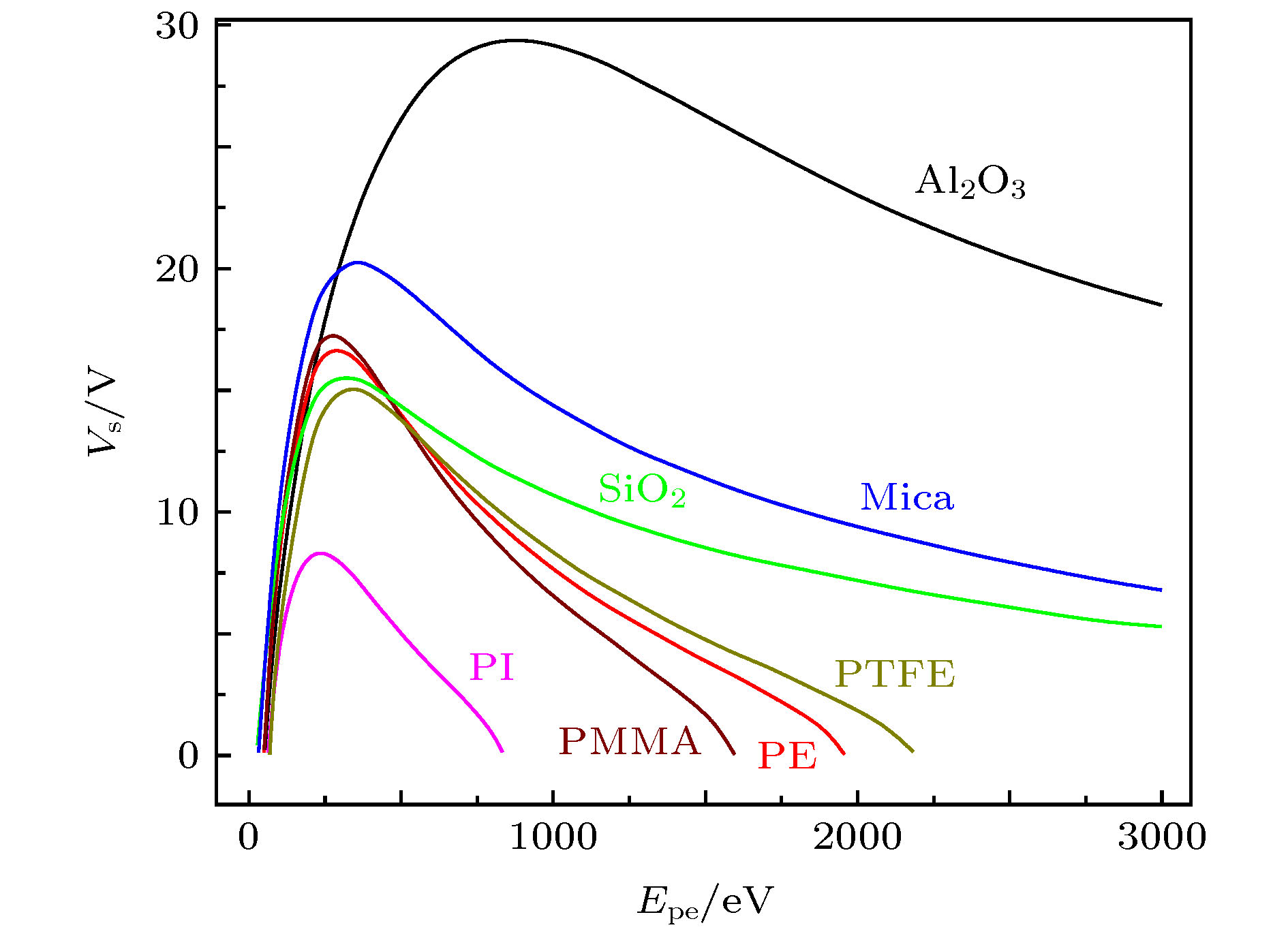
-
For a microwave device filled with dielectrics, the secondary electron (SE) emission has a very important influence on the mechanism of microwave breakdown including low pressure discharge and multipactor. In this work, the SE yields (SEYs) and the SE energy spectra of seven kinds of dielectric materials are first measured and then used to examine their effects. In the positive charging process under electron irradiation, the surface potential of the dielectric layer trends to be steady with the SEY being one. Based on the measurement data, the steady surface potential is calculated under the charging stability condition. The steady surface potential is bigger for a bigger SEY. For a given SEY, the steady surface potential is found to be proportional to the peak energy Epeak of the SE energy spectrum. Furthermore, the effect of steady surface potential on low pressure discharge and multipactor are respectively studied for a parallel plate system filled with a dielectric layer. A static electric field related to the positive charging is introduced. The electron diffusion model in low pressure discharge process is modified by considering the static electric field. The electrons drift in a fixed direction under the action of static electric field, and the electron diffusion length decreases. Consequently, the effective electrons for low discharge decreases and the threshold microwave power increases. Therefore, a dielectric material with higher SEY and bigger Epeak is helpful in suspending the inhibition of low pressure discharge. Furthermore, the effect of steady electric field on multipactor is also explored. Two effects related to dielectric material and metal are analyzed in detail. The SE emission from dielectric material is held back by the steady electric field and some low energy electrons return back to the dielectric materials. The effective SEY thus decreases. On the other hand, the electric field reduces the landing electron energy on the metal, and the corresponding SEY also decreases. The electron oscillation condition with considering both microwave field and stead electric field is derived and the threshold values for microwave power of multipactor are calculated. The susceptibility curves corresponding to different materials are plotted. Our result may be used to choose the filling dielectric materials for a microwave device.
-
Keywords:
- secondary electron yield /
- secondary electron energy spectrum /
- surface potential /
- microwave breakdown
[1] Yu M 2007 IEEE Microwave Mag. 8 88
[2] 常超 2018 科学通报 63 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang C 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 63 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Keneshloo R, Dadashzadeh G, Frotanpour A, Okhovvat, Okhovvat M 2012 J. Commun. Eng. 1 18
[4] Chang C, Liu G Z, Huang H J, Chen C H, Fang J Y 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 083501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ángela C, Germán T P, Carlos V, Benito G, Vicente E B 2008 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55 2505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Apostolos L S, Edén S, Michael M 2014 The 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Hague, Netherlands, April 6−11, 2014 p1469
[7] Germán T P, Ángela C, Benito G M, Isabel M, Carlos V, Vicente E B 2010 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 57 1160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sorolla E, Belhaj M, Sombrin J, Puech J 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 103508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 翟永贵, 王瑞, 王洪广, 林舒, 陈坤, 李永东 2018 67 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhai Y G, Wang R, Wang H G, Lin S, Chen K, Li Y D 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2018 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2018 67 177902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 177902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2017 66 207901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 207901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Weng M, Cao M, Zhao H J, Zhang H B 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 036108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 殷明, 翁明, 刘婉, 王芳, 曹猛 2019 西安交通大学学报 53 163
Yin M, Weng M, Liu W, Wang F, Cao M 2019 Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University 53 163
[15] Weng M, Liu W, Yin M, Wang F, Cao M 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 047901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 翁明, 胡天存, 曹猛, 徐伟军 2015 64 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Weng M, Hu T C, Cao M, Xu W J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Insepov Z, Ivanov V, Frisch H 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 268 3315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lin Y H, Joy D C 2005 Surf. Interface Anal. 37 895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yong Y C, Thong J T L 2000 Scanning 22 161
[20] Lisovskii V A 1999 Tech. Phys. 44 1282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Albert J H, Williams H B 1954 J. Appl. Phys. 25 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Albert J H, Williams H B 1958 Phys. Rev. 112 681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 7种介质材料的SEY参数
Table 1. SEY of seven kinds of dielectric materials
样品 PMMA Al2O3 SiO2 PTFE PE PI Mica δm 2.517 7.355 4.149 2.244 2.564 1.819 4.333 Epm/eV 278.9 881.9 285.4 321.3 279.5 237.6 335.4 y 1.67 1.67 1.50 1.55 1.61 1.67 1.55 W1/eV 56.8 58.8 35.0 75.4 56.2 70.2 38.6 W2/eV 1599 25051 8045 2185 1960 837 7555 表 2 7种材料的能谱特性
Table 2. The characteristics of energy spectrum of seven kinds of materials.
材料 PMMA PTFE PE PI Al2O3 SiO2 Mica Epeak/eV 4.264 4.203 4.023 3.087 2.898 2.376 2.988 FWHM/eV 14.058 13.851 13.284 10.206 9.765 7.857 9.882 -
[1] Yu M 2007 IEEE Microwave Mag. 8 88
[2] 常超 2018 科学通报 63 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang C 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 63 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Keneshloo R, Dadashzadeh G, Frotanpour A, Okhovvat, Okhovvat M 2012 J. Commun. Eng. 1 18
[4] Chang C, Liu G Z, Huang H J, Chen C H, Fang J Y 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 083501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ángela C, Germán T P, Carlos V, Benito G, Vicente E B 2008 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55 2505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Apostolos L S, Edén S, Michael M 2014 The 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Hague, Netherlands, April 6−11, 2014 p1469
[7] Germán T P, Ángela C, Benito G M, Isabel M, Carlos V, Vicente E B 2010 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 57 1160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sorolla E, Belhaj M, Sombrin J, Puech J 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 103508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 翟永贵, 王瑞, 王洪广, 林舒, 陈坤, 李永东 2018 67 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhai Y G, Wang R, Wang H G, Lin S, Chen K, Li Y D 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2018 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2018 67 177902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 177902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2017 66 207901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 207901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Weng M, Cao M, Zhao H J, Zhang H B 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 036108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 殷明, 翁明, 刘婉, 王芳, 曹猛 2019 西安交通大学学报 53 163
Yin M, Weng M, Liu W, Wang F, Cao M 2019 Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University 53 163
[15] Weng M, Liu W, Yin M, Wang F, Cao M 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 047901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 翁明, 胡天存, 曹猛, 徐伟军 2015 64 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Weng M, Hu T C, Cao M, Xu W J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 157901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Insepov Z, Ivanov V, Frisch H 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 268 3315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lin Y H, Joy D C 2005 Surf. Interface Anal. 37 895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yong Y C, Thong J T L 2000 Scanning 22 161
[20] Lisovskii V A 1999 Tech. Phys. 44 1282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Albert J H, Williams H B 1954 J. Appl. Phys. 25 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Albert J H, Williams H B 1958 Phys. Rev. 112 681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8862
- PDF Downloads: 141
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: