-
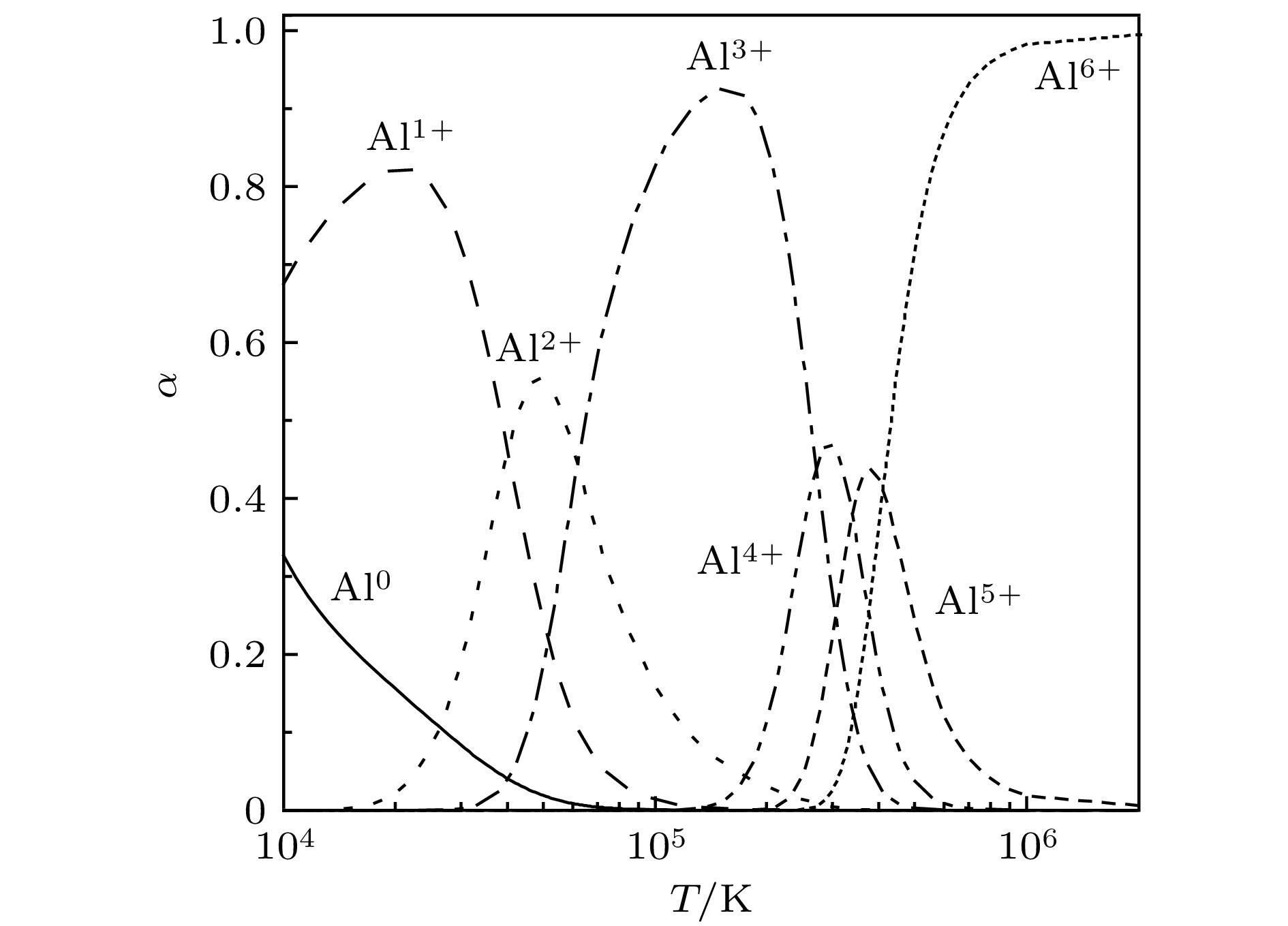
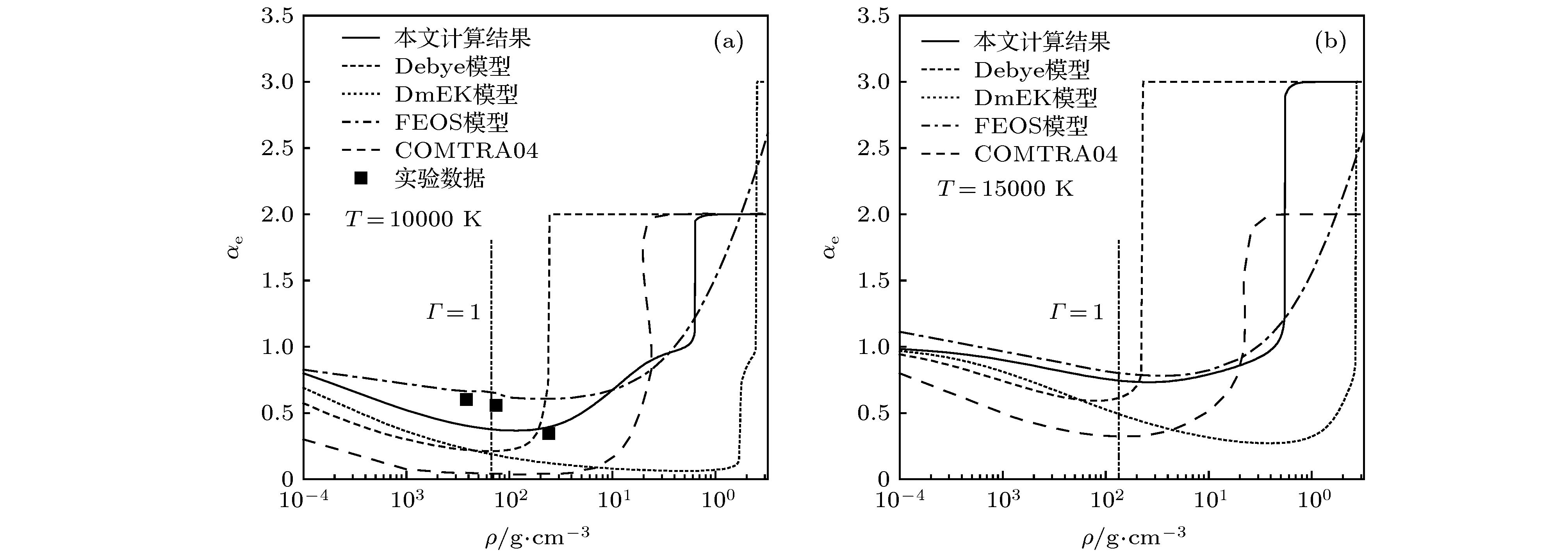
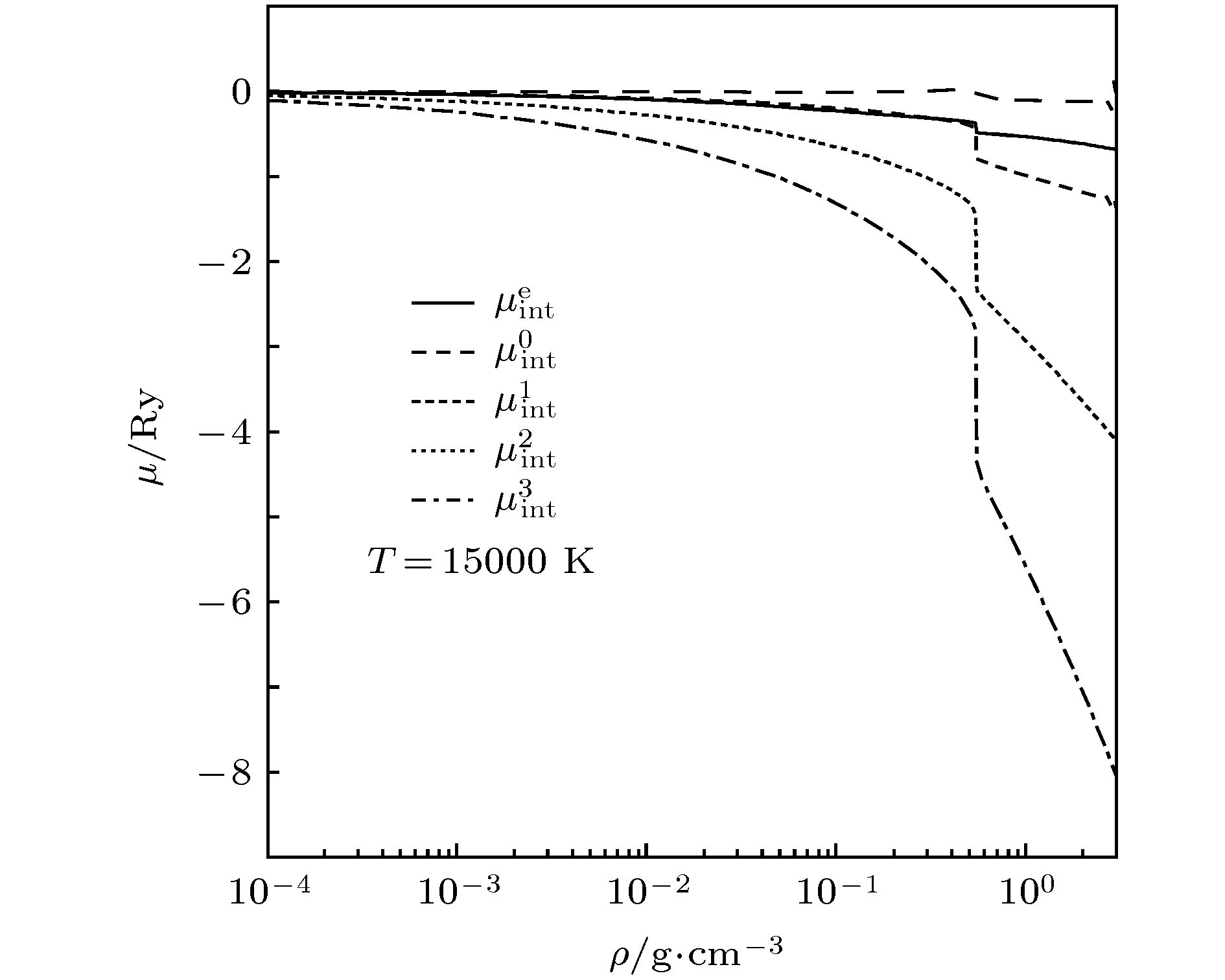
Warm dense matter is widely found in the high-energy-density-physics researches, such as inertial confinement fusion, X-ray source and wire-array Z-pinch. The equation of state and ionization equilibrium of material in warm dense matter regime play a significant role in explaining experimental results and simulations of physical process. In this paper, the Coulomb interaction between charged particles, and the excluded volume effect due to high density and polarization effect between neutral atoms and charged particles are considered in the equation of state for aluminum in warm dense matter regime. A non-ideal Saha equation is used to account for the ionization equilibrium. The data for pressure and concentration of particles of aluminum plasma are derived by iteration between equation of state and ionization equilibrium model. The pressure and average ionization degree of aluminum plasma are consistent with the calculation results from other models and relevant experimental data. The Coulomb interaction, which dominants the non-ideal effects, is insensitive to temperature and increases with density rising especially near the region of critical density. The excluded volume effect peaks at a density of ~0.5 g/cm3. The polarization effect first becomes stronger with density increasing and then decreases at a density of ~0.4 g/cm3. The ionization equilibrium results with density ranging from 1.0 × 10–4 g/cm3 to 3.0 g/cm3 and temperature ranging from 1.0 × 104 K to 3.0 × 104 K reveal that the average ionization degree increases with density sharply increasing near the critical density. The non-ideal effects, which lead the ionization energy to decline and the effective ionization potential of specific ions in aluminum plasma to decrease substantially, are responsible for the sharp increase of average ionization degree near the region of critical density. When the temperature is lower than 12000 K, first and second stage of ionization occur in aluminum plasma, and the system is mainly composed of Al1+, Al2+ and electrons. The average ionization degree can reach 2 at critical density. The third stage of ionization is dominant in the aluminum plasma when plasma temperature is higher than 12000 K. And then, the charged particles in the plasma are composed of Al3+ and electrons, allowing the average ionization degree to reach 3 at critical density.
-
Keywords:
- equation of state /
- ionization equilibrium /
- warm dense matter
[1] 付志坚, 贾丽君, 夏继宏, 唐可, 李召红, 权伟龙, 陈其峰 2016 65 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fu Z J, Jia L J, Xia J H, Tang K, Li Z H, Quan W L, Chen Q F 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wallace M S, Haque S, Neill P, Pereira N R, Presura R 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 015106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Oreshkin V I, Artyomov A P, Chaikovsky S A, Oreshkin E V, Rousskikh A G 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 012703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 格拉齐亚尼F, 德斯贾莱斯M P, 雷德默R, 特里基S B 著 (陈其峰 译) 2018 温稠密物质研究的前沿和挑战 (北京: 原子能出版社) 第vii−x页
Graziani F, Desjarlais M P, Redmer R, Trickey S B (translated by Chen Q F) 2018 Frontiers and Challenges in Warm Dense Matter (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) ppvii−x (in Chinese)
[5] 徐锡申, 张万箱 1986 实用物态方程理论导引 (北京: 科学出版社) 第1−5页
Xu X S, Zhang W X 1986 Introduction to the Theory of Equation of State (Beijing: Science Press) pp1−5 (in Chinese)
[6] Shi Z Q, Wang K, Li Y, Shi Y J, Wu J, Jia S L 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 032702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Eliezer S, Ghatak A, Hora H, Teller E 2002 Fundamentals of Equations of State (Singapore: World Scientific) pp153−164
[8] 陈其峰, 顾云军, 郑君, 李江涛, 李治国, 权伟龙, 付志坚, 李成军 2017 科学通报 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Q F, Gu Y J, Zheng J, Li J T, Li Z G, Quan W L, Fu Z J, Li C J 2017 Chin. Sci. Bull. 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 于继东, 李平, 王文强, 吴强 2014 63 116401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J D, Li P, Wang W Q, Wu Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 116401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Danel J F, Kazandjian L, Zérah G 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 072704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fu Z J, Quan W L, Zhang W, Li Z G, Zheng J, Gu Y J, Chen Q F 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 013303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 汤文辉, 徐彬彬, 冉宪文, 徐志宏 2017 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W H, Xu B B, Ran X W, Xu Z H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张颖, 陈其峰, 顾云军, 蔡灵仓, 卢铁城 2007 56 1318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Chen Q F, Gu Y J, Cai L C, Lu T C 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 1318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen Q F, Cai L C, Gu Y J, Gu Y 2009 Phys. Rev. E 79 016409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen Q F, Zheng J, Gu Y J, Chen Y L, Cai L C 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 112704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Quan W L, Chen Q F, Fu Z J, Sun X W, Zheng J, Gu Y J 2015 Phys. Rev. E 91 023106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Apfelbaum E M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 092703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Apfelbaum E M 2017 High Temp. 55 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kuhlbrodt S, Holst B, Redmer R 2005 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 45 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Moldabekov Z A, Groth S, Dornheim T, Bonitz M, Ramazanov T S 2017 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 57 532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Stolzmann W, Blöcker T 1996 Astron. Astrophys. 314 1024
[22] Fortov V E, Altshuler L V, Trunin R F, Funtikov A I 2004 High-Pressure Shock Compression of Solids VII (New York: Springer) pp437−489
[23] 付志坚, 陈其峰, 陈向荣 2011 60 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fu Z J, Chen Q F, Chen X R 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Redmer R, Rother T, Schmidt K, Kraeft W D, Röpke G 1988 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 28 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Apfelbaum E M 2011 Phys. Rev. E 84 066403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Karakhtanov V S, Redmer R, Reinholz H, Röpke G 2011 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 51 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] More R M, Warren K H, Young D A, Zimmerman G B 1988 Phys. Fluids 31 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Iyetomi H, Ichimaru S 1986 Phys. Rev. A 34 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zaghloul M R 2018 High Energy Density Phys. 26 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wu B, Shin Y C 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 111902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Morel V, Bultel A, Chéron B G 2009 Int. J. Thermophys. 30 1853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Preston T R, Vinko S M, Ciricosta O, Chung H K, Lee R W, Wark J S 2013 High Energy Density Phys. 9 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Stransky M 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 012708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kemp A J, Meyer-Ter-Vehn J 1998 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 415 674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Krisch I, Kunze H J 1998 Phys. Rev. E 58 6557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] 田庆云 2015 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 国防科学技术大学)
Tian Q Y 2015 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[38] Son S K, Thiele R, Jurek Z, Ziaja B, Santra R 2014 Phys. Rev. X 4 031004
[39] Ebeling W, Föster A, Fortov V E, Gryaznov V K, Polishuk A Y 1991 Thermophysical Properties of Hot Dense Plasmas (Stuttgar-Leipzig: Teubner Verlagsgesellshaft) pp39—42
-
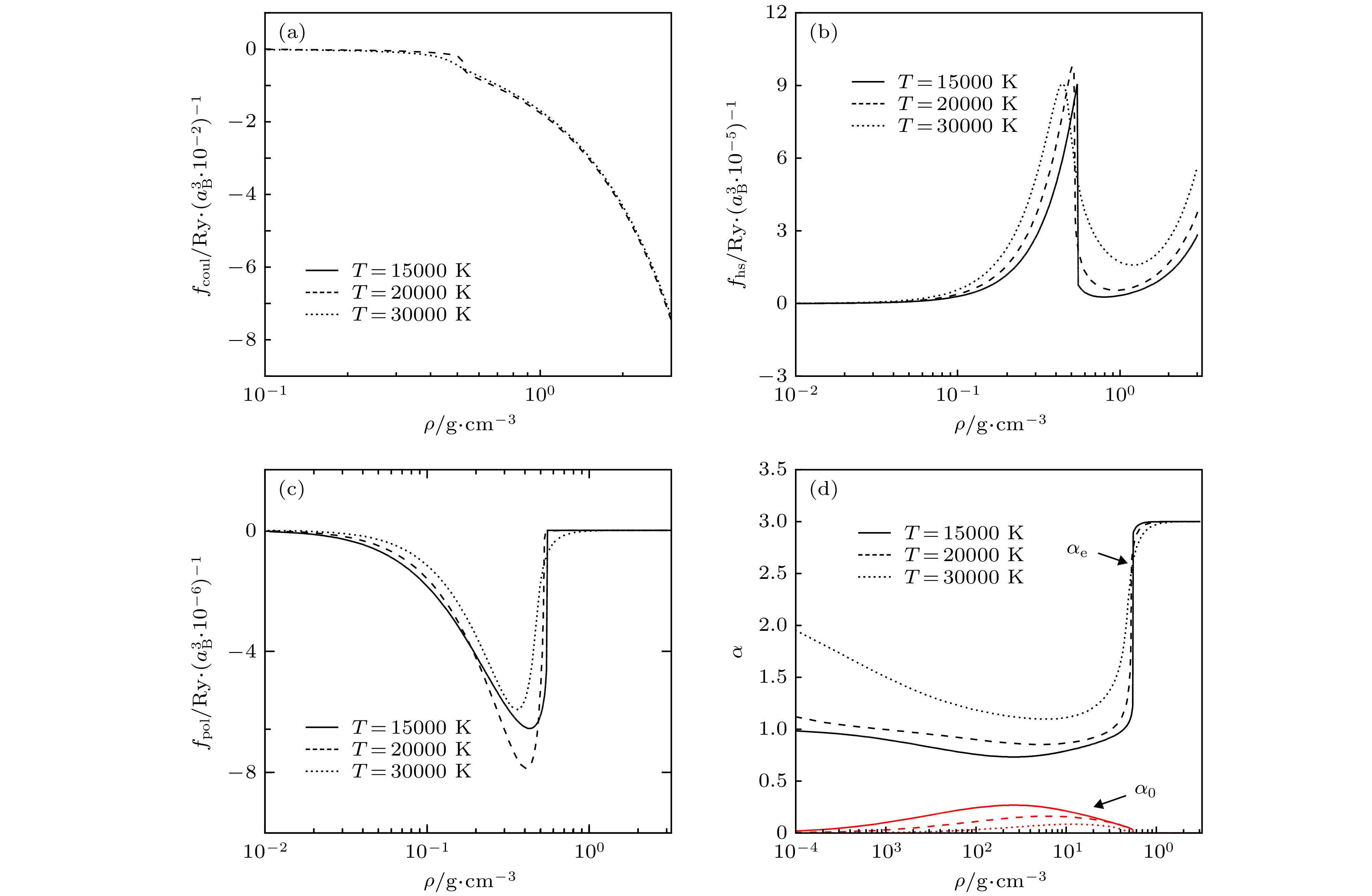
图 5 不同温度下非理想效应自由能密度以及电子、原子相对粒子分数随密度的变化 (a) 库仑相互作用; (b) 排斥体积作用; (c) 极化作用; (d) 电子、原子相对粒子分数
Figure 5. Free energy density of different non-ideal effects and relative particle fraction for electrons and atoms as a function of density at different temperatures: (a) Coulomb interaction; (b) excluded volume effect; (c) polarization effect; (d) relative particle fraction for electrons and atoms.
表 1 物态方程及电离平衡模型参数列表
Table 1. Parameters of equation of state and ionization equilibrium model.
参数 值 参数 值 参数 值 R0 2.5714 R6 0.4167 E3 2.0909 R1 2.3377 rc 1.7712 E4 8.8192 R2 2.1429 mk 24597 E5 11.3059 R3 0.4678 αD 46.281 E6 14.0008 R4 0.4494 E1 0.4400 R5 0.4324 E2 1.3839 -
[1] 付志坚, 贾丽君, 夏继宏, 唐可, 李召红, 权伟龙, 陈其峰 2016 65 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fu Z J, Jia L J, Xia J H, Tang K, Li Z H, Quan W L, Chen Q F 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wallace M S, Haque S, Neill P, Pereira N R, Presura R 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 015106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Oreshkin V I, Artyomov A P, Chaikovsky S A, Oreshkin E V, Rousskikh A G 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 012703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 格拉齐亚尼F, 德斯贾莱斯M P, 雷德默R, 特里基S B 著 (陈其峰 译) 2018 温稠密物质研究的前沿和挑战 (北京: 原子能出版社) 第vii−x页
Graziani F, Desjarlais M P, Redmer R, Trickey S B (translated by Chen Q F) 2018 Frontiers and Challenges in Warm Dense Matter (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) ppvii−x (in Chinese)
[5] 徐锡申, 张万箱 1986 实用物态方程理论导引 (北京: 科学出版社) 第1−5页
Xu X S, Zhang W X 1986 Introduction to the Theory of Equation of State (Beijing: Science Press) pp1−5 (in Chinese)
[6] Shi Z Q, Wang K, Li Y, Shi Y J, Wu J, Jia S L 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 032702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Eliezer S, Ghatak A, Hora H, Teller E 2002 Fundamentals of Equations of State (Singapore: World Scientific) pp153−164
[8] 陈其峰, 顾云军, 郑君, 李江涛, 李治国, 权伟龙, 付志坚, 李成军 2017 科学通报 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Q F, Gu Y J, Zheng J, Li J T, Li Z G, Quan W L, Fu Z J, Li C J 2017 Chin. Sci. Bull. 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 于继东, 李平, 王文强, 吴强 2014 63 116401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J D, Li P, Wang W Q, Wu Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 116401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Danel J F, Kazandjian L, Zérah G 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 072704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fu Z J, Quan W L, Zhang W, Li Z G, Zheng J, Gu Y J, Chen Q F 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 013303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 汤文辉, 徐彬彬, 冉宪文, 徐志宏 2017 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W H, Xu B B, Ran X W, Xu Z H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张颖, 陈其峰, 顾云军, 蔡灵仓, 卢铁城 2007 56 1318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Chen Q F, Gu Y J, Cai L C, Lu T C 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 1318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen Q F, Cai L C, Gu Y J, Gu Y 2009 Phys. Rev. E 79 016409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen Q F, Zheng J, Gu Y J, Chen Y L, Cai L C 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 112704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Quan W L, Chen Q F, Fu Z J, Sun X W, Zheng J, Gu Y J 2015 Phys. Rev. E 91 023106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Apfelbaum E M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 092703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Apfelbaum E M 2017 High Temp. 55 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kuhlbrodt S, Holst B, Redmer R 2005 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 45 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Moldabekov Z A, Groth S, Dornheim T, Bonitz M, Ramazanov T S 2017 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 57 532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Stolzmann W, Blöcker T 1996 Astron. Astrophys. 314 1024
[22] Fortov V E, Altshuler L V, Trunin R F, Funtikov A I 2004 High-Pressure Shock Compression of Solids VII (New York: Springer) pp437−489
[23] 付志坚, 陈其峰, 陈向荣 2011 60 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fu Z J, Chen Q F, Chen X R 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Redmer R, Rother T, Schmidt K, Kraeft W D, Röpke G 1988 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 28 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Apfelbaum E M 2011 Phys. Rev. E 84 066403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Karakhtanov V S, Redmer R, Reinholz H, Röpke G 2011 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 51 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] More R M, Warren K H, Young D A, Zimmerman G B 1988 Phys. Fluids 31 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Iyetomi H, Ichimaru S 1986 Phys. Rev. A 34 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zaghloul M R 2018 High Energy Density Phys. 26 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wu B, Shin Y C 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 111902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Morel V, Bultel A, Chéron B G 2009 Int. J. Thermophys. 30 1853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Preston T R, Vinko S M, Ciricosta O, Chung H K, Lee R W, Wark J S 2013 High Energy Density Phys. 9 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Stransky M 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 012708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kemp A J, Meyer-Ter-Vehn J 1998 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 415 674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Krisch I, Kunze H J 1998 Phys. Rev. E 58 6557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] 田庆云 2015 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 国防科学技术大学)
Tian Q Y 2015 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[38] Son S K, Thiele R, Jurek Z, Ziaja B, Santra R 2014 Phys. Rev. X 4 031004
[39] Ebeling W, Föster A, Fortov V E, Gryaznov V K, Polishuk A Y 1991 Thermophysical Properties of Hot Dense Plasmas (Stuttgar-Leipzig: Teubner Verlagsgesellshaft) pp39—42
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 16103
- PDF Downloads: 133
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: