-
电化学反应过程中离子迁移、氧化还原反应的原位动态观测对研究电解池和电池充放电性能、离子迁移特性、缺陷产生和预防等具有重要意义. 采用电解池模型研究电化学反应过程以方便实验参数调控, 基于运动衬度X射线成像实验研究了其离子迁移和氧化还原反应过程. 结果表明, 同等条件下运动衬度X射线成像比传统的时间减影成像的衬噪比高一个量级以上. 基于运动衬度X射线成像成功观测到起始阶段电化学反应特性, 发现电化学反应在电解池内所有位置同时发生, 而不是通常理解的电场力作用下离子迁移到阴极、得到电子被还原. 电极投影位置运动衬度信号强于电解液其他位置, 说明电极位置氧化还原反应更密集. 在通电电压低到一个临界值、传统时间减影成像很难观测到离子迁移或原子团聚的时候, 运动衬度成像仍可明确揭示离子迁移(原子团簇运动)轨迹. 因此, 运动衬度X射线成像可大幅提升电解质中离子(原子)迁移的观测灵敏度, 在电池、电解池电化学反应特性的原位动态研究中具有重要应用前景.The in-situ dynamic observation of ion migration and redox reactions during electrochemical reactions is critical for the understanding of the charging and discharging performance, ion migration characteristics, causes and preventives of defects in cells and electrolytic cells. For the convenience of parameter tuning, an electrolytic cell is adopted to investigate the electrochemical reaction. The processes of ion migration and redox reaction are investigated based on move contrast X-ray imaging. The experimental results demonstrate that the contrast-to-noise ratio of move contrast X-ray imaging is one order higher than that of the conventional temporal subtraction imaging. The initial status of the electrochemical reaction is successfully revealed by move contrast X-ray imaging. The images show that at the very beginning of the reaction, the signals of move contrast distribute almost evenly in the electrolytic cell, which implicates that the ion migration is initiated as soon as the cell is switched on and redox reaction occurs simultaneously all over the cell, other than the fact that ions are driven by electric field, approach to the cathode and then are reduced through electron gain. The signals of move contrast imaging are obviously stronger at positions inside the shadow of the electrodes than elsewhere. This means that the redox processes react densely at the electrodes. When the electrical voltage is adjusted to a critical value and the conventional methods are hard to observe ion migration or atom accumulation, the move contrast X-ray imaging can still disclose evidently the trace of ion migration or movement of atom clusters. Therefore, the move contrast X-ray imaging can improve significantly the sensitivity of observation to the trace of ions or atoms in the electrolyte and has great potentials in in-situ investigating the characteristics of electrochemical reactions.
-
Keywords:
- electrochemical reactions /
- move contrast /
- X-ray imaging /
- ion migration
[1] Kang B, Ceder G 2009 Nature 458 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Okubo M, Mizuno Y, Yamada H, Kim J, Hosono E, Zhou H S, Kudo T, Honma I 2010 ACS Nano 4 741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ellis B, Perry L K, Ryan D H, Nazar L F 2006 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 11416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao W Y, Sakurai K 2019 J. Synchrotron. Radiat. 26 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen S L, Zhang Y, Zhao J J, Mi Z, Zhang J M, Cao J, Feng J C, Zhang G L, Qi J L, Li J Y, Gao P 2020 Sci. Bull. 65 1643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈树林, 高鹏 2019 物理 48 168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen S L, Gao P 2019 Physics 48 168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘玄玄, 国洪轩, 徐涛, 尹奎波, 孙立涛 2021 70 086701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X X, Guo H X, Xu T, Yin K B, Sun L T 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 086701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang Y C, Gao P, Gaba S, Chang T, Pan X, Lu W 2012 Nat. Commun. 3 732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 陆敬予, 柯承志, 龚正良, 李德平, 慈立杰, 张力, 张桥保 2021 70 198102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu J Y, Ke C Z, Gong Z L, Li D P, Ci L J, Zhang L, Zhang Q B 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 198102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 郭祝崑, 李香庭 1983 32 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo Z K, Li X T 1983 Acta Phys. Sin. 32 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 杨同华, 包宗渝 1984 33 1149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang T H, Bao Z Y 1984 Acta Phys. Sin. 33 1149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Warren J M, Bilheux H Z, Kang M, Voisin S 2013 Plant Soil 366 683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ilott A J, Trease N M, Grey C P, Jerschow A 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou L, Leskes M, Liu T, Grey C P 2015 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 54 14782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zheng J, Tang M X, Hu Y-Y 2016 Angew Chem. Int. Edit. 55 12538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Takanashi T, Kawamura H 2019 World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018 Prague, Czech Republic, June 3–8, 2018 p35
[17] 安汉文, 莫生凯, 李梦璐, 王家钧 2022 储能科学与技术 11 834
An H W, Mo S K, Li M L, Wang J J 2022 Energy Storage Science and Technology 11 834
[18] 周逸凡, 杨慕紫, 佘峰权, 龚力, 张晓琪, 陈建, 宋树芹, 谢方艳 2021 70 178801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y F, Yang M Z, She F Q, Gong L, Zhang X Q, Chen J, Song S Q, Xie F Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 178801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cheng L, Tscheuschner S, Paulus F, Hopkinson P E, Kieling J, Khler A, Vaynzof Y, Huettner S 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 2446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王继飞, 林东旭, 袁永波 2019 68 158801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J F, Lin D X, Yuan Y B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 158801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 果辰, 蔡欣炜, 罗文浩, 黄子耕, 冯庆荣, 甘子钊 2021 70 197401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C, Cai X W, Luo W H, Huang Z G, Feng Q R, Gan Z Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 197401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王丽, 王海波, 王涛, 李发伸 2006 55 6515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L, Wang H B, Wang T, Li F S 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 6515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao W Y, Sakurai K 2017 ACS Omega 2 4363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王飞翔 2019 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学 (中国科学院上海应用物理研究所))
Wang F X 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[25] Wang F X, Zhou P T, Li K, Mamtilahun M, Tang Y H, Du G H, Deng B, Xie H L, Yang G Y, Xiao T Q 2020 IUCrJ 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 李可 2021 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学 (中国科学院上海应用物理研究所))
Li K 2021 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[27] Song X M, Pogue B W, Jiang S D, Doyley M M, Dehghani H, Tosteson T D, Paulsen K D 2004 Appl. Optics 43 1053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xie H L, Deng B, Du G H, Fu Y N, Guo H, Xue Y L, Peng G Y, Tao F, Zhang L, Xiao T Q 2020 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 31 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 郭荣怡, 马红娟, 薛艳玲, 谢红兰, 邓彪, 杜国浩, 王敏, 肖体乔 2010 光学学报 30 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo R Y, Ma H J, Xue Y L, Xie H L, Deng B, Du G H, Wang M, Xiao T Q 2010 Acta Optica Sin. 30 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ju X L, Deng B, Li K, Yu F C, Zhang H P, Xu M W, Du G H, Xie H L, Li B, Xiao T Q 2022 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 实验原理和装置 (a)电解池内离子迁移示意图; (b) 成像光路示意图; (c)包含电解池和探测器的实验装置照片
Fig. 1. Experimental setup for the electrochemical reaction: (a) Schematic diagram of ion migration; (b) schematic diagram of optical path for X-ray imaging; (c) photo for the experimental equipment including electrolytic cell and X-ray detector.
图 3 电解池0.7 V电压通电后化学反应过程动态成像 (a) 传统时间减影成像1—12 s 关键帧; (b)对应的运动衬度成像关键帧
Fig. 3. Dynamic X-ray imaging of electrochemical reaction after electrolytic cell is powered on at a voltage of 0.7 V: (a) Keyframes of traditional temporal subtraction imaging at the time period of 1–12 s; (b) the corresponding keyframes of move contrast imaging.
图 4 电解池0.7 V电压通电初期800 ms内的电化学反应 (a) 时间减影成像关键帧; (b)运动衬度成像关键帧
Fig. 4. The initial stage of electrochemical reaction in the electrolytic cell with the voltage of power supply set to 0.7 V: (a) Keyframes of 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800 ms respectively obtained with temporal subtraction X-ray imaging; (b) the correspondent keyframes of move contrast X-ray imaging.
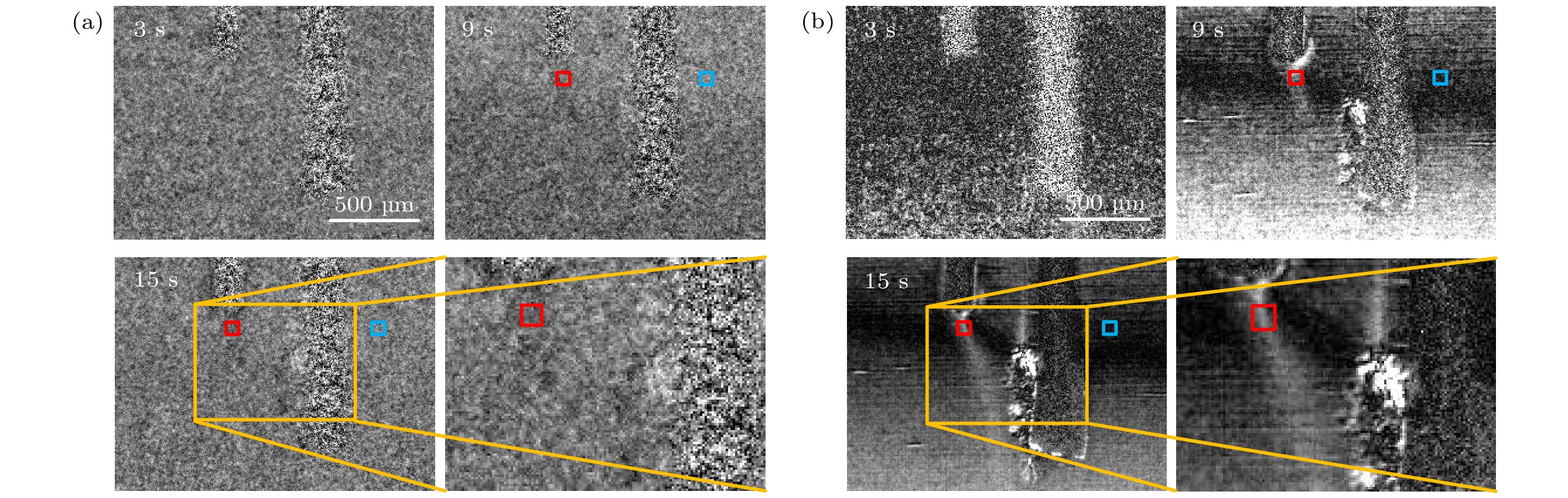
图 5 电解池0.5 V电压通电后的电化学反应过程成像 (a)传统时间减影成像3, 9, 15 s关键帧及在15 s时的局部区域的放大图; (b)运动衬度成像关键帧
Fig. 5. X-ray imaging of electrochemical reaction after electrolytic cell is switched on at a voltage of 0.5 V: (a) Keyframes of 3, 9, 15 s respectively obtained with traditional temporal subtraction imaging supplied with a magnified view of the selected area at 15 s; (b) the corresponding keyframes of move contrast imaging.
-
[1] Kang B, Ceder G 2009 Nature 458 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Okubo M, Mizuno Y, Yamada H, Kim J, Hosono E, Zhou H S, Kudo T, Honma I 2010 ACS Nano 4 741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ellis B, Perry L K, Ryan D H, Nazar L F 2006 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 11416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao W Y, Sakurai K 2019 J. Synchrotron. Radiat. 26 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen S L, Zhang Y, Zhao J J, Mi Z, Zhang J M, Cao J, Feng J C, Zhang G L, Qi J L, Li J Y, Gao P 2020 Sci. Bull. 65 1643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈树林, 高鹏 2019 物理 48 168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen S L, Gao P 2019 Physics 48 168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘玄玄, 国洪轩, 徐涛, 尹奎波, 孙立涛 2021 70 086701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X X, Guo H X, Xu T, Yin K B, Sun L T 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 086701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang Y C, Gao P, Gaba S, Chang T, Pan X, Lu W 2012 Nat. Commun. 3 732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 陆敬予, 柯承志, 龚正良, 李德平, 慈立杰, 张力, 张桥保 2021 70 198102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu J Y, Ke C Z, Gong Z L, Li D P, Ci L J, Zhang L, Zhang Q B 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 198102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 郭祝崑, 李香庭 1983 32 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo Z K, Li X T 1983 Acta Phys. Sin. 32 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 杨同华, 包宗渝 1984 33 1149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang T H, Bao Z Y 1984 Acta Phys. Sin. 33 1149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Warren J M, Bilheux H Z, Kang M, Voisin S 2013 Plant Soil 366 683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ilott A J, Trease N M, Grey C P, Jerschow A 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou L, Leskes M, Liu T, Grey C P 2015 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 54 14782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zheng J, Tang M X, Hu Y-Y 2016 Angew Chem. Int. Edit. 55 12538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Takanashi T, Kawamura H 2019 World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018 Prague, Czech Republic, June 3–8, 2018 p35
[17] 安汉文, 莫生凯, 李梦璐, 王家钧 2022 储能科学与技术 11 834
An H W, Mo S K, Li M L, Wang J J 2022 Energy Storage Science and Technology 11 834
[18] 周逸凡, 杨慕紫, 佘峰权, 龚力, 张晓琪, 陈建, 宋树芹, 谢方艳 2021 70 178801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y F, Yang M Z, She F Q, Gong L, Zhang X Q, Chen J, Song S Q, Xie F Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 178801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cheng L, Tscheuschner S, Paulus F, Hopkinson P E, Kieling J, Khler A, Vaynzof Y, Huettner S 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 2446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王继飞, 林东旭, 袁永波 2019 68 158801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J F, Lin D X, Yuan Y B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 158801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 果辰, 蔡欣炜, 罗文浩, 黄子耕, 冯庆荣, 甘子钊 2021 70 197401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C, Cai X W, Luo W H, Huang Z G, Feng Q R, Gan Z Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 197401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王丽, 王海波, 王涛, 李发伸 2006 55 6515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L, Wang H B, Wang T, Li F S 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 6515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao W Y, Sakurai K 2017 ACS Omega 2 4363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王飞翔 2019 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学 (中国科学院上海应用物理研究所))
Wang F X 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[25] Wang F X, Zhou P T, Li K, Mamtilahun M, Tang Y H, Du G H, Deng B, Xie H L, Yang G Y, Xiao T Q 2020 IUCrJ 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 李可 2021 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学 (中国科学院上海应用物理研究所))
Li K 2021 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[27] Song X M, Pogue B W, Jiang S D, Doyley M M, Dehghani H, Tosteson T D, Paulsen K D 2004 Appl. Optics 43 1053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xie H L, Deng B, Du G H, Fu Y N, Guo H, Xue Y L, Peng G Y, Tao F, Zhang L, Xiao T Q 2020 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 31 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 郭荣怡, 马红娟, 薛艳玲, 谢红兰, 邓彪, 杜国浩, 王敏, 肖体乔 2010 光学学报 30 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo R Y, Ma H J, Xue Y L, Xie H L, Deng B, Du G H, Wang M, Xiao T Q 2010 Acta Optica Sin. 30 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ju X L, Deng B, Li K, Yu F C, Zhang H P, Xu M W, Du G H, Xie H L, Li B, Xiao T Q 2022 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9567
- PDF下载量: 135
- 被引次数: 0
















 下载:
下载: