-
In recent years, the X-ray interferometer using dual phase gratings has been extensively studied. The large periodic fringes produced by the X-ray interferometer using dual phase gratings can be directly detected by ordinary detectors. At the same time, the X-ray interferometer using dual phase gratings can reduce the radiation dose of the sample without using absorption gratings. Meanwhile, a high fringe visibility is always preferred to achieve a high signal-to-noise ratio for X-ray grating interferometry. However, recent studies have reported that experimental fringe visibility in X-ray interferometer using dual rectangular phase gratings is relatively low. Therefore, it is necessary to further increase the fringe visibility in X-ray interferometry using dual phase gratings. This work focuses on the analysis of fringe visibility in X-ray interferometer using dual triangular phase gratings. Based on the fringe intensity distribution formula of X-ray dual phase grating interferometer, the fringe visibility of the dual triangular phase grating interferometer is investigated as a function of the grating spacing under monochromatic and polychromatic illumination, respectively. For comparison, the fringe visibility of the dual rectangular phase grating interferometer is also studied under the same condition. The results show that the maximum fringe visibility of the dual triangular phase grating interferometer increases with the phase shift increasing regardless of monochromatic or polychromatic illumination. Under monochromatic illumination, the maximum fringe visibility of dual 5π/2 triangular phase gratings is about 21% higher than that of dual rectangular phase gratings. Under polychromatic illumination, the fringe visibility of dual 5π/2 triangular phase gratings is at least 23% higher than that of dual rectangular phase gratings. Under polychromatic illumination, the greater the deviation of X-ray average energy from the grating design energy, the greater the decrease of maximum fringe visibility of the dual phase grating interferometer is. In addition, with the increase of the focal size of X-ray source, the maximum fringe visibility of the dual phase grating interferometer decreases, under polychromatic illumination. We hope that those results can be used as guidelines for designing and optimizing X-ray interferometer using dual triangular phase gratings.
-
Keywords:
- X-ray imaging /
- grating interferometer /
- triangular phase grating /
- fringe visibility
[1] Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T, Bunk O, David C 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pfeiffer F, Bech M, Bunk O, Kraft P, Eikenberry E F, Brönnimann C, Grünzweig C, David C 2008 Nat. Mater. 7 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kai S, Lorenz B, Konstantin W, Michael C, Julia H, Pfeiffer F 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10863
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yan A, Wu X, Liu H 2016 Opt. Express 24 15927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Z L, Shi X M, Ren K, Chen H, Ren Y Q, Gao K, Wu Z 2020 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 27 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Vila-Comamala J, Romano L, Jefimovs K, Dejea H, Bonnin A, Cook A C, Planinc I, Cikes M, Wang Z, Stampanoni M 2021 Opt. Express 29 2049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shi Z, Jefimovs K, Romano L, Vila-Comamala J, Stampanoni M 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 3693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu J Q, Wang Z T, Stefano V G, Michał R, Simon S, Stampanoni M 2022 Opt. Express 30 13847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Seifert M, Ludwig V, Kaeppler S, Horn F, Meyer P, Pelzer G, Rieger J, Sand D, Michel T, Mohr J, Riess C, Anton G 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 4199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 戚俊成, 陈荣昌, 刘宾, 陈平, 杜国浩, 肖体乔 2017 66 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi J C, Chen R C, Liu B, Chen P, Du G H, Xiao T Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Z L, Chen Z H, Gu Y, Chen H, Ge X 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 038704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Z L, Zhou R C, Zhao L M, Ren K, Xu W, Liu B, Chen H 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 028702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 杨君, 吴浩, 罗琨皓, 郭金川, 宗方轲 2021 70 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J, Wu H, Luo K H, Guo J C, Zong F K 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Katharina H, Felix G, Thomas M, Konstantin W, Andre Y, Astrid Velroyen, Margarita B, Sigrid A, Maximilian F, Oliver E, Pfeiffer F, Yildirim A Ö 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 2096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lorenzo M, Tamara S, Charlotte K, Marco E, Peter R, Glafkos H, Sam H, Bennie S, Alberto A, Oliver J 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 3663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kagias M, Wang Z, Birkbak M E, Lauridsen E, Abis M, Lovric G, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 5130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kim J, Kagias M, Marone F, Stampanoni M 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 134102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Momose A, Takano H, Wu Y, Hashimoto K, Samoto T, Hoshino M, Seki Y, Shinohara T 2020 Quantum Beam Sci. 4 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yan A, Wu X, Liu H 2018 Opt. Express 26 23142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yan A, Wu X, Liu H 2020 J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 28 1055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ge Y S, Chen J W, Yang J C, Zhu P P, Zhang H T, Zhang A Z, Liang D 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 2791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Organista C, Kagias M, Tang R, Shi Z, Jefimovs K, Boone M, Stampanoni M 2023 Opt. Continuum 2 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tang R, Organista C, Goethals W, Stolp W, Stampanoni M, Aelterman J, Boone M N 2023 Opt. Express 31 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kagias M, Wang Z, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 014105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Miao H, Panna A, Gomella A A, Bennett E E, Znati S, Chen L, Wen H 2016 Nat. Phys. 12 830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Thomas W, Peter B, Florian B, Jürgen D, Wilhelm H 2011 Med. Phys. 38 4133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lei Y H, Liu X, Huang J H, Du Y, Guo J C, Zhao Z G, Li J 2018 J. Phys. D:Appl. Phys. 51 385302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ge Y S, Chen J W, Zhu P P, Yang J, Deng S W, Shi W, Zhang K, Guo J C, Zhang H T, Zheng H R, Liang D 2020 Opt. Express 28 9786
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yaroshenko A, Bech M, Potdevin G, Malecki A, Biernath T, Wolf J, Tapfer A, Schüttler M, Meiser J, Kunka D, Amberger M, Mohr J, Pfeiffer F 2014 Opt. Express 22 547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Viermetz M, Gustschin N, Schmid C, Haeusele J, Noel P B, Proksa R, Loscher S, Koehler T, Pfeiffer F 2023 IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 42 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Munro P, Ignatyev K, Speller R D, Olivo A 2010 Opt. Express 18 19681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Viermetz M, Gustschin N, Schmid C, Jakob H, Maximilian T, Pascal M, Frank B, Tobias L, Roland P, Thomas K, Franz P 2022 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119 e2118799119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Günther B, Hehn L, Jud C, Alexander H, Martin D, Pfeiffer F 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 2494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Shashev Y, Andreas K, Lange A, Müller, Bernd R, Giovanni B 2016 Mater. Test. 58 970
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
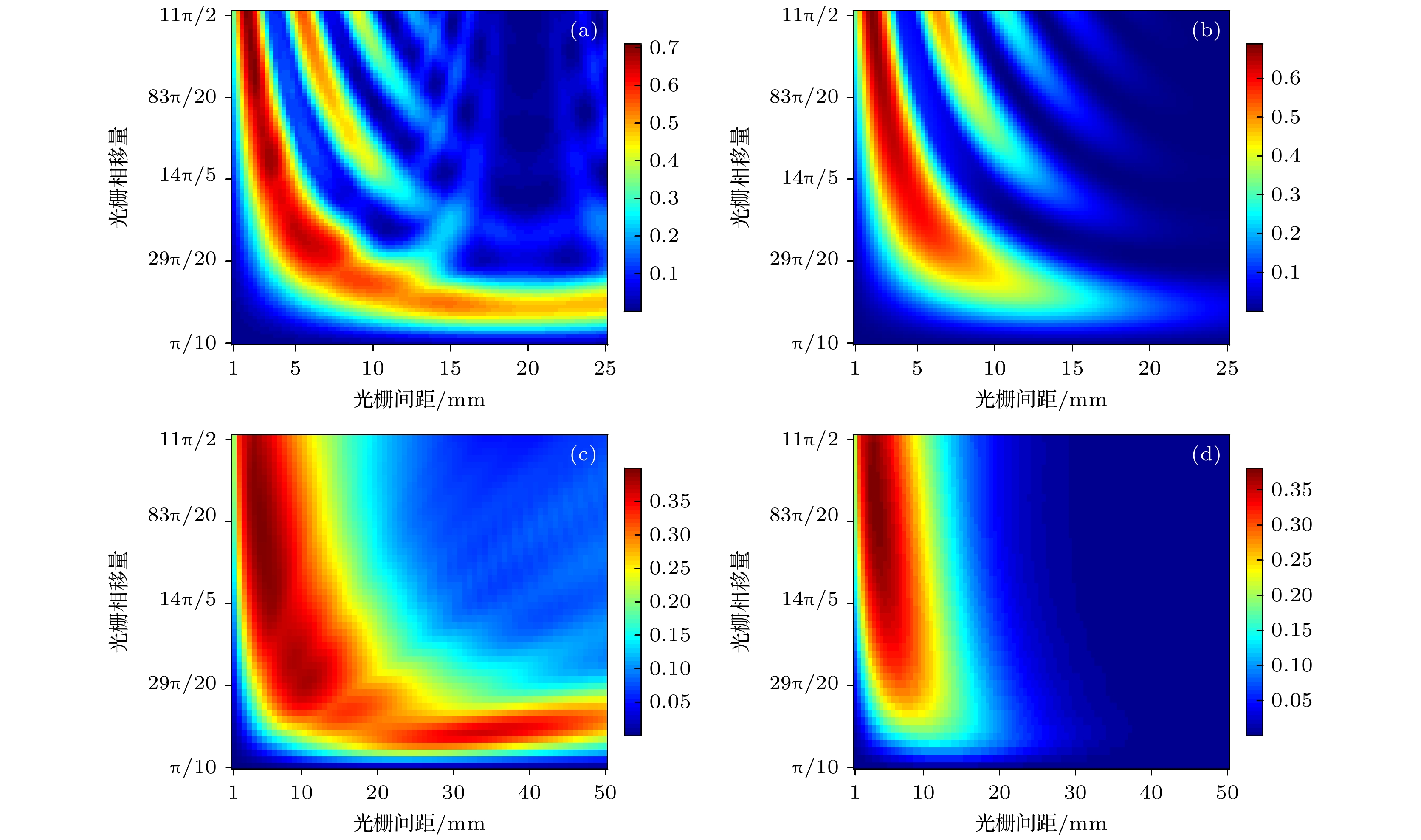
图 2 条纹可见度随光栅间距和光栅相移量的变化 (a) 单色照明, 光源焦点尺寸9.5 μm; (b) 单色照明, 光源焦点尺寸40 μm; (c) 多色照明, 光源焦点尺寸9.5 μm; (d) 多色照明, 光源焦点尺寸40 μm
Figure 2. Fringe visibility as a function of grating spacing and grating phase shift: (a) Monochromatic illumination with a source size of 9.5 μm; (b) monochromatic illumination with a source size of 40 μm; (c) polychromatic illumination with a source size of 9.5 μm; (d) polychromatic illumination with a source size of 40 μm.
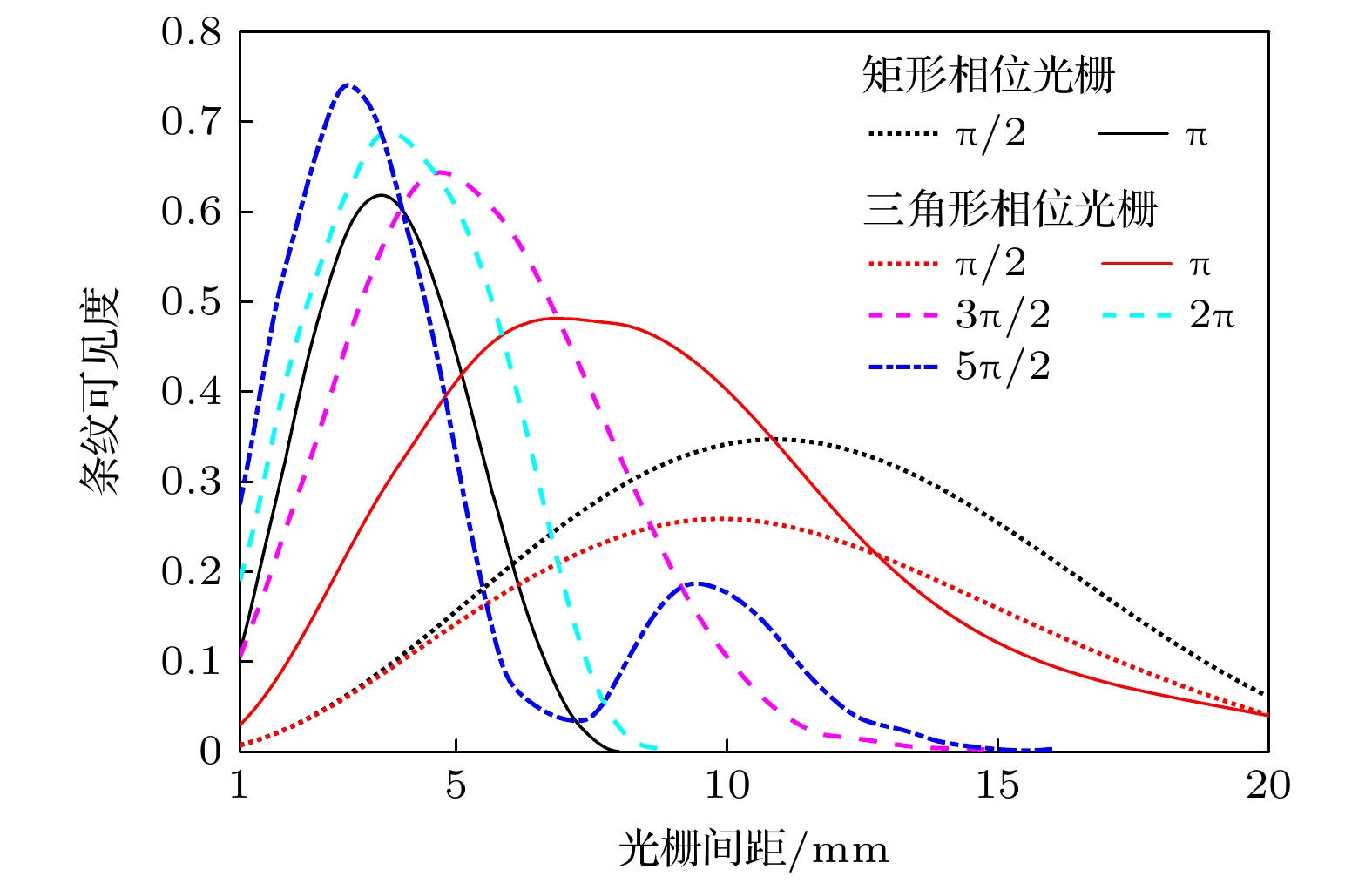
表 1 单色照明下, 条纹可见度峰值、对应的光栅间距和条纹可见度曲线的FWHM
Table 1. Visibility peak, corresponding grating spacing and FWHM of visibility curve under monochromatic illumination.
参数 双三角形相位光栅 双矩形相位光栅 π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2 π/2 π $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.25 0.48 0.64 0.68 0.74 0.34 0.61 s/mm 9.8 6.6. 4.8 3.7 3.0 10.8 3.7 W/mm 12.1 9.1 5.8 4.9 3.4 12.0 3.8 表 2 多色照明下, 条纹可见度峰值、对应的光栅间距和条纹可见度曲线的FWHM
Table 2. Visibility peak, corresponding grating spacing, and FWHM of visibility curve under polychromatic illumination.
参数 双三角形相位光栅 双矩形相位光栅 π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2 π/2 π $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.25 0.41 0.56 0.58 0.63 0.30 0.51 s/mm 9.1 6.5 4.5 3.6 2.8 10.9 3.5 W/mm 12.3 10.4 6.8 5.5 4.2 15.0 4.0 表 3 光源焦点尺寸为7 μm, 峰值电压分别为55, 75和95 kV时, 条纹可见度峰值、对应的光栅间距和条纹可见度曲线的FWHM
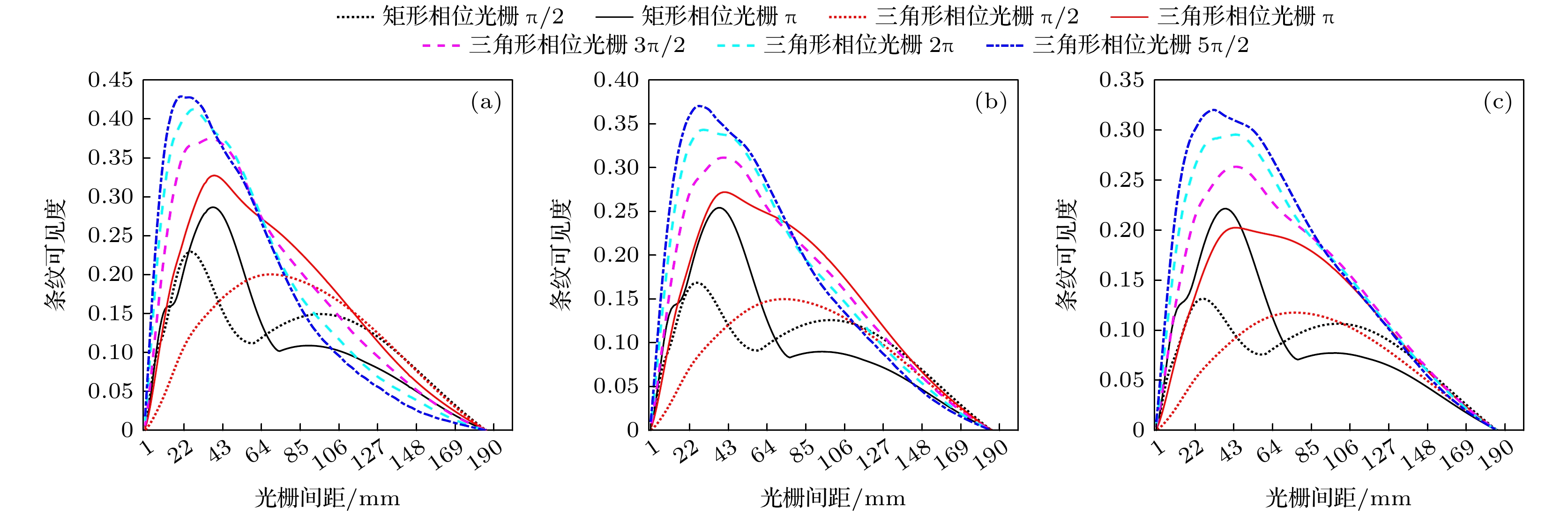
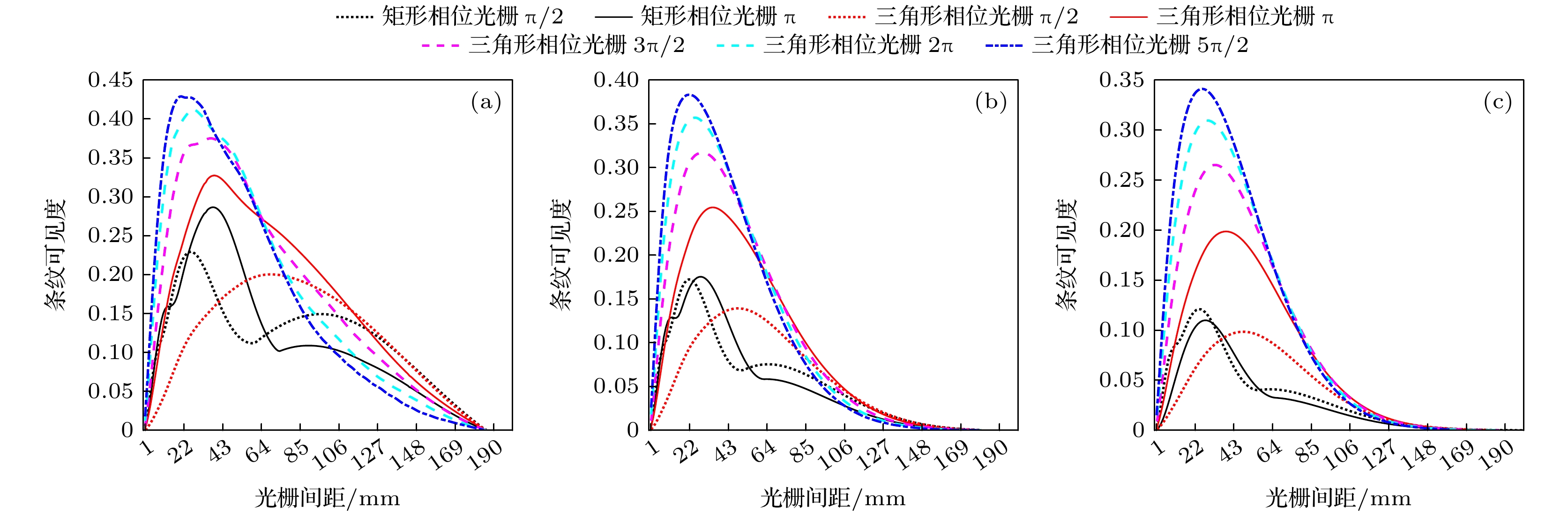
Table 3. Visibility peak, corresponding grating spacing and FWHM of visibility curve with source size of 7 μm and peak voltage of 55, 75, and 95 kV, respectively.
光源峰值电压/kV 参数 双三角形相位光栅 双矩形相位光栅 π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2 π/2 π 55 $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.20 0.32 0.37 0.41 0.42 0.22 0.28 s/mm 67.9 37.3 35.6 26.7 19.5 25.7 37.3 W/mm 117.3 96.3 81.5 69.3 67.6 44.8 52.9 75 $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.14 0.27 0.31 0.34 0.37 0.16 0.25 s/mm 71.0 40.1 38.9 29.4 27.5 26.7 37.4 W/mm 116.7 105.7 96.6 85.8 79.9 51.8 53.6 95 $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.11 0.20 0.26 0.29 0.32 0.13 0.22 s/mm 76.5 41.4 45.4 43.6 32.1 26.7 38.8 W/mm 116.7 111.3 104.1 98.3 92.1 55.3 54.1 表 4 峰值电压分别为55 kV, 光源焦点尺寸为7, 25和40 μm时, 条纹可见度峰值、对应的光栅间距和条纹可见度曲线的FWHM
Table 4. Visibility peak, corresponding grating spacing and FWHM of visibility curve with peak voltage of 55 kV and source size of 7, 25, and 40 μm, respectively.
光源焦点尺/µm 参数 双三角形相位光栅 双矩形相位光栅 π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2 π/2 π 7 $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.20 0.32 0.37 0.41 0.42 0.22 0.28 s/mm 67.9 37.3 35.6 26.7 19.5 25.7 37.3 W/mm 117.3 96.3 81.5 69.3 67.6 44.8 52.9 25 $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.14 0.25 0.31 0.34 0.38 0.17 0.17 s/mm 48.6 35.0 28.3 24.9 21.6 21.5 28.3 W/mm 75.8 66.2 61.3 57.5 54.5 34.3 43.3 40 $ {V_{\text{p}}} $ 0.10 0.19 0.26 0.31 0.34 0.12 0.11 s/mm 36.2 29.2 24.1 21.1 19.3 17.9 21.1 W/mm 52.5 49.1 46.3 44.1 42.3 27.9 25.4 -
[1] Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T, Bunk O, David C 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pfeiffer F, Bech M, Bunk O, Kraft P, Eikenberry E F, Brönnimann C, Grünzweig C, David C 2008 Nat. Mater. 7 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kai S, Lorenz B, Konstantin W, Michael C, Julia H, Pfeiffer F 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10863
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yan A, Wu X, Liu H 2016 Opt. Express 24 15927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Z L, Shi X M, Ren K, Chen H, Ren Y Q, Gao K, Wu Z 2020 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 27 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Vila-Comamala J, Romano L, Jefimovs K, Dejea H, Bonnin A, Cook A C, Planinc I, Cikes M, Wang Z, Stampanoni M 2021 Opt. Express 29 2049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shi Z, Jefimovs K, Romano L, Vila-Comamala J, Stampanoni M 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 3693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu J Q, Wang Z T, Stefano V G, Michał R, Simon S, Stampanoni M 2022 Opt. Express 30 13847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Seifert M, Ludwig V, Kaeppler S, Horn F, Meyer P, Pelzer G, Rieger J, Sand D, Michel T, Mohr J, Riess C, Anton G 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 4199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 戚俊成, 陈荣昌, 刘宾, 陈平, 杜国浩, 肖体乔 2017 66 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi J C, Chen R C, Liu B, Chen P, Du G H, Xiao T Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Z L, Chen Z H, Gu Y, Chen H, Ge X 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 038704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Z L, Zhou R C, Zhao L M, Ren K, Xu W, Liu B, Chen H 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 028702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 杨君, 吴浩, 罗琨皓, 郭金川, 宗方轲 2021 70 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J, Wu H, Luo K H, Guo J C, Zong F K 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Katharina H, Felix G, Thomas M, Konstantin W, Andre Y, Astrid Velroyen, Margarita B, Sigrid A, Maximilian F, Oliver E, Pfeiffer F, Yildirim A Ö 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 2096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lorenzo M, Tamara S, Charlotte K, Marco E, Peter R, Glafkos H, Sam H, Bennie S, Alberto A, Oliver J 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 3663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kagias M, Wang Z, Birkbak M E, Lauridsen E, Abis M, Lovric G, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 5130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kim J, Kagias M, Marone F, Stampanoni M 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 134102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Momose A, Takano H, Wu Y, Hashimoto K, Samoto T, Hoshino M, Seki Y, Shinohara T 2020 Quantum Beam Sci. 4 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yan A, Wu X, Liu H 2018 Opt. Express 26 23142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yan A, Wu X, Liu H 2020 J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 28 1055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ge Y S, Chen J W, Yang J C, Zhu P P, Zhang H T, Zhang A Z, Liang D 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 2791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Organista C, Kagias M, Tang R, Shi Z, Jefimovs K, Boone M, Stampanoni M 2023 Opt. Continuum 2 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tang R, Organista C, Goethals W, Stolp W, Stampanoni M, Aelterman J, Boone M N 2023 Opt. Express 31 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kagias M, Wang Z, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 014105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Miao H, Panna A, Gomella A A, Bennett E E, Znati S, Chen L, Wen H 2016 Nat. Phys. 12 830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Thomas W, Peter B, Florian B, Jürgen D, Wilhelm H 2011 Med. Phys. 38 4133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lei Y H, Liu X, Huang J H, Du Y, Guo J C, Zhao Z G, Li J 2018 J. Phys. D:Appl. Phys. 51 385302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ge Y S, Chen J W, Zhu P P, Yang J, Deng S W, Shi W, Zhang K, Guo J C, Zhang H T, Zheng H R, Liang D 2020 Opt. Express 28 9786
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yaroshenko A, Bech M, Potdevin G, Malecki A, Biernath T, Wolf J, Tapfer A, Schüttler M, Meiser J, Kunka D, Amberger M, Mohr J, Pfeiffer F 2014 Opt. Express 22 547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Viermetz M, Gustschin N, Schmid C, Haeusele J, Noel P B, Proksa R, Loscher S, Koehler T, Pfeiffer F 2023 IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 42 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Munro P, Ignatyev K, Speller R D, Olivo A 2010 Opt. Express 18 19681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Viermetz M, Gustschin N, Schmid C, Jakob H, Maximilian T, Pascal M, Frank B, Tobias L, Roland P, Thomas K, Franz P 2022 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119 e2118799119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Günther B, Hehn L, Jud C, Alexander H, Martin D, Pfeiffer F 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 2494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Shashev Y, Andreas K, Lange A, Müller, Bernd R, Giovanni B 2016 Mater. Test. 58 970
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5094
- PDF Downloads: 80
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: