-
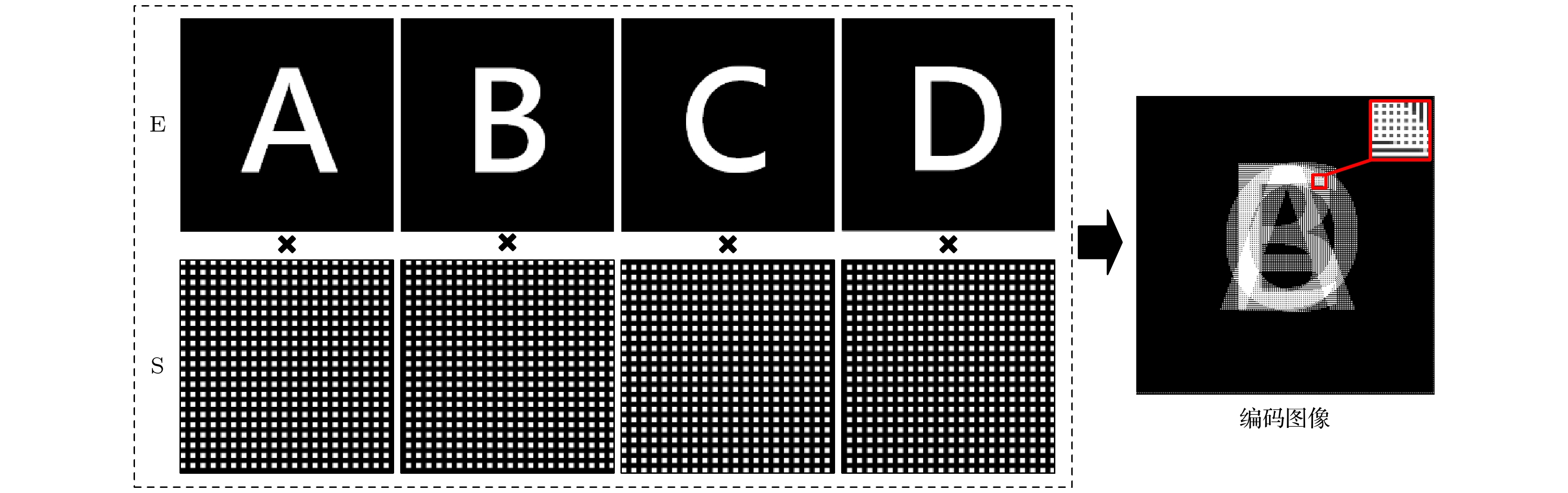
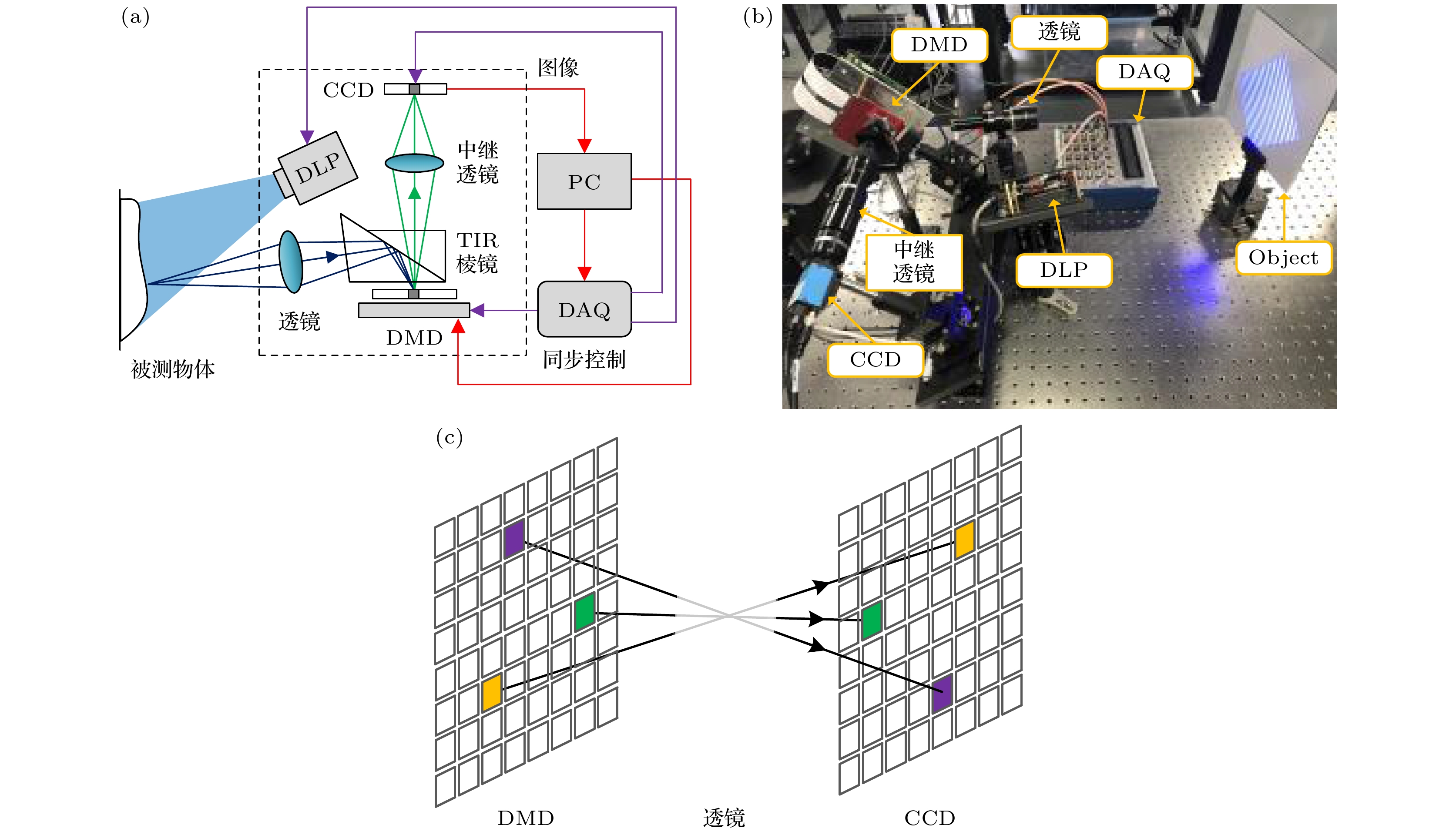
像素编码曝光成像技术是一种先进的高速成像技术, 其利用数字微镜器件(digital micromirror device, DMD)对相机每个像素的曝光进行编码, 将多帧图像信息融入到单帧编码图像中, 然后再利用解码算法进行图像重构, 将低帧频相机的图像采集速率提升数倍, 实现低帧频相机的高速成像. 在该技术中, DMD的像素与相机像素之间的精确匹配是实现编码曝光成像的前提, 因此, 相关研究人员主要关注于如何实现像素的精确匹配. 然而, 两者之间中继成像系统的分辨率作为编码曝光成像的另一重要影响因素, 却鲜有人研究和分析. 为此, 本文从理论上分析了中继成像系统的分辨率对解码图像重建效果的影响, 并结合模拟和实际成像实验对理论分析进行验证. 在此基础上, 搭建了像素编码曝光成像系统, 提出了一种基于条纹相位的成像系统点扩散函数估计方法, 并将Richard-Lucy反卷积算法引入到编码图像的重构过程中, 有效改善编码曝光成像的质量, 对于像素编码曝光成像技术的发展具有重要的意义.Pixel-wise coded exposure (PCE) imaging based on digital micromirror device (DMD) is an advanced high-speed imaging technology, which can realize the high-speed imaging by using a low-frame-rate camera. During exposure time, the multi-frame image information of a dynamic object can be integrated into one encoded image, and then the multi-frame sub-exposure images can be extracted by the post-processing algorithm. Therefore, the accurate pixel-to-pixel alignment between the DMD and the camera is the key step to realize PCE imaging, which has drawn much attention from researchers. So their studies mainly focused on how to achieve accurate pixel matching. However, the resolution of the relay imaging lens, as another important influence factor of PCE imaging, also has a significant influence on the imaging results, but few people have studied and analyzed it. To solve this problem, in this work, we theoretically analyze the influence of the resolution of the relay imaging system on the reconstructed decoded images, and verifies the theoretical analysis through simulation and imaging experiments. On this basis, a PCE imaging system is built, and a point spread function (PSF) estimation method of relay lens based on the fringe phase is proposed. Furthermore, a Richard-Lucy deconvolution algorithm is introduced into the reconstruction process of coded image to effectively improve the quality of PCE imaging, which is of great significance in developing the PCE imaging technology.
-
Keywords:
- high-speed imaging /
- pixel-wise coded exposure imaging /
- relay lens /
- digital micromirror device
[1] Akiyama M, Yang Z B, Gnapowski S, Hamid S, Hosseini R, Akiyama H 2014 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 42 3215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李明飞, 莫小范, 赵连洁, 霍娟, 杨然, 李凯, 张安宁 2016 65 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M F, Mo X F, Zhao L J, Huo J, Yang R, Li K, Zhang A N 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang J, Xiong T, Tran T, Chin S, Cummings R E 2016 Opt. Express 24 9013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Khan S R, Feldman M, Gunturk B K 2018 Signal Process. Image Commun. 60 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 冯维, 张福民, 王惟婧, 曲兴华 2017 66 234201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng W, Zhang F M, Wang W J, Qu X H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 234201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qiao Y, Xu X P, Liu T, Pan Y 2015 Appl Opt. 54 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tang C Y, Chen Y T, Li Q, Feng H J, Xu Z H 2015 Optica 35 0410002
[8] Bub G, Tecza M, Helmes M, Lee P, Kohl P 2009 Nat. Methods 7 209
[9] Ri S, Fujigaki M, Morimoto Y 2009 Opt. Eng. 48 103605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu D Y, Gu J W, Hitomi Y, Gupta M, Mitsunaga T, Nayar S K 2013 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (TPAMI) 36 248
[11] Feng W, Zhang F M, Qu X H, Zheng S W 2016 Sensors 16 331
[12] Peng X, Tian J D, Zhang P, Wei L B, Qiu W J, Li E B, Zhang D W 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 1965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Niu B, Qu X H, Guan X H, Zhang F M 2021 Opt. Express 29 27562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gunturk B K, Feldman M 2013 Proc. SPIE 8660 86600P
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Feng W, Zhang F M, Wang W J, Xing W, Qu X H 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 3831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang C M, Tu C 2014 Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 7 217
[17] Gao L, Liang J Y, Li C Y, Wang L H 2014 Nature 516 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Adekunle A, Barakat N 2009 Opt. Express 17 1831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y, Wang Z F 2015 J. Visual Commun. Image Represent. 31 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gu B, Li W J, Wong J T, Zhu M Y, Wang M H 2012 J. Visual Commun. Image Represent. 23 604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ri S, Fujigaki M, Matui T, Morimoto Y 2006 Appl. Opt. 45 6940
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ri S, Fujigaki M, Matui T, Morimoto Y 2006 Exp. Mech. 46 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
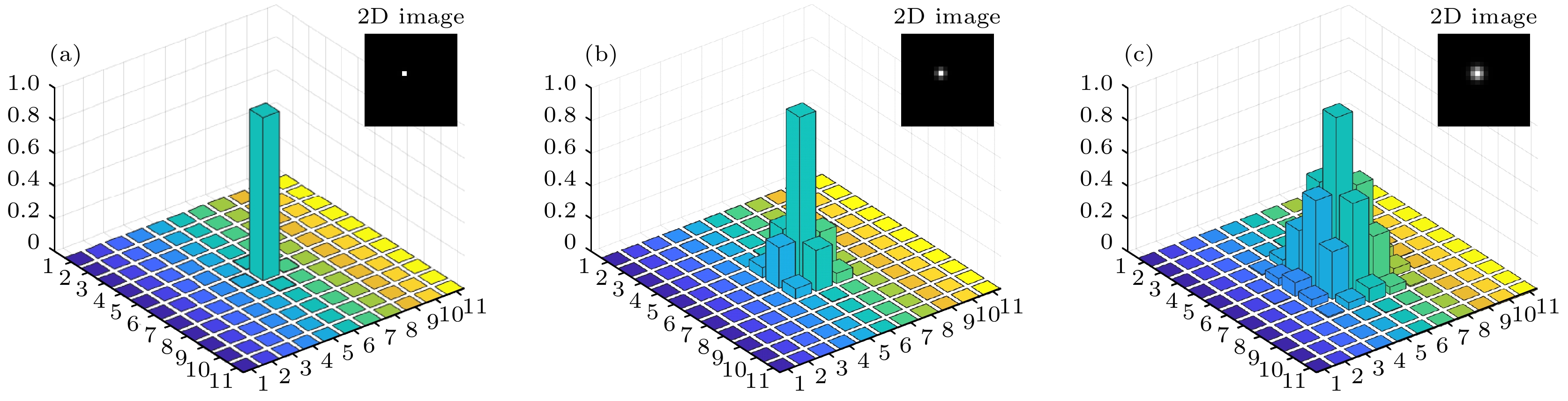
图 3 (a)
$ \sigma $ = 0.3 pixelsize时的成像效果; (b)$ \sigma $ = 0.6 pixelsize时的成像效果; (c)$ \sigma $ = 0.9 pixelsize时的成像效果Fig. 3. (a) Imaging effect of image I when
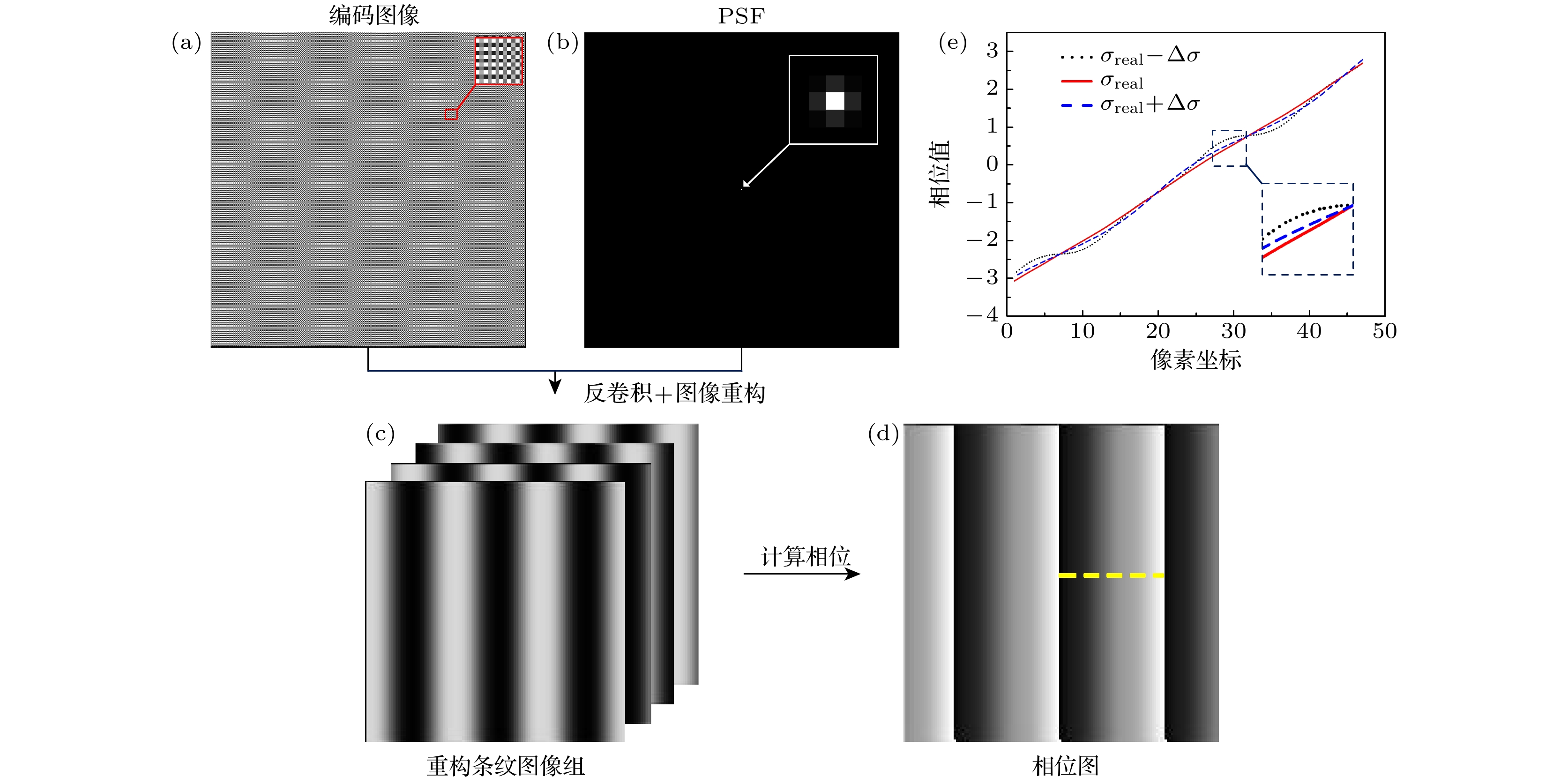
$ \sigma $ = 0.3 pixelsize; (b) imaging effect of imageI when $ \sigma $ = 0.6 pixelsize; (c) imaging effect of image I when$ \sigma $ = 0.9 pixelsize.图 4 (a) 单帧条纹编码图像; (b) 数值模拟产生的PSF; (c) 重构的条纹图像信息; (d) 计算获得的相位图; (e) 图(d)中黄线虚线处的切面相位值
Fig. 4. (a) Single frame fringe encoded image; (b) numerical simulation of PSF; (c) reconstructed fringe image information; (d) calculated phase diagram; (e) section phase value at dotted line of yellow line in Figure (d).
图 8 (a) 低分辨率条件下的编码图像及重构结果; (b) 编码图象(a)经反卷积处理及重构的结果; (c) 高分辨率条件下的编码图像及重构结果; (d) 编码图象(c)经反卷积处理及重构的结果
Fig. 8. (a) Coded images and reconstruction results at low resolution; (b) results of deconvolution and reconstruction of coded image (a); (c) coded images and reconstruction results at high resolution; (d) results of deconvolution and reconstruction of coded image (c).
-
[1] Akiyama M, Yang Z B, Gnapowski S, Hamid S, Hosseini R, Akiyama H 2014 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 42 3215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李明飞, 莫小范, 赵连洁, 霍娟, 杨然, 李凯, 张安宁 2016 65 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M F, Mo X F, Zhao L J, Huo J, Yang R, Li K, Zhang A N 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang J, Xiong T, Tran T, Chin S, Cummings R E 2016 Opt. Express 24 9013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Khan S R, Feldman M, Gunturk B K 2018 Signal Process. Image Commun. 60 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 冯维, 张福民, 王惟婧, 曲兴华 2017 66 234201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng W, Zhang F M, Wang W J, Qu X H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 234201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qiao Y, Xu X P, Liu T, Pan Y 2015 Appl Opt. 54 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tang C Y, Chen Y T, Li Q, Feng H J, Xu Z H 2015 Optica 35 0410002
[8] Bub G, Tecza M, Helmes M, Lee P, Kohl P 2009 Nat. Methods 7 209
[9] Ri S, Fujigaki M, Morimoto Y 2009 Opt. Eng. 48 103605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu D Y, Gu J W, Hitomi Y, Gupta M, Mitsunaga T, Nayar S K 2013 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (TPAMI) 36 248
[11] Feng W, Zhang F M, Qu X H, Zheng S W 2016 Sensors 16 331
[12] Peng X, Tian J D, Zhang P, Wei L B, Qiu W J, Li E B, Zhang D W 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 1965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Niu B, Qu X H, Guan X H, Zhang F M 2021 Opt. Express 29 27562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gunturk B K, Feldman M 2013 Proc. SPIE 8660 86600P
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Feng W, Zhang F M, Wang W J, Xing W, Qu X H 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 3831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang C M, Tu C 2014 Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 7 217
[17] Gao L, Liang J Y, Li C Y, Wang L H 2014 Nature 516 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Adekunle A, Barakat N 2009 Opt. Express 17 1831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y, Wang Z F 2015 J. Visual Commun. Image Represent. 31 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gu B, Li W J, Wong J T, Zhu M Y, Wang M H 2012 J. Visual Commun. Image Represent. 23 604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ri S, Fujigaki M, Matui T, Morimoto Y 2006 Appl. Opt. 45 6940
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ri S, Fujigaki M, Matui T, Morimoto Y 2006 Exp. Mech. 46 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5014
- PDF下载量: 80
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: