-
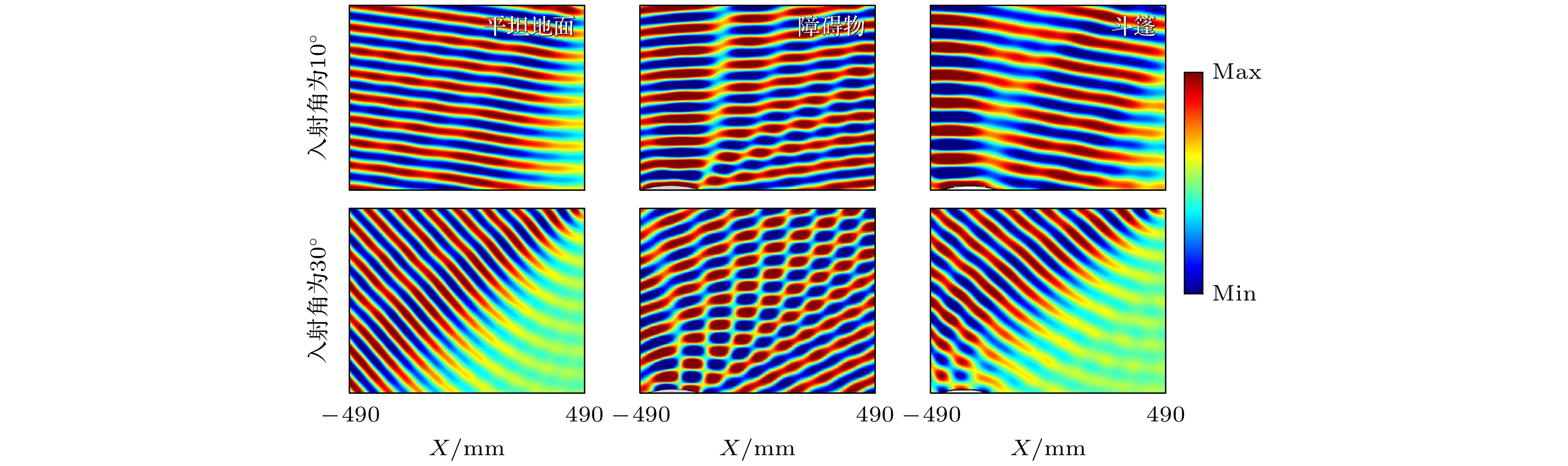
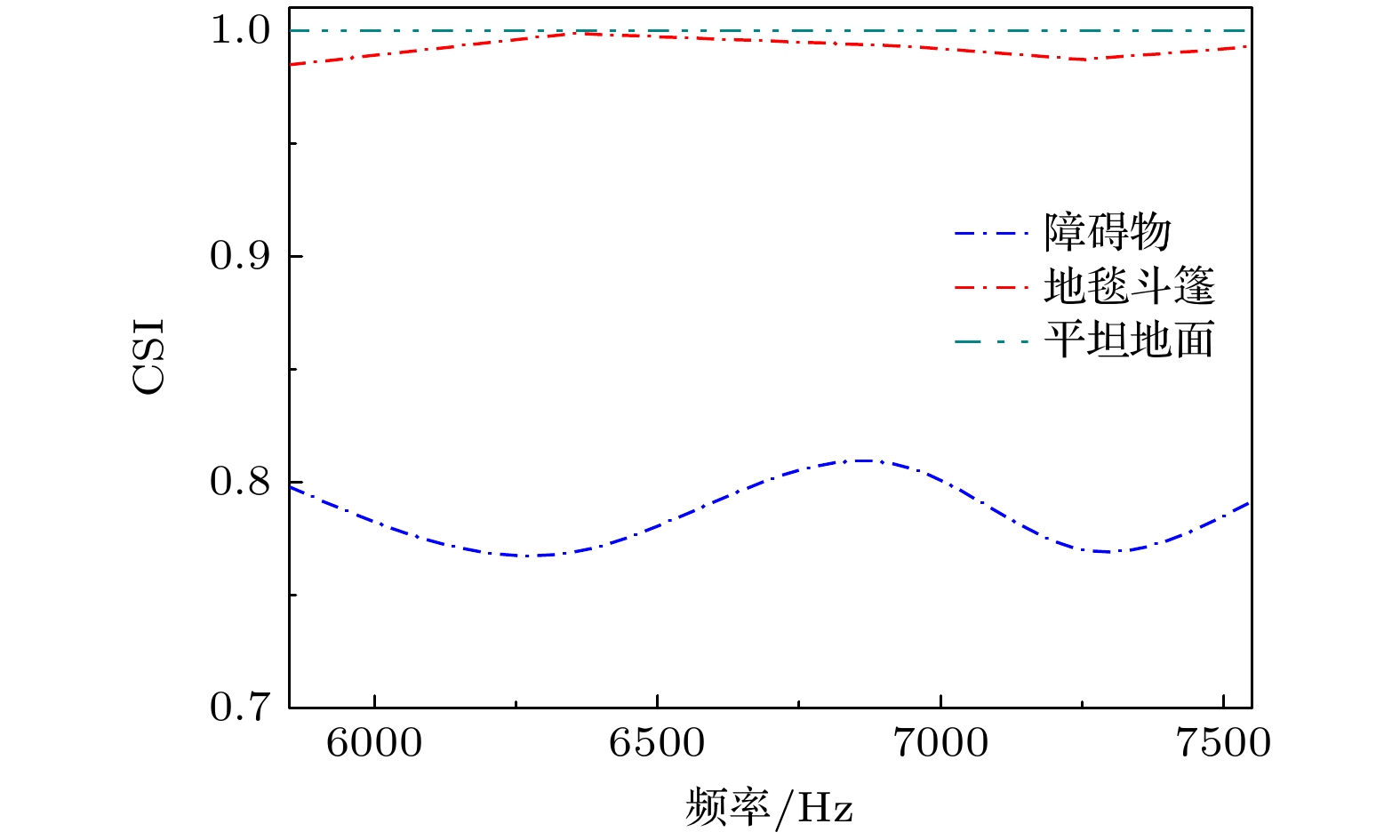
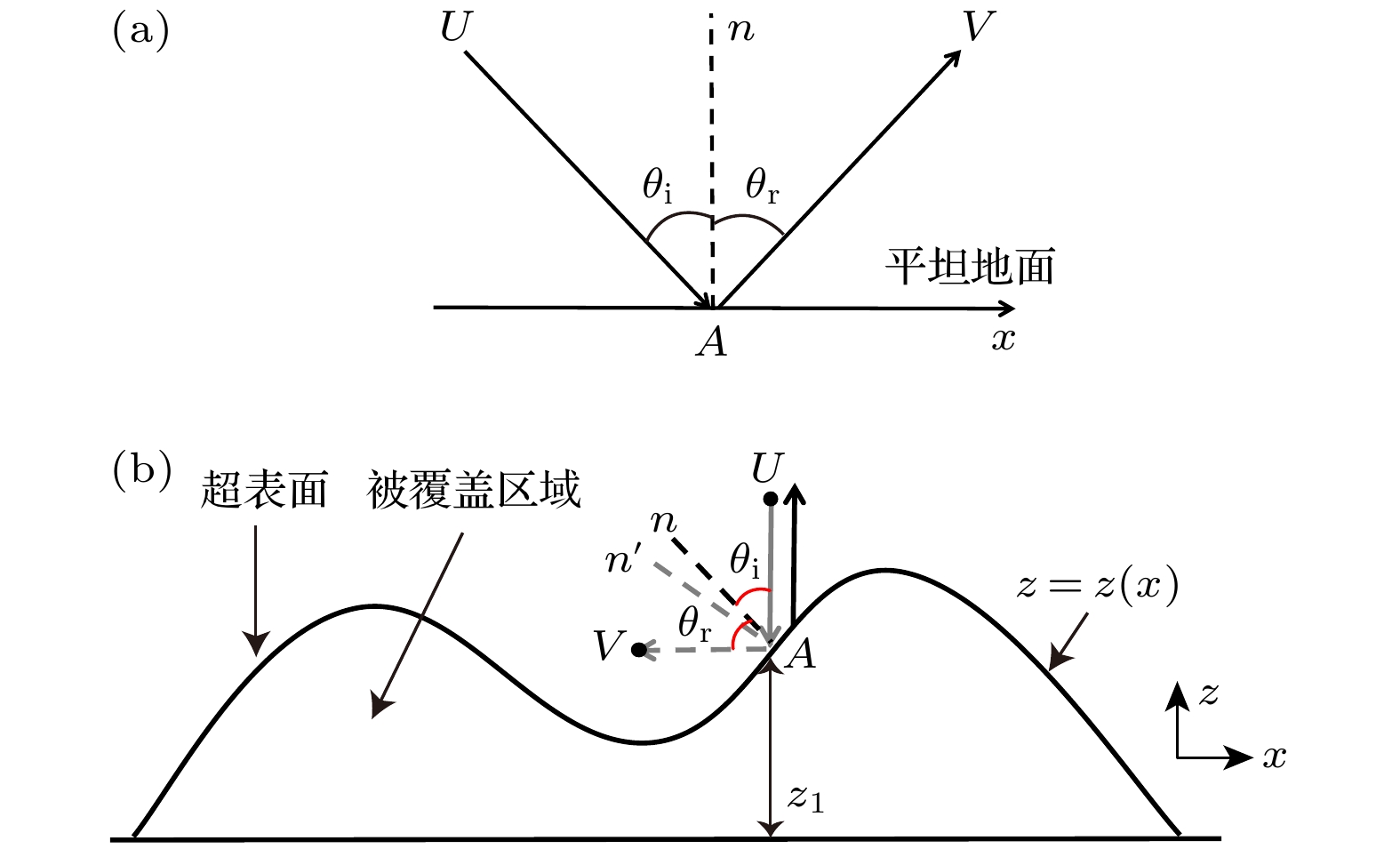
With the development of metamaterials, the acoustic cloaking has attracted extensive attention due to its novel physics and potential applications. In recent years, based on the phase compensation modulation from Generalized Snell’s law and coordinate transformation, the acoustic cloakings in underwater and air have been widely and deeply studied. However, there is still an urgent need to design acoustic cloaks that are thinner and less affected by the incident angle of acoustic waves. Further, the designed cloaks should have a wider operating band and be more suitable for irregular objects. In this paper, an ultrathin curved acoustic metasurface carpet cloaking is studied by using of phase compensation modulation. The phase modulation is based on Helmholtz resonance (HR). The metasurface carpet is immersed in air, since the vibration mode of acoustic wave in the air is relatively single, thus the physical essence can be elucidated more clearly. The carpet cloak is composed of 52 Helmholtz resonant units, and the size of resonant unit is less than 0.2 of working wavelength. The phase change of HR unit is solved analytically by using the Generalized Snell’s law, and confirmed by the Multiphysics COMSOL software. The parameter effects of HR unit on the phase change are studied, demonstrating that the phase change of HR unit is sensitive to the change of height and radius of HR unit, while the change of width of HR cavity neck can make the phase of HR unit change smoothly. Therefore, when building 52 HR units, the width of the HR cavity neck is designed, and the height and radius of HR unit stay fixed. The simulating results demonstrate that the designed cloak works well in a frequency range from 5850 Hz to 7550 Hz. Also, we study the cloaking effect for oblique incidence, and the results show that the carpet cloak works well for incident angle less than 30°. To quantitatively analyze the bandwidth of the cloaking, we calculate the cosine similarity value. It elucidates that the value of the cloak is very close to that of the flat ground in a corresponding working frequency range. The cloak designed in this work is made of ultrathin Helmholtz Resonant structures. This cloak is simple and easy to realize and conducive to potential applications. -
Keywords:
- acousitc metasurface /
- generalized Snell’s law /
- ultra-thin structure /
- carpet cloak
[1] Cummer S A, Christensen J, Alù A 2016 Nat. Rev. Mater. 1 16001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lu M H, Feng L, Chen Y F 2009 Mater. Today 12 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liao G X, Luan C C, Wang Z W, Liu J P, Yao X H, Fu J Z 2021 Adv. Mater. Technol. 6 2000787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zigoneanu L, Popa B I, Cummer S A 2014 Nat. Mater. 13 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bi Y, Jia H, Sun Z, Yang Y, Zhao H, Yang J 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 223502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chen H, Chan C T 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 183518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guild M D, Haberman M R, Alù A 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wei Q, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Z, Huang S, Li D, Zhu J, Li Y 2022 Natl. Sci. Rev. 9 nwab171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y, Tong Y 2021 Opt. Commun. 483 126590
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bi Y, Jia H, Lu W, Ji P, Yang J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen Y, Zheng M, Liu X, Bi Y, Sun Z, Xiang P, Yang J, Hu G 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 180104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sun Z, Sun X, Jia H, Bi Y, Yang J 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 094101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hu W, Fan Y, Ji P, Yang J 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 024911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang S, Xia C, Fang N 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 024301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen Y, Liu X, Hu G 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 15745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo J, Fang Y, Qu R, Zhang X 2023 Mater. Today 66 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ji W Q, Wei Q, Zhu X F, Wu D J 2019 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52 325302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jiang Z, Liang Q, Li Z, Chen T, Li D, Hao Y 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 2000827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Díaz-Rubio A, Tretyakov S A 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 125409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li X S, Wang Y F, Chen A L, Wang Y S 2020 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53 195301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang H, He J, Liu C, Ma F 2023 Appl. Acoust. 213 109639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian Y, Wei Q, Cheng Y, Xu Z, Liu X 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 221906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tang K, Qiu C, Ke M, Lu J, Ye Y, Liu Z 2015 Sci. Rep. 4 6517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Faure C, Richoux O, Félix S, Pagneux V 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 064103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhu Y, Assouar B 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 174109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhou H T, Fan S W, Li X S, Fu W X, Wang Y F, Wang Y S 2020 Smart Mater. Struct. 29 065016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] He J, Liang Q, Lv P, Wu Y, Chen T 2022 Appl. Acoust. 197 108957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhou H T, Fu W X, Wang Y F, Wang Y S, Laude V, Zhang C 2021 Mater. Des. 199 109414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang Y, Cheng Y, Liu X 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhu Y, Fan X, Liang B, Cheng J, Jing Y 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 021034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Yu G, Qiu Y, Li Y, Wang X, Wang N 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl. 15 064064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Guo J, Zhou J 2020 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53 505501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ji G, Huber J 2022 Appl. Mater. Today 26 101260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhu Y, Hu J, Fan X, Yang J, Liang B, Zhu X, Cheng J 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Zhou P, Jia H, Bi Y, Liao B, Yang Y, Yan K, Zhang J, Yang J 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 014050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
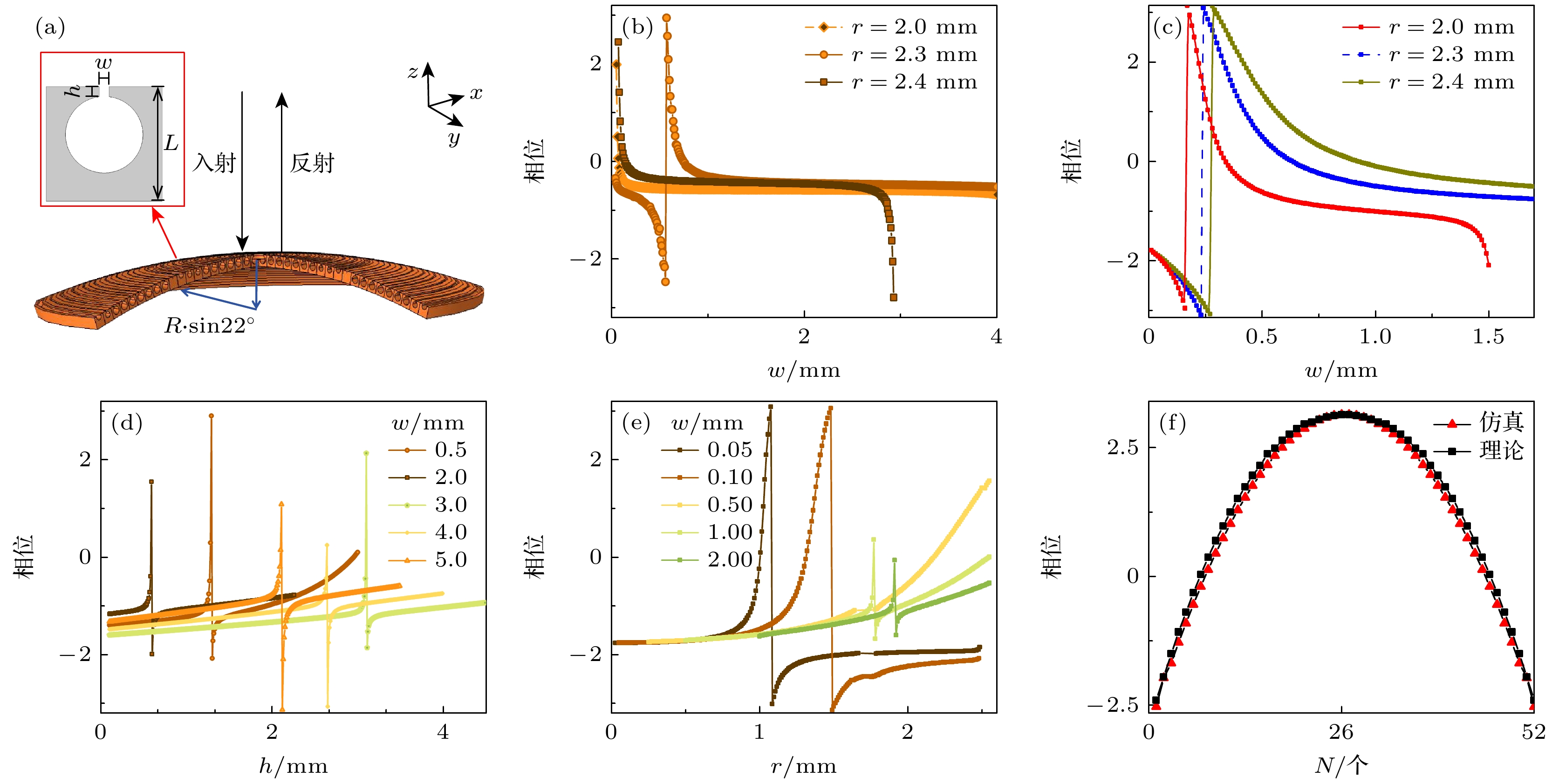
图 2 (a)地毯隐身超表面示意图, 弧形隐身斗篷及斗篷单个共振单元结构(红色框插图), 入射波从–z方向入射; (b), (c) 共振腔中r取不同值时单个共振单元反射相位随w的变化, 其中(b)入射波频率为3430 Hz, (c)入射波频率为6860 Hz; (d)共振腔中w取不同值时单个共振单元反射相位随h的变化; (e)共振腔中w取不同值时单个共振单元反射相位随r的变化; (f) 入射波频率为6860 Hz时, 弧形隐身斗篷中每个共振单元的反射相位(红色曲线)和由(5)式理论计算的相位(黑色曲线)
Figure 2. (a) Schematic sketch of the metasurface for carpet cloaking, the illustration of arc-shaped carpet cloak, inset showing the schematic diagram of the unit-cell for the carpet. The acoustic waves are incident from –z direction. The reflection phase of single HR unit varing with w for acoustic waves normal incidence with different frequency: (b) 3430 Hz; (c) 6860 Hz. For different w, the reflection phase of single HR unit varing with h (d) and varing with r (e) for acoustic waves normal incidence with frequence 6860 Hz. (f) The reflection phase of each HR unit in the designed AMCC (red curve) and that of theoretical calculation from Eq. (5) (black curve) for acoustic waves normal incidence with frequence 6860 Hz.
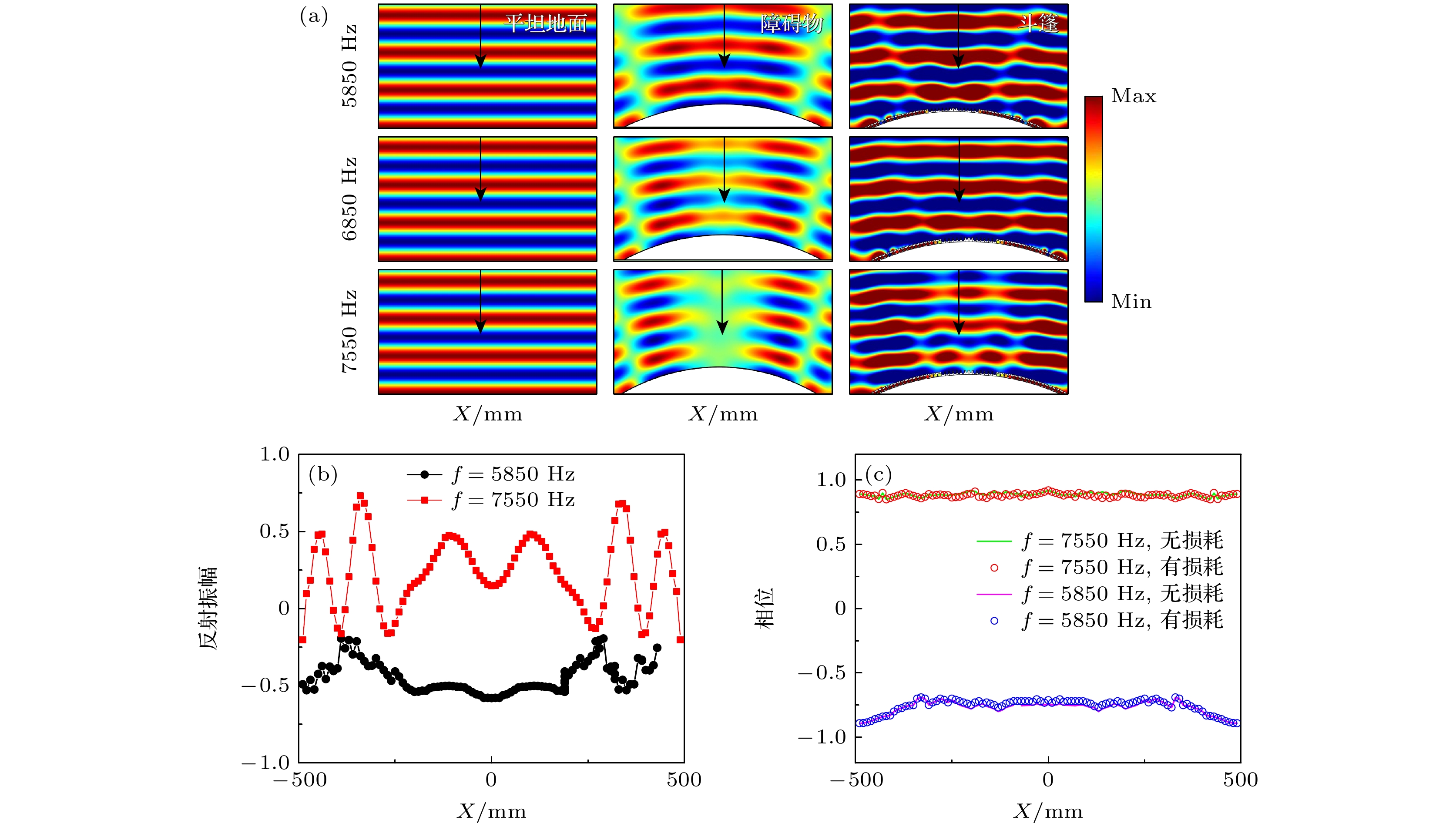
图 3 (a)平面波分别垂直入射至平坦地面、弧形障碍物及覆盖于弧形障碍物上的斗篷时的反射声压场分布; (b) 5850, 7550 Hz频率下Z = 800 mm时归一化反射振幅; (c) 5850, 7550 Hz频率下Z = 800 mm时反射波阵面相位
Figure 3. (a) Reflected pressure field distributions for a plane wave impinging on the flat ground, the arc-shaped object and the arc-shaped cloak; the normalized reflection amplitudes (b) and reflected wavefront phases (c) which located at Z = 800 mm for the incident frequency 5850 Hz and 7550 Hz.
表 1 隐身斗篷每个共振单元颈宽w和半径r参数表
Table 1. Parameter list of neck width w and radii r of resonant unit in the cloak.
序号 w/mm r/mm 序号 w/mm r/mm 1 2.920 1.5 14 0.380 2.4 2 4.455 2.4 15 0.426 2.4 3 4.457 2.4 16 0.472 2.4 4 4.458 2.4 17 0.520 2.4 5 4.459 2.4 18 0.531 2.4 6 4.461 2.4 19 0.621 2.4 7 4.462 2.4 20 0.685 2.4 8 0.060 2.4 21 0.755 2.4 9 0.119 2.4 22 0.852 2.4 10 0.177 2.4 23 0.980 2.4 11 0.233 2.4 24 1.234 2.4 12 0.286 2.4 25 1.574 2.4 13 0.377 2.4 26 3.749 2.4 -
[1] Cummer S A, Christensen J, Alù A 2016 Nat. Rev. Mater. 1 16001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lu M H, Feng L, Chen Y F 2009 Mater. Today 12 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liao G X, Luan C C, Wang Z W, Liu J P, Yao X H, Fu J Z 2021 Adv. Mater. Technol. 6 2000787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zigoneanu L, Popa B I, Cummer S A 2014 Nat. Mater. 13 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bi Y, Jia H, Sun Z, Yang Y, Zhao H, Yang J 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 223502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chen H, Chan C T 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 183518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guild M D, Haberman M R, Alù A 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wei Q, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Z, Huang S, Li D, Zhu J, Li Y 2022 Natl. Sci. Rev. 9 nwab171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y, Tong Y 2021 Opt. Commun. 483 126590
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bi Y, Jia H, Lu W, Ji P, Yang J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen Y, Zheng M, Liu X, Bi Y, Sun Z, Xiang P, Yang J, Hu G 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 180104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sun Z, Sun X, Jia H, Bi Y, Yang J 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 094101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hu W, Fan Y, Ji P, Yang J 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 024911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang S, Xia C, Fang N 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 024301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen Y, Liu X, Hu G 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 15745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo J, Fang Y, Qu R, Zhang X 2023 Mater. Today 66 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ji W Q, Wei Q, Zhu X F, Wu D J 2019 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52 325302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jiang Z, Liang Q, Li Z, Chen T, Li D, Hao Y 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 2000827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Díaz-Rubio A, Tretyakov S A 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 125409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li X S, Wang Y F, Chen A L, Wang Y S 2020 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53 195301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang H, He J, Liu C, Ma F 2023 Appl. Acoust. 213 109639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian Y, Wei Q, Cheng Y, Xu Z, Liu X 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 221906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tang K, Qiu C, Ke M, Lu J, Ye Y, Liu Z 2015 Sci. Rep. 4 6517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Faure C, Richoux O, Félix S, Pagneux V 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 064103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhu Y, Assouar B 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 174109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhou H T, Fan S W, Li X S, Fu W X, Wang Y F, Wang Y S 2020 Smart Mater. Struct. 29 065016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] He J, Liang Q, Lv P, Wu Y, Chen T 2022 Appl. Acoust. 197 108957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhou H T, Fu W X, Wang Y F, Wang Y S, Laude V, Zhang C 2021 Mater. Des. 199 109414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang Y, Cheng Y, Liu X 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhu Y, Fan X, Liang B, Cheng J, Jing Y 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 021034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Yu G, Qiu Y, Li Y, Wang X, Wang N 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl. 15 064064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Guo J, Zhou J 2020 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53 505501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ji G, Huber J 2022 Appl. Mater. Today 26 101260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhu Y, Hu J, Fan X, Yang J, Liang B, Zhu X, Cheng J 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Zhou P, Jia H, Bi Y, Liao B, Yang Y, Yan K, Zhang J, Yang J 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 014050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4785
- PDF Downloads: 155
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: