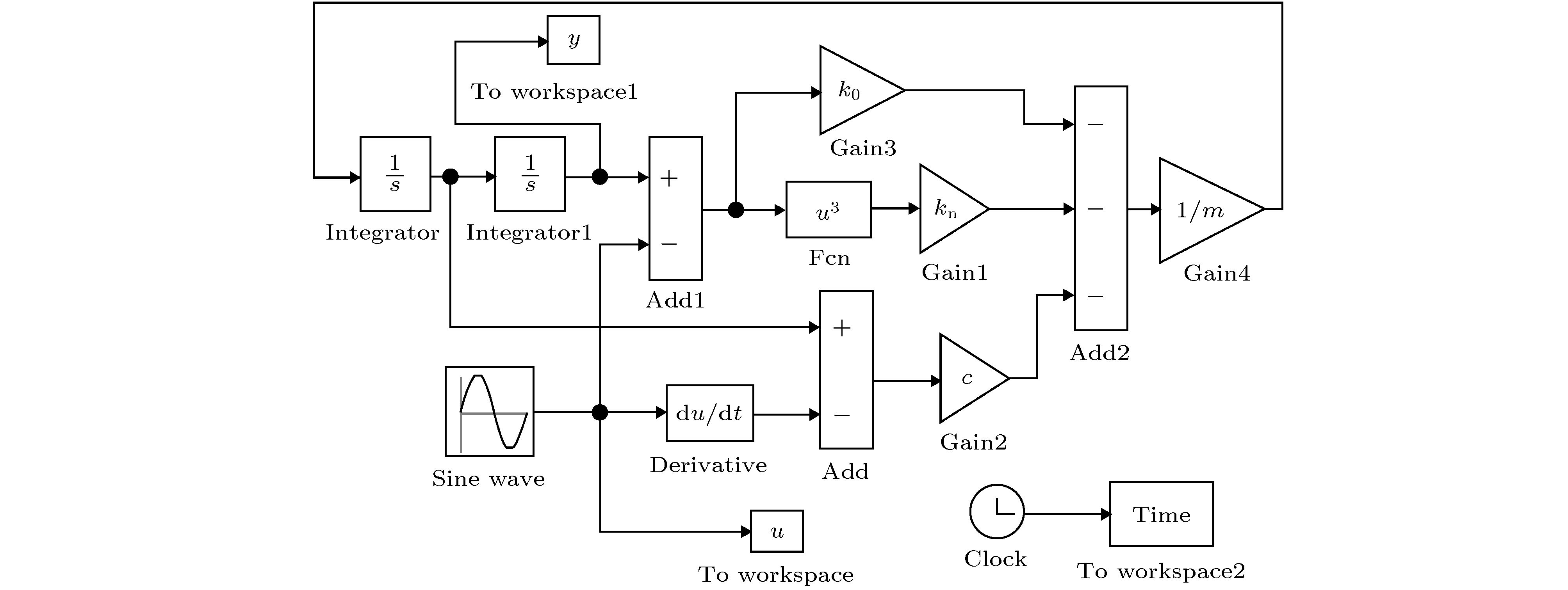
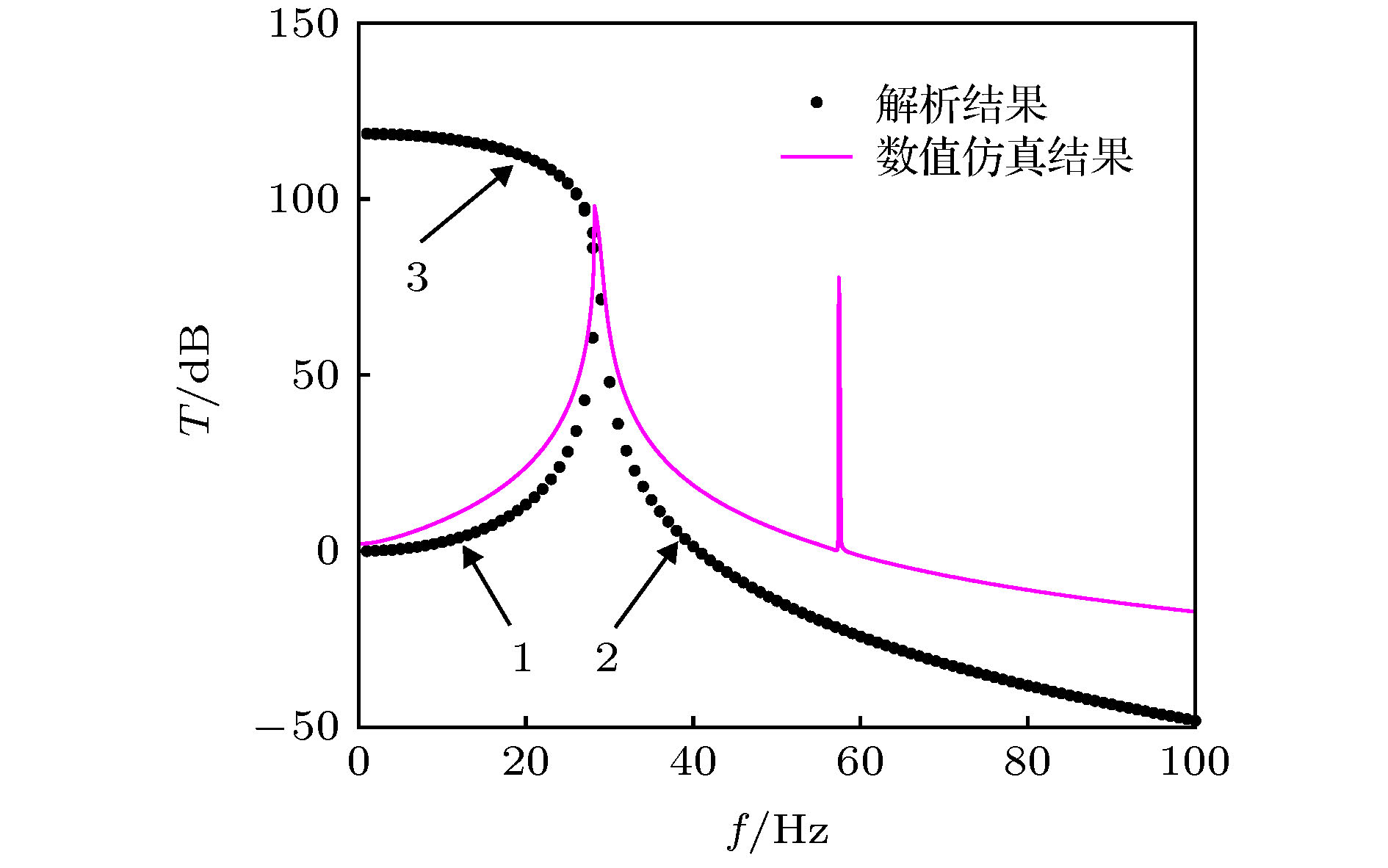
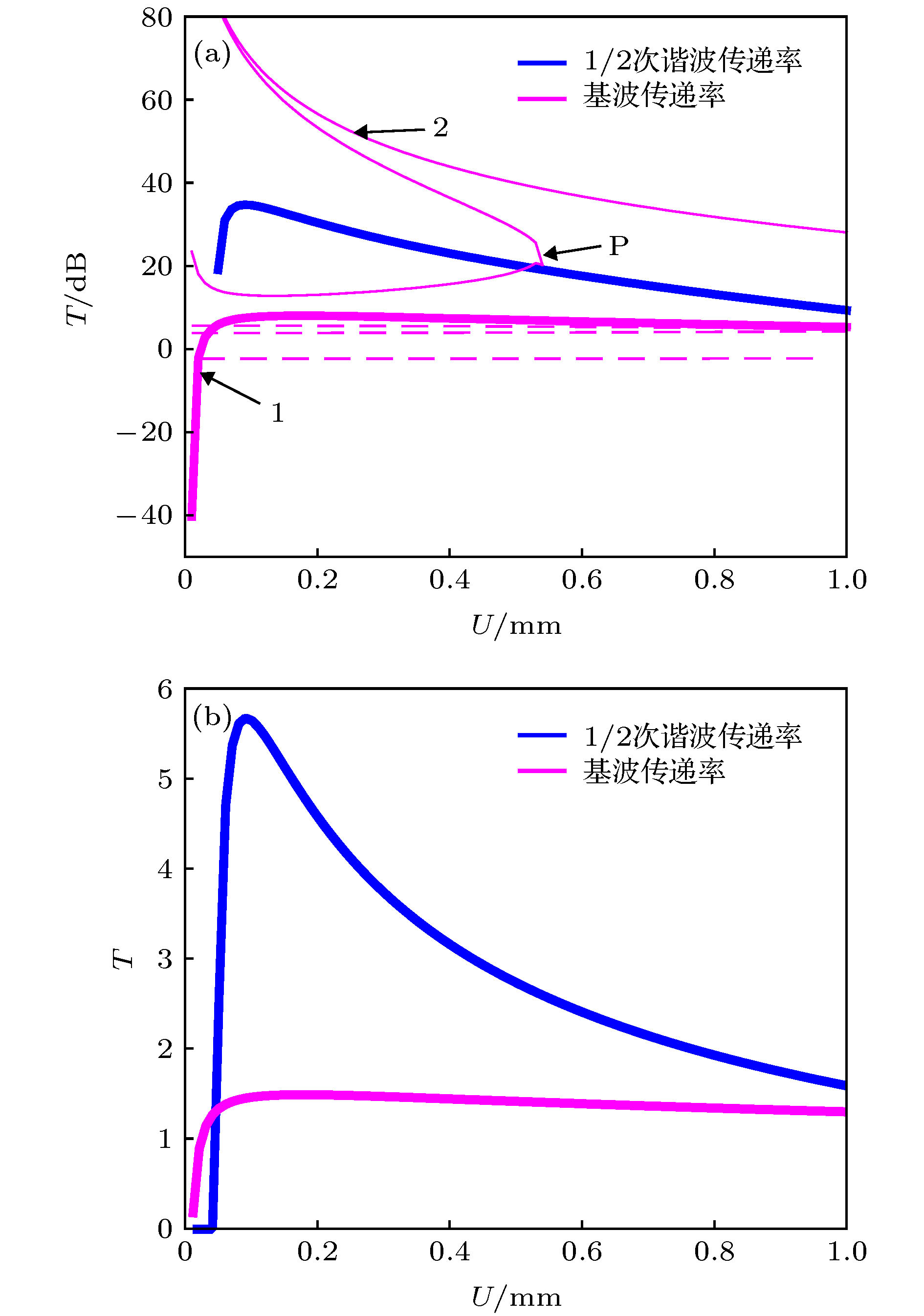
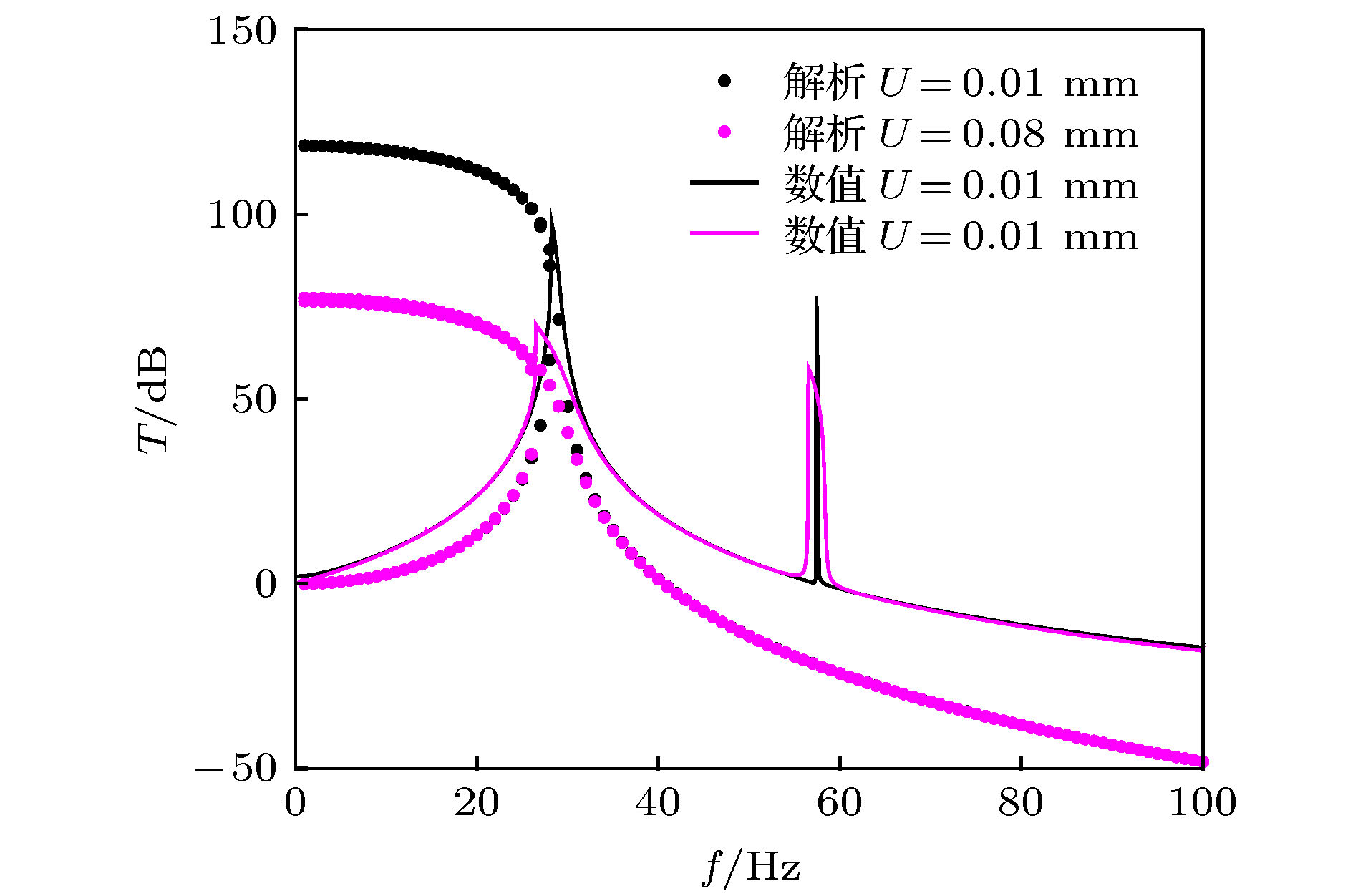
-
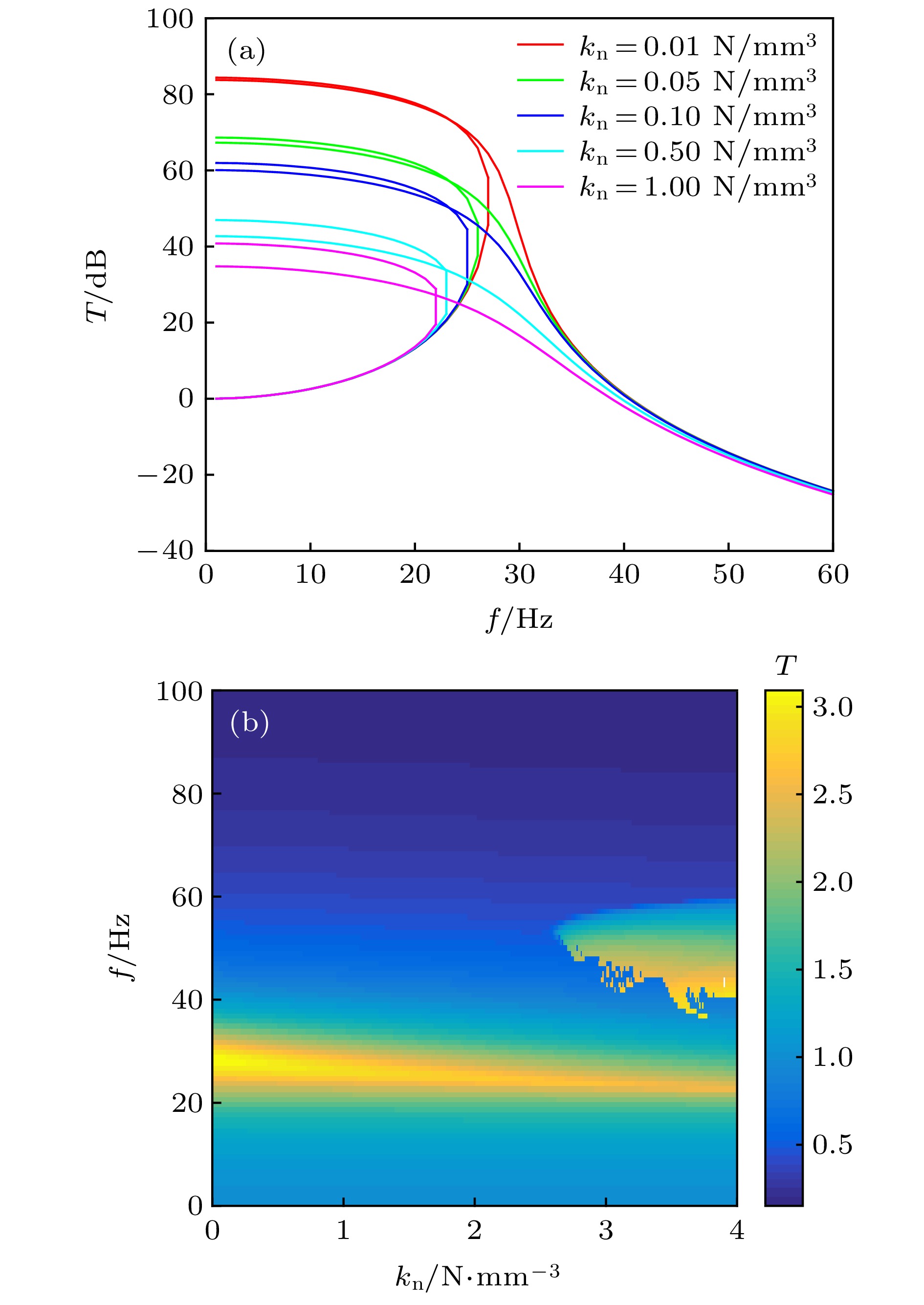
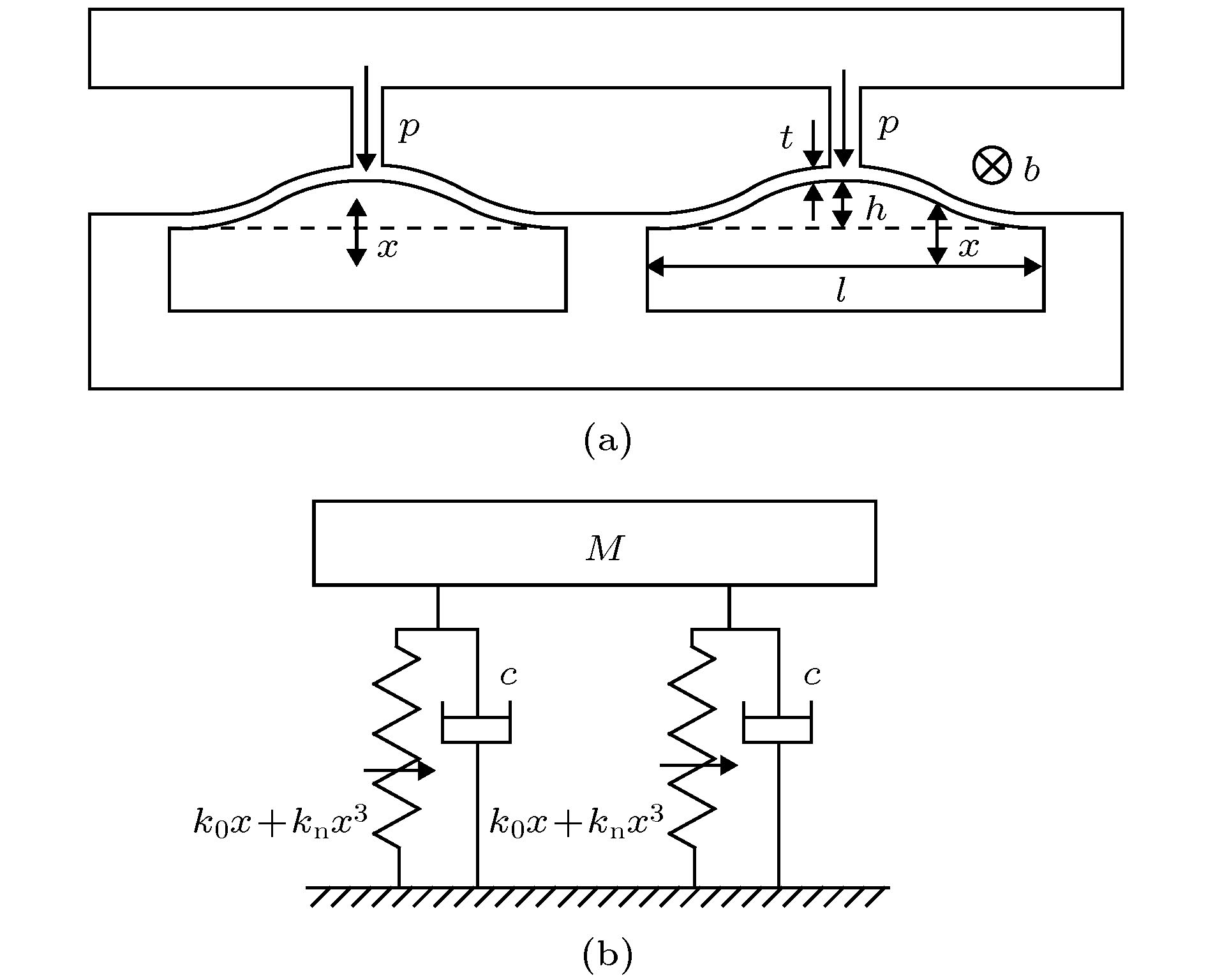
In the extensive modern applications, the low-frequency and heavy-load isolators are needed to reduce the vibration transmissions. The unique properties of nonlinear systems, such as jumping, bifurcation and chaos, provide new ideas for designing the new functional structures. Bistable system is a typical non-linear system, features highly static and low dynamic stiffness, which promises to realize a low-frequency isolator with ensuring heavy load capacity. However, more studies are necessary to clarify the sub-harmonic resonance and its generation process, parameter influences, vibration isolation characteristics of the bistable structure. By adopting the equivalent, analytical, numerical and experimental methods, we study the 1/2 sub-harmonic resonance, evolution process and its influence on the vibration isolation characteristics of the bistable structure in this paper. When the amplitude or nonlinear stiffness coefficient kn increases to a certain extent, 1/2 sub-harmonic resonance appears, where the response contains high-amplitude ω/2 component under the excitation frequency ω, so the energy is transferred from high frequency to low frequency. We study the bifurcation and varying processes of the fundamental and 1/2 sub-harmonic transmission by increasing the amplitude. At critical bifurcation amplitude, the sub-harmonic transmission rapidly increases from 0 to a large peak value. And then, it decreases gradually when the damping is absent. However, the peak value of 1/2 sub-harmonic does not cause the fundamental transmission to change suddenly. When considerable damping appears with the increase of the amplitude, 1/2 sub-harmonic does not always exist, instead, it follows an interesting “generation-enhancement-degeneration-disappearance” process. This process possesses great significance in applying the 1/2 sub-harmonic to vibration manipulation or avoiding the resonant enhancement induced by it. Moreover, in this process, both the peak frequency and the peak transmission of the bistable isolation system descend first. The optimal combination of the parameters can reduce the resonance frequency by 17.8% through increasing the driving amplitude. However, they jump to large values when 1/2 sub-harmonic plays a dominant role. Additionally, the negative stiffness k0 has a significant effect on the primary resonance characteristics: as |k0| increases under a specified excitation amplitude, the resonance peak shifts toward higher frequency and the transmission increases. Besides the main effect on the sub-harmonic resonance and the equilibrium point, the nonlinear coefficient kn also affects the peak and resonance frequency of the system, but the effect is much less than the influence caused by k0. Furthermore, the sub-harmonic resonances, bifurcations and vibration isolation characteristics of the bistable bulking beam structure are demonstrated experimentally. The experimental results show that: 1) the 1/2 sub-harmonic resonance can appear in a certain bandwidth and it is not monochromic; 2) the increase of the driving amplitude can reduce the transmission of the fundamental wave; 3) the transmission of 1/2 sub-harmonic jumps from 0 upward to a large value at a critical amplitude, and then it decreases gradually. The experimental results are consistent with the analytical and numerical results. The experiment also demonstrates the law of frequency shifting and the transmission reduction of peak values. Therefore, the appropriate increase of the amplitude can improve the vibration isolation capacity. However, sub-harmonic resonance will reduce the isolation effect. In practical engineering, the strong sub-harmonic resonance should be avoided in a nonlinear vibration isolation system. -
Keywords:
- bistable structure /
- sub-harmonic resonance /
- vibration isolation characteristics /
- buckling beam
[1] Fang X, Wen J, Bonello B, Yin J, Yu D 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 1288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fang X, Wen J, Yu D, Yin J 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 054049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fang X, Wen J, Yu D, Huang G, Yin J 2018 New J. Phys. 20 123028
[4] 刘树勇, 位秀雷, 王基, 俞翔 2017 振动与冲击 36 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S Y, Wei X L, Wang J, Yu X 2017 J. Vib. Shock 36 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 孙舒, 曹树谦 2012 61 210505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun S, Cao S Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 210505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 程凯 2018 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Cheng K 2018 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[7] Shaw A D, Neild S A, Wagg D J, Weaver P M, Carrella A 2013 J. Sound Vib. 332 6265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fang X, Wen J, Yin J, Yu D 2017 Nonlinear Dyn. 87 2677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sergio P P, Nima T, Mark S, Just L H 2012 J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 24 1303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zheng R, Nakano K, Hu H, Su D, Cartmell M P. 2014 J. Sound Vib. 333 2568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Harne R L, Zhang C, Li B, Wang K W 2016 J. Sound Vib. 373 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 唐玮, 王小璞, 曹景军 2014 63 240504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W, Wang X P, Cao J J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 240504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘丽兰, 任博林, 朱国栋, 杨倩倩 2017 振动与冲击 36 91
Liu L L, Ren B L, Zhu G D, Yang Q Q 2017 J. Vib. Shock 36 91
[14] 房轩, 李艳宁, 鄢志丹, 傅星, 胡小唐 2008 光电子·激光 19 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang X, Li Y N, Yan Z D, Fu X, Hu X T 2008 J. Optoelectronics · Laser 19 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘瑶璐, 胡宁, 邓明晰, 赵友选, 李卫彬 2017 力学进展 47 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y L, Hu N, Deng M X, Zhao Y X, Li W B 2017 Adv. Mech. 47 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Arrieta A F, Hagedorn P, Erturk A, Inman D J 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 104102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 肖锡武, 肖光华, Jacques Druez 2003 振动与冲击 22 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao X W, Xiao G H, Jacques D 2003 J. Vib. Shock 22 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Thomas H, Adrien B, Olivier D, Mickaël L 2018 Appl. Energy 226 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 孟宗, 付立元, 宋明厚 2013 62 054501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng Z, Fu L Y, Song M H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 054501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Drummond P D, McNeil K J, Walls D F 1981 Optica Acta 28 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 陆泽琦, 陈立群 2017 力学学报 49 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Z Q, Chen L Q 2017 J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 49 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Taher M, Saif A 2000 J. Microelectromech. Syst. 9 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Cazottes P, Fernandes A, Pouget J, Hafez M 2009 J. Mech. Design 131 101001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Senba A, Ikeda T, Ueda T 2010 Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference Oelando, Florida, USA, April 12–15, 2010 p2744
[25] Arrieta A F, Bilgen O, Friswell M I, Hagedorn P 2012 AIP Adv. 2 032118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Camescasse B, Fernandes A, Pouget J 2014 Int J. Solids Struct. 51 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yang K, Harne R L, Wang K W, Huang H 2014 J. Sound Vib. 333 6651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Marvin G C, Daisuke S, Enno L, Jong H L, Hrayr S K, Alan G, James N W, Zhilin Q 2012 Heart Rhythm 9 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Dennis J T, Brian P M 2014 Physica D 268 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 刘兴天, 黄修长, 张志谊, 华宏星 2013 机械工程学报 49 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X T, Huang X C, Zhang Z Y, Hua H X 2013 J. Mech. Eng. 49 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Jin Q, Jeffrey H L, Alexander H S 2004 J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 15 系统40 Hz处的次谐波共振现象 (a) U = 1.251 mm时的响应和激励频谱; (b), (c)U = 1.351 mm时的响应和激励频谱; (d)U = 1.351 mm时的时域波形
Figure 15. Sub-harmonic resonance phenomena at 40 Hz: (a) Response and excitation spectrum with U = 1.251 mm; (b), (c) response and excitation spectrum with U = 1.351 mm; (d) time-domain waveform with U = 1.351 mm.
-
[1] Fang X, Wen J, Bonello B, Yin J, Yu D 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 1288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fang X, Wen J, Yu D, Yin J 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 054049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fang X, Wen J, Yu D, Huang G, Yin J 2018 New J. Phys. 20 123028
[4] 刘树勇, 位秀雷, 王基, 俞翔 2017 振动与冲击 36 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S Y, Wei X L, Wang J, Yu X 2017 J. Vib. Shock 36 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 孙舒, 曹树谦 2012 61 210505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun S, Cao S Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 210505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 程凯 2018 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Cheng K 2018 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[7] Shaw A D, Neild S A, Wagg D J, Weaver P M, Carrella A 2013 J. Sound Vib. 332 6265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fang X, Wen J, Yin J, Yu D 2017 Nonlinear Dyn. 87 2677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sergio P P, Nima T, Mark S, Just L H 2012 J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 24 1303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zheng R, Nakano K, Hu H, Su D, Cartmell M P. 2014 J. Sound Vib. 333 2568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Harne R L, Zhang C, Li B, Wang K W 2016 J. Sound Vib. 373 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 唐玮, 王小璞, 曹景军 2014 63 240504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W, Wang X P, Cao J J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 240504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘丽兰, 任博林, 朱国栋, 杨倩倩 2017 振动与冲击 36 91
Liu L L, Ren B L, Zhu G D, Yang Q Q 2017 J. Vib. Shock 36 91
[14] 房轩, 李艳宁, 鄢志丹, 傅星, 胡小唐 2008 光电子·激光 19 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang X, Li Y N, Yan Z D, Fu X, Hu X T 2008 J. Optoelectronics · Laser 19 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘瑶璐, 胡宁, 邓明晰, 赵友选, 李卫彬 2017 力学进展 47 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y L, Hu N, Deng M X, Zhao Y X, Li W B 2017 Adv. Mech. 47 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Arrieta A F, Hagedorn P, Erturk A, Inman D J 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 104102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 肖锡武, 肖光华, Jacques Druez 2003 振动与冲击 22 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao X W, Xiao G H, Jacques D 2003 J. Vib. Shock 22 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Thomas H, Adrien B, Olivier D, Mickaël L 2018 Appl. Energy 226 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 孟宗, 付立元, 宋明厚 2013 62 054501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng Z, Fu L Y, Song M H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 054501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Drummond P D, McNeil K J, Walls D F 1981 Optica Acta 28 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 陆泽琦, 陈立群 2017 力学学报 49 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Z Q, Chen L Q 2017 J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 49 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Taher M, Saif A 2000 J. Microelectromech. Syst. 9 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Cazottes P, Fernandes A, Pouget J, Hafez M 2009 J. Mech. Design 131 101001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Senba A, Ikeda T, Ueda T 2010 Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference Oelando, Florida, USA, April 12–15, 2010 p2744
[25] Arrieta A F, Bilgen O, Friswell M I, Hagedorn P 2012 AIP Adv. 2 032118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Camescasse B, Fernandes A, Pouget J 2014 Int J. Solids Struct. 51 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yang K, Harne R L, Wang K W, Huang H 2014 J. Sound Vib. 333 6651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Marvin G C, Daisuke S, Enno L, Jong H L, Hrayr S K, Alan G, James N W, Zhilin Q 2012 Heart Rhythm 9 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Dennis J T, Brian P M 2014 Physica D 268 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 刘兴天, 黄修长, 张志谊, 华宏星 2013 机械工程学报 49 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X T, Huang X C, Zhang Z Y, Hua H X 2013 J. Mech. Eng. 49 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Jin Q, Jeffrey H L, Alexander H S 2004 J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 21697
- PDF Downloads: 249
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: