-
In this work, we develop a two-dimensional fluid model to study the spatial density distributions of dust particles in a radio frequency capacitively coupled silane plasma. Unlike those scenarios based on the one-dimensional fluid model, in this work, the nonuniformity of the radial density distributions of dust particles is attributed mainly to the radial components of the electric field force and the ion drag force acting on the dust particles, leading to the two local density peaks near the electrode edges. It seems that dust particles tend to overcome the support of the electric field force and move much closer to the electrodes, as one of the density peaks indicates. Moreover, with the decrease of the radii of the discharge electrodes or the distance between them, the radial component of the ion drag force is enhanced, resulting in more dust particles gathering near the electrode edge region, and forming a ring-shaped particle density distribution. In the case of the discharge electrodes wrapped with dielectric materials, the uniformity of the radial density distributions of dust particles between the two electrodes is improved. Finally, the vortex motion of a single dust particle near the electrode edge region is also simulated in this work.
-
Keywords:
- capacitively coupled silane plasma /
- dust particles /
- ion drag force /
- two-dimensional fluid model
[1] Selwyn G S, Singh J, Bennett R S 1989 J. Vac. Sci. Techool. A 7 2758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fortov V E, Khrapak A G, Khrapak S A, Molotkov V I, Petrov O F 2004 Phys. Usp. 47 447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Melzer A, Nunomura S, Samsonov D, Ma Z W, Goree J 2000 Phys. Rev. E 62 4162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Thomas H, Morfill G E, Demmel V, Goree J, Feuerbacher B, Möhlmann D 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ivlev A V, Steinberg V, Kompaneets R, Höfner H, Sidorenko I, Morfill G E 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 145003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Samsonov D, Goree J, Ma Z W, Bhattacharjee A, Thomas H M, Morfill G E 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 3649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Goree J, Morfill G E, Tsytovieh V N, Vladimirov S V 1999 Phys. Rev. E 59 7055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chai K B, Bellan P M 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 023701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Morfill G E, Thomas H M, Konopka U, Rothermel H, Zuzic M, Ivlev A, Goree J 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 1598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Akdim M R, Goedheer W J 2003 Phys. Rev. E 67 056405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rozsa K, Bano G, Gallagher A 2001 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 29 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] De Bleecker K, Bogaerts A, Goedheer W 2004 Phys. Rev. E 70 056407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jia W Z, Zhang Q Z, Wang X F, Song Y H, Zhang Y Y, Wang Y N 2019 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52 015206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bleecker K D, Bogaerts A, Goedheer W 2006 New J. Phys. 8 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Akdim M R, Goedheer W J 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] De Bleecker K, Bogaerts A, Goedheer W 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 026405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Barnes M S, Keller J H, Forster J C, Neill J A, Coultas D K 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 68 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gallagher A, Howling A A, Hollenstein C 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 91 5571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Norberg S A, Johnsen E, Kushner M J 2015 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 24 035026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Boufendi L, Bouchoule A 1994 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 3 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lieberman M A, Lichtenberg A J 2005 Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing (Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ) pp23–43
-
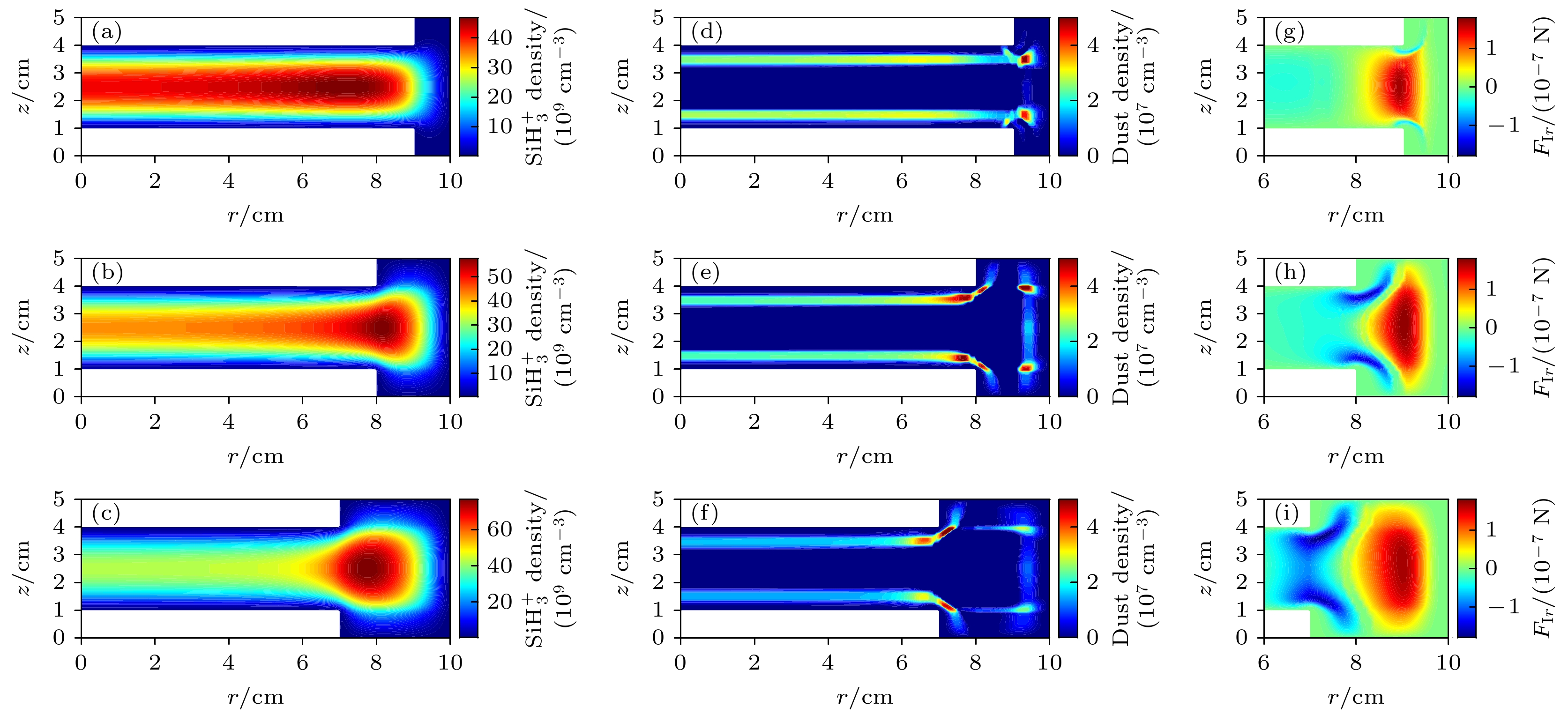
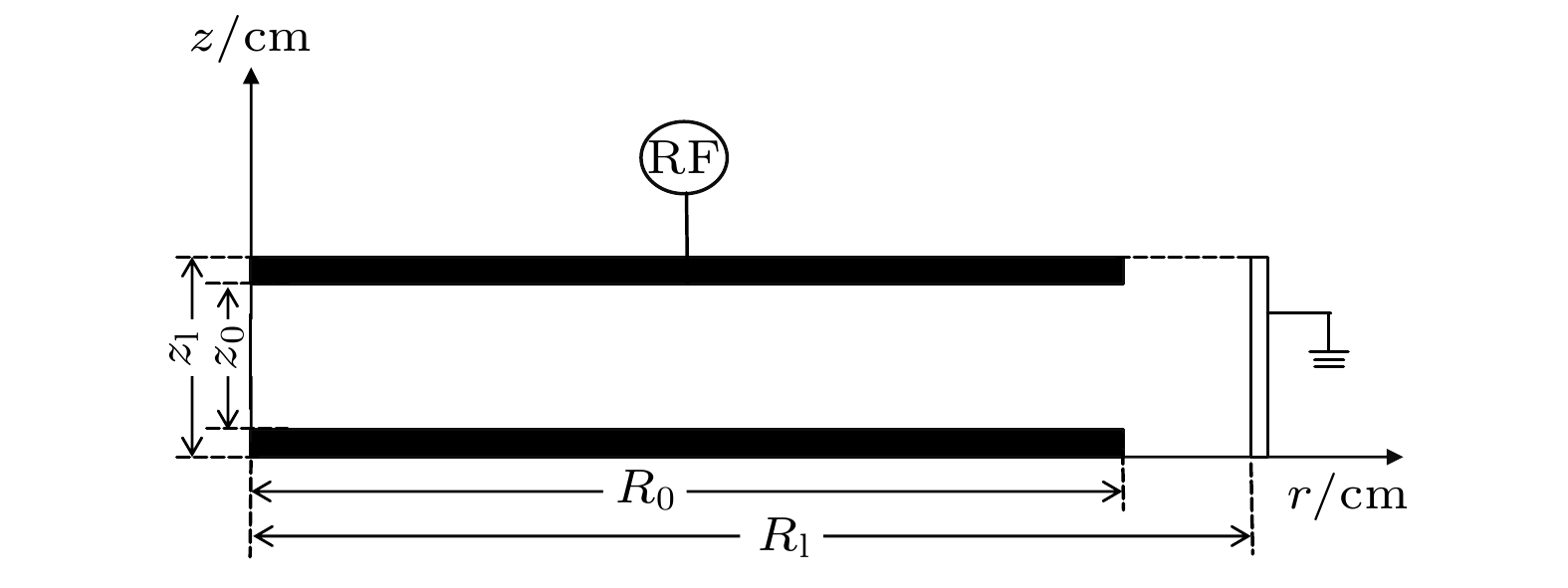
图 5 极板间距z0 = 3 cm, 极板半径不同时,
$ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + $ 密度(a)—(c), 尘埃颗粒密度(d)—(f), 离子拖拽力径向分量(g)—(i)的二维空间分布情况 (a), (d), (g) R0 = 9 cm; (b), (e), (h) R0 = 8 cm; (c), (f), (i) R0 = 7 cmFigure 5. Spatial distributions of
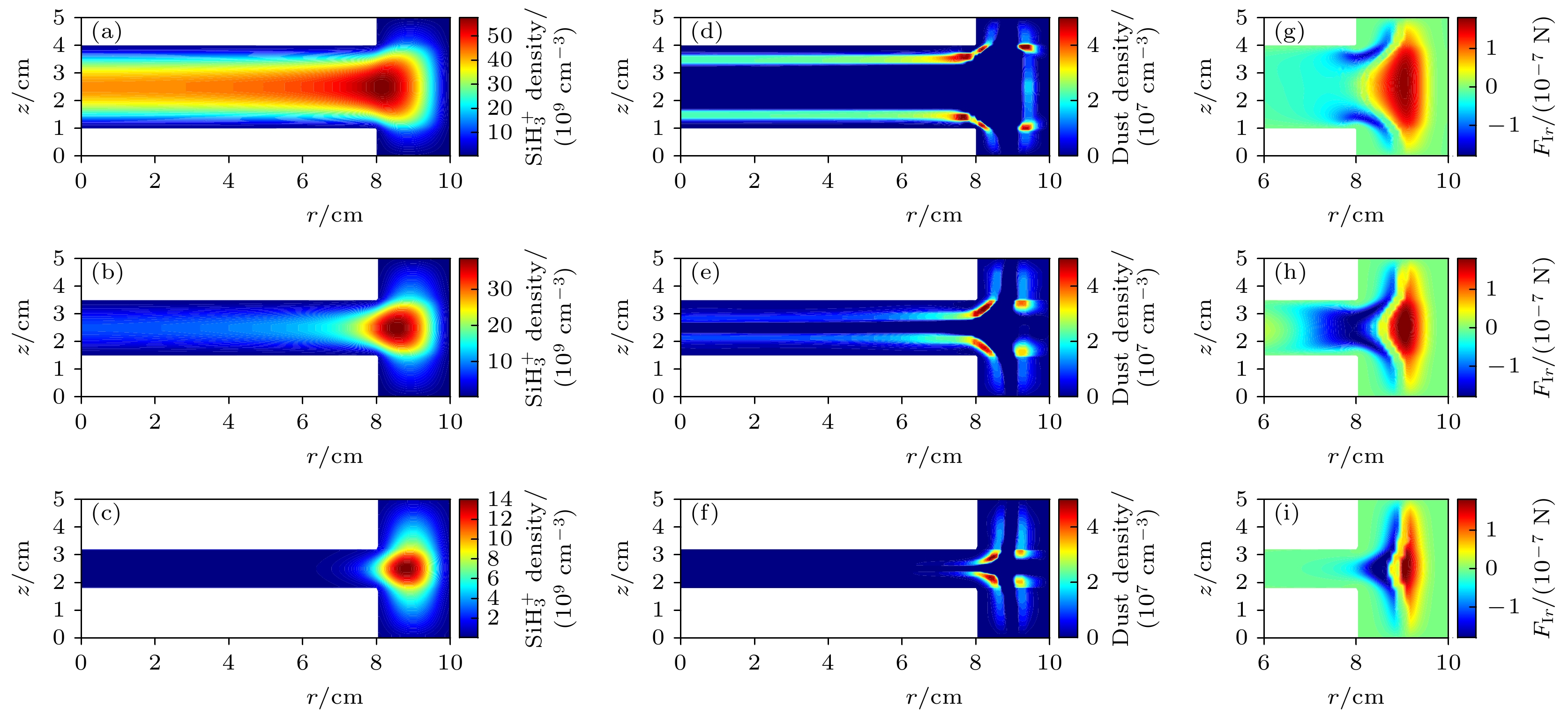
$ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + $ densities (a)–(c), dust particles densities (d)–(f) and radial component of the ion drag force (g)–(i) at the different electrode radius and z0 = 3 cm: (a), (d), (g) R0 = 9 cm; (b), (e), (h) R0 = 8 cm; (c), (f), (i) R0 = 7 cm.图 6 电极半径R0 = 8 cm, 极板间距不同时,
$ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + $ 密度(a)—(c), 尘埃颗粒密度(d)—(f), 离子拖拽力径向分量(g)—(i)的二维空间分布情况 (a), (d), (g) z0 = 3.0 cm; (b), (e), (h) z0 = 2.0 cm; (c), (f), (i) z0 = 1.4 cmFigure 6. Spatial distributions of (a)–(c)
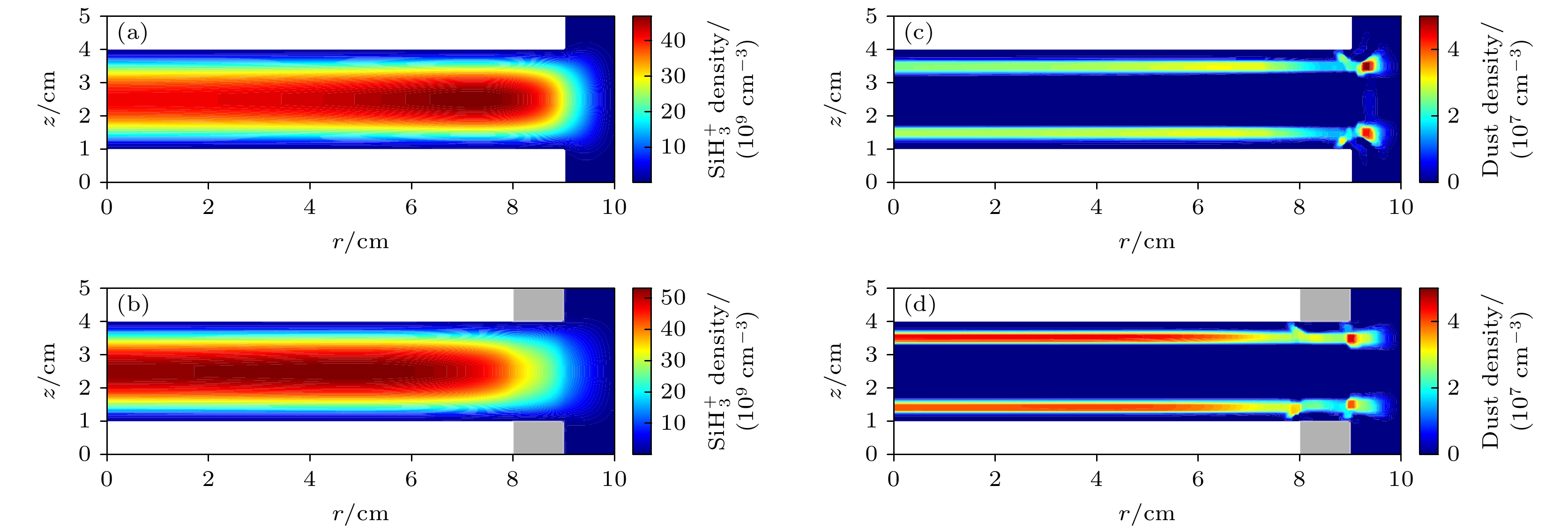
$ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + $ densities, (d)–(f) dust particles densities and (g)–(i) radial component of the ion drag force at the different electrode spacing and R0 = 8 cm: (a), (d), (g) z0 = 3.0 cm; (b), (e), (h) z0 = 2.0 cm; (c), (f), (i) z0 = 1.4 cm.图 7 z0 = 3 cm, R0 = 9 cm时, 上下极板在无介质层包裹和有介质层包裹的情况下
$ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + $ 密度(a), (b)和尘埃颗粒密度(c), (d)Figure 7. Spatial distributions of
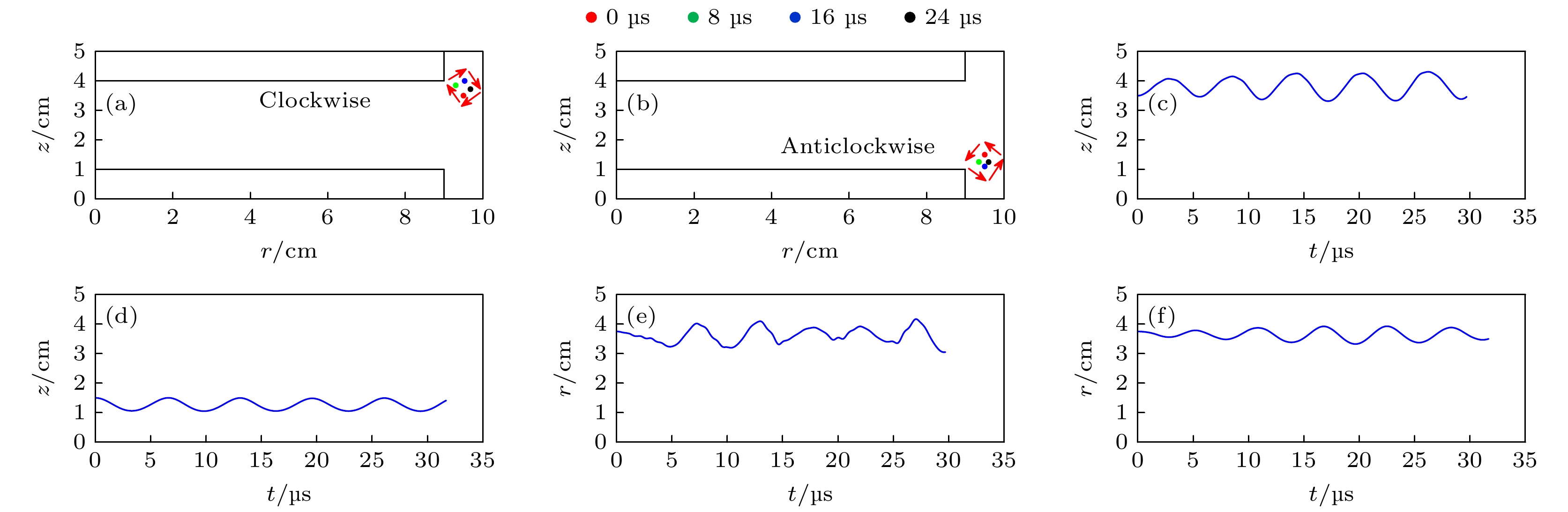
$ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + $ densities (a), (b) and dust particles densities (c), (d) in the case of discharge electrode without or with dielectric materials at z0 = 3 cm and R0 = 9 cm.图 8 上极板边缘(a)和下极板边缘(b)位置处的尘埃颗粒涡旋运动轨迹; 尘埃颗粒轴向位置(c), (d)及径向位置(e), (f)随时间演化过程(极板间距z0 = 3 cm, 电极半径R0 = 9 cm)
Figure 8. Vortex trajectory of dust particles at the edge of (a) the upper plate and (b) the lower plate; axial position (c), (d) and radial position (e), (f) of dust particles over time (Gap distance z0 = 3 cm and the electrode radius R0 = 9 cm).
表 1 除电子外, 模型中包含的不同粒子情况
Table 1. Overview of the different species incorporated in the model, besides the electrons.
Molecules Ions Radicals SiH4, SiH4(2-4), SiH4(1-3) $ {\text{SiH}}_3^ + , {\text{ S}}{{\text{i}}_{2}}{\text{H}}_4^ + $ SiH3, Si2H4 H2 $ {\text{H}}_2^ + $ H Si2H6, Si3H8, Si4H10, Si5H12 $ \begin{gathered} {\text{S}}{{\text{i}}_{5}}{\text{H}}_5^ - , {\text{ S}}{{\text{i}}_{3}}{\text{H}}_7^ - , {\text{ S}}{{\text{i}}_{4}}{\text{H}}_9^ - , {\text{ S}}{{\text{i}}_{5}}{\text{H}}_{11}^ - ,\end{gathered} $
$ {\text{S} }{ {\text{i} }_{2} }{\text{H} }_4^ - , {\text{ S} }{ {\text{i} }_3}{\text{H} }_6^ - , {\text{ S} }{ {\text{i} }_{4} }{\text{H} }_8^ - , {\text{ S} }{ {\text{i} }_{5} }{\text{H} }_{10}^ - , $
dustSi2H5, Si3H7, Si4H9, Si5H11 , Si2H4, Si3H6, Si4H8, Si5H10 -
[1] Selwyn G S, Singh J, Bennett R S 1989 J. Vac. Sci. Techool. A 7 2758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fortov V E, Khrapak A G, Khrapak S A, Molotkov V I, Petrov O F 2004 Phys. Usp. 47 447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Melzer A, Nunomura S, Samsonov D, Ma Z W, Goree J 2000 Phys. Rev. E 62 4162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Thomas H, Morfill G E, Demmel V, Goree J, Feuerbacher B, Möhlmann D 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ivlev A V, Steinberg V, Kompaneets R, Höfner H, Sidorenko I, Morfill G E 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 145003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Samsonov D, Goree J, Ma Z W, Bhattacharjee A, Thomas H M, Morfill G E 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 3649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Goree J, Morfill G E, Tsytovieh V N, Vladimirov S V 1999 Phys. Rev. E 59 7055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chai K B, Bellan P M 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 023701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Morfill G E, Thomas H M, Konopka U, Rothermel H, Zuzic M, Ivlev A, Goree J 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 1598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Akdim M R, Goedheer W J 2003 Phys. Rev. E 67 056405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rozsa K, Bano G, Gallagher A 2001 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 29 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] De Bleecker K, Bogaerts A, Goedheer W 2004 Phys. Rev. E 70 056407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jia W Z, Zhang Q Z, Wang X F, Song Y H, Zhang Y Y, Wang Y N 2019 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52 015206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bleecker K D, Bogaerts A, Goedheer W 2006 New J. Phys. 8 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Akdim M R, Goedheer W J 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] De Bleecker K, Bogaerts A, Goedheer W 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 026405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Barnes M S, Keller J H, Forster J C, Neill J A, Coultas D K 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 68 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gallagher A, Howling A A, Hollenstein C 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 91 5571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Norberg S A, Johnsen E, Kushner M J 2015 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 24 035026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Boufendi L, Bouchoule A 1994 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 3 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lieberman M A, Lichtenberg A J 2005 Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing (Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ) pp23–43
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6775
- PDF Downloads: 116
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: