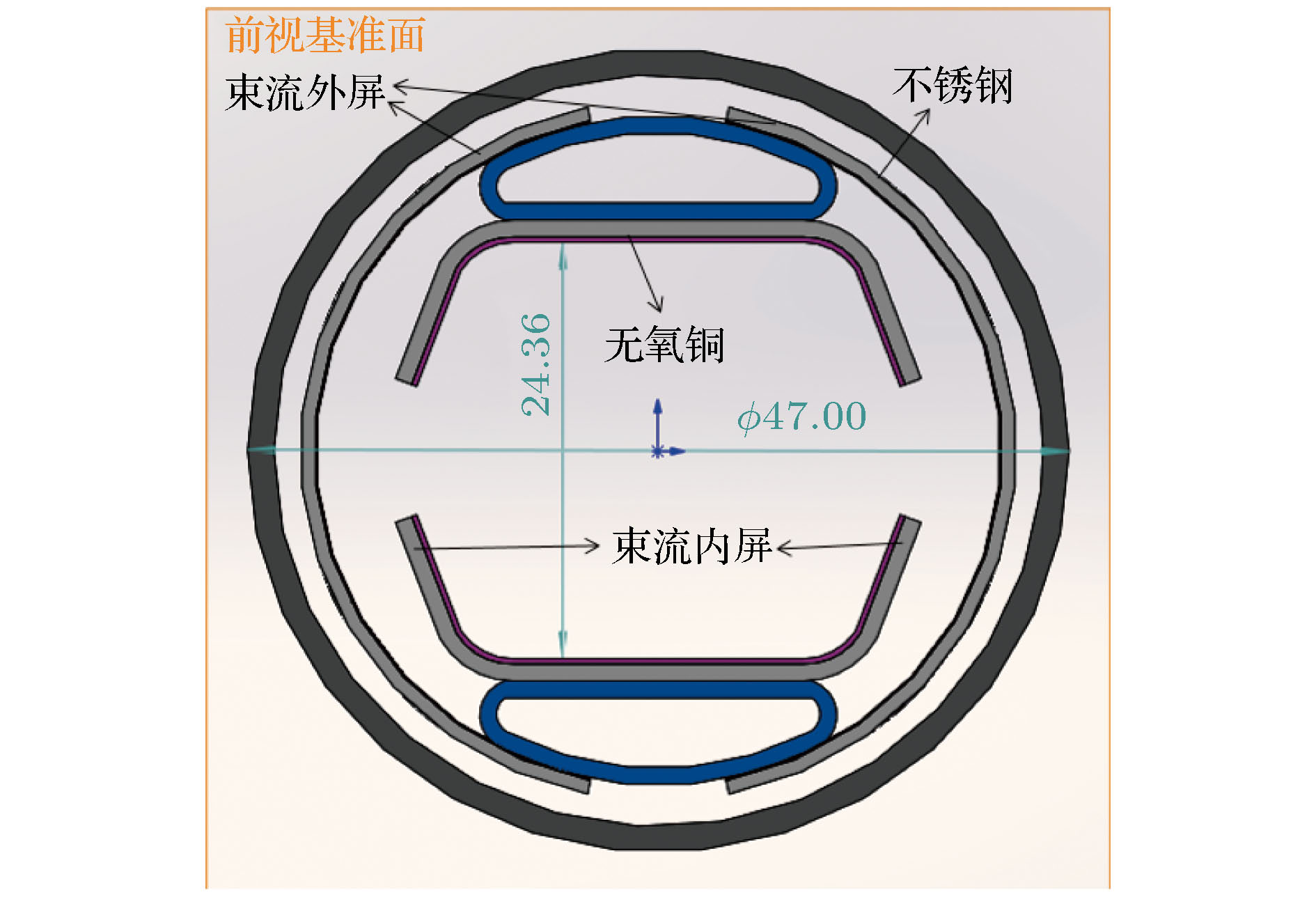
-
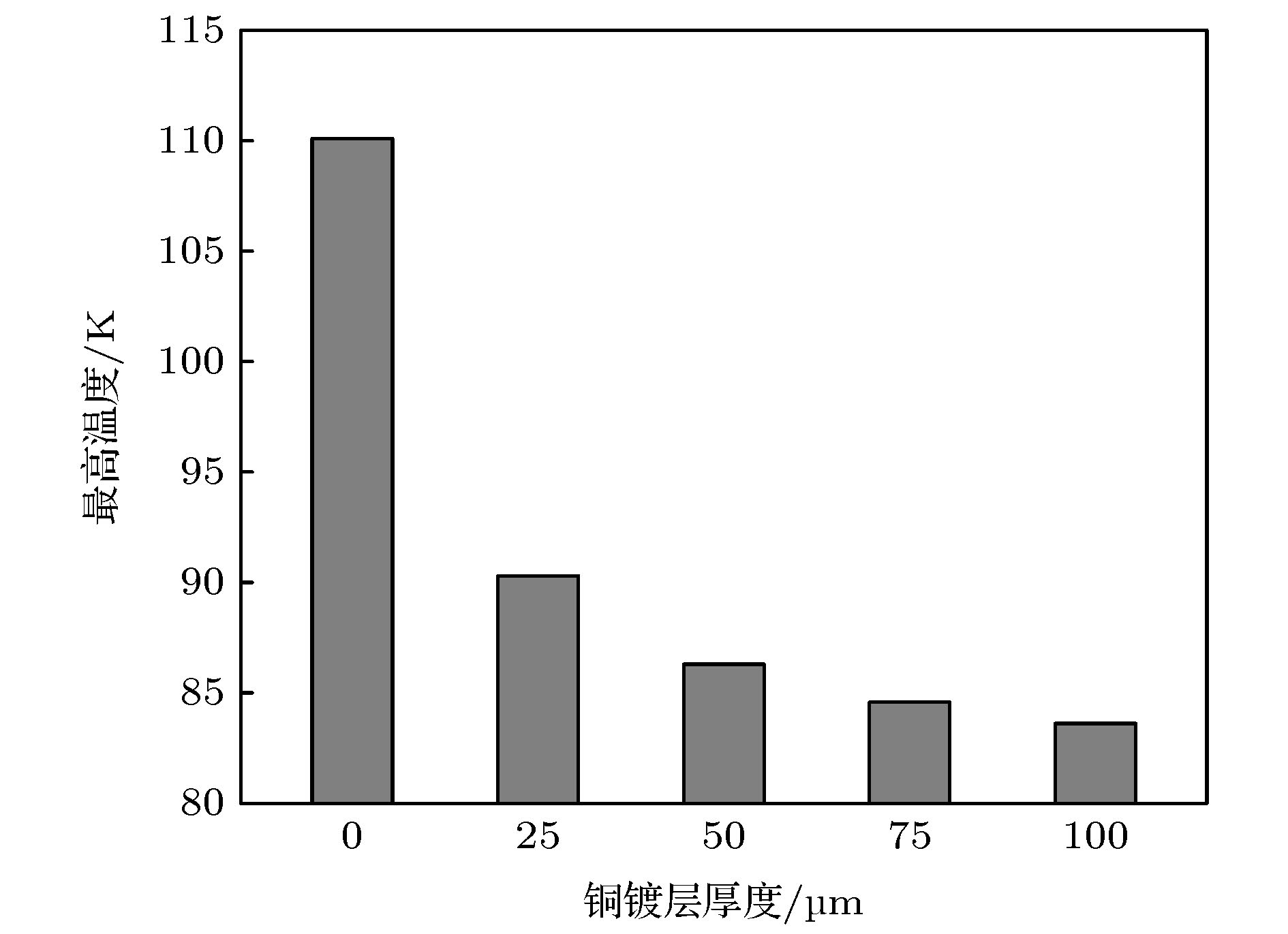
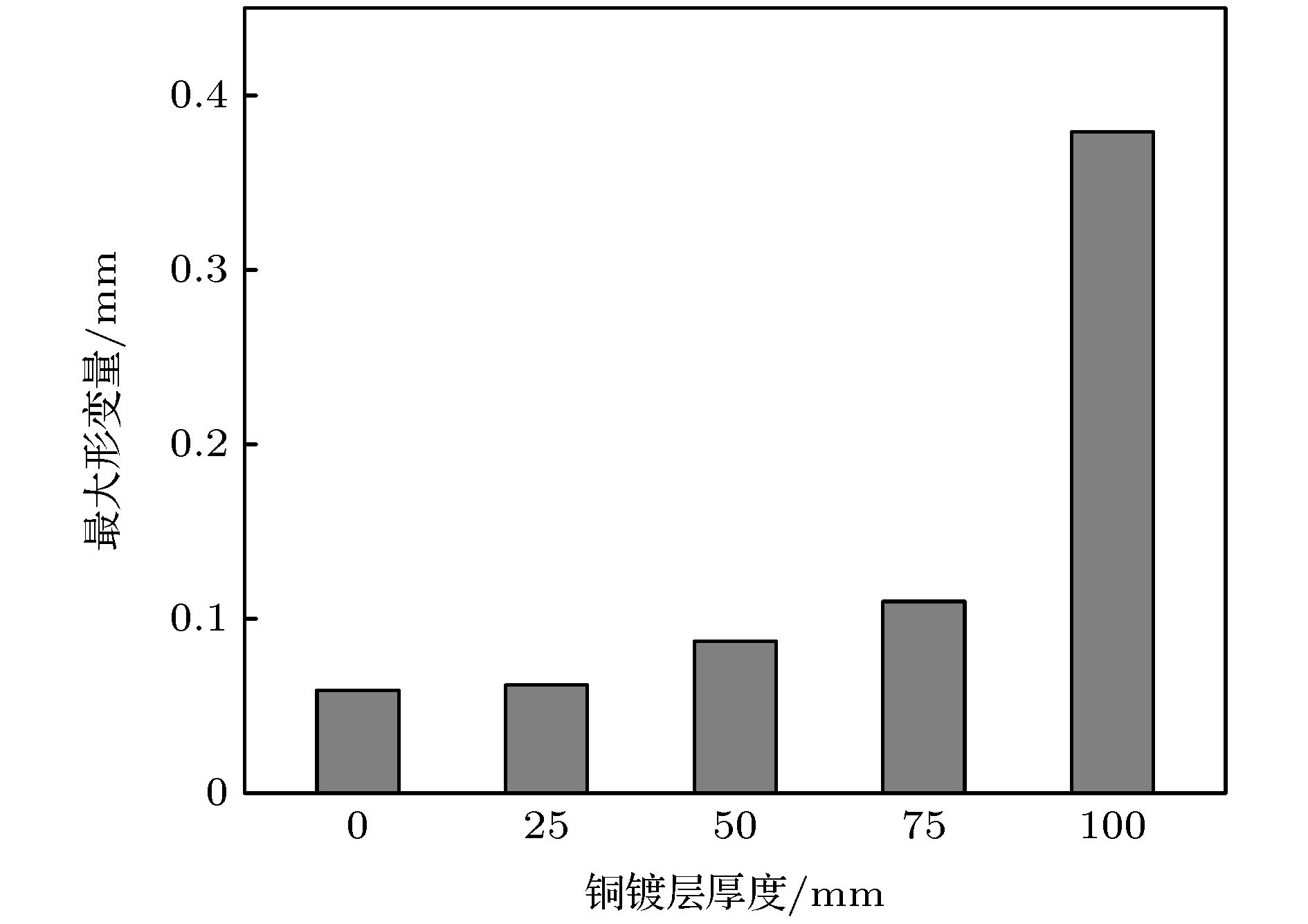
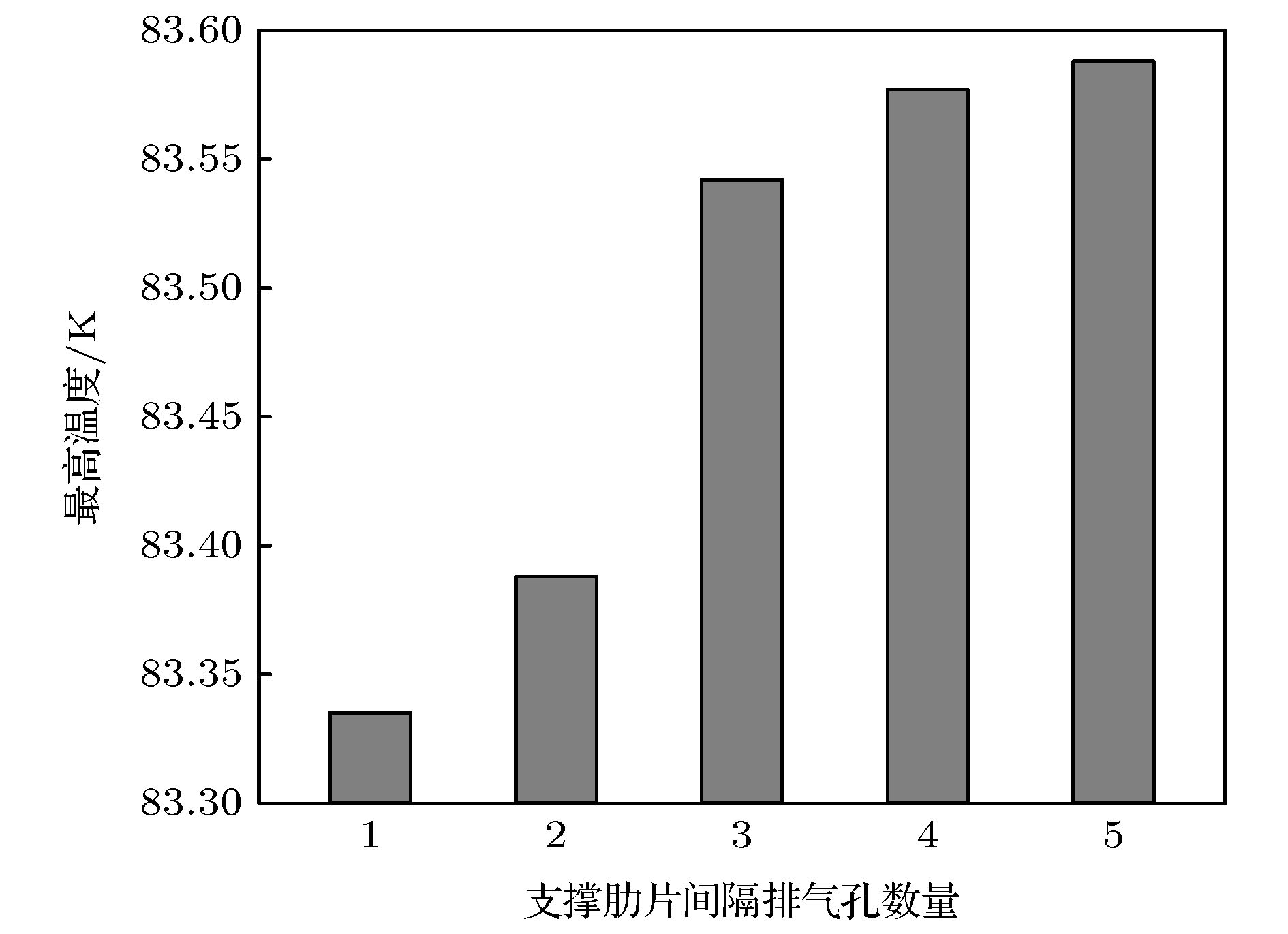
High-energy colliders play an indispensable role in particle physics and high-energy physics. Beam screen is one of the key parts in the high-energy collider. It is used to transfer the heat generated by the beam in the pipeline to a cooling system, and absorb the residual gas to the cold bore through the pumping holes on the wall of the beam screen to ensure the vacuum stability at the same time. However, in the process of transferring thermal load, the deformation caused by temperature change will affect the structural stability of the beam screen. How to reduce the deformation as much as possible while ensuring the good heat transfer performance of the beam screen is one of the key issues in optimizing the structural design of the beam screen. In this paper, the heat transfer performance and mechanical property of the beam screen model are simulated and optimized based on the ANSYS simulation results to ensure the normal and stable operation of the beam in the super proton-proton collider. For the inner surface of the outer screen of the beam screen, the method of reducing the thickness of the copper coating is used to reduce the Lorentz force generated during operation. The calculation results from the relevant theoretical models show that when the thickness of the copper coating varies from 0 to 100 μm, the copper coating with a thickness of 75 μm can reduce the maximum deformation of the outer screen of the beam screen by 70.9%, while the maximum temperature of the beam screen can be increased by 1.1%. For the inner screen of the beam screen, a design scheme in which supporting ribs are arranged at intervals is used to reinforce the structure and improve the overall structural stability of the beam screen. The calculation results show that the maximum deformation of the inner screen of the beam screen can be reduced by 86.8% and the maximum temperature of the beam screen is reduced by 7.69%, compared with the case without supporting fins, when the interval between two adjacent supporting fins is 1 pumping hole. The research results provide important theoretical reference for the design of beam screen, which is the key component of the vacuum system of the new-generation high energy particle accelerator.
-
Keywords:
- particle accelerator /
- collider /
- beam screen
[1] Aad G, Abajyan T, Abbott B, Abdallah J, Khalek S A, Abdelalim A A, Abdinov O, Aben R, Abi B, Abolins M 2012 Phys. Lett. B. 716 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Vien V V 2020 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 47 055007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Alexander S, McDonough E, Pullen A, Shapiro B 2020 J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1 032
[4] Sirunyan A, Tumasyan A, Adam W, Ambrogi F, Bergauer T, Brandstetter J, Dragicevic M, Ero J, Del Valle A, Flechl M 2020 Eur. Phys. J. C 80 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Group CEPC Study 2018 arXiv: 1809.00285 [ap−ph]
[6] Gröbner O 2001 Vacuum 60 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Cern 2004 LHC Design Report (Geneva, Cern, CM-B00029745[R])
[8] Cruikshank P, Artoos K, Bertinelli F, Brunet J C, Calder R, Campedel C, Collins I, Dalin J M, Feral B, Grobner O 1997 Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference (Cat. No. 97 CH36167) Vancouver, BC, Canada May 16, 1997 p3586
[9] Zimmermann F, Guillermo Cantón G, Osborne J, Todesco E, Oide K, Bruce R, Giovannozzi M, Martinez Mirave P, Cai Y, Fartoukh S 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1067 022009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Calder R, Gröbner O, Mathewson A, Anashin V, Dranichnikov A, Malyshev O 1996 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 14 2618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Baglin V, Bregliozzi G, Lanza G, Jimenez J 2011 2nd International Particle Accelerator Conference San Sebastian, Spain, Sep 4−9, 2011 pTUPS019
[12] Baglin V, Lebrun P, Tavian L, van Weelderen R 2012 24th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2012 Fukuoka, Japan, May 14−18, 2012 p006
[13] Ruggiero F, Berg J, Bruning O, Caspers F, Morvillo M, D'Yachkov M 1997 Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference (Cat. No. 97 CH36167) Vancouver, BC, Canada May 16, 1997 p107
[14] 周洪吉 2013 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Zhou H J 2013 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[15] 吴锡, 袁平, 马力祯, 张小奇, 何源, 吴巍, 姚庆高, 郭蓓蕾 2010 強激光与粒子束 22 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X, Yuan P, Ma L Z, Zhang X Q, He Y, Wu W, Yao Q G, Guo B L 2010 High Pow. Las.Part. Beam 22 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 范佳锟, 王洁, 高勇, 游志明, 严涛, 张静, 王盛, 许章炼 2019 原子能科学技术 53 1670
Fan J K, Wang J, Gao Y, You Z M, Yan T, Zhang J, Wang S, Xu Z L 2019 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 53 1670
[17] Sgobba S 2006 CAS-CERN Accelerator School and ALBA Synchrotron Light Facility: Course on Vacuum in Accelerators Platja d'Aro, Spain, May 16 − 24, 2006 p117
[18] Couturier K, Sgobba S 2000 Materials Week Munich, Germany, Sep 25−28, 2000 p006
[19] Sgobba S, Kumpula M, Liimatainen J, Savary F 2000 2000 Powder Metallurgy World Congress Kyoto, Japan, Nov 12−16, 2000 p008
[20] 刘沛航 2017 硕士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Liu P H 2017 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[21] 王坤, 嵇辉, 刘沛航, 金环, 秦经刚, 武玉 2016 低温与超导 44 24
Wang K, Ji H, Liu P H, Jin H, Qin J G, Wu Y 2016 Cryogenics Supercond. 44 24
[22] 陈光 2018 硕士学位论文 (合肥: 合肥工业大学)
Chen G 2018 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: Hefei University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[23] 张华辉 2017 硕士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Zhang H H 2017 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[24] Thompson C A, Manganaro W M, Fickett F R https://www.copper.org/resources/properties/cryogenic/ [2020−3.15]
[25] 赵维娟, 张春堂, 于利军 1986 低温与特气 02 81
Zhao W J, Zhang C T, Yu L J 1986 Low Temp. Specialty Gases 02 81
[26] 丁坤和, 赵素馨, 葛翠英 1981 宇航材料工艺 01 31
Ding K H, Zhao S X, Ge C Y 1981 Aerosp. Mater. Technol. 01 31
[27] Iadarola G, Rumolo G, Arduini G, Bartosik H, Shaposhnikova E, Maury Cuna G, Esteban Muller J, Tavian L, Baglin V, Zimmermann F 2013 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference Shanghai, China, May 12−17, 2013 p1331
[28] Berg S 1997 Energy Gain in an Electron Cloud During the Passage of a Bunch (Geneva, Cern, LHC Project Note 97[R])
-
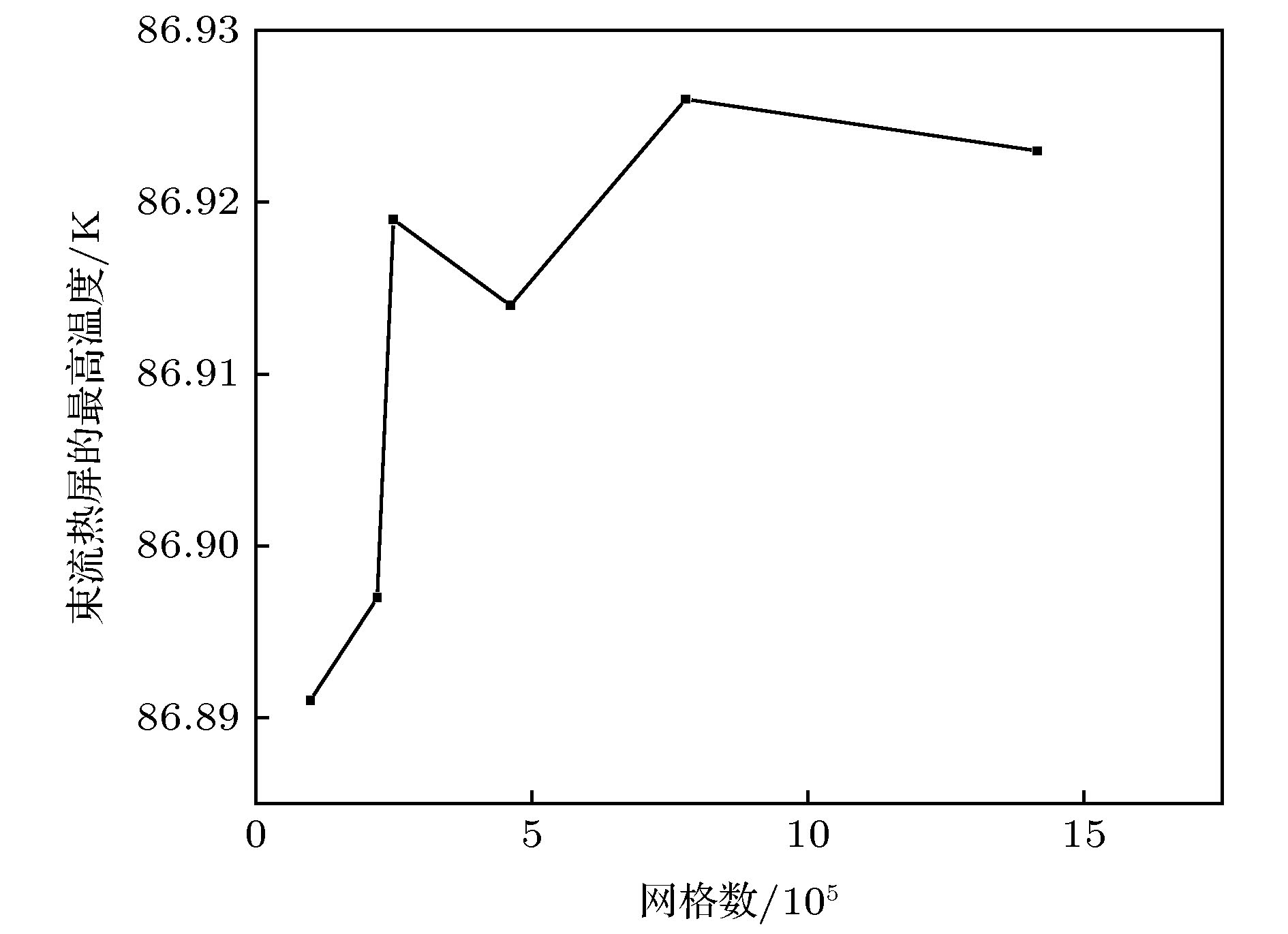
图 3 不同路径和束流热屏形变随不同路径的变化 (a) 路径1、路径2、路径3和路径4的示意图; (b) 束流热屏内屏形变量沿着路径1的变化; (c) 束流热屏外屏形变量沿着路径3的变化.
Figure 3. Different paths and variations with distance along paths in beam screen. (a) Schematic of paths 1, 2, 3 and 4; (b) variations of the inner screen with distance along path 1 in beam screen; (c) variations of the outer screen with distance along path 3 in beam screen.
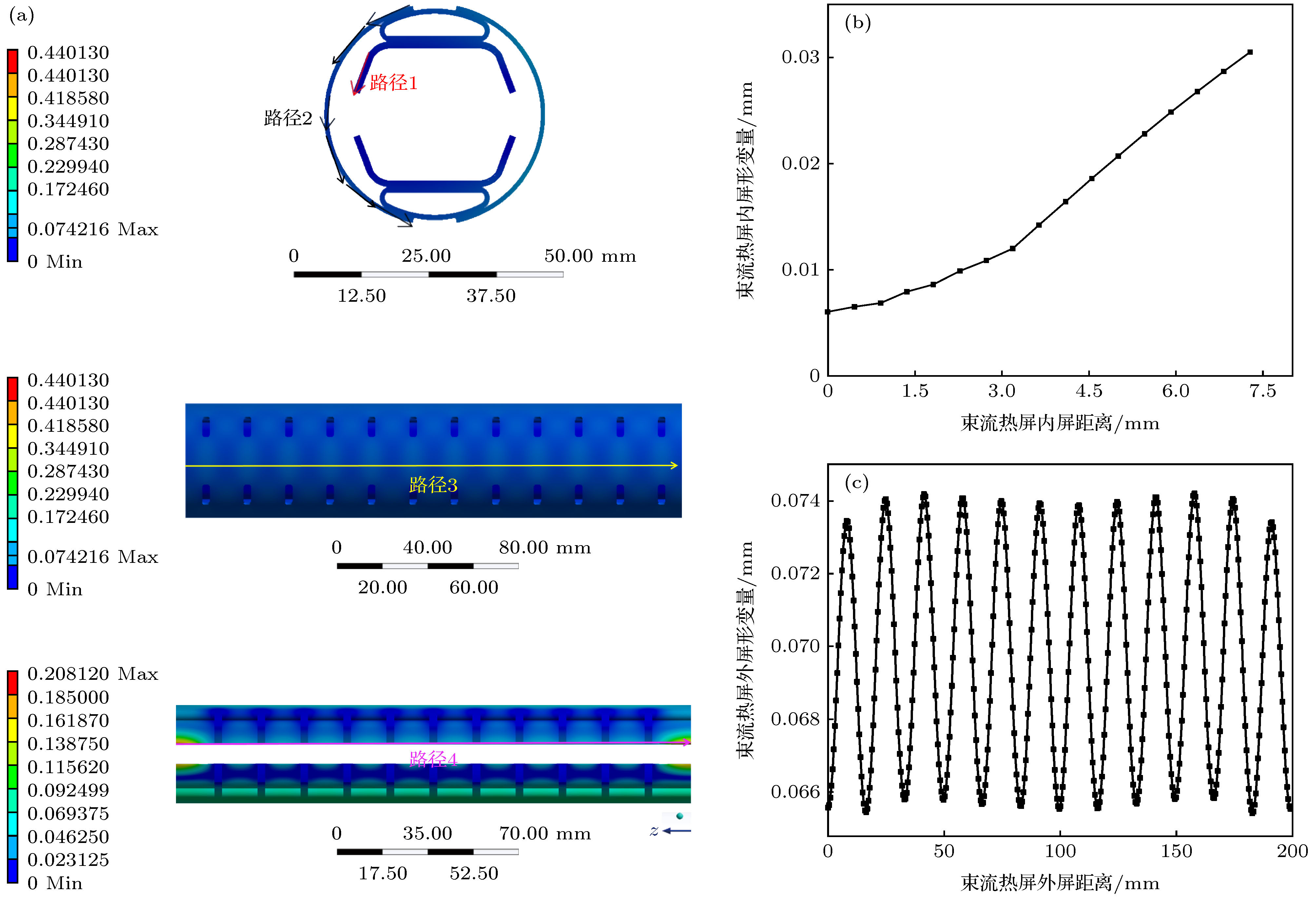
图 4 有洛伦兹力情况下的热-结构耦合模拟结果 (a) 总体形变分布; (b) X方向上的形变分布云图; (c) Y方向上的形变分布云图; (d) Z方向上的形变分布云图
Figure 4. Simulation results of thermal-structure coupling with Lorentz force: (a) Overall deformation distribution; (b) cloud map of deformation distributions in X direction; (c) cloud map of deformation distributions in Y direction; (d) cloud map of deformation distributions in Z direction.
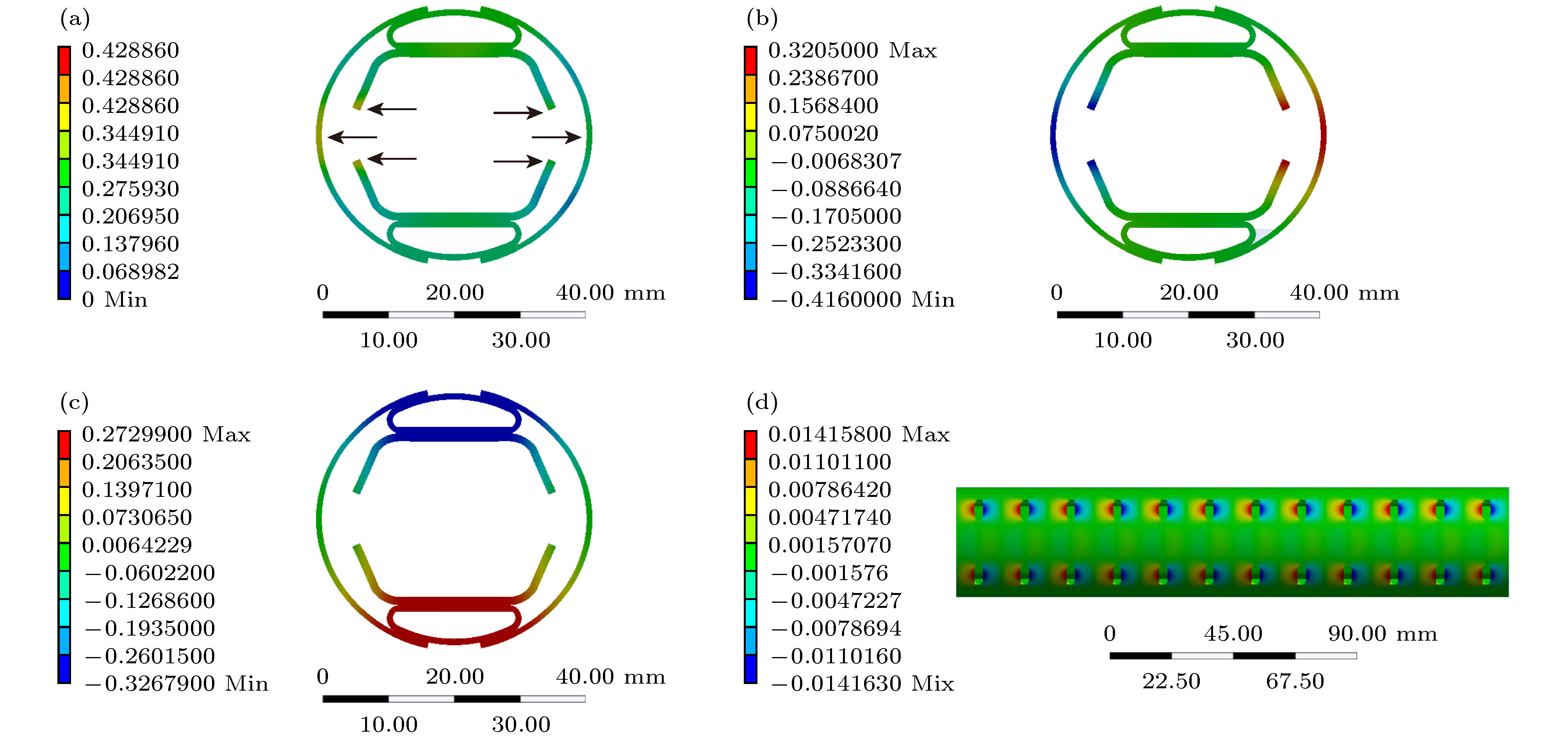
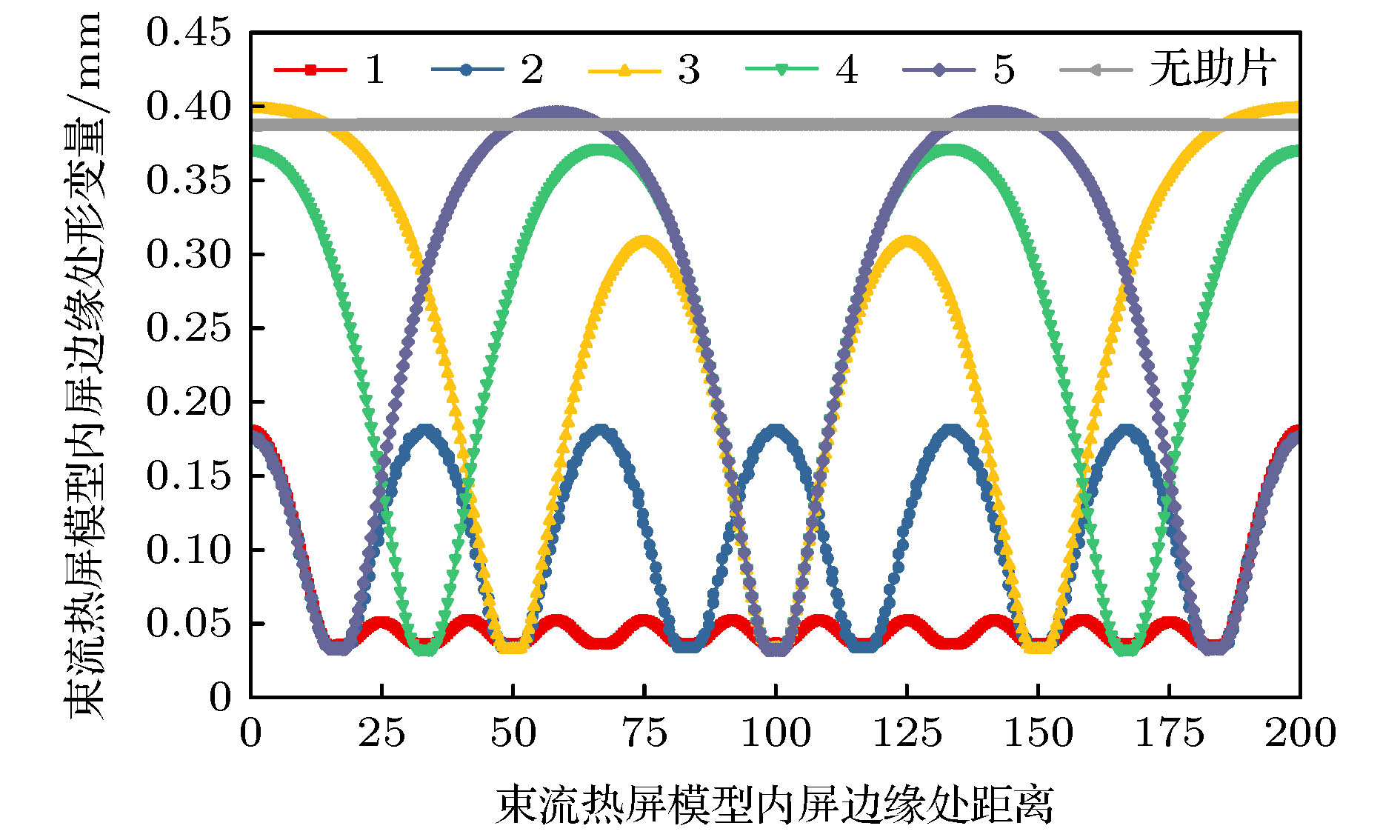
图 5 束流热屏形变随不同路径的变化 (a) 束流热屏内屏处形变量沿着路径1的变化; (b) 束流热屏外屏边缘处沿着路径2的形变量; (c) 束流热屏外屏形变量沿着路径3的变化
Figure 5. Variations with distance along paths in beam screen: (a) Variations of the inner screen along path 1 in beam screen; (b) variations of the edge of outer screen along path 2 in beam screen; (c) variations of the outer screen along path 3 in beam screen.
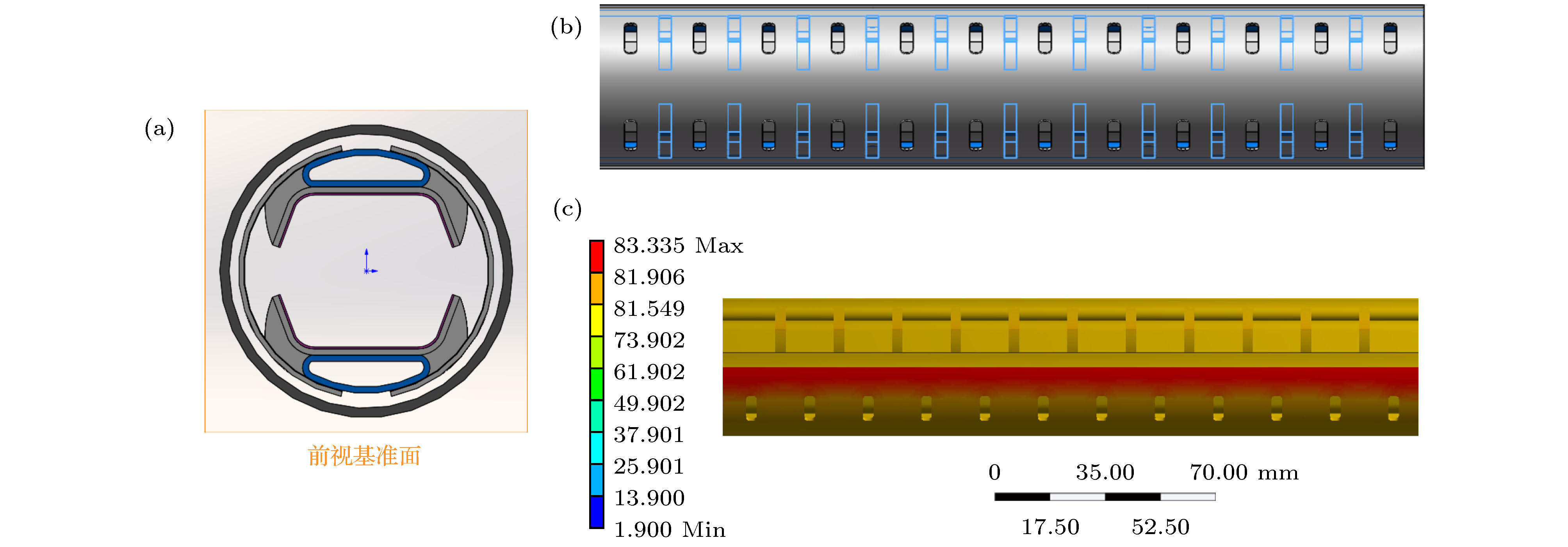
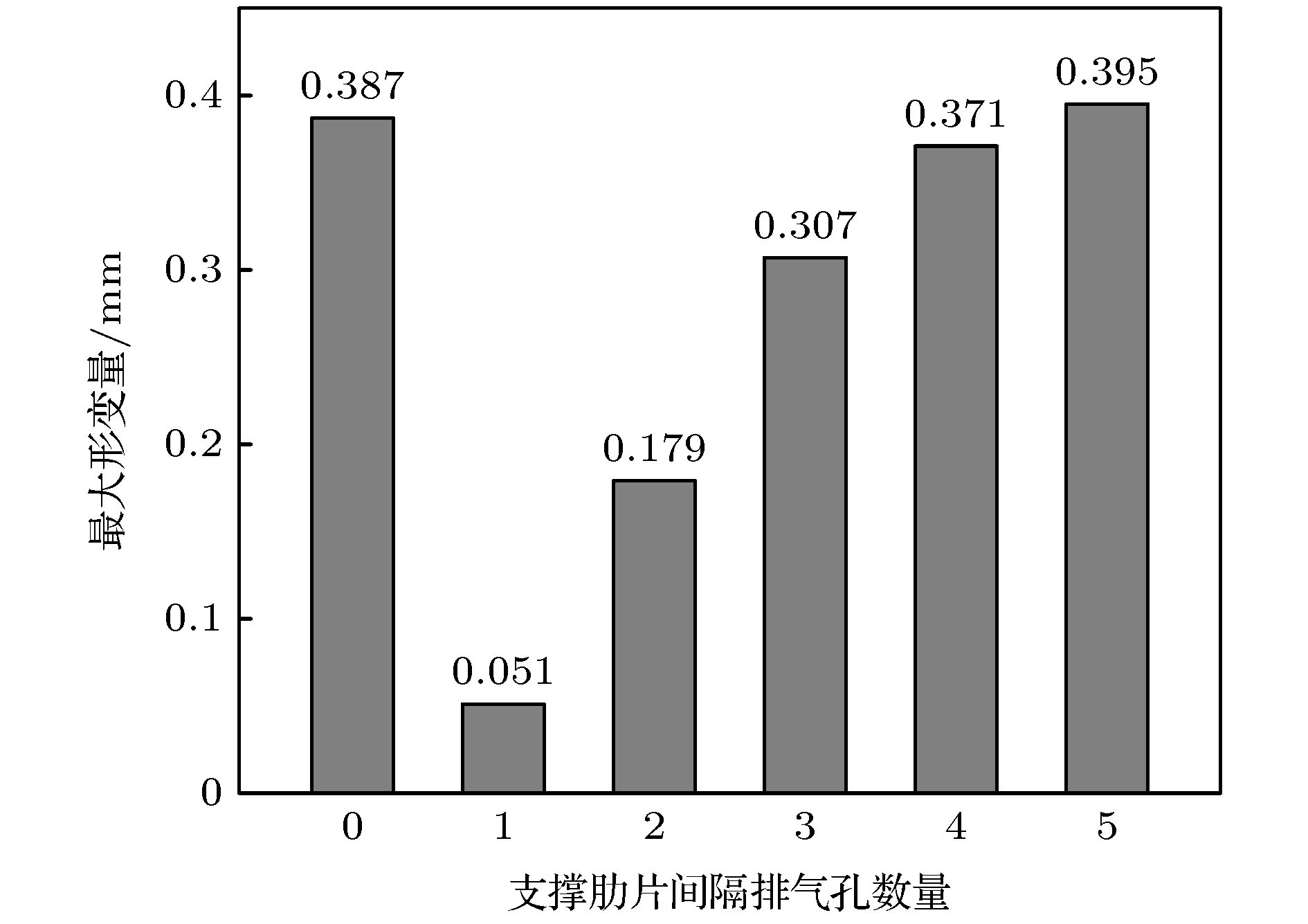
图 8 (a)增加支撑肋片的束流热屏模型; (b)相邻支撑肋片间隔排气孔数量为1个时的支撑肋片分布; (c)相邻支撑肋片间隔排气孔数量为1个时束流热屏模型的温度分布图
Figure 8. (a) Beam screen model with added support ribs; (b) distributions of support fins when the number of exhaust holes between adjacent support fins is one; (c) temperature distribution diagram of the beam screen model when the number of exhaust holes between adjacent support fins is one.
表 1 温度为80 K时, 无氧铜和316LN不锈钢的材料属性
Table 1. Material properties of oxygen-free copper and 316LN stainless steel at 80 K.
材料性能
材料密度/kg·m–3 杨氏模量/GPa 泊松比 导热系数/W·m–1·K–1 热膨胀系数/10–6 K–1 316LN不锈钢 7900 209 0.3 8.12 10.4 无氧铜 8933 137 0.338 540 8 -
[1] Aad G, Abajyan T, Abbott B, Abdallah J, Khalek S A, Abdelalim A A, Abdinov O, Aben R, Abi B, Abolins M 2012 Phys. Lett. B. 716 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Vien V V 2020 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 47 055007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Alexander S, McDonough E, Pullen A, Shapiro B 2020 J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1 032
[4] Sirunyan A, Tumasyan A, Adam W, Ambrogi F, Bergauer T, Brandstetter J, Dragicevic M, Ero J, Del Valle A, Flechl M 2020 Eur. Phys. J. C 80 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Group CEPC Study 2018 arXiv: 1809.00285 [ap−ph]
[6] Gröbner O 2001 Vacuum 60 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Cern 2004 LHC Design Report (Geneva, Cern, CM-B00029745[R])
[8] Cruikshank P, Artoos K, Bertinelli F, Brunet J C, Calder R, Campedel C, Collins I, Dalin J M, Feral B, Grobner O 1997 Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference (Cat. No. 97 CH36167) Vancouver, BC, Canada May 16, 1997 p3586
[9] Zimmermann F, Guillermo Cantón G, Osborne J, Todesco E, Oide K, Bruce R, Giovannozzi M, Martinez Mirave P, Cai Y, Fartoukh S 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1067 022009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Calder R, Gröbner O, Mathewson A, Anashin V, Dranichnikov A, Malyshev O 1996 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 14 2618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Baglin V, Bregliozzi G, Lanza G, Jimenez J 2011 2nd International Particle Accelerator Conference San Sebastian, Spain, Sep 4−9, 2011 pTUPS019
[12] Baglin V, Lebrun P, Tavian L, van Weelderen R 2012 24th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2012 Fukuoka, Japan, May 14−18, 2012 p006
[13] Ruggiero F, Berg J, Bruning O, Caspers F, Morvillo M, D'Yachkov M 1997 Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference (Cat. No. 97 CH36167) Vancouver, BC, Canada May 16, 1997 p107
[14] 周洪吉 2013 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Zhou H J 2013 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[15] 吴锡, 袁平, 马力祯, 张小奇, 何源, 吴巍, 姚庆高, 郭蓓蕾 2010 強激光与粒子束 22 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X, Yuan P, Ma L Z, Zhang X Q, He Y, Wu W, Yao Q G, Guo B L 2010 High Pow. Las.Part. Beam 22 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 范佳锟, 王洁, 高勇, 游志明, 严涛, 张静, 王盛, 许章炼 2019 原子能科学技术 53 1670
Fan J K, Wang J, Gao Y, You Z M, Yan T, Zhang J, Wang S, Xu Z L 2019 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 53 1670
[17] Sgobba S 2006 CAS-CERN Accelerator School and ALBA Synchrotron Light Facility: Course on Vacuum in Accelerators Platja d'Aro, Spain, May 16 − 24, 2006 p117
[18] Couturier K, Sgobba S 2000 Materials Week Munich, Germany, Sep 25−28, 2000 p006
[19] Sgobba S, Kumpula M, Liimatainen J, Savary F 2000 2000 Powder Metallurgy World Congress Kyoto, Japan, Nov 12−16, 2000 p008
[20] 刘沛航 2017 硕士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Liu P H 2017 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[21] 王坤, 嵇辉, 刘沛航, 金环, 秦经刚, 武玉 2016 低温与超导 44 24
Wang K, Ji H, Liu P H, Jin H, Qin J G, Wu Y 2016 Cryogenics Supercond. 44 24
[22] 陈光 2018 硕士学位论文 (合肥: 合肥工业大学)
Chen G 2018 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: Hefei University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[23] 张华辉 2017 硕士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Zhang H H 2017 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[24] Thompson C A, Manganaro W M, Fickett F R https://www.copper.org/resources/properties/cryogenic/ [2020−3.15]
[25] 赵维娟, 张春堂, 于利军 1986 低温与特气 02 81
Zhao W J, Zhang C T, Yu L J 1986 Low Temp. Specialty Gases 02 81
[26] 丁坤和, 赵素馨, 葛翠英 1981 宇航材料工艺 01 31
Ding K H, Zhao S X, Ge C Y 1981 Aerosp. Mater. Technol. 01 31
[27] Iadarola G, Rumolo G, Arduini G, Bartosik H, Shaposhnikova E, Maury Cuna G, Esteban Muller J, Tavian L, Baglin V, Zimmermann F 2013 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference Shanghai, China, May 12−17, 2013 p1331
[28] Berg S 1997 Energy Gain in an Electron Cloud During the Passage of a Bunch (Geneva, Cern, LHC Project Note 97[R])
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8522
- PDF Downloads: 64
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: