-
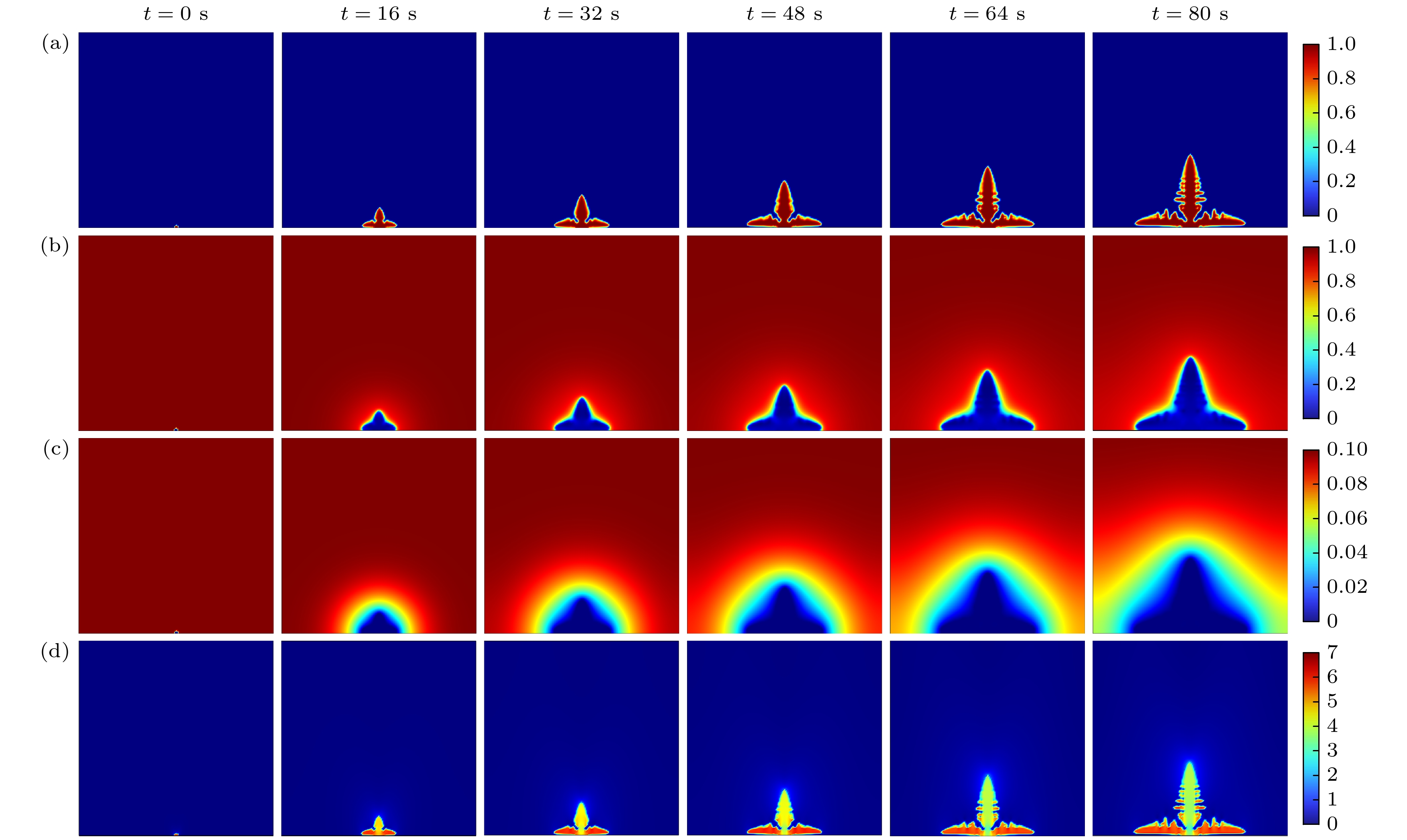
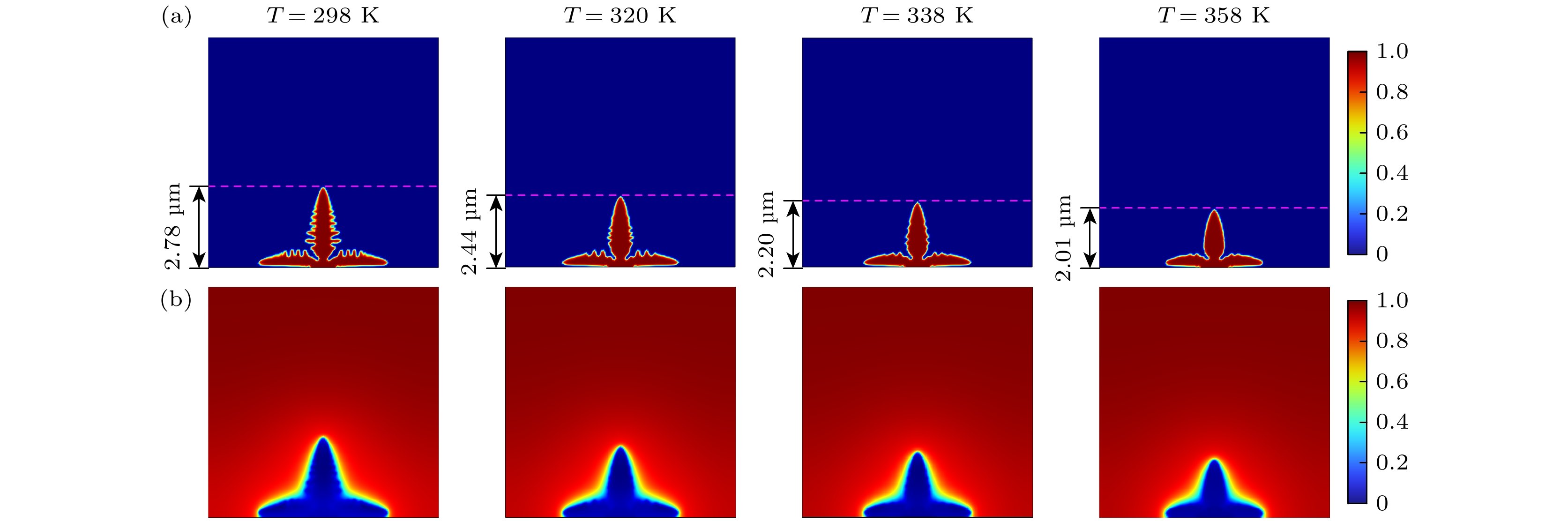
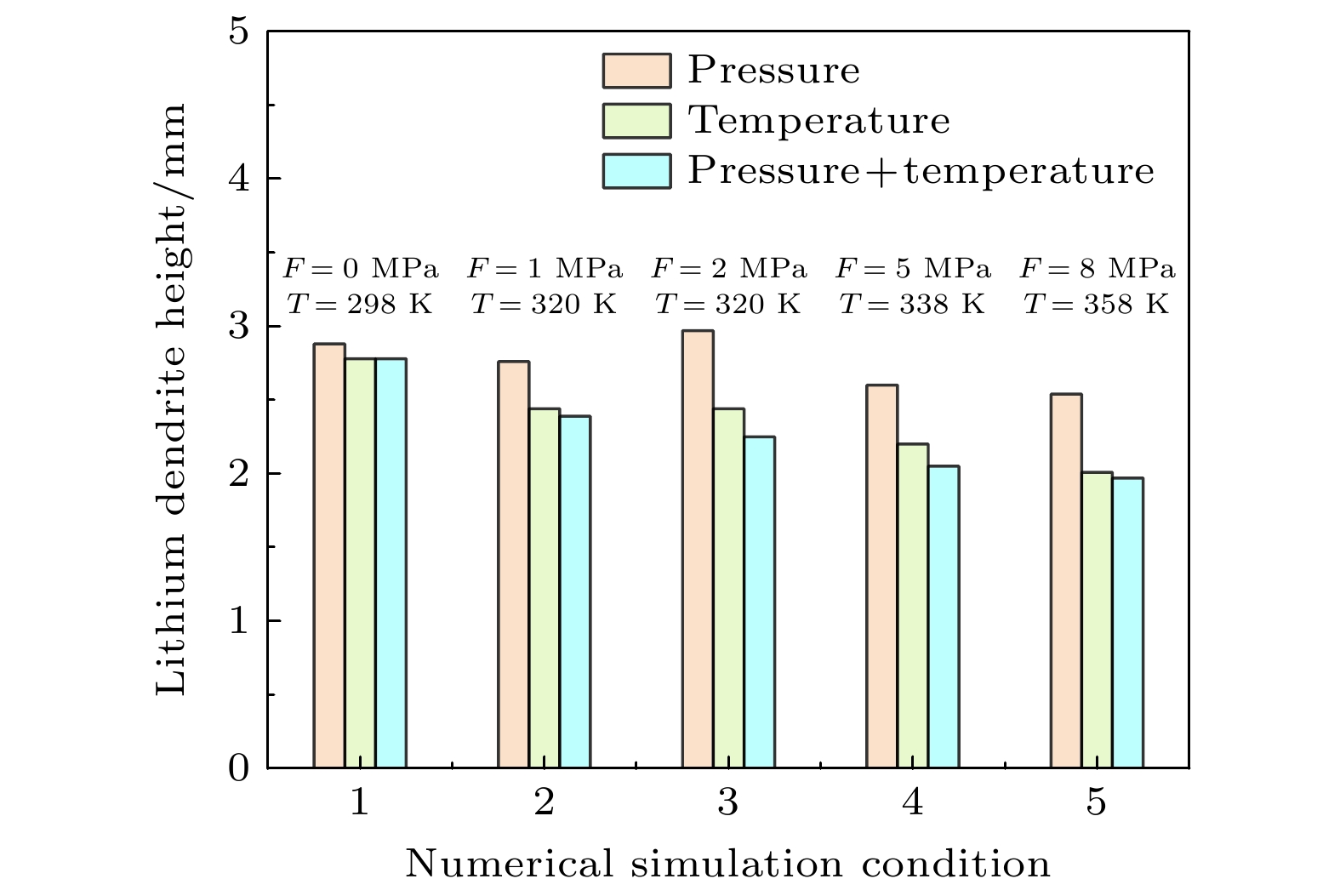
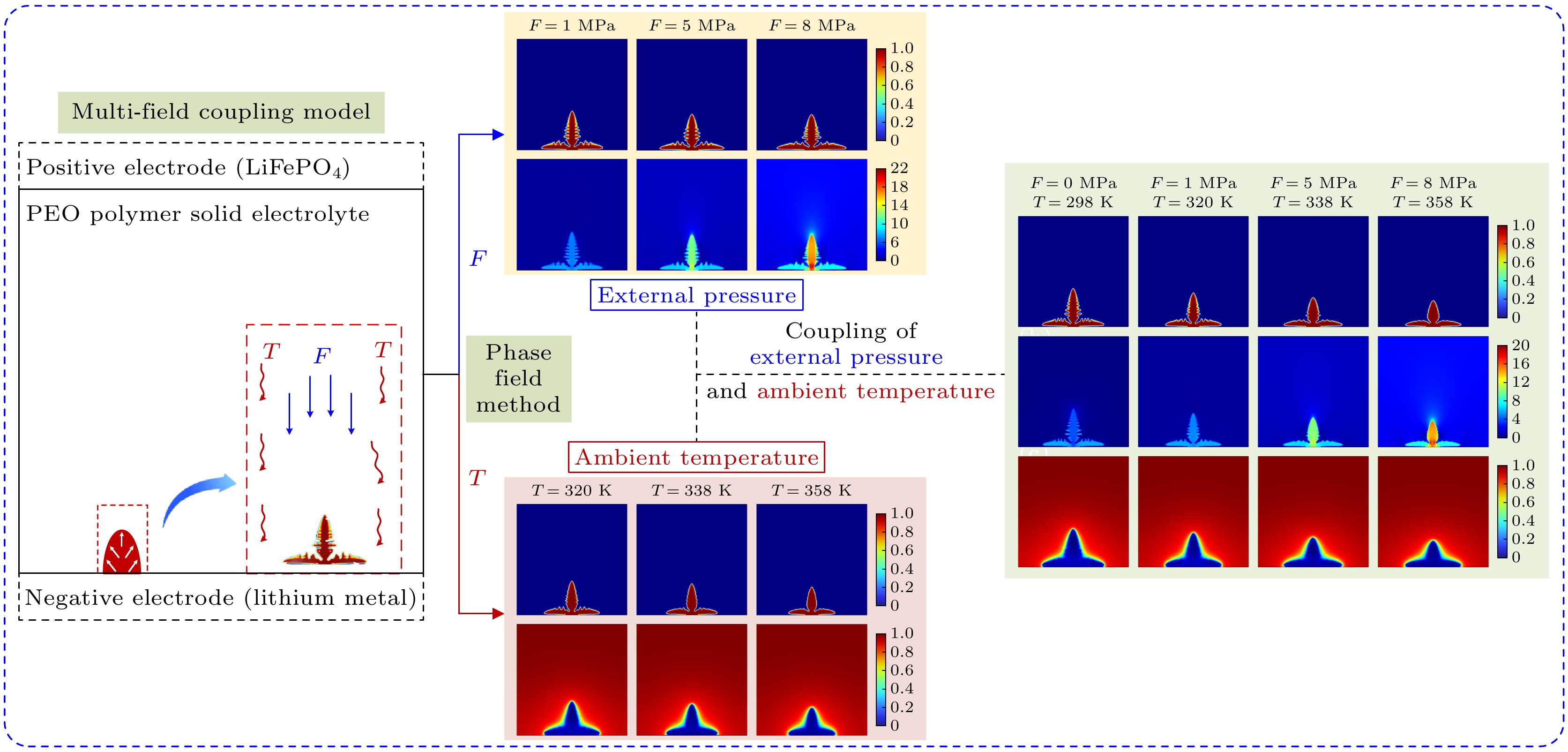
固态电解质锂电池具有能量密度大、循环稳定性强、机械强度高、不易燃、安全性高、使用寿命长等优点, 广泛应用于航空航天、新能源汽车和移动设备等领域. 但是在锂电池的电极/电解质界面处存在的锂枝晶生长问题一直是制约其性能提升和安全应用的关键因素, 锂枝晶在电解质中生长不仅会降低电池的库仑效率, 而且可能刺穿电解质导致电池内部正负极短路. 本文针对固态锂电池中的锂枝晶生长问题, 基于相场理论进行数值模拟研究, 建立了耦合应力场、热场和电化学场的锂枝晶生长相场模型, 研究了环境温度、外压力以及该两种条件耦合作用下的锂枝晶生长形态以及演化规律. 研究结果表明, 在较高温度和较大外应力作用下, 锂枝晶生长缓慢, 侧枝数量减少, 表面更光滑, 电沉积较为均匀. 施加外压越大时, 锂枝晶纵向生长受到抑制, 呈压缩状态, 致密度更高, 但机械不稳定性也会增强; 环境温度越高, 锂离子的扩散速率和反应速率越大, 锂枝晶生长速率和大小也受到抑制, 且二者耦合作用对枝晶生长有明显的抑制效果, 应力集中在根部, 使得枝晶更侧重于横向生长, 有利于形成平坦和密集的锂沉积.Solid-state lithium batteries possess numerous advantages, such as high energy density, excellent cycle stability, superior mechanical strength, non-flammability, enhanced safety, and extended service life. These characteristics make them highly suitable for applications in aerospace, new energy vehicles, and portable electronic devices. However, the growth of lithium dendrite at the electrode/electrolyte interface remains a critical challenge, limiting both performance and safety. The growth of lithium dendrites in the electrolyte not only reduces the Coulombic efficiency of the battery but also poses a risk of puncturing the electrolyte, leading to internal short circuits between the anode and cathode. This study is to solve the problem of lithium dendrite growth in solid-state lithium batteries by employing phase-field theory for numerical simulations. A phase-field model is developed by coupling the mechanical stress field, thermal field, and electrochemical field, to investigate the morphology and evolution of lithium dendrites under the condition of different ambient temperatures, external pressures, and their combined effects. The results indicate that higher temperature and greater external pressure significantly suppress lithium dendrite growth, leading to fewer side branches, smoother surfaces, and more uniform electrochemical deposition. Increased external pressure inhibits longitudinal dendrite growth, resulting in a compressed morphology with higher compactness, but at the cost of increased mechanical instability. Similarly, elevated ambient temperature enhances lithium-ion diffusion and reaction rate, which further suppress dendrite growth rate and size. The combined effect of temperature and pressure exhibits a pronounced inhibitory influence on dendrite growth, with stress concentrating at the dendrite roots. This stress distribution promotes lateral growth, facilitating the formation of flatter and denser lithium deposits.
-
Keywords:
- solid-state lithium batteries /
- phase-field model /
- lithium dendrites /
- mechaincal-thermo-electrochemical coupling
[1] Goodenough J B, Singh P 2015 J. Electrochem. Soc. 162 A2387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Peters B K, Rodriguez K X, Reisberg S H, Beil S B, Hickey D P, Y Kawamata, Collins M, Starr J, Chen L, Udyavara S, Klunder K, Gorey T J, Anderson S L, Neurock M, Minteer S D, Baran P S 2019 Science. 363 838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 耿晓彬, 李顶根, 徐波 2023 72 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng X B, Li D G, Xu B 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Viswanathan V, Epstein A H, Chiang Y M, Esther T, Bradley M, Langford J, Winter M 2022 Nature. 601 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lee M J, Han J, Lee K, Lee Y J, Kim B G, Jung K N, Kim B J, Lee S W 2022 Nature. 601 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hao F, Verma A, Mukherjee P P 2018 J. Mater. Chem. A 6 19664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu Z, Qi Y, Lin Y X, Chen L, Lu P, Chen L Q 2016 J. Electrochem. Soc. 163 A592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张更, 王巧, 沙立婷, 李亚捷, 王达, 施思齐 2020 69 226401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G, Wang Q, Sha L T, Li Y J, Wang D, Shi S Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 226401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sripad S, Viswanathan V 2017 Electrochem. Soc. 164 E3635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sripad S, Viswanathan V 2017 ACS Energy Lett. 2 1669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guttenberg M, Sripad S, Viswanathan V 2017 ACS Energy Lett. 2 2642
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Guyer J E, Boettinger W J, Warren J A, McFadden G B 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 021603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kobayashi R 1993 Physica D 63 410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liang L Y, Qi Y, Xue F, Bhattacharya S, Harris S J, Chen L Q 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 051609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen L, Zhang H W, Liang L Y, Liu Z, Qi Y, Lu P, Chen J, Chen L Q 2015 J. Power Sources 300 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shen X, Zhang R, Shi P, Chen X, Zhang Q 2021 Adv. Energy Mater. 11 2003416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yan H H, Bie Y H, Cui X Y, Xiong G P, Chen L 2018 Energy Convers Manag. 161 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hong Z J, Viswanathan V 2019 ACS Energy Lett. 4 1012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yurkiv V, Foroozan T, Ramasubramanian A, Shahbazian-Yassar R, Mashayek F 2018 MRS Commun. 8 1285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Qi G Q, Liu X L, Dou R F, Wen Z, Zhou W N, Liu L 2024 J. Energy Storage 101 113899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Arguello M E, Labanda N A, Calo V M, Gumulya M, Utikar R, Derksen J 2022 J. Energy Storage 53 104892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jiang W J, Wang Z H, Hu L Z, Wang Y, Ma Z S 2024 J. Energy Storage 86 111126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 梁辰, 邢鹏飞, 吴孟武, 秦训鹏 2024 储能科学与技术 1125 2095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang C, Xing P F, Wu M W, Qin X P 2024 Energy Storage Sci. Techn. 1125 2095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cahn J W, Allen S M 1977 J. Phys. IV 38 C7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Allen S M, Cahn J W 1979 Acta Metall. 27 1085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 梁宇皓, 范丽珍 2020 69 226201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Y H, Fan L Z 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 226201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wu W, Xiao X, Huang X S 2012 Electrochim. Acta 83 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Doyle M, Newman J, Góźdź A S, Schmutz C, Tarascon J M 1996 J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 1890
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Stewart S G, Newman J 2008 J. Electrochem. Soc. 155 F13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang Y X, Li Y F, Shen W J, Li K, Lin Y X 2023 ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 6 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yang H D, Wang Z J 2023 J. Solid State Electr. 27 2607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 崔锦, 石川, 赵金保 2021 化工学报 72 3511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui J, Shi C, Zhao J B 2021 CIESC J. 72 3511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yin X S, Tang W, Jung I D, Phua K C, Adams S., Lee S W, Zheng G W 2018 Nano Energy 50 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 王其钰, 王朔, 周格, 张杰男, 郑杰允, 禹习谦, 李泓 2018 67 128501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Y, Wang S, Zhou G, Zhang J N, Zheng J Y, Yu X Q, Li H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 128501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 乔东格, 刘训良, 温治, 豆瑞峰, 周文宁 2022 储能科学与技术 11 1008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao D G, Liu X L, Wen Z, Dou R F, Zhou W N 2022 ESST 11 1008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yan K, Wang J Y, Zhao S Q, Zhou D, Sun B, Cui Y, Wang G X 2019 Angew Chem. Int. Edit. 58 11364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
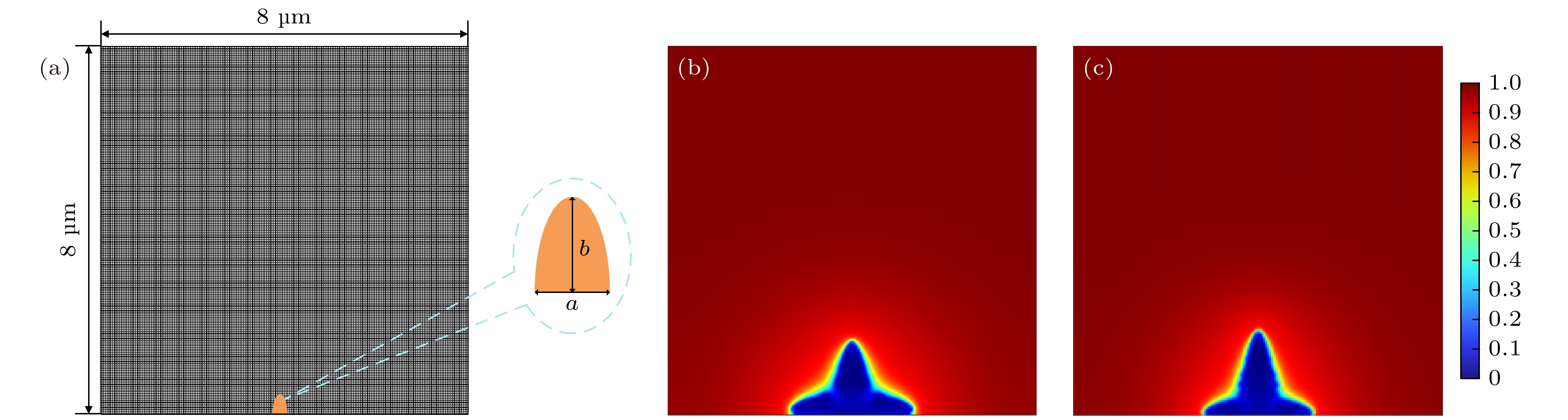
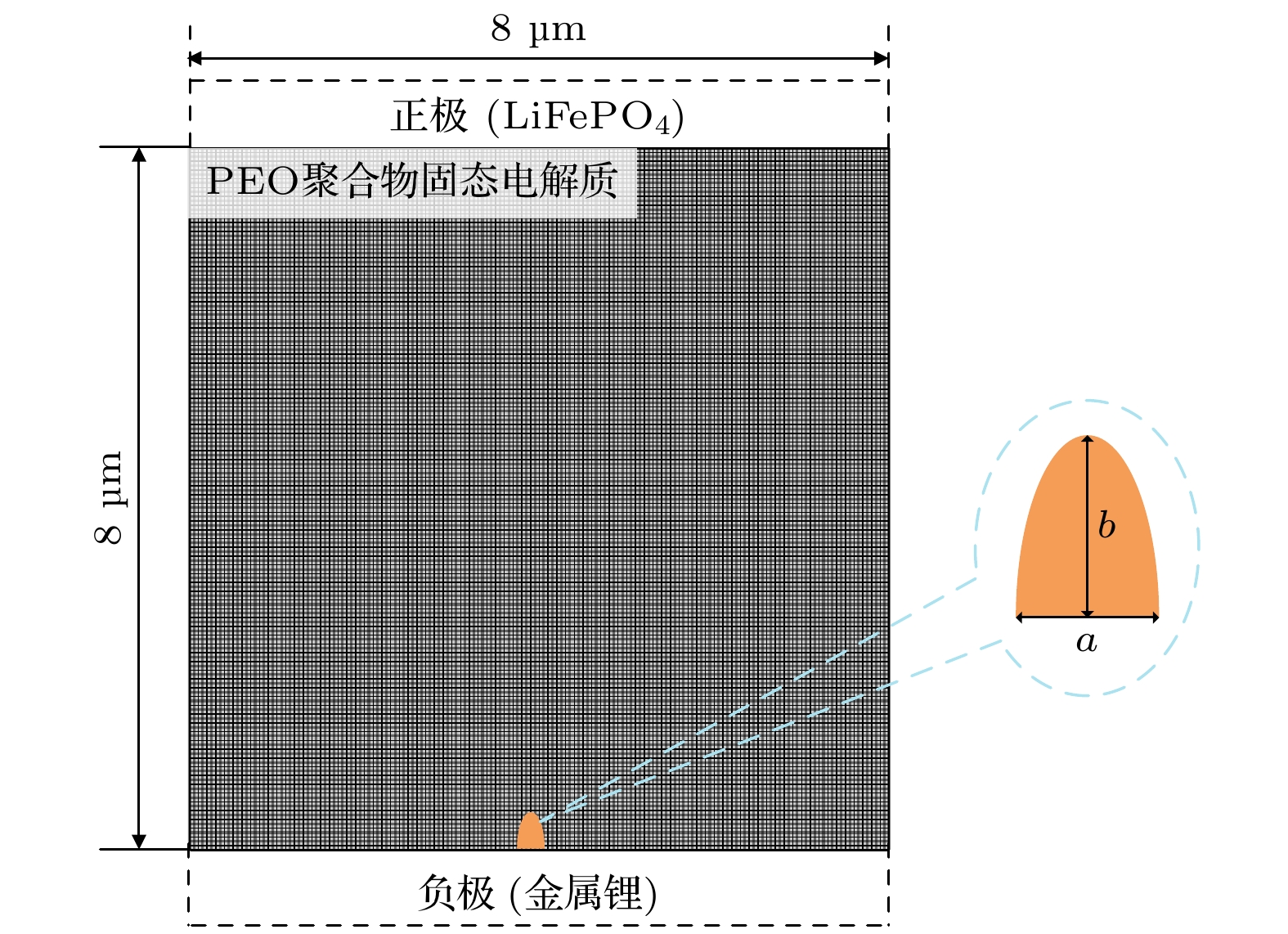
图 2 有限元结果验证 (a) 有限元网格与初始形核点位置设置; (b) 当t = 40 s时当前模型的锂离子浓度; (c) 当t = 40 s时Yang等[31]得到的锂离子浓度
Fig. 2. Verification of finite element results: (a) Setting of finite element mesh and initial nucleation point; (b) lithium-ion concentration (mol/m3) of current model when t = 40 s; (c) lithium-ion concentration (mol/m3) morphology obtained by Yang et al. [31] when t = 40 s.
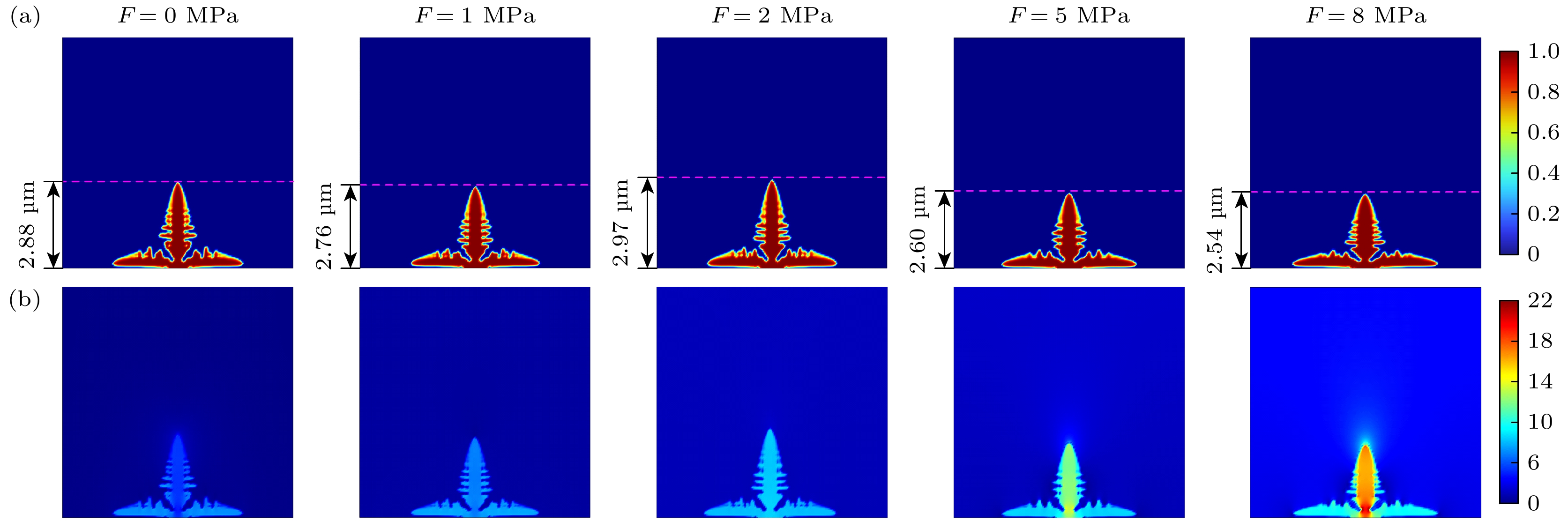
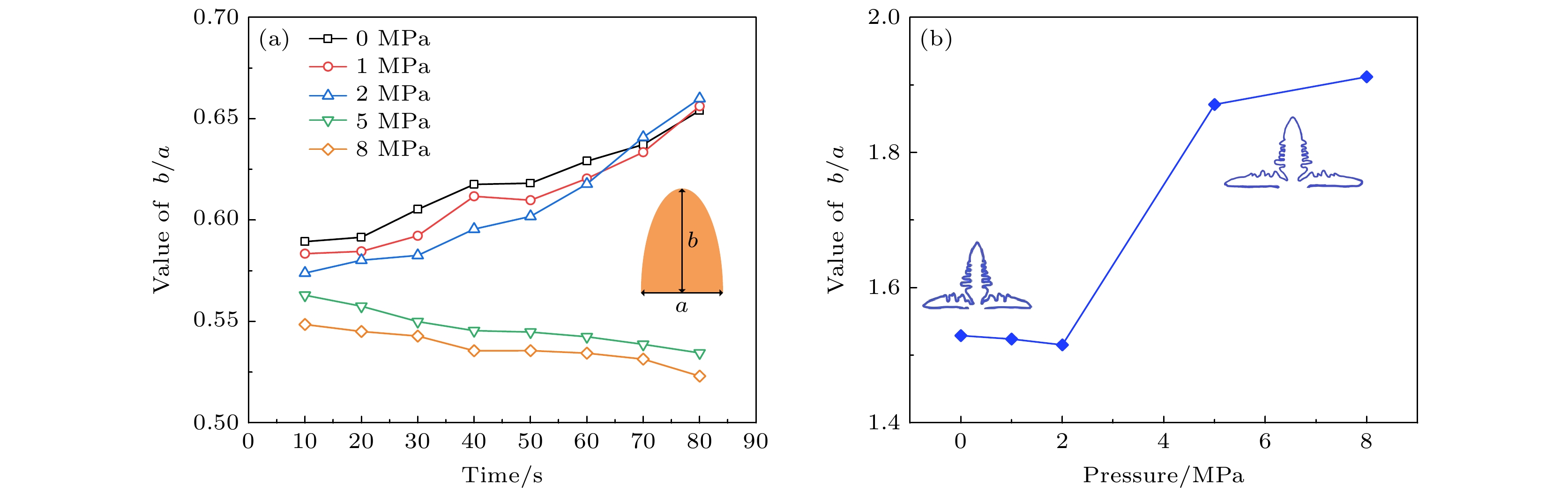
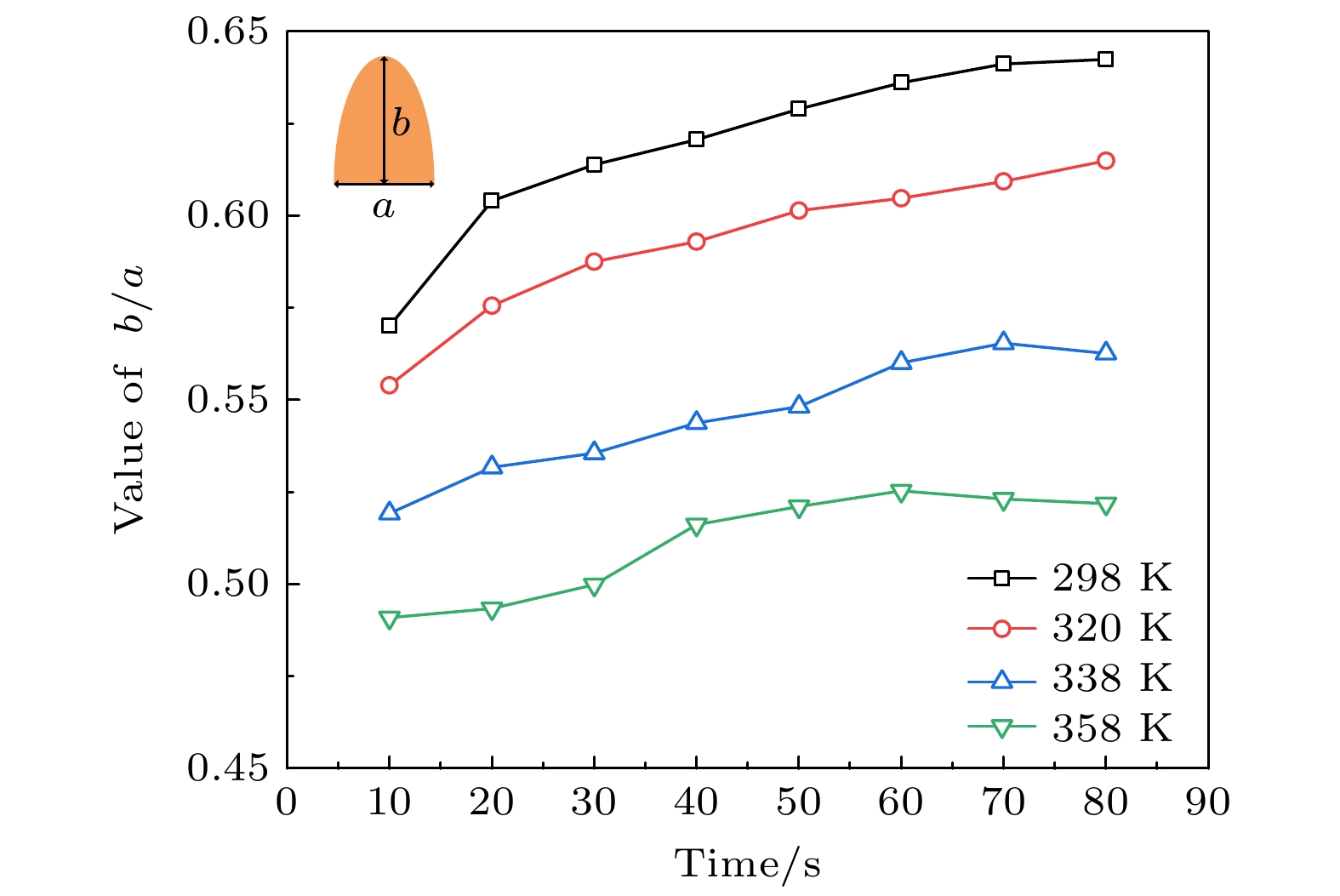
图 5 不同外压力下锂枝晶生长趋势结果 (a) 锂枝晶高度与宽度的比值(b/a)随时间的变化; (b) 锂枝晶宽度与高度的比值(a/b)随压力的变化
Fig. 5. Results of lithium dendrite growth trend under different external pressures: (a) The ratio of height to width (b/a) of lithium dendrite changes with time; (b) the ratio of width to height (a/b) of lithium dendrite changes with pressure.
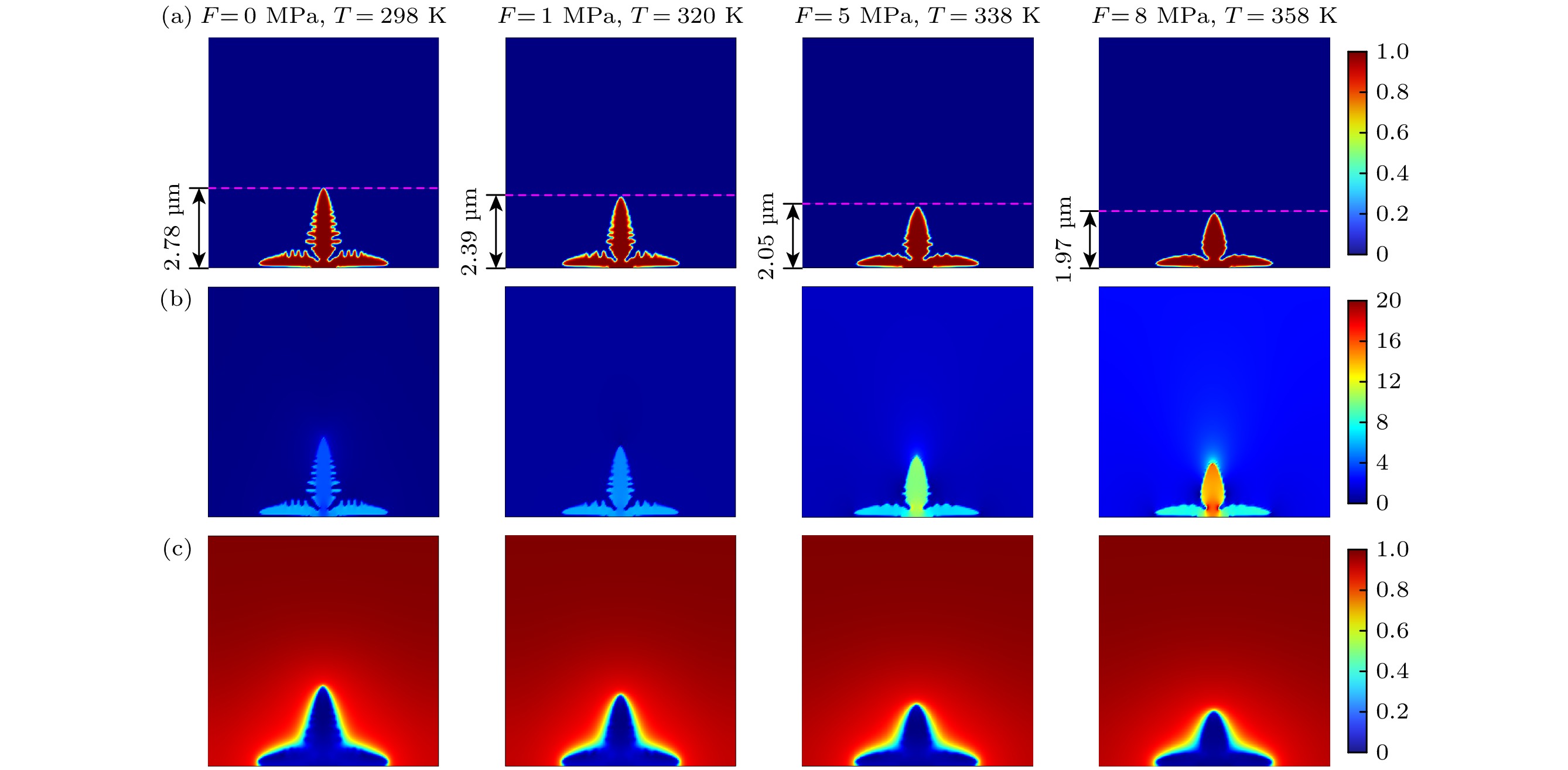
图 8 不同环境温度和外压力耦合作用下锂枝晶生长演化结果 (a) 锂枝晶生长形貌; (b) von Mises应力分布(MPa); (c) 锂离子浓度(mol/m3)
Fig. 8. Evolution results of lithium dendrite growth under coupling of external pressure and ambient temperature: (a) Growth morphology of lithium dendrites; (b) von Mises stress (MPa); (c) lithium-ion concentration (mol/m3).
参数名 参数符号 数值 参数名 参数符号 数值 界面迁移率 Lσ/(m3·J–1·s–1) 1×10–6 化学反应常数 Lη/s–1 0.5 各向异性强度 δ 0.05 各项异性模数 ω 4 电极扩散系数 De/(m2·s–1) 1.7×10–15 电解质扩散系数 Ds/(m2·s–1) 2×10–15 电极电导率 σe/(S·m–1) 1×107 电解质电导率 σs/(S·m–1) 0.1 电荷转移系数 α 0.5 势垒高度 W/(J·m–3) 105 电解质初始浓度 c0/(mol·m–3) 1000 电极初始浓度 cs/(mol·m–3) 7.69×104 梯度能量系数 k/(J·m–1) 1×10–10 电极杨氏模量 Ee/GPa 7.8 电解质杨氏模量 Es/GPa 1 电极泊松比 Ve 0.42 电解质泊松比 Vs 0.3 电极比热容 Cpe/(J·kg–1·K–1) 1200 Vegard 应变系数 λi –0.866×10–3 电解质比热容 Cps/(J·kg–1·K–1) 133 –0.773×10–3 电极导热系数 Re/(W·m–1·K–1) 1.04 –0.529×10–3 电解质导热系数 Rs/(W·m–1·K–1) 0.45 扩散势垒 ${E_{{\text{a}}, D_{{\text{Li}}}^{+}}}$/eV 0.34 电化学反应势垒 ${E_{{\text{a}}, {L_{\mathrm{η}}}}}$/eV 0.3 -
[1] Goodenough J B, Singh P 2015 J. Electrochem. Soc. 162 A2387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Peters B K, Rodriguez K X, Reisberg S H, Beil S B, Hickey D P, Y Kawamata, Collins M, Starr J, Chen L, Udyavara S, Klunder K, Gorey T J, Anderson S L, Neurock M, Minteer S D, Baran P S 2019 Science. 363 838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 耿晓彬, 李顶根, 徐波 2023 72 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng X B, Li D G, Xu B 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Viswanathan V, Epstein A H, Chiang Y M, Esther T, Bradley M, Langford J, Winter M 2022 Nature. 601 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lee M J, Han J, Lee K, Lee Y J, Kim B G, Jung K N, Kim B J, Lee S W 2022 Nature. 601 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hao F, Verma A, Mukherjee P P 2018 J. Mater. Chem. A 6 19664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu Z, Qi Y, Lin Y X, Chen L, Lu P, Chen L Q 2016 J. Electrochem. Soc. 163 A592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张更, 王巧, 沙立婷, 李亚捷, 王达, 施思齐 2020 69 226401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G, Wang Q, Sha L T, Li Y J, Wang D, Shi S Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 226401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sripad S, Viswanathan V 2017 Electrochem. Soc. 164 E3635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sripad S, Viswanathan V 2017 ACS Energy Lett. 2 1669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guttenberg M, Sripad S, Viswanathan V 2017 ACS Energy Lett. 2 2642
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Guyer J E, Boettinger W J, Warren J A, McFadden G B 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 021603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kobayashi R 1993 Physica D 63 410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liang L Y, Qi Y, Xue F, Bhattacharya S, Harris S J, Chen L Q 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 051609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen L, Zhang H W, Liang L Y, Liu Z, Qi Y, Lu P, Chen J, Chen L Q 2015 J. Power Sources 300 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shen X, Zhang R, Shi P, Chen X, Zhang Q 2021 Adv. Energy Mater. 11 2003416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yan H H, Bie Y H, Cui X Y, Xiong G P, Chen L 2018 Energy Convers Manag. 161 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hong Z J, Viswanathan V 2019 ACS Energy Lett. 4 1012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yurkiv V, Foroozan T, Ramasubramanian A, Shahbazian-Yassar R, Mashayek F 2018 MRS Commun. 8 1285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Qi G Q, Liu X L, Dou R F, Wen Z, Zhou W N, Liu L 2024 J. Energy Storage 101 113899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Arguello M E, Labanda N A, Calo V M, Gumulya M, Utikar R, Derksen J 2022 J. Energy Storage 53 104892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jiang W J, Wang Z H, Hu L Z, Wang Y, Ma Z S 2024 J. Energy Storage 86 111126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 梁辰, 邢鹏飞, 吴孟武, 秦训鹏 2024 储能科学与技术 1125 2095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang C, Xing P F, Wu M W, Qin X P 2024 Energy Storage Sci. Techn. 1125 2095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cahn J W, Allen S M 1977 J. Phys. IV 38 C7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Allen S M, Cahn J W 1979 Acta Metall. 27 1085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 梁宇皓, 范丽珍 2020 69 226201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Y H, Fan L Z 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 226201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wu W, Xiao X, Huang X S 2012 Electrochim. Acta 83 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Doyle M, Newman J, Góźdź A S, Schmutz C, Tarascon J M 1996 J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 1890
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Stewart S G, Newman J 2008 J. Electrochem. Soc. 155 F13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang Y X, Li Y F, Shen W J, Li K, Lin Y X 2023 ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 6 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yang H D, Wang Z J 2023 J. Solid State Electr. 27 2607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 崔锦, 石川, 赵金保 2021 化工学报 72 3511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui J, Shi C, Zhao J B 2021 CIESC J. 72 3511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yin X S, Tang W, Jung I D, Phua K C, Adams S., Lee S W, Zheng G W 2018 Nano Energy 50 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 王其钰, 王朔, 周格, 张杰男, 郑杰允, 禹习谦, 李泓 2018 67 128501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Y, Wang S, Zhou G, Zhang J N, Zheng J Y, Yu X Q, Li H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 128501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 乔东格, 刘训良, 温治, 豆瑞峰, 周文宁 2022 储能科学与技术 11 1008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao D G, Liu X L, Wen Z, Dou R F, Zhou W N 2022 ESST 11 1008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yan K, Wang J Y, Zhao S Q, Zhou D, Sun B, Cui Y, Wang G X 2019 Angew Chem. Int. Edit. 58 11364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6258
- PDF下载量: 280
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: