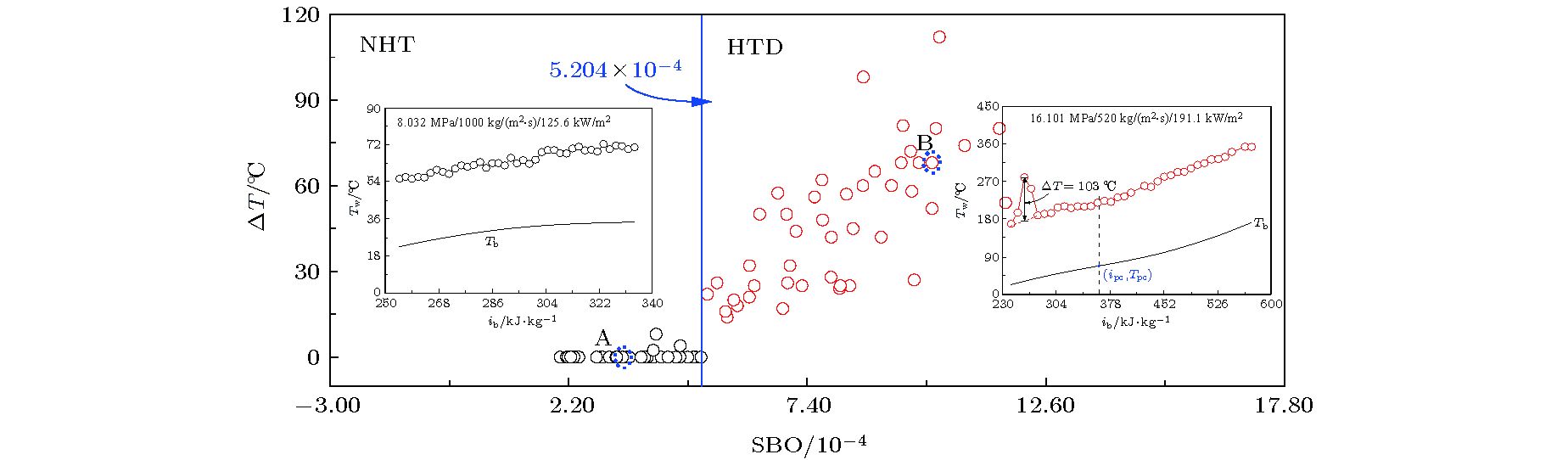
-
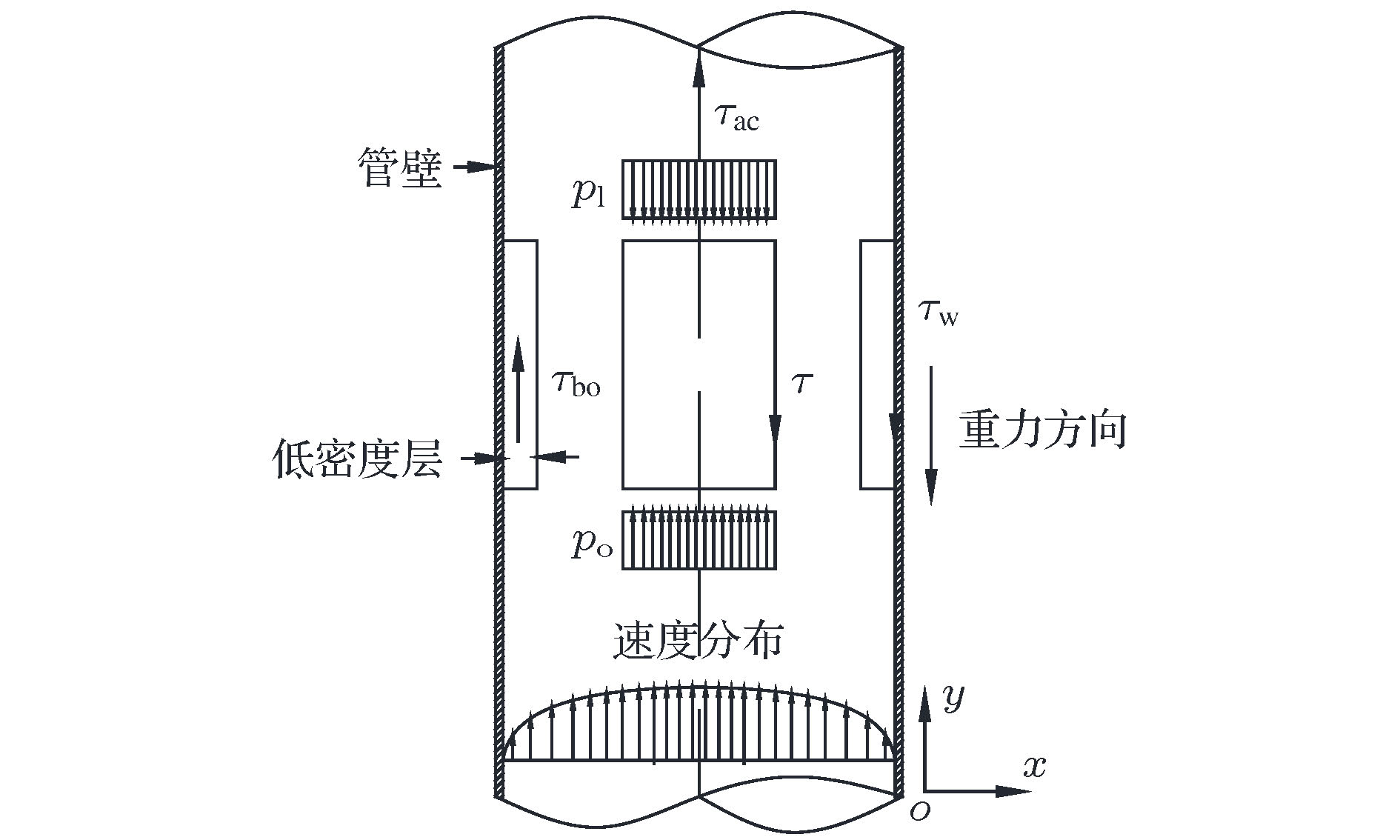
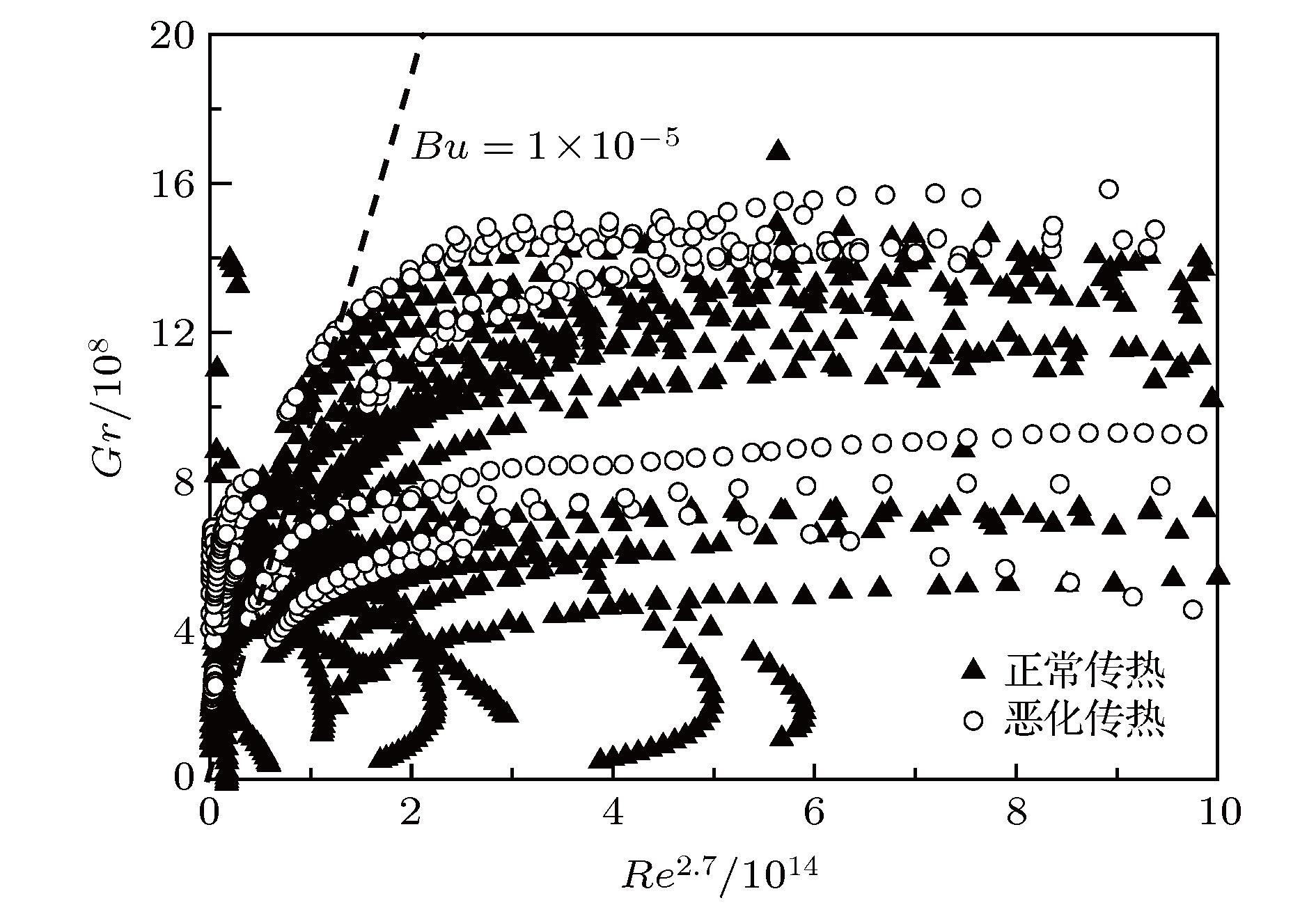
Based on the concept of single-phase fluid, the abnormal heat transfer behavior of supercritical fluid has been investigated for many years. However, there is no unified understanding of the mechanism of its flow and heat transfer. In this paper, we first review the reported effects of buoyancy and acceleration on supercritical fluids, and then study the effects of buoyancy and acceleration on the flow structure and heat transfer for the upward vertically flowing of supercritical CO2 fluid in a tube theoretically and experimentally. The results show that there is no conclusive experimental evidence that the abnormal heat transfer behavior of supercritical fluid is directly related to buoyancy and flow acceleration, and the existing criteria for estimating buoyancy and acceleration effect are based on the constant physical fluid and a lot of assumptions, as a result, different conclusions are obtained, though the same prediction method is used. Finally, we investigate the heat transfer deterioration of supercritical fluids based on the pseudo-boiling theory, and the proposed supercritical-boiling-number distinguishes the normal heat transfer deterioration from heat transfer deterioration of supercritical fluid. Our work paves a new way to understanding the supercritical fluid flow and heat transfer mechanism. The supercritical-boiling-number is important for establishing the optimum operating conditions for the supercritical fluid power cycle used in different technologies.
-
Keywords:
- supercritical carbon dioxide /
- heat transfer deterioration /
- buoyancy /
- acceleration /
- pseudo-boiling
[1] Crespi F, Gavagnin G, Sánchez, David, Martinez, Gonzalo S 2017 Appl. Energy 195 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xu J L, Sun E H, Li M J, Liu H, Zhu B G 2018 Energy 157 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ehsan M M, Guan Z, Klimenko A Y 2018 Renewable Sustainale Energy Rev. 92 658
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shiralkar, B S, Griffith P 1969 J. Heat Transfer 91 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bourke P J, Pulling D J, Gill L E, Denton, W H 1970 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 13 1339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bae Y Y 2011 Nucl. Eng. Des. 241 3164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Brassington D J, Cairns D N H 1977 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 20 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hall W B, Jackson J D 1978 Advances in Heat Transfer 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mceligot D M, Coon C W, Perkins H C 1970 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 13 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu S H, Huang Y P, Liu G X, Wang J F, Leung L K 2017 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 106 1144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang D, Wu Z, Sunden B, Li W 2016 Appl. Energy 162 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dang G X, Zhong F Q, Chen L H, Chang X Y 2013 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bruch A, Bontemps A, Colasson S 2009 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 52 2589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liao S M, Zhao T S 2002 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45 5025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kim D E 2011 Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 32 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 徐肖肖, 吴杨杨, 刘朝, 王开正, 叶建 2015 64 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X X, Wu Y Y, Liu C, Wang K Z, Ye J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kurganov V A, Kaptilnyi A G 1993 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 36 3383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Simeoni G G, Bryk T, Gorelli F A Krisch M, Ruocco G, Santoro M, Scopigno T 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gorelli F A, Bryk T, Krisch M, Ruocco G, Santoro M, Scopigno T 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Banuti D T 2015 J. Supercrit. Fluids 98 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Q, Li H X, Lei X L, Zhang J, Kong X F 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 127 674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kandlikar S G 2004 J. Heat Transfer 126 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
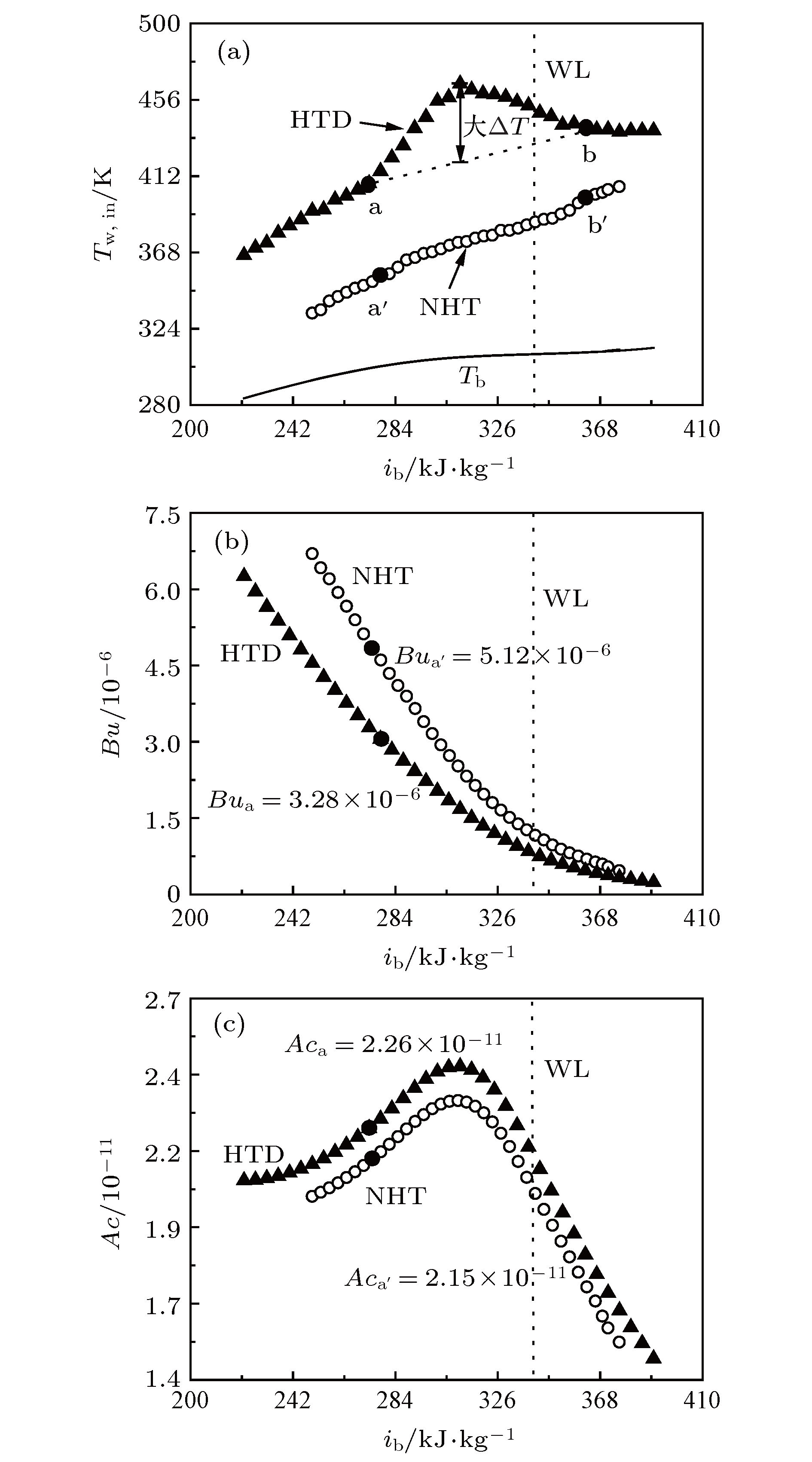
图 4 局部壁温Tw,in, Bu, Ac随主流焓值ib的分布关系 (a) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 200 kg/(m2·s), qw = 60 kW/m2, (b) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 520 kg/(m2·s), qw = 42 kW/m2
Figure 4. Local inner wall (Tw, in), Bu, Ac distributions with bulk fluid enthalpy (ib): (a) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 200 kg/(m2·s), qw = 60 kW/m2, (b) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 520 kg/(m2·s), qw = 42 kW/m2.
图 5 局部壁温Tw,in, Bu, Ac随主流焓值ib的分布关系 (a) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 700 kg/(m2·s), qw = 245 kW/m2, (b) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 1000 kg/(m2·s), qw = 245 kW/m2
Figure 5. Local inner wall (Tw, in), Bu, Ac distributions with bulk fluid enthalpy (ib): (a) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 700 kg/(m2·s), qw = 245 kW/m2, (b) P = 8.220 MPa, G = 1000 kg/(m2·s), qw = 245 kW/m2.
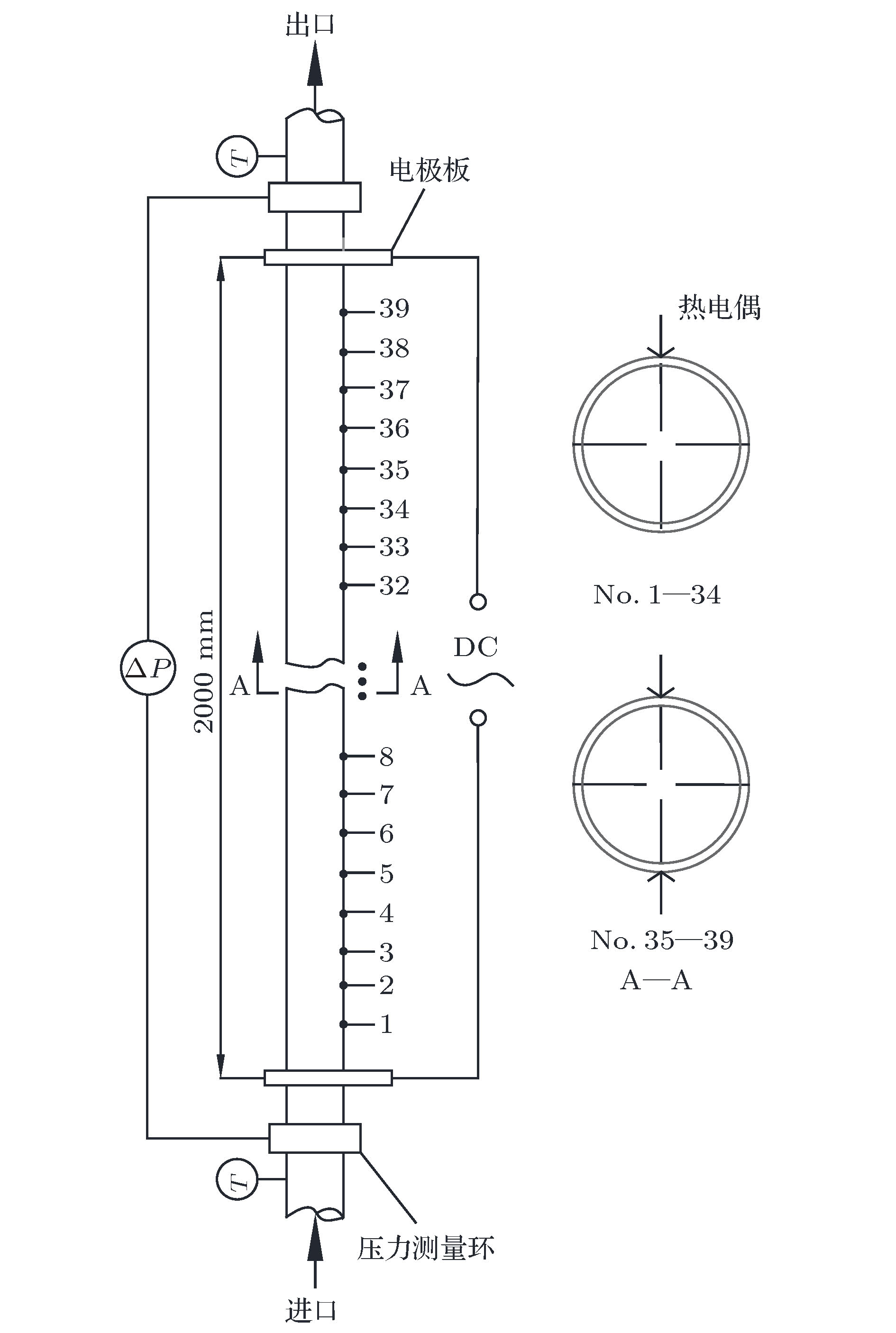
表 1 测量仪器的精度和范围
Table 1. Accuracies and ranges of measuring instruments.
参数 范围 不确定度 压力p/MPa 7.510—25.231 ± 1.42% 进口温度 Tin/℃ 5—70 ± 0.75% 出口温度 Tout/℃ 25—500 ± 0.75% 外壁面温度 Tw,o/℃ 30—450 ± 0.75% 质量流速 G/kg·m–2·s–1 488—2000 ± 2.05% 热流密度qw/kW·m–2 30—400.36 ± 8.06% -
[1] Crespi F, Gavagnin G, Sánchez, David, Martinez, Gonzalo S 2017 Appl. Energy 195 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xu J L, Sun E H, Li M J, Liu H, Zhu B G 2018 Energy 157 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ehsan M M, Guan Z, Klimenko A Y 2018 Renewable Sustainale Energy Rev. 92 658
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shiralkar, B S, Griffith P 1969 J. Heat Transfer 91 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bourke P J, Pulling D J, Gill L E, Denton, W H 1970 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 13 1339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bae Y Y 2011 Nucl. Eng. Des. 241 3164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Brassington D J, Cairns D N H 1977 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 20 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hall W B, Jackson J D 1978 Advances in Heat Transfer 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mceligot D M, Coon C W, Perkins H C 1970 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 13 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu S H, Huang Y P, Liu G X, Wang J F, Leung L K 2017 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 106 1144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang D, Wu Z, Sunden B, Li W 2016 Appl. Energy 162 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dang G X, Zhong F Q, Chen L H, Chang X Y 2013 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bruch A, Bontemps A, Colasson S 2009 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 52 2589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liao S M, Zhao T S 2002 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45 5025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kim D E 2011 Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 32 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 徐肖肖, 吴杨杨, 刘朝, 王开正, 叶建 2015 64 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X X, Wu Y Y, Liu C, Wang K Z, Ye J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kurganov V A, Kaptilnyi A G 1993 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 36 3383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Simeoni G G, Bryk T, Gorelli F A Krisch M, Ruocco G, Santoro M, Scopigno T 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gorelli F A, Bryk T, Krisch M, Ruocco G, Santoro M, Scopigno T 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Banuti D T 2015 J. Supercrit. Fluids 98 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Q, Li H X, Lei X L, Zhang J, Kong X F 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 127 674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kandlikar S G 2004 J. Heat Transfer 126 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11347
- PDF Downloads: 184
- Cited By: 0














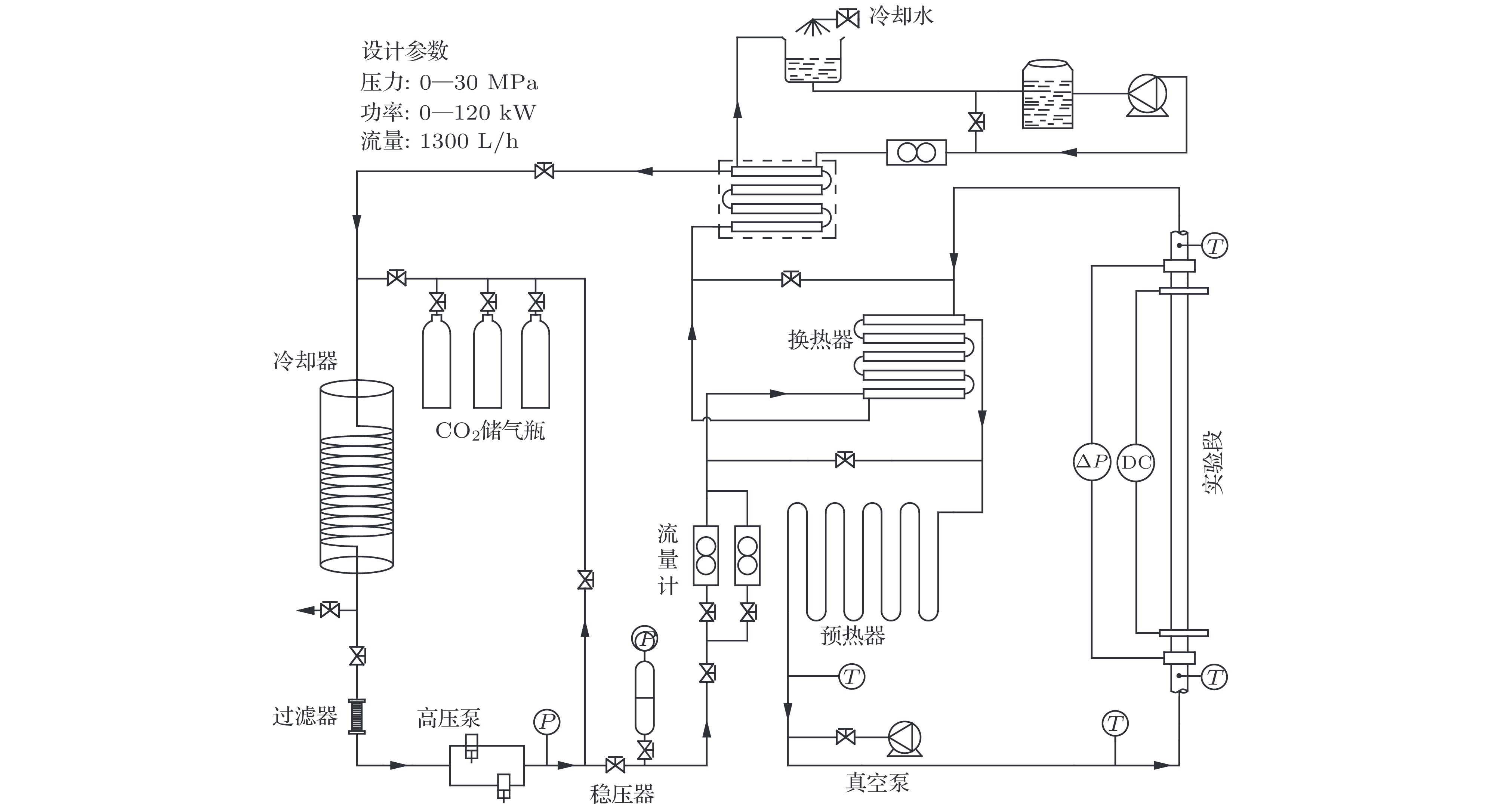
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: