-
Black phosphorus (BP) has been attracting intense interest due to its unique anisotropic properties. The investigations on phonon dispersion and electronic band structure could expand the understanding of the properties of BP and promote its application on next generation nano-electronic devices. As the fingerprint of materials, Raman spectroscopy can provide the information of their phonon dispersion and electronic band structure. According to the Raman selection rule, Raman process involving multiple (two or more) phonons can be used to probe the phonon density of states within the whole Brillouin zone. However, the intensity of high-order Raman modes is much lower than that of the first-order Raman mode. To break through the limit of low intensity, here, we measured the resonant Raman spectroscopy of BP excited by several wavelength lasers and observed rich information about high-order Raman modes in the spectral range of 680–930 cm–1. To further investigate high-order Raman modes and avoid the birefringence effects from optical anisotropy on Raman intensity, we employ a special polarization configuration to obtain resonant Raman spectra and Raman intensity as a function of excitation wavelength. All the observed high-order Raman modes are certainly assigned, according to the phonon dispersion and symmetry analysis of related phonons. This indicates the great contribution of phonons within the Brillouin zone to the second- and third-order Raman scattering. This work proposes a general and systematical method to investigate high-order Raman modes, and paves ways for the researches of phonon dispersion and resonance Raman spectroscopy in other anisotropic materials.
-
Keywords:
- black phosphorus /
- second-order Raman mode /
- third-order Raman mode /
- resonant Raman scattering /
- optical anisotropy
[1] Qiao J, Kong X, Hu Z, Yang F, Ji W 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cai Y, Ke Q, Zhang G, Feng Y P, Shenoy V B, Zhang Y W 2015 Adv. Funct. Mater. 25 2230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ling X, Huang S, Hasdeo E H, Liang L, Parkin W M, Tatsumi Y, Nugraha A R, Puretzky A A, Das P M, Sumpter B G 2016 Nano Lett. 16 2260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen P F, Li N, Chen X Z, Ong W J, Zhao X J 2017 2D Mater. 5 014002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Malard L, Pimenta M, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus M 2009 Phys. Rep. 473 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang X, Qiao X F, Shi W, Wu J B, Jiang D S, Tan P H 2015 Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 2757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shi W, Zhang X, Li X L, Qiao X F, Wu J B, Zhang J, Tan P H 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 057801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shi W, Lin M L, Tan Q H, Qiao X F, Zhang J, Tan P H 2016 2D Mater. 3 025016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lin T, Cong X, Lin M L, Liu X L, Tan P H 2018 Nanoscale 10 8704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mao N, Wu J, Han B, Lin J, Tong L, Zhang J 2016 Small 12 2627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ribeiro H B, Pimenta M A, De Matos C J, Moreira R L, Rodin A S, Zapata J D, De Souza E A, Castro Neto A H 2015 ACS Nano 9 4270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kim J, Lee J U, Lee J, Park H J, Lee Z, Lee C, Cheong H 2015 Nanoscale 7 18708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang X, Mao N, Luo W, Kitadai H, Ling X 2018 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9 2830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Favron A, Goudreault F A, Gosselin V, Groulx J, Cote M, Leonelli R, Germain J F, Phaneuf L, Heureux A L, Francoeur S, Martel R 2018 Nano Lett. 18 1018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sugai S, Shirotani I 1985 Solid State Commun. 53 753
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang J W, Wang B S, Park H S 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 165401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu J B, Lin M L, Cong X, Liu H N, Tan P H 2018 Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 1822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu J B, Zhang X, Ijäs M, Han W P, Qiao X F, Li X L, Jiang D S, Ferrari A C, Tan P H 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 5309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Saito R, Jorio A, Filho A G S, Dresselhaus G, Pimenta M A 2002 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41 4878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Carvalho B R, Malard L M, Alves J M, Fantini C, Pimenta M A 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 136403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Clark R J H, Dines T J 1986 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 25 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu X L, Zhang X, Lin M L, Tan P H 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 067802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
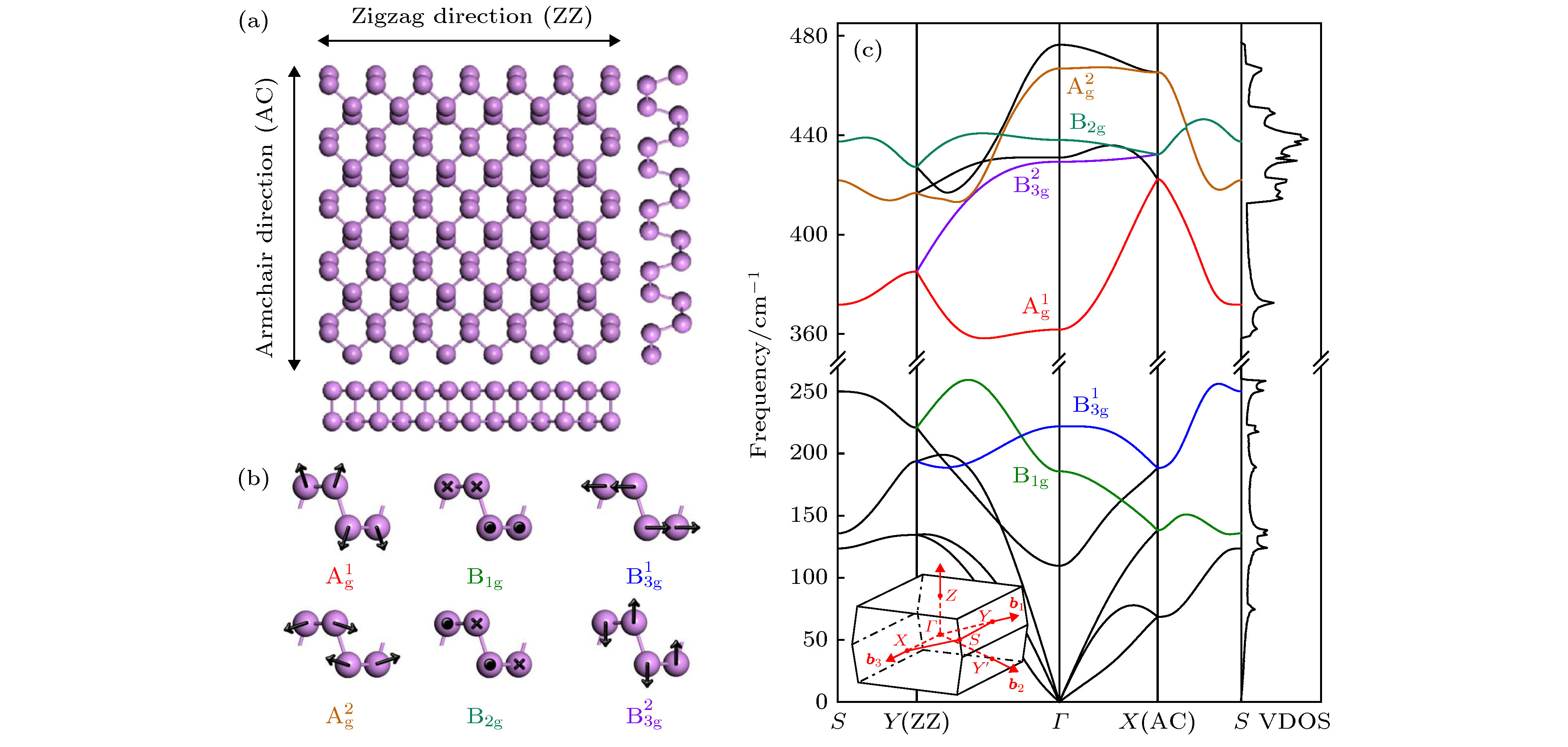
图 1 (a)黑磷的晶体结构; (b)声子模的原子位移示意图; (c)黑磷的声子色散、声子态密度以及第一布里渊区示意图; 布里渊区中心的各拉曼模已在图中标出[9]
Figure 1. (a) Crystal structure of black phosphorus; (b) atomic displacements of phonon modes in black phosphorus; (c) phonon dispersion, vibration density of states (VDOS) and schematic diagram of first Brillouin zone of bulk black phosphorus. Raman modes at the Brillouin zone center are labeled[9]
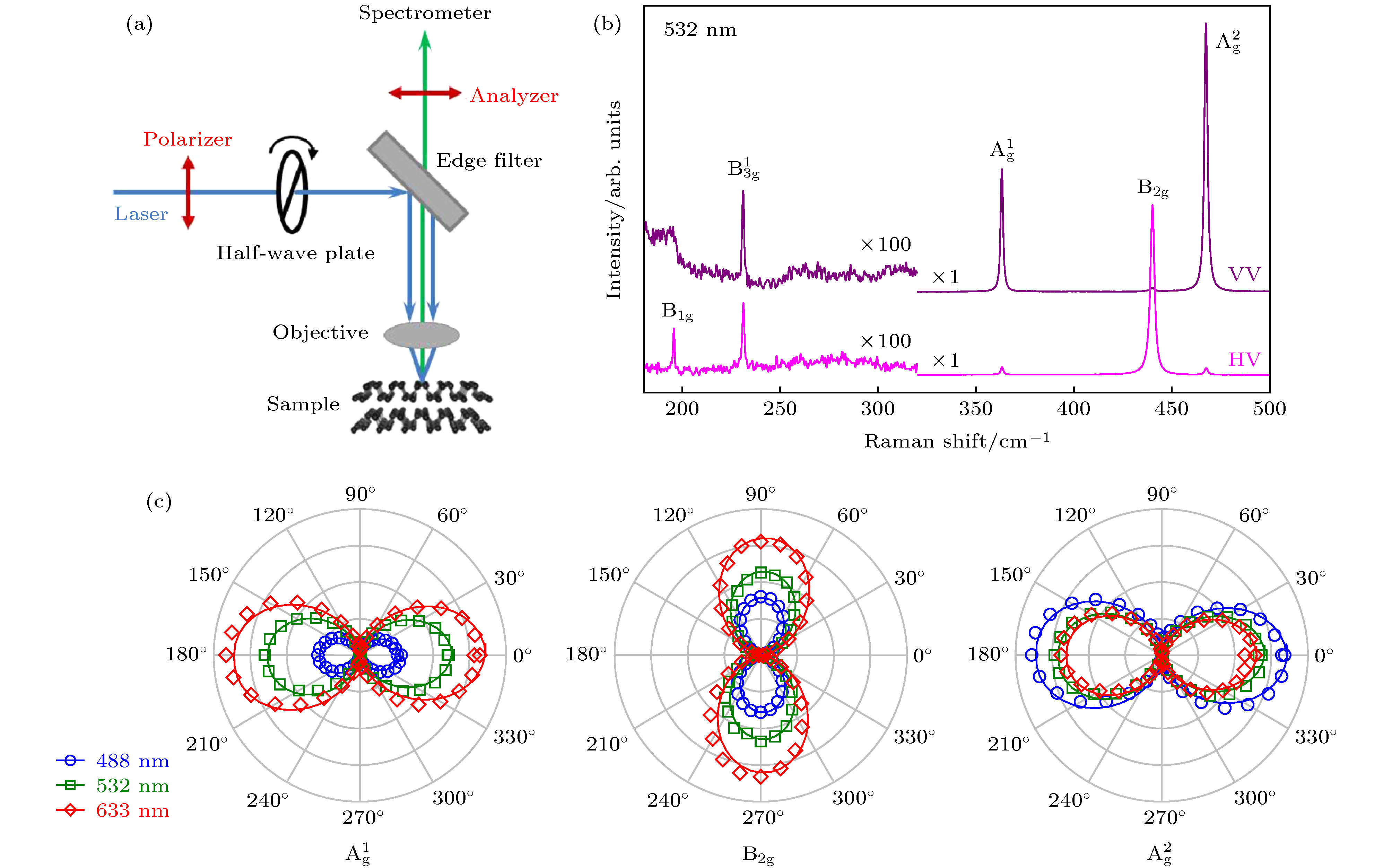
图 2 (a)偏振拉曼实验的配置. 固定拉曼信号光路上检偏器的检偏方向(
$\theta_{\rm s} = 0$ ), 以探测具有相应偏振方向的散射光. 通过旋转半波片, 可以改变激发光与x轴的夹角$\theta_{\rm i}$ ; (b)在VV($\theta_{\rm i}=0^{\circ}$ )和HV($\theta_{\rm i}=90^{\circ}$ )偏振配置下, 包含$ {\rm{B}_{1g}}$ ,$\rm B_{3 g}^1$ ,$ {\rm{A}^1_g} $ ,$ {\rm{A}^2 _g}$ 和$ {\rm{B}_{2g}} $ 一阶拉曼模的拉曼光谱; (c)在不同波长激光的激发下, 黑磷三个主要的一阶拉曼模的峰强与$\theta_{\rm i}$ 的依赖关系. 不同颜色对应不同的激发波长, 符号散点给出了峰强的实验值, 实线给出了峰强随$\theta_{\rm i}$ 变化的拟合结果Figure 2. (a) Experimental configuration. The polarization direction of Raman signal is fixed (
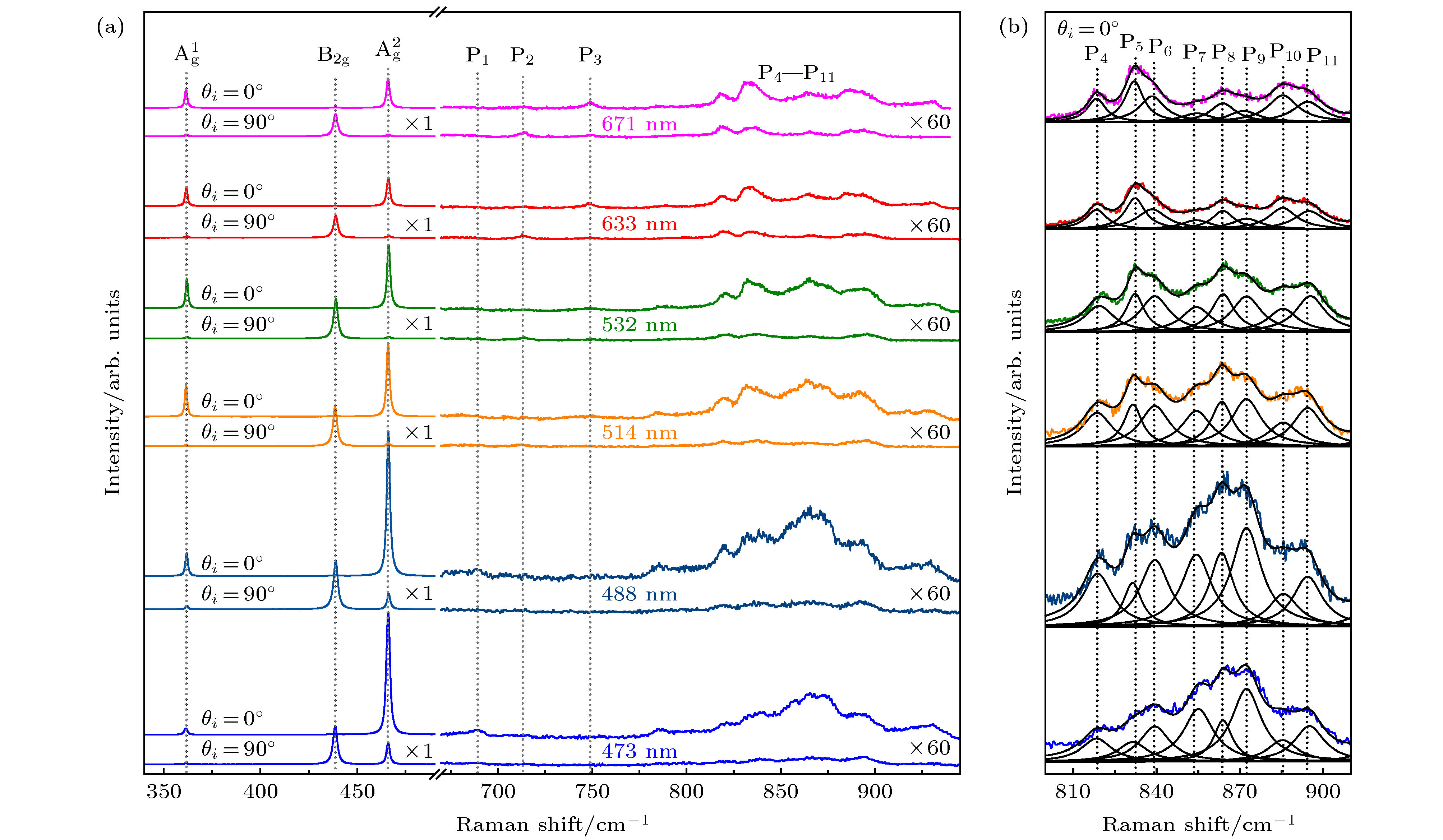
$\theta_{\rm s} = 0$ ). The angle between polarization direction of incident light and x axis is$\theta_{\rm i}$ , which can be changed by rotating a half-wave plate; (b) Raman spectra in the range of$ {\rm{B}_{1g}} $ ,$\rm B_{3 g}^1$ ,$ {\rm{A}^1 _g}$ ,$ {\rm{A}^2 _g}$ and$ {\rm{B}_{2g}} $ modes, under the VV($\theta_{\rm i}=0^{\circ}$ ) and HV($\theta_{\rm i}=90^{\circ}$ ) configurations; (c) the$\theta_{\rm i}$ -dependent Raman intensity excited by different wavelengths. The solid lines indicate fitting results.图 3 (a) 473—671 nm之间6个波长激光激发下的拉曼光谱. 每一组谱线都给出了
$\theta_{\rm i}=0^{\circ}$ 和$\theta_{\rm i}=90^{\circ}$ 两种配置下的情况. 竖虚线标出了3个主要的一阶拉曼峰以及能够辨识出的11个高阶拉曼峰(P1—P11); (b) 6个波长激光激发下在$\theta_{\rm i}=0^{\circ}$ 时P4—P11各谱线的拟合情况Figure 3. (a) Raman spectra of black phosphorus excited by six excitation wavelengths between 473–671 nm. Raman spectra at
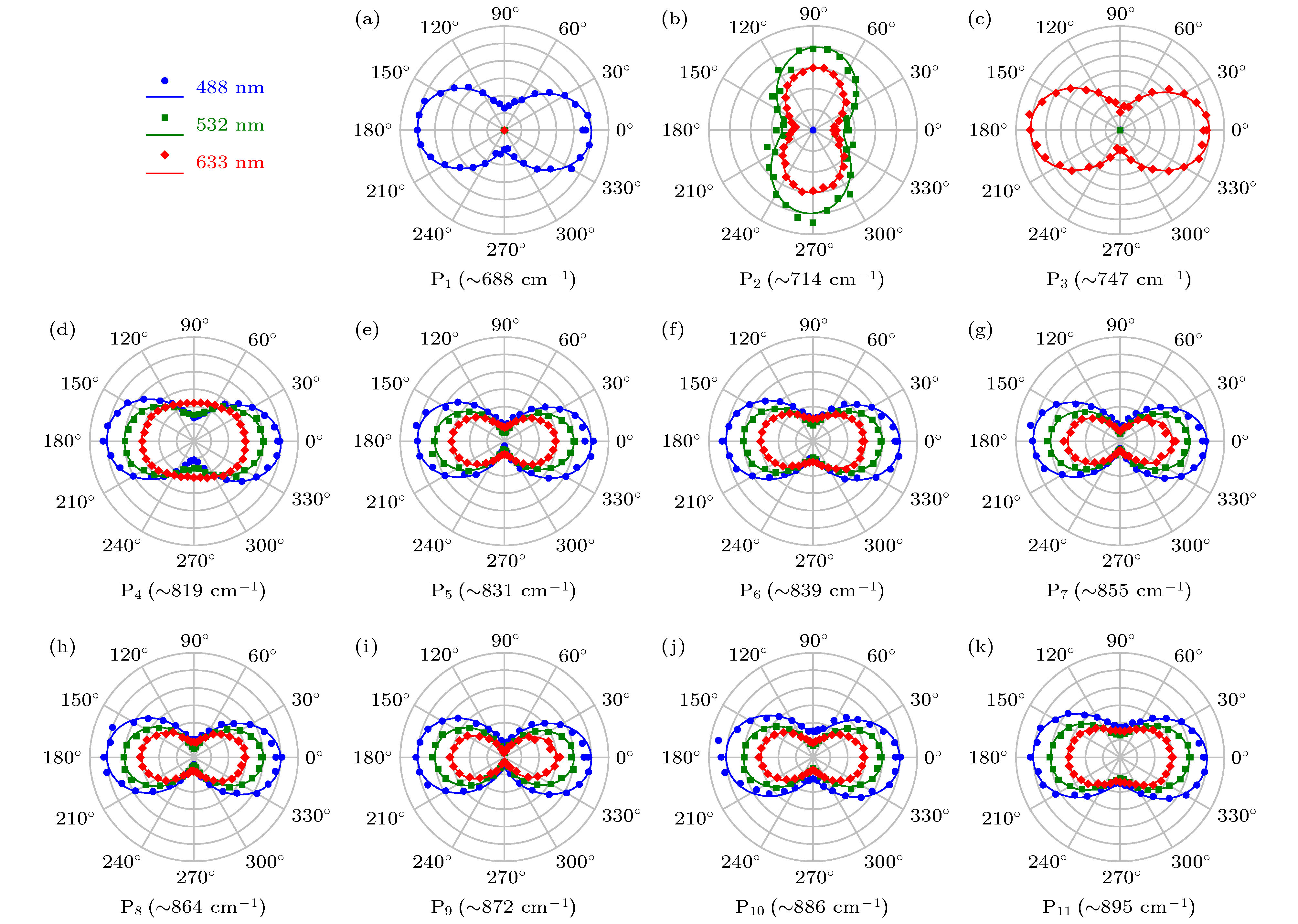
$\theta_{\rm i}=0^{\circ}$ and$\theta_{\rm i}=90^{\circ}$ are given for each excitation. Three main first-order Raman peaks and eleven high-order Raman peaks (P1–P11) are marked by vertical dotted lines; (b) the fitting result of P4–P11 for Raman spectra by six excitations at$\theta_{\rm i}=0^{\circ}$ .表 1 实验所观察到的黑磷多声子拉曼峰的指认
Table 1. Assignments of high order Raman peaks of BP.
Peaks Raman shift /cm–1 Assigned mode Assigned mode in Ref. [13] Calculated frequency/cm–1 P1 ~688 ${\rm A}_{\rm g}^2 (\varGamma)+B_{3 {\rm g}}^1 (\varGamma)$ ${\rm A}_{\rm g}^2+B_{3 {\rm g}}^1$ 689 P2 ~714 ${\rm B}_{2 {\rm g}} (\varGamma)+2\cdot B_{1 {\rm g}} (X)$ – 715 P3 ~747 $2 \cdot {\rm{A}}_{\rm{g}}^2(\varGamma ){\rm{ - B}}_{{\rm{3 g}}}^{\rm{1}}(\varGamma )$ $2 \cdot {\rm{A}}_{\rm{g}}^2-{{\rm{B}}_{{\rm{1 g}}}}$ 749 P4 ~819 ${\rm B}_{2 {\rm g}} (\varGamma)+B_{1 {\rm g}} (S)+B_{3 {\rm g}}^1 (S)$ – 821 P5 ~831 $2 \cdot {\rm{A} }_{\rm{g} }^2({\rm {near} }\;{{Y} })$ – 832 P6 ~839 $2 \cdot {\rm{A} }_{\rm{g} }^2({{S} })$ – 842 P7 ~855 $2 \cdot {\rm{B} }_{ {\rm{3 g} } }^2(\varGamma )$ – 858 P8 ~864 $2 \cdot { {\rm{B} }_{ {\rm{2 g} } } }({{X} })$ – 864 P9 ~872 $2 \cdot { {\rm{B} }_{2{\rm{g} } } }(\varGamma \;{\rm {or} }\;{ {S} })$ – 874 P10 ~886 ${\rm A}_{\rm g}^1 (X)+ A_{\rm g}^2 (X)$ – 888 P11 ~895 $2 \cdot { {\rm{B} }_{2{\rm{g} } } }({\rm {between}}\;{{X} }\;{\rm {and}}\;{{S} })$ – 896 -
[1] Qiao J, Kong X, Hu Z, Yang F, Ji W 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cai Y, Ke Q, Zhang G, Feng Y P, Shenoy V B, Zhang Y W 2015 Adv. Funct. Mater. 25 2230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ling X, Huang S, Hasdeo E H, Liang L, Parkin W M, Tatsumi Y, Nugraha A R, Puretzky A A, Das P M, Sumpter B G 2016 Nano Lett. 16 2260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen P F, Li N, Chen X Z, Ong W J, Zhao X J 2017 2D Mater. 5 014002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Malard L, Pimenta M, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus M 2009 Phys. Rep. 473 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang X, Qiao X F, Shi W, Wu J B, Jiang D S, Tan P H 2015 Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 2757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shi W, Zhang X, Li X L, Qiao X F, Wu J B, Zhang J, Tan P H 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 057801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shi W, Lin M L, Tan Q H, Qiao X F, Zhang J, Tan P H 2016 2D Mater. 3 025016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lin T, Cong X, Lin M L, Liu X L, Tan P H 2018 Nanoscale 10 8704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mao N, Wu J, Han B, Lin J, Tong L, Zhang J 2016 Small 12 2627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ribeiro H B, Pimenta M A, De Matos C J, Moreira R L, Rodin A S, Zapata J D, De Souza E A, Castro Neto A H 2015 ACS Nano 9 4270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kim J, Lee J U, Lee J, Park H J, Lee Z, Lee C, Cheong H 2015 Nanoscale 7 18708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang X, Mao N, Luo W, Kitadai H, Ling X 2018 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9 2830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Favron A, Goudreault F A, Gosselin V, Groulx J, Cote M, Leonelli R, Germain J F, Phaneuf L, Heureux A L, Francoeur S, Martel R 2018 Nano Lett. 18 1018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sugai S, Shirotani I 1985 Solid State Commun. 53 753
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang J W, Wang B S, Park H S 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 165401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu J B, Lin M L, Cong X, Liu H N, Tan P H 2018 Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 1822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu J B, Zhang X, Ijäs M, Han W P, Qiao X F, Li X L, Jiang D S, Ferrari A C, Tan P H 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 5309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Saito R, Jorio A, Filho A G S, Dresselhaus G, Pimenta M A 2002 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41 4878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Carvalho B R, Malard L M, Alves J M, Fantini C, Pimenta M A 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 136403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Clark R J H, Dines T J 1986 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 25 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu X L, Zhang X, Lin M L, Tan P H 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 067802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 17015
- PDF Downloads: 515
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: