-
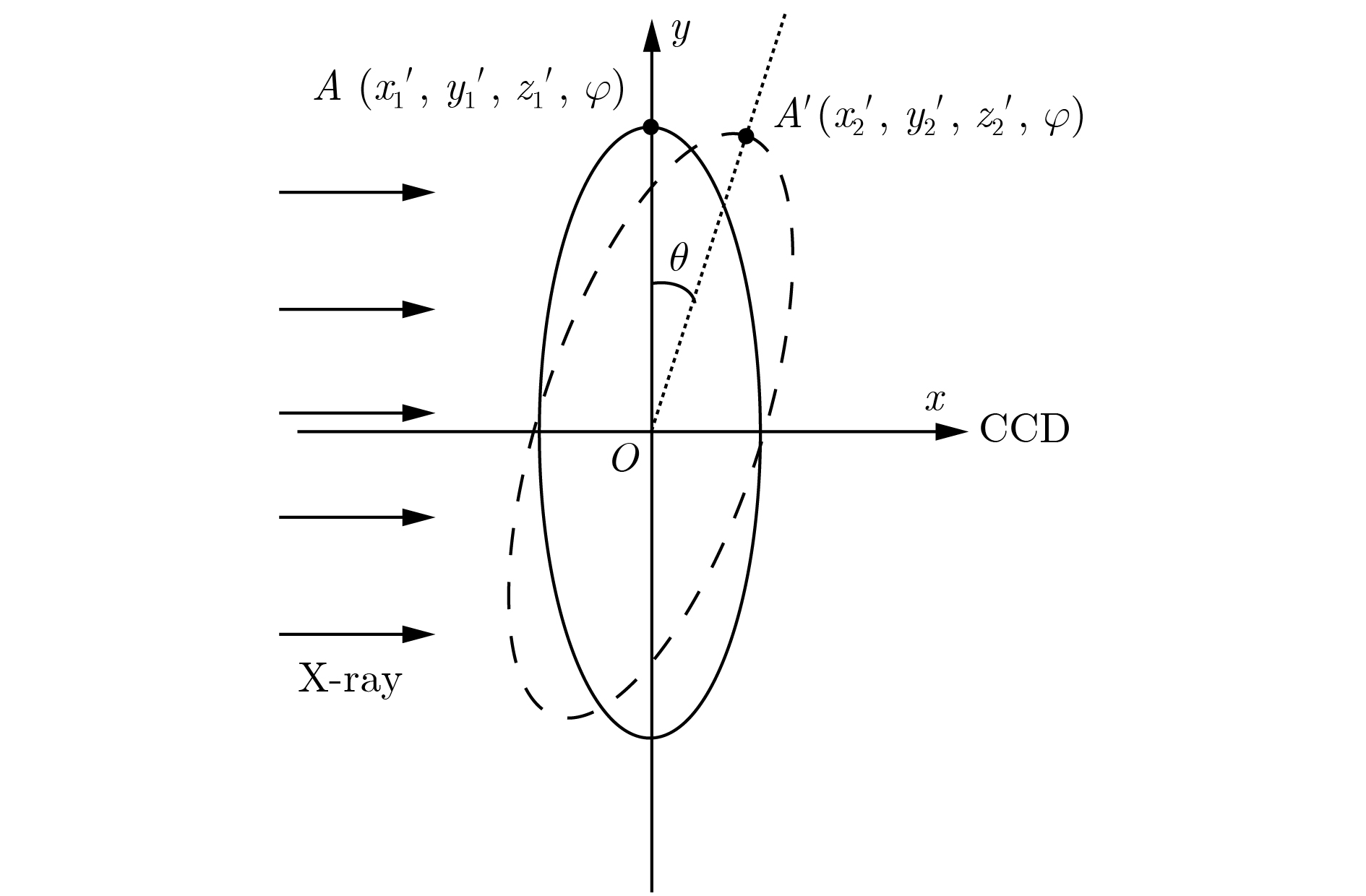
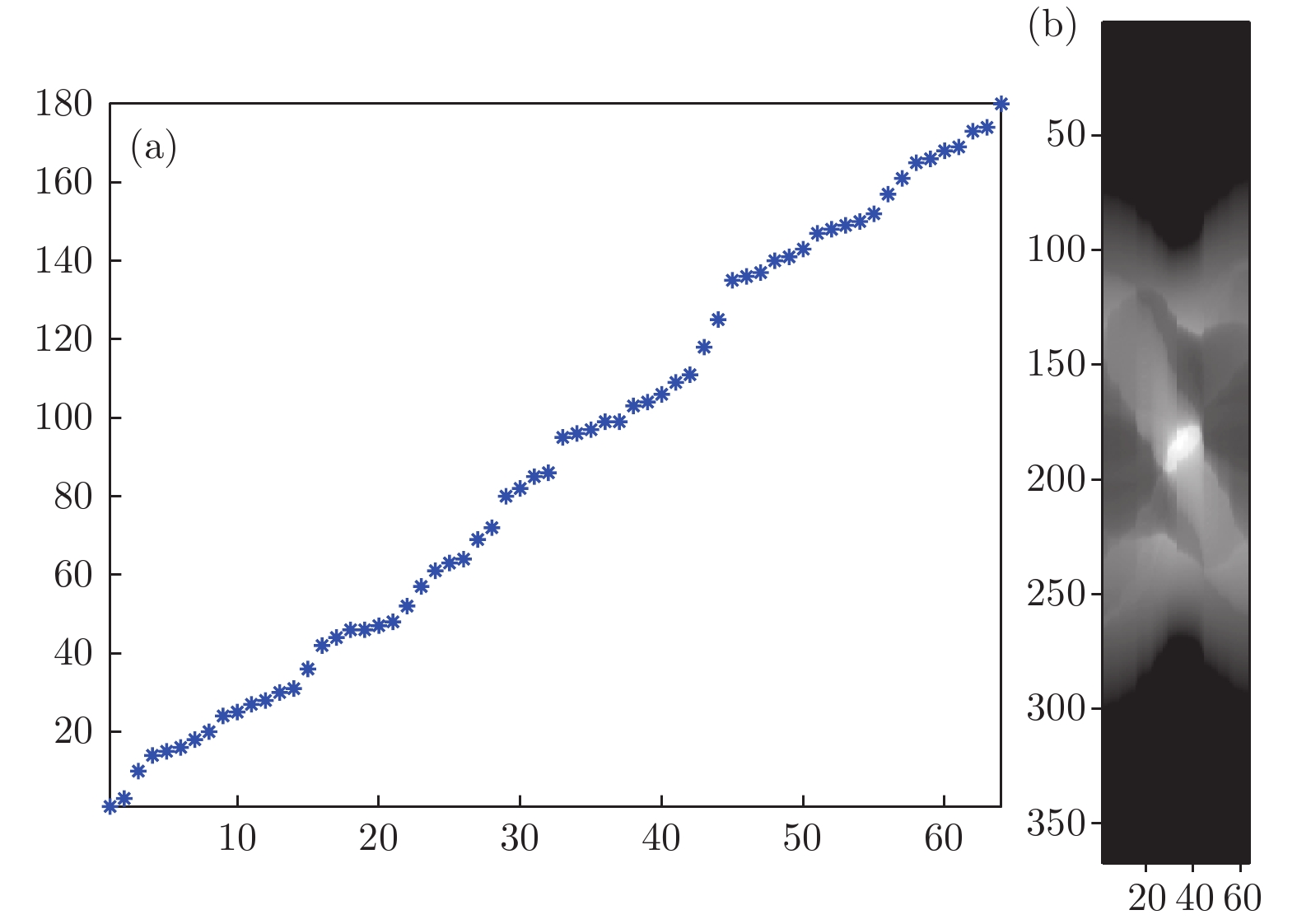
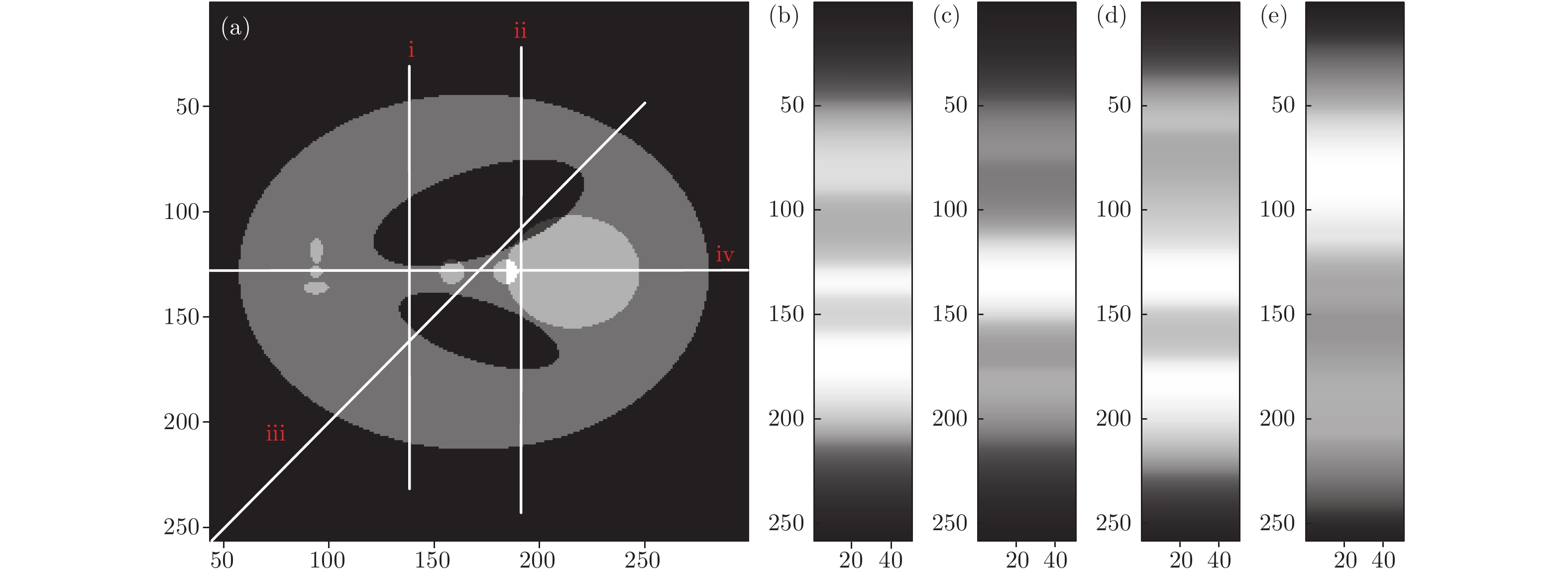
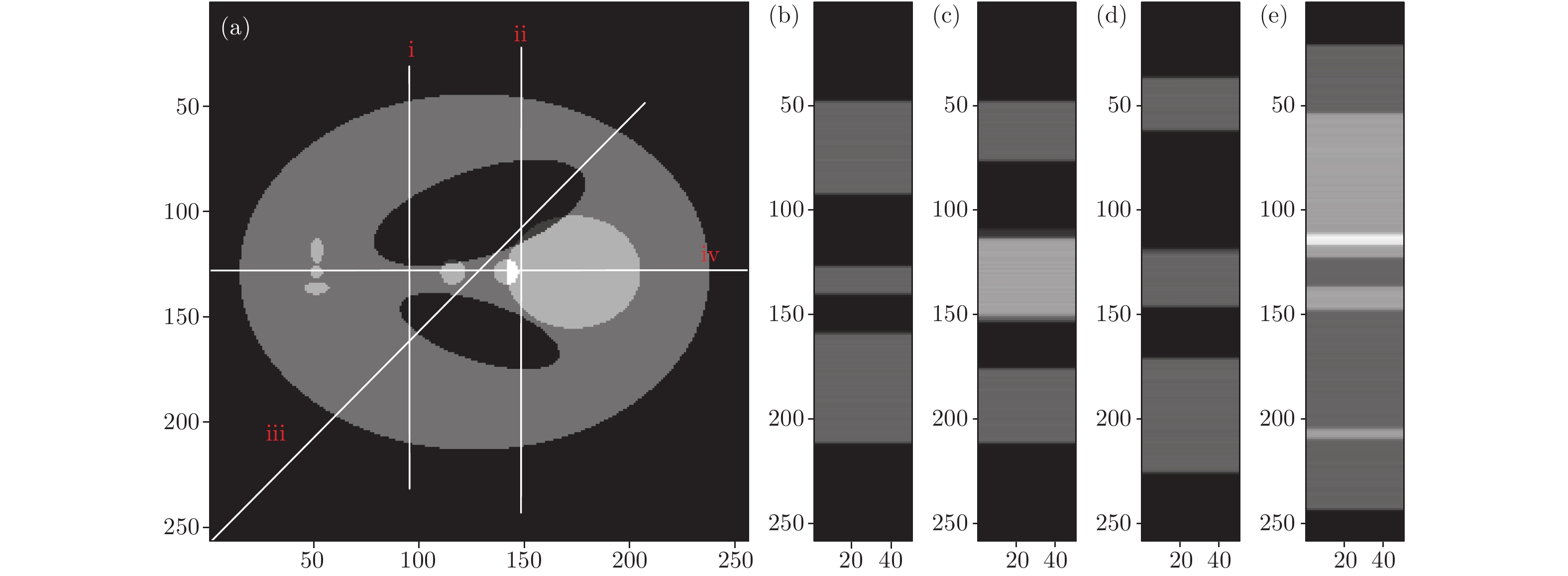
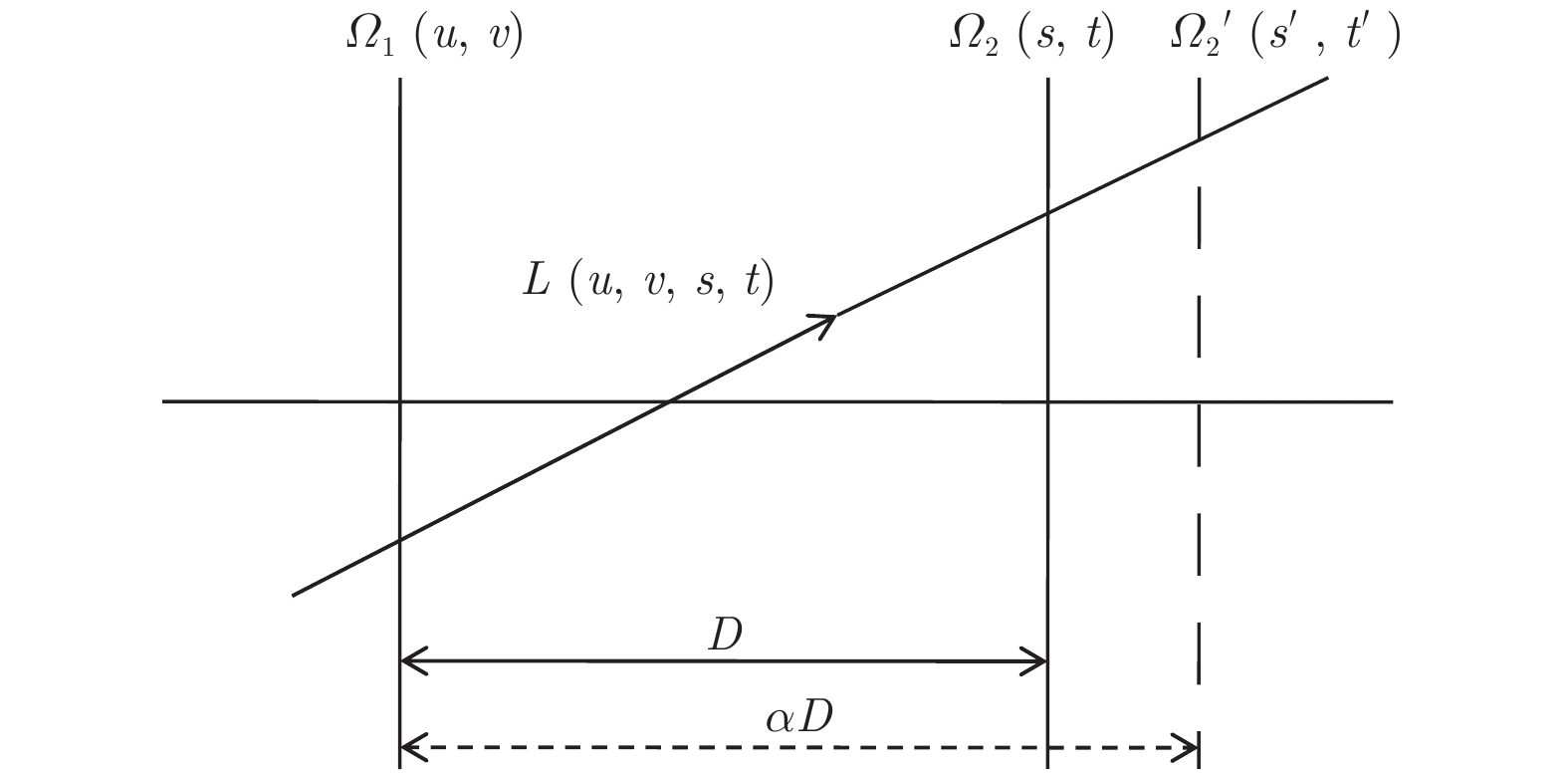
X射线三维成像技术是目前国内外X射线成像研究领域的一个研究热点. 但针对一些特殊成像目标, 传统X射线计算层析(CT)成像模式易出现投影信息缺失等问题, 影响CT重建的图像质量, 使得CT成像的应用受到一定的限制. 本文主要研究了基于光场成像理论的X射线三维立体成像技术. 首先从同步辐射光源模型出发, 对X射线光场成像进行建模; 然后, 基于光场成像数字重聚焦理论, 对成像目标场在深度方向上进行切片重建. 结果表明: 该方法可以实现对成像目标任一视角下任一深度的内部切片重建, 但是由于光学聚焦过程中的离焦现象, 会引入较为严重的背景噪声. 当对其原始数据进行滤波后, 再进行X射线光场重聚焦, 可以有效消除重建伪影, 提高图像的重建质量. 本研究既有算法理论意义, 又可应用于工业、医疗等较复杂目标的快速检测, 具有较大的应用价值.X-ray three-dimensional (3D) imaging technology is a research hotspot in the field of X-ray imaging. However, for some special imaging targets, the imaging mode of the traditional computer tomography (CT) circular trajectory is prone to lack of projection information, and thus affects the quality of CT reconstruction images, which limites the application of CT imaging. Light field imaging technology, in which a microlens array is inserted between the sensor and main lens in a traditional camera, achieves four-dimensional (4D) light field data with sensor during imaging including both the two-dimensional (2D) directional information of the radiance propagation and 2D spatial distribution information of object radiation. Through computer calculation imaging, 3D imaging such as digital refocusing, slice in the depth direction, stereo imaging, and depth estimation is realized. This article focuses on the 3D X-ray imaging based on the theory of light field imaging in visible light. Based on the model of parallel X-ray of synchrotron radiation source, the data of the X-ray light field with many projection views are acquired by rotating the image sample. Then, the light passing through any voxel in the imaging target is acquired by a geometric projection method, and based on integral imaging theory of light field imaging, the gray value of the slice in depth dimension is reconstructed and the depth information of reconstructed target is acquired. The reconstruction results show that this method can be used to reconstruct the internal slices at any depth in any viewing direction of the imaging target. In the optical imaging, the scene beyond the depth of field is blurred, making the scene more prominent and the imaging effect better. However, for the X-ray imaging, the imaging mode that is completely transmissive, and the light passing through the foreground carry the information about the background. In the refocusing process, the object at the refocusing depth is focused, and other background information is defocused. Excessive background information overwhelms the real useful information, and makes the slice, especially the edge of the image, blurred. Consequently more severe background noise is introduced due to the defocusing phenomenon in the optical refocusing process. Referring to the reconstruction method of the X-ray 3D imaging and light field imaging, the S-L filter is applied to the original data in the article. After filtering the original data, the X-ray "light field refocusing" is processed. The reconstruction results shown that the method can effectively eliminate reconstruction artifacts and improve image reconstruction quality in the reconstruction depth slice. And in this paper, the light field data are collected by rotating the sample with low time resolution. For the fast imaging, according to the digital refocusing theory of the light field imaging, the array X-ray source and detector can be used. After being calibrated, the system can realize the 3D reconstruction of the light field of the target field with high time resolution. This research has not only the theoretical significance in algorithm, but also great application value in the rapid detection of more complicated targets such as industry and medical treatment.
-
Keywords:
- X-ray imaging /
- light field imaging /
- sliced base on depth /
- three-dimensional reconstruction
[1] Zhu P P, Zhang K, Wang Z L, Liu Y J, Liu X S, Wu Z Y, McDonald S A, Marone F, Stampanoni M 2010 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107 13576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 戚俊成, 任玉琦, 杜国浩, 陈荣昌, 王玉丹, 和友, 肖体乔 2013 光学学报 33 1034001
Qi J C, Ren Y Q, Du G H, Chen R C, Wang Y D, He Y, Xiao T Q 2013 Acta Opt. Sin. 33 1034001
[3] 薛艳玲, 肖体乔, 吴立宏, 陈灿, 郭荣怡, 杜国浩, 谢红兰, 邓彪, 任玉琦, 徐洪杰 2010 59 5496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue Y L, Xiao T Q, Wu L H, Chen C, Guo R Y, Du G H, Xie H L, Deng B, Ren Y Q, Xu H J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 5496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zeng J, Bian F, Wang J, Li X, Wang Y, Tian F, Zhou P 2017 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 24 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hounsfield G N 1973 Brit. J. Radiol 46 1016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 戚俊成, 陈荣昌, 刘宾, 陈平, 杜国浩, 肖体乔 2017 66 054202
Qi J C, Chen R C, Liu B, Chen P, Du G H, Xiao T Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054202
[7] 王飞翔, 邓彪, 王玉丹, 任玉琦, 孙天希, 肖体乔 2016 光学学报 36 0834004
Wang F X, Deng B, Wang Y D, Ren Y Q, Sun T X, Xiao T Q 2016 Acta Opt. Sin. 36 0834004
[8] Mokso R, Oberta P 2015 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 22 1078
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hoshino M, Uesugi K, Pearson J, Sonobe T, Shirai M, Yagi N 2011 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 18 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 邾继贵, 李艳军, 叶声华, 唐大林, 张国全 2005 光学学报 25 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J G, Li Y J, Ye S H, Tang D L, Zhang G Q 2005 Acta Opt. Sin. 25 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Adelson E H, Wang J Y A 1992 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ng R, Levoy M, Bredif M, Duval G, Horowitz M, Hanrahan P 2005 Stanford Tech. Report CTSR 2005-02
[13] Berry M V, Klein S 1996 J. Mod. Opt. 43 2139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] You S, Lu Y, Zhang W, Yang B, Peng R, Zhuang S 2015 Opt. Commun. 355 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Park J H, Jung S, Choi H, Kim Y, Lee B 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 4882
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wanner S, Goldluecke B 2014 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach Intell. 36 606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ma Z, Cen Z, Li X 2017 Opt. Lett. 56 6603
[18] Lin X, Wu J M, Zheng G A, Dai Q H 2015 Biomed. Opt. Express 6 3179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Carles G, Downing J, Harvey A R 2014 Appl. Opt. 39 1889
[20] Ng R 2005 ACM Trans. Graph. 24 735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 杨富强, 张定华, 黄魁东, 王鹍, 徐哲 2014 63 058701
Yang F Q, Zhang D H, Huang K D, Wang K, Xu Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 058701
-
-
[1] Zhu P P, Zhang K, Wang Z L, Liu Y J, Liu X S, Wu Z Y, McDonald S A, Marone F, Stampanoni M 2010 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107 13576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 戚俊成, 任玉琦, 杜国浩, 陈荣昌, 王玉丹, 和友, 肖体乔 2013 光学学报 33 1034001
Qi J C, Ren Y Q, Du G H, Chen R C, Wang Y D, He Y, Xiao T Q 2013 Acta Opt. Sin. 33 1034001
[3] 薛艳玲, 肖体乔, 吴立宏, 陈灿, 郭荣怡, 杜国浩, 谢红兰, 邓彪, 任玉琦, 徐洪杰 2010 59 5496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue Y L, Xiao T Q, Wu L H, Chen C, Guo R Y, Du G H, Xie H L, Deng B, Ren Y Q, Xu H J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 5496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zeng J, Bian F, Wang J, Li X, Wang Y, Tian F, Zhou P 2017 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 24 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hounsfield G N 1973 Brit. J. Radiol 46 1016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 戚俊成, 陈荣昌, 刘宾, 陈平, 杜国浩, 肖体乔 2017 66 054202
Qi J C, Chen R C, Liu B, Chen P, Du G H, Xiao T Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054202
[7] 王飞翔, 邓彪, 王玉丹, 任玉琦, 孙天希, 肖体乔 2016 光学学报 36 0834004
Wang F X, Deng B, Wang Y D, Ren Y Q, Sun T X, Xiao T Q 2016 Acta Opt. Sin. 36 0834004
[8] Mokso R, Oberta P 2015 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 22 1078
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hoshino M, Uesugi K, Pearson J, Sonobe T, Shirai M, Yagi N 2011 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 18 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 邾继贵, 李艳军, 叶声华, 唐大林, 张国全 2005 光学学报 25 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J G, Li Y J, Ye S H, Tang D L, Zhang G Q 2005 Acta Opt. Sin. 25 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Adelson E H, Wang J Y A 1992 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ng R, Levoy M, Bredif M, Duval G, Horowitz M, Hanrahan P 2005 Stanford Tech. Report CTSR 2005-02
[13] Berry M V, Klein S 1996 J. Mod. Opt. 43 2139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] You S, Lu Y, Zhang W, Yang B, Peng R, Zhuang S 2015 Opt. Commun. 355 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Park J H, Jung S, Choi H, Kim Y, Lee B 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 4882
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wanner S, Goldluecke B 2014 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach Intell. 36 606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ma Z, Cen Z, Li X 2017 Opt. Lett. 56 6603
[18] Lin X, Wu J M, Zheng G A, Dai Q H 2015 Biomed. Opt. Express 6 3179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Carles G, Downing J, Harvey A R 2014 Appl. Opt. 39 1889
[20] Ng R 2005 ACM Trans. Graph. 24 735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 杨富强, 张定华, 黄魁东, 王鹍, 徐哲 2014 63 058701
Yang F Q, Zhang D H, Huang K D, Wang K, Xu Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 058701
计量
- 文章访问数: 11285
- PDF下载量: 188
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: