-
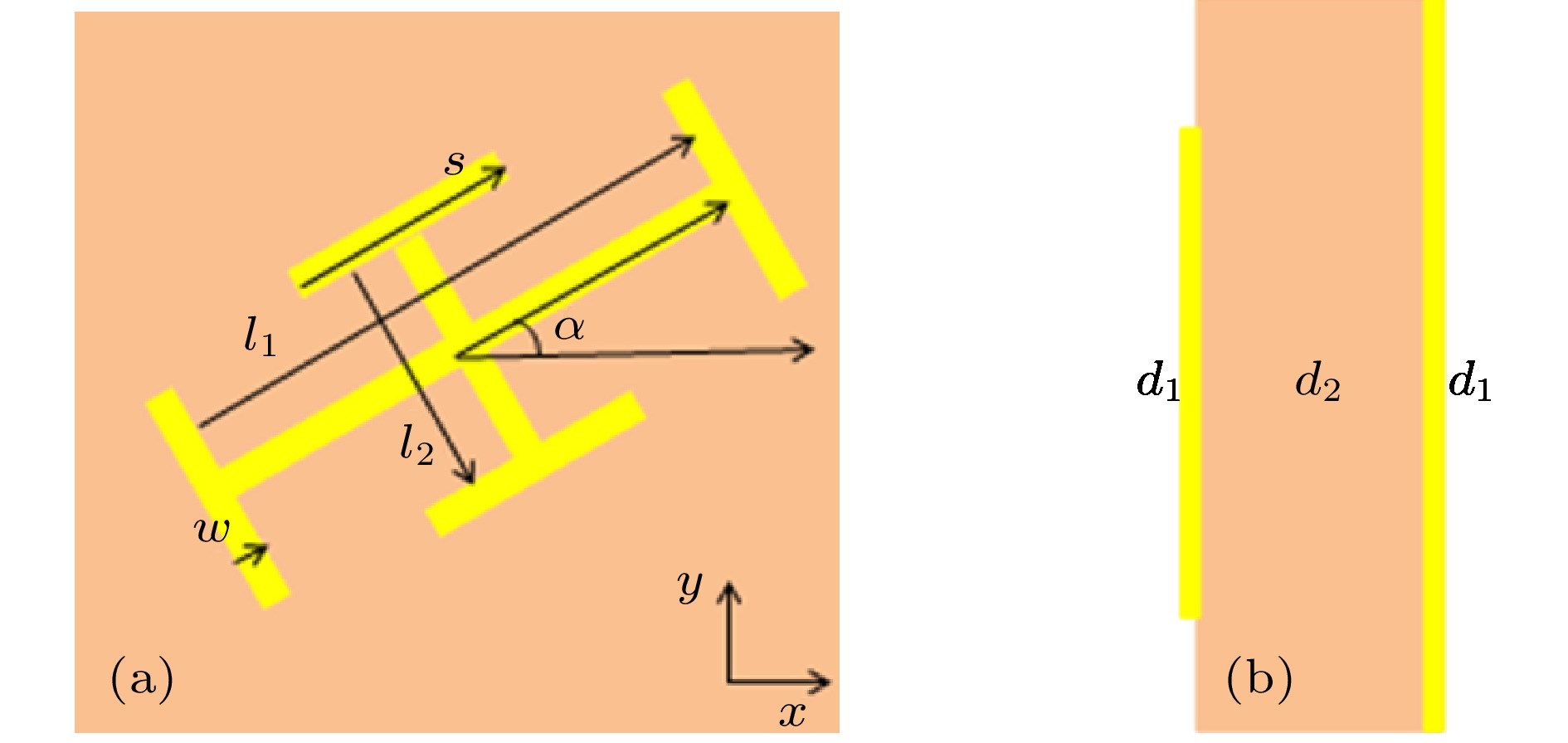
具有螺旋波前的电磁波是携带轨道角动量的涡旋波束, 涡旋波束存在的相位奇点, 使其在微粒操控和通讯等领域有特殊的应用. 本文提出了一种基于反射型超表面的太赫兹宽带涡旋波束产生器, 该器件由超表面-电介质-金属三层结构构成, 顶层为两个正交I形金属结构单元组成的超表面, 中间层是聚酰亚胺介质, 最底层为金属. 通过对超表面单元结构参数的优化设计, 可以实现在不同旋转角度下反射波振幅高达90%以上, 同时反射波相位随旋转角线性变化的目的. 进一步利用这些单元结构按照Pancharatnam-Berry相位原理进行超表面布阵, 在0.8—1.4 THz频率范围内, 可以将圆偏振太赫兹波束转换为具有轨道角动量的涡旋波束, 这一器件的工作带宽相对较宽, 结构简单, 转换效率高, 在太赫兹涡旋波束产生方面具有潜在的应用价值.The electromagnetic wave with spiral wavefront is a vortex beam carrying orbital angular momentum. The phase singularity of the vortex beam has special applications in the fields of particle manipulation and communication. In this paper, a terahertz (THz) wide-band vortex beam generator based on reflective metasurface is proposed and simulated. The device consists of a metasurface-dielectric-metal three-layer structure, and the top layer is a metasurface composed of two orthogonal I-shaped metal structural units. The intermediate layer of polyimide medium, and the bottom layer is of metal as a reflecting plate. The CST microwave studio is used to simulate the reflection performance of unit cell. The structure parameters are optimized to obtain the better performance. A set of optimed structure parameters is determined. According to the phase principle of Pancharatnam-Berry (P-B), by rotating the angle of the top-layer I-type metal structure, the reflection amplitudes of the unit cell structure at different rotation angles are required to approximately equal while the phase changes linearly with rotation angle and reaches a range of 2lπ for the topological charge number l. These cell structures are arranged according to the phase principle mentioned above. The metasurfaces of different topological charge numbers are designed to generate the corresponding vortex beams. In this paper, the metasurfaces with topological charge numbers 1 and 2 are designed. The reflection amplitude and phase of the circularly polarized THz beam incident vertically on the metasurface are simulated by using CST microwave studio. The simulation results show that in a frequency range of 0.8−1.4 THz, the metasurface can convert the circularly polarized terahertz beam into a vortex beam with a different topological charge number. In addition, in order to illustrate that the metasurface designed can produce a higher topological charge number of vortex beam, a metasurface with a topological charge number of 3 is designed as an example. The reflection amplitude and phase of the circularly polarized THz beam at a frequency of 1.1 THz is simulated. The results show that the designed metasurface can produce a vortex beam with a topological charge number of 3. The higher topological charges of vortex beam can also be generated according to the corresponding phase arrangement. The device has a relatively wide operating bandwidth, simple structure, high conversion efficiency, and has the potential application in terahertz vortex beam generation.
-
Keywords:
- terahertz /
- vortex beam /
- broadband /
- metasurface
[1] Beard M C, Turner G M, Schmuttenmaer C A 2002 J. Phys. Chem. B 106 7146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Vieweg N, Fischer B M, Reuter M, Kula P, Dabrowsk R, Celik M A, Frenking G, Koch M, Jepsen P U 2012 Opt. Express 20 28249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Janek M, Zich D, Naftaly M 2014 Mater. Chem. Phys. 145 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu B B, Nuss M C 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 1716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mittleman D M, Gupta M, Neelamani R, Baraniuk R G, Rudd J V, Koch M 1999 Appl. Phys. B 68 1085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kohler R, Tredicucci A, Beltram F, Beere H E, Linfield E H, Davies A G, Ritchie D A, Lotti R C, Rossi F 2002 Nature 417 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang Z W, Wang K J, Lei Y, Zhang Z Y, Zhao Y M, Li C Y, Gu A, Shi N C, Zhao K, Zhan H L, Zhang C L 2015 Science China 58 124202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Heljo V P, Nordberg A, Tenho M, Virtanen T, Jouppila K, Salonen J, Maunu S L, Juppo A M 2012 Pharm. Res. 29 2684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kirilenko M S, Khonina S N 2013 Optical Memory and Neural Networks 22 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chavez-Cerda S, Padgett M J, Allison I, New G H C, Gutierrez-Vega J C, Neil A T O, Vicar I M, Courtial J 2002 J. Optics B: Quantum Semiclass Opt. 4 S52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Genevet P, Lin J, Kats M A, Capasso F 2012 Nature Comm. 3 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Mohammadi S M, Daldorff L K S, Bergman J E S, Karlsson R L, Thidé B, Forozesh K, Carozzi T D, Isham B 2010 IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 58 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Thide B, Then H, SjoHolm J, Palmer K, Bergman J, Carozzi T D, Istomin Y N, Ibragimov N H, Khamitova R 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 087701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 付亚男, 张新群, 赵国忠, 李永花, 于佳怡 2017 66 180701
Fu Y N, Zhang X Q, Zhao G Z, Li Y H, Yu J Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 180701
[15] 李永花, 周璐, 赵国忠 2018 中国激光 45 0314001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y H, Zhou L, Zhao G Z 2018 Chin. J. Lasers 45 0314001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li H, Xiao B Y, Huang X J, Yang H L 2015 Phys. Scr. 90 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Enoch S, Tayeb G, Sabouroux P, Guerin N, Vincent P 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 213902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Huang J, Pogorzelski R J 1998 IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 46 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Martynyuk A E, Martinez-Lopez J I, Martynyuk N A 2004 IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 52 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 周璐, 赵国忠, 李晓楠 2019 68 108701
Zhou L, Zhao G Z, Li X N 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 108701
[21] Genevet P, Yu N F, Aieta F, Lin J, Kats M A, et al. 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 013101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yu N, Genevet P, Kats M A, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Science 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang K, Yuan Y Y, Zhang D W, Ding X M, Rstni B, Burokur S N, Lu M J, Tang J, Wu Q 2018 Opt. Express 26 1351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Luo W J, Sun S L, Xu H X, He Q, Zhou L 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 044033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xu H H, Wang G M, Cai T, Xiao J, Zhuang Y Q 2016 Opt. Express 24 27836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
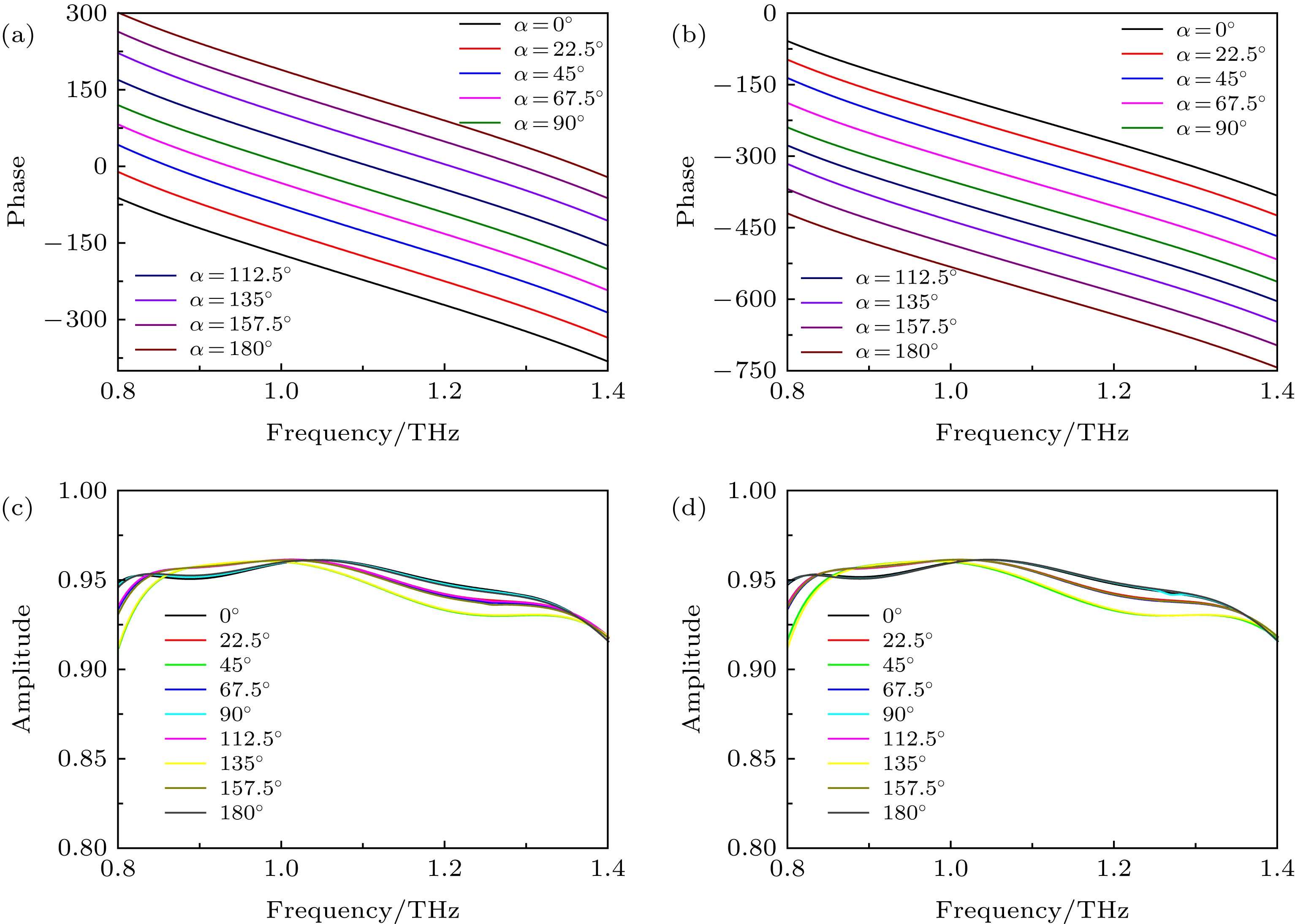
图 4 不同转角单元结构的反射相位和振幅谱 (a) LCP入射的相位谱; (b) RCP入射的相位谱; (c) LCP入射的振幅谱; (d) RCP入射的振幅谱
Fig. 4. Reflective phase and amplitude spectra of unit cell structure under different rotation angle: (a) Phase spectra at LCP incident; (b) phase spectra at RCP incident; (c) amplitude spectra at LCP incident; (d) amplitude spectra at RCP incident.
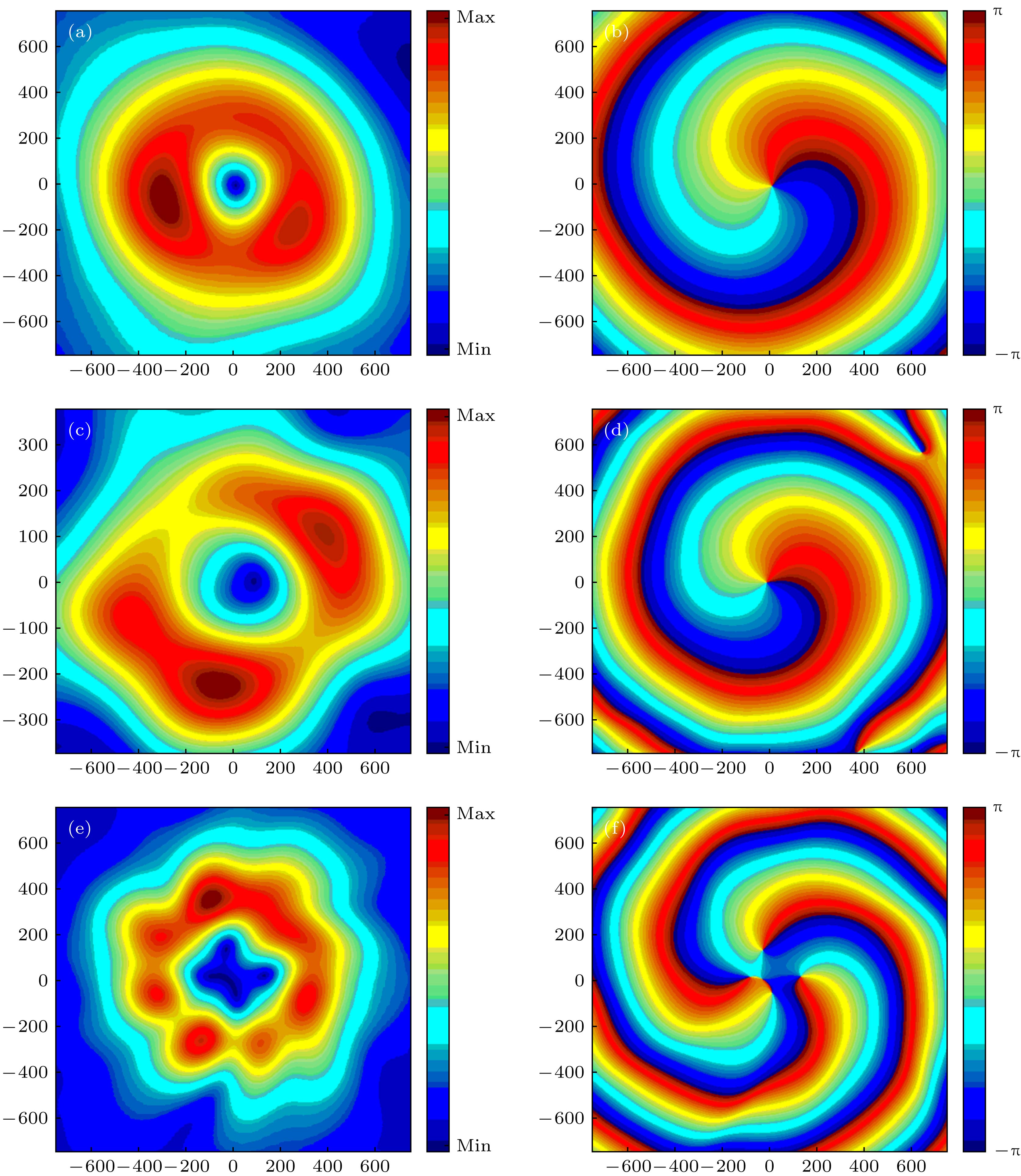
图 6 超表面产生l = 1和l = 2的涡旋波束反射振幅和相位分布 LCP入射l = 1超表面的(a)振幅分布和(b)相位分布; RCP入射l = 2超表面的(c)振幅分布和(d)相位分布
Fig. 6. Reflective amplitude and phase distributions of vortex beams with l = 1 and l = 2 generated by metasurface. LCP incident l = 1 metasurface: (a) amplitude distribution and (b) phase distribution; RCP incident l = 2 metasurface: (c) amplitude distribution and (d) phase distribution.
图 7 不同频率下l = 1和l = 3超表面产生的反射涡旋波束振幅、相位分布 l = 1超表面(a) 0.8 THz频率下振幅分布, (b) 0.8 THz频率下相位分布, (c) 1.4 THz频率下振幅分布, (d) 1.4 THz频率下相位分布; l = 3超表面(e) 1.1 THz频率下振幅分布, (f) 1.1 THz频率下相位分布
Fig. 7. The amplitude and phase distribution of reflective vortex beam generated by the LCP incident l = 1 and l = 3 metasurface at different frequencies. l = 1: (a) amplitude distribution at 0.8 THz, (b) phase distribution at 0.8 THz, (c) amplitude distribution at 1.4 THz, (d) phase distribution at 1.4 THz. l = 3: (e) amplitude distribution at 1.1 THz, (f) phase distribution at 1.1 THz.
-
[1] Beard M C, Turner G M, Schmuttenmaer C A 2002 J. Phys. Chem. B 106 7146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Vieweg N, Fischer B M, Reuter M, Kula P, Dabrowsk R, Celik M A, Frenking G, Koch M, Jepsen P U 2012 Opt. Express 20 28249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Janek M, Zich D, Naftaly M 2014 Mater. Chem. Phys. 145 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu B B, Nuss M C 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 1716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mittleman D M, Gupta M, Neelamani R, Baraniuk R G, Rudd J V, Koch M 1999 Appl. Phys. B 68 1085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kohler R, Tredicucci A, Beltram F, Beere H E, Linfield E H, Davies A G, Ritchie D A, Lotti R C, Rossi F 2002 Nature 417 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang Z W, Wang K J, Lei Y, Zhang Z Y, Zhao Y M, Li C Y, Gu A, Shi N C, Zhao K, Zhan H L, Zhang C L 2015 Science China 58 124202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Heljo V P, Nordberg A, Tenho M, Virtanen T, Jouppila K, Salonen J, Maunu S L, Juppo A M 2012 Pharm. Res. 29 2684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kirilenko M S, Khonina S N 2013 Optical Memory and Neural Networks 22 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chavez-Cerda S, Padgett M J, Allison I, New G H C, Gutierrez-Vega J C, Neil A T O, Vicar I M, Courtial J 2002 J. Optics B: Quantum Semiclass Opt. 4 S52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Genevet P, Lin J, Kats M A, Capasso F 2012 Nature Comm. 3 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Mohammadi S M, Daldorff L K S, Bergman J E S, Karlsson R L, Thidé B, Forozesh K, Carozzi T D, Isham B 2010 IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 58 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Thide B, Then H, SjoHolm J, Palmer K, Bergman J, Carozzi T D, Istomin Y N, Ibragimov N H, Khamitova R 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 087701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 付亚男, 张新群, 赵国忠, 李永花, 于佳怡 2017 66 180701
Fu Y N, Zhang X Q, Zhao G Z, Li Y H, Yu J Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 180701
[15] 李永花, 周璐, 赵国忠 2018 中国激光 45 0314001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y H, Zhou L, Zhao G Z 2018 Chin. J. Lasers 45 0314001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li H, Xiao B Y, Huang X J, Yang H L 2015 Phys. Scr. 90 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Enoch S, Tayeb G, Sabouroux P, Guerin N, Vincent P 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 213902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Huang J, Pogorzelski R J 1998 IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 46 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Martynyuk A E, Martinez-Lopez J I, Martynyuk N A 2004 IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 52 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 周璐, 赵国忠, 李晓楠 2019 68 108701
Zhou L, Zhao G Z, Li X N 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 108701
[21] Genevet P, Yu N F, Aieta F, Lin J, Kats M A, et al. 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 013101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yu N, Genevet P, Kats M A, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Science 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang K, Yuan Y Y, Zhang D W, Ding X M, Rstni B, Burokur S N, Lu M J, Tang J, Wu Q 2018 Opt. Express 26 1351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Luo W J, Sun S L, Xu H X, He Q, Zhou L 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 044033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xu H H, Wang G M, Cai T, Xiao J, Zhuang Y Q 2016 Opt. Express 24 27836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 18907
- PDF下载量: 557
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: