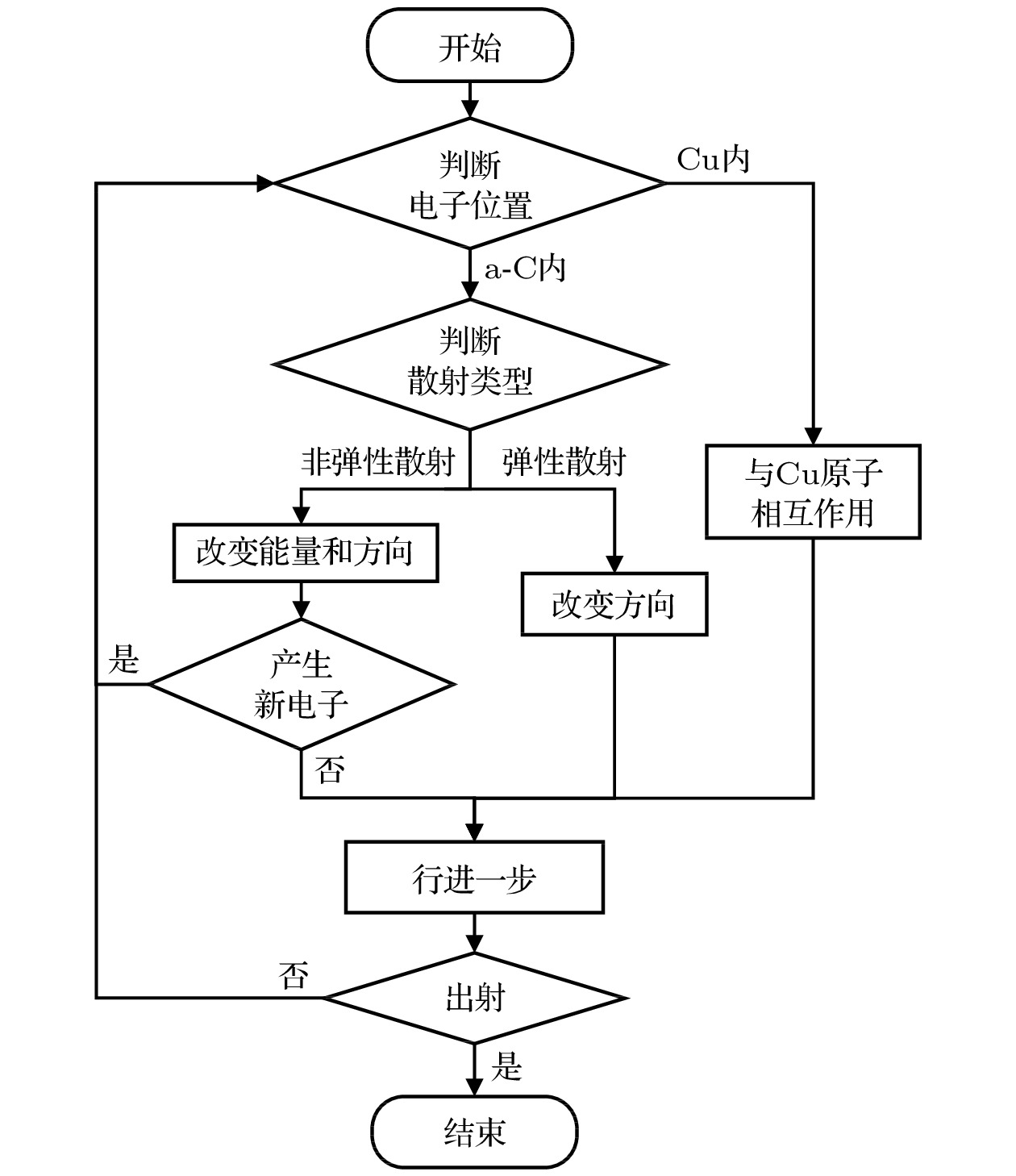
-
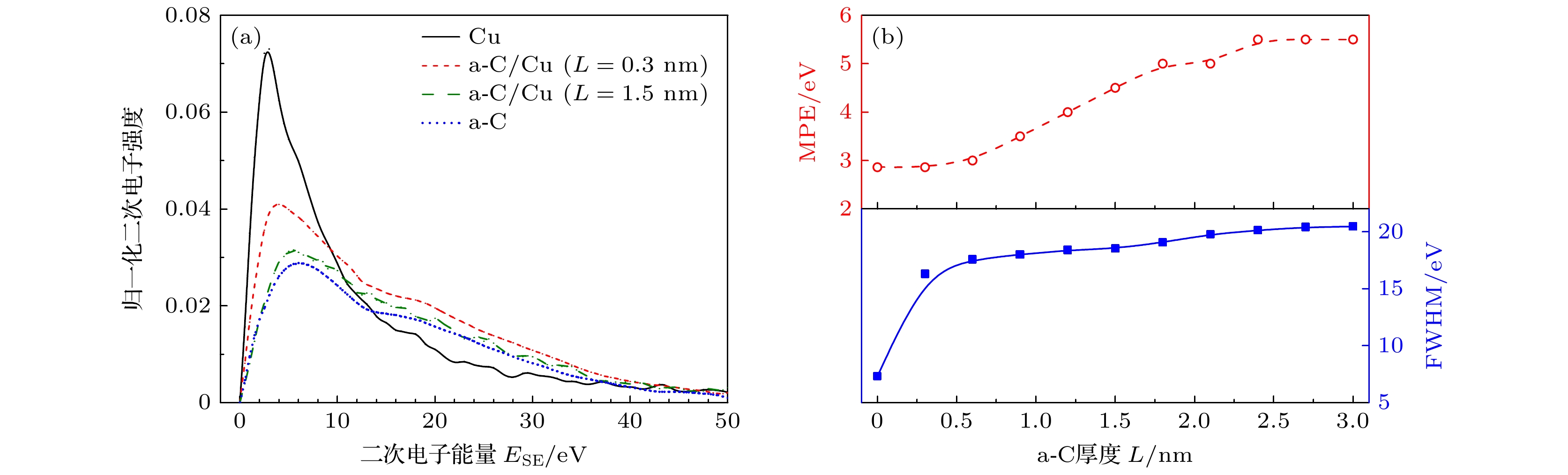
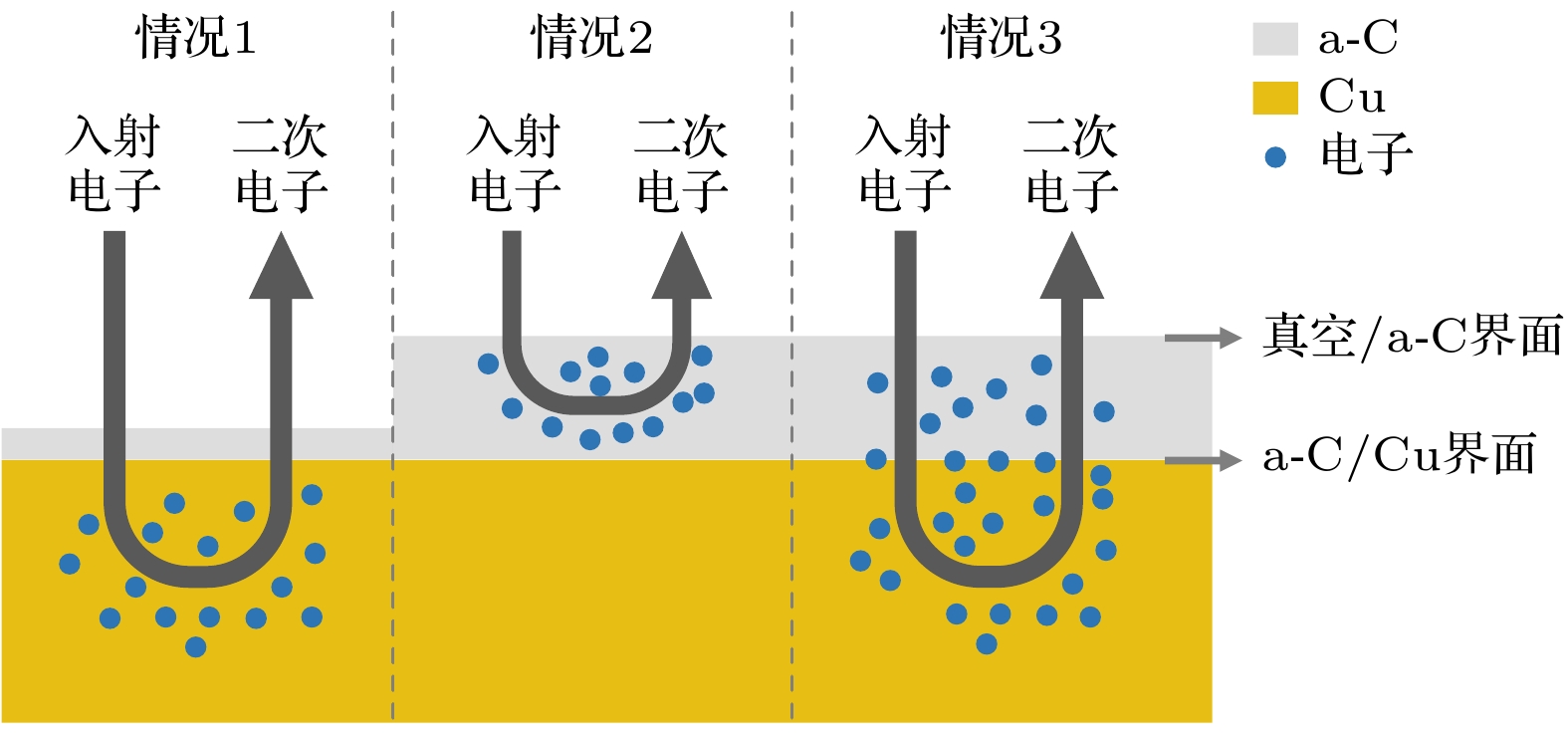
非晶态碳薄膜由于具有极低的二次电子发射系数(secondary electron yield, SEY), 在真空微波器件与设备异常放电领域引起了广泛关注. 然而, 非晶态碳薄膜对二次电子发射影响的动态过程及微观机理仍缺乏了解. 本文采用Monte Carlo方法, 建立了Cu表面非晶态碳薄膜的二次电子发射数值模拟模型, 能够精确地模拟电子与薄膜及基底材料的散射及二次电子发射的微观物理过程. 结果表明, 随着薄膜厚度从0 nm增加至1.5 nm时, SEY峰值下降了大约20%; 继续增大厚度, SEY峰值不再下降. 然而, 当薄膜厚度大于0.9 nm时, SEY曲线呈现出双峰形态, 但随着薄膜厚度增加至3 nm, 第二峰逐渐减弱甚至消失. 电子散射轨迹和二次电子能量分布结果, 表明这种双峰现象是由于电子在两种材料中散射所致. 相比以往模型, 所提模型考虑了功函数的变化以及界面势垒对电子散射路径的影响. 该模型从微观层面上解释了SEY曲线双峰现象形成的原因, 相关的计算结果为非晶态碳薄膜对SEY的抑制规律提供了理论预测.
-
关键词:
- 二次电子发射 /
- 非晶态碳薄膜 /
- 金属 /
- Monte Carlo模拟
Amorphous carbon films have attracted much attention in the field of abnormal discharge of vacuum microwave devices and equipment due to their extremely low secondary electron yields (SEYs). However, the dynamic process and microscopic mechanism of the effect of amorphous carbon film on secondary electron emission are still poorly understood. In this work, a numerical simulation model of the secondary electron emission of amorphous carbon film on copper surface is developed by the Monte Carlo method, which can accurately simulate the dynamic processes of electron scattering and emission of the film and the substrate. The results show that the maximum SEY decreases by about 20% when the film thickness increases from 0 to 1.5 nm. Further increasing the thickness, the SEY no longer decreases. However, when the film is thicker than 0.9 nm, the SEY curve exhibits a double-hump form, but with the thickness increasing to 3 nm, the second peak gradually weakens or even disappears. The electron scattering trajectories and energy distribution of secondary electrons indicate that this double-hump phenomenon is caused by electron scattering in two different materials. Compared with previous models, the proposed model takes into account the change of work function and the effect of interfacial barrier on electron scattering path. Our model can explain the formation of the double-hump of SEY curve and provides theoretical predictions for suppressing the SEY by amorphous carbon film.-
Keywords:
- secondary electron emission /
- amorphous carbon film /
- metal /
- Monte Carlo simulation
[1] Kirby R E, King F K 2001 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. , Sect. A 469 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yater J E 2023 J. Appl. Phys. 133 050901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李鹏飞, 袁华, 程紫东, 钱立冰, 刘中林, 靳博, 哈帅, 万城亮, 崔莹, 马越, 杨治虎, 路迪, Reinhold Schuch, 黎明, 张红强, 陈熙萌 2022 71 074101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li P F, Yuan H, Cheng Z D, Qian L B, Liu Z L, Jin B, Ha S, Wan C L, Cui Y, Ma Y, Yang Z H, Lu D, Schuch R, Li M, Zhang H Q, Chen X M 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 074101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Valizadeh R, Malyshev O B, Wang S H, Zolotovskaya S A, Allan Gillespie W, Abdolvand A 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 231605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2018 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 邓晨晖, 韩立, 王岩, 高召顺, 牛耕 2023 材料导报 37 22030065
Deng C H, Han L, Wang Y, Gao Z S, Niu G 2023 Mater. Rep. 37 22030065
[7] 胡笑钏, 陈彦璋, 孙广哲, 吕毅 2023 高电压技术 49 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu X C, Chen Y Z, Sun G Z, Lü Y 2023 High Voltage Eng. 49 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 王丹, 贺永宁, 叶鸣, 崔万照 2018 67 087902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D, He Y N, Ye M, Cui W Z 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 087902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 朱香平, 王丹, 汪辉, 周润东, 李相鑫, 洪云帆, 靳川, 韦永林, 罗朝鹏, 赵卫 2022 科学通报 67 2811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu X P, Wang D, Wang H, Zhou R D, Li X X, Hong Y F, Jin C, Wei Y L, Luo C P, Zhao W 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull. 67 2811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li J, Liu B Y, Wu S L, Li Y D, Hu W B 2022 Mater. Lett. 327 133085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张宇心, 王一刚, 葛晓琴, 张波, 尉伟, 裴香涛, 范乐, 王勇 2018 真空科学与技术学报 38 1065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y X, Wang Y G, Ge X Q, Zhang B, Wei W, Pei X T, Fan L, Wang Y 2018 Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 38 1065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Larciprete R, Grosso D R, Di Trolio A, Cimino R 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 328 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li J, Yi X K, Hu W B, Gao B Y, Li Y D, Wu S L, Lin S, Zhang J T 2019 Materials 12 2631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yu S, Jeong T, Yi W, Lee J, Jin S, Heo J, Kimb J M, Jeon D 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 3281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ye M, Feng P, Wang D, Song B P, He Y N, Cui W Z 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 077901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Cohen-Tannoudji C, Diu B, Laloe F 1977 Quantum Mechanics (Vol. 1) (Paris: Wiley-VCH Press) pp216–224
[17] Hu X C, Xiao J, Zhu W, Yu Y X 2018 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51 385203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 彭敏, 程文杰, 曹猛 2022 空间电子技术 19 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng M, Cheng W J, Cao M 2022 Space Electron. Technol. 19 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nguyen H K A, Mankowski J, Dickens J C, Neuber A A, Joshi R P 2018 AIP Adv. 8 015325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Joy D C 1991 Scanning Microsc. 5 329
[21] Bethe H 1930 Ann. Phys. 397 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cao M, Zhang N, Hu T C, Wang F, Cui W Z 2015 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phs. 48 055501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Mott N F 1929 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 126 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Czyżewski Z, MacCallum D O N, Romig A, Joy D C 1990 J. Appl. Phys. 68 3066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shinotsuka H, Tanuma S, Powell C J, Penn D R 2015 Surf. Interface Anal. 47 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Da B, Li Z Y, Chang H C, Mao S F, Ding Z J 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 124307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Palik E D 1997 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (San Diego: Academic Press) pp837–852
[28] Inguimbert C, Gibaru Q, Caron P, Angelucci M, Spallino L, Cimino R 2022 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. , Sect. B 526 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Angelucci M, Novelli A, Spallino L, Liedl A, Larciprete R, Cimino R 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 032030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 张恒, 崔万照 2016 空间电子技术 3 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Cui W Z 2016 Space Electron. Technol. 3 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 胡笑钏, 黄逸清, 陈彦璋, 吕毅 2022 西安交通大学学报 56 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu X C, Huang Y Q, Chen Y Z, Lü Y 2022 J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 56 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
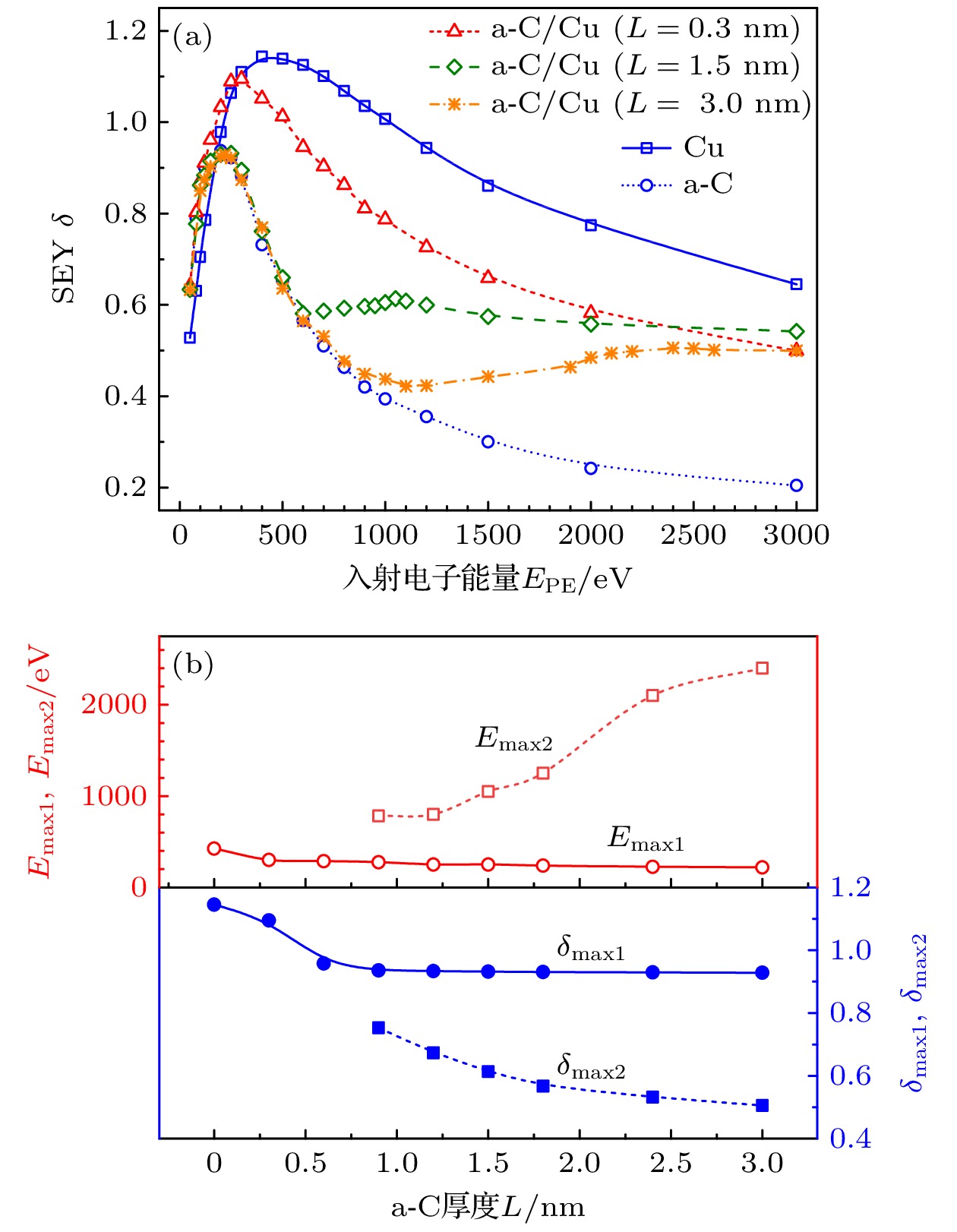
图 5 厚度L对SEY $\delta $的影响 (a)不同L下, $\delta $与$ {E_{{\text{PE}}}} $的关系; (b) ${\delta _{\max1}}$, ${\delta _{\max2}}$, ${E_{\max1}}$和${E_{\max2}}$与L的关系
Fig. 5. Effects of the thickness L on the SEY $\delta $: (a) $\delta $vs.$ {E_{{\text{PE}}}} $at different L; (b) ${\delta _{\max1}}$, ${\delta _{\max2}}$, ${E_{\max1}}$ and ${E_{\max2}}$vs. L.
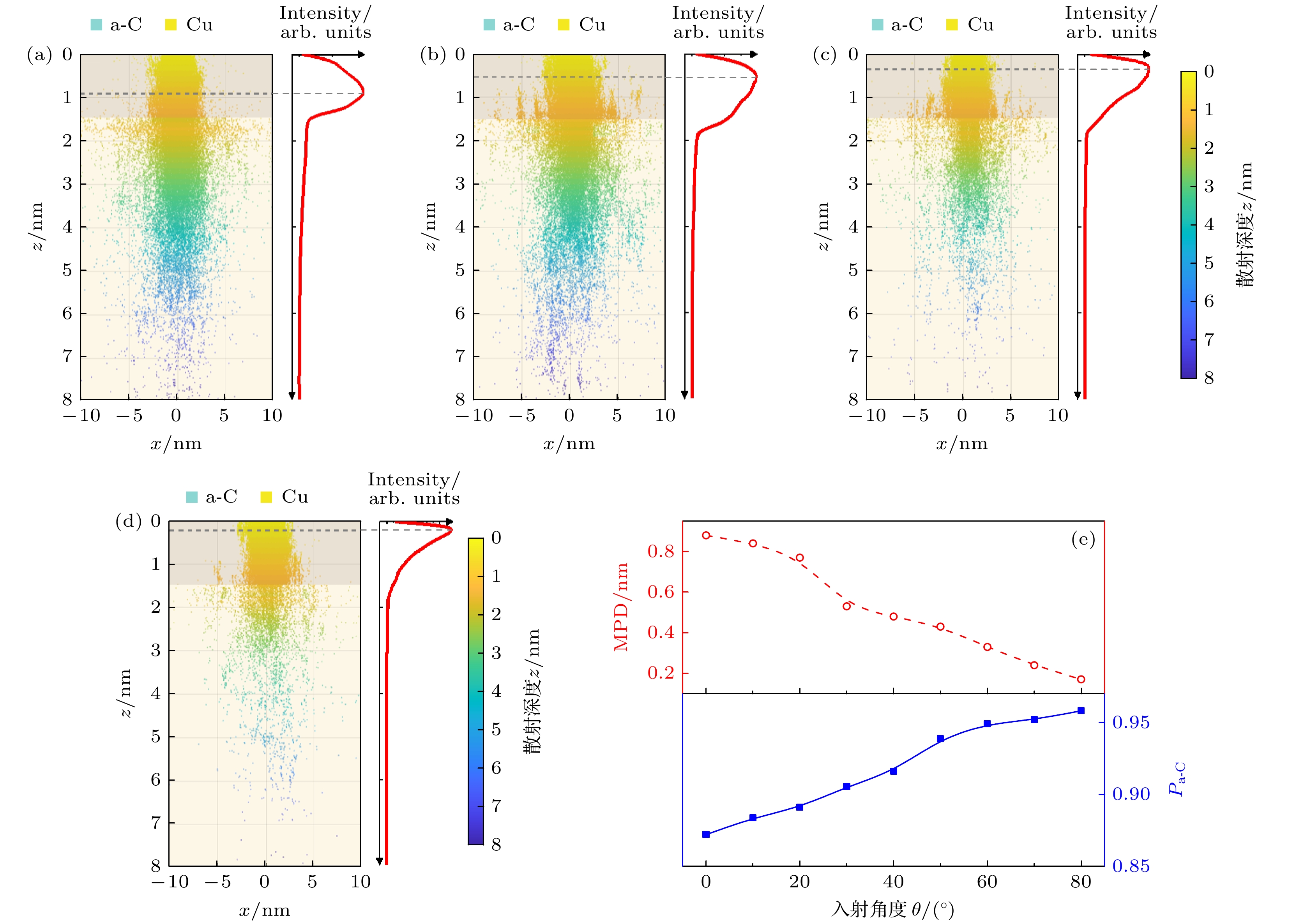
图 6 不同厚度L下的电子散射轨迹分布及规律 (a) L = 0 nm; (b) L = 0.9 nm; (c) L = 1.5 nm; (d) L = 2.4 nm; (e) MPD和${P_{{\text{a-C}}}}$与L的关系. 图(a)—(d)中, 灰色点线表示MPD的位置, 红色曲线表示归一化的电子密度分布
Fig. 6. Distribution and pattern of electron scattering trajectories with different L: (a) L = 0; (b) L = 0.9 nm; (c) L = 1.5 nm; (d) L = 2.4 nm; (e) MPD and ${P_{{\text{a-C}}}}$ vs. L. In panels (a)–(d), the gray dot line represents the position of the MPD, and the red curve represents the normalized electron density distribution.
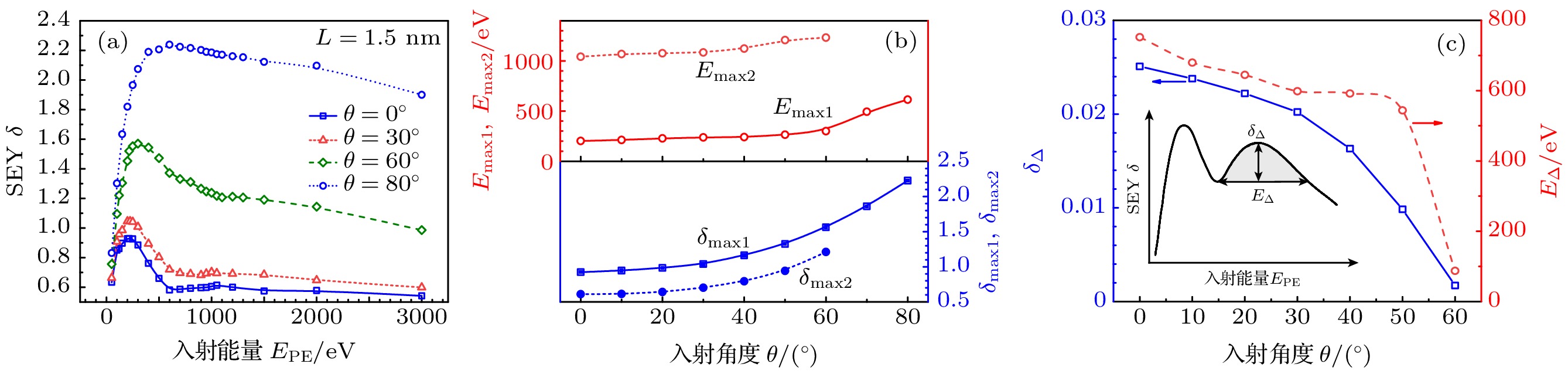
图 7 入射角度$\theta $对SEY $\delta $的影响 (a) 不同$\theta $下, $\delta $与$ {E_{{\text{PE}}}} $的关系; (b) ${\delta _{\max1}}$, ${\delta _{\max2}}$, ${E_{\max1}}$和${E_{\max2}}$与$\theta $的关系; (c) ${\delta _\Delta }$和${E_\Delta }$与$\theta $的关系. 其中, 图(c)中的内插图为${\delta _\Delta }$和${E_\Delta }$的示意图
Fig. 7. Effects of incident angle $\theta $ on the SEY $\delta $: (a) $\delta $ vs. $ {E_{{\text{PE}}}} $ at different $\theta $; (b) ${\delta _{\max1}}$, ${\delta _{\max2}}$, ${E_{\max1}}$and ${E_{\max2}}$ vs. $\theta $; (c) ${\delta _\Delta }$ and ${E_\Delta }$ vs. $\theta $. In panel (c), the interpolation diagram is a schematic diagram of ${\delta _\Delta }$ and ${E_\Delta }$.
图 8 不同入射角度$\theta $下的电子的散射轨迹分布及规律(L = 1.5 nm) (a) $\theta $= 0°; (b) $\theta $= 30°; (c) $\theta $= 60°; (d) $\theta $= 80°; (e) MPD和${P_{{\text{a-C}}}}$与$\theta $的关系. 图(a)—(d)中, 灰色点线表示MPD的位置, 红色曲线表示归一化的电子密度分布
Fig. 8. Distribution and pattern of electron scattering trajectories with different $\theta $ (L = 1.5 nm): (a) $\theta $= 0°; (b) $\theta $= 30°; (c) $\theta $= 60°; (d) $\theta $= 80°; (e) the MPD and ${P_{{\text{a-C}}}}$ vs. $\theta $. In panels (a)–(d), the gray dot line represents the position of the MPD, and the red curve represents the normalized electron density distribution.
-
[1] Kirby R E, King F K 2001 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. , Sect. A 469 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yater J E 2023 J. Appl. Phys. 133 050901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李鹏飞, 袁华, 程紫东, 钱立冰, 刘中林, 靳博, 哈帅, 万城亮, 崔莹, 马越, 杨治虎, 路迪, Reinhold Schuch, 黎明, 张红强, 陈熙萌 2022 71 074101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li P F, Yuan H, Cheng Z D, Qian L B, Liu Z L, Jin B, Ha S, Wan C L, Cui Y, Ma Y, Yang Z H, Lu D, Schuch R, Li M, Zhang H Q, Chen X M 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 074101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Valizadeh R, Malyshev O B, Wang S H, Zolotovskaya S A, Allan Gillespie W, Abdolvand A 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 231605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 董烨, 刘庆想, 庞健, 周海京, 董志伟 2018 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Liu Q X, Pang J, Zhou H J, Dong Z W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 邓晨晖, 韩立, 王岩, 高召顺, 牛耕 2023 材料导报 37 22030065
Deng C H, Han L, Wang Y, Gao Z S, Niu G 2023 Mater. Rep. 37 22030065
[7] 胡笑钏, 陈彦璋, 孙广哲, 吕毅 2023 高电压技术 49 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu X C, Chen Y Z, Sun G Z, Lü Y 2023 High Voltage Eng. 49 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 王丹, 贺永宁, 叶鸣, 崔万照 2018 67 087902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D, He Y N, Ye M, Cui W Z 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 087902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 朱香平, 王丹, 汪辉, 周润东, 李相鑫, 洪云帆, 靳川, 韦永林, 罗朝鹏, 赵卫 2022 科学通报 67 2811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu X P, Wang D, Wang H, Zhou R D, Li X X, Hong Y F, Jin C, Wei Y L, Luo C P, Zhao W 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull. 67 2811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li J, Liu B Y, Wu S L, Li Y D, Hu W B 2022 Mater. Lett. 327 133085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张宇心, 王一刚, 葛晓琴, 张波, 尉伟, 裴香涛, 范乐, 王勇 2018 真空科学与技术学报 38 1065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y X, Wang Y G, Ge X Q, Zhang B, Wei W, Pei X T, Fan L, Wang Y 2018 Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 38 1065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Larciprete R, Grosso D R, Di Trolio A, Cimino R 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 328 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li J, Yi X K, Hu W B, Gao B Y, Li Y D, Wu S L, Lin S, Zhang J T 2019 Materials 12 2631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yu S, Jeong T, Yi W, Lee J, Jin S, Heo J, Kimb J M, Jeon D 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 3281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ye M, Feng P, Wang D, Song B P, He Y N, Cui W Z 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 077901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Cohen-Tannoudji C, Diu B, Laloe F 1977 Quantum Mechanics (Vol. 1) (Paris: Wiley-VCH Press) pp216–224
[17] Hu X C, Xiao J, Zhu W, Yu Y X 2018 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51 385203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 彭敏, 程文杰, 曹猛 2022 空间电子技术 19 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng M, Cheng W J, Cao M 2022 Space Electron. Technol. 19 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nguyen H K A, Mankowski J, Dickens J C, Neuber A A, Joshi R P 2018 AIP Adv. 8 015325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Joy D C 1991 Scanning Microsc. 5 329
[21] Bethe H 1930 Ann. Phys. 397 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cao M, Zhang N, Hu T C, Wang F, Cui W Z 2015 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phs. 48 055501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Mott N F 1929 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 126 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Czyżewski Z, MacCallum D O N, Romig A, Joy D C 1990 J. Appl. Phys. 68 3066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shinotsuka H, Tanuma S, Powell C J, Penn D R 2015 Surf. Interface Anal. 47 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Da B, Li Z Y, Chang H C, Mao S F, Ding Z J 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 124307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Palik E D 1997 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (San Diego: Academic Press) pp837–852
[28] Inguimbert C, Gibaru Q, Caron P, Angelucci M, Spallino L, Cimino R 2022 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. , Sect. B 526 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Angelucci M, Novelli A, Spallino L, Liedl A, Larciprete R, Cimino R 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 032030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 张恒, 崔万照 2016 空间电子技术 3 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Cui W Z 2016 Space Electron. Technol. 3 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 胡笑钏, 黄逸清, 陈彦璋, 吕毅 2022 西安交通大学学报 56 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu X C, Huang Y Q, Chen Y Z, Lü Y 2022 J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 56 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3410
- PDF下载量: 90
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: