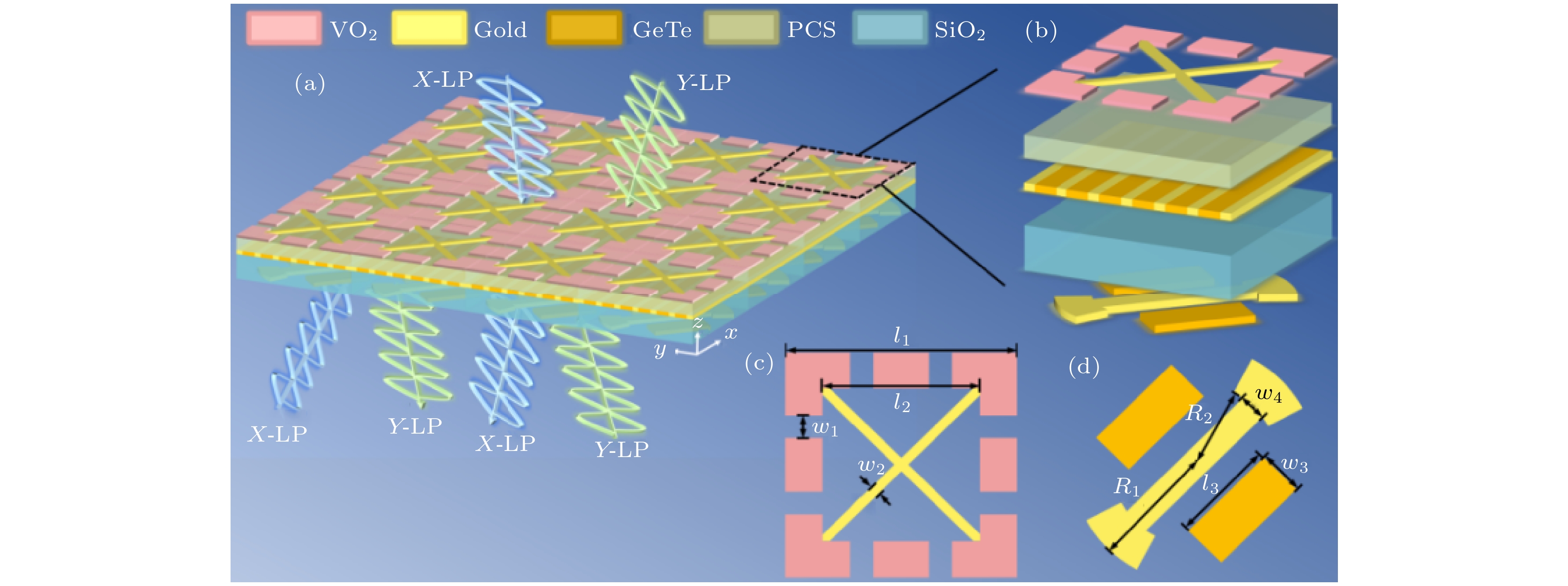
-
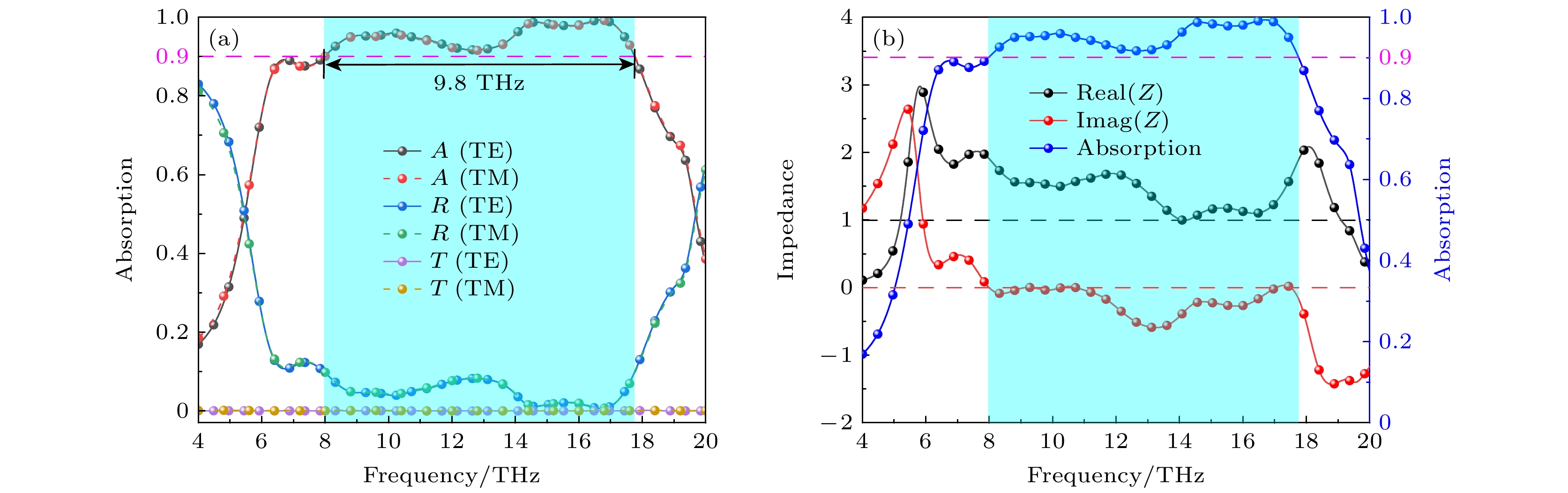
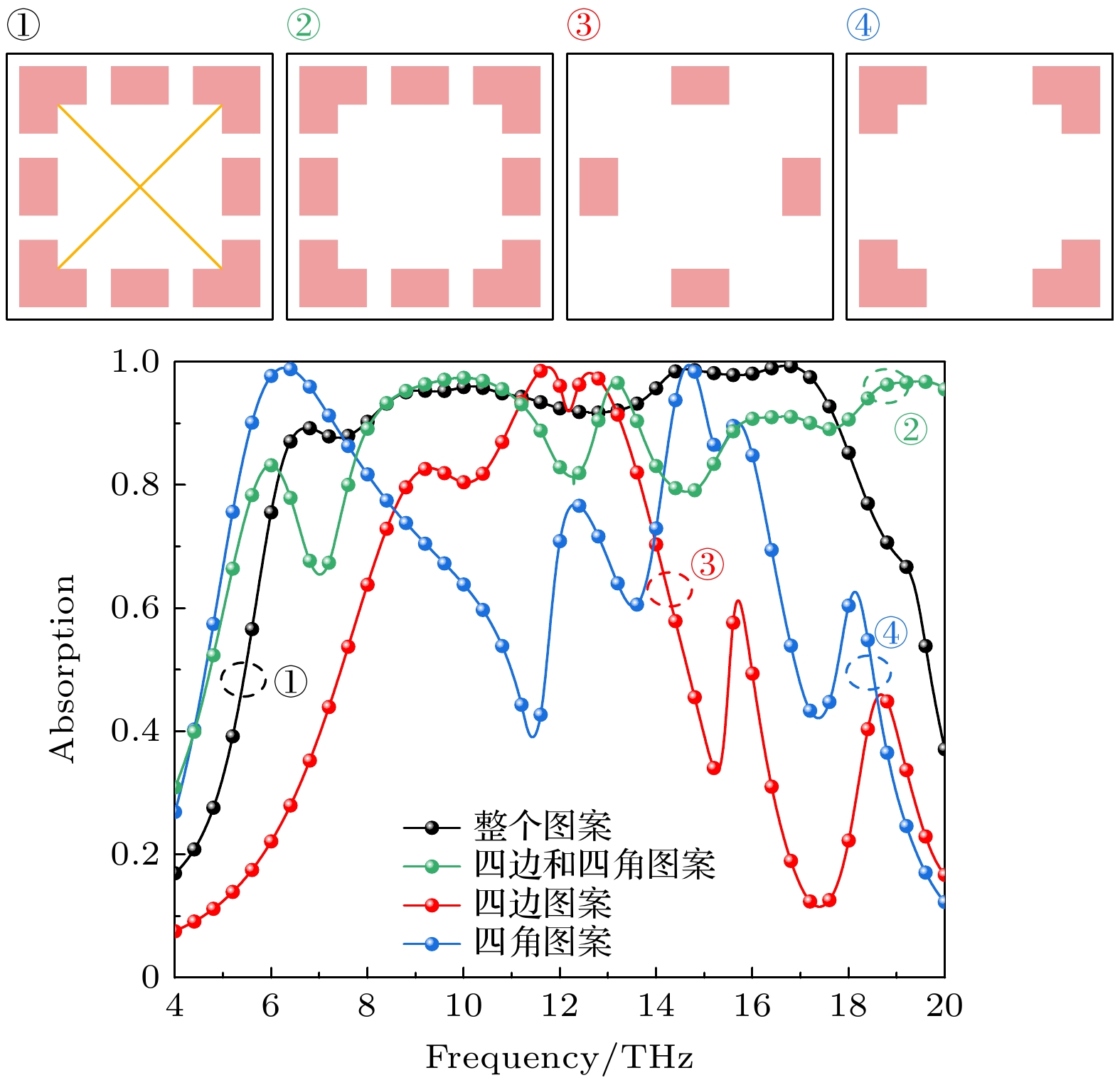
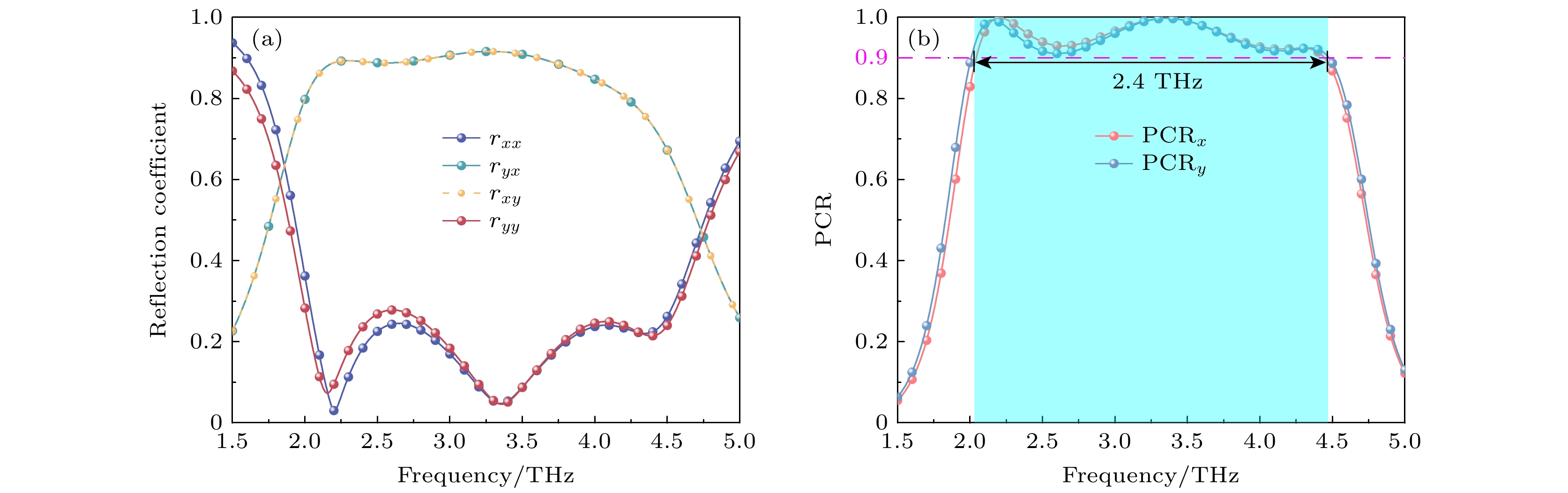
In this paper, we propose a vanadium dioxide and germanium telluride composite metasurface. The conductivity of vanadium dioxide and germanium telluride is varied by changing the temperature, which enables the switching of functions such as ultra-broadband absorption, reflective-type polarization, and transmissive-type polarization. When vanadium dioxide is metallic and germanium telluride is crystalline, the terahertz wave is incident along the –z direction, and the metasurface can be used as a broadband absorber, with an absorption rate greater than 90% in a frequency range of 7.96–17.76 THz, and the absorption bandwidth reaches 9.8 THz, with a relative bandwidth of 76.2%. In addition, the designed metasurface absorber is polarization-insensitive and exhibits good absorption performance at large incidence angles. Terahertz waves are incident along the +z direction, and this metasurface can be used as a reflective polarization converter with a polarization conversion ratio greater than 0.9 for x– and y–polarized waves in the frequency band from 2.04 to 4.44 THz. The effects of incidence angle and structural parameters on polarization conversion performance are also investigated. When vanadium dioxide is in the dielectric state and germanium telluride is in the amorphous state, the metasurface can be used as a transmissive polarization converter, with a polarization conversion rate of greater than 0.9 in a frequency band of 0.65–5.07 THz . And the high polarization conversion performance can be maintained in a wide range of incidence angles. Finally, the physical mechanism of polarization conversion is analyzed using surface currents. The results show that the metasurface structure has bi-directional, switchable and multi-functional characteristics for terahertz wave manipulation, and has broad application prospects in terahertz wave sensing, imaging and communication.
-
Keywords:
- reflective polarization conversion /
- transmissive polarization conversion /
- ultra-broadband absorption /
- metasurface
-
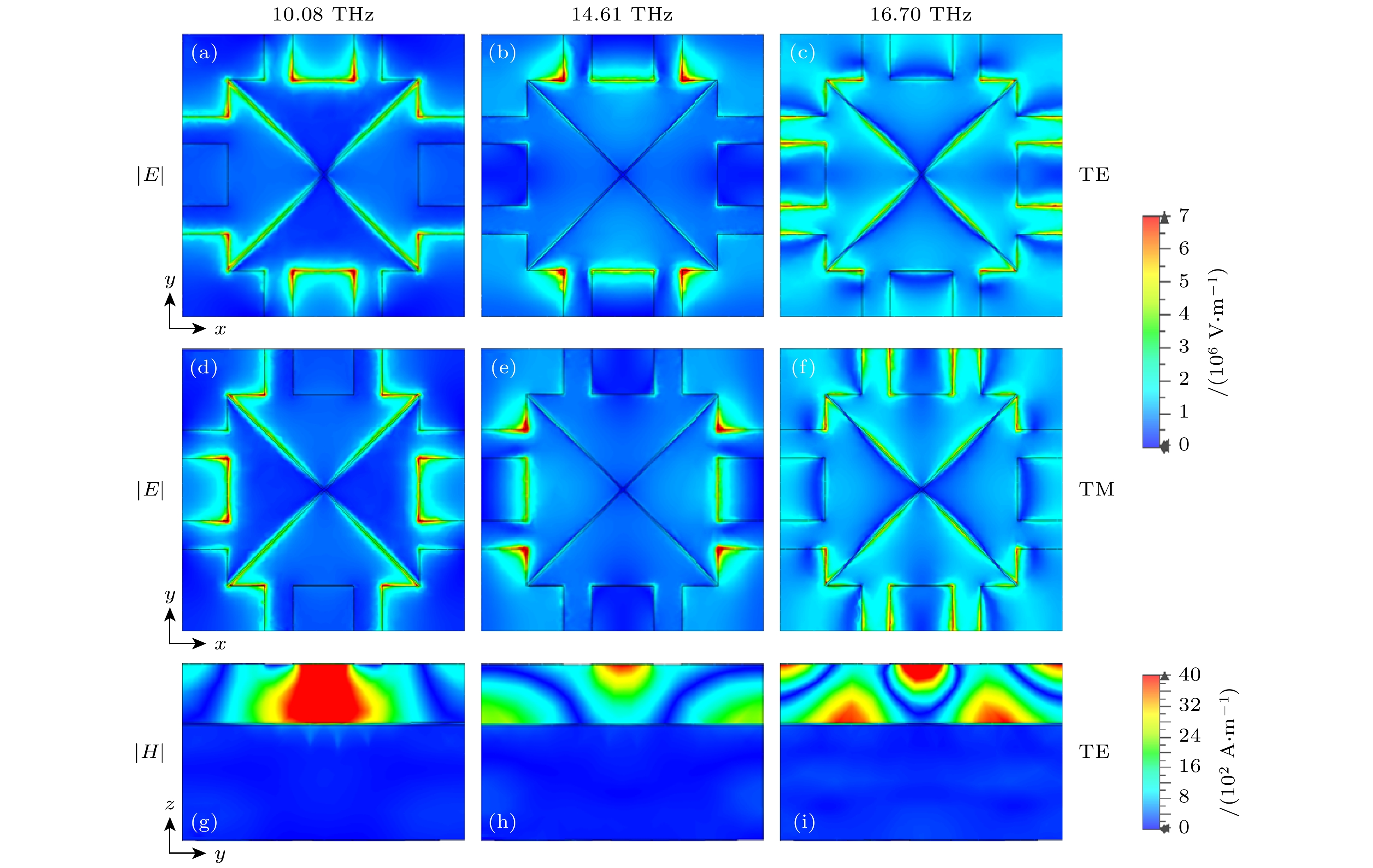
图 4 太赫兹波沿–z方向入射吸收器谐振频点处的电磁场分布 (a)—(c) TE模式和(d)—(f) TM模式下, 谐振频点处的电场分布俯视图; (g)—(i) TE模式下, 谐振频点处的磁场分布侧视图
Figure 4. Electromagnetic field distribution at the resonant frequency points of the absorber for a terahertz wave incident along the –z direction: Top view of the electric field distribution at the resonant frequency point in (a)–(c) TE mode and (d)–(f) TM mode; (g)–(i) side view of the magnetic field distribution at the resonant frequency point in TE mode.
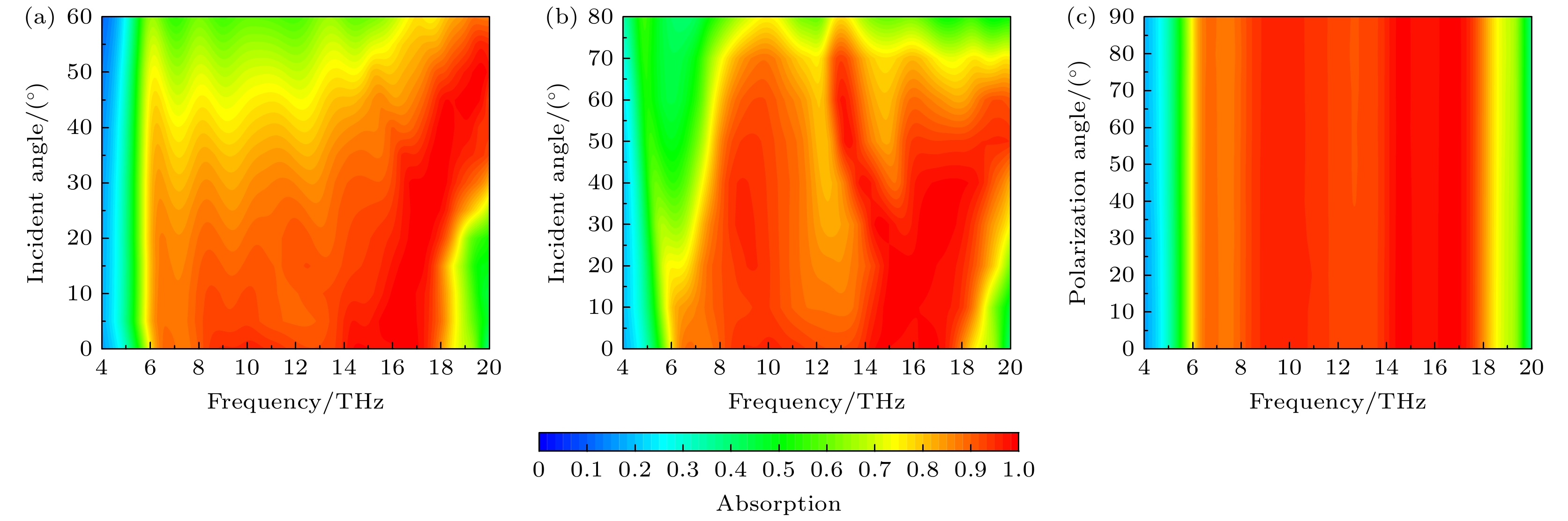
图 5 太赫兹波沿–z方向入射时入射角与极化角对吸收性能的影响 (a) TE模式和(b) TM模式下, 不同入射角对吸收性能的影响; (c)不同极化角对吸收性能的影响
Figure 5. Effect of incidence angle and polarization angle on absorption performance for terahertz waves incident along –z direction: Effect of different incidence angles on the absorption performance in (a) TE mode and (b) TM mode; (c) effect of different polarization angles on the absorption performance.
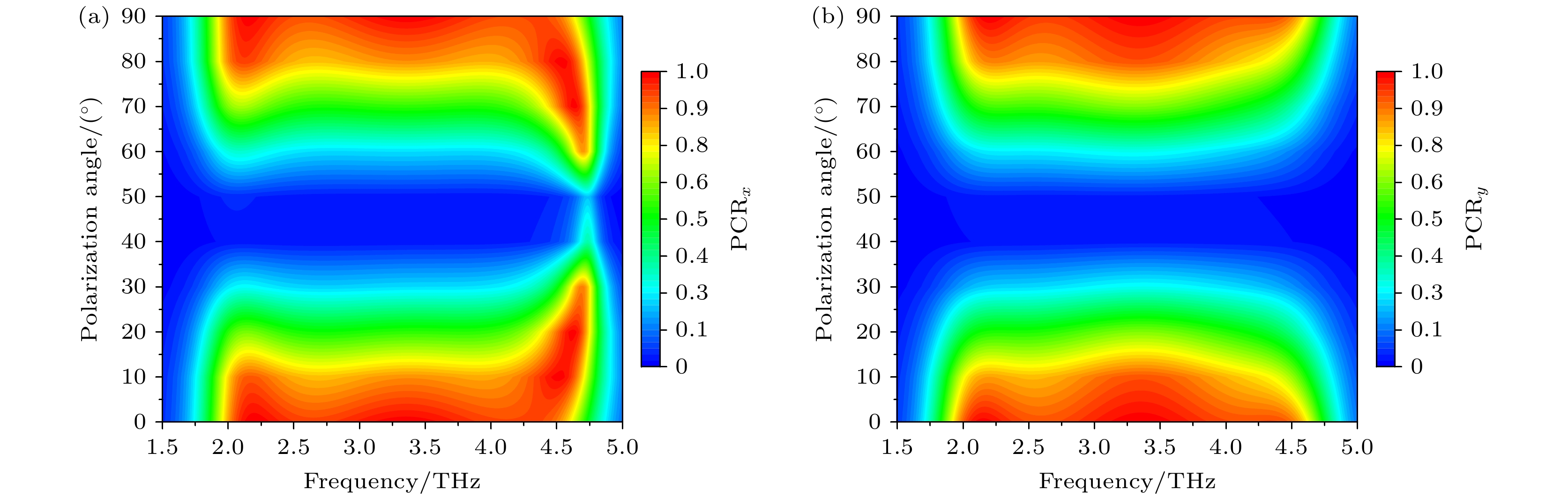
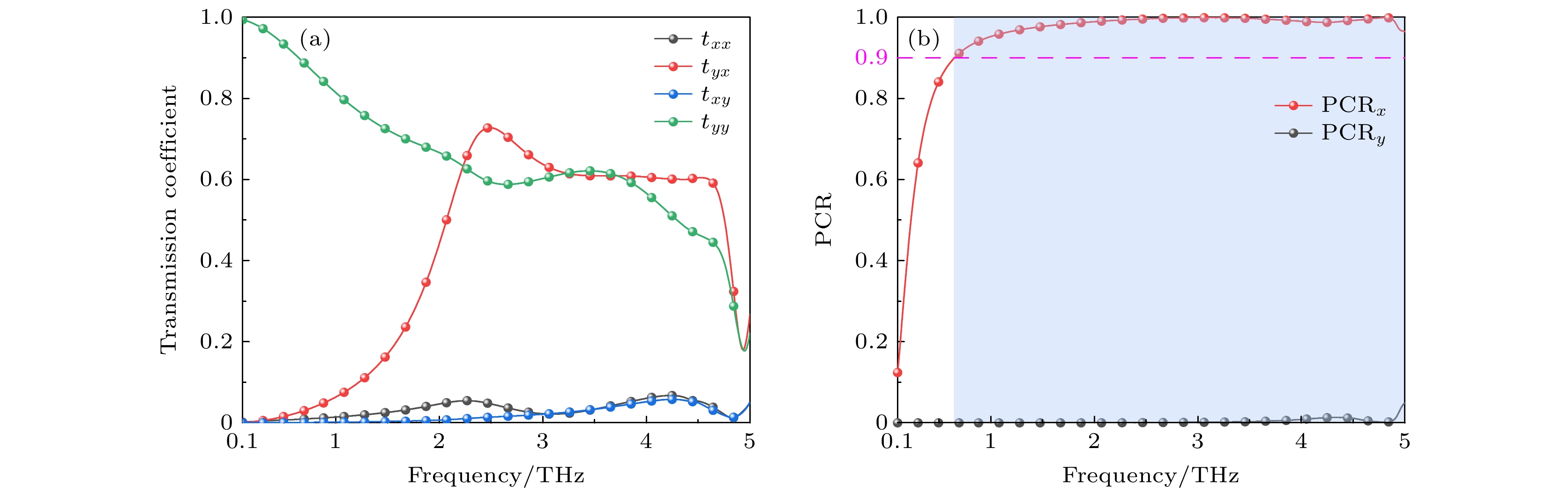
图 7 太赫兹波沿+z方向入射下, 不同极化角对PCR影响 (a) x偏振波入射下, 不同极化角对PCR影响; (b) y偏振波入射下, 不同极化角对PCR影响
Figure 7. Effect of different polarization angles on PCR under the incidence of terahertz waves along the +z direction: (a) The effect of different polarization angles on PCR under x–polarized wave incidence; (b) the effect of different polarization angles on PCR under y–polarized wave incidence.
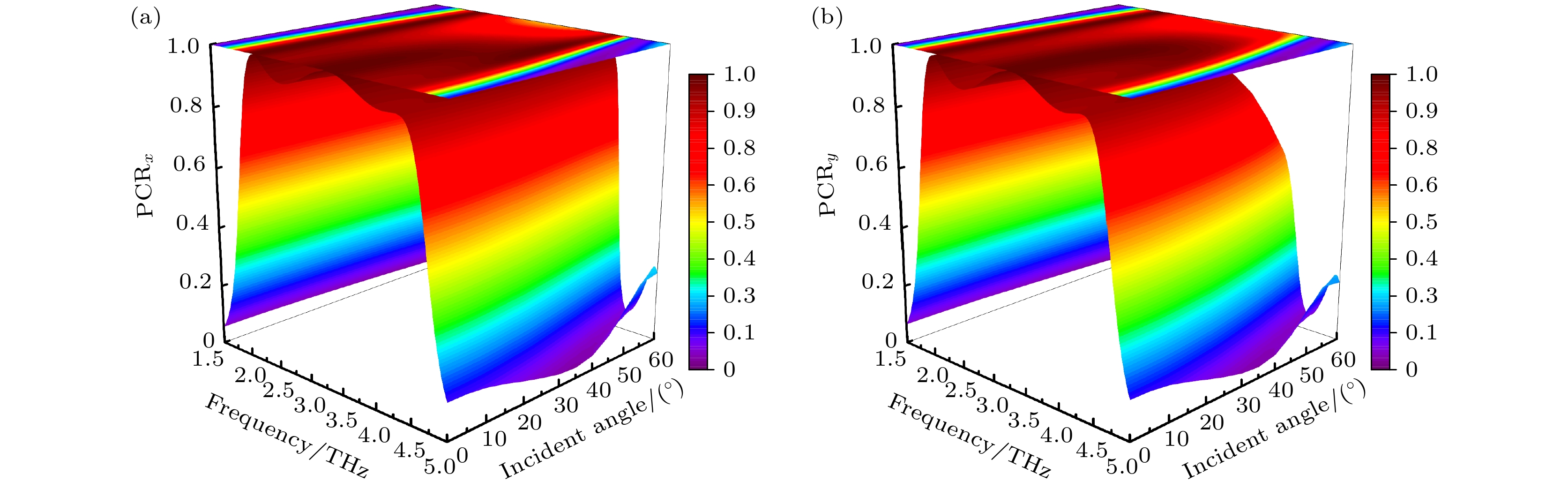
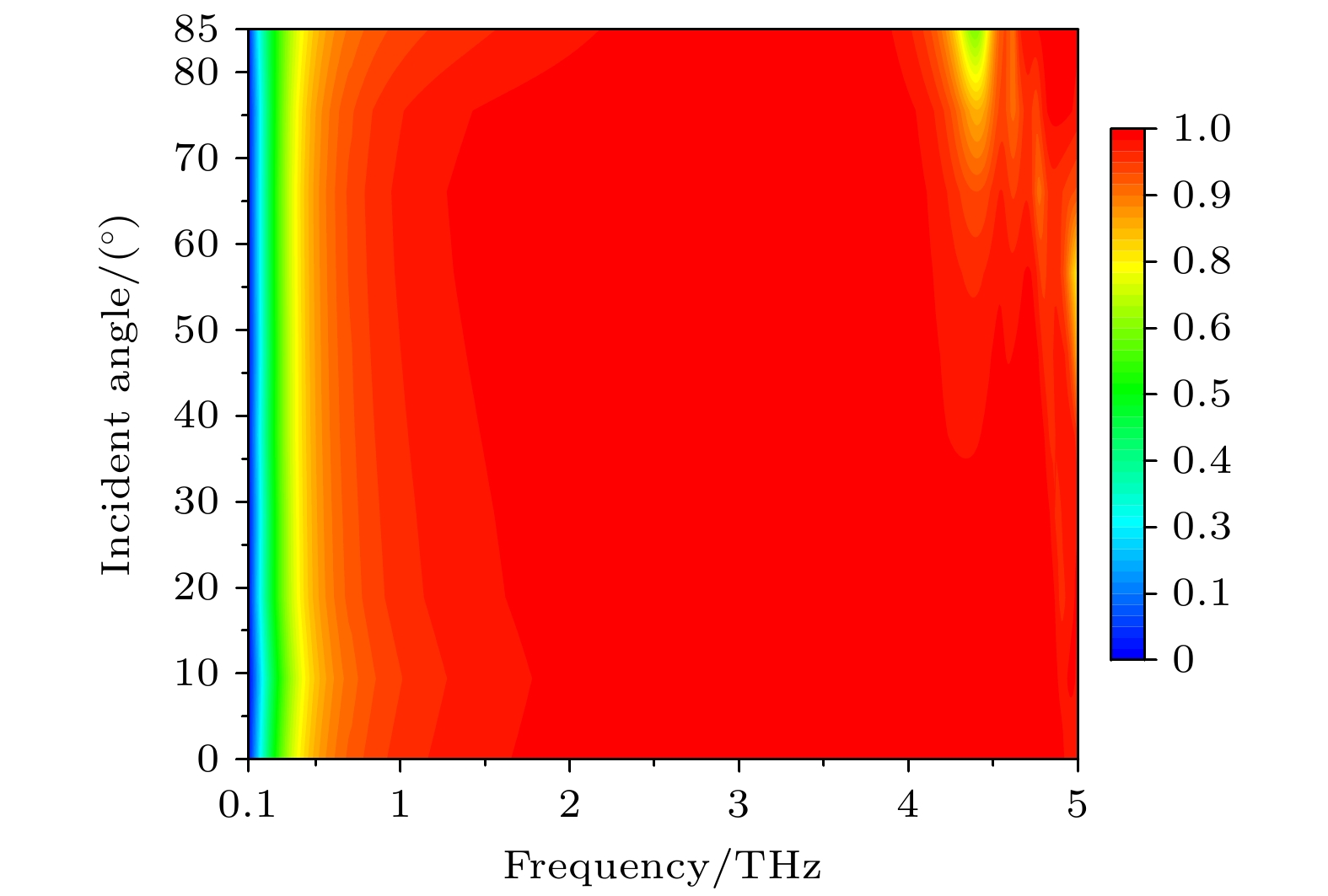
图 8 太赫兹波沿+z方向入射下, 不同入射角对PCR影响 (a) x偏振波入射下, 不同入射角对PCR影响; (b) y偏振波入射下, 不同入射角对PCR影响
Figure 8. Effect of different incidence angles on PCR under the incidence of terahertz waves along the +z direction: (a) The effect of different incidence angles on PCR under x–polarized wave incidence; (b) the effect of different incidence angles on PCR under y–polarized wave incidence.
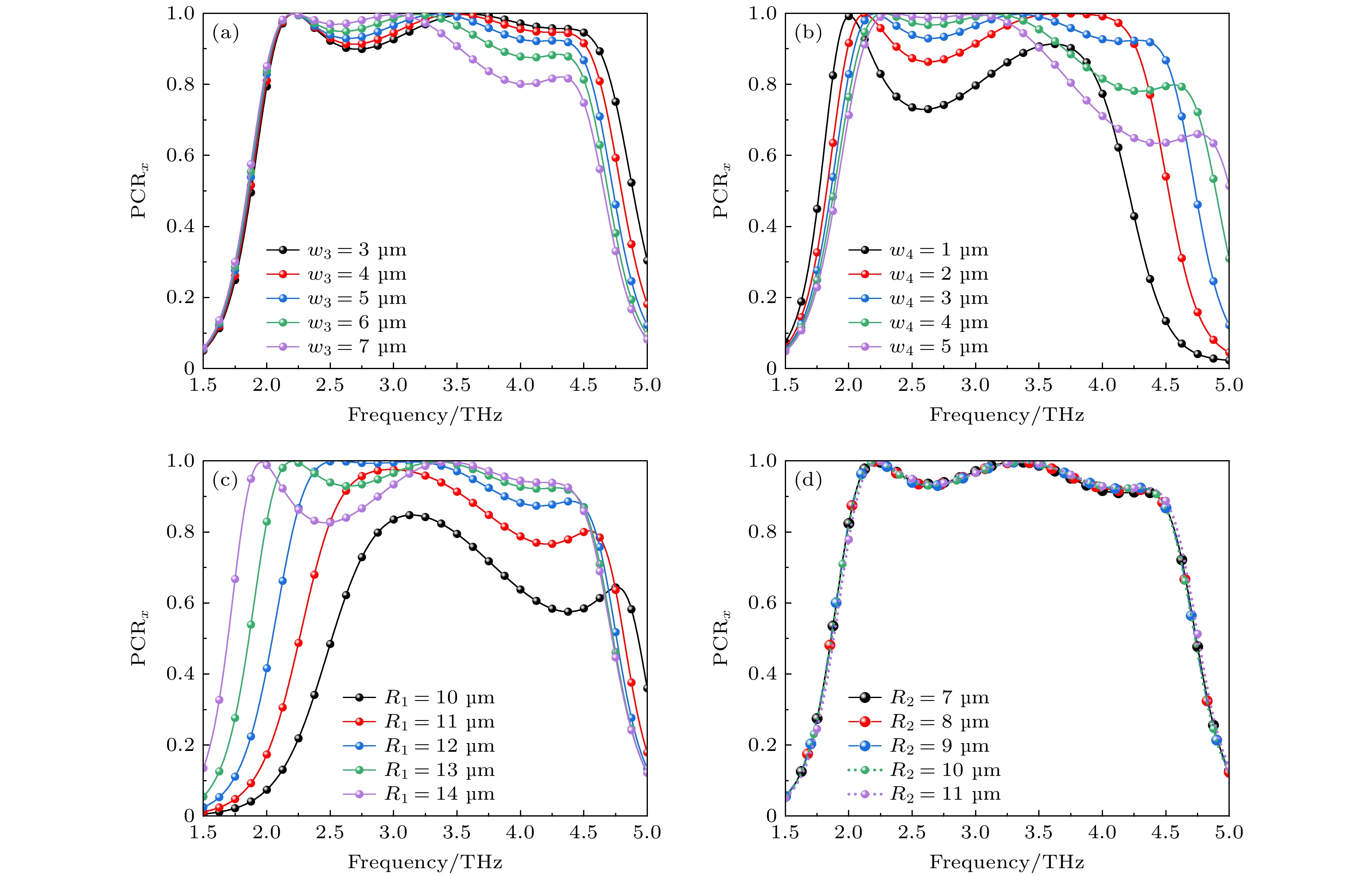
图 9 太赫兹波沿+z方向入射下, 不同结构参数对PCRx影响 (a)两边矩形谐振器宽度w3; (b)中间条形谐振器宽度w4; (c)外环半径R1; (d)内环半径R2
Figure 9. Effect of different structural parameters on PCRx under the incidence of terahertz wave along +z direction: (a) Width of the rectangular resonator on both sides w3; (b) width of the strip resonator in the middle w4; (c) outer ring radius R1; (d) inner ring radius R2.
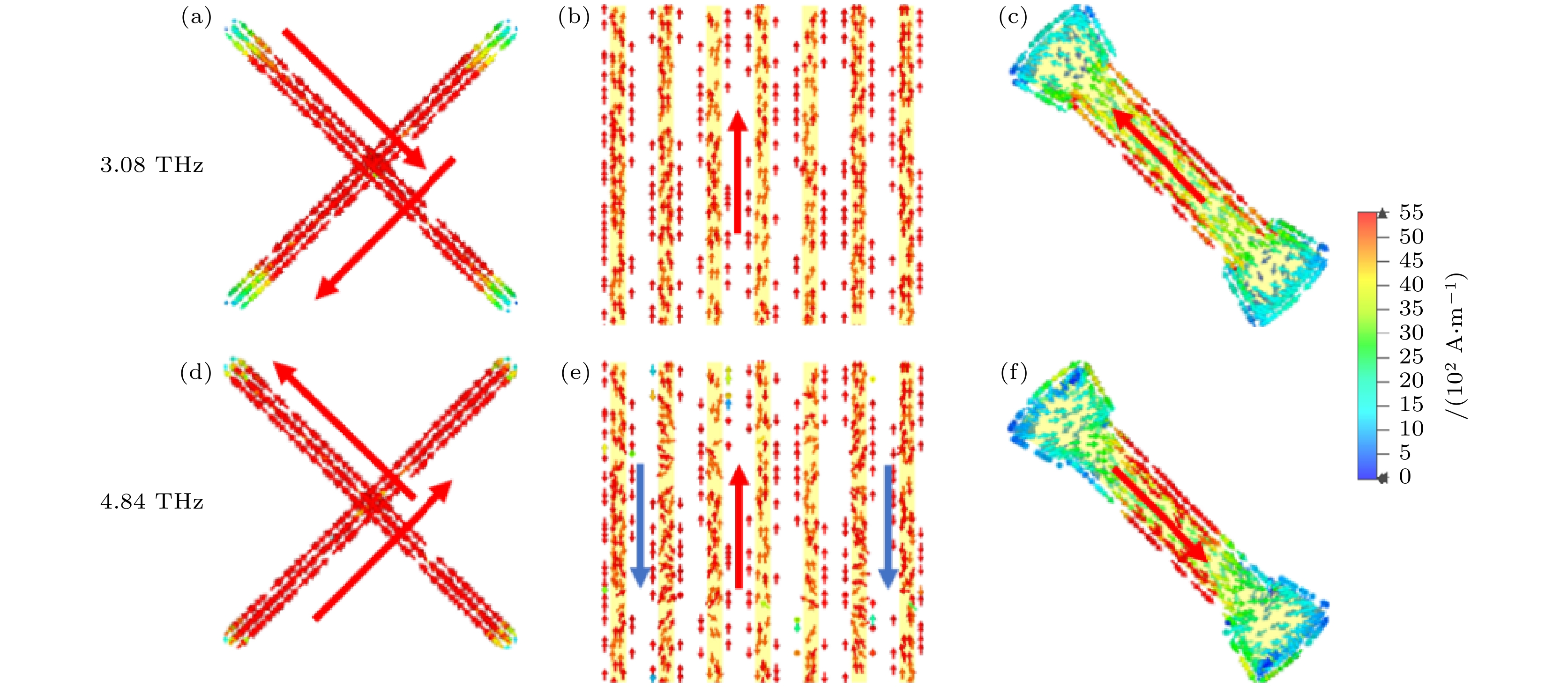
图 12 太赫兹波沿+z方向入射下, 顶层、中间和底层结构在谐振频点处的电流分布图, 不同谐振频率下 (a), (d)顶层十字架结构; (b), (e)中间光栅层; (c), (f)底层“工”形结构的电流分布Fig. 12. Current distributions of the top, intermediate and bottom layers of the structure at the resonance frequencies under terahertz wave incidence along the +z direction, current distributions at different resonant frequencies for (a), (d) the top cross structure; (b), (e) the intermediate grating layer; (c), (f) the bottom “工” structure.
表 1 本文提出结构与其他文献报道成果对比
Table 1. Comparison of the proposed structure in this paper with previously reported works.
文献 可调材料 功能 性能 带宽 [18] Graphene 宽带吸收和极化转换 1.74—3.52 THz: A≥90%
1.54—2.55 THz: PCRr≥90%吸收1.78 THz
反射极化转换1.01 THz[19] VO2和Si 宽带吸收和极化转换 0.68—1.60 THz: A≥90%
0.82—1.60 THz: PCRr≥90%吸收0.92 THz
反射极化转换0.78 THz[20] VO2 宽带吸收和极化转换 3.33—5.62 THz: A≥90%
2.54—4.55 THz: PCRr≥90%吸收2.29 THz
反射极化转换2.01 THz[10] VO2 宽带吸收和极化转换 1.49—3.58 THz: A≥90%
1.1—3.2 THz: PCRr≥90%吸收2.09 THz
反射极化转换2.1 THz本文 VO2和GeTe 宽带吸收和极化转换 7.96—17.76 THz: A≥90%
2.04—4.44 THz: PCRr≥90%
0.65—5.07 THz: PCRt≥90%吸收9.8 THz
反射极化转换2.4 THz
透射极化转换4.42 THz -
[1] Zheng C L, Li J, Yue Z, Li J T, Liu J Y, Wang G C, Wang S L, Zhang Y T, Zhang Y, Yao J Q 2022 Laser Photonics Rev. 16 2200051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Huang X J, Cao M, Wang D Q, Li X W, Fan J D, Li X Y 2022 Opt. Mater. Express 12 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bader A D, Saghaei H 2023 Opt. Express 31 12653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Luo B, Qi Y P, Zhou Z H, Shi Q, Wang X X 2024 Nanotechnology 35 195205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] King J, Wan C H, Park T J, Deshpande S, Zhang Z, Ramanathan S, Kats M A 2024 Nat. Photonics 18 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zeng Y, Wang J Q, Yang X S, Yao J Q, Li P N, He Q, Xu M, Miao X S 2023 Opt. Mater. 136 113447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen Z, Chen J J, Tang H W, Shen T, Zhang H 2022 Opt. Express 30 6778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jiang X X, Xiao Z Y, Wang X W, Cheng P 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 3519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Phan H L, Nguyen T Q H, Nguyen T M, Nguyen N H, Le D T, Bui X K, Vu D L, Kim J M, 2024 Opt. Mater. 154 115682
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y, Xue W R, Du Y D, Liang J L, Li C Y 2024 Opt. Mater. 149 114984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin Q W, Wong H, Huitema L, Crunteanu A 2022 Adv. Opt. Mater. 10 2101699
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li W X, Yi Y T, Yang H, Cheng S B, Yang W X, Zhang H F, Yi Z, Yi Y G, Li H L 2023 Commun. Theor. Phys. 75 045503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Nguyen H Q, Nguyen T Q H, Nguyen T M 2024 Phys. Scr. 99 115534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang P Y, Chen G Q, Hou Z Y, Zhang Y Z, Shen J, Li C Y, Zhao M L, Gao Z Z, Li Z Q, Tang T T 2022 Micromachines 13 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang R Y, Luo Y A, Xu J K, Wang H Y, Han H Y, Hu D, Zhu Q F, Zhang Y 2021 Opt. Express 29 42989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li N C, Mei J S, Gong D G, Shia Y C 2022 Opt. Commun. 521 128581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jiang X Q, Fan W H, Qin C, Chen X 2021 Nanomaterials 11 2895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li Z H, Yang R C, Wang J Y, Zhao Y J, Tian J P, Zhang W M 2021 Opt. Mater. Express 11 3507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang H, He X C, Zhang D, Zhang H F 2022 Opt. Express 30 23341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Niu J H, Yao Q Y, Mo W, Li C H, Zhu A J 2023 Opt. Commun. 527 128953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Metrics
- Abstract views: 280
- PDF Downloads: 8
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: