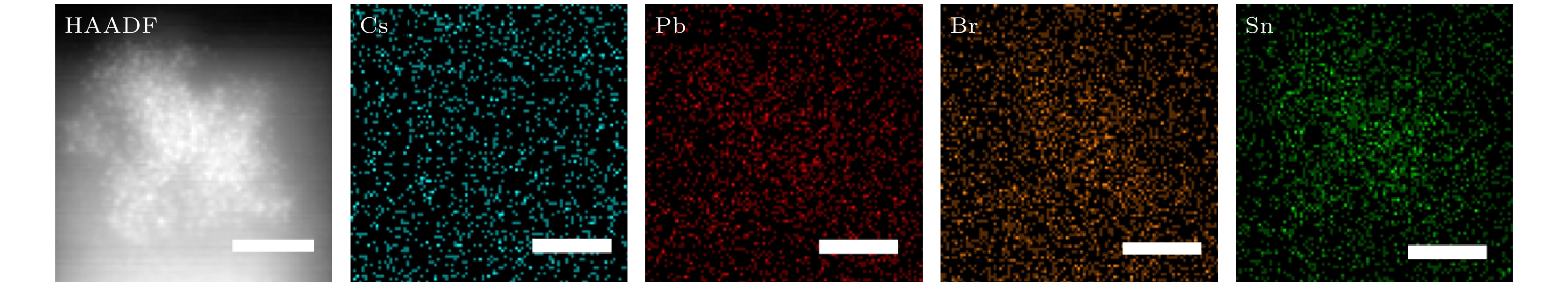
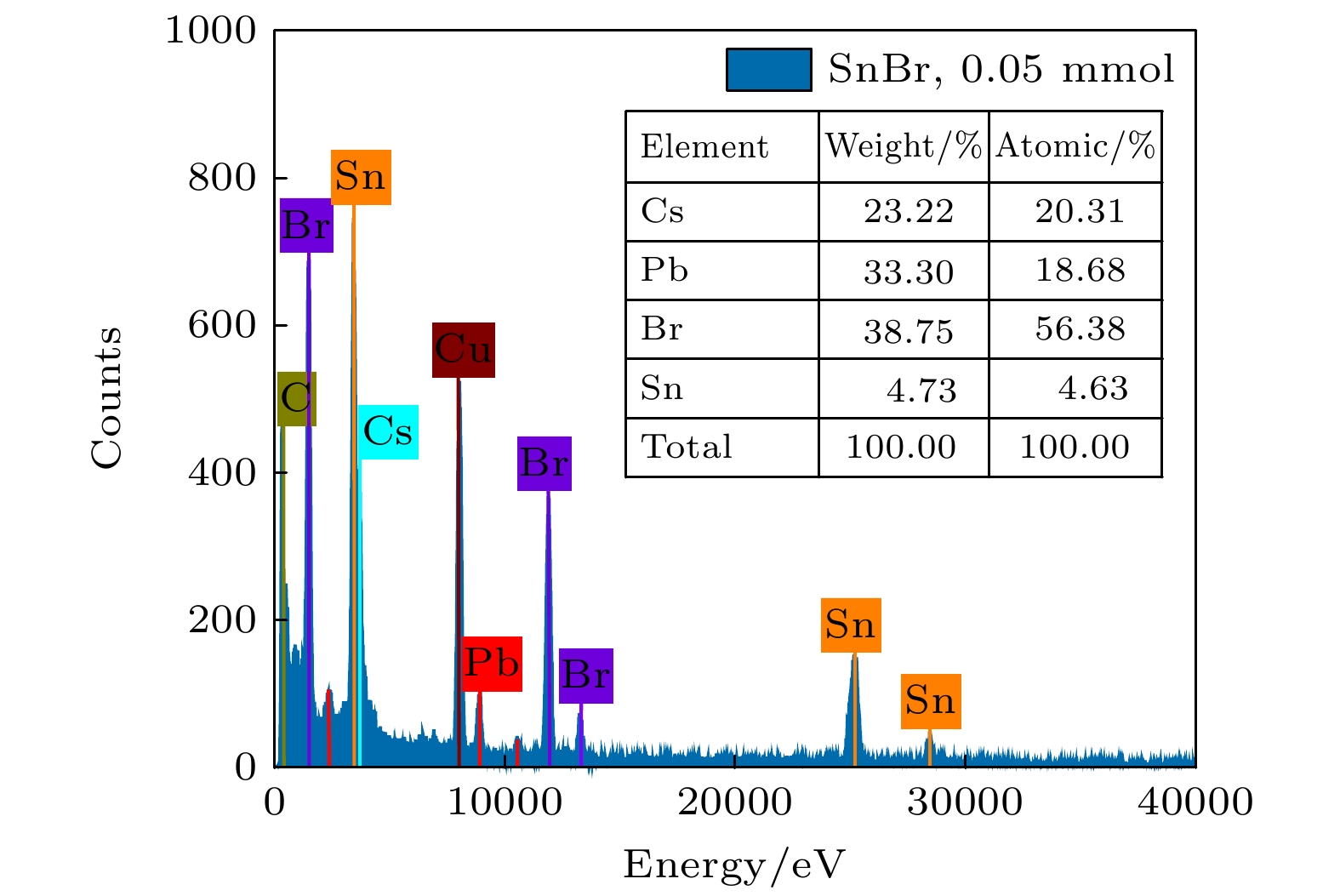
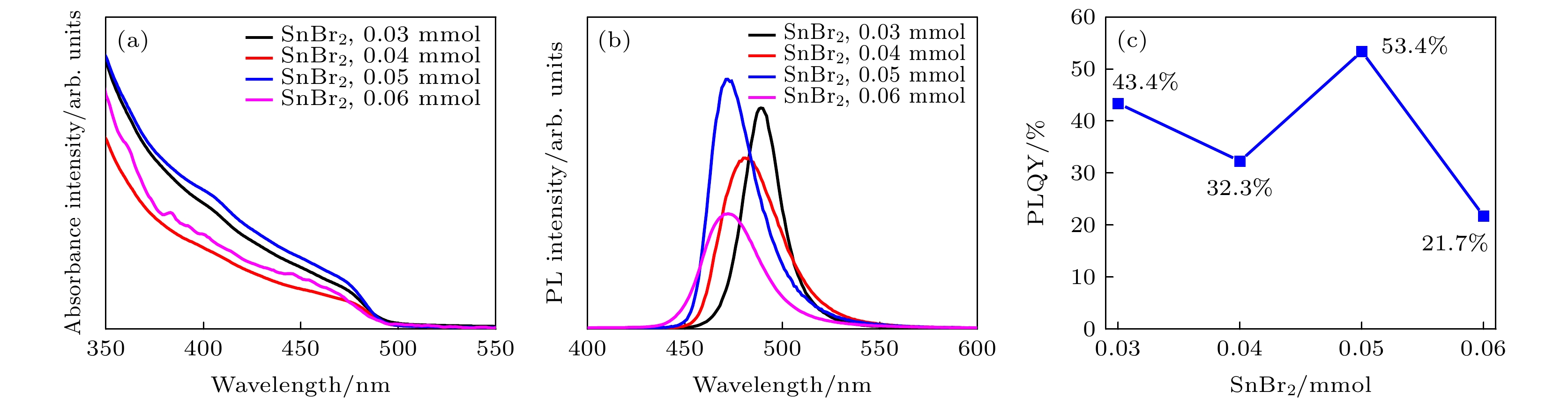
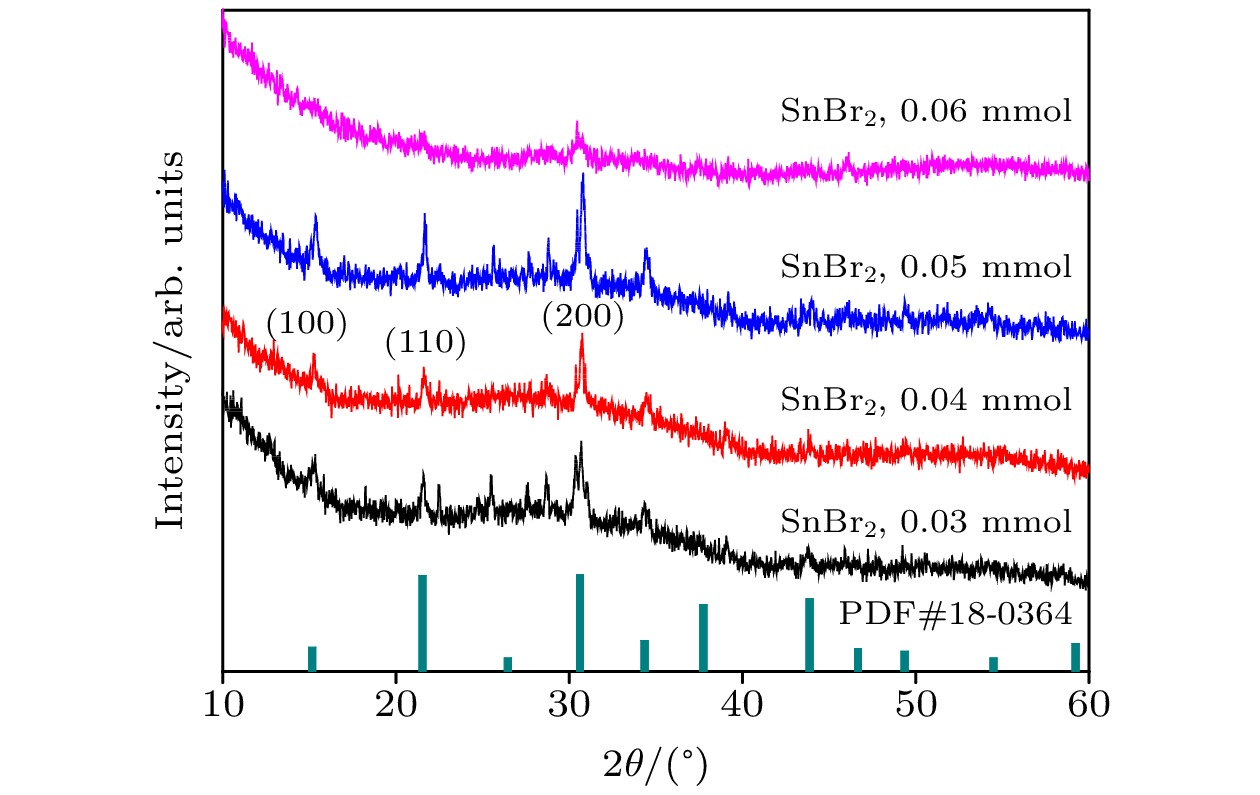
-
All-inorganic perovskite CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br and I) quantum dots (QDs) have been wildly utilized in optoelectronic devices due to their tunable photoluminescence, high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY), and narrow-line width photoluminescence. However, the blue luminescence PLQY of CsPbX3 perovskite quantum dots is still lower than their red and green luminescence counterparts (PLQYs nearly 100%). Here in this work, we present a handy strategy to synthesise the ultra-small blue luminescence Tin-doped CsPbBr3 perovskite QDs by supersaturated recrystallization synthetic approach at room temperature, and the particle size of as-prepared QDs is lower than 4 nm. The crystal structure and optical property of Tin doped CsPbBr3 QDs are characterized by XRD, TEM, ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, and fluorescence spectrophotometer. The results show that the particle size of as-prepared QDs is slightly shrunk from 3.33 nm (SnBr2 0.03 mmol) to 2.23 nm (SnBr2 0.06 mmol) as the SnBr2 adding quantity increases, but there is no obvious change in the lattice spacing of doped QDs. The partial substitution of Pb for Tin leads the optical spectra to blue-shift from 490 nm (SnBr2 0.03 mmol) to 472 nm (SnBr2 0.06 mmol). The highest PLQY and the strongest XRD diffraction of ultra-small Tin doped CsPbBr3blue luminescence QDs are obtained by adding SnBr2 0.05 mmol, and the blue luminescence peak is located at 472 nm with the PLQY of 53.4%. There is no any change in PL peak of Tin doped CsPbBr3 QDs (SnBr2 0.05 mmol) by storing it under the ambient atmosphere for 15 days, and the PLQY of Sn2+ doped QDs is still 80% of the initial after 15 days. It is concluded that the crystallization and optical property can be effectively improved in Tin doped CsPbBr3 QDs by partially replacing appropriate quantity of Pb by Tin.
-
Keywords:
- ultra-small /
- tin doped CsPbBr3 quantum dots /
- optical property /
- stable luminescence
[1] Li C L, Han C, Zhang Y B, Zang Z G, Wang M, Tang X S, Du J 2017 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 172 341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li C L, Zang Z G, Han C, Hu Z P, Tang X S, Du J, Leng Y X, Sun K 2017 Nano Energy 40 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Song J Z, Tao F, Li J H, Xu L M, Zhang F J, Han B N, Shan Q S, Zeng H B 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1805409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tang X S, Hu Z P, Chen W W, Xing X, Zang Z G, Hu W, Qiu J, Du J, Leng Y X, Jiang X F, Mai L Q 2016 Nano Energy 28 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang X, Lin H, Huang H, Reckmeier C, Zhang Y, Choy W C, Rogach A L 2016 Nano Lett. 16 1415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 瞿子涵, 储泽马, 张兴旺, 游经碧 2019 68 158504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qu Z H, Chu Z M, Zhang X W, You J B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 158504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shirasaki Y, Supran G J, Bawendi M G, Bulović V 2012 Nat. Photon. 7 13
[8] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, Krieg F, Caputo R, Hendon C H, Yang R X, Walsh A, Kovalenko M V 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu F, Zhang Y H, Ding C, Kobayashi S, Izuishi T, Nakazawa N, Toyoda T, Ohta T, Hayase S, Minemoto T, Yoshino K, Dai S, Shen Q 2017 ACS Nano 11 10373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 段聪聪, 程露, 殷垚, 朱琳 2019 68 158503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan C C, Cheng L, Yin Y, Zhu L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 158503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 石文奇, 田宏, 陆玉新, 朱虹, 李芬, 王小霞, 刘燕文 2021 70 087303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi W Q, Tian H, Lu Y X, Zhu H, Li F, Wang X X, Liu Y W 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 087303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen W W, Xin X, Zang Z G, Tang X S, Li C L, Hu W, Zhou M, Du J 2017 J. Solid State Chem. 255 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Guner T, Demir M M 2018 Phys. Status Solidi A 215 1800120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li X M, Wu Y, Zhang S L, Cai B, Gu Y, Song J Z, Zeng H B 2016 Adv. Funct. Mater. 26 2435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bi C H, Wang S X, Li Q, Kershaw S V, Tian J J, Rogach A L 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu H W, Wu Z N, Shao J R, Yao D, Gao H, Liu Y, Yu W L, Zhang H, Yang B 2017 ACS Nano 11 2239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] van der Stam W, Geuchies J J, Altantzis T, van den Bos K H, Meeldijk J D, Van Aert S, Bals S, Vanmaekelbergh D, de Mello Donega C 2017 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 4087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu M, Zhong G H, Yin Y M, Miao J S, Li K, Wang C Q, Xu X R, Shen C, Meng H 2017 Adv. Sci. 4 1700335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li M, Zhang X, Matras-Postolek K, Chen H S, Yang P 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 5506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pradeep K R, Chakraborty S, Viswanatha R 2019 Mater. Res. Express 6 114004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang H C, Wang W G, Tang A C, Tsai H Y, Bao Z, Ihara T, Yarita N, Tahara H, Kanemitsu Y, Chen S M, Liu R S 2017 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 56 13650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang X T, Wang H, Hu Y, Pei Y X, Wang S X, Shi Z F, Colvin V L, Wang S N, Zhang Y, Yu W W 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang X L, Cao W Y, Wang W G, Xu B, Liu S, Dai H T, Chen S M, Wang K, Sun X W 2016 Nano Energy 30 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Veldhuis S A, Boix P P, Yantara N, Li M, Sum T C, Mathews N, Mhaisalkar S G 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 6804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang H C, Bao Z, Tsai H Y, Tang A C, Liu R S 2018 Small 14 1702433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang H, Susha A S, Kershaw S V, Hung T F, Rogach A L 2015 Adv. Sci. 2 1500194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Pan G C, Bai X, Xu W, Chen X, Zhai Y, Zhu J Y, Shao H, Ding N, Xu L, Dong B, Mao Y L, Song H W 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 14195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang S X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X T, Shen X Y, Zhuang X W, Lu P, Yu W W, Kershaw S V, Rogach A L 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 锡掺杂CsPbBr3量子点的TEM图谱(标尺为20 nm) (a) SnBr2为0.03 mmol; (b) SnBr2为0.05 mmol; (c) SnBr2为0.06 mmol. (a) (b)中插图为对应TEM图量子点的HRTEM图谱(标尺为2 nm)
Figure 2. TEM images of tin doped CsPbBr3 quantum dots (scale bars represent 20 nm): (a) SnBr2 is 0.03 mmol; (b) SnBr2 is 0.05 mmol; (c) SnBr2 is 0.06 mmol. Inset pictures show the HRTEM of corresponding quantum dots (scale bars represent 2 nm).
表 1 锡掺杂CsPbBr3量子点的衰减曲线拟合参数
Table 1. Fitting results fitted by time-resolved PL decays curve of tin doped CsPbBr3 quantum dots.
SnBr2/
mmolA1/
%τ1/
nsA2/
%τ2/
nsA3/
%τ3/
nsτavg/
ns0.03 12.36 3.60 69.05 9.33 18.59 26.17 16.09 0.04 4.52 1.83 69.01 9.16 26.48 22.92 15.81 0.05 7.43 2.09 63.97 8.96 28.60 25.07 17.73 0.06 4.42 1.65 69.56 8.10 26.03 21.64 14.78 表 2 τr, τnr, κr和κnr计算结果
Table 2. Calculate results of τr, τnr, κr和κnr.
SnBr2/
mmolτavg/
nsPLQY/
%τr/
nsτnr/
nsκr×107/
s–1κnr×107/
s–10.03 16.09 43.4 37.07 28.43 2.70 3.52 0.04 15.81 32.3 48.95 23.35 2.04 4.28 0.05 17.73 53.4 33.20 38.05 3.01 2.63 0.06 14.78 21.7 68.11 18.88 1.47 5.30 -
[1] Li C L, Han C, Zhang Y B, Zang Z G, Wang M, Tang X S, Du J 2017 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 172 341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li C L, Zang Z G, Han C, Hu Z P, Tang X S, Du J, Leng Y X, Sun K 2017 Nano Energy 40 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Song J Z, Tao F, Li J H, Xu L M, Zhang F J, Han B N, Shan Q S, Zeng H B 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1805409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tang X S, Hu Z P, Chen W W, Xing X, Zang Z G, Hu W, Qiu J, Du J, Leng Y X, Jiang X F, Mai L Q 2016 Nano Energy 28 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang X, Lin H, Huang H, Reckmeier C, Zhang Y, Choy W C, Rogach A L 2016 Nano Lett. 16 1415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 瞿子涵, 储泽马, 张兴旺, 游经碧 2019 68 158504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qu Z H, Chu Z M, Zhang X W, You J B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 158504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shirasaki Y, Supran G J, Bawendi M G, Bulović V 2012 Nat. Photon. 7 13
[8] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, Krieg F, Caputo R, Hendon C H, Yang R X, Walsh A, Kovalenko M V 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu F, Zhang Y H, Ding C, Kobayashi S, Izuishi T, Nakazawa N, Toyoda T, Ohta T, Hayase S, Minemoto T, Yoshino K, Dai S, Shen Q 2017 ACS Nano 11 10373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 段聪聪, 程露, 殷垚, 朱琳 2019 68 158503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan C C, Cheng L, Yin Y, Zhu L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 158503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 石文奇, 田宏, 陆玉新, 朱虹, 李芬, 王小霞, 刘燕文 2021 70 087303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi W Q, Tian H, Lu Y X, Zhu H, Li F, Wang X X, Liu Y W 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 087303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen W W, Xin X, Zang Z G, Tang X S, Li C L, Hu W, Zhou M, Du J 2017 J. Solid State Chem. 255 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Guner T, Demir M M 2018 Phys. Status Solidi A 215 1800120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li X M, Wu Y, Zhang S L, Cai B, Gu Y, Song J Z, Zeng H B 2016 Adv. Funct. Mater. 26 2435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bi C H, Wang S X, Li Q, Kershaw S V, Tian J J, Rogach A L 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu H W, Wu Z N, Shao J R, Yao D, Gao H, Liu Y, Yu W L, Zhang H, Yang B 2017 ACS Nano 11 2239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] van der Stam W, Geuchies J J, Altantzis T, van den Bos K H, Meeldijk J D, Van Aert S, Bals S, Vanmaekelbergh D, de Mello Donega C 2017 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 4087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu M, Zhong G H, Yin Y M, Miao J S, Li K, Wang C Q, Xu X R, Shen C, Meng H 2017 Adv. Sci. 4 1700335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li M, Zhang X, Matras-Postolek K, Chen H S, Yang P 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 5506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pradeep K R, Chakraborty S, Viswanatha R 2019 Mater. Res. Express 6 114004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang H C, Wang W G, Tang A C, Tsai H Y, Bao Z, Ihara T, Yarita N, Tahara H, Kanemitsu Y, Chen S M, Liu R S 2017 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 56 13650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang X T, Wang H, Hu Y, Pei Y X, Wang S X, Shi Z F, Colvin V L, Wang S N, Zhang Y, Yu W W 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang X L, Cao W Y, Wang W G, Xu B, Liu S, Dai H T, Chen S M, Wang K, Sun X W 2016 Nano Energy 30 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Veldhuis S A, Boix P P, Yantara N, Li M, Sum T C, Mathews N, Mhaisalkar S G 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 6804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang H C, Bao Z, Tsai H Y, Tang A C, Liu R S 2018 Small 14 1702433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang H, Susha A S, Kershaw S V, Hung T F, Rogach A L 2015 Adv. Sci. 2 1500194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Pan G C, Bai X, Xu W, Chen X, Zhai Y, Zhu J Y, Shao H, Ding N, Xu L, Dong B, Mao Y L, Song H W 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 14195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang S X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X T, Shen X Y, Zhuang X W, Lu P, Yu W W, Kershaw S V, Rogach A L 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7844
- PDF Downloads: 144
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: