-
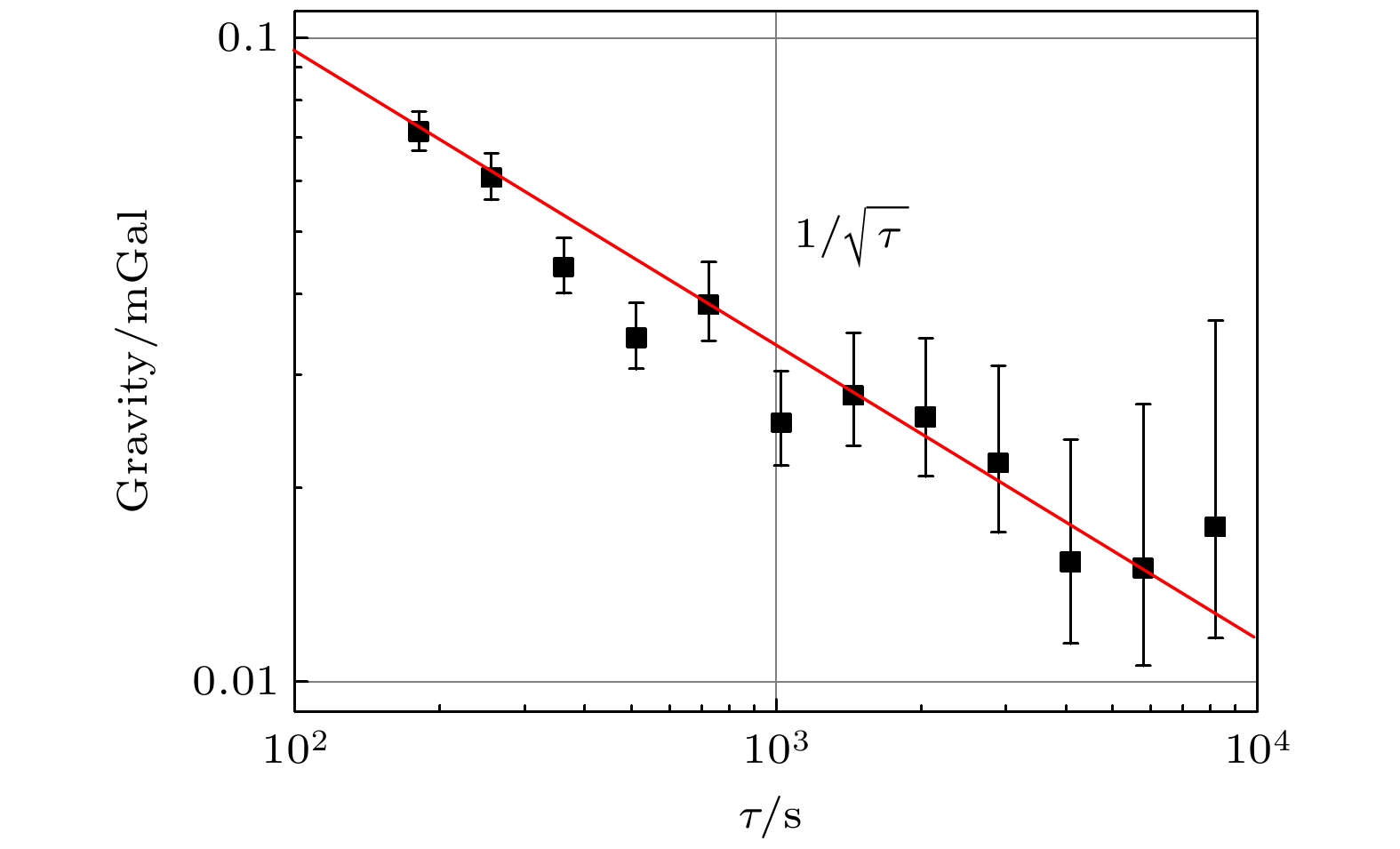
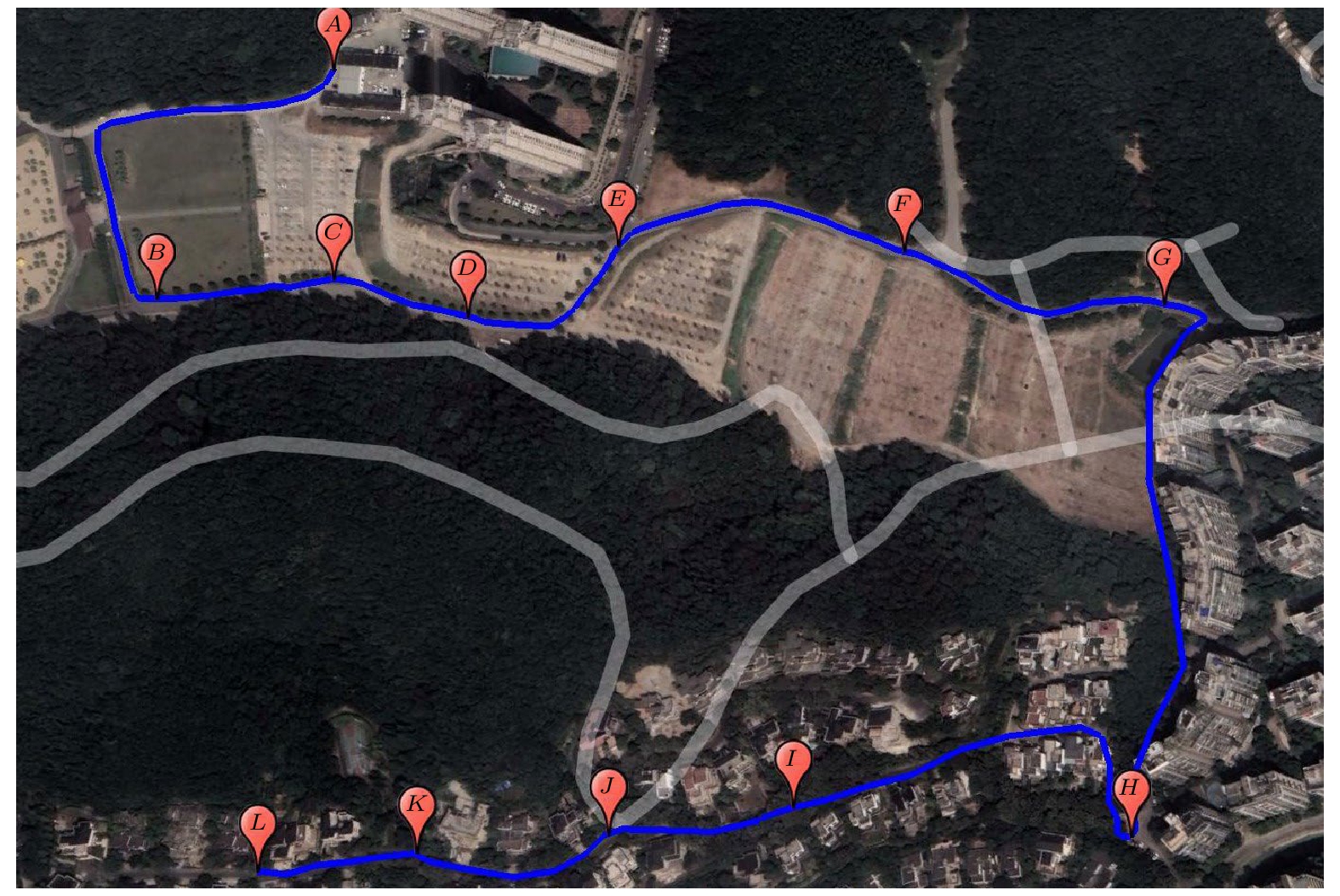
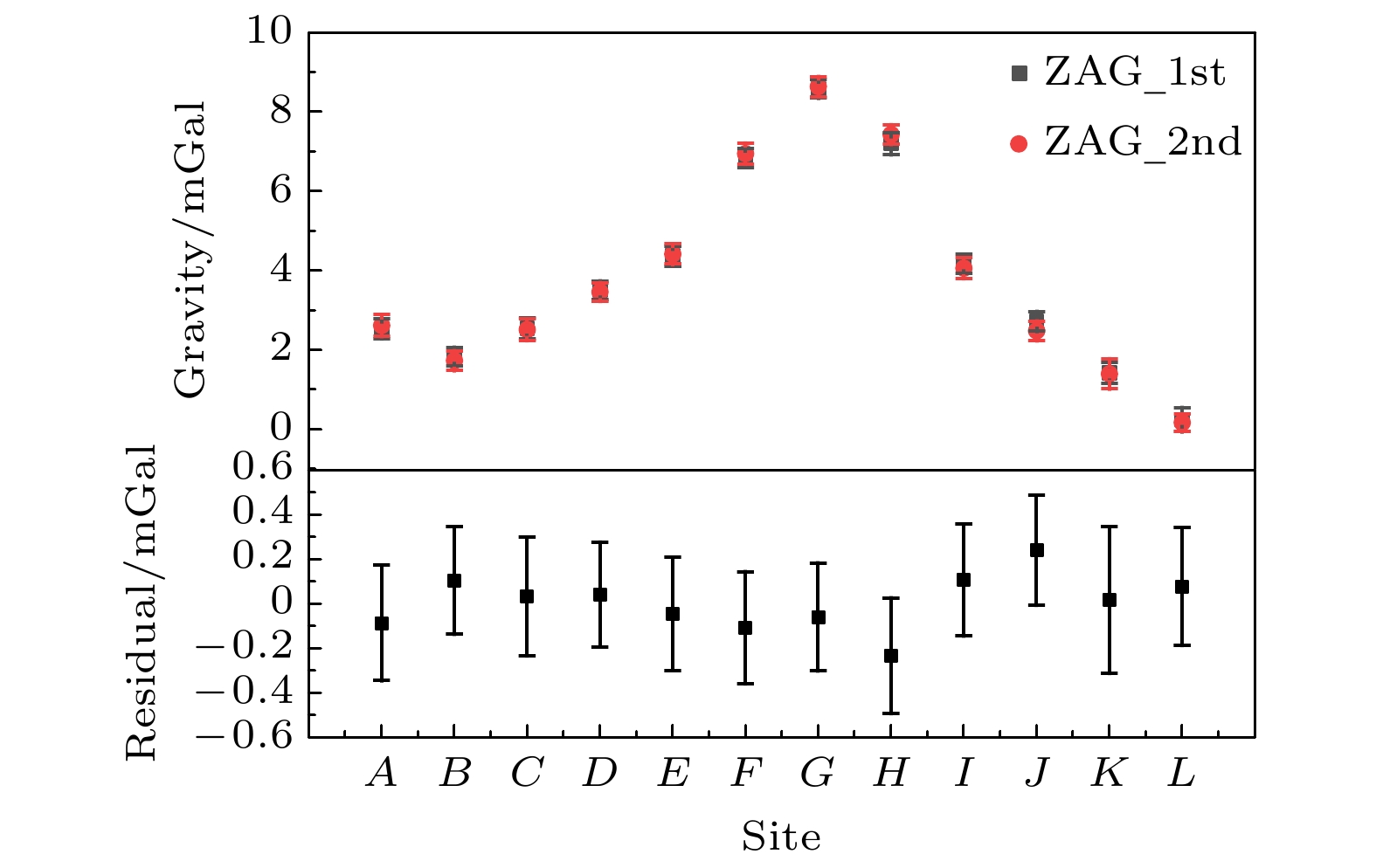
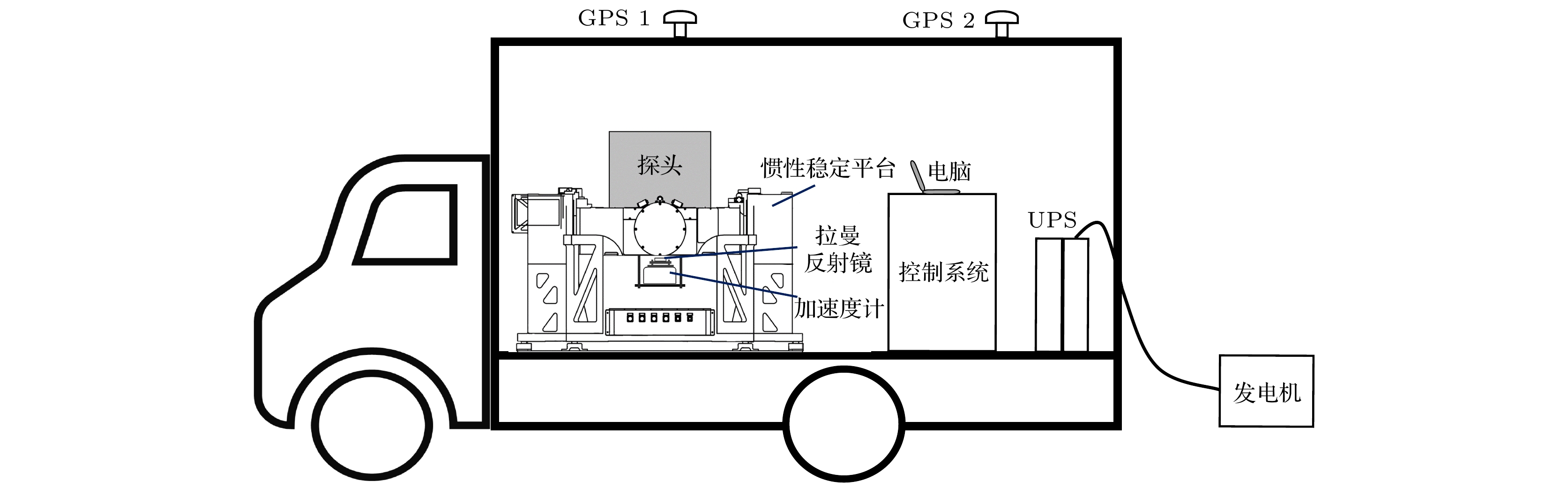
The information about Earth’s gravity field is an important basic information necessarily for geodesy, geophysics, geodynamics and other disciplines. The mapping of gravity field is an effective mean to obtain the gravity field information. Compared with the surveying of gravity field based on satellite, ship, and airplane, vehicle-mounted gravity mapping has advantages of strong flexibility, high spatial resolution and high accuracy. A short baseline or a small-scale gravity field mapping can be realized based on the combination of relative gravimeters and the high-precision absolute gravity reference point. However, this method is not suitable for the situation of a long baseline or a large-scale gravity field surveying due to the drift of relative gravimeter. In this work, a vehicle-mounted system for rapid surveying of the absolute gravity field is built up based on a miniaturized atomic gravimeter. The inner precision of the instrument is evaluated to be 0.123 mGal, and the outer precision is 0.112 mGal in a field test which contains 12 points for 3 km distance. Furthermore, with this system, the absolute gravity data are obatined within 2 min for adjusting and 5 min for measuring in downtown for each measured point. A rapid surveying of absolute gravity field for 19 points is carried out and the route covers 24 km. The inner precision of the instrument is evaluated to be 0.162 mGal, and the outer precision is 0.169 mGal. Finally, the free-air gravity anomalies obtained from the measured data of atomic gravimeter and the fitting results of satellite gravity model are analyzed, and it is found that the trends of changing are basically consistent with each other. This paper provides a new proposal for the rapid surveying of the absolute gravity field.
-
Keywords:
- cold atomic gravimeter /
- absolute gravity survey /
- atomic interference
[1] Van Camp M, De Viron O, Watlet A, Meurers B, Francis O, Caudron C 2017 Rev. Geophys. 55 938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Peters A, Chung K Y, Chu S 1999 Nature 400 849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kasevich M, Chu S 1992 Appl. Phys. B 54 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu Z K, Sun B L, Duan X C, Zhou M K, Chen L L, Zhan S, Zhang Q Z, Luo J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 043610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Freier C, Hauth M, Schkolnik V, Leykauf B, Schilling M, Wziontek H, Scherneck H G, Muller J, Peters A 2016 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 723 012050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu B, Wang Z Y, Cheng B, Wang Q Y, Xu A P, Lin Q 2014 Metrologia 51 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Le Gouët J, Mehlstäubler T E, Kim J, Merlet S, Clairon A, Landragin A, Pereira Dos Santos F 2008 Appl. Phys. B 92 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Peters A, Chung K Y, Chu S 2001 Metrologia 38 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hauth M, Freier C, Schkolnik V, Senger A, Schmidt M, Peters A 2013 Appl. Phys. B 113 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schmidt M, Senger A, Hauth M, Freier C, Schkolnik V, Peters A 2011 Gyroscopy Navig. 2 170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bodart Q, Merlet S, Malossi N, Dos Santos F P, Bouyer P, Landragin A 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 96 134101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴彬, 程冰, 付志杰, 朱栋, 周寅, 翁堪兴, 王肖隆, 林强 2018 67 190302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu B, Cheng B, Fu Z J, Zhu D, Zhou Y, Weng K X, Wang X L, Lin Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 190302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wu X J, Zi F, Dudley J, Bilotta R J, Canoza P, Muller H 2017 Optica 4 1545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang X W, Zhong J Q, Tang B, Chen X, Zhu L, Huang P W, Wang J, Zhan M S 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 6545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Huang P W, Tang B, Chen X, Zhong J Q, Xiong Z Y, Zhou L, Wang J, Zhan M S 2019 Metrologia 56 045012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang S K, Zhao Y, Zhuang W, Li T C, Wu S Q, Feng J Y, Li C J 2018 Metrologia 55 360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Heine N, Matthias J, Sahelgozin M, Herr W, Abend S, Timmen L, Müller J, Rasel E M 2020 Eur. Phys. J. D 74 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen B, Long J, Xie H, Li C, Chen L, Jiang B, Chen S 2020 Chin. Opt. Lett. 18 090201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhu D, Zhou Y, Wu B, Weng K X, Wang K N, Cheng B, Lin Q 2021 Appl. Opt. 60 7910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gillot P, Francis O, Landragin A, Dos Santos F P, Merlet S 2014 Metrologia 51 L15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fu Z J, Wu B, Cheng B, Zhou Y, Weng K X, Zhu D, Wang Z Y, Lin Q 2019 Metrologia 56 025001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bidel Y, Carraz O, Charriere R, Cadoret M, Zahzam N, Bresson A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 144107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 程冰, 周寅, 陈佩军, 张凯军, 朱栋, 王凯楠, 翁堪兴, 王河林, 彭树萍, 王肖隆, 吴彬, 林强 2021 70 040304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng B, Zhou Y, Chen P J, Zhang K J, Zhu D, Wang K N, Weng K X, Wang H L, Peng S P, Wang X L, Wu B, Lin Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu X J, Pagel Z, Malek B S, Nguyen T H, Zi F, Scheirer D S, Muller H 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 eaax0800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bidel Y, Zahzam N, Bresson A, Blanchard C, Cadoret M, Olesen A V, Forsberg R 2020 J. Geod. 94 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Bidel Y, Zahzam N, Blanchard C, Bonnin A, Cadoret M, Bresson A, Rouxel D, Lequentrec-Lalancette M F 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang J Y, Xu W J, Sun S D, Shu Y B, Luo Q, Cheng Y, Hu Z K, Zhou M K 2021 AIP Adv. 11 115223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Guo J, Ma S, Zhou C, Liu J, Wang B, Pan D, Mao H 2021 Preprints 202111.0255.v1
[29] 吴彬, 周寅, 程冰, 朱栋, 王凯楠, 朱欣欣, 陈佩军, 翁堪兴, 杨秋海, 林佳宏, 张凯军, 王河林, 林强 2020 69 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu B, Zhou Y, Cheng B, Zhu D, Wang K N, Zhu X X, Chen P J, Weng K X, Yang Q H, Lin J H, Zhang K J, Wang H L, Lin Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
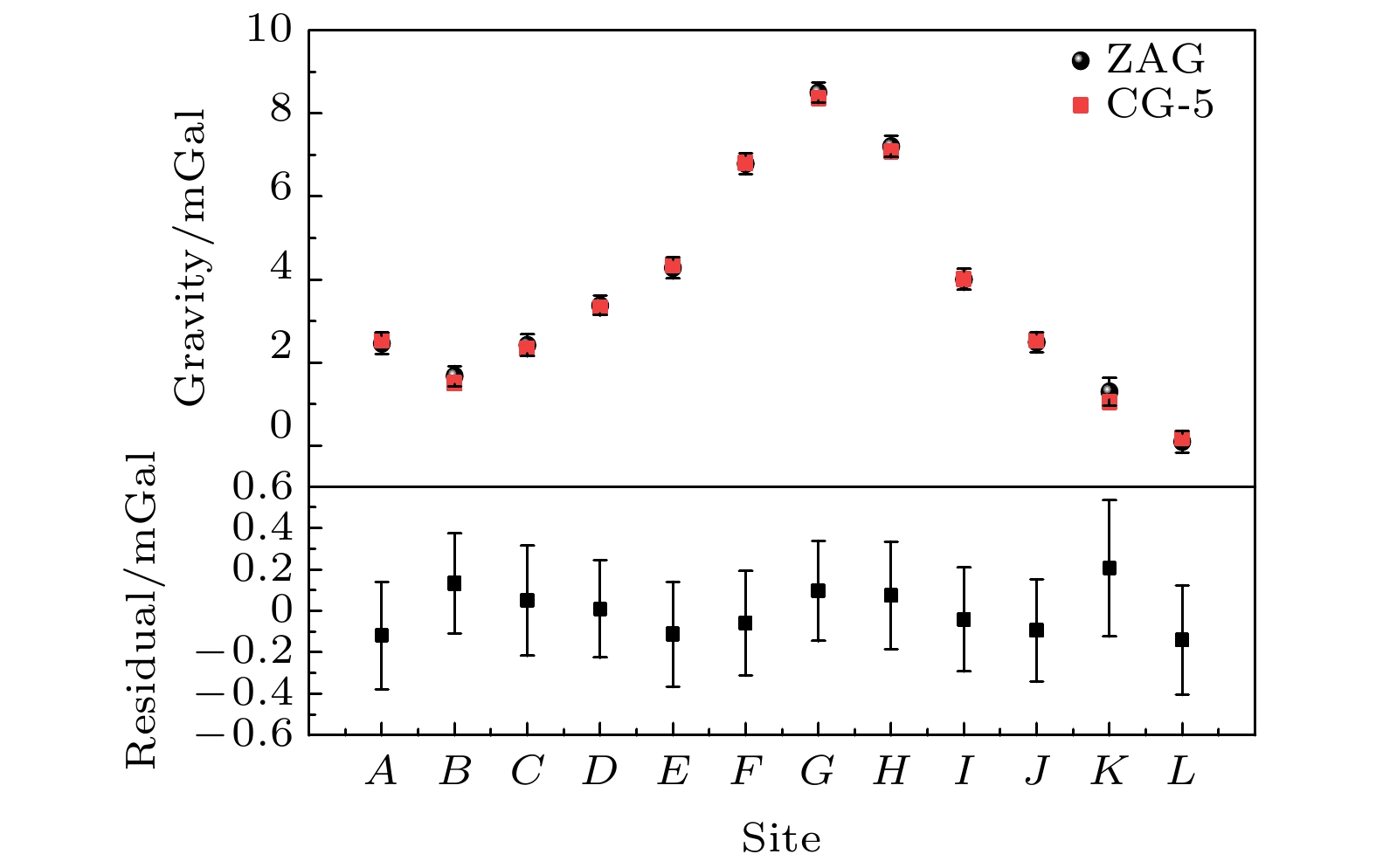
图 7 在杭州宝寿山由原子重力仪与CG-5相对重力仪测绘的数据及两者的残差数据. 图中黑点为原子重力仪两次测绘结果的平均值, 红点为相对重力仪两次测绘结果的平均值
Figure 7. Gravity data surveyed by atomic gravimeter and relative gravimeter of CG-5 on Baoshou Mountain in Hangzhou city and the residuals data between them. The black dots and red dots are the average values of measured gravity data of two repeated lines with atomic gravimeter and relative gravimeter CG-5, respectively.
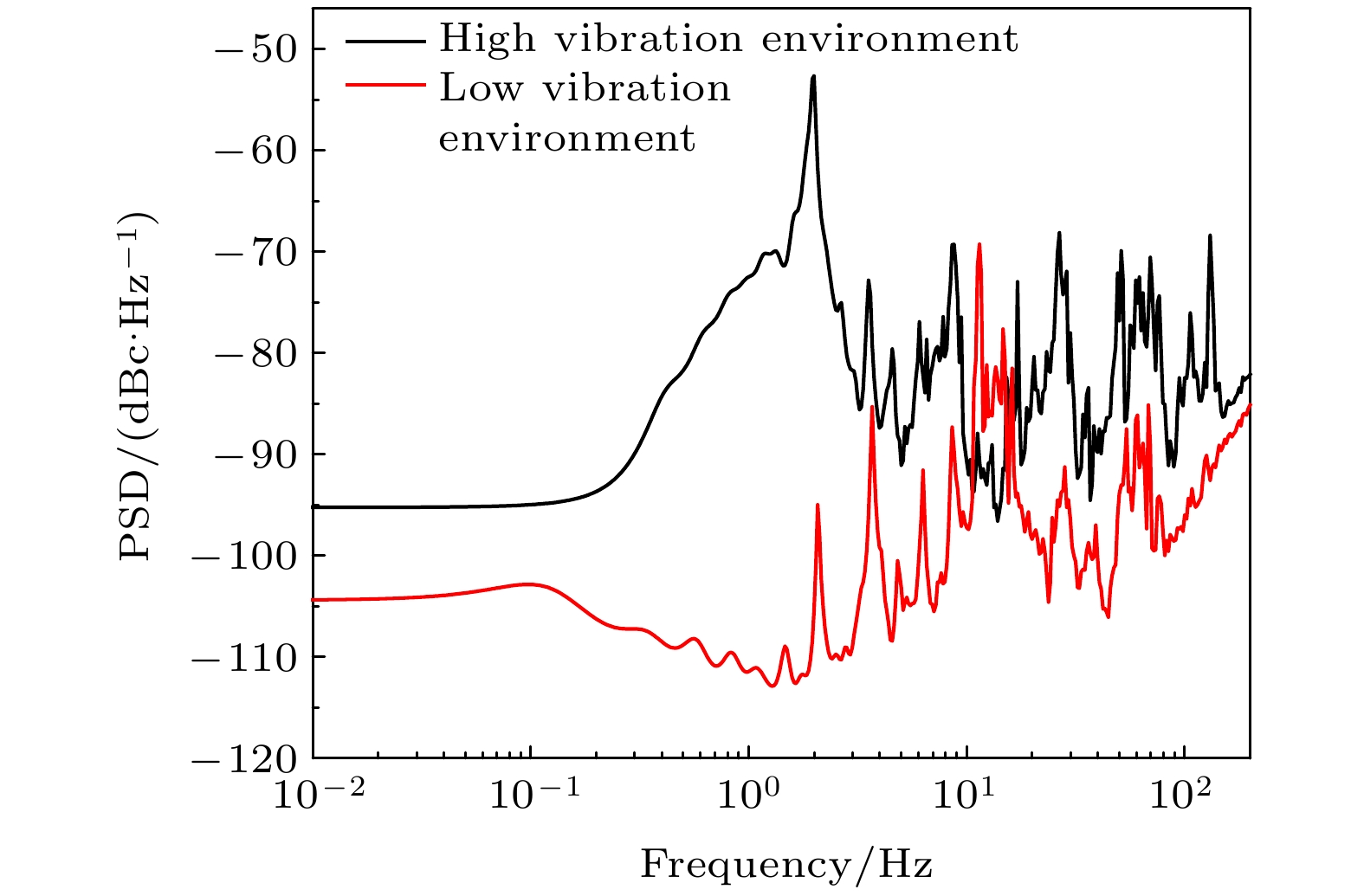
图 10 高振动噪声环境下由原子重力仪与相对重力仪CG-5测绘的数据及两者的残差数据, 图中黑点为原子重力仪两次测绘结果的平均值, 红点为相对重力仪三次测绘结果的平均值
Figure 10. Gravity data surveyed by atomic gravimeter and relative gravimeter of CG-5 in the environment of high vibration noise and the residuals data between them. The black dots and red dots are the average values of measured gravity data of two repeated lines with atomic gravimeter and three repeated lines with relative gravimeter CG-5, respectively.
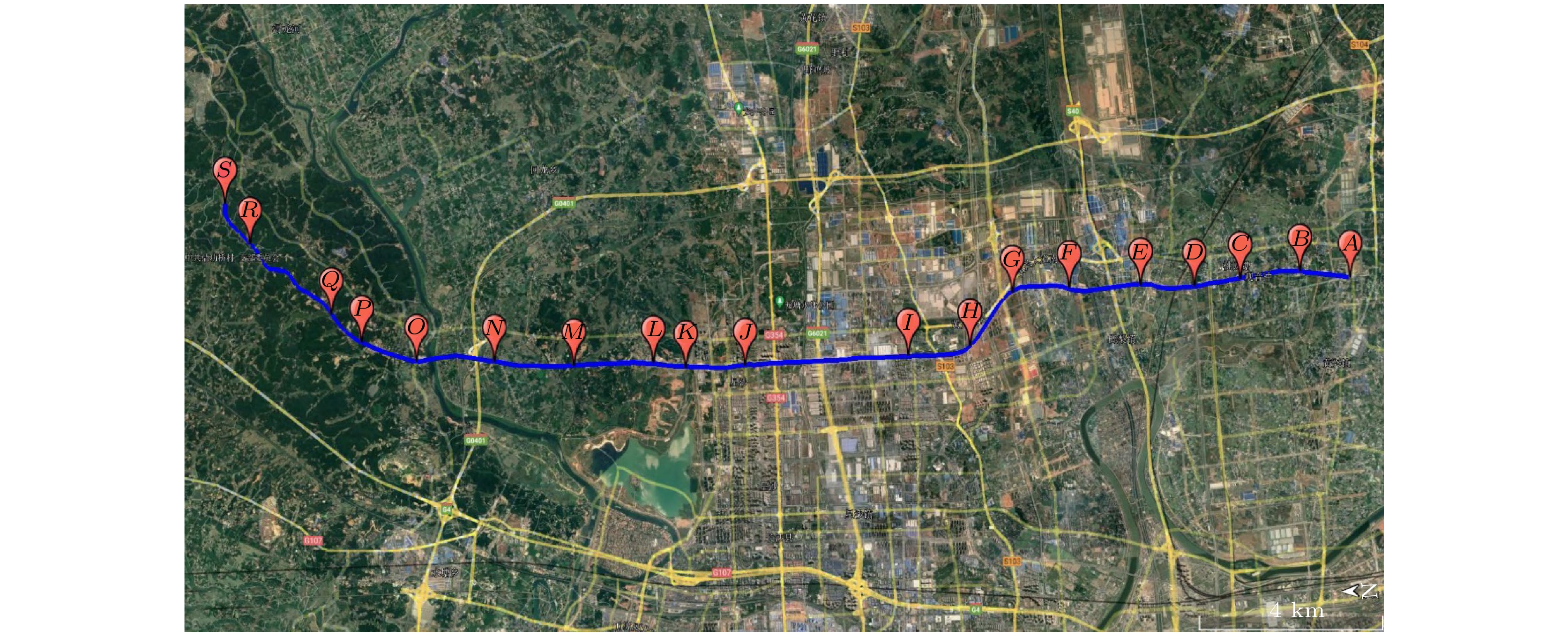
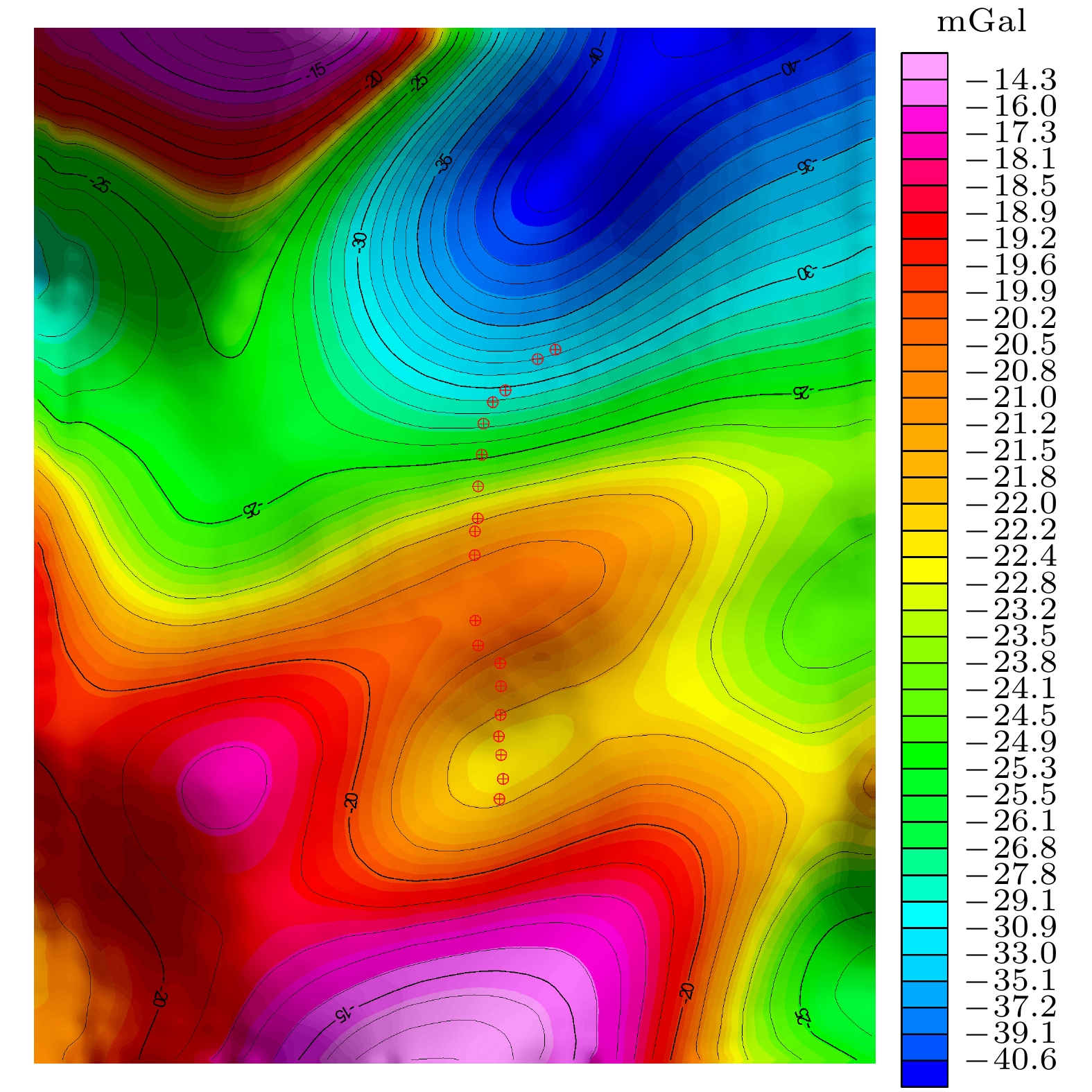
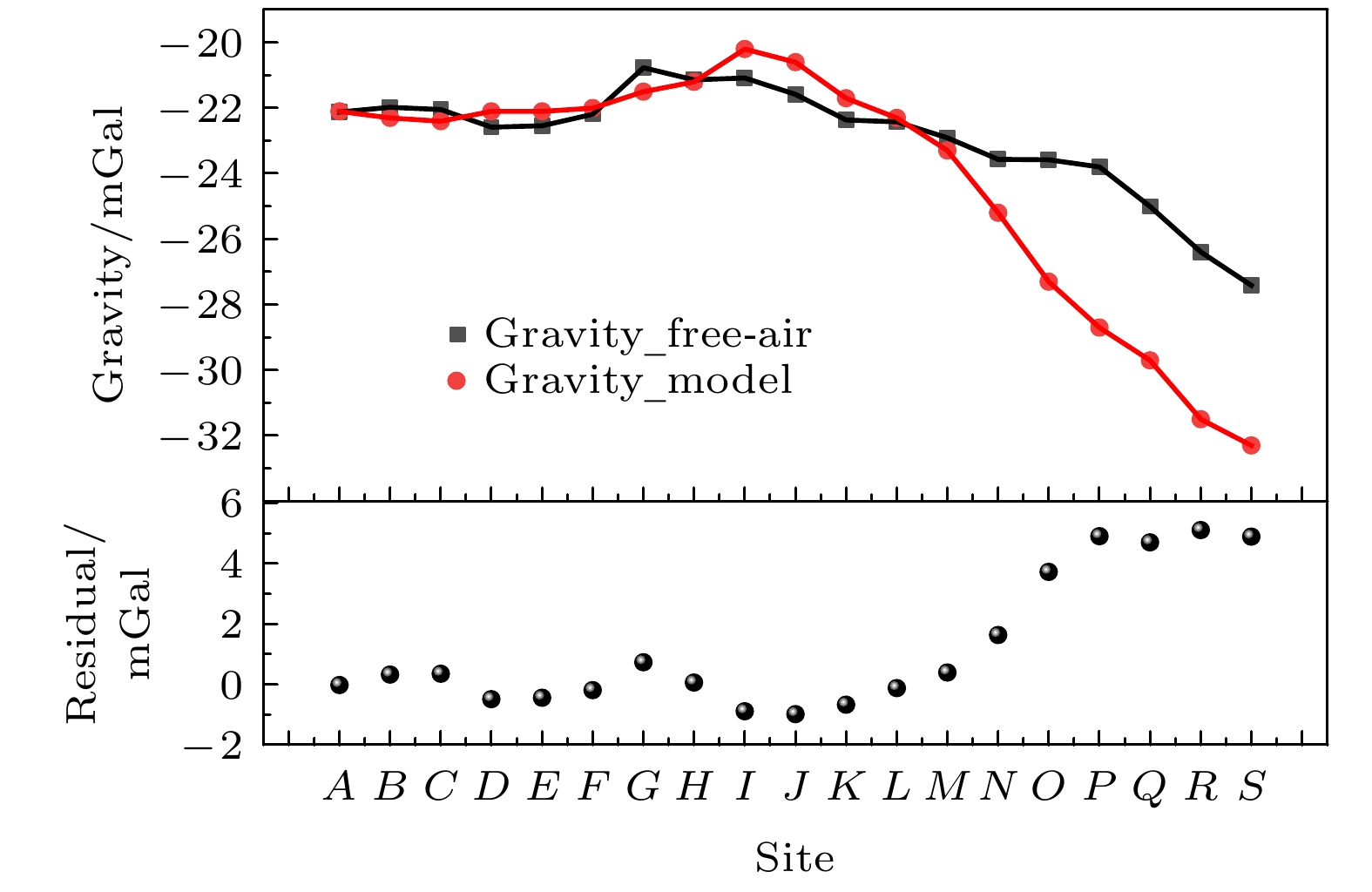
图 13 实测与模型计算的自由空间重力异常数据及其残差, 图中红色点为由卫星重力模型拟合获取的测点自由空间重力异常, 黑色点为原子重力仪测量值改正后的测点自由空间重力异常
Figure 13. Free-air gravity anomalies obtained by the measured data with atomic gravimeter and the fitting of gravity model and the residual date between them. The black and red dots are the results acquired by atomic gravimeter and the theoretical model, respectively.
表 1 车载快速绝对重力测量系统B类不确定度表
Table 1. Class B uncertainty table for vehicle-mounted rapid absolute gravimetry system
项目 修正量/μGal 不确定度/μGal 科里奥利力效应 39.00 3.06 双光子频移 –13.23 2.52 激光波长 –5.50 1.10 参考频率 0.00 1.00 射频相移 –131.47 10.81 自引力效应 –2.70 0.10 残余边带 –241.56 103.00 其他修正量 0.17 2.00 合成结果 –355.29 103.61 -
[1] Van Camp M, De Viron O, Watlet A, Meurers B, Francis O, Caudron C 2017 Rev. Geophys. 55 938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Peters A, Chung K Y, Chu S 1999 Nature 400 849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kasevich M, Chu S 1992 Appl. Phys. B 54 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu Z K, Sun B L, Duan X C, Zhou M K, Chen L L, Zhan S, Zhang Q Z, Luo J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 043610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Freier C, Hauth M, Schkolnik V, Leykauf B, Schilling M, Wziontek H, Scherneck H G, Muller J, Peters A 2016 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 723 012050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu B, Wang Z Y, Cheng B, Wang Q Y, Xu A P, Lin Q 2014 Metrologia 51 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Le Gouët J, Mehlstäubler T E, Kim J, Merlet S, Clairon A, Landragin A, Pereira Dos Santos F 2008 Appl. Phys. B 92 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Peters A, Chung K Y, Chu S 2001 Metrologia 38 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hauth M, Freier C, Schkolnik V, Senger A, Schmidt M, Peters A 2013 Appl. Phys. B 113 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schmidt M, Senger A, Hauth M, Freier C, Schkolnik V, Peters A 2011 Gyroscopy Navig. 2 170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bodart Q, Merlet S, Malossi N, Dos Santos F P, Bouyer P, Landragin A 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 96 134101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴彬, 程冰, 付志杰, 朱栋, 周寅, 翁堪兴, 王肖隆, 林强 2018 67 190302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu B, Cheng B, Fu Z J, Zhu D, Zhou Y, Weng K X, Wang X L, Lin Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 190302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wu X J, Zi F, Dudley J, Bilotta R J, Canoza P, Muller H 2017 Optica 4 1545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang X W, Zhong J Q, Tang B, Chen X, Zhu L, Huang P W, Wang J, Zhan M S 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 6545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Huang P W, Tang B, Chen X, Zhong J Q, Xiong Z Y, Zhou L, Wang J, Zhan M S 2019 Metrologia 56 045012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang S K, Zhao Y, Zhuang W, Li T C, Wu S Q, Feng J Y, Li C J 2018 Metrologia 55 360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Heine N, Matthias J, Sahelgozin M, Herr W, Abend S, Timmen L, Müller J, Rasel E M 2020 Eur. Phys. J. D 74 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen B, Long J, Xie H, Li C, Chen L, Jiang B, Chen S 2020 Chin. Opt. Lett. 18 090201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhu D, Zhou Y, Wu B, Weng K X, Wang K N, Cheng B, Lin Q 2021 Appl. Opt. 60 7910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gillot P, Francis O, Landragin A, Dos Santos F P, Merlet S 2014 Metrologia 51 L15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fu Z J, Wu B, Cheng B, Zhou Y, Weng K X, Zhu D, Wang Z Y, Lin Q 2019 Metrologia 56 025001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bidel Y, Carraz O, Charriere R, Cadoret M, Zahzam N, Bresson A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 144107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 程冰, 周寅, 陈佩军, 张凯军, 朱栋, 王凯楠, 翁堪兴, 王河林, 彭树萍, 王肖隆, 吴彬, 林强 2021 70 040304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng B, Zhou Y, Chen P J, Zhang K J, Zhu D, Wang K N, Weng K X, Wang H L, Peng S P, Wang X L, Wu B, Lin Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu X J, Pagel Z, Malek B S, Nguyen T H, Zi F, Scheirer D S, Muller H 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 eaax0800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bidel Y, Zahzam N, Bresson A, Blanchard C, Cadoret M, Olesen A V, Forsberg R 2020 J. Geod. 94 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Bidel Y, Zahzam N, Blanchard C, Bonnin A, Cadoret M, Bresson A, Rouxel D, Lequentrec-Lalancette M F 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang J Y, Xu W J, Sun S D, Shu Y B, Luo Q, Cheng Y, Hu Z K, Zhou M K 2021 AIP Adv. 11 115223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Guo J, Ma S, Zhou C, Liu J, Wang B, Pan D, Mao H 2021 Preprints 202111.0255.v1
[29] 吴彬, 周寅, 程冰, 朱栋, 王凯楠, 朱欣欣, 陈佩军, 翁堪兴, 杨秋海, 林佳宏, 张凯军, 王河林, 林强 2020 69 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu B, Zhou Y, Cheng B, Zhu D, Wang K N, Zhu X X, Chen P J, Weng K X, Yang Q H, Lin J H, Zhang K J, Wang H L, Lin Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8624
- PDF Downloads: 161
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: