-
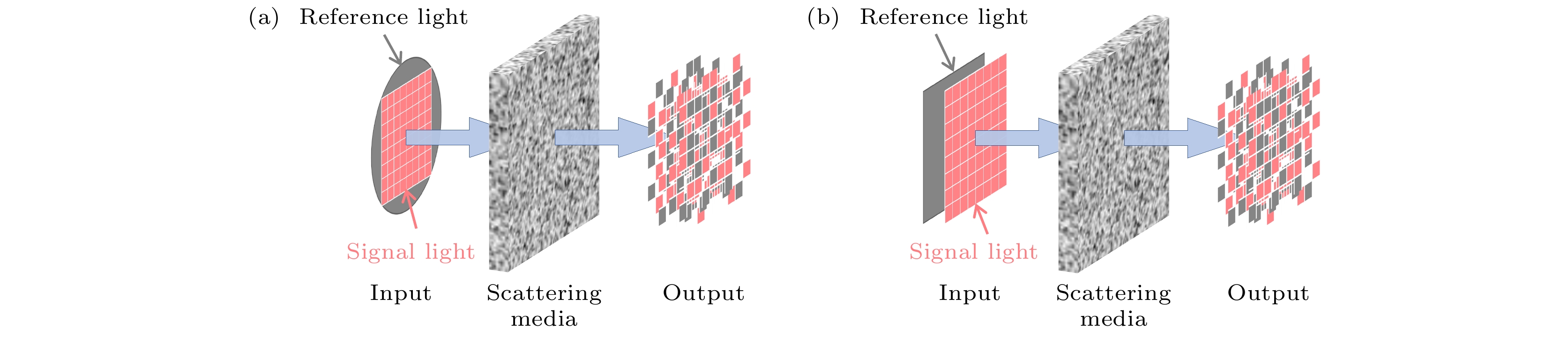
When light propagates through complex medium, such as biological tissue and multimode fiber, refractive index inhomogeneity causes multiple scattering and distortion. This phenomenon is usually seen as obstacles for biomedical imaging, telecommunications, photodynamic therapy and so on. Thus, manipulation of the incident wavefront to compensate for the wavefront distortion due to multiple scattering has been an interdisciplinary subject of interest. Fortunately, wavefront shaping technologies have emerged to provide versatile solutions to minimize the influence of light scattering. By modulating the incident light into a special wavefront with a spatial light modulator, focusing through scattering medium is obtained. To date, several wavefront shaping techniques have been proposed, mainly including transmission matrix inversion, feedback based iterative optimization, and digital optical phase conjugation. Unlike a planar wavefront, the modulated light with special wavefront is transformed into a bright optical focus spot or a desired focus pattern after the scattering medium. Among the proposed approaches, the transmission matrix is considered as a significant tool to characterize a multiple scattering medium with the purpose of manipulating light propagation through it, which contains all the information related to the input field and the scattered output field. In this work, we experimentally measure the transmission matrix of scattering media based on self-reference interference method with a digital micromirror device. Unlike the conventional setup, which divides the incident wavefront into a signal part and reference part, in the self-reference interference method, the reference light is superimposed directly on the signal light to form a new set of input light fields. This self-reference interference method effectively improves the degree of freedom of optical field modulation. Moreover, the intensity ratio between the signal light and the reference light can be adjusted conveniently. In our experiment, this superimposed field is generated by a digital micromirror device with superpixel method. We measure the Hadamard basis and the OAM-basis transmission matrices of scattering medium, respectively. With the measured transmission matrices, single-spot, multi-spot and vortex focusing are achieved after scattering medium, verifying the accuracy of the measured transmission matrices. The strong diagonal presented in the norm of focusing operator also proves the accuracy of the measured transmission matrices. The proposed method may have potential applications in optical imaging and optical communication under scattering environment.
-
Keywords:
- self-reference interference /
- transmission matrix /
- digital micromirror device /
- scattering media
[1] Feng S, Kane C, Lee P A, Stone A D 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Freund I, Rosenbluh M, Feng S 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 2328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 2309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Volpe G, Kurz L, Callegari A, Volpe G, Gigan S 2014 Opt. Express 22 18159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu Y, Shen Y, Ruan H, Brodie F L, Wong T T W, Yang C, Wang L V 2018 J. Biomed. Opt. 23 010501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Boniface A, Dong J, Gigan S 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 6154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P 2008 Opt. Commun. 281 3071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Conkey D B, Brown A N, Caravaca-Aguirre A M, Piestun R 2012 Opt. Express 20 4840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang J, He Q, Liu L, Qu Y, Shao R, Song B, Zhao Y 2021 Light Sci. Appl. 10 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Woo C M, Zhao Q, Zhong T, Li H, Yu Z, Lai P 2022 APL Photonics 7 046109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yaqoob Z, Psaltis D, Feld M S, Yang C 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vellekoop I M, Cui M, Yang C 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 081108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu L X, Liang W J, Qu Y, He Q Z, Shao R J, Ding C X, Yang J M 2022 Opt. Express 30 31614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Carminati R, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Popoff S, Lerosey G, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Nat. Commun. 1 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2011 New J. Phys. 13 123021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Conkey D B, Caravaca-Aguirre A M, Piestun R 2012 Opt. Express 20 1733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yu H, Hillman T R, Choi W, Lee J O, Feld M S, Dasari R R, Park Y 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 153902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xu J, Ruan H W, Liu Y, Zhou H J, Yang C H 2017 Opt. Express 25 27234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang H K, Zhang B, Liu Q 2020 Opt. Express 28 15006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yoon J H, Lee K R, Park J C, Park Y K 2015 Opt. Express 23 10158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Drémeau A, Liutkus A, Martina D, Katz O, Schülke C, Krzakala F, Gigan S, Daudet L 2015 Opt. Express 23 11898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Huang G Q, Wu D X, Luo J W, Huang Y, Shen Y C 2020 Opt. Express 28 9487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Huang G, Wu D, Luo J, Lu L, Li F, Shen Y, Li Z 2021 Photonics Res. 9 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Goorden S A, Bertolotti J, Mosk A P 2014 Opt. Express 22 17999
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang H, Zhang B, Feng Q, Ding Y, Liu Q 2020 Appl. Opt. 59 7547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Dubois A, Vabre L, Boccara A C, Beaurepaire E 2002 Appl. Opt. 41 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Prada C, Fink M 1994 Wave Motion 20 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gong L, Zhao Q, Zhang H, Hu X Y, Huang K, Yang J M, Li Y M 2019 Light Sci. Appl. 8 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Akbulut D, Huisman T J, Putten E G van, Vos W L, Mosk A P 2011 Opt. Express 19 4017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ma C, Di J, Zhang Y, Li P, Xiao F, Liu K, Bai X, Zhao J 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 3333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
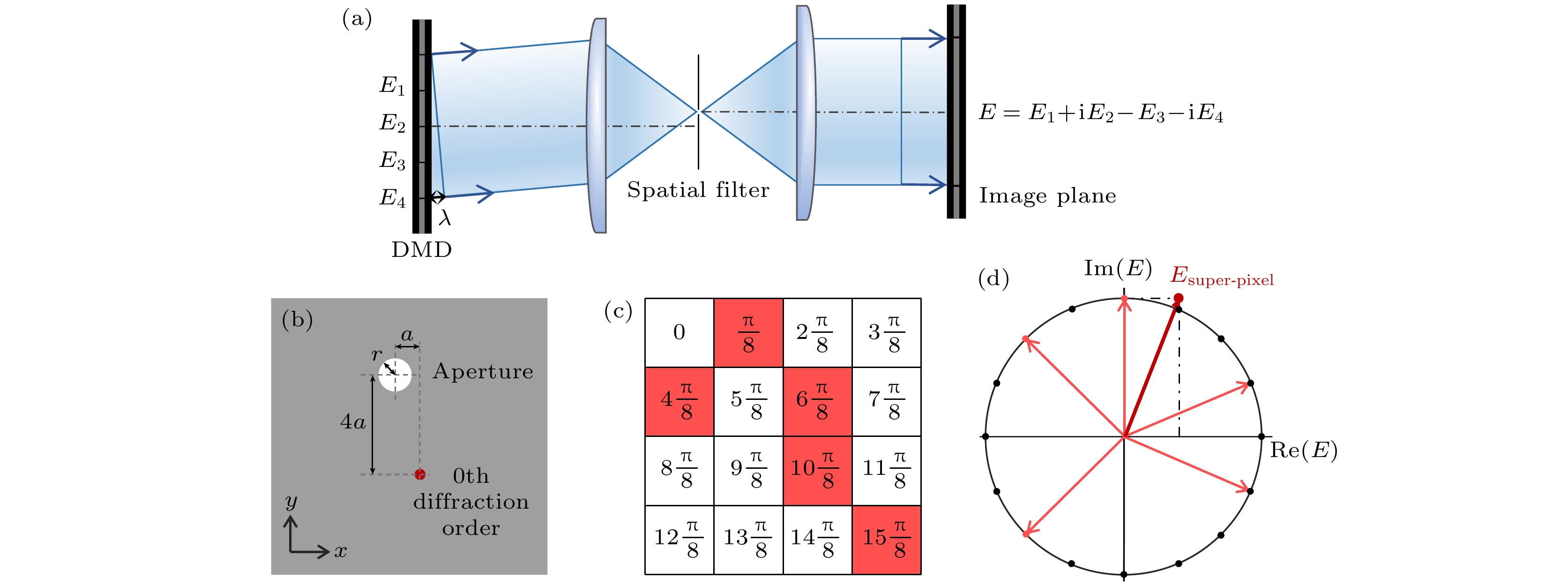
图 2 (a) 超像素法原理图; (b) 空间滤波器的孔径中心位置; (c) 一个超像素的4×4相位掩模; (d) 一个超像素的复振幅为开态子像素的复振幅叠加
Figure 2. (a) Principle of superpixel method; (b) position of the spatial filter in the Fourier plane; (c) 4×4 phase mask for one superpixel; (d) a complex-amplitude superpixel value as the superposition of complex-amplitude of all open-state subpixel.
图 3 (a) Hadamard基信号光相位分布; (b) 参考光相位分布; (c)—(f) 产生不同相移时信号光与参考光复合场的DMD超像素掩膜, 其中(c)
$\alpha = 0$ ; (d)$\alpha = {\text{π /}}2$ ; (e)$\alpha = {\text{π}}$ ; (f)$\alpha = 3{\text{π /}}2$ Figure 3. (a) Phase profile of the Hadamard-based signal light; (b) phase profile of the reference light; (c)–(f) DMD superpixel masks for generating the superposed fields of the signal and reference light with four-step phase shifting, where (c)
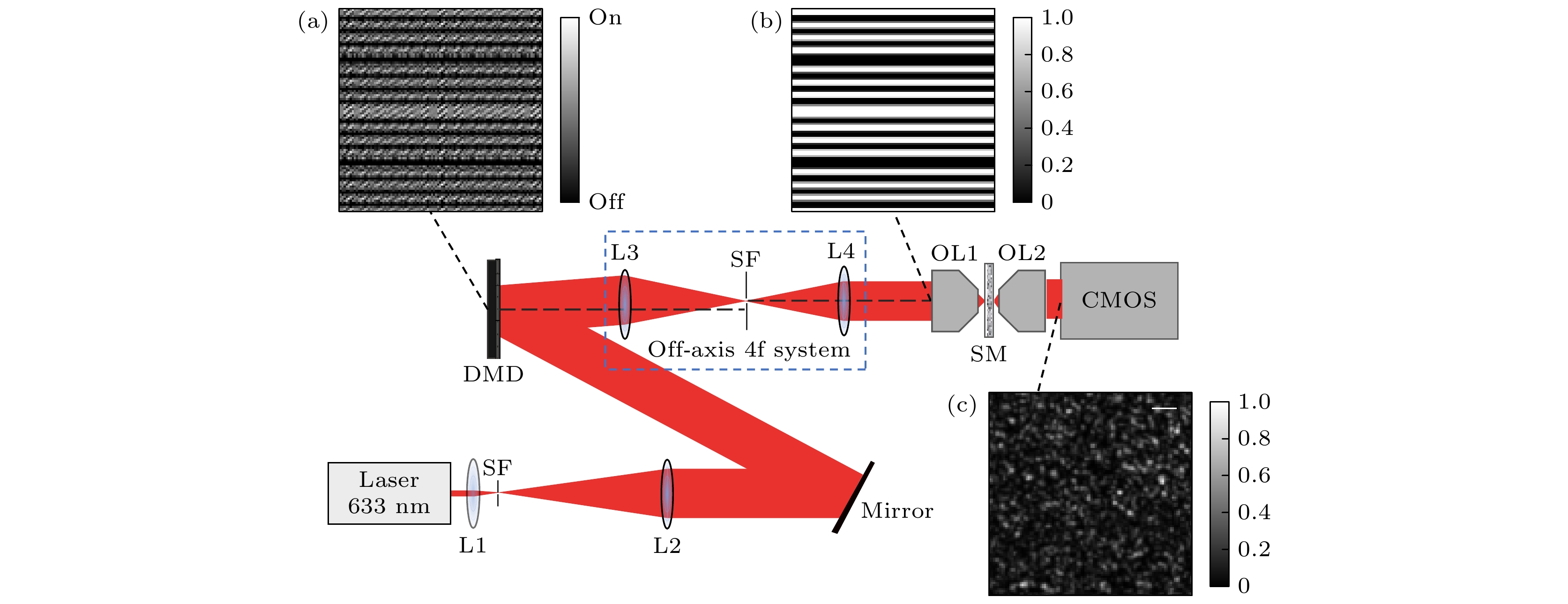
$\alpha = 0$ ; (d)$\alpha = {\text{π /}}2$ ; (e)$\alpha = {\text{π }}$ ; (f)$\alpha = 3{\text{π /}}2$ .图 4 传输矩阵测量实验装置图, L为透镜, DMD为数字微镜器件, SF为空间滤波器, SM为散射介质, OL为显微物镜 (a) 32×32阶Hadamard基(第10列)对应的超像素掩模; (b) 显微物镜入瞳处的输入光强分布; (c) CMOS相机采集的散斑图. 图中比例尺: 100 μm
Figure 4. Optical system setup for measuring the TM, L is focusing lens, DMD is digital micromirror device, SF is spatial filter, SM is scattering medium, OL is objective lens: (a) Superpixel mask for 32×32 Hadamard-basis (the 10th column); (b) intensity profile at the entrance pupil of the objective lens; (c) speckle pattern captured by the CMOS camera. Scale bar: 100 μm.
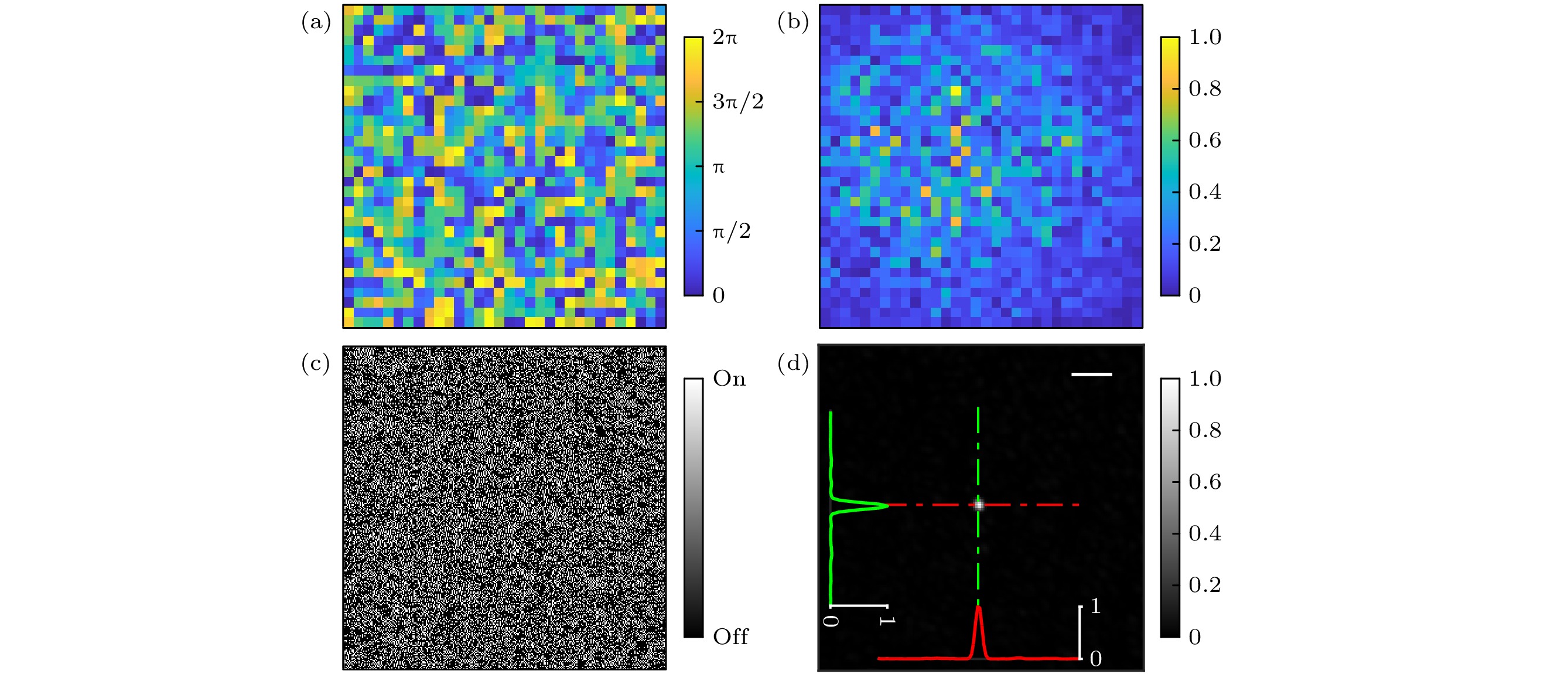
图 5 Hadamard基传输矩阵单点聚焦结果 (a) 输入光场相位分布; (b) 输入光场振幅分布; (c) DMD超像素掩模; (d) 输出光强分布. 图中比例尺: 100 μm (插图为焦点沿水平和垂直方向的归一化光强曲线图)
Figure 5. Single-spot focusing achieved with Hadamard-basis transmission matrix: (a) Phase profile of input light; (b) amplitude profile of input light; (c) DMD superpixel mask; (d) intensity profile of output light. Scale bar: 100 μm (Inset shows normalized intensity profile of focus point along horizontal and vertical directions).
图 6 Hadamard基传输矩阵多点聚焦结果 (a) 两点聚焦输出光强分布; (b) 三点聚焦输出光强分布. 图中比例尺: 100 μm (插图为聚焦点沿两个正交方向的归一化光强曲线图)
Figure 6. Multiple-spot focusing achieved with Hadamard-basis transmission matrix: (a) Intensity profile of 2-spot focusing output light; (b) intensity profile of 3-spot focusing output light. Scale bar: 100 μm (Insets show normalized intensity profile of focus points along two orthogonal directions).
图 7 (a) OAM基信号光相位分布; (b) OAM基信号光振幅分布; (c)—(f) 信号光四步相移后与参考光的叠加场的DMD超像素掩膜, 其中(c)
$\alpha = 0$ ; (d)$\alpha = {\text{π/}}2$ ; (e)$\alpha = {\text{π}}$ ; (f)$\alpha = 3{\text{π/}}2$ Figure 7. (a) Phase profile of the OAM-basis signal light; (b) amplitude profile of the OAM-basis signal light; (c)–(f) DMD superpixel masks for generating the superposed fields of the signal light with four-step phase shifting and the reference light, where (c)
$\alpha = 0$ ; (d)$\alpha = {\text{π/}}2$ ; (e)$\alpha = {\text{π}}$ ; (f)$\alpha = 3{\text{π/}}2$ .图 8 OAM基传输矩阵单点聚焦结果 (a) 输入光场相位分布; (b) 输入光场振幅分布; (c) DMD超像素掩模; (d) 输出光强分布. 图中比例尺: 100 μm (插图为聚焦点沿两正交方向的归一化光强曲线图)
Figure 8. Single-spot focusing achieved with OAM-basis transmission matrix: (a) Phase profile of input light; (b) amplitude profile of input light; (c) DMD superpixel mask; (d) intensity profile of output light. Scale bar: 100 μm (Inset shows normalized intensity profile of focus point along two orthogonal directions).
图 9 OAM基传输矩阵多点聚焦结果 (a) 水平三点聚焦光强分布; (b) 垂直三点聚焦光强分布; (c) 五点聚焦光强分布. 图中比例尺: 100 μm (插图为聚焦点沿两正交方向的归一化光强曲线图)
Figure 9. Multiple-spot focusing achieved with OAM-basis transmission matrix: (a) Intensity profile of horizontal 3-spot focusing output light; (b) intensity profile of vertical 3-spot focusing output light; (c) intensity profile of 5-spot focusing output light. Scale bar: 100 μm (Insets show normalized intensity profile of focus points along two orthogonal directions).
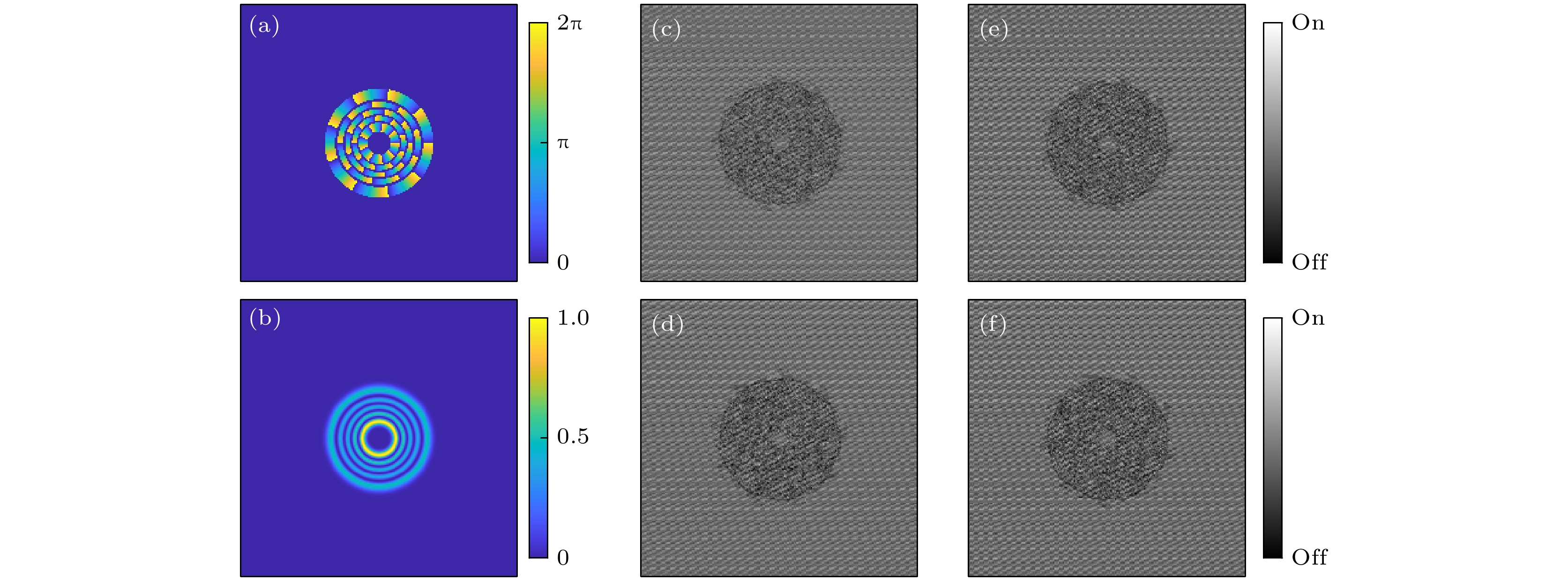
图 10 OAM基传输矩阵涡旋聚焦结果 (a) DMD超像素掩模; (b) TC = 1涡旋光束强度分布, 图中比例尺: 100 μm (插图为聚焦点沿某一方向的归一化光强曲线图); (c) 像散变换光强分布
Figure 10. Vortex focusing achieved with OAM-basis transmission matrix: (a) DMD superpixel mask; (b) intensity profile of vortex beam with TCs of 1, scale bar: 100 μm (Insets show normalized intensity profile of focus points along two orthogonal directions); (c) astigmatic transformation patterns of the vortex beams.
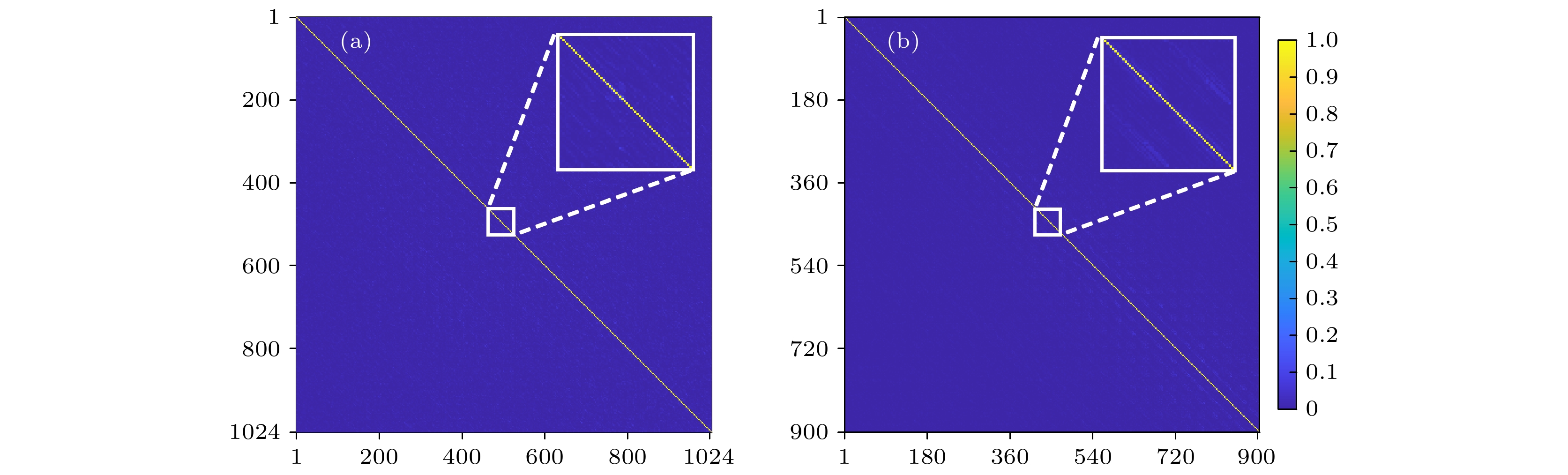
图 11 (a) Hadamard基传输矩阵聚焦算符的归一化强度分布; (b) OAM基传输矩阵聚焦算符归一化强度分布. 插图为局部放大视图
Figure 11. (a) Normalized intensity profile of the Hadamard-basis transmission matrix time focusing operator; (b) normalized intensity profile of OAM-basis transmission matrix time focusing operator. The magnified view of the local part is displayed in upper inset
-
[1] Feng S, Kane C, Lee P A, Stone A D 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Freund I, Rosenbluh M, Feng S 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 2328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 2309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Volpe G, Kurz L, Callegari A, Volpe G, Gigan S 2014 Opt. Express 22 18159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu Y, Shen Y, Ruan H, Brodie F L, Wong T T W, Yang C, Wang L V 2018 J. Biomed. Opt. 23 010501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Boniface A, Dong J, Gigan S 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 6154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P 2008 Opt. Commun. 281 3071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Conkey D B, Brown A N, Caravaca-Aguirre A M, Piestun R 2012 Opt. Express 20 4840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang J, He Q, Liu L, Qu Y, Shao R, Song B, Zhao Y 2021 Light Sci. Appl. 10 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Woo C M, Zhao Q, Zhong T, Li H, Yu Z, Lai P 2022 APL Photonics 7 046109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yaqoob Z, Psaltis D, Feld M S, Yang C 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vellekoop I M, Cui M, Yang C 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 081108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu L X, Liang W J, Qu Y, He Q Z, Shao R J, Ding C X, Yang J M 2022 Opt. Express 30 31614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Carminati R, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Popoff S, Lerosey G, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Nat. Commun. 1 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2011 New J. Phys. 13 123021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Conkey D B, Caravaca-Aguirre A M, Piestun R 2012 Opt. Express 20 1733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yu H, Hillman T R, Choi W, Lee J O, Feld M S, Dasari R R, Park Y 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 153902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xu J, Ruan H W, Liu Y, Zhou H J, Yang C H 2017 Opt. Express 25 27234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang H K, Zhang B, Liu Q 2020 Opt. Express 28 15006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yoon J H, Lee K R, Park J C, Park Y K 2015 Opt. Express 23 10158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Drémeau A, Liutkus A, Martina D, Katz O, Schülke C, Krzakala F, Gigan S, Daudet L 2015 Opt. Express 23 11898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Huang G Q, Wu D X, Luo J W, Huang Y, Shen Y C 2020 Opt. Express 28 9487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Huang G, Wu D, Luo J, Lu L, Li F, Shen Y, Li Z 2021 Photonics Res. 9 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Goorden S A, Bertolotti J, Mosk A P 2014 Opt. Express 22 17999
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang H, Zhang B, Feng Q, Ding Y, Liu Q 2020 Appl. Opt. 59 7547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Dubois A, Vabre L, Boccara A C, Beaurepaire E 2002 Appl. Opt. 41 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Prada C, Fink M 1994 Wave Motion 20 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gong L, Zhao Q, Zhang H, Hu X Y, Huang K, Yang J M, Li Y M 2019 Light Sci. Appl. 8 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Akbulut D, Huisman T J, Putten E G van, Vos W L, Mosk A P 2011 Opt. Express 19 4017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ma C, Di J, Zhang Y, Li P, Xiao F, Liu K, Bai X, Zhao J 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 3333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5374
- PDF Downloads: 120
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: