-
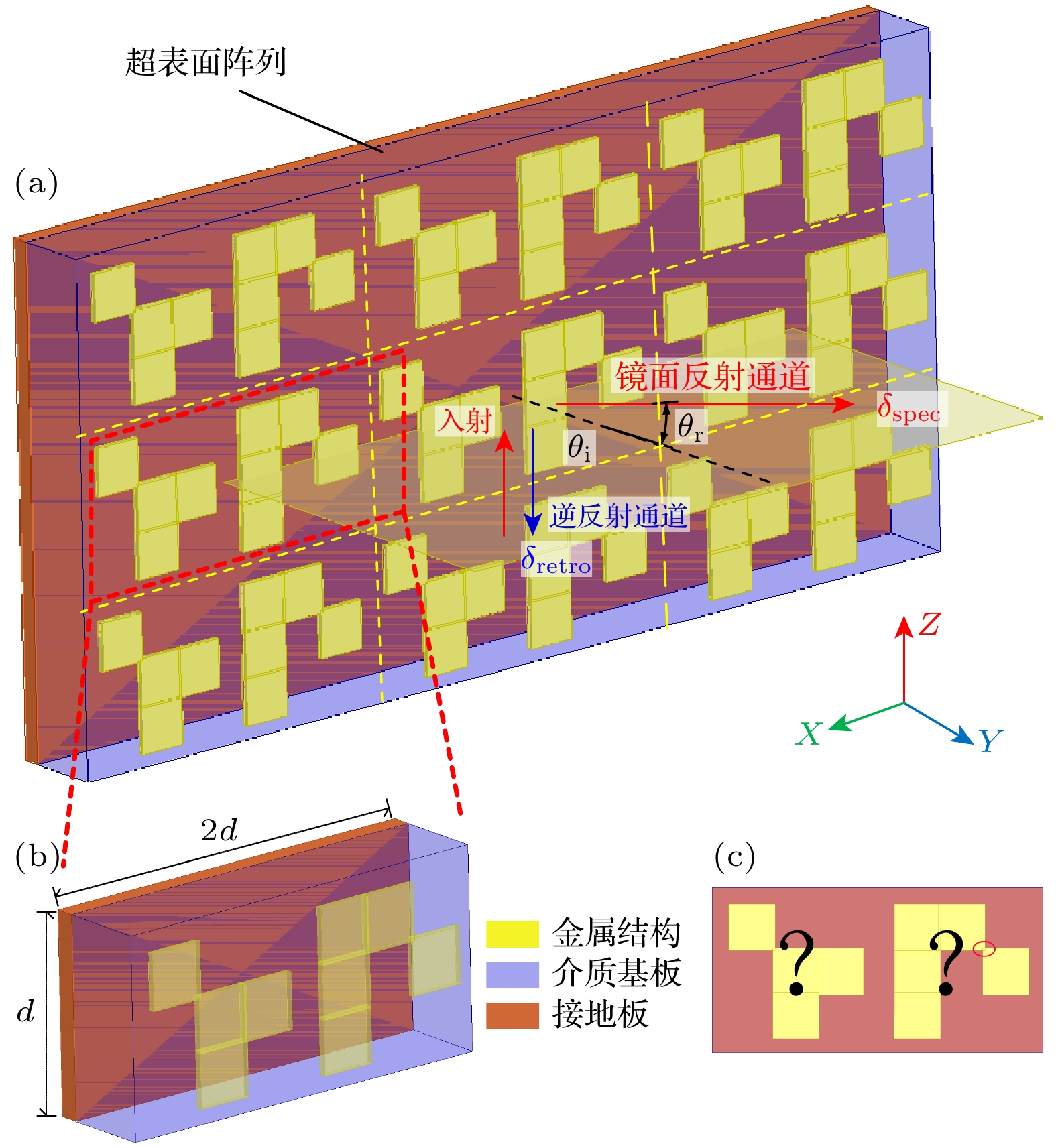
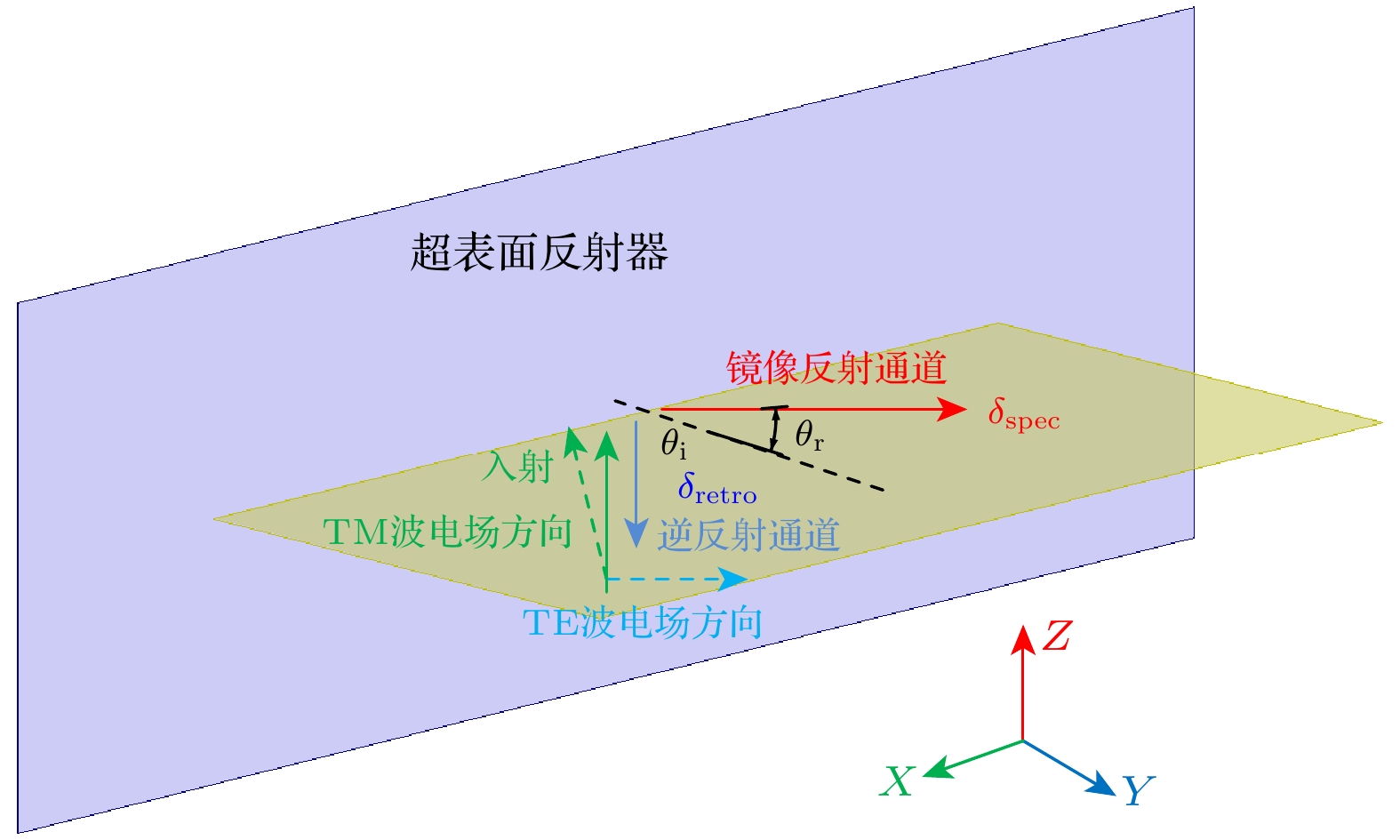
对斜入射电磁波产生包含逆反射通道的双反射通道, 对于提高目标识别性能、导航性能等具有重要意义. 在双通道反射中, 控制逆反射与镜像反射占比则是实现反射功率分配的关键. 为实现双通道反射功率占比的可控, 本文提出了一种双通道反射超表面微结构拓扑优化设计方法. 构建了包括逆反射的双通道反射超表面实现机理及物理模型, 建立了具有特定逆反射与镜像反射幅值比值或占比的超表面微结构拓扑优化模型. 作为数值算例, 针对TE模式下频率为10 GHz俯仰角
$-30^\circ$ 方向入射平面波, 对逆反射与镜像反射功率比1∶1的双通道反射器进行设计, 所设计超表面在$ \pm 30^\circ $ 方向表现出较强的方向性, 两方向反射幅值大小相等. 同时, 对具有最大逆反射占比的反射超表面进行设计, 逆反射功率占总功率比值为0.093, 无镜像反射及其他方向奇异反射, 超表面强反射集中在$-30^\circ $ , 主波束功率占总反射功率比为0.900. 仿真及实验测试结构均验证了所提方法的可行性.For oblique incident electromagnetic waves, the generation of double reflection channels including retroreflection channel is of great significance in improving target recognition performance and navigation performance. In double channel reflection, controlling the ratio of retroreflection to specular reflection is the key to realizing reflection power distribution. In order to realize the control of the proportion of the reflected power in each channel, a topology optimization method for designing the reflective metasurface microstructure with dual channel is proposed in this paper. The implementation mechanism is investigated, physical model of metasurface with dual reflection channel including retroreflection channel is established, and the topology optimization model of metasurface microstructure with specific power ratio of the retroreflection to specular reflection is established. As a numerical example, a dual channel metasurface reflector with a 1∶1 ratio of retroreflection power to specular reflection power is designed for a 10 GHz plane wave in the TE mode with a pitch angle of –30°. The designed metasurface exhibits strong directionality in the retroreflective direction, and the reflection amplitudes in both directions are similar. The retroreflective metasurface with the maximum retroreflection ratio is designed. The retroreflection ratio of the designed metasurface is 0.093. There is no specular reflection or other singular reflection, and the strong reflection on the metasurface is concentrated at –30°. The ratio of the main beam power to the total reflection power is 0.900. The simulated and experimental results verify the feasibility of the proposed method.-
Keywords:
- metasurface /
- dual channel /
- topology optimization
[1] Kuga Y, Ishimaru A 1984 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨丹青, 王莉, 王新龙 2015 64 054301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang D Q, Wang L, Wang X L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 盛泉, 耿婧旎, 王爱华, 王盟, 齐岳, 刘俊杰, 付士杰, 史伟, 姚建铨 2023 72 044203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng Q, Geng J N, Wang A H, Wang M, Qi Y, Liu J J, Fu S J, Shi W, Yao J Q 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 044203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang R, Fan Y, Zhu W, Hu C, Chen S, Wei H, Chen W, Chang C T, Zhao Q, Zhou J, Zhang F, Qiu C W 2023 Laser Photonics Rev. 17 2200975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jin X, Holzman J F 2010 IEEE Sens. J. 10 1875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Vitaz J A, Buerkle A M, Sarabandi K 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58 3539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Deroba J C, Sobczak K D, Good A, Larimore Z, Mirotznik M 2019 IEEE Aero. El. Sys. Mag. 34 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim H, Lee B 2007 Opt. Eng. 46 094002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kadera P, Jimenez-Saez A, Burmeister T, Lacik J, Jakoby R 2020 IEEE Access 8 212765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chang C C, Chen T Y, Tsai J C 2016 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 28 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pon C Y 1964 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 12 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yan L, Shen Z 2020 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 19 736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu N, Genevet P, Kats M A, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Science 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hessel A, Schmoys J, Tseng D Y 1975 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 65 380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jull E V, Heath J W, Ebbeson G R 1977 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 67 557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ra'Di Y, Sounas D L, Alu A 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 067404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hoang T V, Lee C H, Lee J H 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 2451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wong A M H, Eleftheriades G V 2017 Phys. Rev. X 8 011036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wong A M H, Christian P, Eleftheriades G V 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 2892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lee S G, Lee J H 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 69 3588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tao C, Itoh T U 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 6193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Estakhri N M, Alù A 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 041008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang X C, Díaz-Rubio A, Li H, Tretyakov S A, Alù A 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 13 044040
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang X, Díaz-Rubio A, Tretyakov S A 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 024089
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Asadchy V S, Díaz-Rubio A, Tcvetkova S N, et al. 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 031046
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
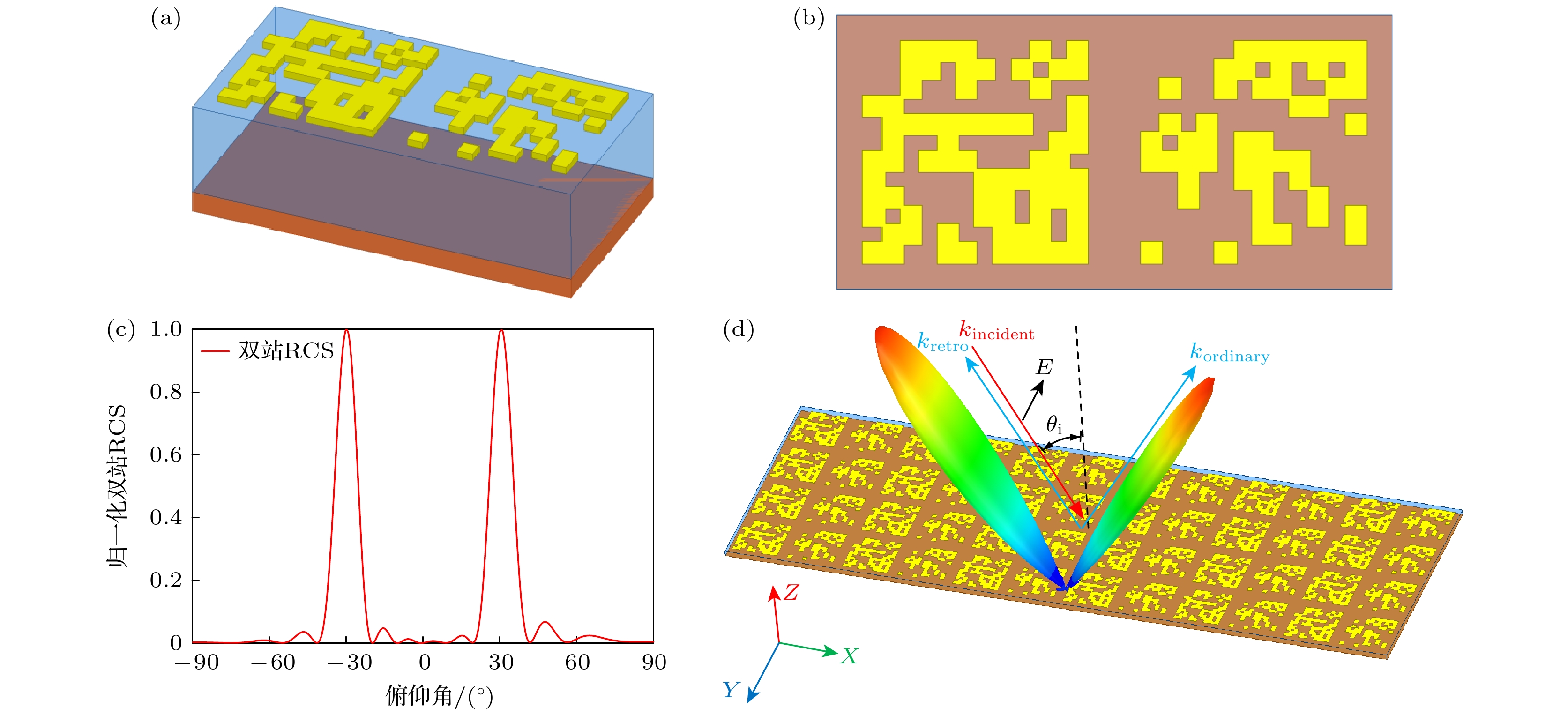
图 4 所设计双通道反射功率1∶1超表面反射器及反射特性 (a) 超胞; (b) 微结构; (c) 反射器俯仰向归一化双站RCS; (d) 三维双站RCS
Fig. 4. Designed double-channel metasurface reflector with a 1∶1 ratio of retroreflection power to specular reflection power and its reflection characteristics: (a) The unit cell; (b) the microstructure; (c) the normalized bistatic RCS in the elevation coordinate; (d) the three-dimensional bistatic RCS of the designed reflector.
图 6 双通道超表面实验测试平台及结果 (a) RCS测试示意图; (b) 所设计超表面试件; (c)测试所得反射特性
Fig. 6. Experimental platform for the double-channel metasurface reflector testing and the tested results: (a) The schematic diagram of the RCS testing platform; (b) the designed metasurface specimen; (c) the tested reflection characteristics.
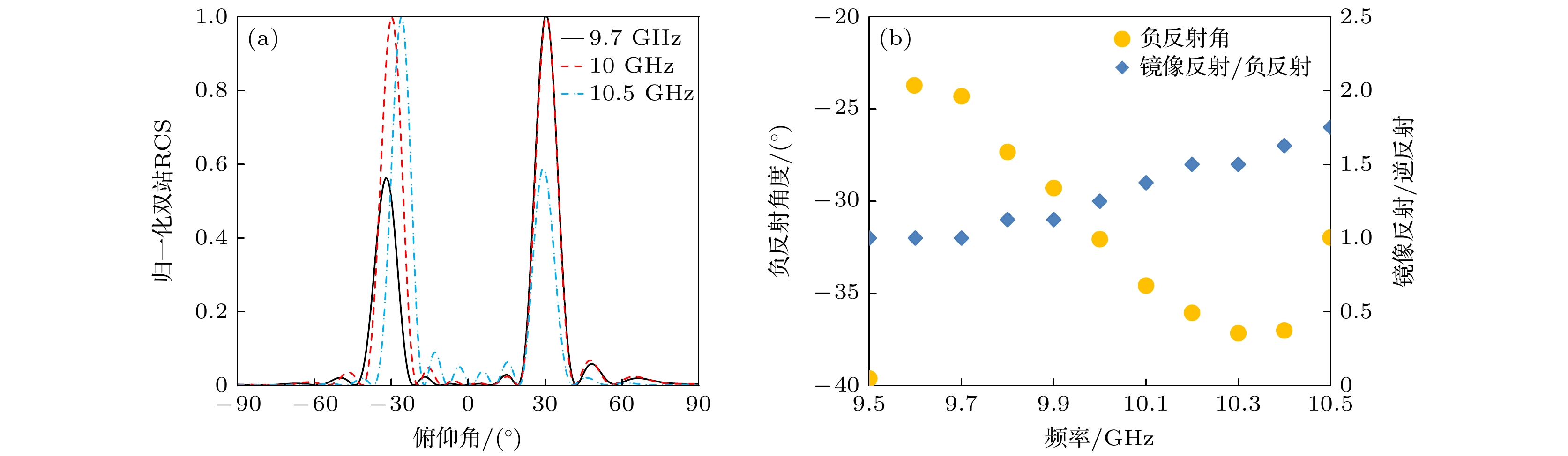
图 7 入射角度偏差下的反射功率1∶1超表面反射特性 (a) 归一化双站RCS; (b) 负反射角度及镜像反射与负反射幅值比
Fig. 7. Reflection characteristics of the metasurface with a 1∶1 ratio of retroreflection power to specular reflection power when the incident angle is adjusted: (a) The normalized bistatic RCS of the metasurface; (b) the retroreflection angle and ratio between the specular reflection and retroreflection.
图 8 入射波频率偏差下的反射功率1∶1超表面反射特性 (a) 归一化双站RCS; (b) 负反射角度及镜像反射与负反射幅值比
Fig. 8. Reflection characteristics of the metasurface with a 1∶1 ratio of retroreflection power to specular reflection power when the frequency of the incident wave is biased: (a) The normalized bistatic RCS of the designed metasurface; (b) the retroreflection angle and the ratio between the specular reflection and retroreflection.
图 9 所设计的逆反射占比最大超表面反射器及反射特性 (a) 超胞; (b) 微结构; (c) 俯仰向归一化双站RCS; (d) 测试所得反射特性及所设计超表面试件
Fig. 9. Designed metasurface reflector with the maximum retroreflection ratio and its reflection characteristics: (a) The unit cell; (b) the microstructure; (c) the normalized bistatic RCS in the elevation coordinate; (d) the tested radiation pattern and the metasurface retroreflector prototype.
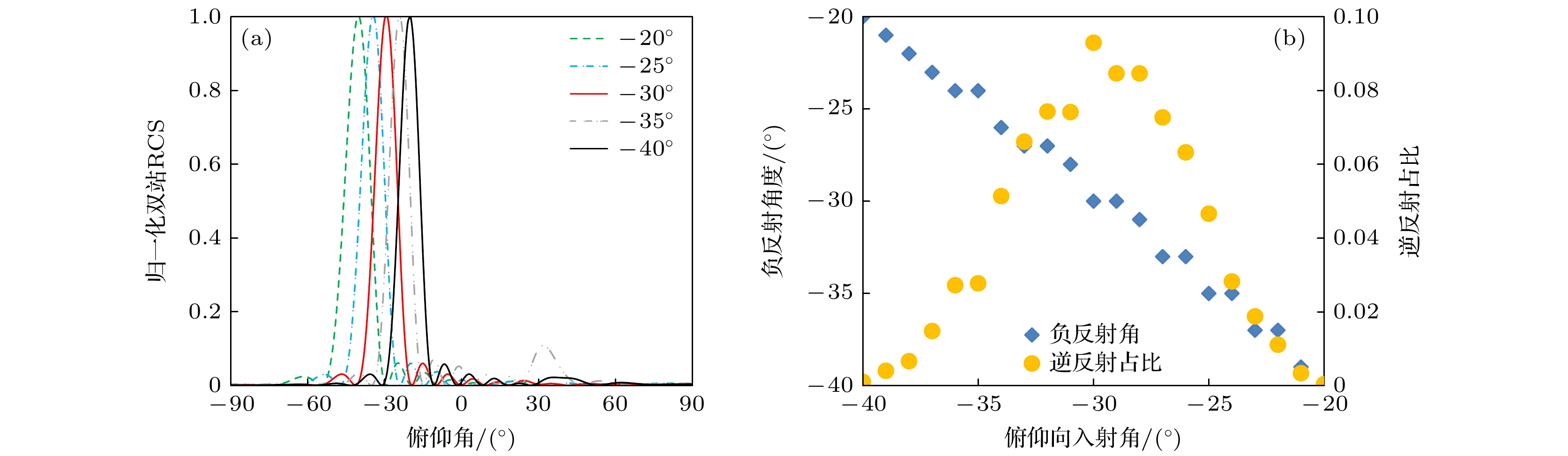
图 10 入射角度偏差下的逆反射占比最大超表面反射特性 (a) 归一化双站RCS; (b) 负反射角度及逆反射功率占比
Fig. 10. Reflection characteristics of the metasurface with the maximum retroreflection ratio when the incident angle is adjusted: (a) The normalized bistatic RCS of the metasurface; (b) the retroreflection angle and retroreflection ratio under excitation of incident waves with different incident angle.
图 11 入射波频率偏差下的逆反射占比最大超表面反射特性 (a) 归一化双站RCS; (b) 负反射角度及逆反射功率占比
Fig. 11. Reflection characteristics of the metasurface with the maximum retroreflection ratio when the frequency of the incident wave is biased: (a) The normalized bistatic RCS of the designed metasurface; (b) the retroreflection angle and retroreflection ratio under excitation of incident waves with different frequencies.
-
[1] Kuga Y, Ishimaru A 1984 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨丹青, 王莉, 王新龙 2015 64 054301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang D Q, Wang L, Wang X L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 盛泉, 耿婧旎, 王爱华, 王盟, 齐岳, 刘俊杰, 付士杰, 史伟, 姚建铨 2023 72 044203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng Q, Geng J N, Wang A H, Wang M, Qi Y, Liu J J, Fu S J, Shi W, Yao J Q 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 044203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang R, Fan Y, Zhu W, Hu C, Chen S, Wei H, Chen W, Chang C T, Zhao Q, Zhou J, Zhang F, Qiu C W 2023 Laser Photonics Rev. 17 2200975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jin X, Holzman J F 2010 IEEE Sens. J. 10 1875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Vitaz J A, Buerkle A M, Sarabandi K 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58 3539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Deroba J C, Sobczak K D, Good A, Larimore Z, Mirotznik M 2019 IEEE Aero. El. Sys. Mag. 34 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim H, Lee B 2007 Opt. Eng. 46 094002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kadera P, Jimenez-Saez A, Burmeister T, Lacik J, Jakoby R 2020 IEEE Access 8 212765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chang C C, Chen T Y, Tsai J C 2016 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 28 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pon C Y 1964 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 12 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yan L, Shen Z 2020 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 19 736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu N, Genevet P, Kats M A, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Science 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hessel A, Schmoys J, Tseng D Y 1975 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 65 380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jull E V, Heath J W, Ebbeson G R 1977 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 67 557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ra'Di Y, Sounas D L, Alu A 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 067404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hoang T V, Lee C H, Lee J H 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 2451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wong A M H, Eleftheriades G V 2017 Phys. Rev. X 8 011036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wong A M H, Christian P, Eleftheriades G V 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 2892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lee S G, Lee J H 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 69 3588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tao C, Itoh T U 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 6193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Estakhri N M, Alù A 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 041008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang X C, Díaz-Rubio A, Li H, Tretyakov S A, Alù A 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 13 044040
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang X, Díaz-Rubio A, Tretyakov S A 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 024089
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Asadchy V S, Díaz-Rubio A, Tcvetkova S N, et al. 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 031046
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3883
- PDF下载量: 168
- 被引次数: 0
















 下载:
下载: