-
Single-pixel imaging (SPI) system modulates the object with a series of patterns, records the corresponding measurements of a bucket detector and forms an image by the algorithm of compressed sensing. In this process, if other objects enter into the field of view of SPI, the accuracy of measurement will be seriously affected, and the quality of the reconstructed image will decrease. Owing to the randomness of the reflectivity and shape of the occlusion, it is difficult to effectively separate the disturbed part from the bucket detector signal. To solve this problem, we propose a self-check method based on the characteristics of Hadamard matrix, that is, using the measurement values of bucket detector to verify the correctness of signal. Usually when using the Hadamard matrix as the measurement matrix in SPI, it is divided into complementary positive pattern and negative pattern. The measurements of these two patterns are subtracted to form the image (the difference value marked by
$ l $ ). Owing to the complementarity of the two patterns, the sum of the corresponding measurements should be a constant (marked by$ u $ ). When dynamic occlusion appears, the value of$ u $ will fluctuate significantly, so we choose$ u $ as the standard to judge whether an occlusion appears. In order to reduce the influence of other factors (such as system noise or fluctuation of the illumination) in the imaging process, we further propose a dynamic occlusion removal method based on the statistical histogram of the values of$ u $ . We first find the position of the maximum value in the histogram, and then expand from this position to both sides of the histogram. We calculate the area of the expanded region, and stop the expansion when this area is greater than the threshold. Then the$ l $ corresponding to$ u $ in the expanded region is the measured value without interference. Experiments show that this method can retain the undisturbed signals of the bucket detector and significantly improve the quality of the reconstructed image. This method is simple and effective, and it is also suitable for general imaging scenes. More importantly, it does not need to introduce additional patterns for verification, which effectively promotes the practical process of single pixel imaging technology.-
Keywords:
- single pixel imaging /
- self-check /
- dynamic occlusion
[1] Pittman T B, Shih Y H, Strekalov D V, Sergienko A V 1995 Phys. Rev. A 52 R3429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bennink R S, Bentley S J, Boyd R W 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 113601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Guo Q, Wang Y X, Chen H W, Chen M H, Yang S Y, Xie S Z 2017 Front. Inf. Tech. EL 18 1261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang Z H, Chen X, Zhao Z H, Song, M Y, Liu Y, Zhao Z D, Lei H D, Yu, Y J, Wu, L A 2022 Opt. Express 30 864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sefi O, Klein Y, Strizhevsky E, Dolbnya, I. P, Shwartz S 2020 Opt. Express 28 24568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu S, Yao X R, Liu X F, Xu D Z, Wang X D, Liu B, Wang C, Zhai G J, Zhao Q 2019 Opt. Express 27 22138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Meyers R E, Deacon K S, Shih Y H 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 111115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang X, Liu Y, Mou X Y, Hu T Y, Yuan F, Cheng E 2021 Opt. Express 29 12010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang C G, He W Q, Han B N, Liao M H, Lu D J, Peng X, Xu C 2019 Opt. Express 27 13469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jiao S M, Feng J, Gao Y, Lei T, Yuan X C 2020 Opt. Express 28 7301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tian N, Guo Q C, Wang A L, Xu D L, Fu L 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 3302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ma Y Y, Yin Y K, Jiang S, Li X Y, Huang F, Sun B Q 2021 Opt. Lasers. Eng 140 106532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X Y, Yin Y K, He W Q, Liu X L, Tang Q J, Peng X 2021 Opt. Express 29 36675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Duarte M F, Davenport M A, Takhar D, Laska J N, Sun T, Kelly K F, Baraniuk R G 2008 IEEE. Signal. Process. Mag 25 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vaz P G, Amaral D, Ferreira L F R, Morgado M, Cardoso J 2020 Opt. Express 28 11666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Z B, Wang X Y, Zheng G A, Zhong J G 2017 Opt. Express 25 19619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun M J, Meng L T, Edgar M P, Padgett M J, Radwell N 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 3464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yu W K 2019 Sensors 19 4122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yu W K, Liu Y M 2019 Sensors 19 5135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jauregui-Sanchez Y, Clemente P, Latorre-Carmona P, Tajahuerce E, Lancis J 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 B67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sun M. J, Xu Z H, Wu L A 2018 Opt. Lasers. Eng. 100 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jiang S, Li X Y, Zhang Z X, Jiang W J, Wang Y P, He G B, Wang Y R, Sun B Q 2019 Opt. Express 27 22499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li C, Yin W, Jiang H, Zhang Y 2013 Comput Optim Appl. 56 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
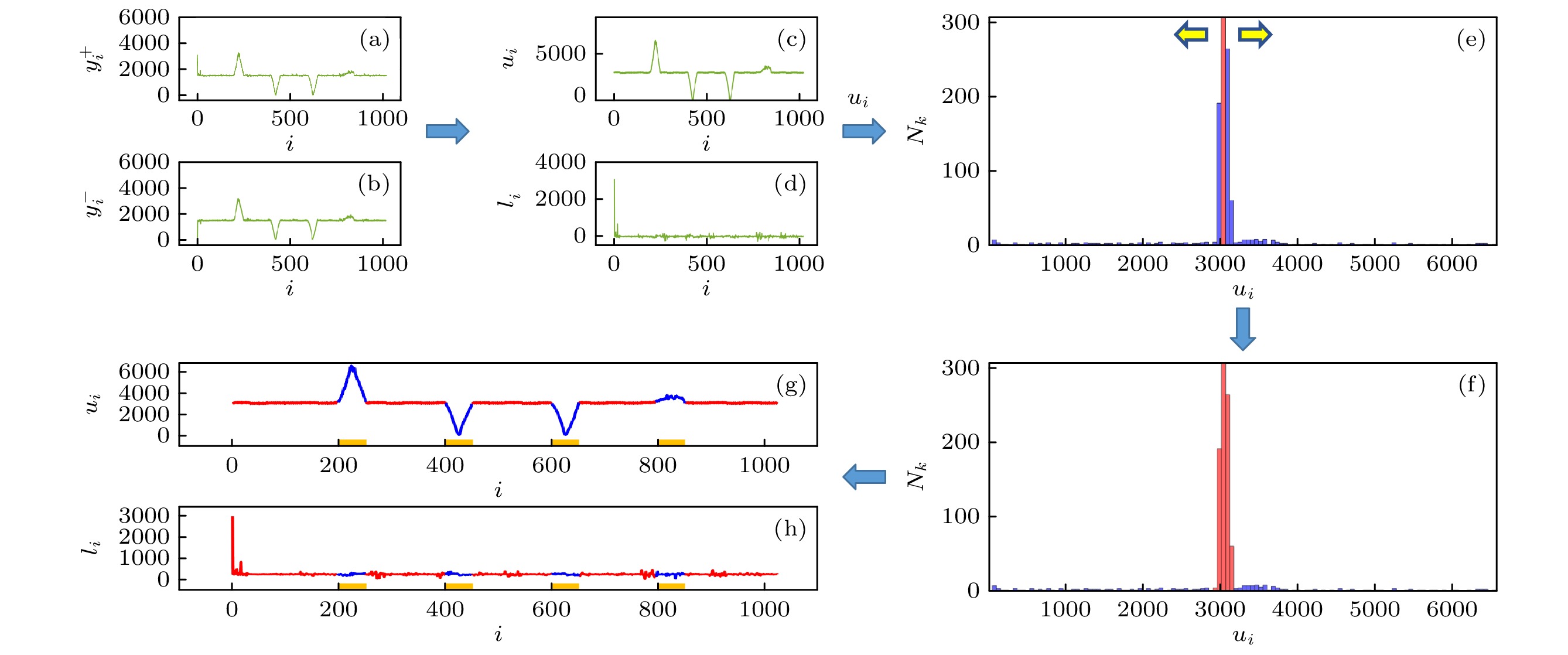
图 1 受干扰信号去除流程图 (a)
${\mathit{H}}_{\mathit{i}}^{+}$ 对应测量信号${y}_{i}^{+}$ ; (b)${ {H}}_{i}^{-}$ 对应测量信号${y}_{i}^{-};$ (c)${ {H}}_{i}$ 对应的自校验信号$ {u}_{i}; $ (d)${ {H}}_{i}$ 对应的用于重构的信号$ {l}_{i} $ ; (e)$ {u}_{i} $ 的统计直方图, 红色区域表示已经生长的区域, 黄色箭头表示生长方向, 蓝色区域表示未生长区域; (f) 使用本文算法后的$ {u}_{i} $ 统计直方图, 红色、蓝色区域分别表示正确和受干扰的桶探测器数值范围; (g), (h)分别是使用本文算法筛选后的$ {u}_{i} $ 和$ {l}_{i} $ , 红色和蓝色分别表示正确和错误测量值, 黄色色块表示真实干扰存在的帧数Figure 1. Flowchart of abnormal signal removal: (a)
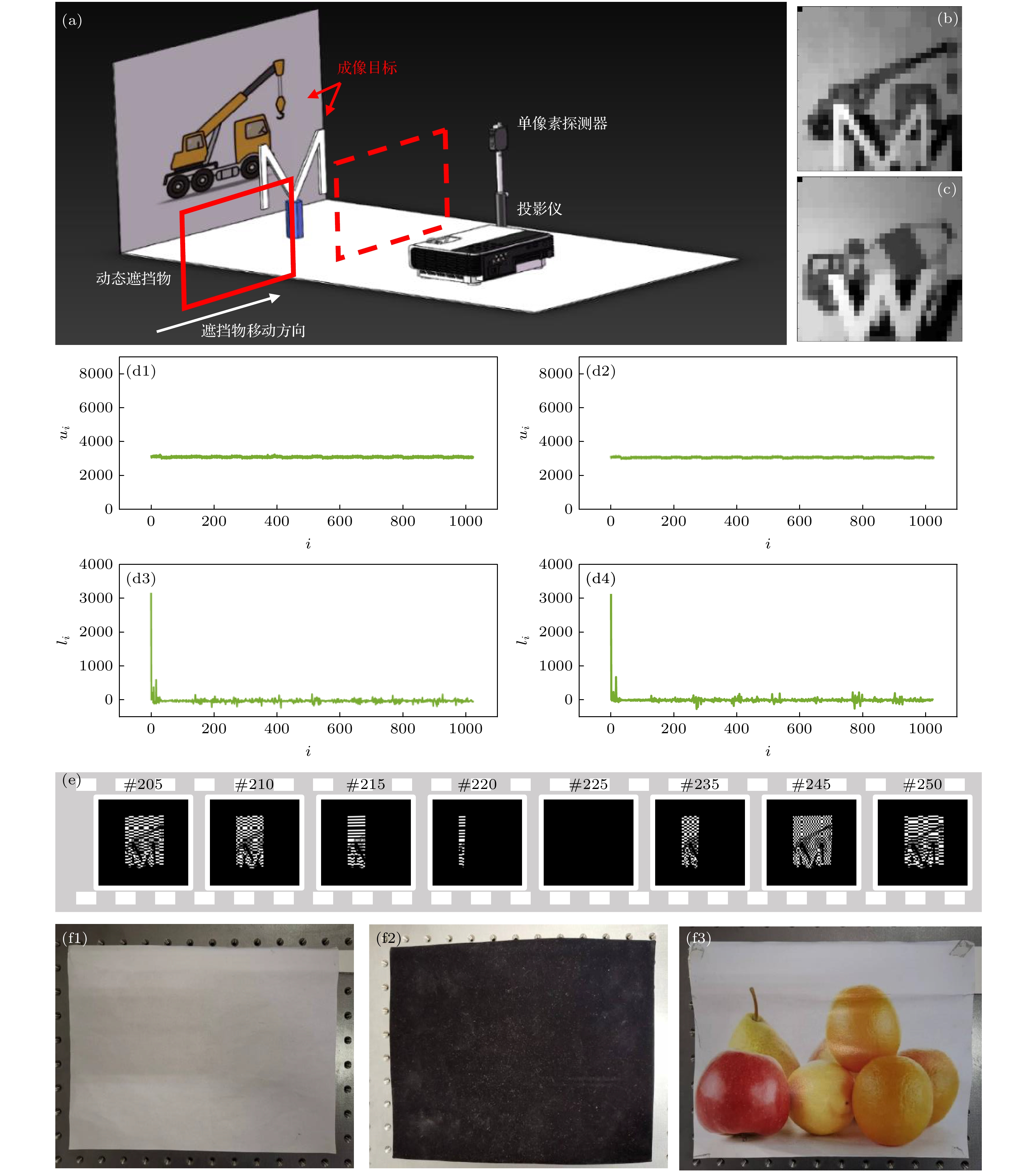
${y}_{i}^{+}$ , measurement value of the pattern${ {H}}_{i}^{+}$ ; (b)${y}_{i}^{-}$ , measurement value of the pattern${ {H}}_{i}^{-}$ ; (c)$ {u}_{i} $ , the signal for self-check, corresponding to$ {\mathit{H}}_{i} $ ; (d)$ {l}_{i} $ , the signal for reconstruction, corresponding to$ {\mathit{H}}_{i} $ ; (e) statistical histogram of$ {u}_{i} $ ; red areas indicate the area that have grown, yellow arrows indicate growth direction, blue areas indicate ungrown areas; (f) statistical histogram of$ {u}_{i} $ obtained by the proposed algorithm in this paper, the red and blue areas represent the ranges of correct and disturbed bucket detector value respectively; (g), (h)$ {u}_{i} $ and$ {l}_{i} $ obtained by the proposed algorithm in this paper, respectively, red and blue dots indicate correct and incorrect measurements, respectively, the yellow color block indicates the number of frames where the real occlusion exists.图 2 成像系统示意图 (a)成像系统; (b)场景1无干扰情况下的重构图像; (c)场景2无干扰情况下的重构图像; (d1), (d2) 场景1, 2无干扰时
$ {u}_{i} $ 曲线; (d3), (d4) 场景1, 2无干扰时$ {l}_{i} $ 曲线; (e)干扰物为黑布时, 目标成像过程中的遮挡情况; (f1)—(f3)干扰物(A4纸、黑绒布、彩色水果图案)Figure 2. Schematic diagram of imaging system: (a) Imaging system; (b) reconstructed image of scene 1 without occlusion; (c) reconstructed image of scene 2 without occlusion; (d1), (d2)
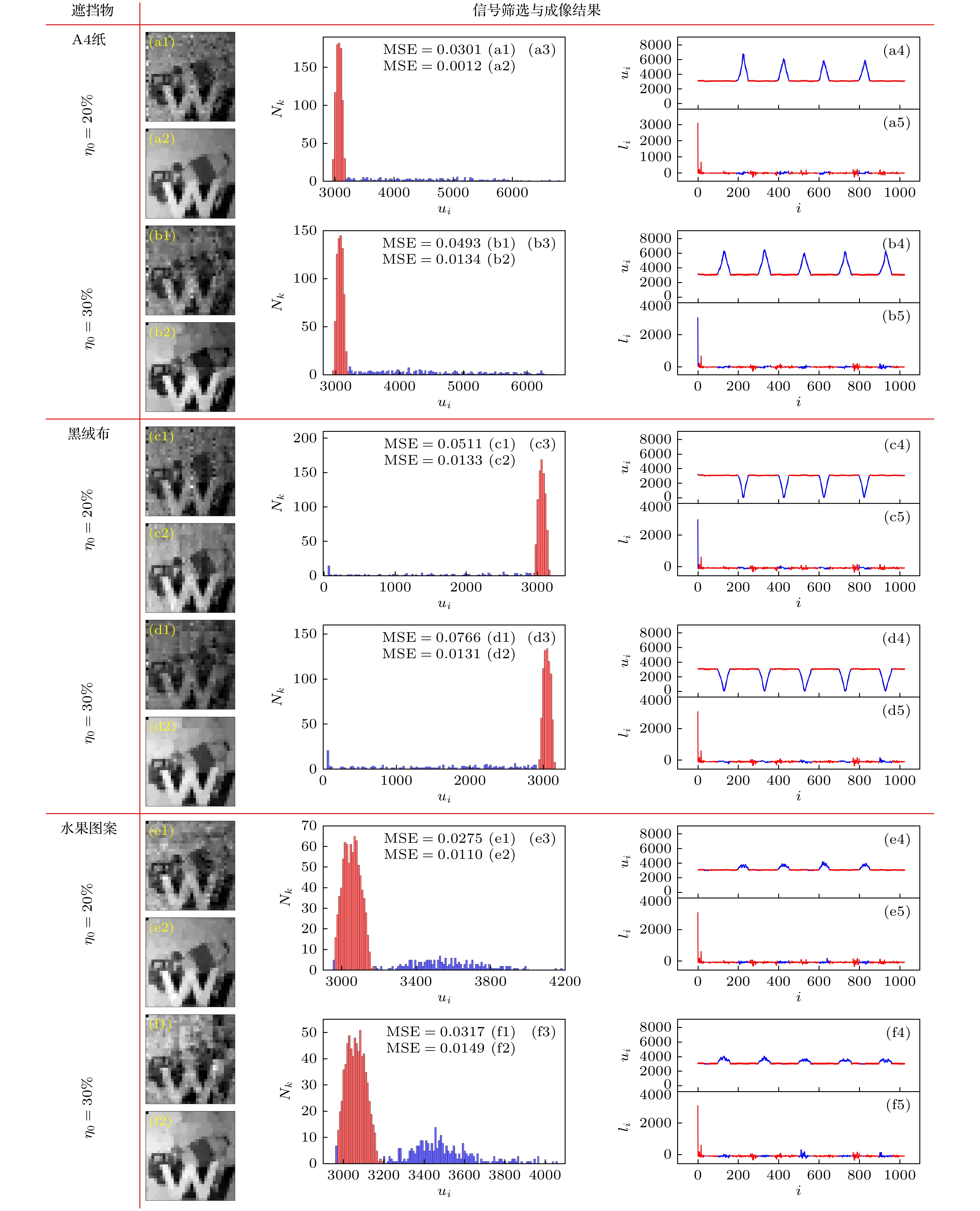
$ {u}_{i} $ , curves of scene 1 and 2 respectively; (d3), (d4)$ {l}_{i} $ , curves of scene 1 and 2 respectively; (e) occlusion (black cloth) during single-pixel imaging; (f1)–(f3) occlusion (A4 paper, black cloth and color fruit pattern).图 3 场景1重构情况 (a1)—(f1)未去除干扰的重构图像; (a2)—(f2)去除干扰后的重构图像; (a3)—(f3)
$ {u}_{i} $ 的统计直方图; (a4)—(f4)$ {u}_{i} $ 强度值; (a5)—(f5)$ {l}_{i} $ 强度值; 图中红色表示使用本方法得到的正确桶探测器检验值$ {u}_{i} $ (直方图中为$ {u}_{i} $ 的强度范围)和用于重构的强度值$ {l}_{i} $ , 蓝色表示由本方法得到的干扰值Figure 3. Reconstruction in scene 1: (a1)–(f1) Reconstructed image without removing occlusion; (a2)–(f2) reconstructed image after removing occlusion; (a3)–(f3) statistical histogram of
$ {u}_{i} $ ; (a4)–(f4)$ {u}_{i} $ value; (a5)–(f5)$ {l}_{i} $ value; in the figure, red represents the correct value of$ {u}_{i} $ (or the intensity range of$ {u}_{i} $ in the histogram) and the value of$ {l}_{i} $ used for reconstruction, while blue one represents the wrong values.图 4 场景2重构情况 (a1)—(f1)未去除干扰的重构图像; (a2)—(f2)去除干扰后的重构图像; (a3)—(f3)
$ {u}_{i} $ 的统计直方图; (a4)—(f4)$ {u}_{i} $ 强度值; (a5)—(f5)$ {l}_{i} $ 强度值; 图中红色表示使用本方法得到的正确桶探测器检验值$ {u}_{i} $ (直方图中为$ {u}_{i} $ 的强度范围)和用于重构的强度值$ {l}_{i} $ , 蓝色表示由本方法得到的干扰值Figure 4. Reconstruction in scene 2: (a1)–(f1) Reconstructed image without removing occlusion; (a2)–(f2) reconstructed image after removing occlusion; (a3)–(f3) statistical histogram of
$ {u}_{i} $ ; (a4)–(f4)$ {u}_{i} $ value; (a5)–(f5)$ {l}_{i} $ value; the red curves represents the correct value of$ {u}_{i} $ (or the intensity range of$ {u}_{i} $ in the histogram) and the value of$ {l}_{i} $ used for reconstruction, while blue one represents the wrong values.图 5 多种干扰条件下的单像素系统抗干扰能力测试 (a1), (b1)未去除干扰的重构图像; (a2), (b2)去除干扰后的重构图像; (a3), (b3)
$ {u}_{i} $ 的统计直方图; (a4), (b4)$ {u}_{i} $ 强度值; (a5), (b.5)$ {l}_{i} $ 强度值; 图中红色表示使用本方法得到的正确桶探测器检验值$ {u}_{i} $ (直方图中为$ {u}_{i} $ 的强度范围)和用于重构的强度值$ {l}_{i} $ , 蓝色表示由本方法得到的干扰值Figure 5. Test of dynamic occlusion removal under various occlusion conditions: (a1), (b1) Reconstructed image without removing occlusion; (a2), (b2) reconstructed image after removing occlusion; (a3), (b3) statistical histogram of
$ {u}_{i} $ ; (a4), (b4) the value of$ {u}_{i} $ ; (a5), (b5) the value of$ {l}_{i} $ ; the red curves represents the correct value of$ {u}_{i} $ (or the intensity range of$ {u}_{i} $ in the histogram) and the value of$ {l}_{i} $ used for reconstruction, while blue one represents the wrong values. -
[1] Pittman T B, Shih Y H, Strekalov D V, Sergienko A V 1995 Phys. Rev. A 52 R3429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bennink R S, Bentley S J, Boyd R W 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 113601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Guo Q, Wang Y X, Chen H W, Chen M H, Yang S Y, Xie S Z 2017 Front. Inf. Tech. EL 18 1261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang Z H, Chen X, Zhao Z H, Song, M Y, Liu Y, Zhao Z D, Lei H D, Yu, Y J, Wu, L A 2022 Opt. Express 30 864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sefi O, Klein Y, Strizhevsky E, Dolbnya, I. P, Shwartz S 2020 Opt. Express 28 24568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu S, Yao X R, Liu X F, Xu D Z, Wang X D, Liu B, Wang C, Zhai G J, Zhao Q 2019 Opt. Express 27 22138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Meyers R E, Deacon K S, Shih Y H 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 111115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang X, Liu Y, Mou X Y, Hu T Y, Yuan F, Cheng E 2021 Opt. Express 29 12010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang C G, He W Q, Han B N, Liao M H, Lu D J, Peng X, Xu C 2019 Opt. Express 27 13469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jiao S M, Feng J, Gao Y, Lei T, Yuan X C 2020 Opt. Express 28 7301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tian N, Guo Q C, Wang A L, Xu D L, Fu L 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 3302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ma Y Y, Yin Y K, Jiang S, Li X Y, Huang F, Sun B Q 2021 Opt. Lasers. Eng 140 106532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X Y, Yin Y K, He W Q, Liu X L, Tang Q J, Peng X 2021 Opt. Express 29 36675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Duarte M F, Davenport M A, Takhar D, Laska J N, Sun T, Kelly K F, Baraniuk R G 2008 IEEE. Signal. Process. Mag 25 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vaz P G, Amaral D, Ferreira L F R, Morgado M, Cardoso J 2020 Opt. Express 28 11666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Z B, Wang X Y, Zheng G A, Zhong J G 2017 Opt. Express 25 19619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun M J, Meng L T, Edgar M P, Padgett M J, Radwell N 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 3464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yu W K 2019 Sensors 19 4122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yu W K, Liu Y M 2019 Sensors 19 5135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jauregui-Sanchez Y, Clemente P, Latorre-Carmona P, Tajahuerce E, Lancis J 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 B67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sun M. J, Xu Z H, Wu L A 2018 Opt. Lasers. Eng. 100 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jiang S, Li X Y, Zhang Z X, Jiang W J, Wang Y P, He G B, Wang Y R, Sun B Q 2019 Opt. Express 27 22499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li C, Yin W, Jiang H, Zhang Y 2013 Comput Optim Appl. 56 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5949
- PDF Downloads: 68
- Cited By: 0








































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: