-
Black phosphorus(BP) is a kind of two-dimensional (2D) material with direct bandgap. Its adjustable bandgap fills the gap between graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides(TMDCs). At the same time, the black phosphorusalso has a higher charge carrier mobility. The unique fold-like crystal structure of the black phosphorus leads to in-plane anisotropy and it makes the photoelectric response anisotropic. It shows that the properties of black phosphorus can be dynamically adjusted by various methods. These characteristics make black phosphorus a two-dimensional material with great potential applications in the visible light to mid-infrared region and even terahertz bands. In view of this, this paper focuses on the magneto-optical response of black phosphorus. In this paper, we design a magneto-optical device in Au grating/black phosphorus/silicon hybrid plasmonic structures. The inducing of abnormal transmission through the metal grating significantly enhances the transmittance, while the Faraday rotation effect is enhanced through the mode coupling between the TE and TM in the THz range. The rigorous coupled wave analysis (RCWA) is used to calculate the transmittance of the grating. The finite element software COMSOL Multiphysics is used to calculate the transmittance and simulate the electric field distribution of the magneto-optical device. Under the optimal parameters, the Faraday rotation can increase 14.434 times, reaching to 2.7426°, and the transmittance is more than 85% with an external magnetic field of 5 T at the operation frequency (1.5 THz). We plot the electric profiles of the magneto-optical device with and without BP to prove that the Faraday rotation is a result of the magneto-optical property of the monolayer phosphorus and that the enhancement is due to the mode coupling between the TE and TM. Moreover, we extract the tunable character of the magneto-optical device with the external magnetic field and the carrier density of the black phosphorus. The external magnetic field can effectively tune the Faraday rotation angle while keeping the working wavelength and the transmittance substantially unchanged. The increasing of the carrier density will not improve the Faraday rotation angle, for the changes in surface conductivity under fixed structural parameters will disrupt the mode coupling. At the same time the transmittance will decrease, because the larger carrier density will enhance the absorption of the BP. Therefore, to obtain a higher FR angle with apparent transmittance, the carrier density should not be too high. Finally, the effects of the spoof surface plasmons on the waveguide mode and the Faraday magneto-optical effect are also discussed.
[1] Royer F, Varghese B, Gamet E, Neveu S, Jourlin Y, Jamon D 2020 ACS Omega 5 2886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Da H, Gao L, Ding W, Yan X 2017 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8 3805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tymchenko M, Nikitin A Yu, Martín-Moreno L 2013 ACS Nano 7 9780
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Deeter M N, Rose A H, Day G W 1990 J. Lightwave Technol. 8 1838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Rochford K B, Rose A H, Deeter M N, Day G W 1944 Opt. Lett. 19 1903
[6] Luo X, Zhou M, Liu J, Qiu T, Yu Z 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 131104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Morimoto R, Goto T, Pritchard J, et al. 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 38679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bossini D, Belotelov V I, Zvezdin A K, Kalish A N, Kimel A V 2016 ACS Photonics 3 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Dolatabady A, Granpayeh N 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dou R, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Zhuang N, Liu W, He Y, Chen Y, Cheng M, Luo J, Sun D 2019 Opt. Mater. 96 109272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dong D X, Liu Y W, Fei Y, Fan Y Q, Li J S, Fu Y Y 2020 Opt. Mater. 102 109809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bychkov I V, Kuzmin D A, Tolkachev V A, Plaksin P S, Shavrov V G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sadowski M L, Martinez G, Potemski M, Berger C, de Heer W A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 266405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou X, Lou W K, Zhai F, Chang K 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 165405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiang Y, Roldán R, Guinea F, Low T 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 085408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hoi B D, Yarmohammadi M 2018 Mater. Res. Express 6 015903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yi Y, Sun Z, Li J, Chu P K, Yu X 2019 Small Methods 3 1900165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Debnath P C, Park K, Song Y-W 2018 Small Methods 2 1700315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou Y, Zhang M X, Guo Z N, Miao L L, Han S T, Wang Z Y, Zhang X W, Zhang H, Peng Z C 2017 Mater. Horiz. 4 997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang X, Lan S 2016 Adv. Opt. Photon. 8 618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li X J, Yu J H, Luo K, Wu Z H, Yang W 2018 Nanotechnology 29 174001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Low T, Roldán R, Wang H, Xia F, Avouris P, Moreno L M, Guinea F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 106802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhou X Y, Zhang R, Sun J P, Zou Y L, Zhang D, Lou W K, Cheng F, Zhou G H, Zhai F, Chang K 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 12295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] You Y, Gonçalves P A D, Shen L, Wubs M, Deng X, Xiao S 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Da H X, Yan X 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Smith K, Carroll T, Bodyfelt J D, Vitebskiy I, Chabanov A A 2013 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46 165002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Qin J, Xia S, Jia K, Wang C, Tang T, Lu H, Zhang L, Zhou P, Peng B, Deng L, Bi L 2018 APL Photonics 3 016103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li L, Yang F, Ye G J, et al. 2016 Nat. Nanotechnol. 11 593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang J, Jiang Y 2017 Opt. Express 25 5206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qing Y M, Ma H F, Cui T J 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4985
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Nemilentsau A, Low T, Hanson G 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 066804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kang P, Kim K H, Park H G, Nam S 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Xiao S, Liu T, Cheng L, Zhou C, Jiang X, Li Z, Xu C 2019 J. Lightwave Technol. 37 3290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 袁英豪 2011博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Yuan Y H Ph. D. Dissertation (WuHan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[35] 王清 2014 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 国防科学技术大学)
Wang Q 2014 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[36] 冯月, 沈涛, 胡超 2017 光子学报 43 294
Feng Y, Shen T, Hu C 2017 Acta Photon. Sin. 43 294
[37] Dong D, Liu Y, Fei Y, Fan Y, Li J, Feng Y, Fu Y 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 3862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Woolf D, Kats M A, Capasso F 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 磁光器件结构图 (a) 三维结构图, 底部为硅基底, 上部为金属光栅, 中间为黑磷, 磁场垂直黑磷水平面, 入射光为线偏振光; (b) 垂直面二维图, 光栅周期L, 金属条厚度da, 宽度W, 基底厚度ds
Figure 1. Schematic of the magneto-optical device: (a) 3D structure diagram. The Si layer is the substrate, the grating is in the top layer, and the black phosphorus (BP) is in the center laye; (b) 2D vertical plane diagram. The period of the grating is L, the thickness and the width of the metal are da and W, and the thickness of the substrate is ds.
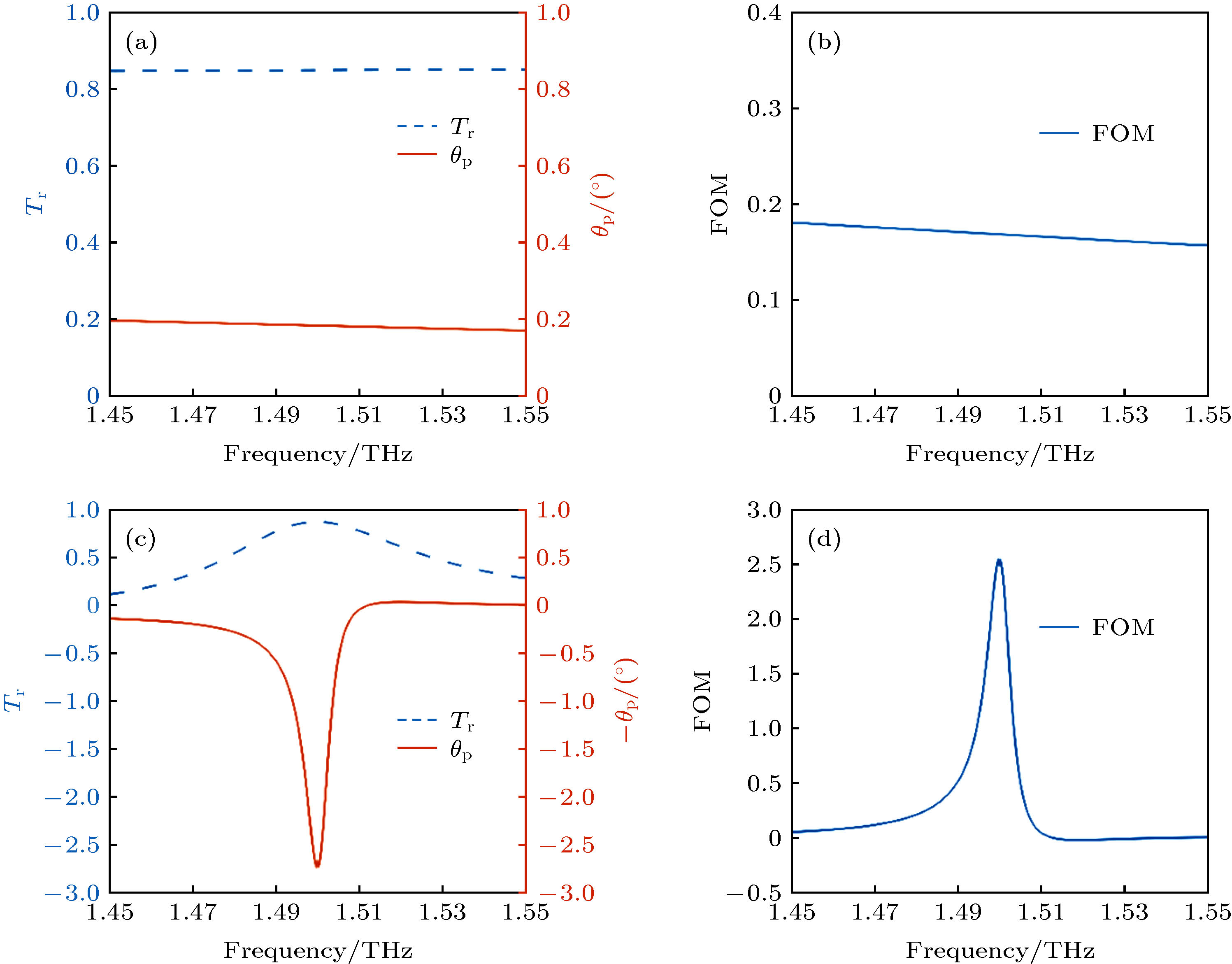
图 2 单层黑磷和磁光器件透射谱、法拉第旋转角度和品质因数谱 (a) 虚线为单层黑磷的透射率频谱图, 实线为法拉第旋转角度频谱图; (b) 单层黑磷的品质因数频谱图; (c) GBPS结构的透射率频谱图和法拉第旋转角度频谱图; (d) GBPS结构的品质因数频谱图
Figure 2. The transmittance, Faraday rotation angle and the figure of merit (FOM) of the monolayer BP and magneto-optical device verse the frequency: (a) The dotted line is the transmittance of the monolayer BP, and the solid line is the Faraday rotation angle of the monolayer BP; (b) the FOM of the monolayer BP; (c) the dotted line is the transmittance of the magneto-optical device with GBPS structure, and the solid line is the Faraday rotation angle of the magneto-optical device with GBPS structure; (d) the FOM of the magneto-optical device with GBPS structure.
图 3 磁光器件电场分布图和TE/TM透射谱 (a) GS结构, 1.5 THz时TM模式下的Ex, Ey分布图; (b) GBPS结构, 1.5 THz时TM模式下的的Ex, Ey分布图, Ey分布图中放大部分为金属光栅端子上的场分布; (c) TE模式下透射率随频率和光栅周期的变化图; (d) TM模式下透射率随频率和光栅周期的变化图
Figure 3. The electric field distribution and the TE/TM transmittance spectrum of the magneto-optical device: (a) The Ex and Ey of the device without the monolayer BP in TM mode at 1.5 THz; (b) the Ex and Ey of the device with GBPS structure in TM mode at 1.5 THz, and the electric field distribution on the metal grating terminal is shown in the enlarged part of Ey; (c) variations of transmittance with frequency and grating period in TE mode; (d) variations of transmittance with frequency and grating period in TM mode.
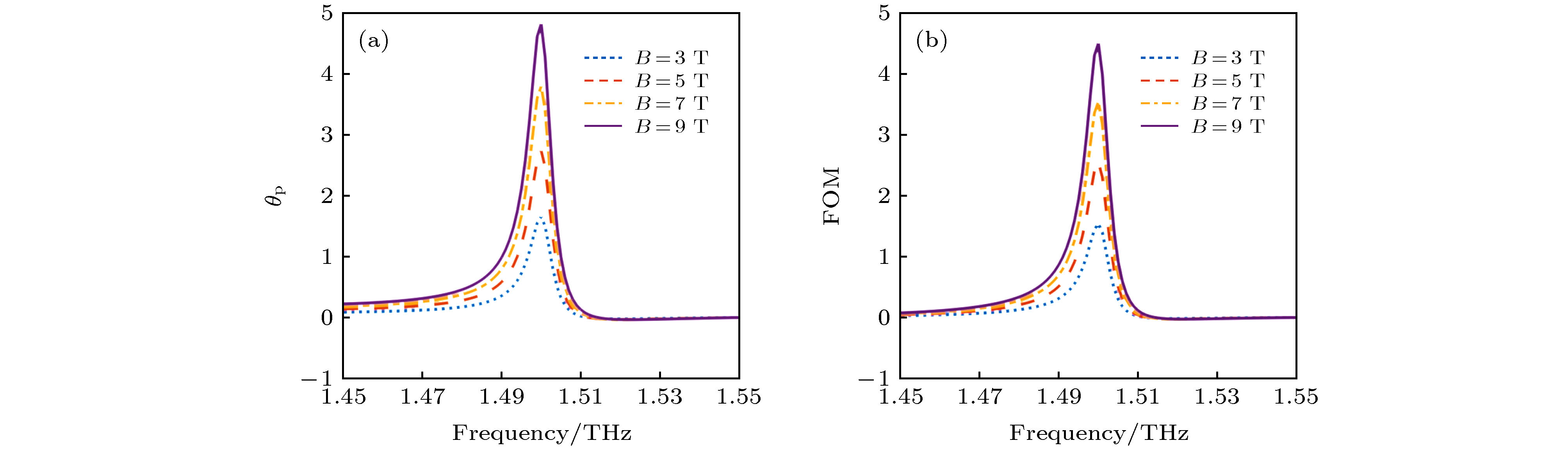
图 5 不同载流子浓度下的磁光器件响应图 (a) GBPS结构的透射率频谱; (b) GBPS结构的法拉第旋转角度频谱. 黑磷载流子浓度度分别为0.5n0, 1.0n0, 1.5 n0, 2.0 n0 (n0 = 1 × 1013 cm–2)
Figure 5. Magneto-optical response diagrams of the device with different carrier density of BP: (a) Transmission and (b) faraday rotation angle of the device with GBPS structure. The carrier density of BP are set as 0.5n0, 1.0n0, 1.5 n0, 2.0 n0 (n0 = 1 × 1013 cm–2).
表 1 磁光器件不同结构参数下的法拉第旋转角度和透射率
Table 1. Faraday rotation and transmittance of the MO device with different structure parameters.
No. f/THz L/μm W/μm ds/μm T/% θp/(°) 1 1.40 170.580 118.150 31.377 84.354 4.3845 2 1.45 164.650 113.160 30.750 85.256 3.4711 3 1.50 159.000 109.365 29.285 86.968 2.7426 4 1.55 153.500 105.915 28.414 87.123 2.1730 5 1.60 148.800 102.810 27.455 86.679 2.1443 -
[1] Royer F, Varghese B, Gamet E, Neveu S, Jourlin Y, Jamon D 2020 ACS Omega 5 2886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Da H, Gao L, Ding W, Yan X 2017 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8 3805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tymchenko M, Nikitin A Yu, Martín-Moreno L 2013 ACS Nano 7 9780
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Deeter M N, Rose A H, Day G W 1990 J. Lightwave Technol. 8 1838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Rochford K B, Rose A H, Deeter M N, Day G W 1944 Opt. Lett. 19 1903
[6] Luo X, Zhou M, Liu J, Qiu T, Yu Z 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 131104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Morimoto R, Goto T, Pritchard J, et al. 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 38679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bossini D, Belotelov V I, Zvezdin A K, Kalish A N, Kimel A V 2016 ACS Photonics 3 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Dolatabady A, Granpayeh N 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dou R, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Zhuang N, Liu W, He Y, Chen Y, Cheng M, Luo J, Sun D 2019 Opt. Mater. 96 109272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dong D X, Liu Y W, Fei Y, Fan Y Q, Li J S, Fu Y Y 2020 Opt. Mater. 102 109809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bychkov I V, Kuzmin D A, Tolkachev V A, Plaksin P S, Shavrov V G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sadowski M L, Martinez G, Potemski M, Berger C, de Heer W A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 266405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou X, Lou W K, Zhai F, Chang K 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 165405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiang Y, Roldán R, Guinea F, Low T 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 085408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hoi B D, Yarmohammadi M 2018 Mater. Res. Express 6 015903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yi Y, Sun Z, Li J, Chu P K, Yu X 2019 Small Methods 3 1900165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Debnath P C, Park K, Song Y-W 2018 Small Methods 2 1700315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou Y, Zhang M X, Guo Z N, Miao L L, Han S T, Wang Z Y, Zhang X W, Zhang H, Peng Z C 2017 Mater. Horiz. 4 997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang X, Lan S 2016 Adv. Opt. Photon. 8 618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li X J, Yu J H, Luo K, Wu Z H, Yang W 2018 Nanotechnology 29 174001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Low T, Roldán R, Wang H, Xia F, Avouris P, Moreno L M, Guinea F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 106802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhou X Y, Zhang R, Sun J P, Zou Y L, Zhang D, Lou W K, Cheng F, Zhou G H, Zhai F, Chang K 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 12295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] You Y, Gonçalves P A D, Shen L, Wubs M, Deng X, Xiao S 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Da H X, Yan X 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Smith K, Carroll T, Bodyfelt J D, Vitebskiy I, Chabanov A A 2013 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46 165002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Qin J, Xia S, Jia K, Wang C, Tang T, Lu H, Zhang L, Zhou P, Peng B, Deng L, Bi L 2018 APL Photonics 3 016103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li L, Yang F, Ye G J, et al. 2016 Nat. Nanotechnol. 11 593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang J, Jiang Y 2017 Opt. Express 25 5206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qing Y M, Ma H F, Cui T J 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4985
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Nemilentsau A, Low T, Hanson G 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 066804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kang P, Kim K H, Park H G, Nam S 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Xiao S, Liu T, Cheng L, Zhou C, Jiang X, Li Z, Xu C 2019 J. Lightwave Technol. 37 3290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 袁英豪 2011博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Yuan Y H Ph. D. Dissertation (WuHan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[35] 王清 2014 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 国防科学技术大学)
Wang Q 2014 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[36] 冯月, 沈涛, 胡超 2017 光子学报 43 294
Feng Y, Shen T, Hu C 2017 Acta Photon. Sin. 43 294
[37] Dong D, Liu Y, Fei Y, Fan Y, Li J, Feng Y, Fu Y 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 3862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Woolf D, Kats M A, Capasso F 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9082
- PDF Downloads: 134
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: