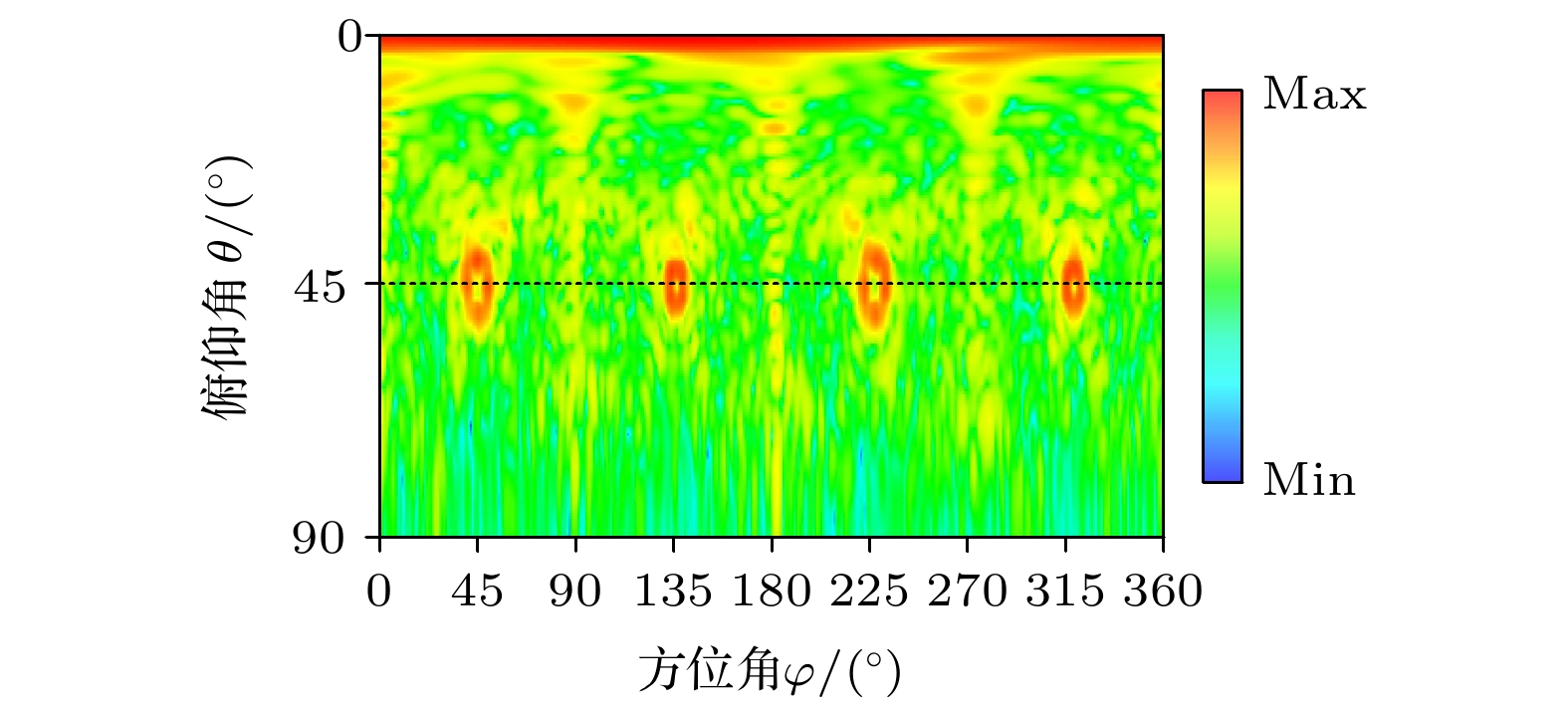
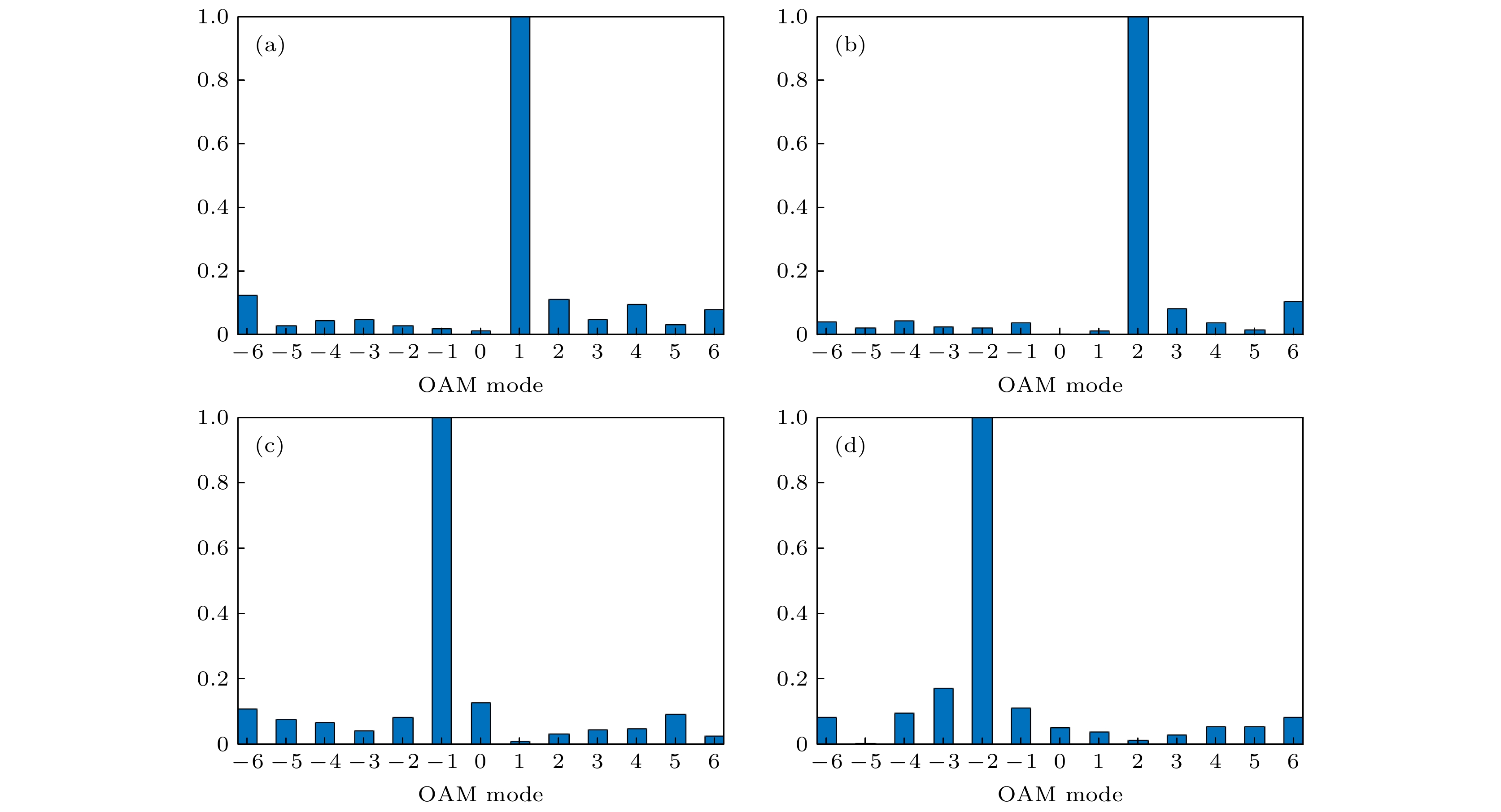
The generating of vortex beams in the terahertz (THz) band attracts significant attention due to their applications in high-speed communication and high-resolution imaging. In this article, a novel reflective metasurface working in the THz band is designed to generate four vortex beams with different topological charges in different directions. The unit cell is designed based on the geometric phase, and it consists of two metallic (gold) layers and one dielectric layer in between. The top layer of the unit cell includes an elliptic patch and a circular ring, and the bottom layer of the unit cell is a metallic ground. The reflection efficiency of the unit cell is very high due to the presence of metallic ground. To break through the limitations of traditional methods, the metasurface is a good choice to generate beams that carry orbital angular momentum (OAM). Using the concept of geometric phase, the reflection phase of reflective circular polarization (CP) electromagnetic waves can be controlled in an ingenious way. Owing to the property of the geometric phase, inverse phase shift can be achieved for left-handed circular polarization and right-handed circular polarization waves. By utilizing this trait of geometric phase, one can decompose a linear polarization wave into two orthogonal circular polarization waves and control their properties respectively. By rotating the top layer of the unit cell, 360-degree phase shift and the phase distribution satisfying the requirement for generating the multi-beam multi-mode vortex beam can be achieved. In order to control the direction and the topological charge of each beam, based on the geometric phase, the theory of reflectarray and the phase composition principle, the phase distribution of the reflective metasurface is calculated to provide the phase compensation to make the vortex beams point to certain directions. It is worthwhile to point out that the method presented in this paper provides a way to generate complex multi-mode vortex beams in the THz band. The simulations and measurements show that the metasurface can generate four vortex beams with topological charges l = ± 1 and ± 2 in different directions in the THz band. These results also indicate that our design has great potential applications in wireless communication and high-resolution imaging.
-
Keywords:
- terahertz vortex beams /
- beam control /
- metasurface
[1] Karpowicz N, Zhong H, Zhang C L, Lin K L, Hwang J S, Xu J Z, Zhang X C 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 054105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gompf B, Gebert N, Heer H, Dressel M 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 082104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dobroiu A, Yamashita M, Ohshima Y N 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 5637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen Z F, Chen X Q, Tao L, et al. 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 4909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fujishima M, Amakawa S, Takano K, Katayama K, Yoshida T 2015 IEICE Trans. Electron. E98-C 1091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yan Y, Xie G D, Lavery M P J, et al. 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4876
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu K, Cheng Y Q, Gao Y, Li X, Qin Y L, Wang H Q 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 164102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu K, Li X, Gao Y, Wang H Q, Cheng Y Q 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 124903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang Z F, Zheng S L, Chen Y L, Jin X F, Chi H, Zhang X M 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 25418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Tamburini F, Mari E, Thide B, Barbieri C, Romanato F 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bai X D, Liang X L, Li J P, Wang K, Geng J P, Jin R H 2016 Sci. Rep 6 27815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shi H Y, Wang L Y, Chen X M, Zhang A X, Xu Z 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 126 063108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu S, Li L, Shi G, Zhu C, Zhou X, Shi Y 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 121903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang X Q, Tian Z, Yue W S, Gu J Q, Zhang S, Han J G, Zhang W L 2013 Adv. Mater. 25 4567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu S, Zhang L, Yang Q L, et al. 2016 Adv. Opt. Mater. 4 1965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李晓楠, 周璐, 赵国忠 2019 68 238101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X N, Zhou L, Zhao G Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 238101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周璐, 赵国忠, 李晓楠 2019 68 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou L, Zhao G Z, Li X N 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhao H, Quan B G, Wang X K, Gu C Z, Li J J, Zhang Y 2018 ACS Phot. 5 1726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jiang Z H, Lei K, Wei H, Werner, D. H 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 9 064009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shi H Y, Li J X, Zhang A X, Jiang Y S, Wang J F, Xu Zhuo, Xia Song 2015 IEEE Ant. Wir. Prop. Lett. 14 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李佳辉, 张雅婷, 李吉宁, 等 2020 69 228101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J H, Zhang Y T, Li J N, et al. 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 228101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng R Y, Xu S H, Yang F, Li M K 2017 IEEE Ant. Wir. Prop. Lett. 16 884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu H X, Xue H, Liu Y J, Li L 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 7219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun S L, He Q, Xiao S Y, Xu Q, Li X, Zhou L 2012 Nat. Mater. 11 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yu N F, Genevet P, Kats M A, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Sci. 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Nayeri P, Yang F, Elsherbeni A Z 2018 Reflectarray Antennas: Theory, Designs, and Applications (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons) pp9−13
[27] Shi H Y, Wang L Y, Peng G T, Chen X M, Li J X, Zhu S T, Zhang A X, Xu Z 2019 IEEE Ant. Wir. Prop. Lett. 18 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Karpowicz N, Zhong H, Zhang C L, Lin K L, Hwang J S, Xu J Z, Zhang X C 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 054105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gompf B, Gebert N, Heer H, Dressel M 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 082104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dobroiu A, Yamashita M, Ohshima Y N 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 5637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen Z F, Chen X Q, Tao L, et al. 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 4909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fujishima M, Amakawa S, Takano K, Katayama K, Yoshida T 2015 IEICE Trans. Electron. E98-C 1091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yan Y, Xie G D, Lavery M P J, et al. 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4876
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu K, Cheng Y Q, Gao Y, Li X, Qin Y L, Wang H Q 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 164102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu K, Li X, Gao Y, Wang H Q, Cheng Y Q 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 124903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang Z F, Zheng S L, Chen Y L, Jin X F, Chi H, Zhang X M 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 25418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Tamburini F, Mari E, Thide B, Barbieri C, Romanato F 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bai X D, Liang X L, Li J P, Wang K, Geng J P, Jin R H 2016 Sci. Rep 6 27815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shi H Y, Wang L Y, Chen X M, Zhang A X, Xu Z 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 126 063108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu S, Li L, Shi G, Zhu C, Zhou X, Shi Y 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 121903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang X Q, Tian Z, Yue W S, Gu J Q, Zhang S, Han J G, Zhang W L 2013 Adv. Mater. 25 4567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu S, Zhang L, Yang Q L, et al. 2016 Adv. Opt. Mater. 4 1965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李晓楠, 周璐, 赵国忠 2019 68 238101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X N, Zhou L, Zhao G Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 238101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周璐, 赵国忠, 李晓楠 2019 68 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou L, Zhao G Z, Li X N 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhao H, Quan B G, Wang X K, Gu C Z, Li J J, Zhang Y 2018 ACS Phot. 5 1726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jiang Z H, Lei K, Wei H, Werner, D. H 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 9 064009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shi H Y, Li J X, Zhang A X, Jiang Y S, Wang J F, Xu Zhuo, Xia Song 2015 IEEE Ant. Wir. Prop. Lett. 14 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李佳辉, 张雅婷, 李吉宁, 等 2020 69 228101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J H, Zhang Y T, Li J N, et al. 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 228101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng R Y, Xu S H, Yang F, Li M K 2017 IEEE Ant. Wir. Prop. Lett. 16 884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu H X, Xue H, Liu Y J, Li L 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 7219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun S L, He Q, Xiao S Y, Xu Q, Li X, Zhou L 2012 Nat. Mater. 11 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yu N F, Genevet P, Kats M A, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Sci. 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Nayeri P, Yang F, Elsherbeni A Z 2018 Reflectarray Antennas: Theory, Designs, and Applications (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons) pp9−13
[27] Shi H Y, Wang L Y, Peng G T, Chen X M, Li J X, Zhu S T, Zhang A X, Xu Z 2019 IEEE Ant. Wir. Prop. Lett. 18 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9440
- PDF Downloads: 404
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: