-
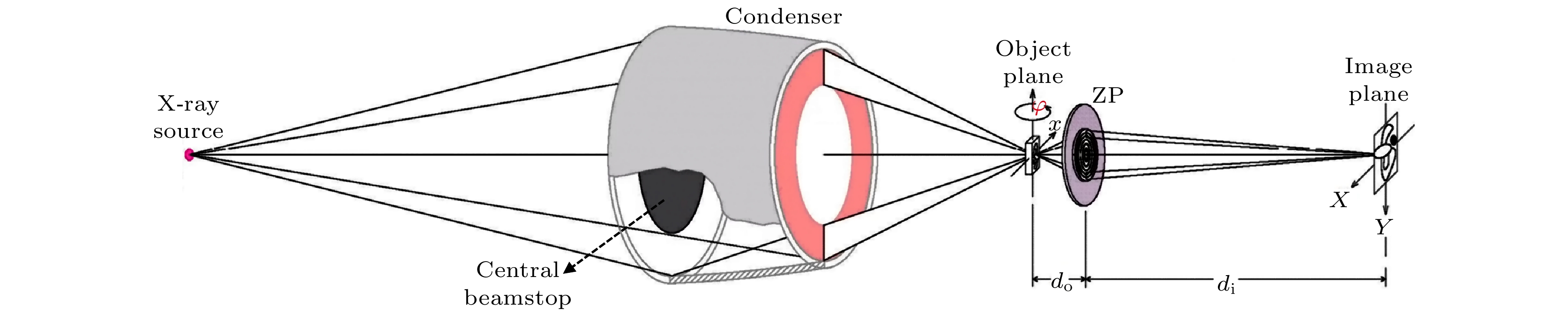
Transmission X-ray microscope (TXM) is a high-precision, cutting-edge X-ray imaging instrument, which is a marvel of modern science and technology. It enables non-destructive imaging on a nanoscale, providing a powerful research tool for various scientific fields such as physics, life science, materials science, and chemistry. Although many synchrotron radiation facilities at home and abroad have established nano-CT experimental stations with TXM as the core, currently only a few companies internationally can provide commercial TXM instrument based on laboratory X-ray sources. The primary reason is that this instrument involves numerous engineering challenges, including high-brightness laboratory X-ray sources, high-resolution X-ray optical elements, high-precision sample stage systems, high-sensitivity detectors, and extremely strict requirements for environmental factors such as temperature and vibration. In order to promote the development of high-end X-ray imaging instruments, it is necessary to overcome the technological bottlenecks encountered in the development of X-ray nano-CT. Discussed in this work mainly are the instrument design of a laboratory transmission X-ray microscope with working energy of 5.4 keV and the results of full-field imaging experiments. To start with, the design of the TXM instrument is introduced in detail. The TXM instrument is equipped with several key components, including laboratory X-ray source, condenser, sample stage module, zone plate, and imaging detector. The TXM instrument adopts a modular vibration isolation design and is equipped with a dedicated temperature control system. The main imaging magnifications of the TXM instrument are 50×, 75×, and 100×, and the corresponding optical parameters and photos are introduced. The X-ray source used is a micro-focus X-ray source, operating in Cr target mode, with a focal spot size of 20 μm and a Ka characteristic spectrum brightness of
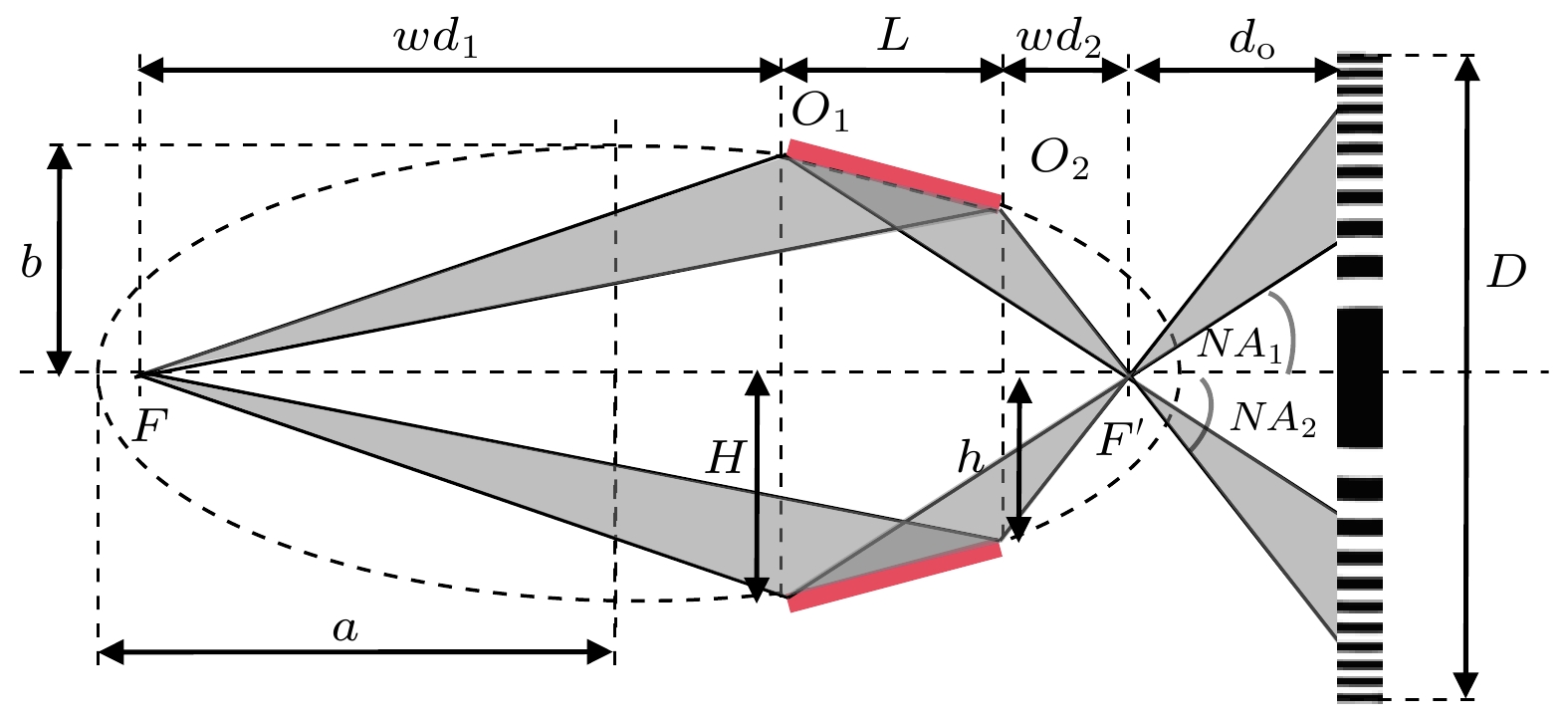
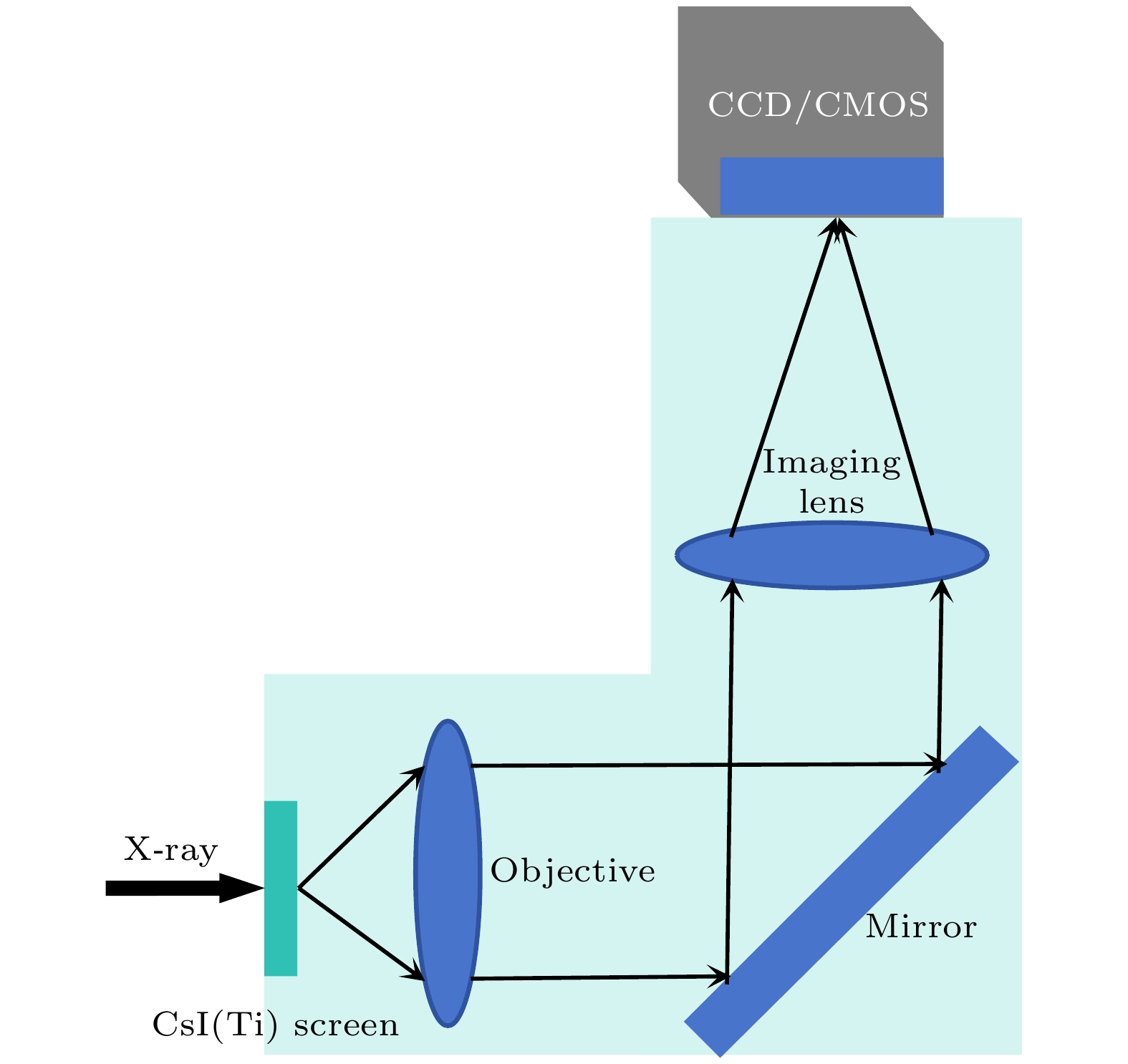
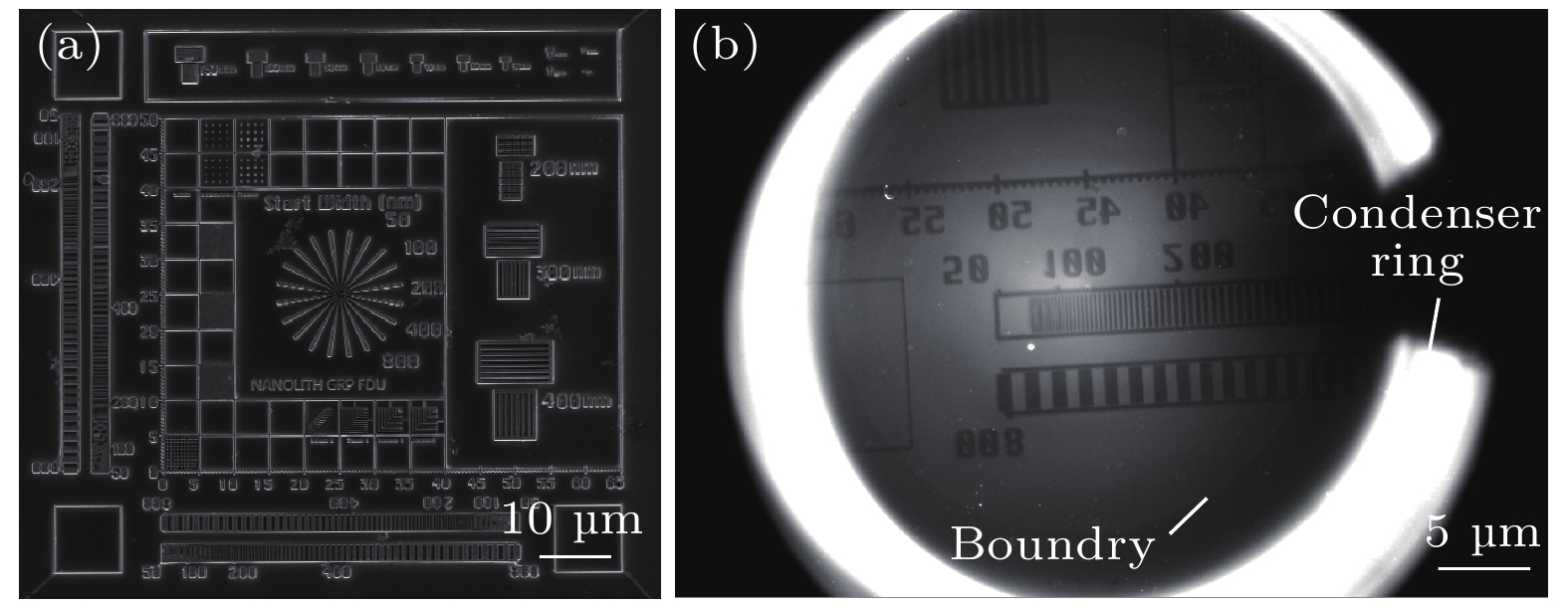
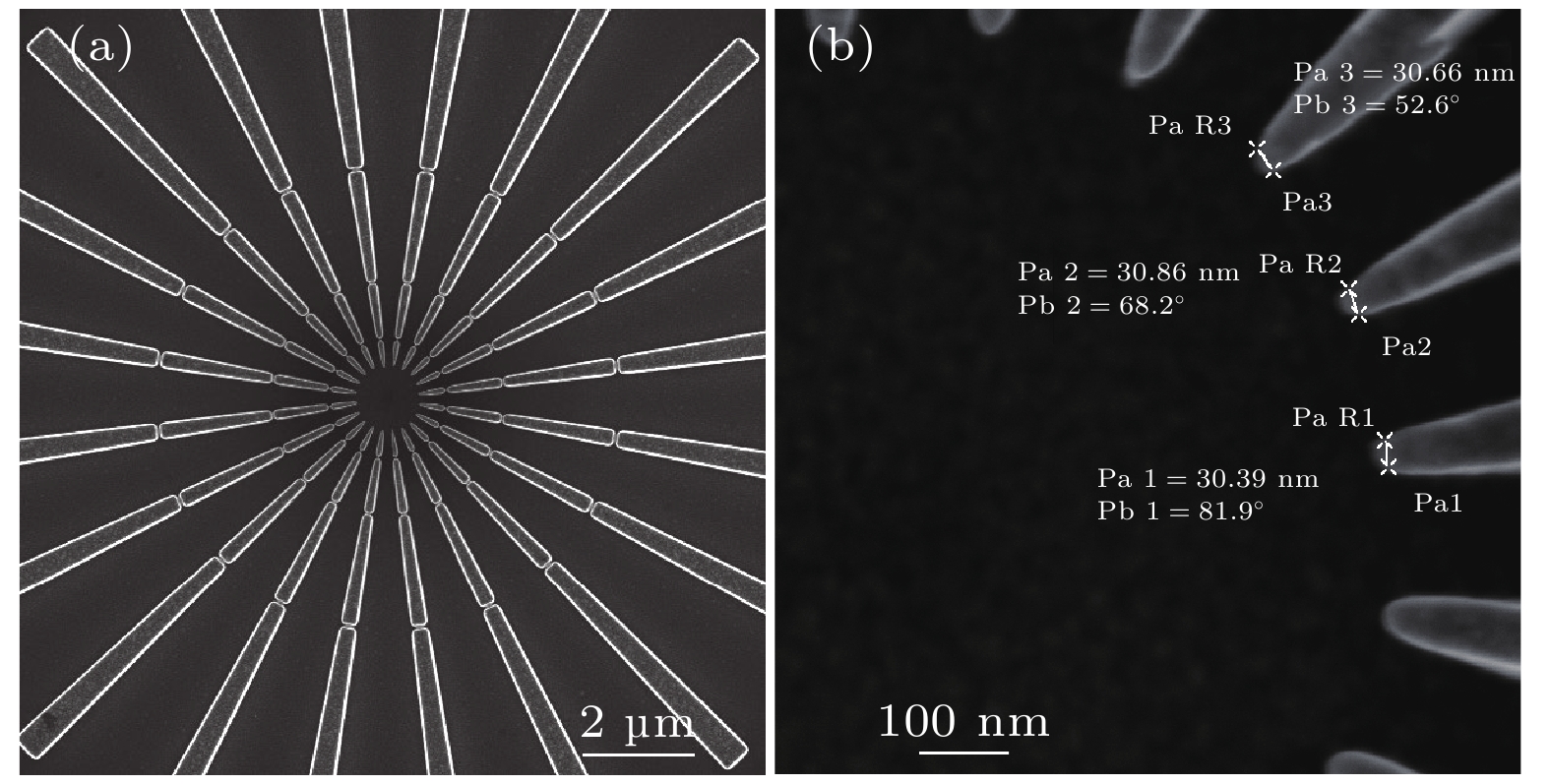
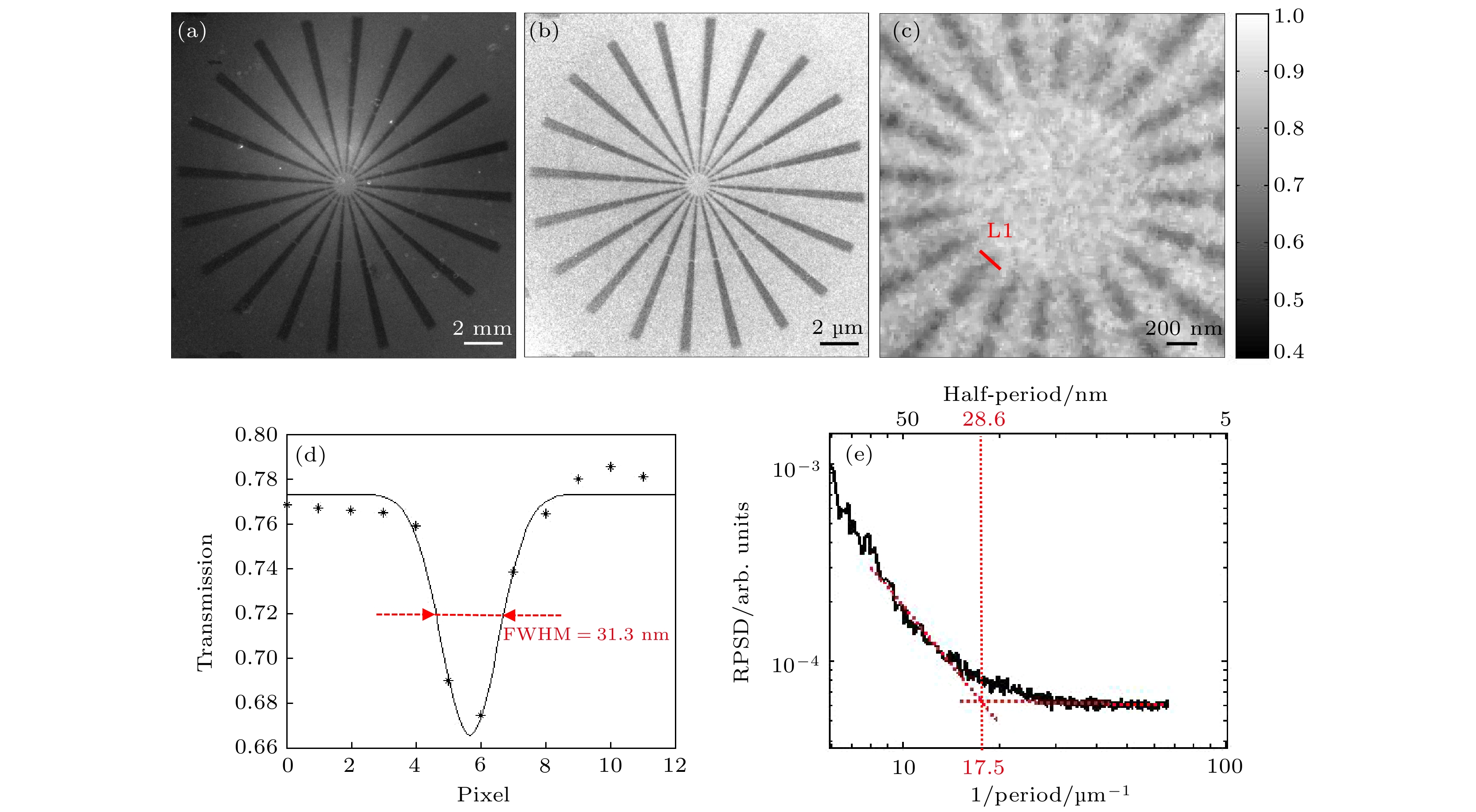
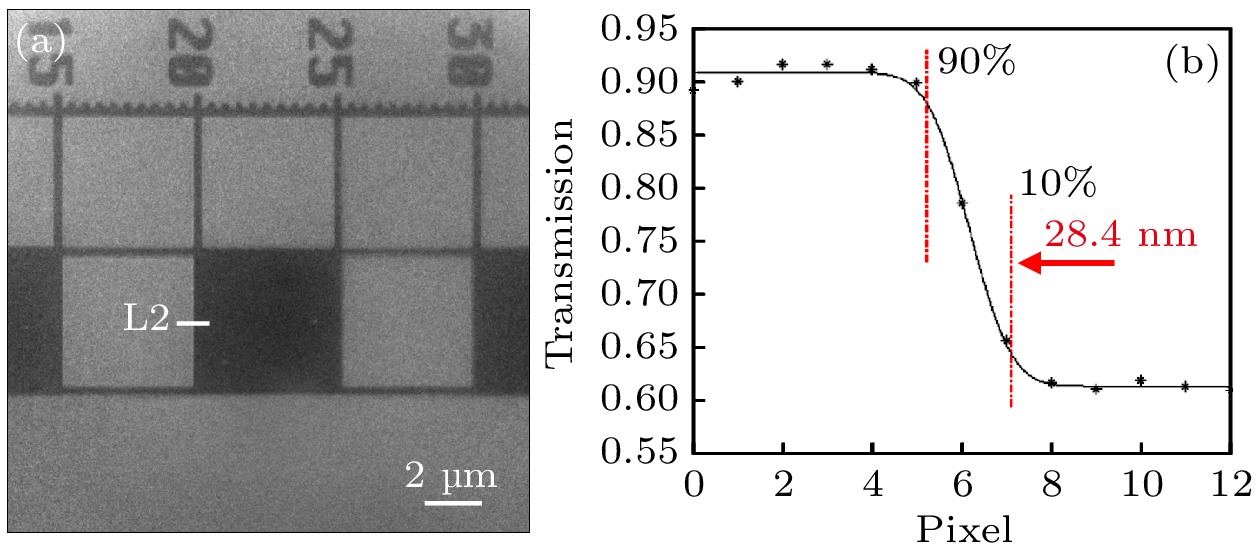
$ 5\times {10}^{9}~\rm {photons}/({mm}^2\cdot {mrad}^2\cdot s)$ . The X-ray source provides illumination for the sample after being focused by an ellipsoidal condenser. The outer ring of the condenser's illumination ring corresponds to a numerical aperture (NA) of$ {NA}_{2} = 3.196~\rm mrad $ , and the inner ring corresponds to a numerical aperture of$ {NA}_{1} = 1.9086~\rm mrad $ . Under these conditions, the limit resolution of this TXM instrument is 22 nm. The zone plate has a diameter of 70μm, a focal length of 8.7mm, and 616 zones. The TXM instrument uses a high-resolution optical coupling detector equipped with a scientific-grade CMOS camera with an effective pixel size of 7.52μm. The optical coupling detector is equipped with 2× and 10× high numerical aperture objectives. When the TXM instrument magnification is 50×, the effective pixel size of the TXM instrument is 15 nm. In addition , a gold resolution test card is used as the sample to determine the imaging field of view of the TXM instrument by observing the size of the imaging area of the test card on the detector, and to determine the imaging resolution of the TXM instrument by observing the line width of the star-shaped target in the center of the test card. Experimental results show that the TXM instrument has an imaging field of view of 26μm and can achieve the clear imaging of characteristic structure with a line width of 30 nm. The radial power spectrum curve of the Siemens Star shows this TXM instrument has the potential to resolve 28.6-nm half pitch line pair features. Finally, we draw some conclusions and present outlook. At present, imaging of 30-nm-wide line features has been realized, but the imaging of 30-nm half pitch line pair feature has not yet been achieved, and the limit resolution has not reached the design value, either. We will continue to explore the potential for upgrading the imaging resolution of the laboratory TXM in future work.-
Keywords:
- X-ray imaging /
- X-ray microscope /
- scientific instruments
[1] Zhao L M, Wang T X, Ma R K, Gu Y, Luo M S, Chen H, Wang Z L, Ge X 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Z L, Chen Z H, Gu Y, Chen H, Ge X 2023 Chinese Phys. B 32 038704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Winarski R P, Holt M V, Rose V, Fuesz P, Carbaugh D, Benson C, Shu D, Kline D, Stephenson G B, McNulty I, Maser J 2012 J. Synchrotron Rad. 19 1056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 周光照, 胡哲, 杨树敏, 廖可梁, 周平, 刘科, 滑文强, 王玉柱, 边风刚, 王劼 2020 69 034102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou G Z, Hu Z, Yang S M, Liao K L, Zhou P, Liu K, Hua W Q, Wang Y Z, Bian F G, Wang J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 034102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 聂勇敢, 高梓宸, 佟亚军, 范家东, 刘功发, 江怀东 2024 73 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie Y G, Gao Z C, Tong Y J, Fan J D, Liu G F, Jiang H D 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] von Hofsten O, Bertilson M, Reinspach J, Holmberg A, Hertz H M, Vogt U 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 2631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Mao W L, Lin Y, Liu Y, Liu J 2019 Engineering 5 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Flenner S, Hagemann J, Wittwer F, et al. 2023 J. Synchrotron Rad. 30 390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] De Andrade V, Nikitin V, Wojcik M, et al. 2021 Adv. Mater. 33 2008653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yuan Q, Zhang K, Hong Y, et al. 2012 J. Synchrotron Rad. 19 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen J, Li W, Liu Y, et al. 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 186 012005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tao F, Wang J, Du G, Su B, Zhang L, Hou C, Deng B, Xiao T 2023 J. Synchrotron Rad. 30 815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zeiss, https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/en/products/X-ray-microscopy.html [2024-6-11]
[14] Sigray, https://www.sigray.com/trilambda-30/#resolution [2024-6-11]
[15] 周腊珍, 夏文静, 许倩倩, 陈赞, 李坊佐, 刘志国, 孙天希 2022 71 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou L Z, Xia W J, Xu Q Q, Chen Z, Li F Z, Liu Z G, Sun T X 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yun W, Lai B, Cai Z, Maser J, Legnini D, Gluskin E, Chen Z, Krasnoperova A A, Vladimirsky Y, Cerrina F, Di Fabrizio E, Gentili M 1999 Review of Scientific Instruments 70 2238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chao W L, Harteneck B D, Liddle J A, Anderson E H, Attwood D T 2005 Nature 435 1210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李乾利, 胡亚华, 马逸凡, 孙志祥, 王敏, 刘小林, 赵景泰, 张志军 2020 69 102902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q L, Hu Y H, Ma Y F, Sun Z X, Wang M, Liu X L, Zhao J T, Zhang Z J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 102902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tong X, Chen Y, Xu Z, Li Y, Xing Z, Mu C, Zhao J, Zhen X, Mao C, Tai R 2023 J. Synchrotron Rad. 30 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhu J, Chen Y, Xie S, Zhang L, Wang C, Tai R 2020 Microelectron. Eng. 225 111254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu J, Li X, Chen S, Zhang S, Xie S, Xu C, Chen Y, Deng B, Mao C 2017 J. Synchrotron Rad. 24 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang S, Zhang K, Huang W, Gao L, Yang F, Li M, Zhu P, Yuan Q 2021 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 993 165089
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liao K L, He Q L, Li P Y, Song M H, Zhao H F, Zhu P P 2024 Proc. SPIE 13155 1315518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 陶芬, 王玉丹, 任玉琦, 丰丙刚, 佟亚军, 杜国浩, 邓彪, 孙天希, 谢红兰, 肖体乔 2017 光学学报 37 1034002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tao F, Wang Y D, Ren Y Q, Feng B G, Tong Y J, Du G H, Deng B, Sun T X, Xie H L, Xiao T Q 2017 Acta Opt. Sin. 37 1034002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
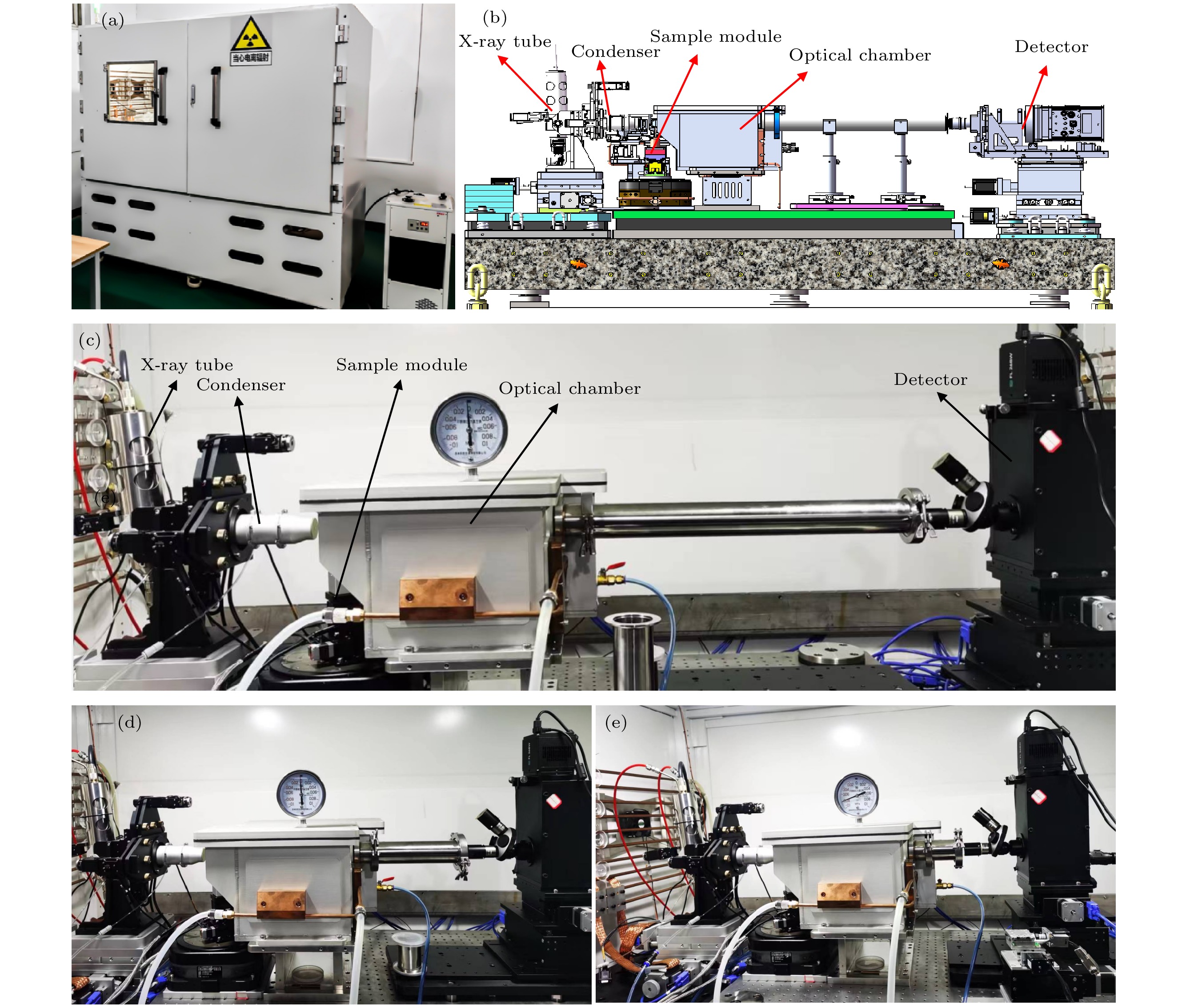
图 2 基于TXM的纳米CT仪器设计与仪器实物图 (a) TXM仪器实物图; (b) TXM仪器的主体结构设计图; (c) 100×放大倍率; (d) 75×放大倍率; (e) 50×放大倍率
Figure 2. Schematic and photograph of the TXM instrument: (a) Photograph of the TXM instrument; (b) schematic of the main structure of the TXM; photograph of the main structure of the TXM under (c) 100×, (d) 75×, (e) 50× magnification ratio.
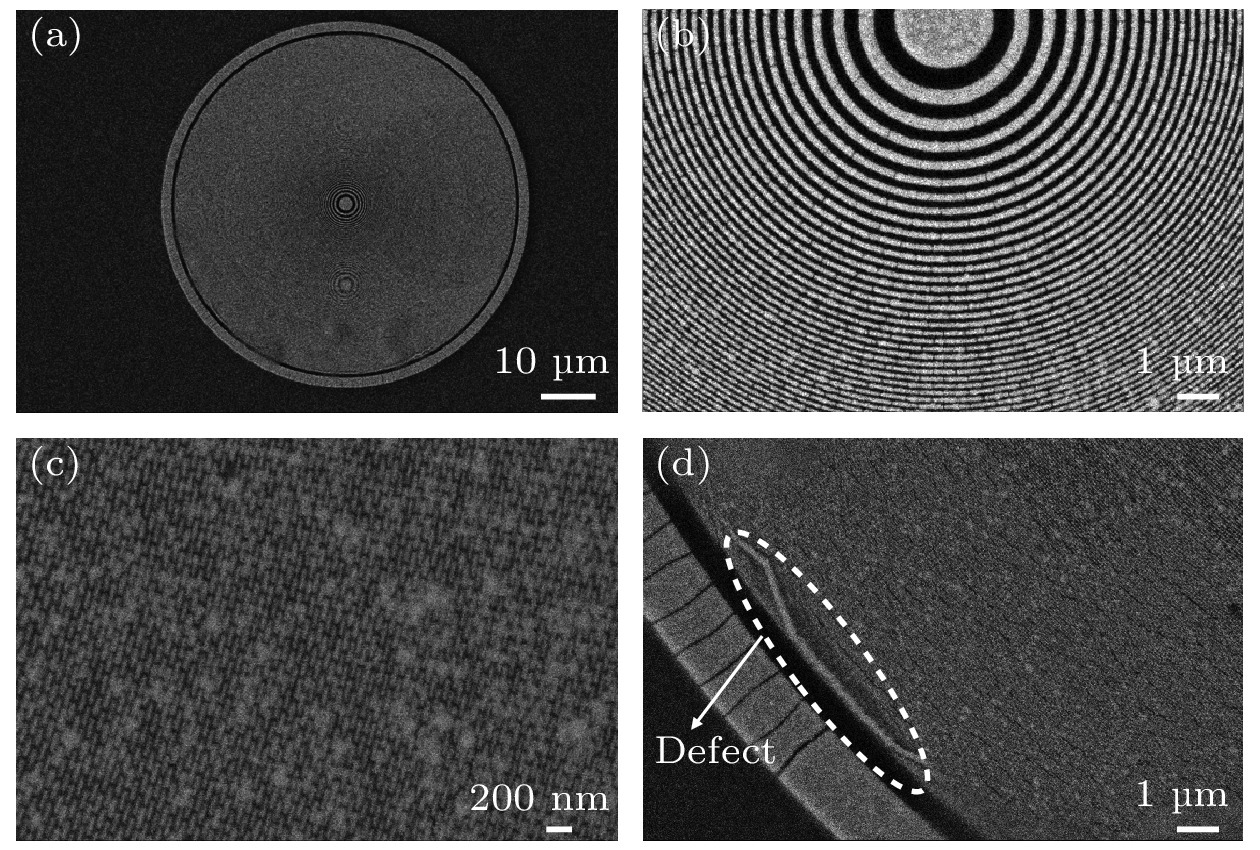
图 8 分辨率测试卡TXM测试结果 (a) 西门子星结构的TXM图像; (b)扣除背底后的西门子星结构的透过率图像; (c)西门子星结构的内环结构局部放大图; (d) 30 nm线宽的栅条结构的透过率分布曲线; (e)径向功率谱强度曲线
Figure 8. TXM results of the resolution test card: (a) TXM graph of the Siemens star; (b) partial enlarged view of the inner ring structure of the Siemens star; (c) the local structure of the Siemens star; (d) the transmission curve of 30 nm line width grating structure; (e) the radial power spectrum density curve.
表 1 不同放大倍率M下的光路参数
Table 1. Optical parameters under different magnification M.
放大倍数M 物距 do/mm 像距 di/mm 光路总长/mm 50 8.874 443.7 752.574 75 8.816 661.2 970.016 100 8.787 878.7 1187.487 表 2 波带片参数
Table 2. Parameter of zone plate.
能量
E/keV材
料直径
D/μm最外环宽度
$ {{\Delta r}}$/nm波带数
N高度/
nm焦距
f/mm5.41 Au 70 28.5 616 ≥800 8.7 -
[1] Zhao L M, Wang T X, Ma R K, Gu Y, Luo M S, Chen H, Wang Z L, Ge X 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Z L, Chen Z H, Gu Y, Chen H, Ge X 2023 Chinese Phys. B 32 038704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Winarski R P, Holt M V, Rose V, Fuesz P, Carbaugh D, Benson C, Shu D, Kline D, Stephenson G B, McNulty I, Maser J 2012 J. Synchrotron Rad. 19 1056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 周光照, 胡哲, 杨树敏, 廖可梁, 周平, 刘科, 滑文强, 王玉柱, 边风刚, 王劼 2020 69 034102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou G Z, Hu Z, Yang S M, Liao K L, Zhou P, Liu K, Hua W Q, Wang Y Z, Bian F G, Wang J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 034102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 聂勇敢, 高梓宸, 佟亚军, 范家东, 刘功发, 江怀东 2024 73 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie Y G, Gao Z C, Tong Y J, Fan J D, Liu G F, Jiang H D 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] von Hofsten O, Bertilson M, Reinspach J, Holmberg A, Hertz H M, Vogt U 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 2631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Mao W L, Lin Y, Liu Y, Liu J 2019 Engineering 5 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Flenner S, Hagemann J, Wittwer F, et al. 2023 J. Synchrotron Rad. 30 390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] De Andrade V, Nikitin V, Wojcik M, et al. 2021 Adv. Mater. 33 2008653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yuan Q, Zhang K, Hong Y, et al. 2012 J. Synchrotron Rad. 19 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen J, Li W, Liu Y, et al. 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 186 012005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tao F, Wang J, Du G, Su B, Zhang L, Hou C, Deng B, Xiao T 2023 J. Synchrotron Rad. 30 815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zeiss, https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/en/products/X-ray-microscopy.html [2024-6-11]
[14] Sigray, https://www.sigray.com/trilambda-30/#resolution [2024-6-11]
[15] 周腊珍, 夏文静, 许倩倩, 陈赞, 李坊佐, 刘志国, 孙天希 2022 71 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou L Z, Xia W J, Xu Q Q, Chen Z, Li F Z, Liu Z G, Sun T X 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yun W, Lai B, Cai Z, Maser J, Legnini D, Gluskin E, Chen Z, Krasnoperova A A, Vladimirsky Y, Cerrina F, Di Fabrizio E, Gentili M 1999 Review of Scientific Instruments 70 2238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chao W L, Harteneck B D, Liddle J A, Anderson E H, Attwood D T 2005 Nature 435 1210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李乾利, 胡亚华, 马逸凡, 孙志祥, 王敏, 刘小林, 赵景泰, 张志军 2020 69 102902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q L, Hu Y H, Ma Y F, Sun Z X, Wang M, Liu X L, Zhao J T, Zhang Z J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 102902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tong X, Chen Y, Xu Z, Li Y, Xing Z, Mu C, Zhao J, Zhen X, Mao C, Tai R 2023 J. Synchrotron Rad. 30 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhu J, Chen Y, Xie S, Zhang L, Wang C, Tai R 2020 Microelectron. Eng. 225 111254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu J, Li X, Chen S, Zhang S, Xie S, Xu C, Chen Y, Deng B, Mao C 2017 J. Synchrotron Rad. 24 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang S, Zhang K, Huang W, Gao L, Yang F, Li M, Zhu P, Yuan Q 2021 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 993 165089
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liao K L, He Q L, Li P Y, Song M H, Zhao H F, Zhu P P 2024 Proc. SPIE 13155 1315518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 陶芬, 王玉丹, 任玉琦, 丰丙刚, 佟亚军, 杜国浩, 邓彪, 孙天希, 谢红兰, 肖体乔 2017 光学学报 37 1034002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tao F, Wang Y D, Ren Y Q, Feng B G, Tong Y J, Du G H, Deng B, Sun T X, Xie H L, Xiao T Q 2017 Acta Opt. Sin. 37 1034002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4675
- PDF Downloads: 492
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: