-
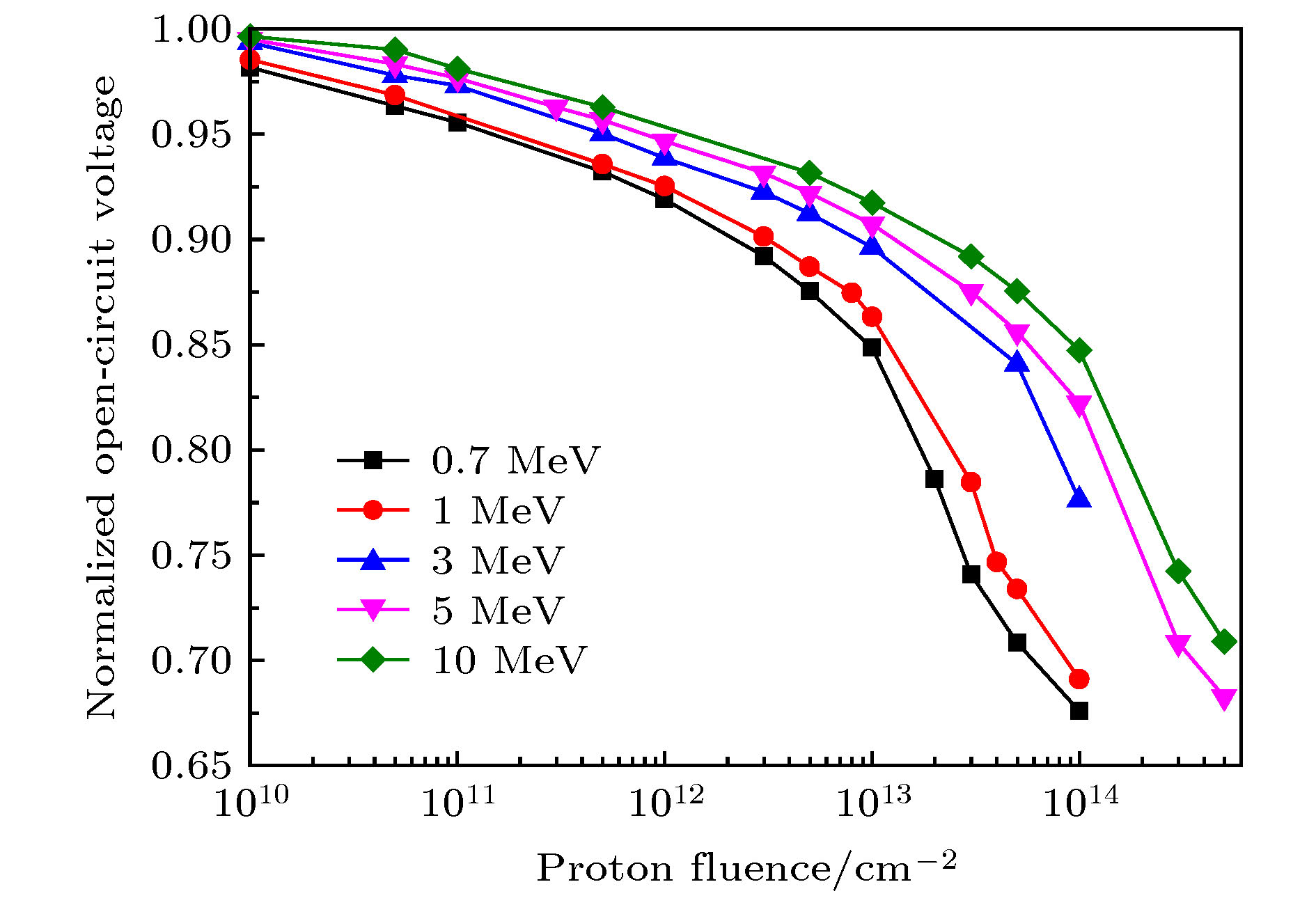
The GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells have been widely used for spacecraft energy sources because of their simple manufacturing process, stable structures, high conversion efficiency, and low cost. The performances of the GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells show a remarkable degradation after space proton irradiation. At present, the experimental researches of proton irradiation of GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells with different energy and fluence have been carried out. However, the experimental researches can analyze the proton radiation damage only under the specific energy and fluence, but cannot analyze the proton radiation damage under the complete space energy spectrum. The numerical simulation of triple-junction solar cells can be used to accurately analyze the degradation of major parameters under different energy proton irradiations which cannot be achieved experimentally. In this paper, the modeling of degradation for GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells, induced by proton irradiation with different energy is studied by numerical simulation. The energy values include 0.7 MeV, 1 MeV, 3 MeV, 5 MeV, and 10 MeV. The structure of GaInP/GaAs/Ge model and proton irradiation-induced defect model with different energy and fluence are established. The I-V curves and spectral response curves under different proton irradiation conditions are obtained. The simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results. The degradation of major parameters of GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells, caused by different energy and fluence proton irradiations, is studied, these parameters being the short circuit current, open circuit voltage, minority carrier lifetime, electron current density, external quantum efficiency, and maximum power. The degradation curve of the maximum power with displacement damage dose is obtained by fitting the degradation simulation results under different proton irradiation conditions. Displacement damage defects induced by protons are introduced into triple-junction solar cells, which lead the minority carrier diffusion length to degrade. The degradation increases with the proton energy decreasing. In the meanwhile, it will lead the related electrical parameters to degrade, which increases with the proton energy decreasing. The simulation results show that related electrical parameters decrease with the proton irradiation fluence increasing. Under the same proton irradiation condition, the external quantum efficiency degradation of GaAs sub-cell is larger than that of GaInP sub-cell because the irradiation resistance of GaAs is poor. Among the degradations of spectral response of GaAs sub-cell at different wavelengths, the degradation in the long wave is greater than that in the short wave. It is found that the degradations of GaAs sub-cell related electrical parameters are mainly due to the damage to the base region. -
Keywords:
- GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells /
- irradiation-induced defects /
- proton irradiation model /
- numerical simulation
[1] 张忠卫, 陆剑峰, 池卫英, 王亮兴, 陈鸣波 2003 上海航天 03 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z W, Lu J F, Chi W Y, Wang L X, Chen M B 2003 Aerospace Shanghai 03 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Jones P A, Spence B R 2011 IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 26 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lohmeyer W Q, Cahoy K 2013 Space Weather 11 476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zainud-Deen S H, Dawoud M, Malhat E A, Aboul-Dahab M A 2019 Wirel. Pers. Commun. 1 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Campesato R, Baur C, Casale M, Gervasi M, Gombia E, Greco E, Kingma A, Rancoita P G, Rozza D, Tacconi M 2018 arXiv: 1809. 07157 [physics. ins-det]
[6] 张延清 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Zhang Y Q 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[7] 吴宜勇, 岳龙, 胡建民, 蓝慕杰, 肖景东, 杨德庄, 何世禹, 张忠卫, 王训春, 钱勇, 陈鸣波 2011 60 098110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y Y, Yue L, Hu J M, Lan M J, Xiao J D, Yang D Z, He S Y, Zhang Z W, Wang X C, Qian Y, Chen M B 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 098110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wu R, Wang J L, Yan G, Wang R 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 046101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 齐佳红, 胡建民, 盛延辉, 吴宜勇, 徐建文, 王月媛, 杨晓明, 张子锐, 周扬 2015 64 108802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi J H, Hu J M, Sheng Y H, Wu Y Y, Xu J W, Wang Y Y, Yang X M, Zhang Z R, Zhou Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 108802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bi Z, Zhang J C, Lv L, Hao Y 2014 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 26 1492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo H L, Shi L F, Wu Y Y, Sun Q, Yu H, Xiao J D, Guo B 2018 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 431 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang R, Lu M, Yi T C, Yang K, Ji X X 2014 Chin. Phys. Lett. 31 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Elahidoost A, Fathipour M, Mojab A 2012 20th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering Tehran, Iran, May 15−17, 2012 p113
[14] Yan Y Y, Fang M H, Tang X B, Chen F D, Huang H, Sun X Y, Ji L L 2019 Nucl. Instrum. Methods. Phys. Res. B 451 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Y M, Sun Y, Rockett A 2012 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 98 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 施敏 2003 半导体器件物理与工艺 (苏州: 苏州大学出版社) 第522页
Shi M 2003 Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology (Suzhou: Suzhou University Press) p522 (in Chinese)
[17] Wang R, Guo Z L, Zhang X H, Zhai Z X 2003 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 77 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Khan A, Yamaguchi M, Dharmaso N, Bourgoin J, Ando K, Takamoto T 2002 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41 1241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dharmarasu N, Yamaguchi M, Bourgoin J C, Takamoto T, Ohshima T, Itoh H, Imaizumi M, Matsuda S 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li S S, Loo R Y 1991 Solar Cells 31 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 朱美芳, 熊绍珍 2014 太阳电池基础与应用 (上卷) (北京: 科学出版社) 第110页
Zhu M F, Xiong S Z 2014 Foundation and Application of Solar Cells (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) p110 (in Chinese)
[22] Silvaco Atlas User’s Manual http://www.silvaco.com.cn [2019-10-20]
[23] Lu M, Wang R, Liu Y H, Hu W T, Feng Z, Han Z L 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 269 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王祖军, 唐本奇, 肖志刚, 刘敏波, 黄绍艳, 张勇 2010 59 4136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z J, Tang B Q, Xiao Z G, Liu M B, Huang S Y, Zhang Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 4136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sato S, Miyamoto H, Imaizumi M, Shimazaki K, Morioka C, Kawano K, Ohshima T 2009 Sol Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 93 768
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 胡建民, 吴宜勇, 钱勇, 杨德庄, 何世禹 2009 58 5051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu J M, Wu Y Y, Qian Y, Yang D Z, Yang S Y 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 5051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Norde H 1979 J. Appl. Phys. 50 5052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Herlufsen S, Schmidt J, Hinken D, Bothe K, Boendel R 2008 Phys. Status Solidi 2 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 常晓阳, 尧舜, 张奇灵, 张杨, 吴波, 占荣, 杨翠柏, 王智勇 2016 65 108801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang X Y, Yao S, Zhang Q L, Zhang Y, Wu B, Zhan R, Yang C B Wang Z Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 108801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Anspaugh B E 1996 GaAs Solar Cell Radiation Handbook (Pasadena: Jet Propulsion Laboratory Publication) p5
-
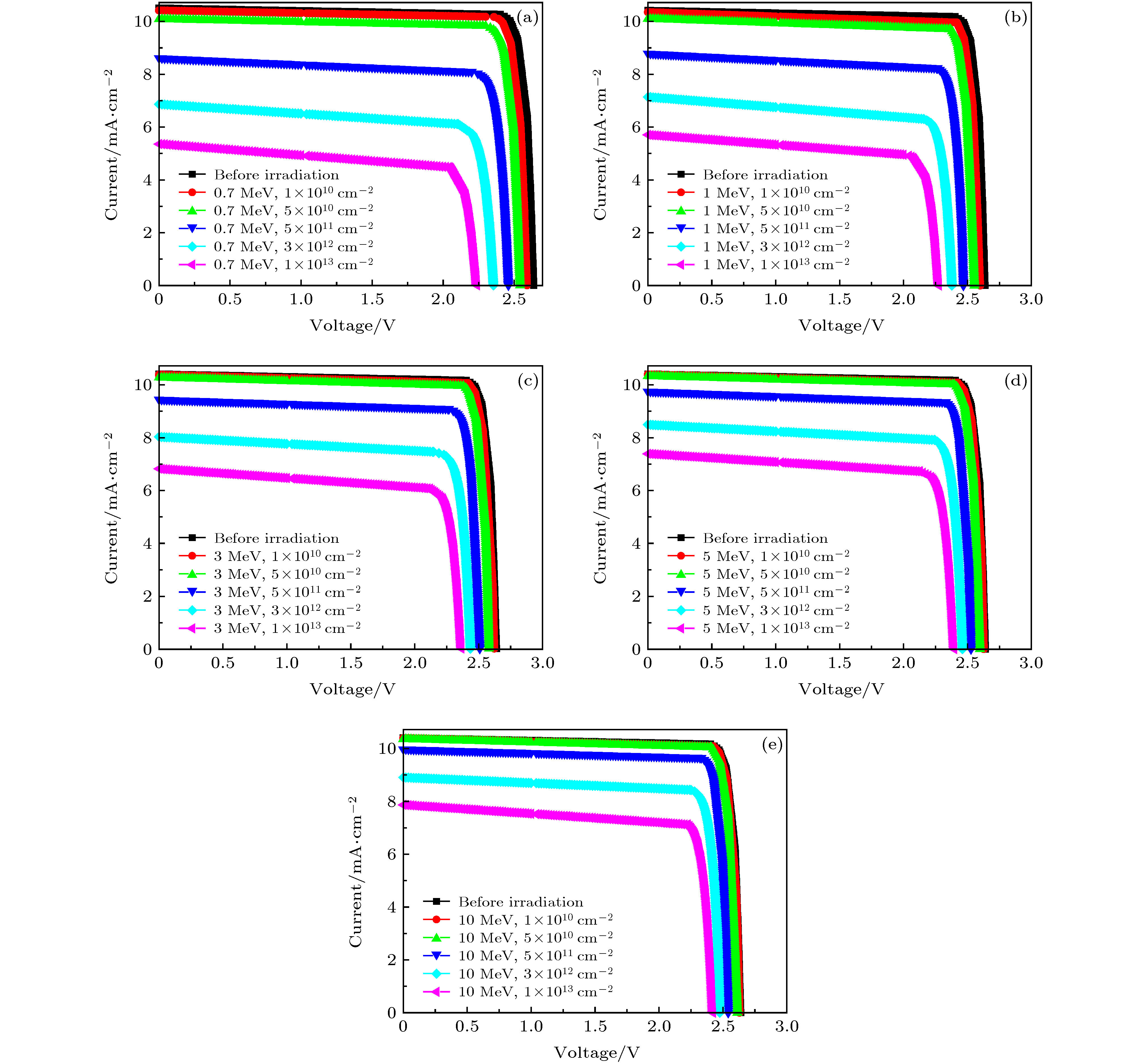
图 3 不同能量和注量的质子辐照后, GaInP/GaAs/Ge三结太阳电池的I-V曲线 (a) 0.7 MeV; (b) 1 MeV; (c) 3 MeV; (d) 5 MeV; (e) 10 MeV
Figure 3. Simulation results of I-V curves of GaInP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells irradiated by protons with different energy and fluence: (a) 0.7 MeV; (b) 1 MeV; (c) 3 MeV; (d) 5 MeV; (e) 10 MeV.
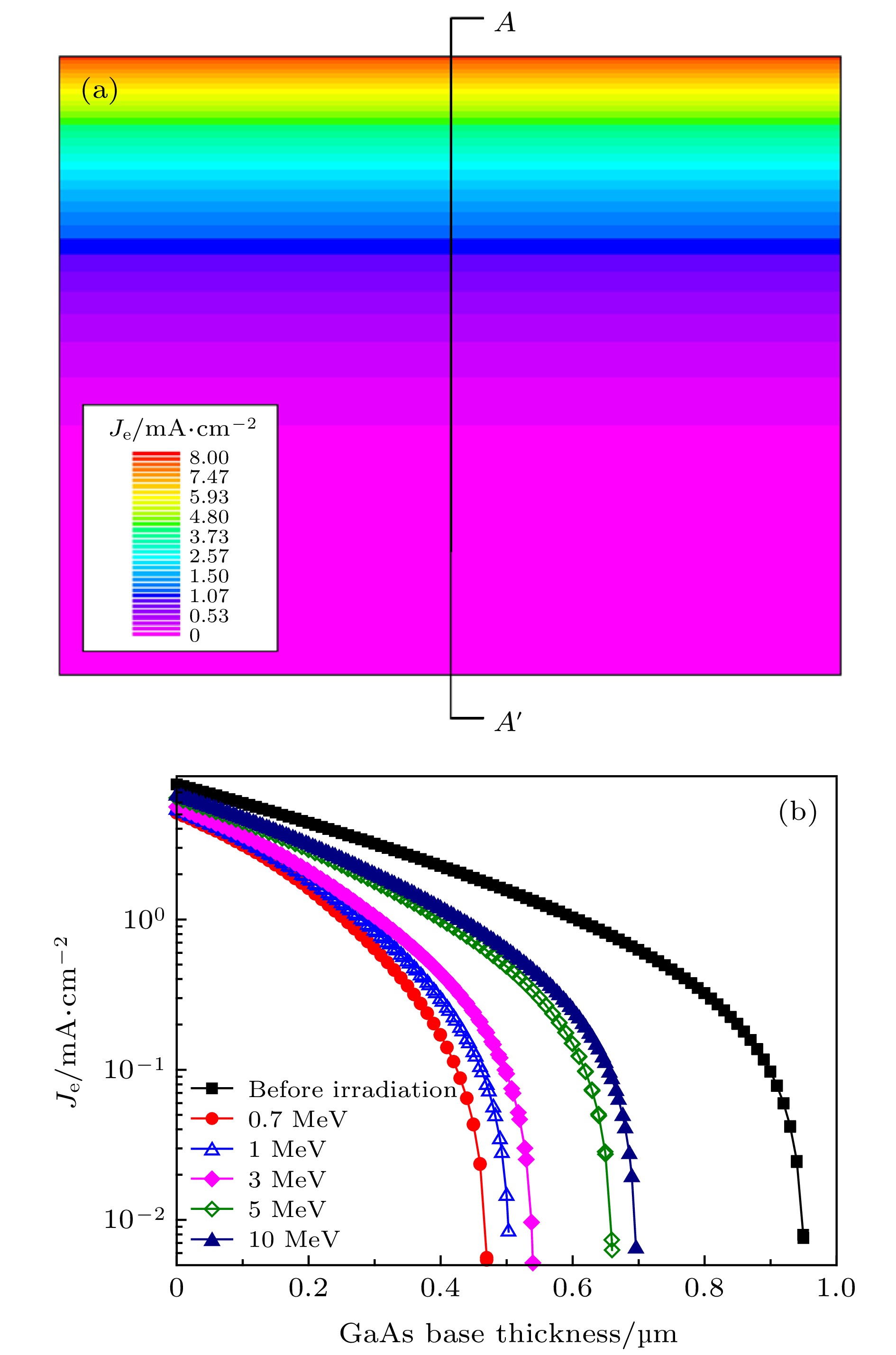
图 7 (a)初始中电池GaAs的基区少数载流子(电子)电流(Je)的模拟结果; (b)不同能量质子辐照下, 沿A-A′ 切线的中电池GaAs基区电子电流密度随基区厚度的变化
Figure 7. (a) Simulation results of current density (Je) of minority carriers (electron) of GaAs middle cell base region before irradiation; (b) simulation results of current density of minority carriers (electron) versus base thickness for GaAs middle cell base region before and after different energy proton irradiation with the fluence of 3 × 1012 cm–2.
表 1 能量为3 MeV, 注量为1 × 1013 cm–2质子辐照后, 顶电池GaInP的能级缺陷[19]
Table 1. GaInP defect parameters after 3 MeV proton irradiation with the fluence of 1 × 1013 cm–2.
Deep level E/eV NT/1014 cm–3 H1 Ev + 0.55 eV 2.70 H2 Ev + 0.71 eV 4.05 H3 Ev + 0.90 eV 1.80 E1 Ec – 0.20 eV 4.60 E2 Ec – 0.36 eV 1.00 E3 Ec – 0.54 eV 2.22 E4 Ec – 0.79 eV 3.60 表 2 能量为3 MeV, 注量为1 × 1013 cm–2质子辐照后, 中电池GaAs的能级缺陷[20]
Table 2. GaAs defect parameters after 3 MeV proton irradiation with the fluence of 1 × 1013 cm–2.
Deep level E/eV NT/1014 cm–3 H1 Ev + 0.18 eV 4.030 H2 Ev + 0.23 eV 4.370 H3 Ev + 0.27 eV 4.790 H4 Ev + 0.77 eV 1.780 E1 Ec – 0.14 eV 1.600 E2 Ec – 0.25 eV 0.448 E3 Ec – 0.54 eV 0.557 E4 Ec – 0.72 eV 2.480 -
[1] 张忠卫, 陆剑峰, 池卫英, 王亮兴, 陈鸣波 2003 上海航天 03 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z W, Lu J F, Chi W Y, Wang L X, Chen M B 2003 Aerospace Shanghai 03 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Jones P A, Spence B R 2011 IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 26 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lohmeyer W Q, Cahoy K 2013 Space Weather 11 476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zainud-Deen S H, Dawoud M, Malhat E A, Aboul-Dahab M A 2019 Wirel. Pers. Commun. 1 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Campesato R, Baur C, Casale M, Gervasi M, Gombia E, Greco E, Kingma A, Rancoita P G, Rozza D, Tacconi M 2018 arXiv: 1809. 07157 [physics. ins-det]
[6] 张延清 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Zhang Y Q 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[7] 吴宜勇, 岳龙, 胡建民, 蓝慕杰, 肖景东, 杨德庄, 何世禹, 张忠卫, 王训春, 钱勇, 陈鸣波 2011 60 098110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y Y, Yue L, Hu J M, Lan M J, Xiao J D, Yang D Z, He S Y, Zhang Z W, Wang X C, Qian Y, Chen M B 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 098110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wu R, Wang J L, Yan G, Wang R 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 046101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 齐佳红, 胡建民, 盛延辉, 吴宜勇, 徐建文, 王月媛, 杨晓明, 张子锐, 周扬 2015 64 108802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi J H, Hu J M, Sheng Y H, Wu Y Y, Xu J W, Wang Y Y, Yang X M, Zhang Z R, Zhou Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 108802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bi Z, Zhang J C, Lv L, Hao Y 2014 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 26 1492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo H L, Shi L F, Wu Y Y, Sun Q, Yu H, Xiao J D, Guo B 2018 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 431 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang R, Lu M, Yi T C, Yang K, Ji X X 2014 Chin. Phys. Lett. 31 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Elahidoost A, Fathipour M, Mojab A 2012 20th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering Tehran, Iran, May 15−17, 2012 p113
[14] Yan Y Y, Fang M H, Tang X B, Chen F D, Huang H, Sun X Y, Ji L L 2019 Nucl. Instrum. Methods. Phys. Res. B 451 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Y M, Sun Y, Rockett A 2012 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 98 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 施敏 2003 半导体器件物理与工艺 (苏州: 苏州大学出版社) 第522页
Shi M 2003 Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology (Suzhou: Suzhou University Press) p522 (in Chinese)
[17] Wang R, Guo Z L, Zhang X H, Zhai Z X 2003 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 77 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Khan A, Yamaguchi M, Dharmaso N, Bourgoin J, Ando K, Takamoto T 2002 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41 1241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dharmarasu N, Yamaguchi M, Bourgoin J C, Takamoto T, Ohshima T, Itoh H, Imaizumi M, Matsuda S 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li S S, Loo R Y 1991 Solar Cells 31 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 朱美芳, 熊绍珍 2014 太阳电池基础与应用 (上卷) (北京: 科学出版社) 第110页
Zhu M F, Xiong S Z 2014 Foundation and Application of Solar Cells (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) p110 (in Chinese)
[22] Silvaco Atlas User’s Manual http://www.silvaco.com.cn [2019-10-20]
[23] Lu M, Wang R, Liu Y H, Hu W T, Feng Z, Han Z L 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 269 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王祖军, 唐本奇, 肖志刚, 刘敏波, 黄绍艳, 张勇 2010 59 4136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z J, Tang B Q, Xiao Z G, Liu M B, Huang S Y, Zhang Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 4136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sato S, Miyamoto H, Imaizumi M, Shimazaki K, Morioka C, Kawano K, Ohshima T 2009 Sol Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 93 768
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 胡建民, 吴宜勇, 钱勇, 杨德庄, 何世禹 2009 58 5051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu J M, Wu Y Y, Qian Y, Yang D Z, Yang S Y 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 5051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Norde H 1979 J. Appl. Phys. 50 5052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Herlufsen S, Schmidt J, Hinken D, Bothe K, Boendel R 2008 Phys. Status Solidi 2 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 常晓阳, 尧舜, 张奇灵, 张杨, 吴波, 占荣, 杨翠柏, 王智勇 2016 65 108801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang X Y, Yao S, Zhang Q L, Zhang Y, Wu B, Zhan R, Yang C B Wang Z Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 108801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Anspaugh B E 1996 GaAs Solar Cell Radiation Handbook (Pasadena: Jet Propulsion Laboratory Publication) p5
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12488
- PDF Downloads: 277
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: