-
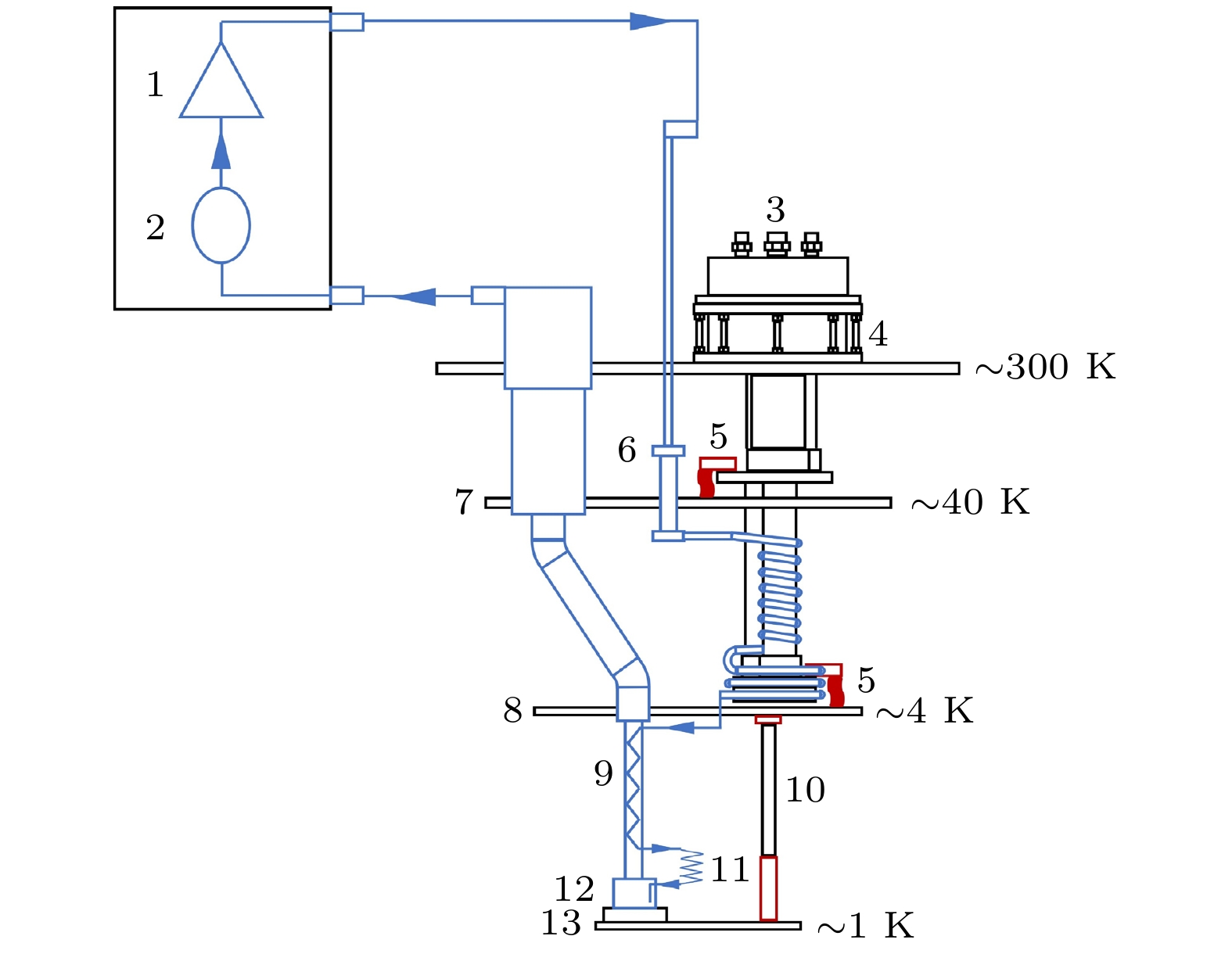
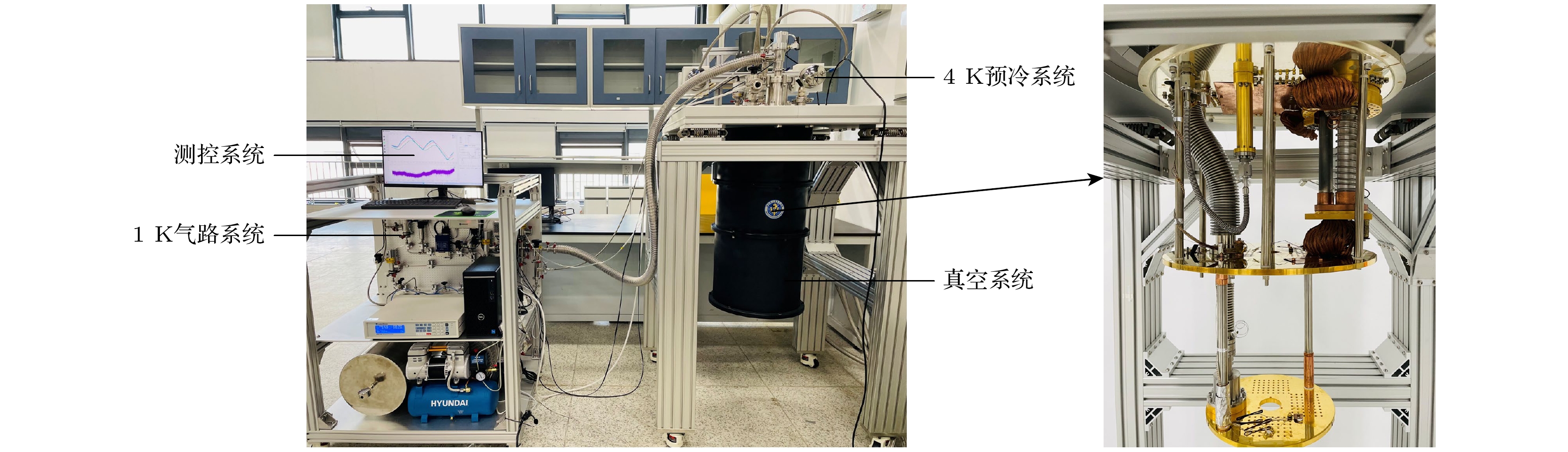
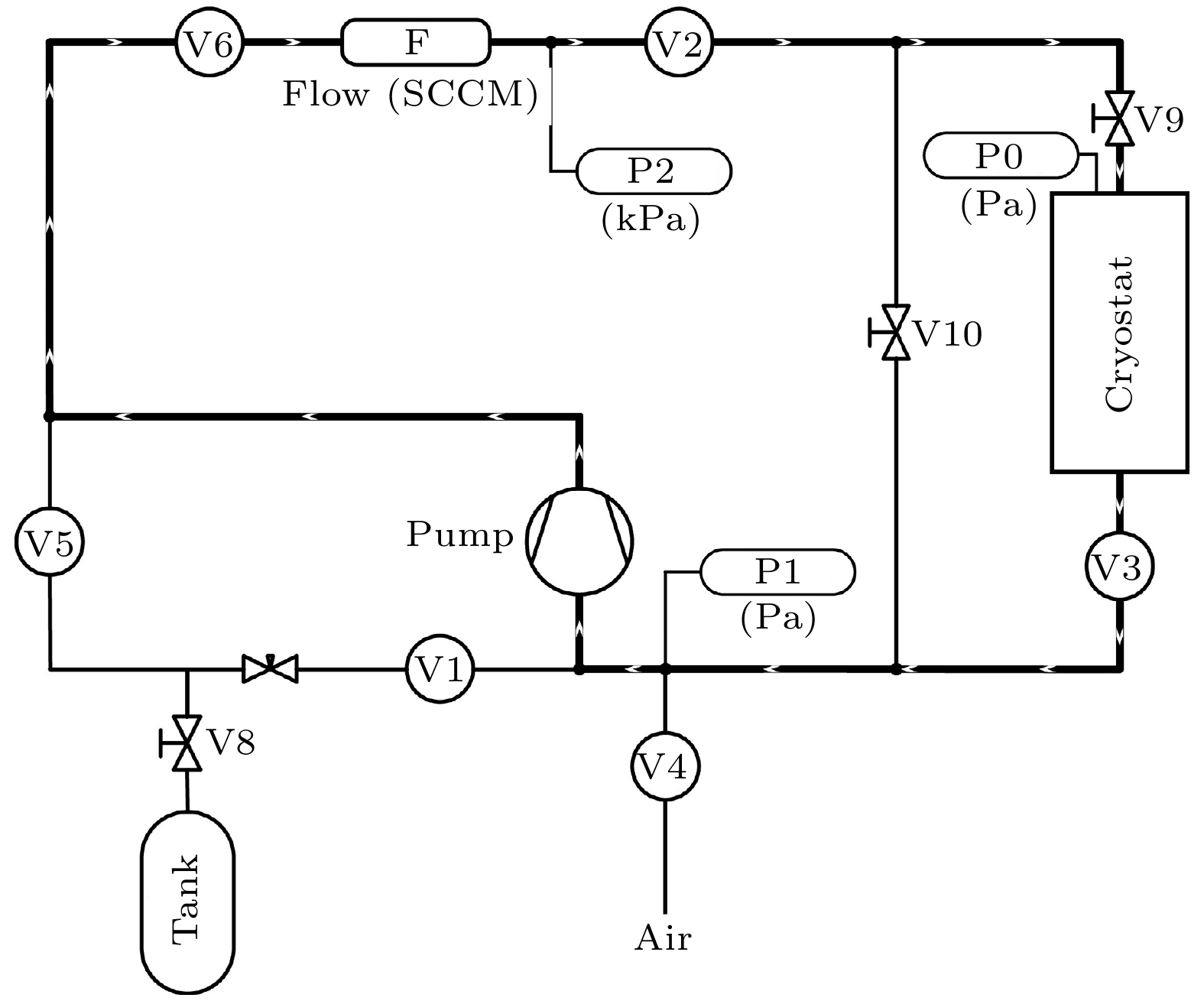
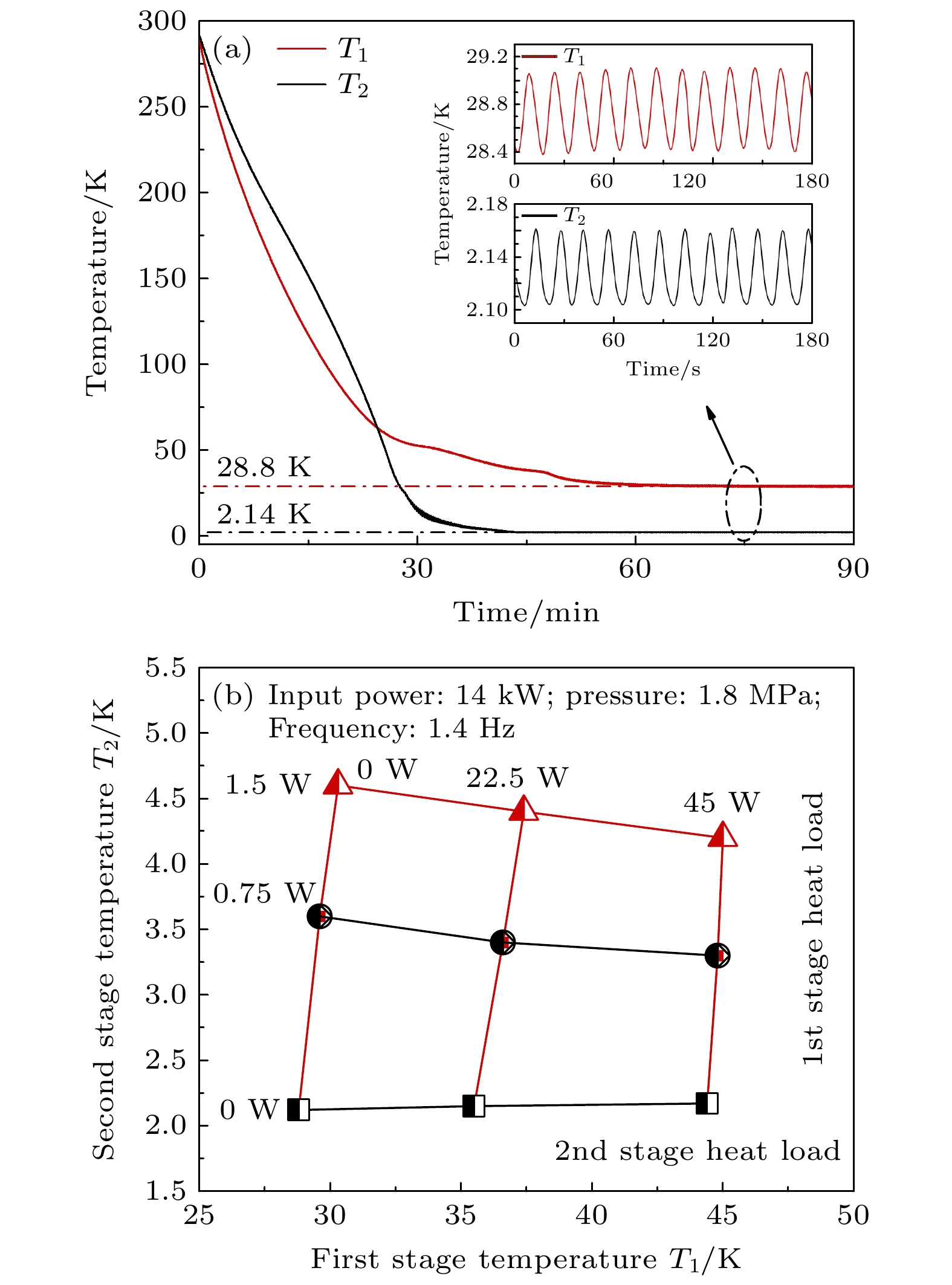
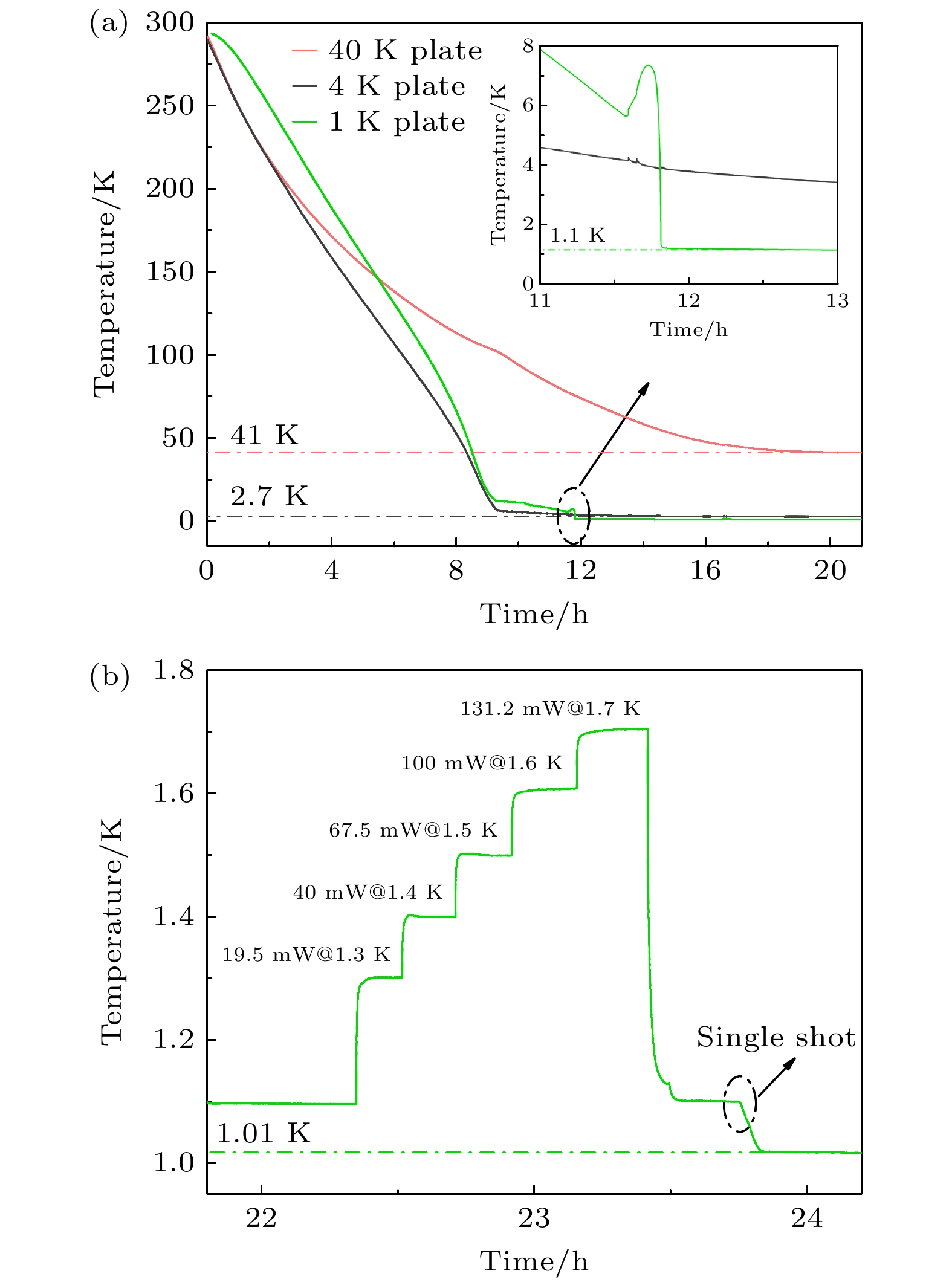
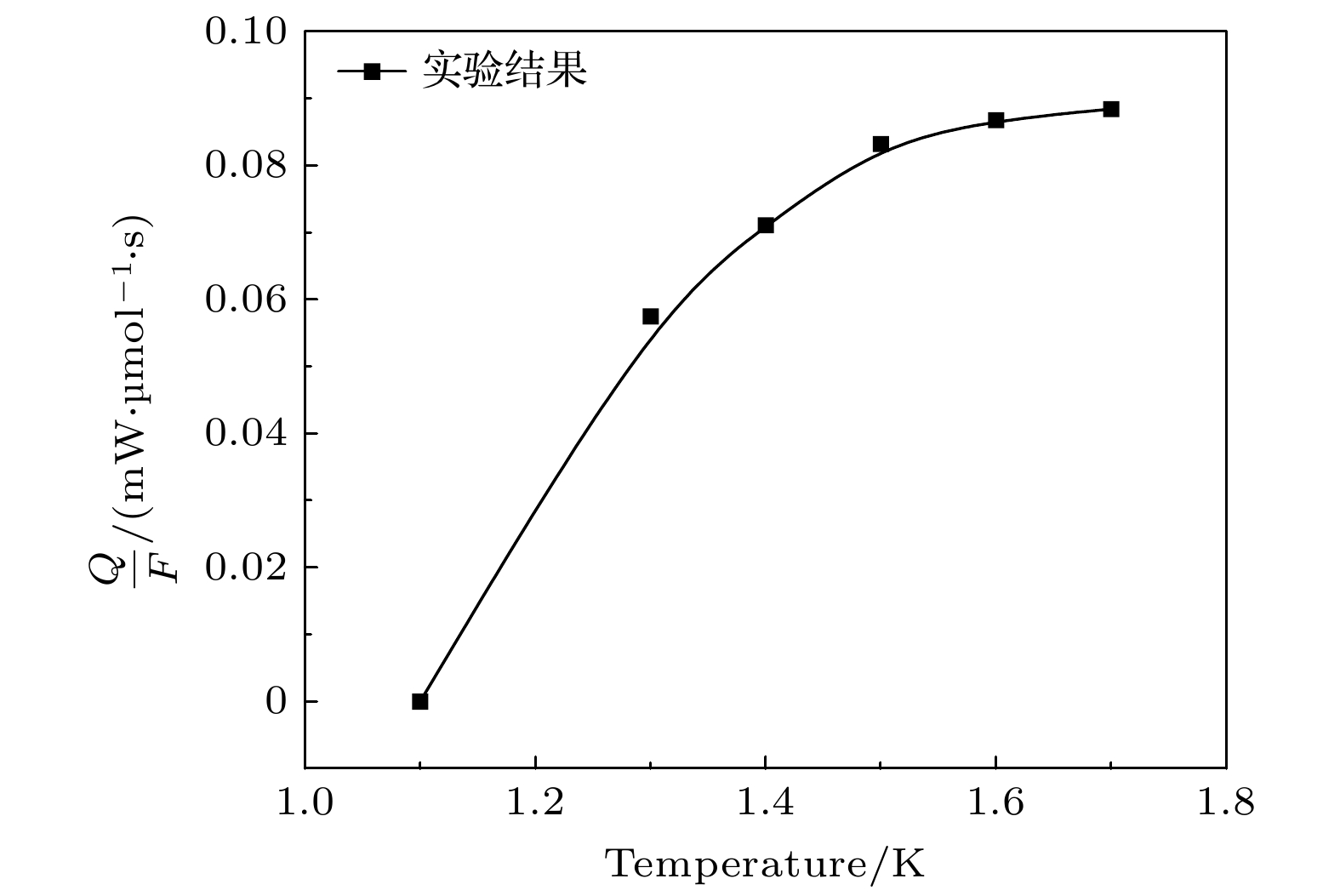
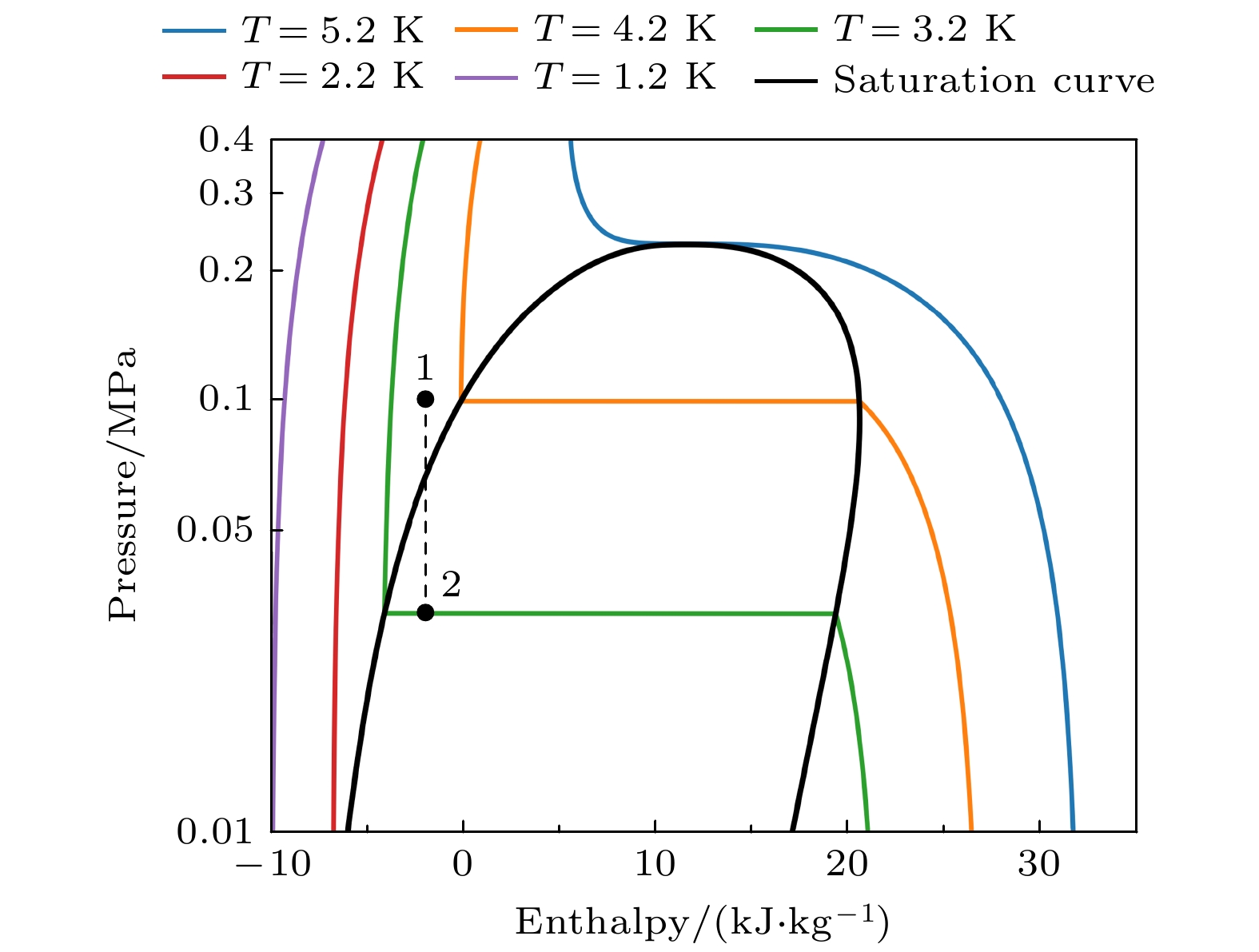
A 1-K cryogenic system can provide a stable and necessary low-temperature environment for some fields such as quantum computing, condensed matter physics research, and cryogenic scientific instruments. Specifically, in the field of basic research, 1 K is an ideal condition for studying quantum phenomena in low-temperature physics, such as quantum Hall effect and topological phase transition; in the field of technical applications, 1 K is a necessary condition for some quantum devices, such as superconducting quantum interferometers and single-photon detectors, to achieve high-sensitivity operation; in the field of ultra-low temperature technology, 1 K is the pre-cooling stage of refrigeration technologies, such as dilution refrigerators, and is also the basis for further achieving mK temperature ranges and lower temperatures. At present, in most of domestic 1-K systems, GM (Gifford-McMahon) cryocoolers are used for pre-cooling. These systems encounter some difficulties in achieving lower vibration control, lower electrical noise interference, lower pre-cooling temperature, and higher liquefaction efficiency. The 1-K systems based on pulse tube cryocoolers pre-cooling have inherent advantages in solving these problems. In this work, a 4-K GM-type pulse tube cryocooler is first developed by using a domestic helium compressor and a developed rotary valve, and the cold-end heat exchanger and the room-temperature phase shifters are redesigned in order to achieve a minimum cooling temperature of 2.14 K, and provide 1.5 W at 4.2 K and 45 W at 45 K cooling capacity simultaneously. With the home-made pulse tube cryocooler as the pre-cooling stage, a 1-K cryogenic system is further constructed. By designing key components such as JT flow resistance, combined thermal switch, and anti-superflow structure, a minimum cooling temperature of 1.1 K is achieved, with a cooling capacity of 100 mW at 1.6 K. This study lays an important foundation for subsequently developing dilution refrigerators with larger cooling capacity.
-
Keywords:
- pulse tube cryocooler /
- GM-type /
- 1-K system /
- Dilution refrigeration
[1] Zhao Z Y, Wang C 2019 Cryogenic Engineering and Technologies: Principles and Applications of Cryogen-Free Systems (CRC Press) p233
[2] 李珂, 王亚男, 刘萍, 禹芳秋, 戴巍, 沈俊 2023 72 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li K, Wang Y N, Liu P, Yu F Q, Dai W, Shen J 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 俎红叶, 程维军, 王亚男, 王晓涛, 李珂, 戴巍 2023 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zu H Y, Cheng W J, Wang Y N, Wang X T, Li K, Dai W 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王昌, 李珂, 沈俊, 戴巍, 王亚男, 罗二仓, 沈保根, 周远 2021 70 090702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Li K, Shen J, Dai W, Wang Y N, Luo E C, Shen B G, Zhou Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 090702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zheng M W, Guo H W, Wei L J, Pan Z J, Zou J R, Li R X, Zhao M G, Chen H L, Liang J T 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 230701 (In Chinese) [郑茂文, 郭浩文, 卫铃佼, 潘子杰, 邹佳润, 李瑞鑫, 赵密广, 陈厚磊, 梁惊涛 2024 73 230701]
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng M W, Guo H W, Wei L J, Pan Z J, Zou J R, Li R X, Zhao M G, Chen H L, Liang J T 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 230701 (In Chinese)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Guan X, Fan J, Bian Y B, Cheng Z G, Ji Z Q 2024 Chin. Phys. B 33 070701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jahromi A E, Miller F K 2014 Cryogenics 61 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] DeMann A, Mueller S, Field S B 2016 Cryogenics 73 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cao H 2021 J. Low Temp. Phys. 204 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bluefors and Cryomech 1 K systems products https://bluefors.com/products/1k-systems/
[11] Oxford Instruments 1 K cryostats products https://nanoscience.oxinst.com/dry-systems/products/teslatronpt
[12] Quantum Design 1 K measurement systems products https://www.qd-china.com/zh/pro/detail3/1/1912091422155/1909260926498
[13] Wang L G, Qu Q X, Chen H, Dai N N, Zhao W Y, Jia P, Xu D, Li L F 2025 Cryogenics 145 103992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pengli 1 K cryostats products https://isite.baidu.com/site/wjzru1zo/96a2066c-8800-4095-9ec4-a0489538571f?ch=48&wid=6dfbf96df3554e288101d75dc1ec8912_0_0&uniqId=c4db65aa10714a8697008f3c034cf058
[15] ZL Cryogenic 1 K cryostats products http://zlcryogenic.com/display/141459.html
[16] Radebaugh R. 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 164219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu X M, Chen L B, Wu X L, Yang B, Wang J, Zhu W X, Wang J J, Zhou Y 2020 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang C 2016 Cryocoolers 19 299
[19] Wang C, Hanrahan T, Johnson M 2018 Cryogenics 95 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang C, Lichtenwalter B, Friebel A, Tang H X 2014 Cryogenics 64 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qu Q X, Wang L G, Chen H, Dai N N, Jia P, Xu D, Li L F 2024 Cryogenics 138 103797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wu S G, Zhao B J, Tan J, Zhao Y J, Zhai Y J, Xue R J, Tan H, Ma D, Wu D R, Dang H Z 2023 Energy 277 127691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shen Y W, Liu D L, Chen S F, Zhao Q Y, Liu L, Gan Z H, Qiu M 2020 Appl. Therm. Eng. 166 114667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li X, Xu D, Wang W, Lin P, Liu H M, Nishimura A, Shen F Z, Li L F 2019 Cryogenics 102 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Uhlig K 2002 Cryogenics 42 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang C 2001 Cryogenics 41 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu X M, Pan C Z, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Guo W J, Yu D P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190701 (In Chinese) [刘旭明, 潘长钊, 张宇, 廖奕, 郭伟杰, 俞大鹏 2023 72 190701]
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X M, Pan C Z, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Guo W J, Yu D P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190701 (In Chinese)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 自研脉管制冷机与国外产品比较
Table 1. Comparison between the developed prototype and foreign 4 K GM-type PTRs.
时间 最低温度 一级制冷量 二级制冷量 功耗 备注 Cryomech PT415-RM <60 min <2.8 K 40 W @ 45 K 1.35 W @ 4.2 K 9.2 kW 阀分离 住友RP-182B2S <60 min <2.8 K 36 W @ 48 K 1.5 W @ 4.2 K 11.8 kW 阀分离 本文 <40 min 2.14 K 45 W @ 45 K 1.5 W @ 4.2 K 14 kW 阀分离 -
[1] Zhao Z Y, Wang C 2019 Cryogenic Engineering and Technologies: Principles and Applications of Cryogen-Free Systems (CRC Press) p233
[2] 李珂, 王亚男, 刘萍, 禹芳秋, 戴巍, 沈俊 2023 72 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li K, Wang Y N, Liu P, Yu F Q, Dai W, Shen J 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 俎红叶, 程维军, 王亚男, 王晓涛, 李珂, 戴巍 2023 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zu H Y, Cheng W J, Wang Y N, Wang X T, Li K, Dai W 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王昌, 李珂, 沈俊, 戴巍, 王亚男, 罗二仓, 沈保根, 周远 2021 70 090702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Li K, Shen J, Dai W, Wang Y N, Luo E C, Shen B G, Zhou Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 090702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zheng M W, Guo H W, Wei L J, Pan Z J, Zou J R, Li R X, Zhao M G, Chen H L, Liang J T 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 230701 (In Chinese) [郑茂文, 郭浩文, 卫铃佼, 潘子杰, 邹佳润, 李瑞鑫, 赵密广, 陈厚磊, 梁惊涛 2024 73 230701]
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng M W, Guo H W, Wei L J, Pan Z J, Zou J R, Li R X, Zhao M G, Chen H L, Liang J T 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 230701 (In Chinese)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Guan X, Fan J, Bian Y B, Cheng Z G, Ji Z Q 2024 Chin. Phys. B 33 070701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jahromi A E, Miller F K 2014 Cryogenics 61 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] DeMann A, Mueller S, Field S B 2016 Cryogenics 73 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cao H 2021 J. Low Temp. Phys. 204 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bluefors and Cryomech 1 K systems products https://bluefors.com/products/1k-systems/
[11] Oxford Instruments 1 K cryostats products https://nanoscience.oxinst.com/dry-systems/products/teslatronpt
[12] Quantum Design 1 K measurement systems products https://www.qd-china.com/zh/pro/detail3/1/1912091422155/1909260926498
[13] Wang L G, Qu Q X, Chen H, Dai N N, Zhao W Y, Jia P, Xu D, Li L F 2025 Cryogenics 145 103992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pengli 1 K cryostats products https://isite.baidu.com/site/wjzru1zo/96a2066c-8800-4095-9ec4-a0489538571f?ch=48&wid=6dfbf96df3554e288101d75dc1ec8912_0_0&uniqId=c4db65aa10714a8697008f3c034cf058
[15] ZL Cryogenic 1 K cryostats products http://zlcryogenic.com/display/141459.html
[16] Radebaugh R. 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 164219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu X M, Chen L B, Wu X L, Yang B, Wang J, Zhu W X, Wang J J, Zhou Y 2020 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang C 2016 Cryocoolers 19 299
[19] Wang C, Hanrahan T, Johnson M 2018 Cryogenics 95 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang C, Lichtenwalter B, Friebel A, Tang H X 2014 Cryogenics 64 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qu Q X, Wang L G, Chen H, Dai N N, Jia P, Xu D, Li L F 2024 Cryogenics 138 103797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wu S G, Zhao B J, Tan J, Zhao Y J, Zhai Y J, Xue R J, Tan H, Ma D, Wu D R, Dang H Z 2023 Energy 277 127691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shen Y W, Liu D L, Chen S F, Zhao Q Y, Liu L, Gan Z H, Qiu M 2020 Appl. Therm. Eng. 166 114667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li X, Xu D, Wang W, Lin P, Liu H M, Nishimura A, Shen F Z, Li L F 2019 Cryogenics 102 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Uhlig K 2002 Cryogenics 42 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang C 2001 Cryogenics 41 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu X M, Pan C Z, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Guo W J, Yu D P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190701 (In Chinese) [刘旭明, 潘长钊, 张宇, 廖奕, 郭伟杰, 俞大鹏 2023 72 190701]
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X M, Pan C Z, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Guo W J, Yu D P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190701 (In Chinese)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 1191
- PDF Downloads: 59
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: