-
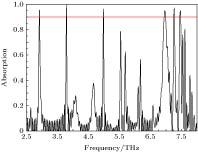
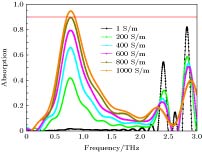
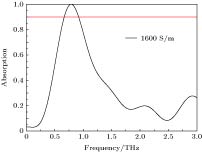
With the increasing scarcity of spectrum resources, terahertz wave technologies have attracted more and more attention in recent decades, and have made tremendous progress. Terahertz wave referring to electromagnetic waves with a frequency in a range of 0.1-10 THz has a wide range of applications in wireless communication, nondestructive imaging and remote sensing. Due to the advantages of high absorption, ultra-thin thickness, frequency selectivity and design flexibility, metamaterial absorbers have attracted more attention in terahertz band. In this paper, two terahertz metamaterial absorbers with different performances are designed which are named “T” terahertz multi-band absorber and “T” terahertz tunable broadband absorber, respectively. The absorbers are both comprised of three layers: metal substrate, matched dielectric layer and surface metamaterial layer. The main structures of these two absorbers are composed of four T-shape Au plates on the top of polyimide dielectric layer and an Au sheet acting as a bottom layer. The only difference between these two absorbers is that the terahertz broadband tunable absorber possesses a square photosensitive silicon in the metamaterial layer. The simulations results show that the terahertz multi-band absorber has six absorption peaks at 2.918, 3.7925, 4.986, 6.966, 7.2685, and 7.4665 THz, with the absorptivity peaks of 95.631%, 99.508%, 96.34%, 94.835%, 96.485%, 94.732%, respectively, and the average absorption rate is 96.26%. Terahertz tunable broadband absorber has the characteristics of broadband absorption. When the conductivity of silicon is 1600 S/m, the absorber reaches its absorption peak at 0.786 THz with the absorptivity of 99.998%, and the frequency bandwidth with the absorption rate exceeding 90% reaches 240 GHz. The more interesting thing is that by changing the conductivity of silicon, the terahertz tunable broadband absorber shows the ability to dynamically control the existence of absorption band and adjust the frequency position of absorption peak. For terahertz tunable broadband absorber, the frequency of absorption peak can be regulated in a bandwidth of about 30 GHz. The terahertz wave absorbers designed in this paper possess rather simple structures, therefore the proposed absorbers are easy to fabricate. Because of these excellent properties, the absorbers may have potential applications in optical switch, optical detection, optical imaging, band-stop devices, and other fields.
-
Keywords:
- terahertz absorber /
- multi-band absorber /
- tunable broadband /
- metamaterial
[1] Landy N I, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 207402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 赵碧辉, 文岐业, 谢云松 2011 电子元件与材料 30 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B H, Wen Q Y, Xie Y S 2011 Electr. Comp. Mater. 30 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 沈晓鹏, 崔铁军, 叶建祥 2012 61 058101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen X P, Cui T J, Ye J X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 058101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 保石, 罗春荣, 张燕萍, 赵晓鹏 2010 59 3187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao S, Luo C R, Zhang Y P, Zhao X P 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 3187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 莫漫漫, 文岐业, 陈智, 杨青慧, 李胜, 荆玉兰, 张怀武 2013 62 237801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mo M M, Wen Q Y, Chen Z, Yang Q H, Li S, Jing Y L, Zhang H W 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 237801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhai Z, Zhang L, Li X, Xiao S 2019 Opt. Commun. 431 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Andryieuski A, Lavrinenko A V 2013 Opt. Express 21 9144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang Y, Feng Y, Zhu B, Zhao J, Jiang T 2014 Opt. Express 22 22743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 程伟, 李九生 2013 电子元件与材料 32 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng W, Li J S 2013 Electr. Comp. Mater. 32 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao X, Wang Y, Schalch J, Duan G, Cremin K, Zhang J D, Chen C X, Averitt R D, Zhang X 2019 ACS Photon. 6 830
[11] Chen M, Yan W, Tong X, Zeng L, Li Z, Yang F 2019 J. Opt. 21 035102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Faraji M, Moravvej-Farshi M K, Yousefi L 2015 Opt. Commun. 355 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yan H, Li X, Chandra B, Tulevski G, Wu Y, Freitag M, Zhu W, Avouris P, Xia F 2012 Nat. Nanotechnol. 7 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kim K S, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee S Y, Kim J M, Kim K S, Ahn J H, Kim P, Choi J J, Hong B H 2009 Nature 457 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 梁兰菊, 闫昕, 姚建铨 2016 枣庄学院学报 33 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang L J, Yao J Q 2016 J. Zaozhuang Univ. 33 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen L, Wei Y M, Zang X F, Zhu Y M, Zhuang S L 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 22027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen L, Liao D G, Guo X G, Zhao J Y, Zhu Y M, Zhuang S L 2019 Front. Inform. Tech. El. 20 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈康, 文岐业, 张怀武 2011 电子元件与材料 30 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen K, Wen Q Y, Zhang H W 2011 Electr. Comp. Mater. 30 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 颜世桃 2016 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学)
Yao S T 2016 M. S. Thesis (Haerbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[20] He X J, Yan S T, Ma Q X, Zhang Q F, Jia P, Wu F M, Jiang J X 2015 Opt. Commun. 340 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gong C, Zhan M Z, Yang J, Wang Z G, Liu H T, Zhao Y J 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 32466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
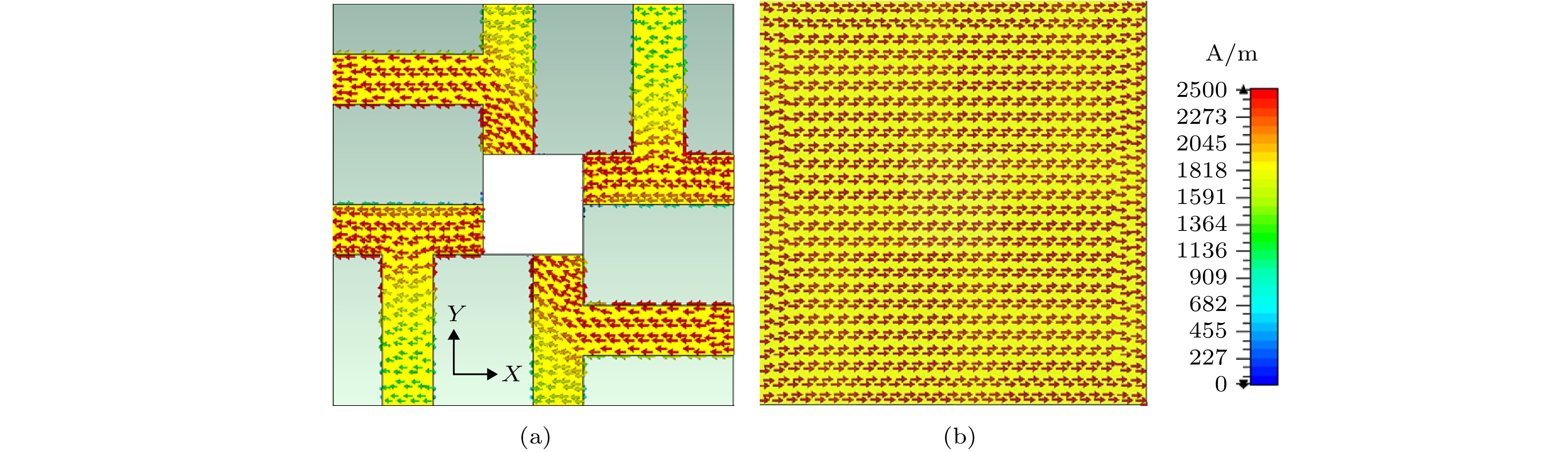
图 1 超材料太赫兹波吸收器结构示意图 (a) 多频吸收器示意图; (b) 宽频可调谐吸收器示意图; (c) 吸收器剖面图; (d) 吸收器表面结构图
Figure 1. Structural schematic diagram of metamaterial terahertz wave absorbers: (a) Schematic diagram of multi-band absorber; (b) schematic diagram of broadband tunable absorber; (c) profile of absorber; (d) surface structure of absorber.
表 1 超材料太赫兹吸收器的结构尺寸
Table 1. Structure dimensions of metamaterial terahertz absorber
参数 a b w p h1 h2 h3 取值/μm 12 4 8 32 1 30 1 -
[1] Landy N I, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 207402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 赵碧辉, 文岐业, 谢云松 2011 电子元件与材料 30 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B H, Wen Q Y, Xie Y S 2011 Electr. Comp. Mater. 30 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 沈晓鹏, 崔铁军, 叶建祥 2012 61 058101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen X P, Cui T J, Ye J X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 058101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 保石, 罗春荣, 张燕萍, 赵晓鹏 2010 59 3187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao S, Luo C R, Zhang Y P, Zhao X P 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 3187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 莫漫漫, 文岐业, 陈智, 杨青慧, 李胜, 荆玉兰, 张怀武 2013 62 237801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mo M M, Wen Q Y, Chen Z, Yang Q H, Li S, Jing Y L, Zhang H W 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 237801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhai Z, Zhang L, Li X, Xiao S 2019 Opt. Commun. 431 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Andryieuski A, Lavrinenko A V 2013 Opt. Express 21 9144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang Y, Feng Y, Zhu B, Zhao J, Jiang T 2014 Opt. Express 22 22743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 程伟, 李九生 2013 电子元件与材料 32 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng W, Li J S 2013 Electr. Comp. Mater. 32 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao X, Wang Y, Schalch J, Duan G, Cremin K, Zhang J D, Chen C X, Averitt R D, Zhang X 2019 ACS Photon. 6 830
[11] Chen M, Yan W, Tong X, Zeng L, Li Z, Yang F 2019 J. Opt. 21 035102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Faraji M, Moravvej-Farshi M K, Yousefi L 2015 Opt. Commun. 355 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yan H, Li X, Chandra B, Tulevski G, Wu Y, Freitag M, Zhu W, Avouris P, Xia F 2012 Nat. Nanotechnol. 7 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kim K S, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee S Y, Kim J M, Kim K S, Ahn J H, Kim P, Choi J J, Hong B H 2009 Nature 457 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 梁兰菊, 闫昕, 姚建铨 2016 枣庄学院学报 33 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang L J, Yao J Q 2016 J. Zaozhuang Univ. 33 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen L, Wei Y M, Zang X F, Zhu Y M, Zhuang S L 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 22027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen L, Liao D G, Guo X G, Zhao J Y, Zhu Y M, Zhuang S L 2019 Front. Inform. Tech. El. 20 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈康, 文岐业, 张怀武 2011 电子元件与材料 30 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen K, Wen Q Y, Zhang H W 2011 Electr. Comp. Mater. 30 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 颜世桃 2016 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学)
Yao S T 2016 M. S. Thesis (Haerbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[20] He X J, Yan S T, Ma Q X, Zhang Q F, Jia P, Wu F M, Jiang J X 2015 Opt. Commun. 340 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gong C, Zhan M Z, Yang J, Wang Z G, Liu H T, Zhao Y J 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 32466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14429
- PDF Downloads: 465
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: