-
Ultra-cold long-range Rydberg molecules, consisting of a Rydberg atom and a ground-state atom or another Rydberg atom or ion, have attracted considerable attention due to their exaggerated properties, such as huge size, long chemical bond, large polarization and electric dipole moment, abundant vibrational states and exotic adiabatic potentials. The binding mechanism of Rydberg molecules is a low-energy scattering interaction between the Rydberg electron and the ground state atom for ground-Rydberg molecules or long-range multipole interaction for Rydberg-atom macrodimers and Rydberg-ion molecules, in contrast to covalent bonds, ionic bonds of normal and van der Waals interaction. Owing to its huge size, the dynamic evolution becomes slow compared with normal diatomic molecules and the ultra-long chemical bonds allow being imaged directly by high resolution imaging technology, which makes it convenient to observe the molecular dynamics process chemical reaction process in real time. The investigation of Rydberg molecules will be significant for understanding the mechanism of molecular collision and quantum chemical reaction. In this work, we study the ultra-cold Rydberg-ground state molecules theoretically and experimentally. Theoretically, we calculate the adiabatic potential energy curve of cesium (36D5/2+ 6S1/2) Rydberg molecule based on the Fermi model of low energy electron scattering by numerically solving the Hamiltonian of Rydberg molecules. And also, we obtain its characteristic parameters, such as the potential depth, binding energy and equilibrium nuclear distance of Rydberg molecule. Experimentally, the Rydberg-ground molecules are investigated by a photoassociation spectroscopy, where two laser pulses are used to achieve a two-photon transition, and their spectra are obtained by ion detection technology. We successfully observe the Rydberg-ground state molecular spectra that correspond to a scattering triplet and a scattering single-triplet mixture (S,TΣ). The measured binding energy of Rydberg-ground state molecules is in good agreement with the theoretical result. In addition, taking the Rydberg-ground state molecules formed by scattering triplet (TΣ) for example, we demonstrate the spectrum broadening of Rydberg molecules in a weak electric field, from which we obtain the permanent electric dipole moments $|\bar{d}|$ of polar Rydberg-ground state molecules about (12.10$ \pm $ 1.65) Debye ((4.76$ \pm $ 0.65) ea0). The results are consistent with the theoretical calculations. Our study provides a feasible scheme for the experimental preparation of D-type Rydberg-ground molecules, which is of great significance in studying the binding mechanism and the spectral characteristics of polar Rydberg molecules.-
Keywords:
- ultra-cold Rydberg-ground molecule /
- photoassociation spectrum /
- adiabatic potential energy curve /
- permanent electric dipole moment
[1] Omont A 1977 J. de Phys. 38 1343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Greene C H, Dickinson A S, Sadeghpour H R 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 2458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Khuskivadze A A, Chibisov M I, Fabrikant I I 2002 Phys. Rev. A 66 042709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chibisov M I, Khuskivadze A A, Fabrikant I I 2002 J. Phys. B 35 L193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hamilton E L, Greene C H, Sadeghpour H R 2002 J. Phys. B 35 L199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lesanovsky I, Schmelcher P, Sadeghpour H R 2006 J. Phys. B 39 L69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bendkowsky V, Bjoern B, Nipper J, Shaffer J P, Robert L, Pfau T 2009 Nature 458 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bellos M A, Carollo R, Banerjee J, Eyler E E, Gould P L 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 053001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Anderson D A, Miller S A, Raithel G 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 163201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Krupp A T, Gaj A, Balewski J B, Ilzhöfer P, Hofferberth S, Löw R, Pfau T, Kurz M, Schmelcher P 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 143008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Maclennan J L, Chen Y J, Raithel G 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 033407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Booth D, Rittenhouse S T, Yang J, Sadeghpour H R, Shaffer J P 2015 Science 348 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Tallant J, Rittenhouse S T, Booth D, Sadeghpour H R, Shaffer J P 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 173202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sassmannshausen H, Merkt F, Deiglmayr J 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 133201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Fey C, Hummel F, Schmelcher P 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 022506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bai S, Han X, Bai J, Jiao Y, Wang H, Zhao J, Jia S 2020 J. Chem. Phys. 152 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bai S, Han X, Bai J, Jiao Y, Zhao J, Jia S, Raithel G 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 033525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Overstreet K R, Schwettmann A, Tallant J, Booth D, Shaffer J P 2009 Nat. Phys 5 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Han X, Bai S, Jiao Y, Hao L, Xue Y, Zhao J, Jia S, Raithel G 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 031403(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Duspayev A, Han X, Viray M A, Ma L, Zhao J, Raithel G 2021 Phys. Rev. Res. 3 023114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Deiß M, Haze S, Denschlag J H 2021 Atoms 9 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zuber N, Anasuri V S V, Berngruber M, Zou Y Q, Meinert F, Löw R, Pfau T 2022 Nature 605 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li W, Pohl T, Rost J M, Rittenhouse S T, Sadeghpour H R, Nipper J, Butscher B, Balewski J B, Bendkowsky V, Löw R 2011 Science 334 1110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Niederprüm T, Thomas O, Eichert T, Lippe C, Pérez-Ríos J, Greene C H, Ott H 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 12820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Weimer H, Müller M, Lesanovsky I, Zoller P, Büchler H 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lukin M D, Fleischhauer M, Côté R, Duan L M, Jaksch D, Cirac J I, Zoller P 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Alizadeh E, Orlando T M, Sanche L 2015 Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 66 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 里德伯-基态分子模型. 以里德伯离子核为中心, 基态原子位于轴矢量
$\boldsymbol{R}$ 的位置, 里德伯电子距离核的距离为r.$ {\widehat{S}}_{1} $ 为里德伯电子自旋,$ {\widehat{S}}_{2} $ 和$ {\widehat{I}}_{2} $ 分别对应基态原子的电子自旋和核自旋Figure 1. Model of a Rydberg-ground molecule. The Rydberg core is located in the center, the ground atom is located at the position of the axial vector
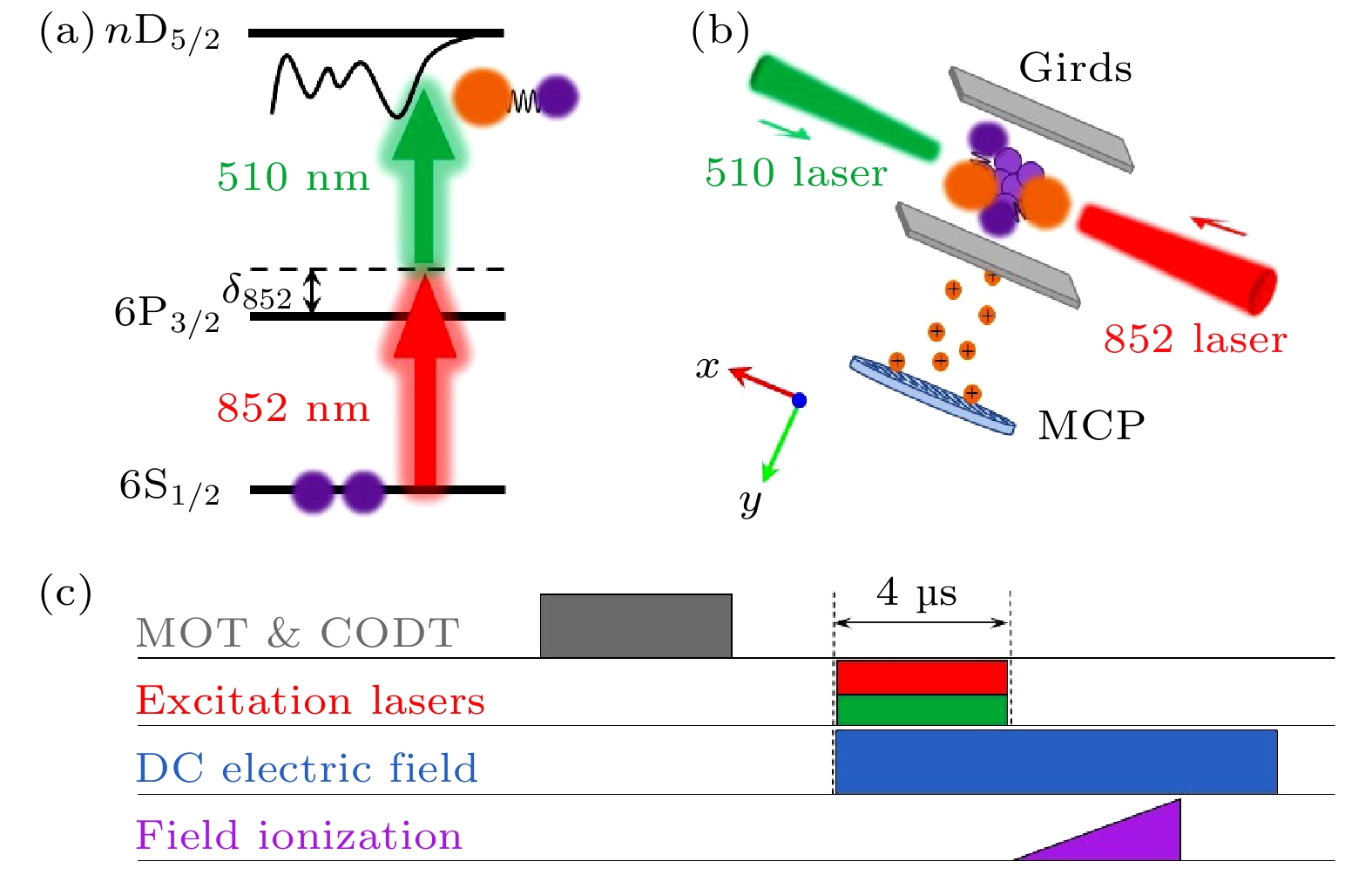
$\boldsymbol{R}$ , and the distance between the Rydberg electron and the core is$ r $ .$ {\widehat{S}}_{1} $ is the spin of Rydberg electron, and$ {\widehat{S}}_{2} $ and$ {\widehat{I}}_{2} $ are the spin of the electron and nuclear of the ground atom.图 3 (a) 双光子激发能级示意图; (b) 两束激发光反向传播作用于MOT&ODT中心; 里德堡原子和分子由脉冲电场电离后到达MCP, 由boxcar采集和计算机记录; (c) 实验时序图; 关断MOT&ODT光之后, 同时打开两束激发光, 之后由斜坡脉冲电离电场电离里德伯原子和分子, 直流电场用于电偶极矩的研究
Figure 3. (a) Schematic diagram of two photon excitation. (b) Schematic diagram of experimental set up. Two excitation lasers overlap in the center of MOT&ODT. Rydberg atoms and molecules ionized by a pulsed electric field arriving at MCP, which is collected with boxcar and recorded by computer. (c) Experimental sequence diagram. After turning off the MOT&ODT, two excitation lasers are turned on at the same time, and the Rydberg atoms and molecules were ionized by a ramp pulse ionization electric field. The direct current electric field is used to study the electric dipole moment.
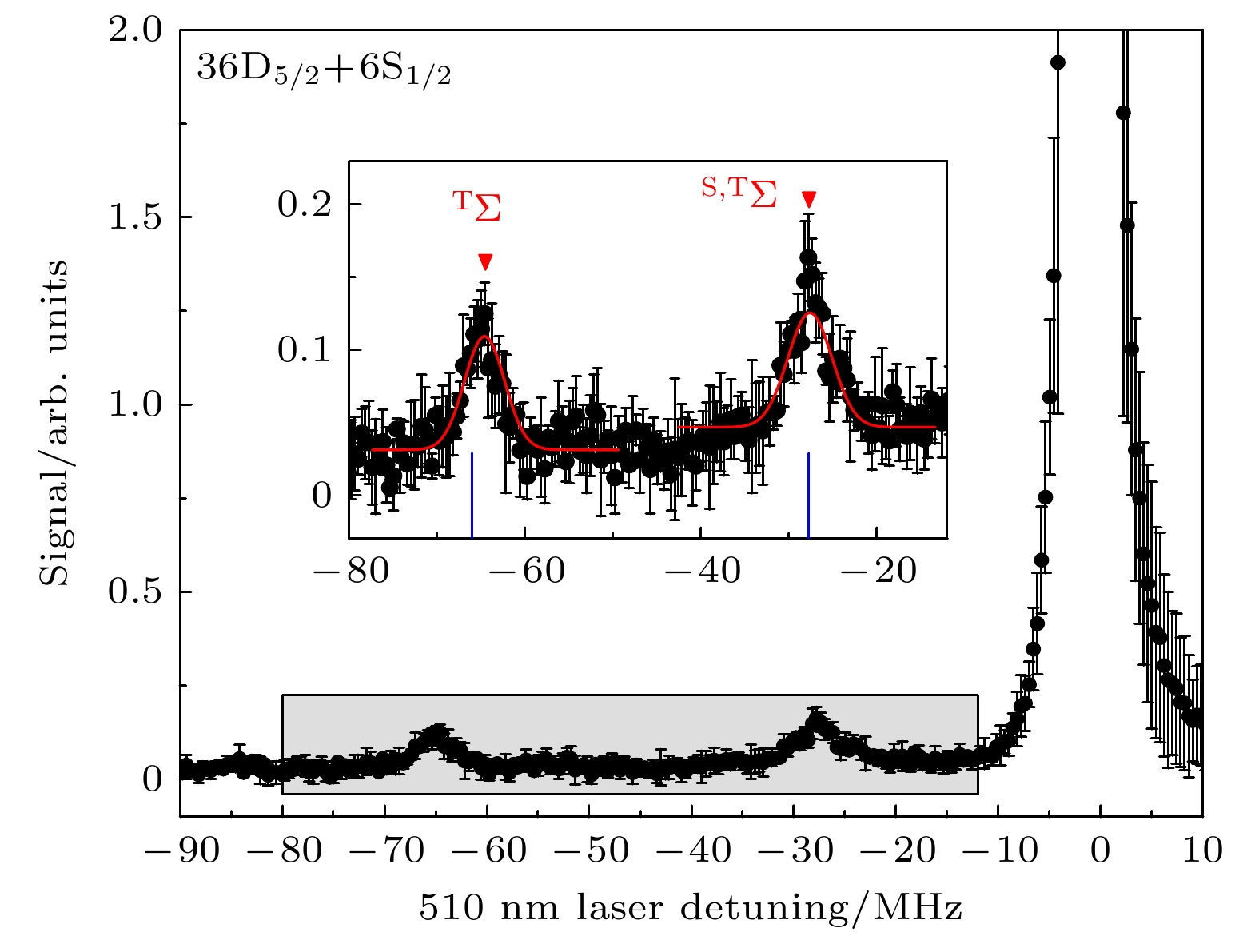
图 4 铯(36D5/2+6S1/2)里德伯-基态分子的双光子光缔合光谱. 红色三角形标记的峰为振动基态
$ \upsilon =0 $ 的里德堡分子信号. 蓝色的短线标记了理论计算的束缚势阱. 插图为阴影区域的放大Figure 4. Two-color photoassociation spectra of Cs (36D5/2+6S1/2) Rydberg-ground molecule. The short blue line marks the theoretically calculated bound potential well. Red triangles denote the Rydberg-molecular signal for
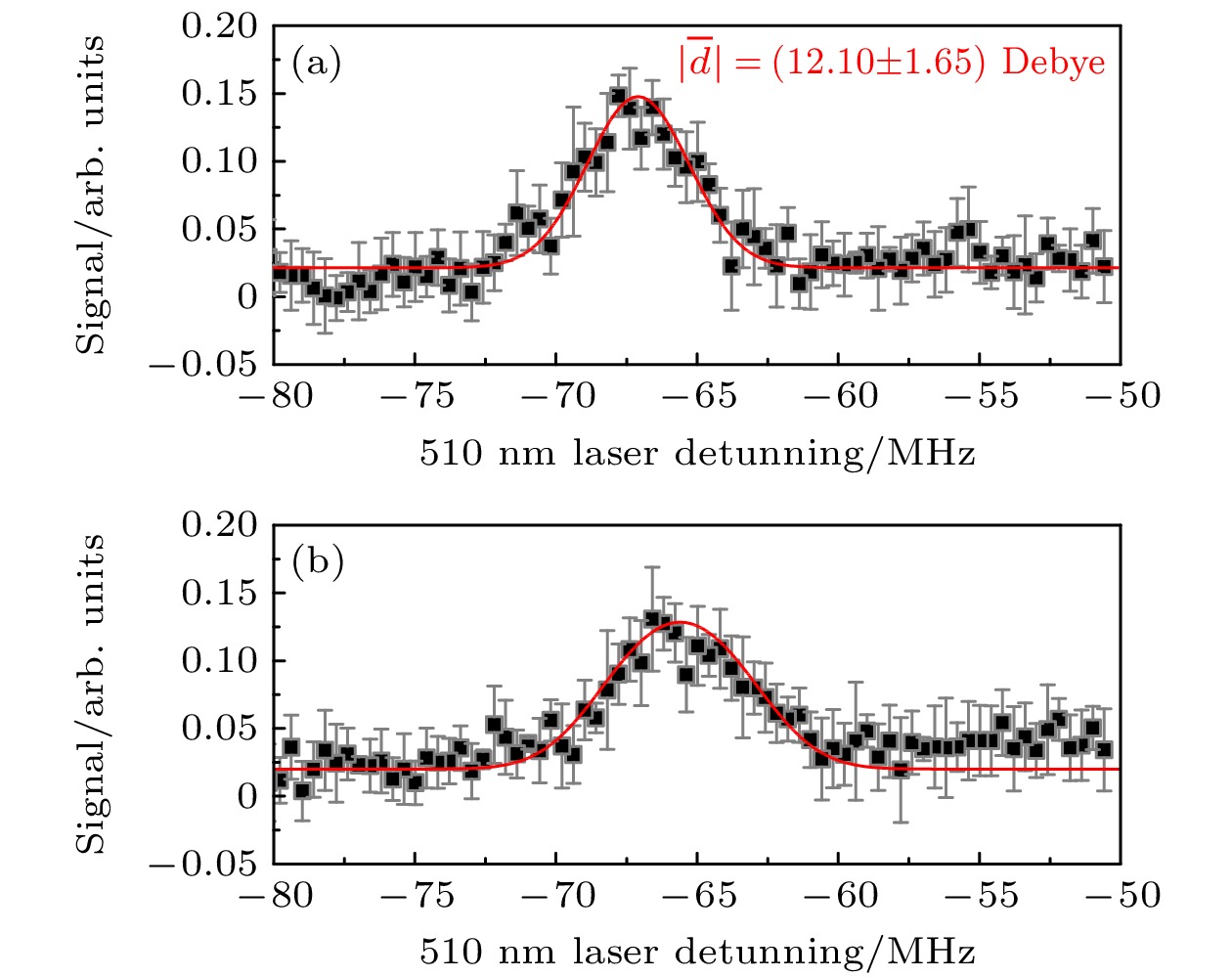
$ \upsilon =0 $ . Inset is an enlargement of the shaded area.图 5 电场为
$ 0.09 $ (a)和$0.37\;\rm{V}/\rm{c}\rm{m}$ (b)时, 三重态相互作用形成的里德伯-基态分子的光缔合光谱. 红色实线为理论拟合的分子电偶极矩Figure 5. Photoassociation spectra of Rydberg ground molecules formed by triplet interaction when the electric field is
$ 0.09 $ (a) and$0.37\;\rm{V}/\rm{c}\rm{m}$ (b). Red solid line are the theoretical fitting of molecular electric dipole moment. -
[1] Omont A 1977 J. de Phys. 38 1343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Greene C H, Dickinson A S, Sadeghpour H R 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 2458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Khuskivadze A A, Chibisov M I, Fabrikant I I 2002 Phys. Rev. A 66 042709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chibisov M I, Khuskivadze A A, Fabrikant I I 2002 J. Phys. B 35 L193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hamilton E L, Greene C H, Sadeghpour H R 2002 J. Phys. B 35 L199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lesanovsky I, Schmelcher P, Sadeghpour H R 2006 J. Phys. B 39 L69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bendkowsky V, Bjoern B, Nipper J, Shaffer J P, Robert L, Pfau T 2009 Nature 458 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bellos M A, Carollo R, Banerjee J, Eyler E E, Gould P L 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 053001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Anderson D A, Miller S A, Raithel G 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 163201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Krupp A T, Gaj A, Balewski J B, Ilzhöfer P, Hofferberth S, Löw R, Pfau T, Kurz M, Schmelcher P 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 143008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Maclennan J L, Chen Y J, Raithel G 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 033407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Booth D, Rittenhouse S T, Yang J, Sadeghpour H R, Shaffer J P 2015 Science 348 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Tallant J, Rittenhouse S T, Booth D, Sadeghpour H R, Shaffer J P 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 173202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sassmannshausen H, Merkt F, Deiglmayr J 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 133201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Fey C, Hummel F, Schmelcher P 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 022506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bai S, Han X, Bai J, Jiao Y, Wang H, Zhao J, Jia S 2020 J. Chem. Phys. 152 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bai S, Han X, Bai J, Jiao Y, Zhao J, Jia S, Raithel G 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 033525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Overstreet K R, Schwettmann A, Tallant J, Booth D, Shaffer J P 2009 Nat. Phys 5 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Han X, Bai S, Jiao Y, Hao L, Xue Y, Zhao J, Jia S, Raithel G 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 031403(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Duspayev A, Han X, Viray M A, Ma L, Zhao J, Raithel G 2021 Phys. Rev. Res. 3 023114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Deiß M, Haze S, Denschlag J H 2021 Atoms 9 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zuber N, Anasuri V S V, Berngruber M, Zou Y Q, Meinert F, Löw R, Pfau T 2022 Nature 605 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li W, Pohl T, Rost J M, Rittenhouse S T, Sadeghpour H R, Nipper J, Butscher B, Balewski J B, Bendkowsky V, Löw R 2011 Science 334 1110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Niederprüm T, Thomas O, Eichert T, Lippe C, Pérez-Ríos J, Greene C H, Ott H 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 12820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Weimer H, Müller M, Lesanovsky I, Zoller P, Büchler H 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lukin M D, Fleischhauer M, Côté R, Duan L M, Jaksch D, Cirac J I, Zoller P 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Alizadeh E, Orlando T M, Sanche L 2015 Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 66 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7194
- PDF Downloads: 130
- Cited By: 0


























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: