-
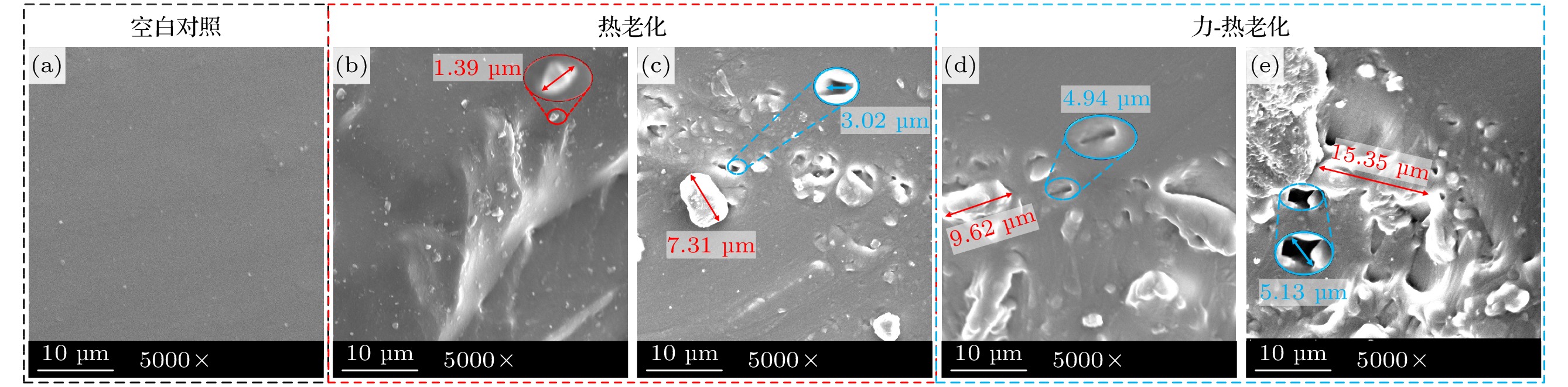
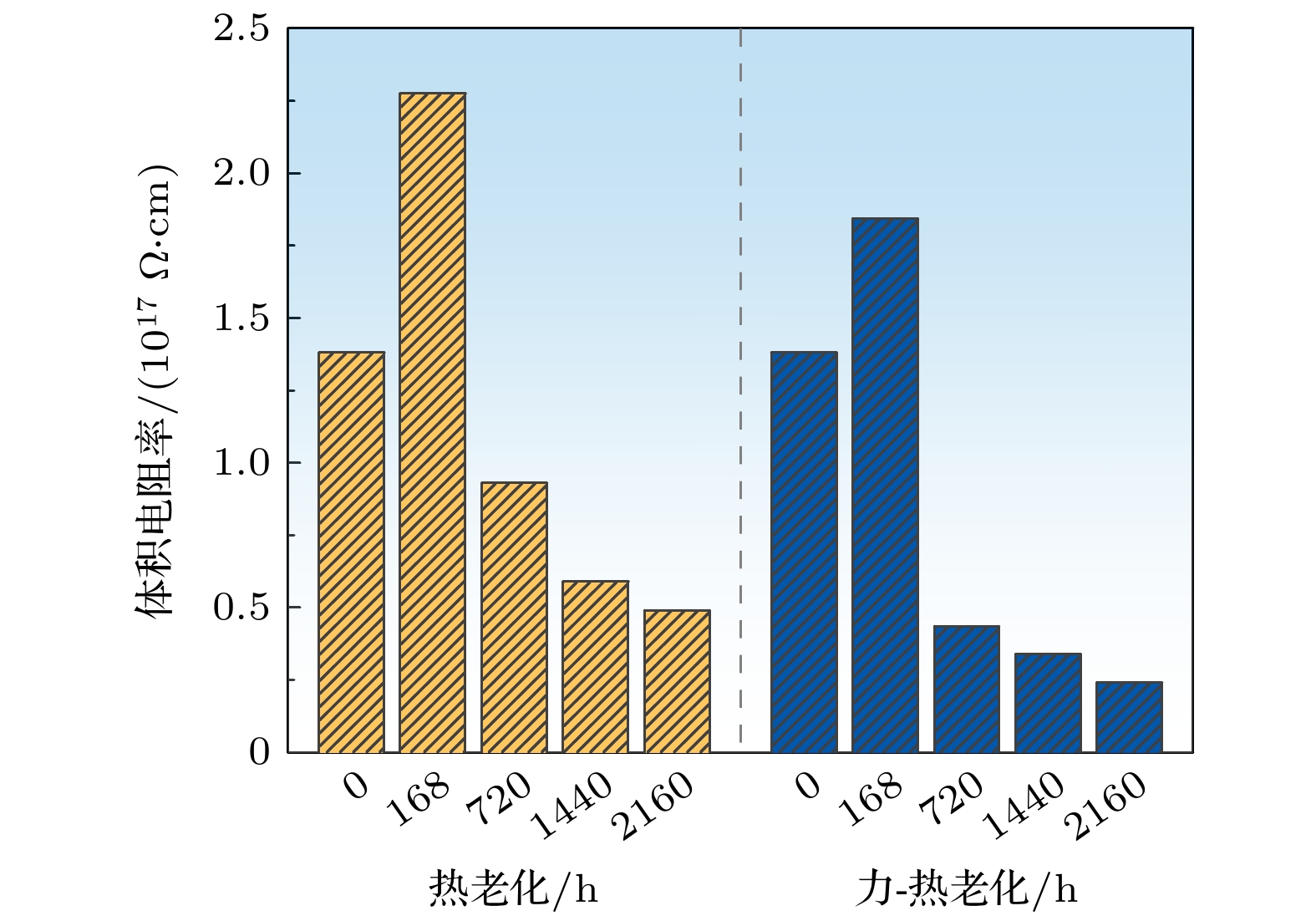
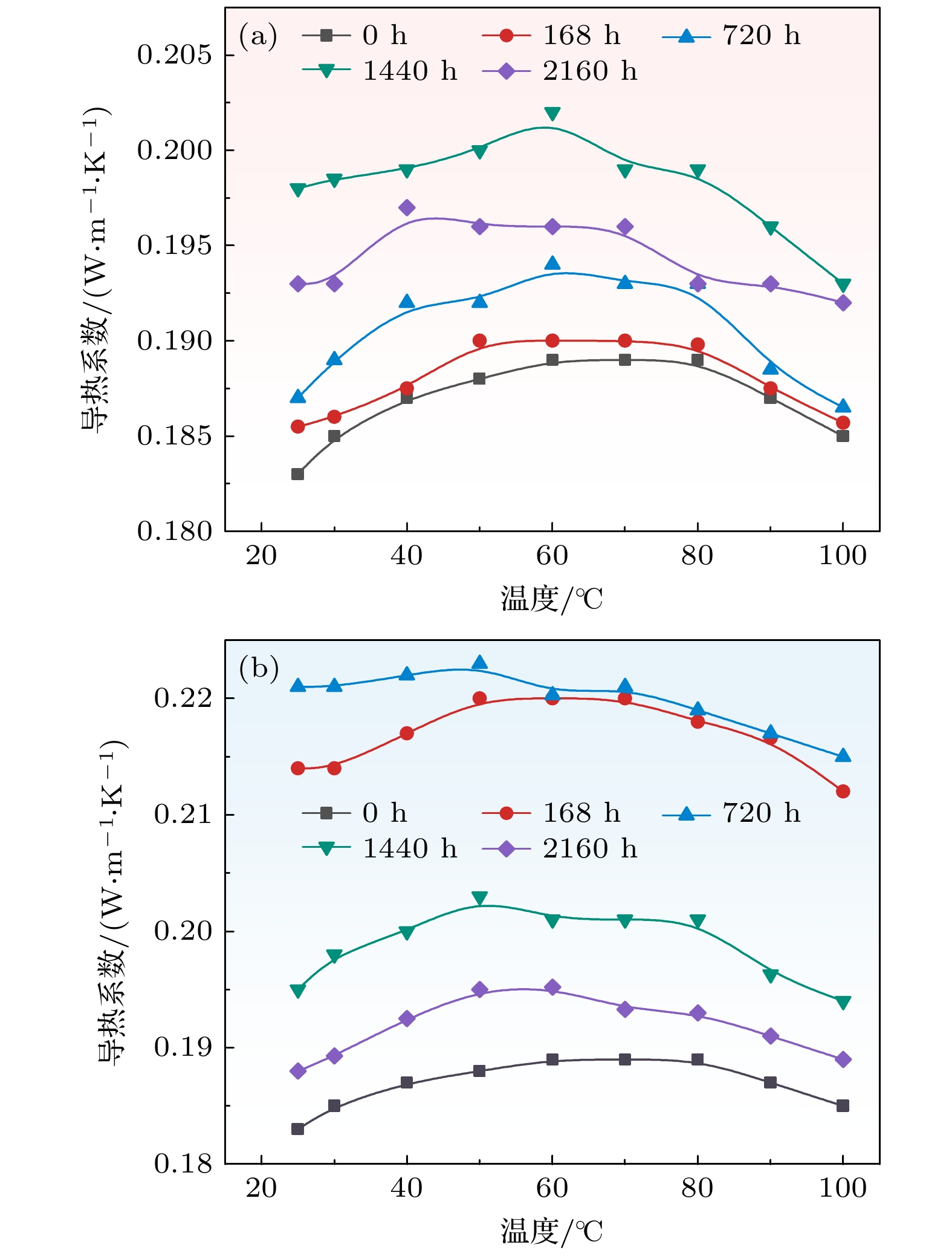
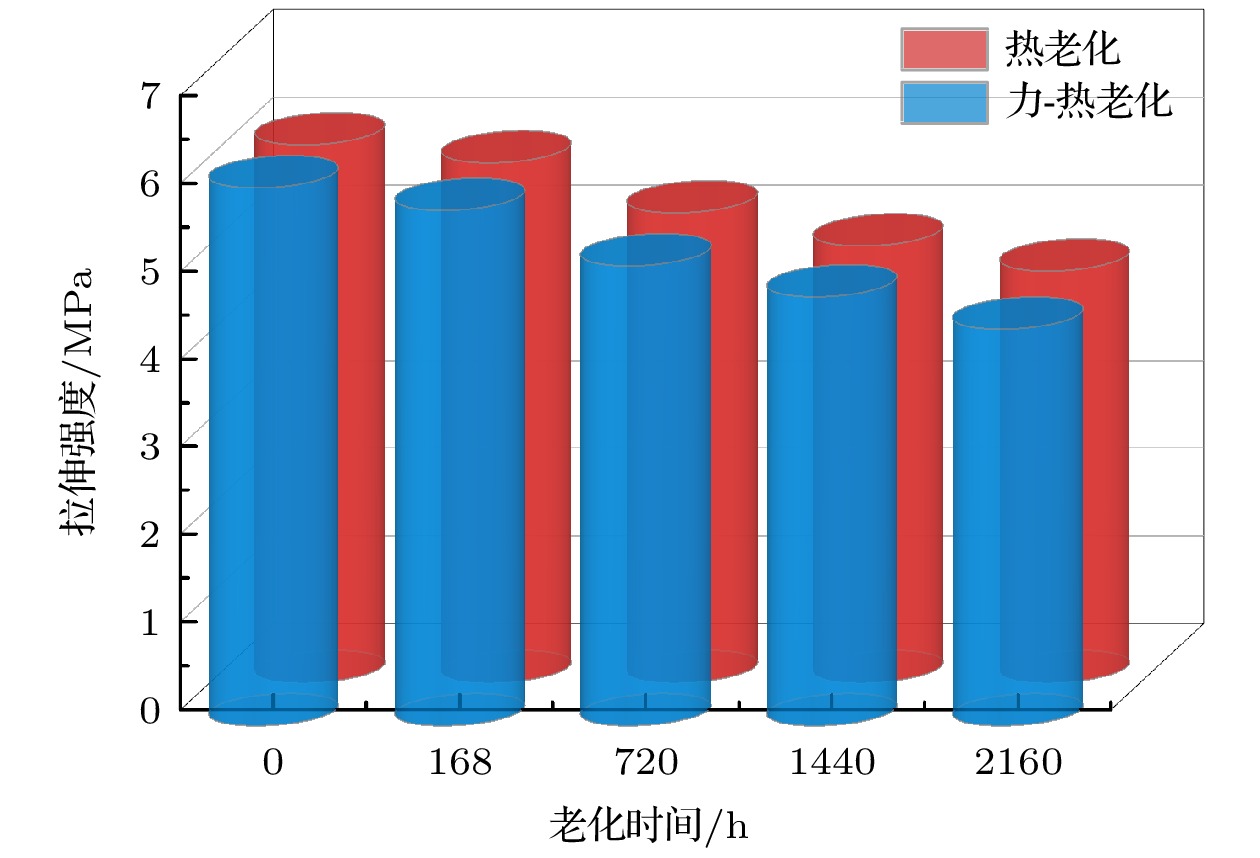
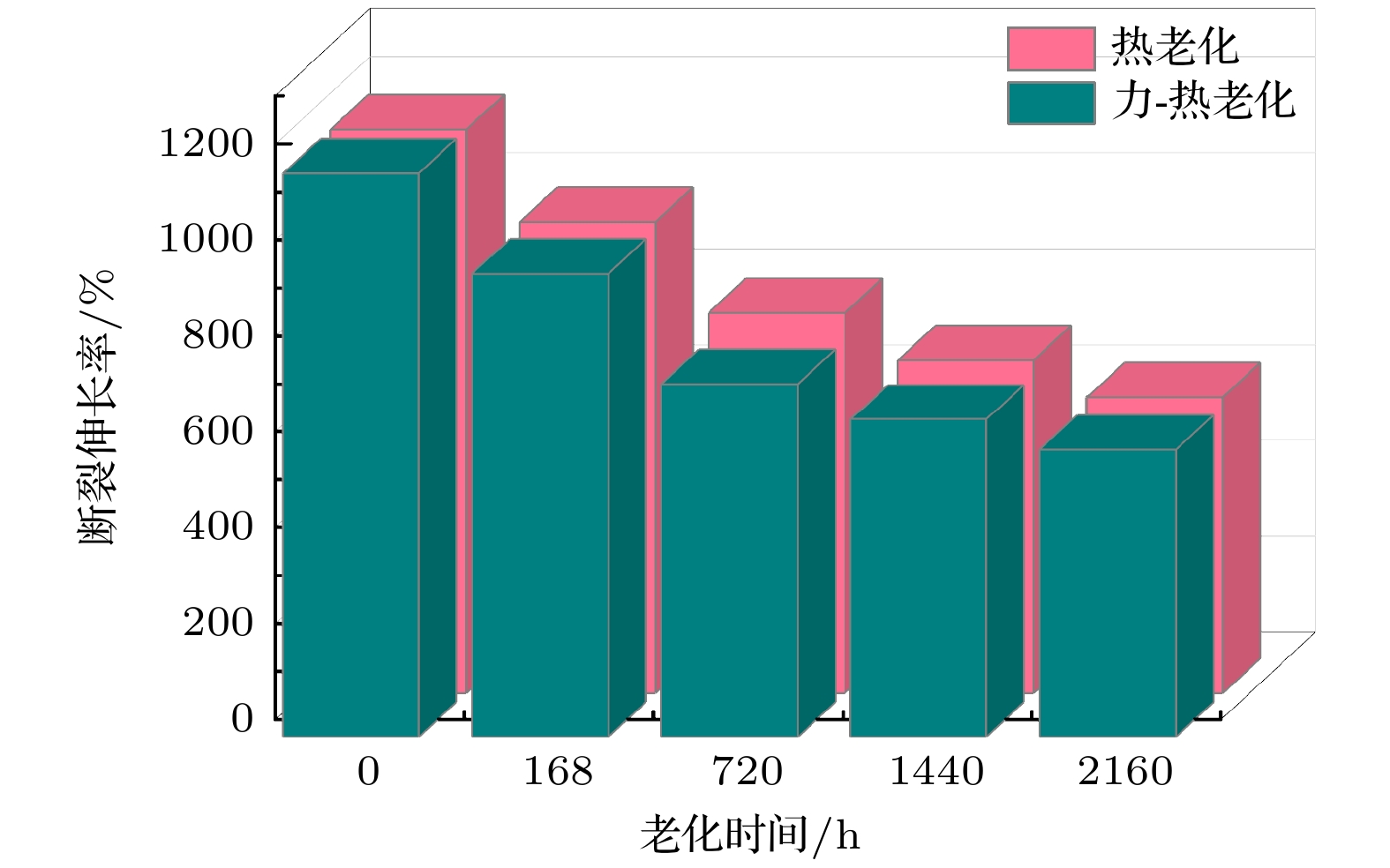
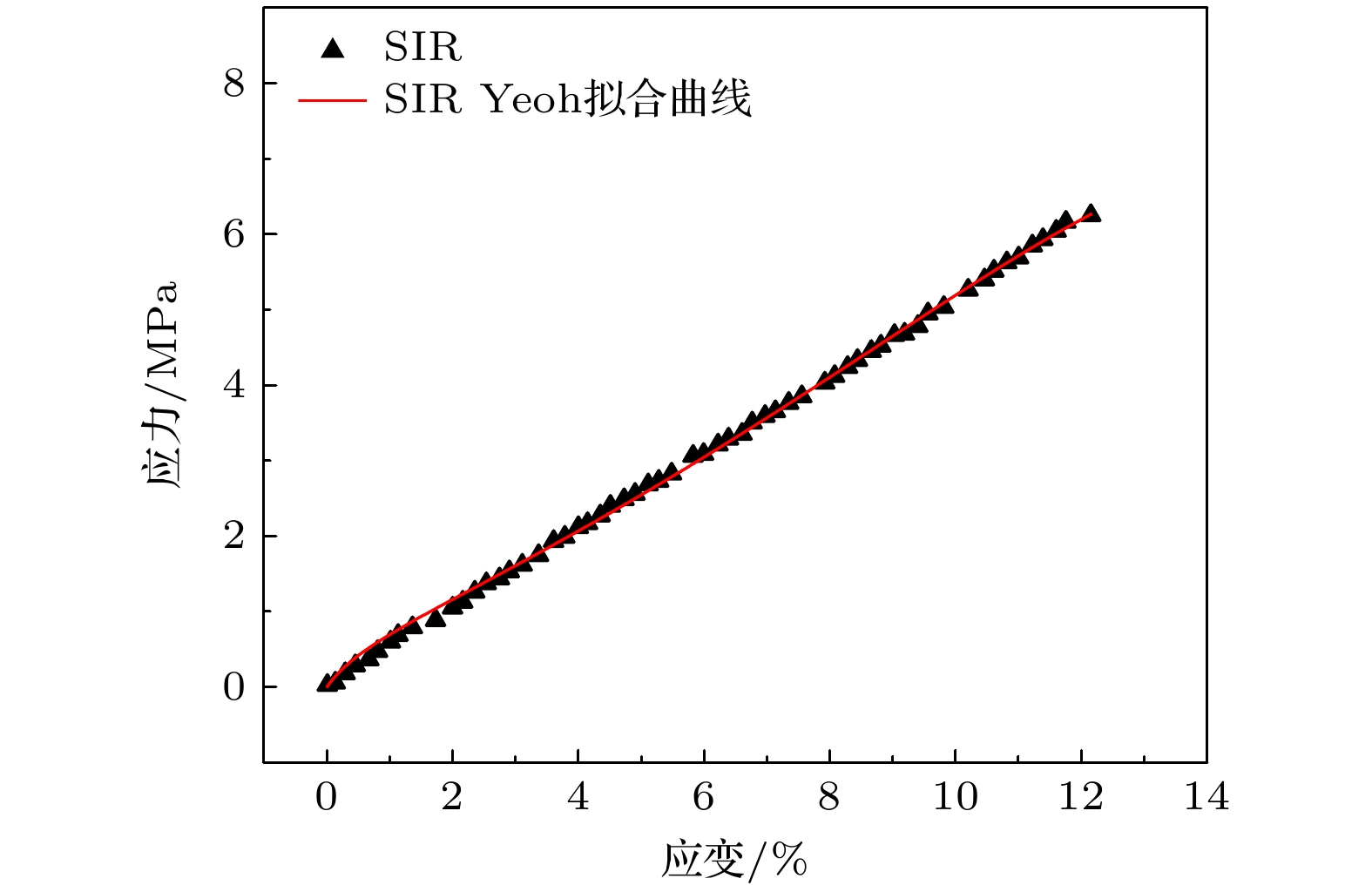
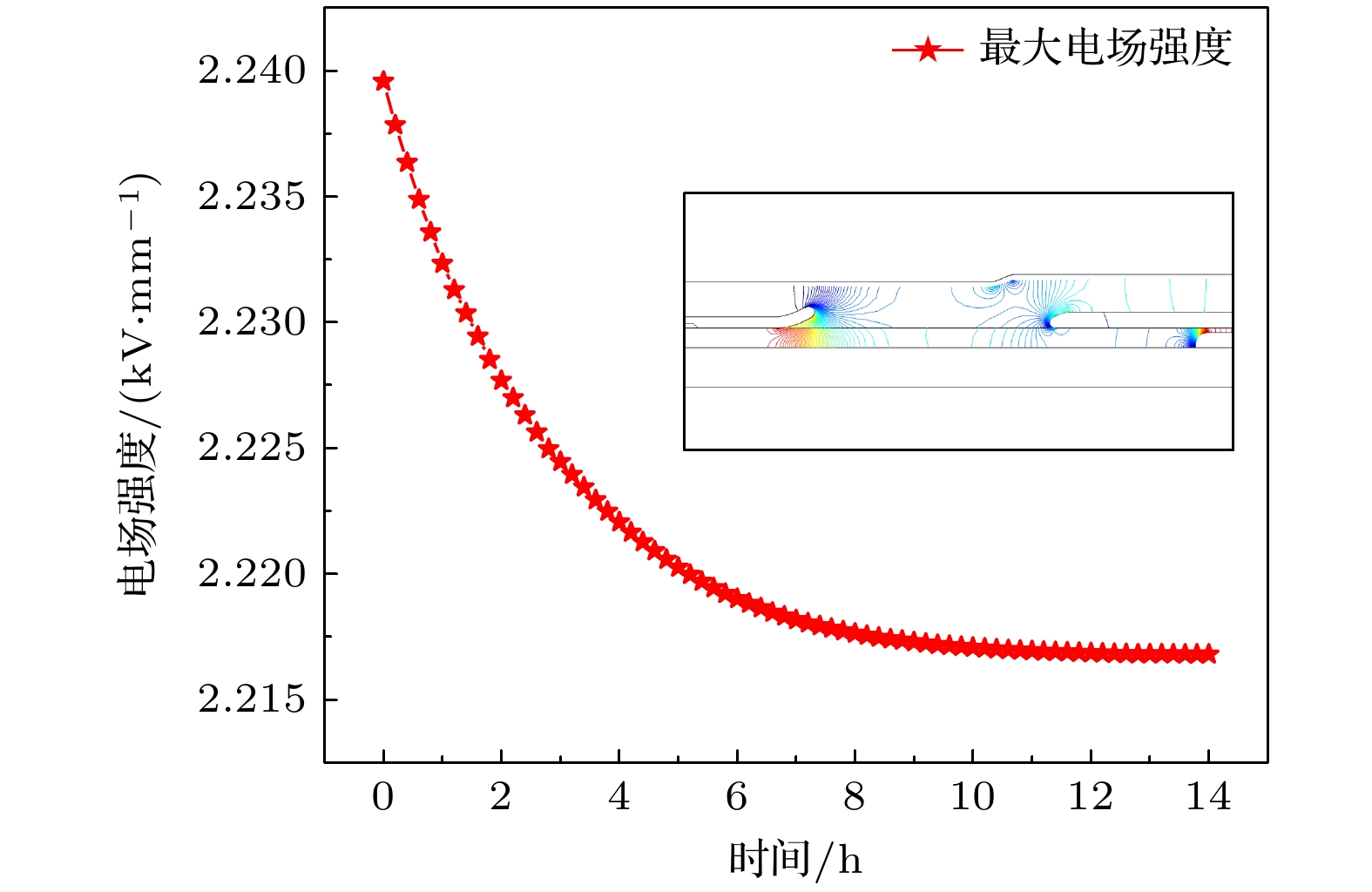
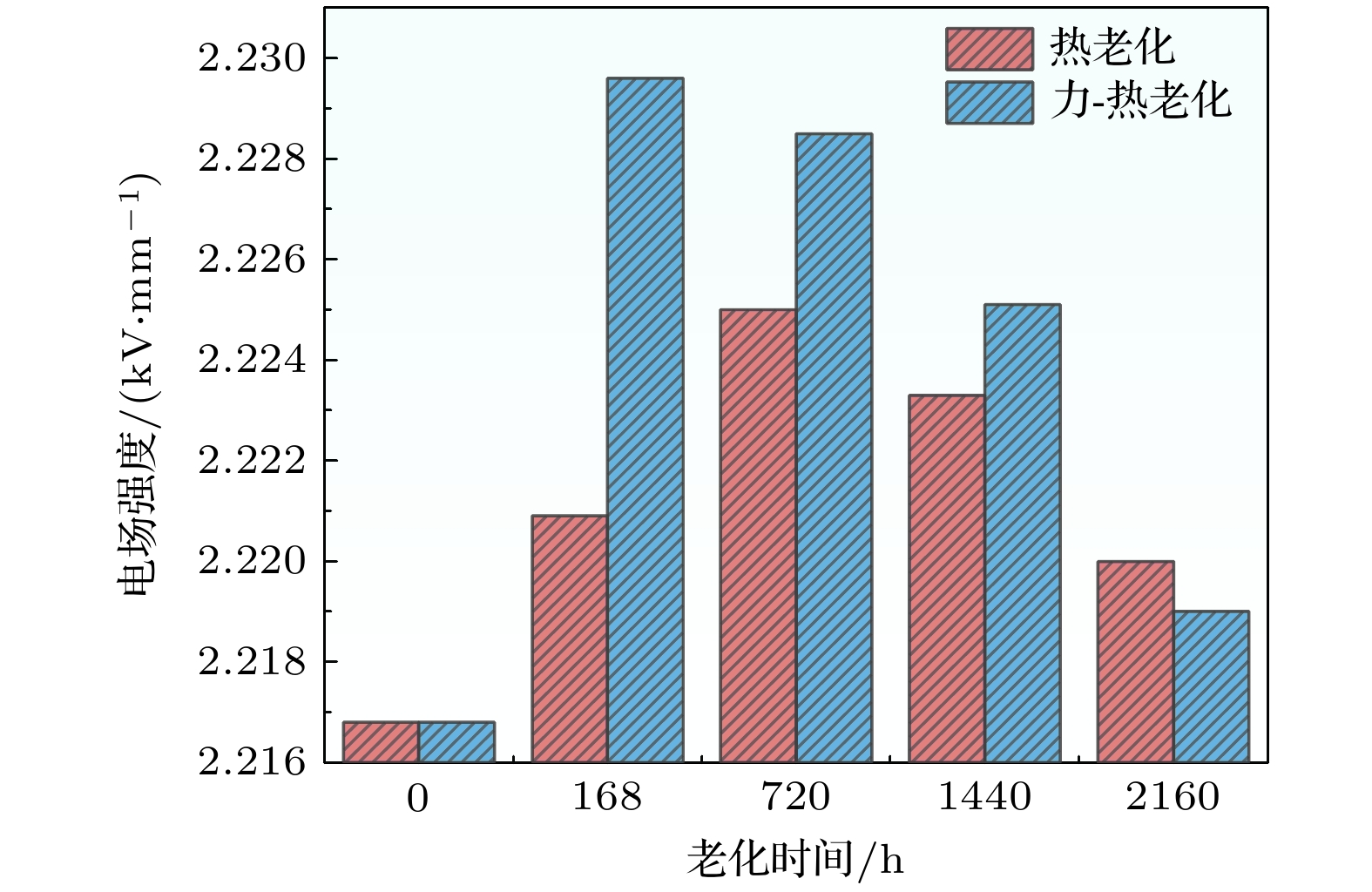
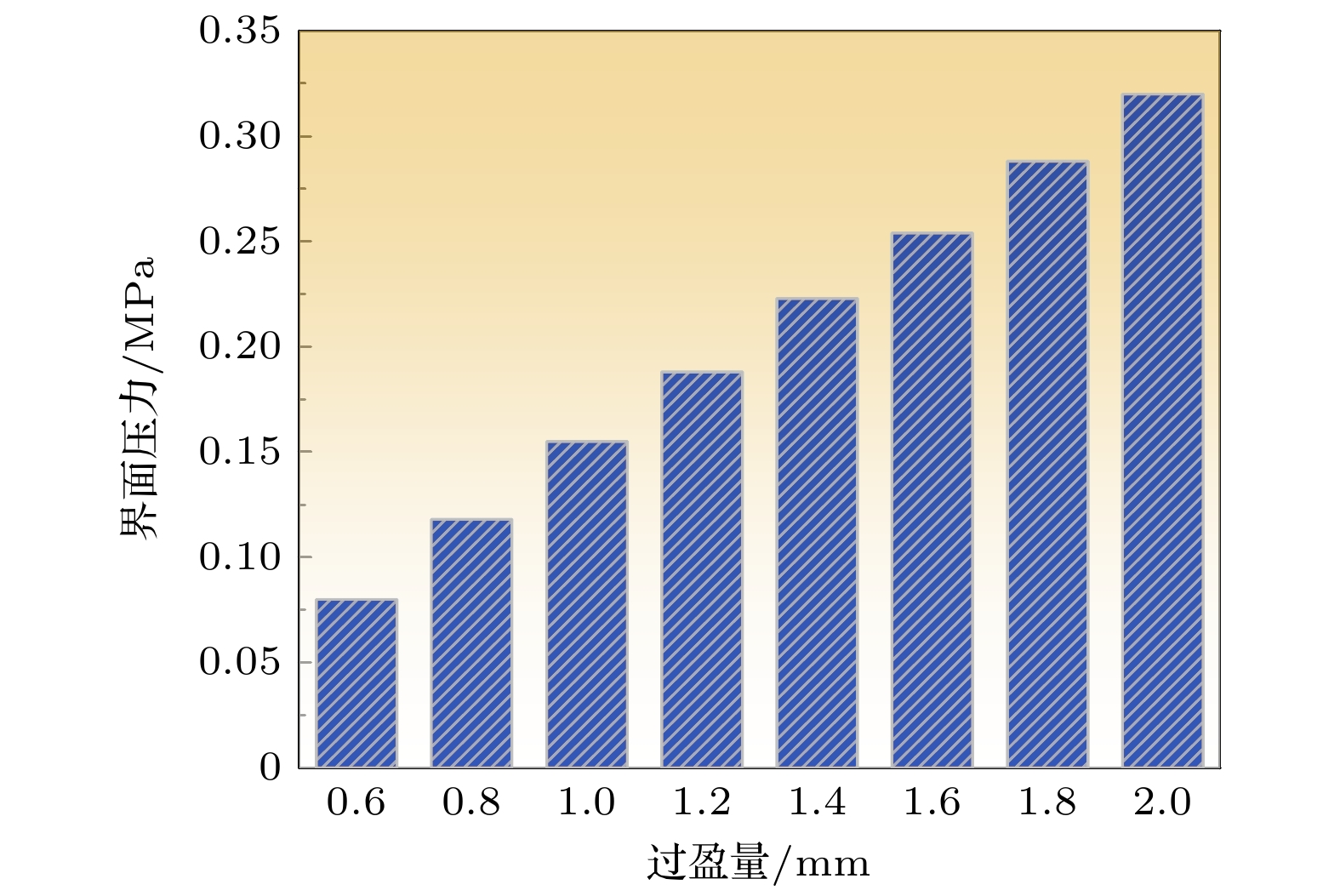
During the long-term operation of a cable, the electrical field, high temperature, and interface stress may age or deteriorate the silicon rubber (SIR) insulation of the cable accessories, affecting the combined electrical-thermal-force performance of the accessories, and easily causing discharge faults. In this work, the electrical-thermal-force properties of silicone rubber for cable accessories under thermal aging and combined force-thermal aging are studied experimentally and numerically. The changes and mechanisms of physical and chemical properties, electrical properties, thermal properties and mechanical properties of silicone rubber are tested and compared before and after aging. The changes of electric, thermal and force field of cable accessories, caused by the change of SIR material parameters under different aging time and aging form, are further simulated. The experimental results show that the crosslinking degree and molecular motion system of SIR will change with the deepening of the aging degree, which will change the electrical-thermal-force properties of the material to different degree. After aging, large agglomeration protrudes and small cavities appear in SIR section, and the damage is more serious under force-thermal aging. The relative dielectric constant first decreases and then increases with the aging time increasing. The volume resistivity, breakdown strength and flashover voltage all first increase and then decrease. The thermal conductivity first increases and then decreases with aging time increasing. In addition, with the increase of aging time, the tensile strength and elongation at break decrease gradually. Considering the change of properties after aging, the destruction of SIR material by force-thermal aging is more serious. The simulation results show that under the two aging modes, the maximum electric field strength at the stress cone root of the cable accessories first increases and then decreases with the increase of time. The electric field strength at the stress cone root of the cable accessories, caused by the force-thermal aging, changes little, maintaining about 2.2 kV/mm. The difference in temperature between the inside and the outside of the insulation layer is obvious under different aging degree, and the temperature difference shows a first decreasing and then increasing trend under both aging modes, and the maximum temperature gradient is 9.15 ℃. The interface stress at the stress cone root decreases from 0.263 to 0.230 MPa, which is about 12.5% lower. This work has guiding significance in evaluating the insulation performance and analyzing the fault of distribution cable accessories.
-
Keywords:
- cable accessories /
- silicone rubber /
- stress-thermal aging /
- electric-thermal-stress coupling simulation
[1] Zhang Z P, Zhao J K, Zhao W, Zhong L S, Hu L X, Rao W B, Zheng M, Meng S X 2022 High Voltage 5 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li Z R, Zhou K, Meng P F, Yuan H, Wang Z K, Chen Y D, Li Y, Zhu G Y 2021 High Voltage 7 802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang X, Wang C, Wu K, Tu D M, Liu S, Peng J K 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu Y, Wang X 2019 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 26 2027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Du B X, Han T, Su J G 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wei Y H, Zhang J H, Li G C, Hu K, Nie Y J, Li S T, Hao C C, Lei Q Q 2023 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 30 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 周远翔, 张征辉, 张云霄, 朱小倩, 黄猛 2022 电工技术学报 37 4474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y X, Zhang Z H, Zhang Y X, Zhu X Q, Huang M 2022 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 37 4474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 程子霞, 刘杰, 张云宵, 周远翔, 张灵, 沙彦超 2019 高电压技术 45 470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng Z X, Liu C, Zhang Y X, Zhou Y X, Zhang L, Sha Y C 2019 High Voltage Eng. 45 470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王若丞, 贺云逸, 康洪玮, 王昭, 金海云 2021 高电压技术 47 3181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang R C, He Y Y, Kang H W, Wang Z, Jin H Y 2021 High Voltage Eng. 47 3181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y Y, Deng Y K, Wei W C, Xu W C, Zha J W 2023 Cellulose 30 5321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 王佩龙 2011 电线电缆 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang P L 2011 Electric Wire Cable 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李国倡, 李雪静, 刘明月, 魏艳慧, 雷清泉, 周自强, 胡列翔, 王少华 2022 高压电器 58 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G C, Li X J, Liu M Y, Wei Y H, Lei Q Q, Zhou Z Q, Hu L X, Wang S H 2022 High Voltage Appar. 58 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Du B X, Zhang M M, Han T, Zhu L W 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zuidema C, Kegerise W, Fleming R, Welker M, Boggs S 2011 IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 4 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 方春华, 刘浩春, 任志刚, 郭卫, 李景, 张帅, 周雨秋 2019 高压电器 55 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang C H, Liu H C, Ren Z G, Guo W, Li J, Zhang S, Zhou Y Q 2019 High Voltage Appar. 55 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Barber K, Alexander G 2013 IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 29 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周远翔, 张云霄, 张旭, 刘睿, 王明渊, 高胜友 2014 高电压技术 40 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y X, Zhang Y X, Zhang X, Liu R, Wang M Y, Gao S Y 2014 High Voltage Eng. 40 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kashi S, Varley R, De Souza M, Al-Assafi S, Di Pietro A, De Lavigne C, Fox B 2018 Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 57 1687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ito S, Hirai N, Ohki Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 27 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 杜伯学, 苏金刚, 徐航, 韩涛 2016 中国电机工程学报 36 6627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du B X, Su J G, Xu H, Han T 2016 Proc. CSEE 36 6627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘昌, 惠宝军, 傅明利, 刘通, 侯帅, 王晓游 2018 高电压技术 44 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu C, Hui B J, Fu M L, Liu T, Hou S, Wang X Y 2018 High Voltage Eng. 44 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王成江, 郭鸣锐, 张扬, 曾洪平, 张婧, 祝梦雅 2022 绝缘材料 55 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C J, Guo M R, Zhang Y, Zeng H P, Zhang J, Zhu M Y 2022 Insul. Mater. 55 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 祝贺, 何峻旭, 郑亚松, 曹煜锋, 郭维 2023 电工技术学报 139 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu H, He J X, Zheng Y S, Cao Y F, Guo W 2023 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 139 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wei W C, Chen H Q, Zha J W, Zhang Y Y 2023 Front. Chem. Sci Eng. 17 991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 老化后SIR试样击穿场强的α和β
Table 1. Breakdown strength α and β of SIR specimens after aging.
老化时间/h 热老化 力-热老化 α/(kV·mm–1) β α/(kV·mm–1) β 0 25.49 26.20 25.49 26.20 168 25.83 48.98 26.39 17.50 720 26.48 41.33 26.48 37.82 1440 26.95 23.27 27.51 20.89 2160 25.83 23.30 25.45 34.53 表 2 老化后SIR试样闪络电压变化
Table 2. Flashover voltage variations of aged SIR specimens.
老化时间/h 老化类型 热老化/kV 力-热老化/kV 0 6.25 6.25 168 6.39 6.52 720 7.36 6.84 1440 5.76 5.55 2160 5.55 5.31 表 3 Yeoh 模型拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting parameters of Yeoh model.
材料类型 Yeoh模型拟合参数/MPa C10 C20 C30 空白对照 0.21 2.21×10–4 –4.11×10–7 表 4 老化后SIR试样Yeoh模型参数
Table 4. Yeoh model parameters of the aged SIR specimens.
老化类型 C10 C20/10–4 C30/10–6 空白对照 0.21 2.12 –0.411 热老化 168 h 0.23 2.24 –0.913 热老化 720 h 0.25 0.356 –1.81 热老化 1440 h 0.32 8.26 –5.30 热老化 2160 h 0.25 1.45 –0.224 力-热老化 168 h 0.22 1.63 –0.644 力-热老化 720 h 0.26 4.59 –2.48 力-热老化 1440 h 0.31 7.03 –4.82 力-热老化 2160 h 0.24 1.75 –1.53 -
[1] Zhang Z P, Zhao J K, Zhao W, Zhong L S, Hu L X, Rao W B, Zheng M, Meng S X 2022 High Voltage 5 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li Z R, Zhou K, Meng P F, Yuan H, Wang Z K, Chen Y D, Li Y, Zhu G Y 2021 High Voltage 7 802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang X, Wang C, Wu K, Tu D M, Liu S, Peng J K 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu Y, Wang X 2019 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 26 2027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Du B X, Han T, Su J G 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wei Y H, Zhang J H, Li G C, Hu K, Nie Y J, Li S T, Hao C C, Lei Q Q 2023 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 30 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 周远翔, 张征辉, 张云霄, 朱小倩, 黄猛 2022 电工技术学报 37 4474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y X, Zhang Z H, Zhang Y X, Zhu X Q, Huang M 2022 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 37 4474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 程子霞, 刘杰, 张云宵, 周远翔, 张灵, 沙彦超 2019 高电压技术 45 470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng Z X, Liu C, Zhang Y X, Zhou Y X, Zhang L, Sha Y C 2019 High Voltage Eng. 45 470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王若丞, 贺云逸, 康洪玮, 王昭, 金海云 2021 高电压技术 47 3181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang R C, He Y Y, Kang H W, Wang Z, Jin H Y 2021 High Voltage Eng. 47 3181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y Y, Deng Y K, Wei W C, Xu W C, Zha J W 2023 Cellulose 30 5321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 王佩龙 2011 电线电缆 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang P L 2011 Electric Wire Cable 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李国倡, 李雪静, 刘明月, 魏艳慧, 雷清泉, 周自强, 胡列翔, 王少华 2022 高压电器 58 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G C, Li X J, Liu M Y, Wei Y H, Lei Q Q, Zhou Z Q, Hu L X, Wang S H 2022 High Voltage Appar. 58 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Du B X, Zhang M M, Han T, Zhu L W 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zuidema C, Kegerise W, Fleming R, Welker M, Boggs S 2011 IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 4 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 方春华, 刘浩春, 任志刚, 郭卫, 李景, 张帅, 周雨秋 2019 高压电器 55 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang C H, Liu H C, Ren Z G, Guo W, Li J, Zhang S, Zhou Y Q 2019 High Voltage Appar. 55 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Barber K, Alexander G 2013 IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 29 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周远翔, 张云霄, 张旭, 刘睿, 王明渊, 高胜友 2014 高电压技术 40 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y X, Zhang Y X, Zhang X, Liu R, Wang M Y, Gao S Y 2014 High Voltage Eng. 40 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kashi S, Varley R, De Souza M, Al-Assafi S, Di Pietro A, De Lavigne C, Fox B 2018 Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 57 1687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ito S, Hirai N, Ohki Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 27 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 杜伯学, 苏金刚, 徐航, 韩涛 2016 中国电机工程学报 36 6627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du B X, Su J G, Xu H, Han T 2016 Proc. CSEE 36 6627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘昌, 惠宝军, 傅明利, 刘通, 侯帅, 王晓游 2018 高电压技术 44 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu C, Hui B J, Fu M L, Liu T, Hou S, Wang X Y 2018 High Voltage Eng. 44 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王成江, 郭鸣锐, 张扬, 曾洪平, 张婧, 祝梦雅 2022 绝缘材料 55 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C J, Guo M R, Zhang Y, Zeng H P, Zhang J, Zhu M Y 2022 Insul. Mater. 55 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 祝贺, 何峻旭, 郑亚松, 曹煜锋, 郭维 2023 电工技术学报 139 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu H, He J X, Zheng Y S, Cao Y F, Guo W 2023 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 139 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wei W C, Chen H Q, Zha J W, Zhang Y Y 2023 Front. Chem. Sci Eng. 17 991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8439
- PDF Downloads: 161
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: