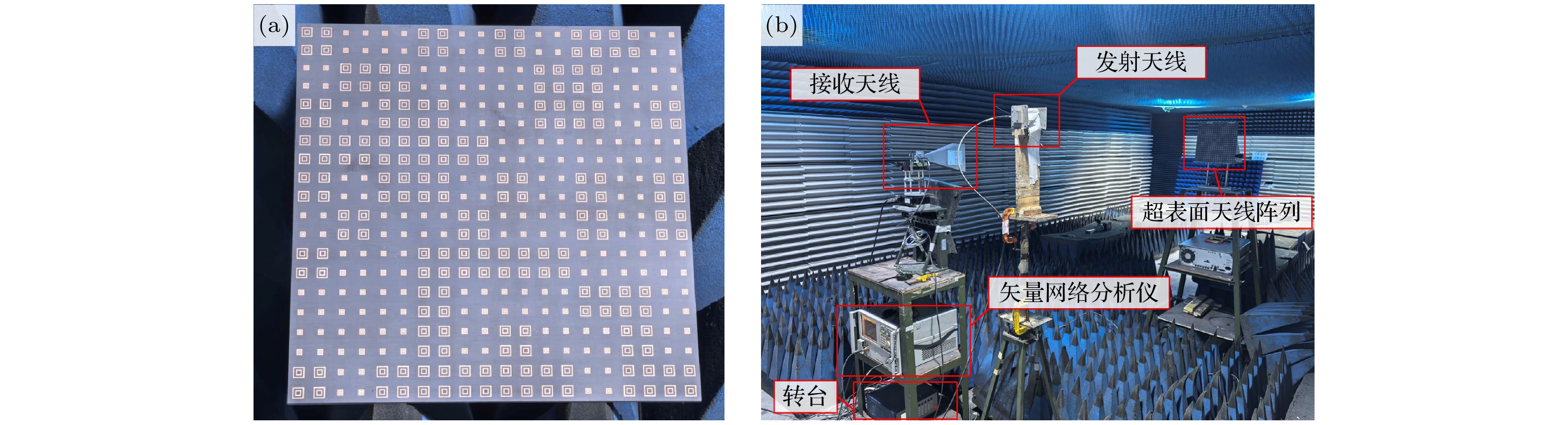
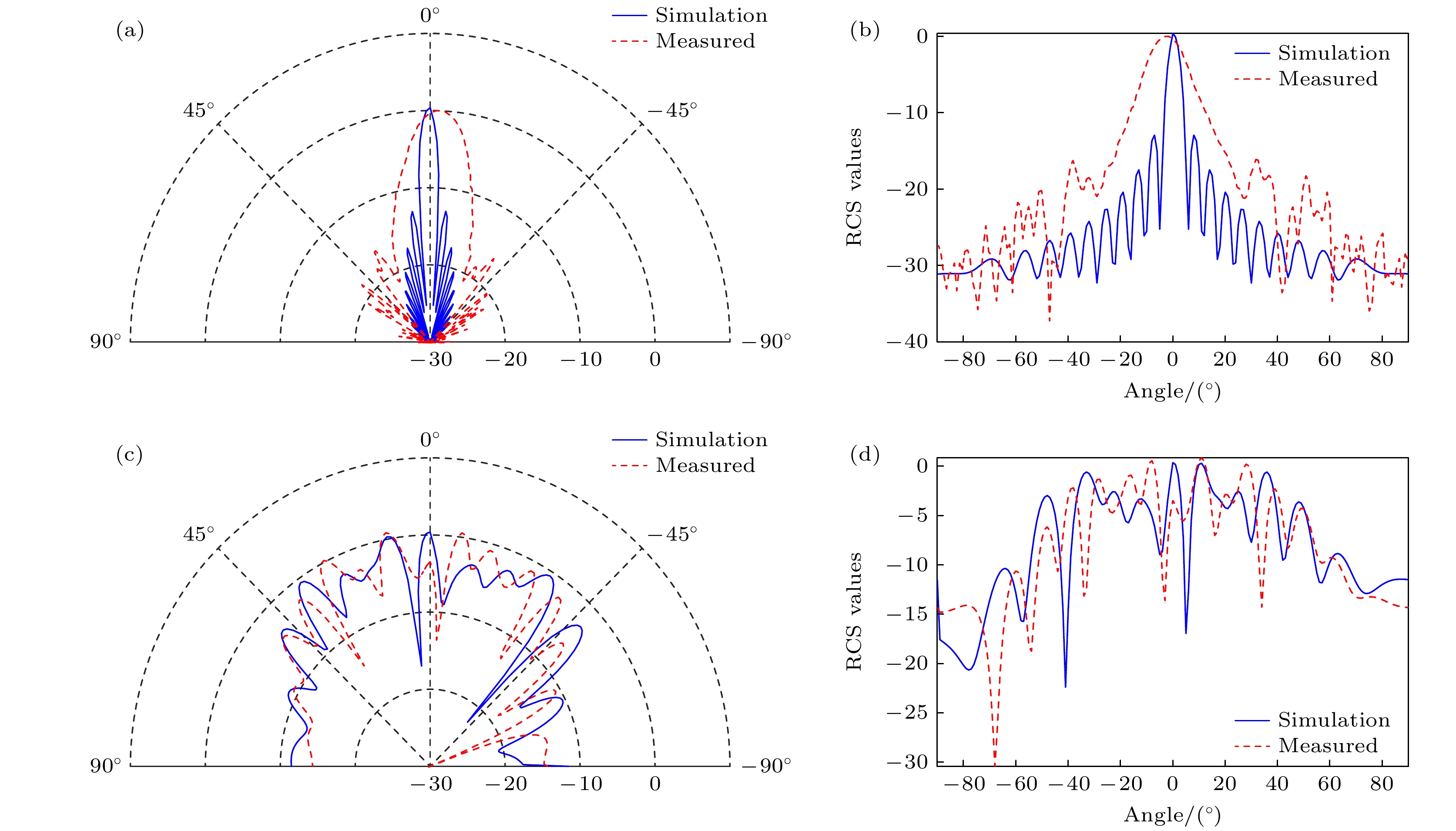
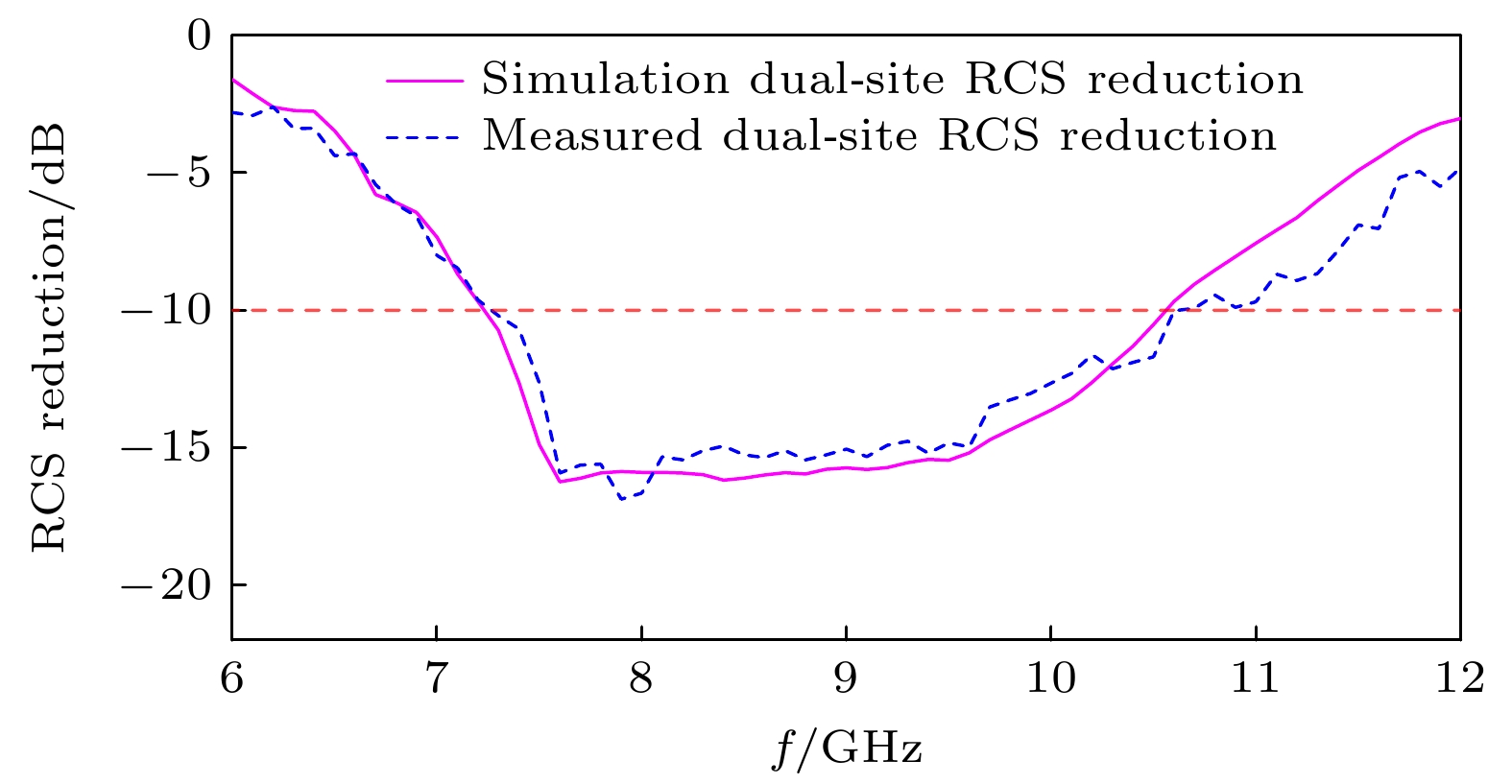
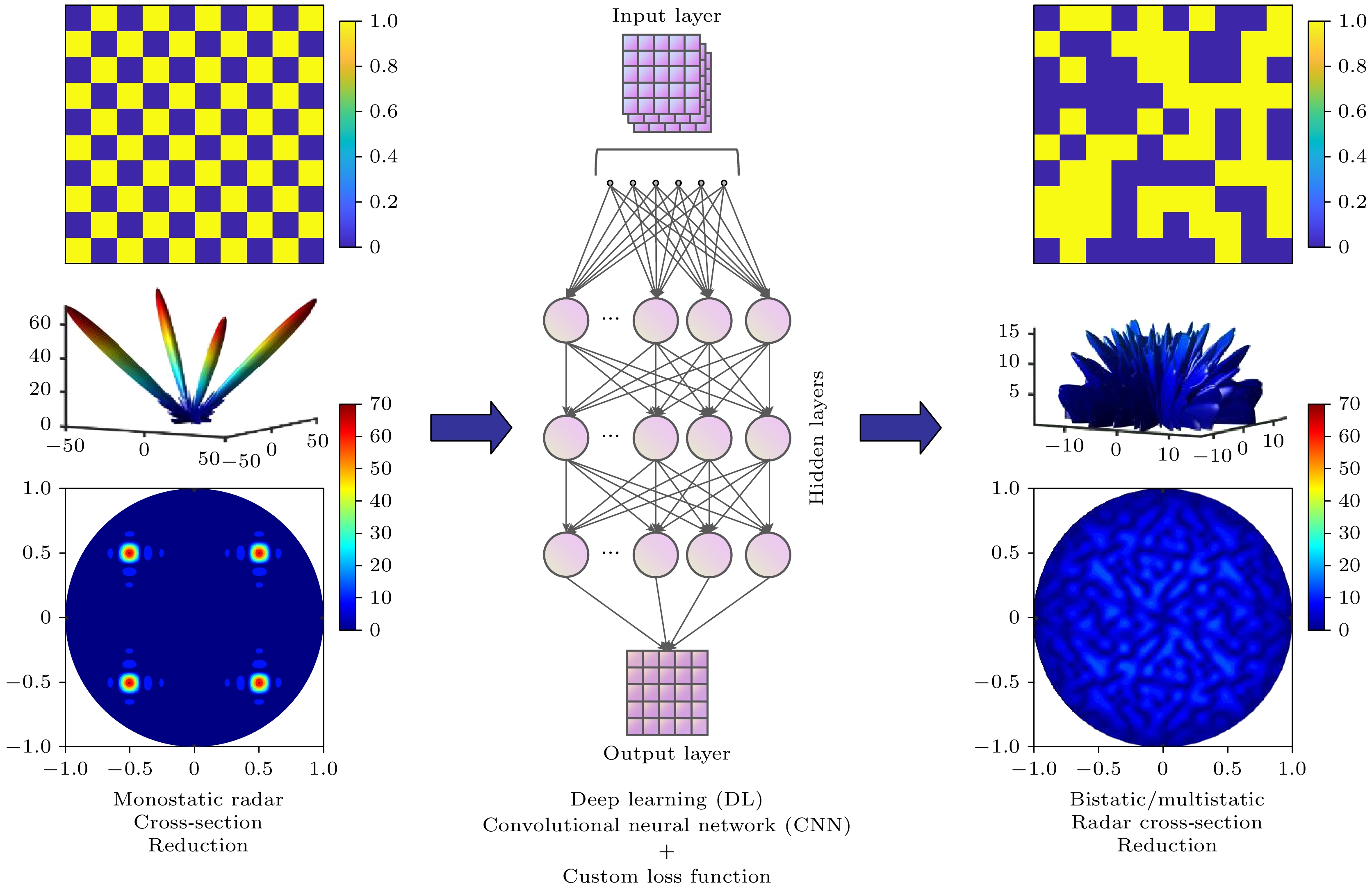
-
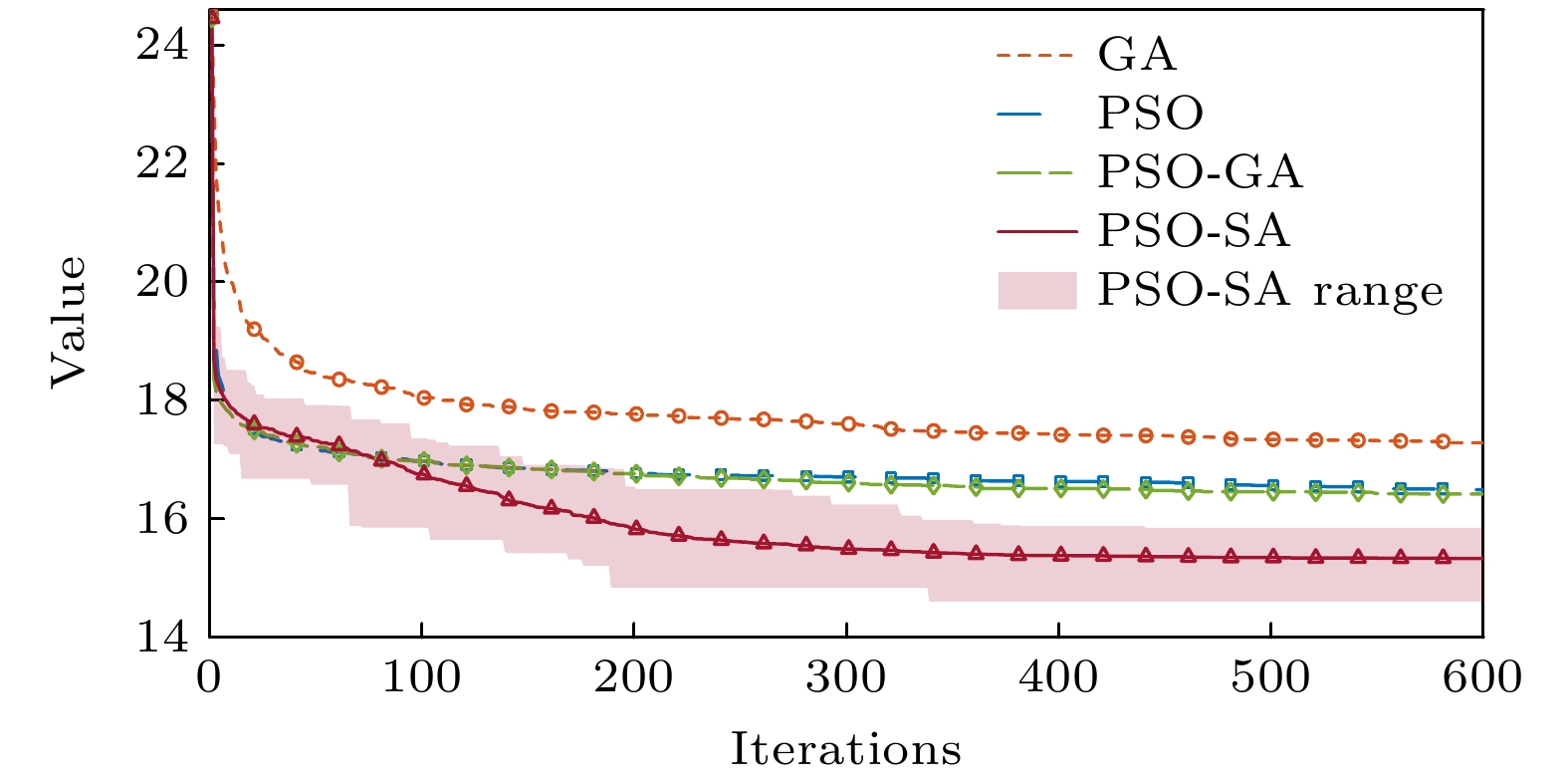
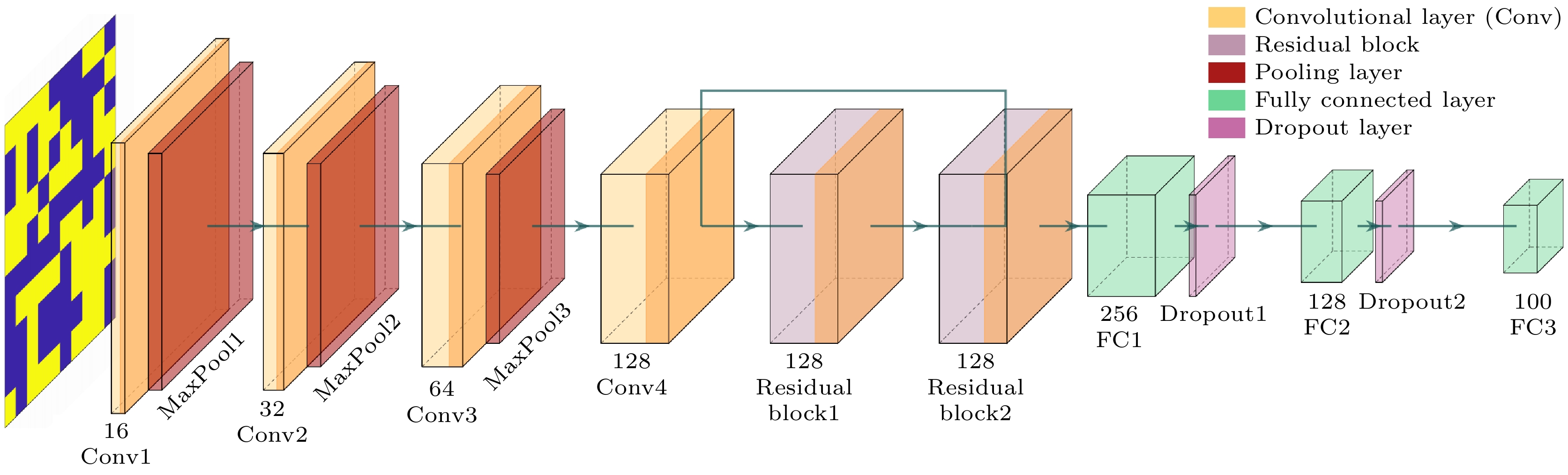
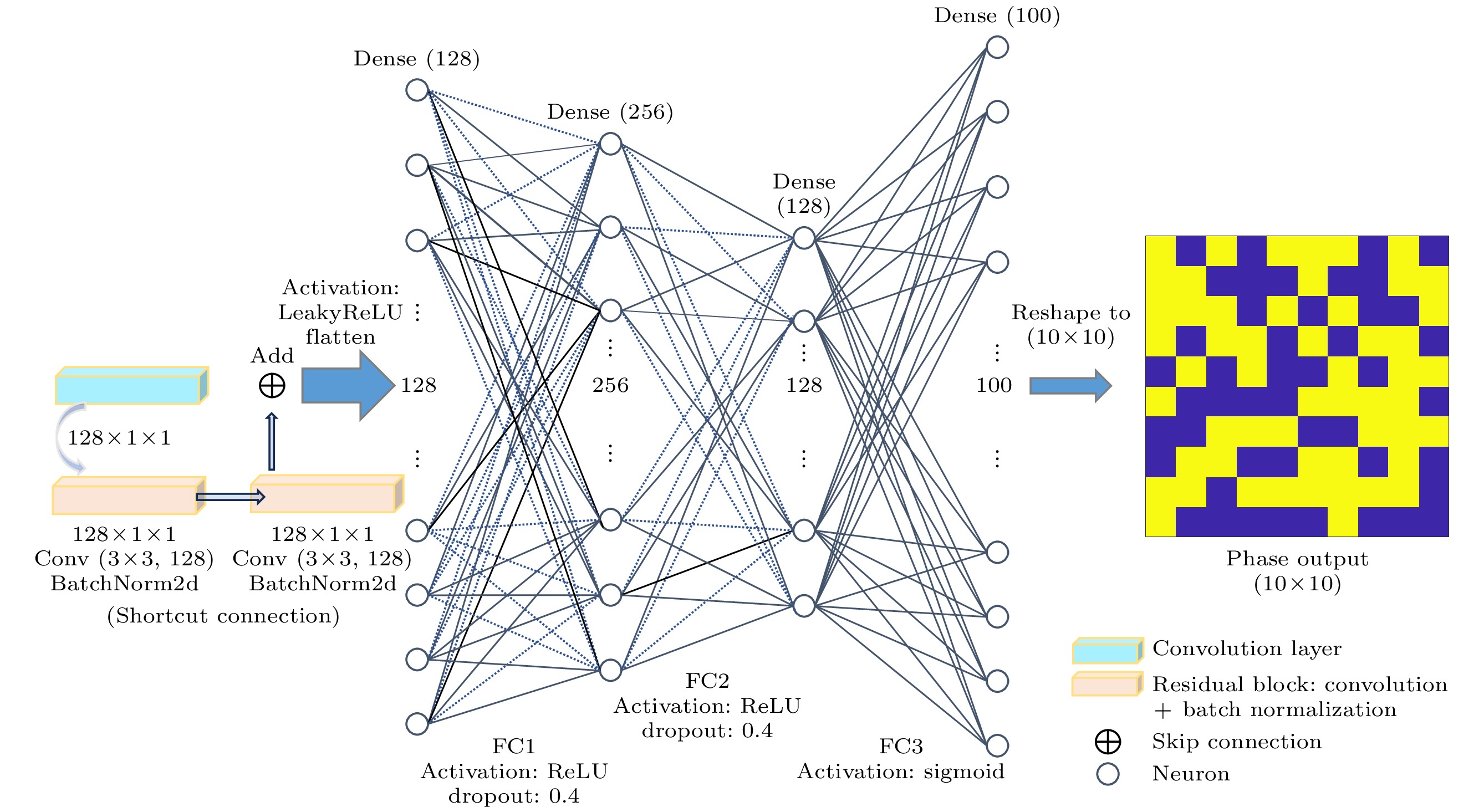
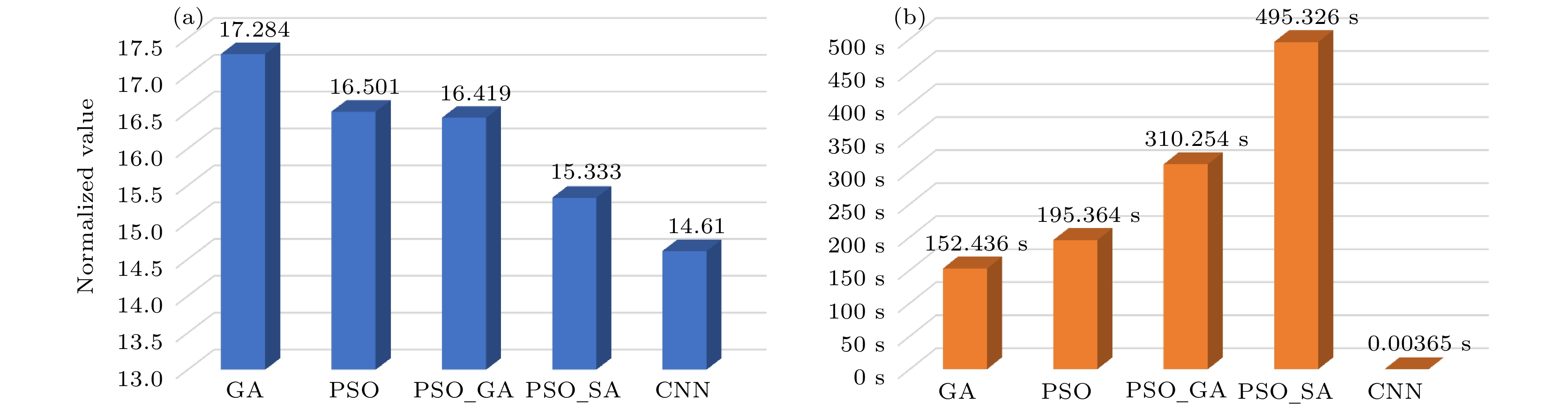
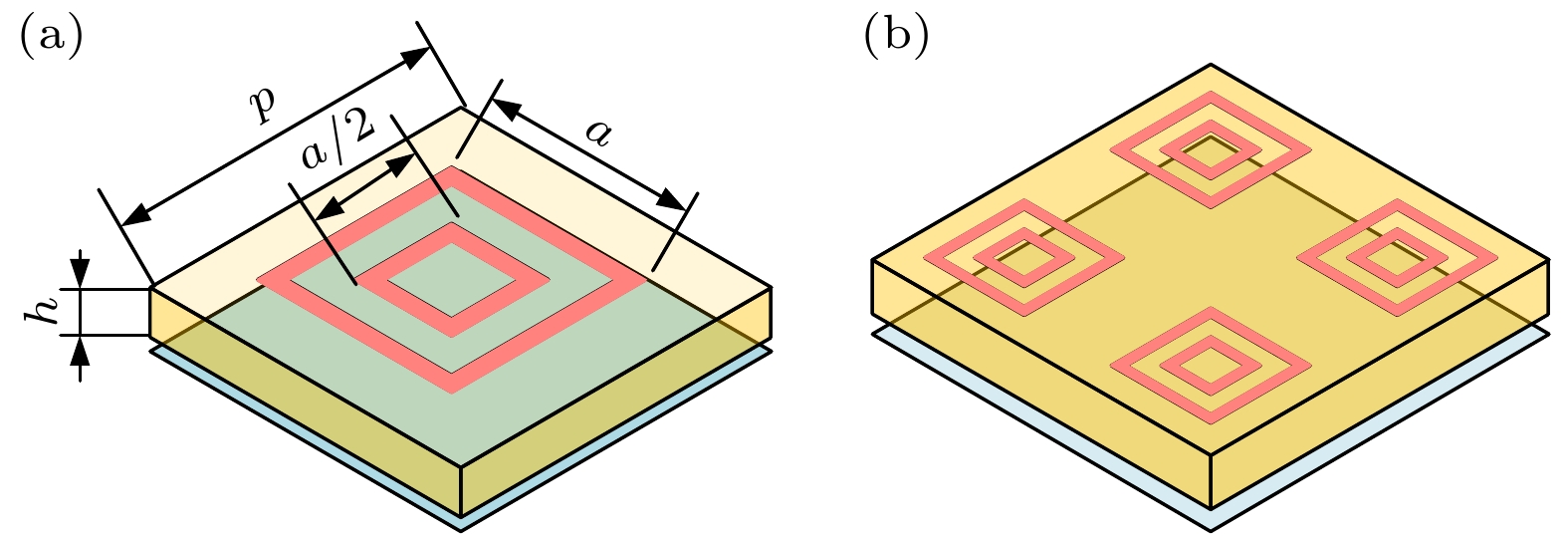
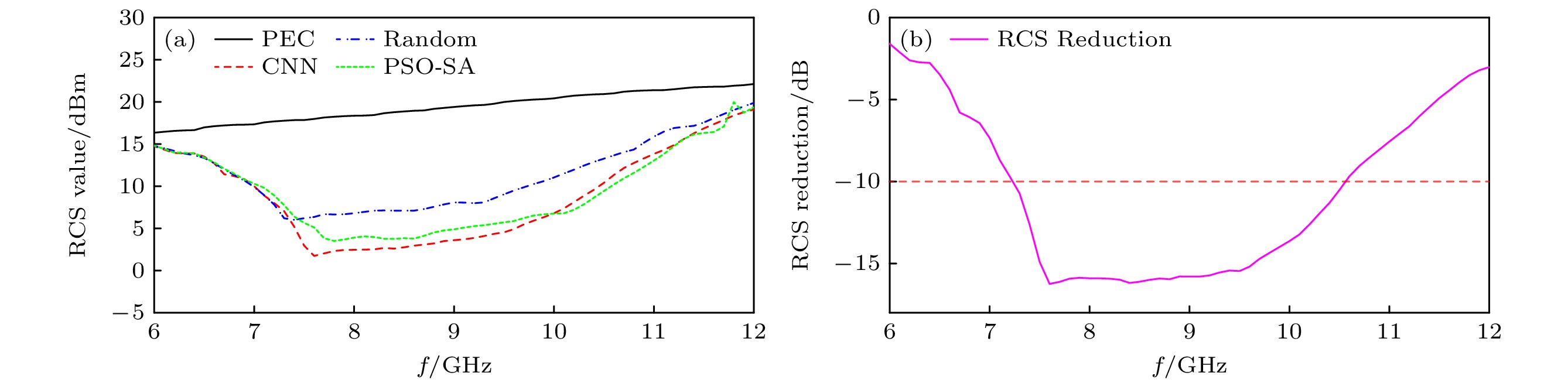
Radar cross section (RCS), a crucial physical quantity that characterizes the backscattering intensity of targets under radar illumination, is the primary metric for assessing stealth capabilities. With the development of radar detection technologies, RCS reduction has become a forefront research topic in radar stealth, aiming to minimize target detectability. With the maturity of radar networking technology, the bistatic radar RCS reduction is becoming increasingly important in future electromagnetic stealth countermeasures compared with the monostatic radar RCS reduction. Artificial electromagnetic metasurfaces have introduced innovative technical approaches for realizing the bistatic radar RCS reduction. However, current metasurface designs still face challenges related to inefficiency and suboptimal performance, mainly due to the time-consuming nature of large-scale array optimization and the global extremum characteristics of bistatic radar RCS reduction. To overcome these limitations, this study proposes a few-shot convolutional neural network (CNN)-based approach, which achieves uniform full-space radar echo scattering by directionally optimizing metasurface phase distributions, thereby enabling effective bistatic radar RCS reduction. This approach integrates convolutional feature extraction, residual enhancement, and fully connected optimization modules with a customized loss function to efficiently capture the complex multidimensional relationships between diffuse reflection phases and the full-space RCS extrema. Theoretical calculations, full-wave simulations, and experimental tests show that the metasurface designed with this approach can achieve over 10 dB of Bistatic Radar RCS reduction in a frequency range from 7.26 GHz to 10.74 GHz. The method also ensures uniform diffuse reflection across the full space for various incidence angles (30°, 45°, 60°). Compared with traditional optimization algorithms, this method enhances RCS reduction by 17.2% while significantly improving computational efficiency. This approach provides a promising new technical paradigm for achieving full-space electromagnetic stealth in advanced weapon systems.
[1] Rao G A, Mahulikar S P 2002 Aeronaut. J. 106 629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ball R E, Albrecht R S, Horne R L 2003 The Fundamentals of Aircraft Combat Survivability: Analysis and Design (2nd Ed.) (Reston: AIAA) pp8–56
[3] Westwick P 2019 Stealth: The Secret Contest to Invent Invisible Aircraft (Oxford: Oxford University Press) pp5–42
[4] Singh H, Antony S, Jha R M 2016 Plasma-based Radar Cross Section Reduction (Singapore: Springer) pp1–46
[5] Knott E F 2012 Radar Cross Section Measurements (New York: Springer) pp12–36
[6] Knott E F, Schaeffer J R, Tuley M T 2004 Radar Cross Section (2nd Ed.) (Reston: SciTech Publishing) pp4–22
[7] Kim S H, Lee S Y, Zhang Y, Park S J, Gu J 2023 Adv. Sci. 10 2303104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ananth P B, Abhiram N, Krishna K H, Nisha M S 2021 Mater. Today Proc. 47 4872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ye D, Wang Z, Xu K, Li H, Huangfu J, Wang Z, Ran L 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 187402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang J, Yang R, Ma R, Tian J, Zhang W 2020 IEEE Access 8 105815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu Y, Zhao X 2014 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13 1473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yu N, Genevet P, Kats Ma, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Science 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gao X, Han X, Cao W P, Li H O, Ma H F, Cui T J 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 3522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Abdullah M, Koziel S 2022 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 70 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Paquay M, Iriarte J C, Ederra I, Gonzalo R, Maagt P de 2007 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 55 3630
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen W, Balanis C A, Birtcher C R 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 2636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sang D, Chen Q, Ding L, Guo M, Fu Y 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 2604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cui T J, Qi M Q, Wan X, Zhao J, Cheng Q 2014 Light Sci. Appl. 3 e218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu X, Gao J, Xu L, Cao X, Zhao Y, Li S 2016 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fu C, Han L, Liu C, Lu X, Sun Z 2021 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70 2352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li W, Huang N, Kang Y, Zou T, Ying Y, Yu J, Zheng J, Qiao L, Li J, Che S 2024 IEICE Electron. Express 21 20240246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Qi W J, Yu C, Du J L, Zhao Y J 2022 Int. J. RF Microwave Comput. Aided Eng. 32 23306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Koziel S, Abdullah M 2020 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 69 2028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tao S, Pan X T, Li M K, Xu S H, Yang F 2020 IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 10 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 杨欣雨 2023 硕士学位论文 (南京: 东南大学)
Yang X Y 2023 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Southeast University
[26] 袁方, 毛瑞棋, 高冕, 郑月军, 陈强, 付云起 2022 71 084102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan F, Mao R Q, Gao M, Chen Q, Fu Q Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 084102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yuan F, Wang G M, Xu H X, Cai T, Zou X J, Pang Z H 2017 EEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 3188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Han X M, Xu H J, Chang Y P, Lin M, Zhang W Y, Xin W 2020 IEEE Access 8 162313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhou Y, Cao X Y, Gao J, Li S, Liu X 2017 Electron. Lett. 53 1381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Katoch S, Chauhan S S, Kumar V 2021 Multimed. Tools Appl. 80 8091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang D S, Tan D P, Liu L 2018 Soft Comput. 22 387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pan X, Xue L, Lu Y, Sun N 2019 Multimed. Tools Appl. 78 29921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Dumoulin V, Visin F 2016 arXiv:1603.07285 [stat.ML]
[34] Xu B, Wang N Y, Chen T Q, Li M 2015 arXiv: 1505.00853 [cs.LG]
[35] Bjorck N, Gomes C P, Selman B, Weinberger K Q 2018 arXiv: 1806.02375 [cs.LG]
[36] Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R 2014 J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15 1929
[37] Dubey S R, Singh S K, Chaudhuri B B 2022 Neurocomputing 503 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhou P, Xie X, Lin Z, Yan S 2024 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 46 6486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Shi G, Zhang J, Li H, Wang C 2019 Neural Process. Lett. 50 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Al-Kababji A, Bensaali F, Dakua S P 2022 arXiv: 2202.06373 [cs.CV]
[41] Yuan F, Xu H X, Jia X Q, Wang G M, Fu Y Q 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 2463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
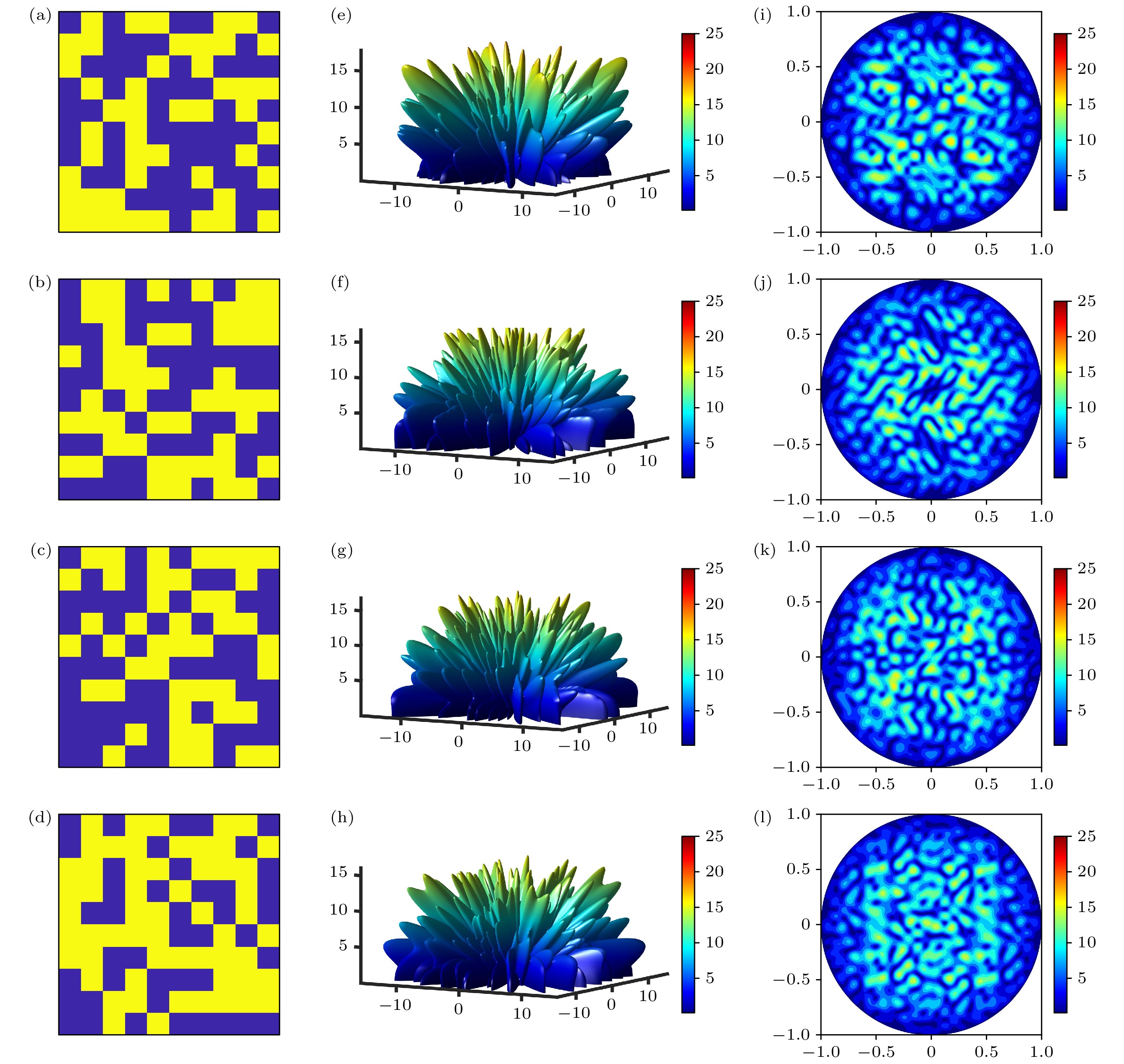
图 2 (a)—(d) GA, PSO, PSO-GA, PSO-SA优化后的相位分布; (e)—(h) 优化相位分布后的3D远场图; (i)—(l)优化相位分布后的2D远场图
Figure 2. (a)–(d) Phase distributions optimized by GA, PSO, PSO-GA, and PSO-SA; (e)–(h) 3D far-field patterns of the optimized phase distributions; (i)–(l) 2D far-field patterns of the optimized phase distributions
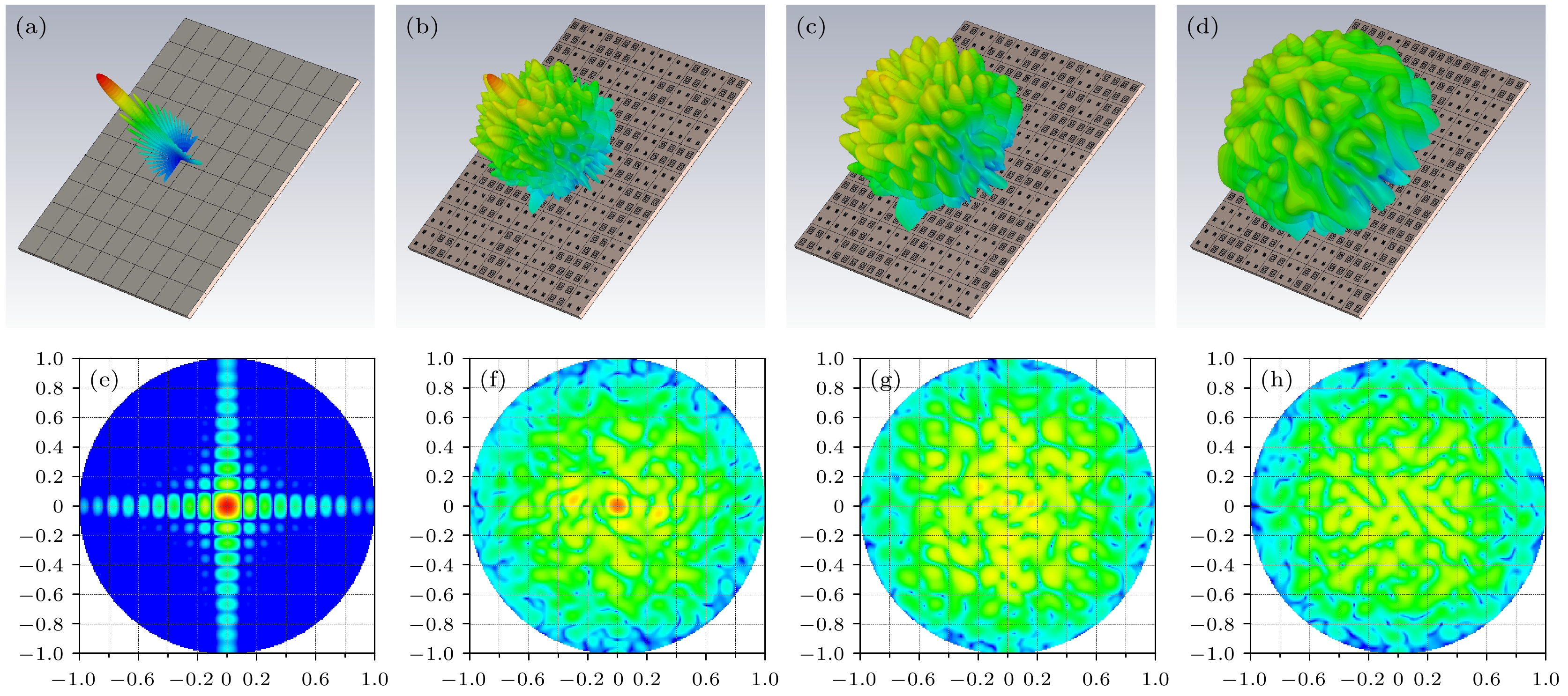
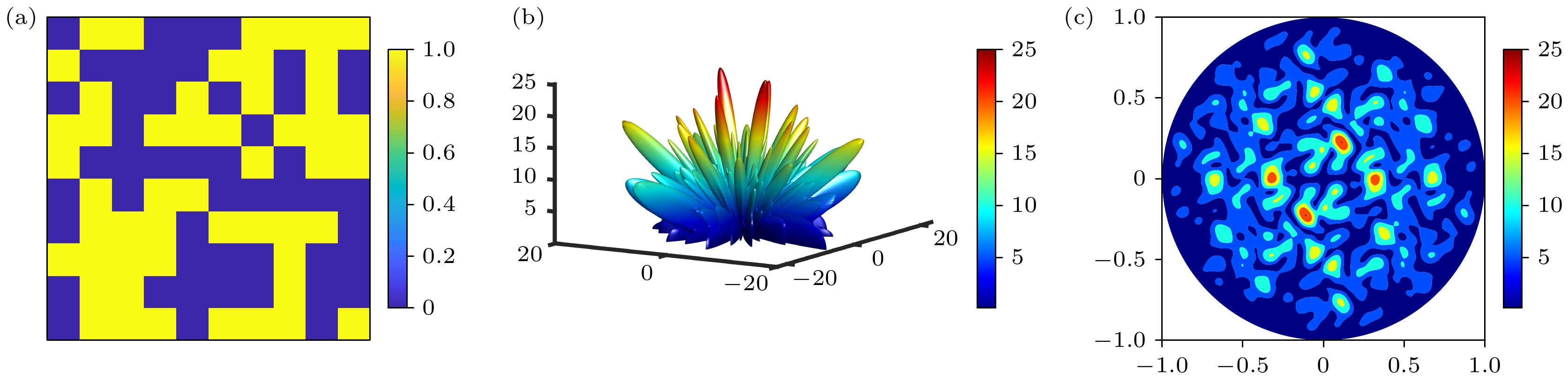
图 11 (a)—(d) PEC, 随机, PSO-SA 优化, CNN 优化相位分布后的3D远场图; (e)—(h) PEC, 随机, PSO-GA优化, CNN优化相位分布后的2D远场图
Figure 11. (a)–(d) 3D far-field patterns after phase distribution optimization by PEC, Random, PSO-SA, and CNN, respectively; (e)–(h) 2D far-field plots after phase distribution optimization by PEC, Random, PSO-SA, and CNN respectively
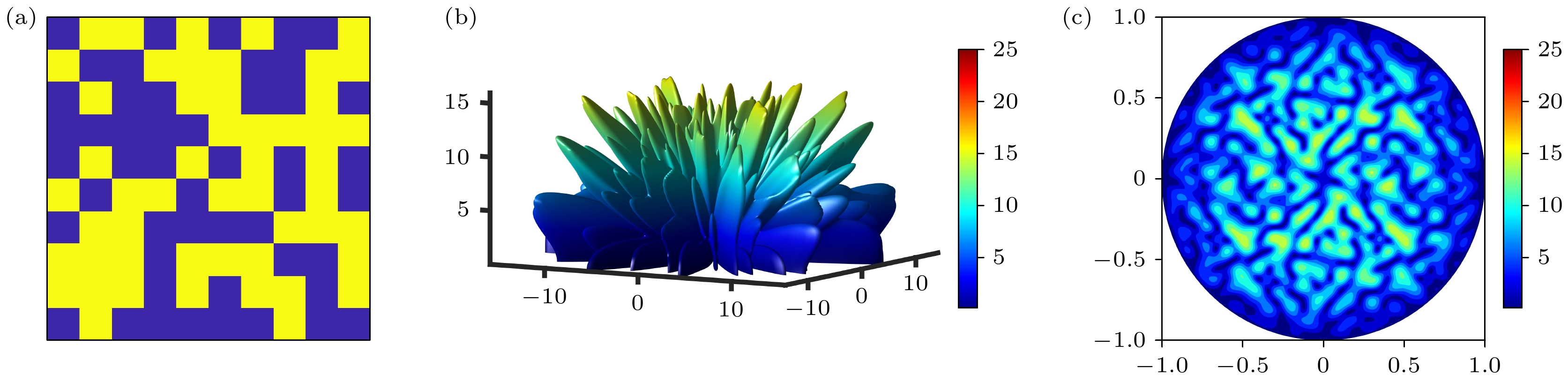
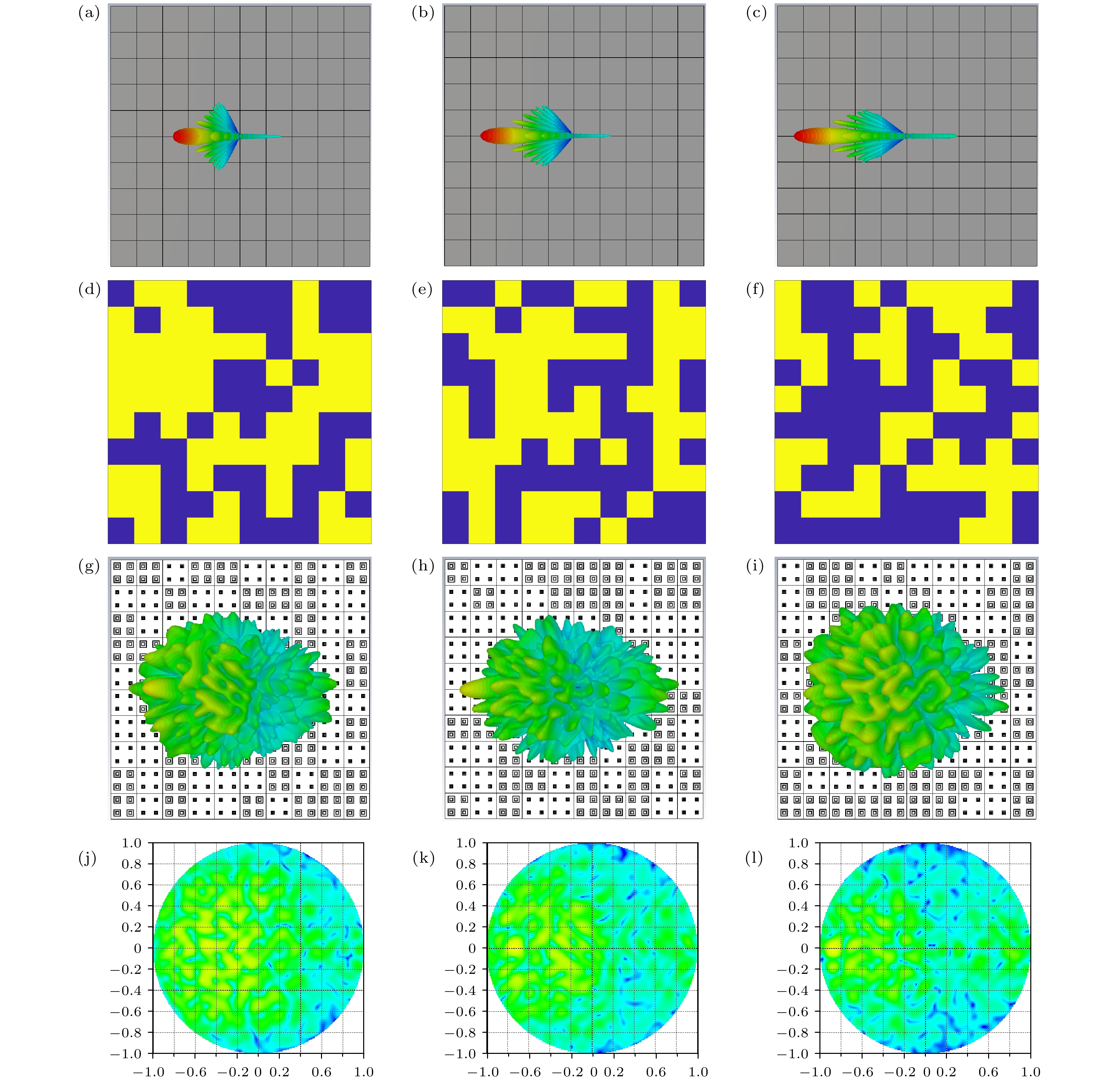
图 12 入射角分别为30°, 45°, 60°时 (a)—(c) CST 全波仿真 PEC 板的3D远场图; (d)—(f) CNN优化后的相位分布; (g)—(i) CNN优化后的相位分布在CST全波仿真的3D远场图; (j)—(l) CNN优化后的相位分布在CST全波仿真的2D远场图
Figure 12. Incident angles of 30°, 45°, 60°: (a)–(c) 3D far-field patterns of CST full-wave simulation of PEC plates; (d)–(f) phase distribution optimized by CNN; (g)–(i) 3D far-field patterns of CST full-wave simulation with CNN-optimized phase distribution; (j)–(l) 2D far-field patterns of CST full-wave simulation with CNN-optimized phase distribution
表 1 损失函数不同权重参数效果对比
Table 1. Comparison of the effects of different weight coefficients of the loss function.
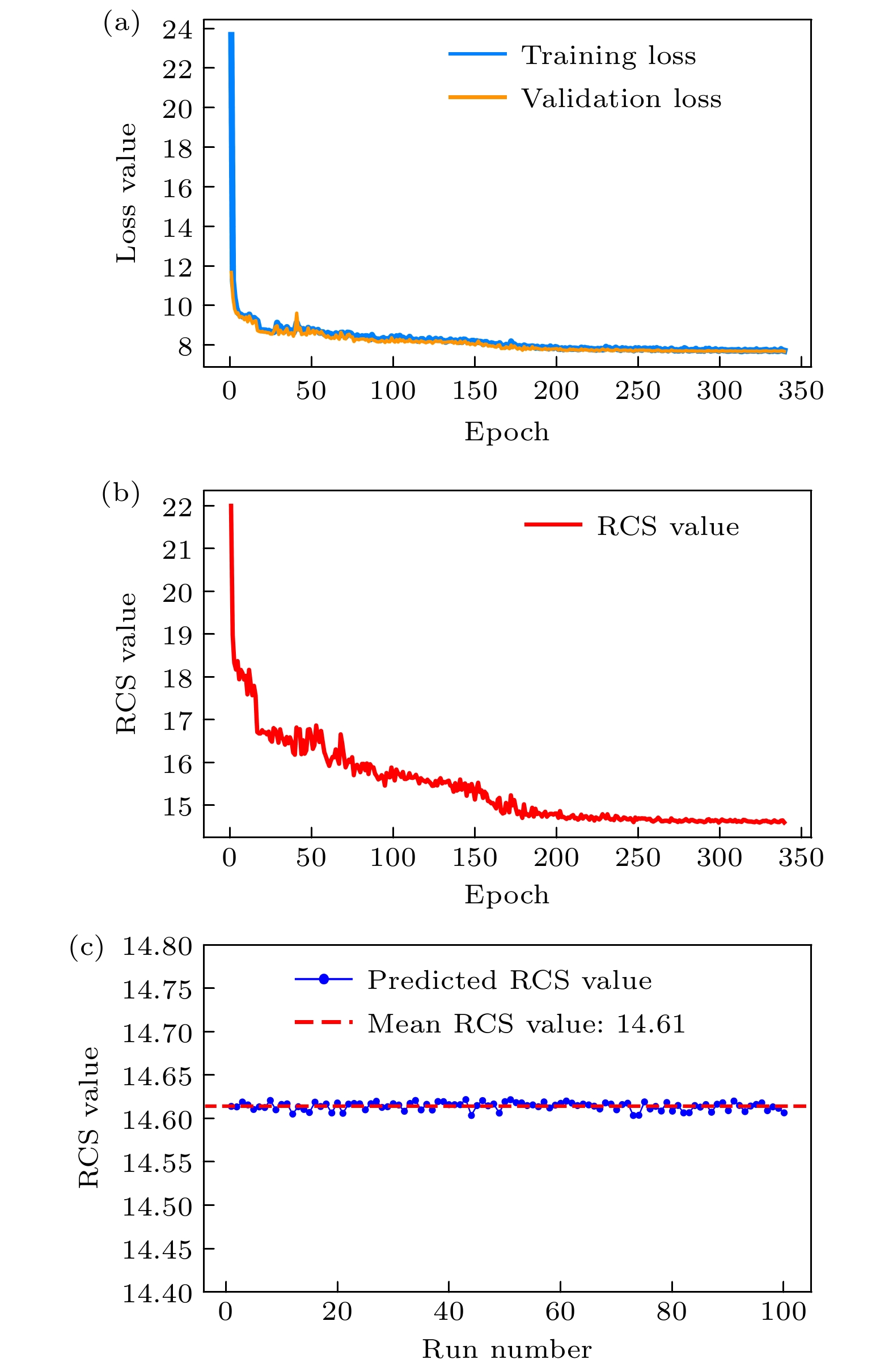
权重参数 参数取值 RCS 值 $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{RCS}}} $ 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 15.5, 14.7, 14.6, 14.6 (收敛速度慢) $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{Phase}}} $ 0.1, 0.3, 0.7, 1.0 16.8, 16.3, 16.2, 16.0 (无法减缩RCS) $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{RCS}}} $ + $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{Phase}}} $ (0.1, 0.1), (0.5, 0.1), (0.5, 0.3)··· 16.3, 14.8, 15.6··· (二值化模糊) $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{RCS}}} $ + $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{Phase}}} $ + $ \gamma_{{\mathrm{Reg}}} $ (0.5, 0.1, 0.5), (0.5, 0.1, 1), (0.5, 0.1, 1.5)··· 14.8, 14.7, 14.6··· 表 A1 实验环境配置
Table A1. Experimental environment configuration.
名称 配置信息 开发语言 Python 3.9 框架 PyTorch 1.10.0 + CUDA 12.0 CPU Intel Core i9 GPU GeForce RTX 4060 Laptop GPU (8G) 内存 8 G NumPy 1.21.3 Matplotlib 3.9.2 torchvision 0.13.0 Pandas 1.3.3 -
[1] Rao G A, Mahulikar S P 2002 Aeronaut. J. 106 629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ball R E, Albrecht R S, Horne R L 2003 The Fundamentals of Aircraft Combat Survivability: Analysis and Design (2nd Ed.) (Reston: AIAA) pp8–56
[3] Westwick P 2019 Stealth: The Secret Contest to Invent Invisible Aircraft (Oxford: Oxford University Press) pp5–42
[4] Singh H, Antony S, Jha R M 2016 Plasma-based Radar Cross Section Reduction (Singapore: Springer) pp1–46
[5] Knott E F 2012 Radar Cross Section Measurements (New York: Springer) pp12–36
[6] Knott E F, Schaeffer J R, Tuley M T 2004 Radar Cross Section (2nd Ed.) (Reston: SciTech Publishing) pp4–22
[7] Kim S H, Lee S Y, Zhang Y, Park S J, Gu J 2023 Adv. Sci. 10 2303104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ananth P B, Abhiram N, Krishna K H, Nisha M S 2021 Mater. Today Proc. 47 4872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ye D, Wang Z, Xu K, Li H, Huangfu J, Wang Z, Ran L 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 187402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang J, Yang R, Ma R, Tian J, Zhang W 2020 IEEE Access 8 105815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu Y, Zhao X 2014 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13 1473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yu N, Genevet P, Kats Ma, Aieta F, Tetienne J P, Capasso F, Gaburro Z 2011 Science 334 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gao X, Han X, Cao W P, Li H O, Ma H F, Cui T J 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 3522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Abdullah M, Koziel S 2022 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 70 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Paquay M, Iriarte J C, Ederra I, Gonzalo R, Maagt P de 2007 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 55 3630
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen W, Balanis C A, Birtcher C R 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 2636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sang D, Chen Q, Ding L, Guo M, Fu Y 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 2604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cui T J, Qi M Q, Wan X, Zhao J, Cheng Q 2014 Light Sci. Appl. 3 e218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu X, Gao J, Xu L, Cao X, Zhao Y, Li S 2016 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fu C, Han L, Liu C, Lu X, Sun Z 2021 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70 2352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li W, Huang N, Kang Y, Zou T, Ying Y, Yu J, Zheng J, Qiao L, Li J, Che S 2024 IEICE Electron. Express 21 20240246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Qi W J, Yu C, Du J L, Zhao Y J 2022 Int. J. RF Microwave Comput. Aided Eng. 32 23306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Koziel S, Abdullah M 2020 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 69 2028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tao S, Pan X T, Li M K, Xu S H, Yang F 2020 IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 10 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 杨欣雨 2023 硕士学位论文 (南京: 东南大学)
Yang X Y 2023 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Southeast University
[26] 袁方, 毛瑞棋, 高冕, 郑月军, 陈强, 付云起 2022 71 084102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan F, Mao R Q, Gao M, Chen Q, Fu Q Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 084102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yuan F, Wang G M, Xu H X, Cai T, Zou X J, Pang Z H 2017 EEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 3188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Han X M, Xu H J, Chang Y P, Lin M, Zhang W Y, Xin W 2020 IEEE Access 8 162313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhou Y, Cao X Y, Gao J, Li S, Liu X 2017 Electron. Lett. 53 1381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Katoch S, Chauhan S S, Kumar V 2021 Multimed. Tools Appl. 80 8091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang D S, Tan D P, Liu L 2018 Soft Comput. 22 387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pan X, Xue L, Lu Y, Sun N 2019 Multimed. Tools Appl. 78 29921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Dumoulin V, Visin F 2016 arXiv:1603.07285 [stat.ML]
[34] Xu B, Wang N Y, Chen T Q, Li M 2015 arXiv: 1505.00853 [cs.LG]
[35] Bjorck N, Gomes C P, Selman B, Weinberger K Q 2018 arXiv: 1806.02375 [cs.LG]
[36] Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R 2014 J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15 1929
[37] Dubey S R, Singh S K, Chaudhuri B B 2022 Neurocomputing 503 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhou P, Xie X, Lin Z, Yan S 2024 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 46 6486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Shi G, Zhang J, Li H, Wang C 2019 Neural Process. Lett. 50 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Al-Kababji A, Bensaali F, Dakua S P 2022 arXiv: 2202.06373 [cs.CV]
[41] Yuan F, Xu H X, Jia X Q, Wang G M, Fu Y Q 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 2463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3293
- PDF Downloads: 133
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: