-
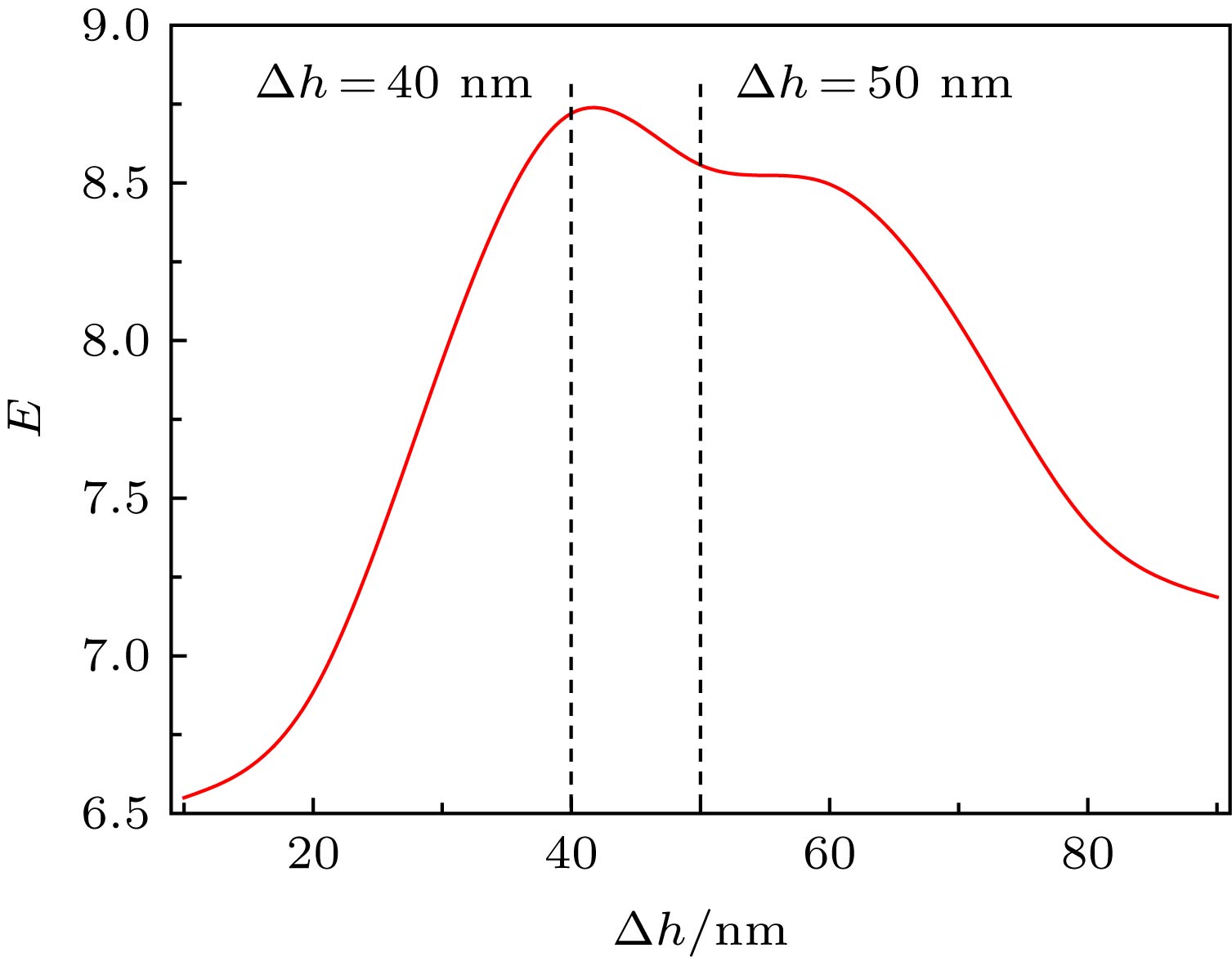
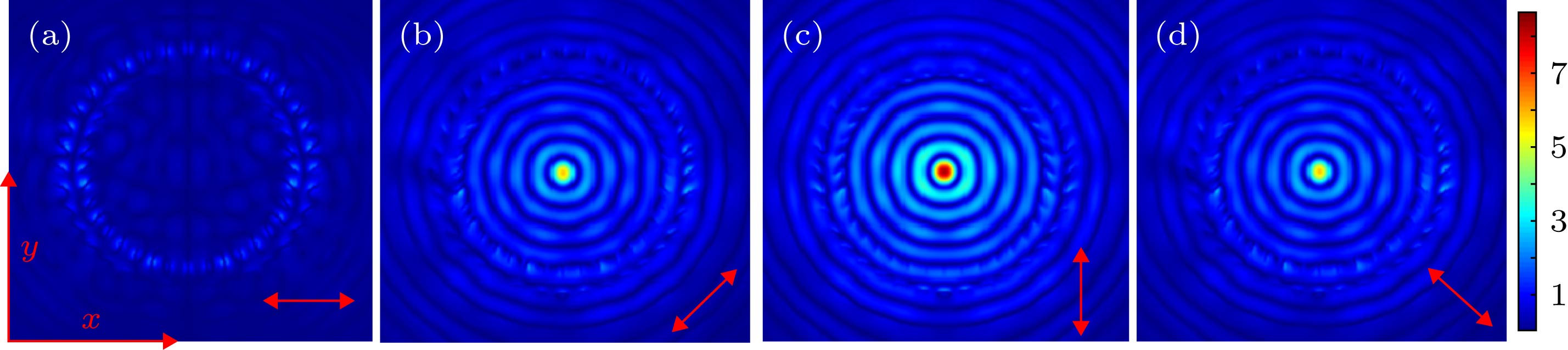
为了实现对入射光的近场亚波长增强聚焦, 设计了一种由内部矩形纳米狭缝圆环阵列和外部多圆环狭缝构成的超表面结构, 得到了该结构激发的表面等离激元电场表达式, 并从物理机理上解释了该结构中心聚焦及增强聚焦的原理. 利用时域有限差分方法仿真研究了该超表面结构在不同偏振态入射光下的激发场聚焦特性. 根据理论推导与仿真结果可得, 该结构在波长为980 nm的圆偏振光入射下于近场的金属表面结构中心处生成半高宽为650 nm左右的亚波长聚焦光斑, 其场分布为近似的第一类贝塞尔函数. 与单一的矩形纳米狭缝圆环阵列结构相比, 带有外部多圆环狭缝的复合结构具有更好的增强聚焦效果, 使得中心焦斑强度提升了一倍, 且更有利于对激发场进行调控. 除此之外, 还讨论了任意偏振方向的线偏振光入射结构激发的电场, 得到了电场的解析表达式, 即入射光偏振角的正弦函数包络乘上第一类贝塞尔函数. 本文的研究对基于超表面结构的亚波长光调控有一定的指导意义, 在光镊、亚波长尺度光信息传输与处理等领域也有一定的应用价值.
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are electromagnetic excitations propagating along the metal-dielectric interface. The SPPs excited by the metal micro/nano structures have the ability to manipulate the light on a subwavelength scale. The SPPs are of interest to researchers for its excellent subwavelength field confinement and local field enhancement. So far, the SPPs have found numerous applications in optical tweezers, biological sensors, and near-field holographic imaging, due to its subwavelength focusing. In order to achieve enhanced near field subwavelength focusing, we propose a metasurface structure in this paper, which is composed of rectangular nanoslit circular arrays and multilayer annular slits. The function of the inner ring arrays is to excite SPPs and the outer ring slits is to enhance focusing. The electric field expression of SPP is studied analytically and theoretically, and then the principle of rectangular nanoslit to excite SPP and the inner ring array structure to generate central focusing are explained. The parameters of the structure are optimized, and the focusing characteristics of the metasurface structure under different polarization light are studied by using the finite difference time domain method. Furthermore, we explain the principle of the external structure enhancing focusing by introducing the theory of Fresnel zone plate and depth modulation. The analytical expressions and simulations show that when the incident polarized light has a wavelength of 980 nm, the focal spot having a full width at half maximum of about 650 nm, and the distribution of the coupled field can be approximately expressed by the first kind Bessel function. Compared with the former single circular array structure, the composite structure proposed in this paper has a good effect of both enhancing the central focusing and inhibiting the outer field divergence, and the center focal spot intensity is doubled. In addition, the electric field excited by the arbitrary linearly polarized light is also discussed, the electric field satisfies the form of the polarization angle sinusoidal function multiplied by a Bessel function. The research results of our study have some applications in subwavelength light modulation, near-field imaging, optical tweezers, and subwavelength scale optical information processing and so on. -
Keywords:
- surface plasmon polaritons /
- subwavelength focusing /
- metasurface structure /
- Bessel optical field
[1] Barnes W L, Dereux A, Ebbesen T W 2003 Nature 424 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fang N, Lee H, Sun C, Zhang X 2005 Science 308 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lieven V, Catrysse P B, Yu Z F, Fan S H 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 033902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yin L, Vlasko-Vlasov V K, Pearson J, Hiller J M, Hua J, Welp U, Brown D E, Kimball C W 2005 Nano Lett. 5 1399
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shen Z, Hu Z J, Yuan G H, Min C J, Fang H, Yuan X C 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 4627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang J J, Duan G T, Liu G Q, Yue L, Chen Z X, Lei X, Cai W P 2016 J. Hazard. Mater. 303 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Coluccio M L, Francardi M, Gentile F, Candeloro P, Ferrara L, Perozziello G, Fabrizio E D 2014 Sensors 14 6056
[8] Song W T, Fang Z Y, Huang S, Lin F, Zhu X 2010 Opt. Express 18 14762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Holmgaard T, Gosciniak J, Bozhevolnyi S I 2010 Opt. Express 18 23009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Raghunathan S B, Gan C H, Dijk T V, Kim B E, Schouten H F, Ubachs W, Lalanne P, Visser T D 2012 Opt. Express 20 15326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Song E Y, Lee Y L, Hong J, Lee K, Lee Y, Lee G Y, Kim H, Lee B 2016 Laser Photon. Rev. 10 299
[12] López-Tejeira F, Rodrigo S G, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J, Devaux E, Ebbesen T W, Krenn J R, Radko I P, Bozhevolnyi S I, González M U 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Radko I P, Bozhevolnyi S I, Brucoli G, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J, Boltasseva A 2009 Opt. Express 17 7228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li X W, Huang L L, Tan Q F, Bai B F, Jin G F 2011 Opt. Express 19 6541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li L, Li T, Wang S, Zhu S, Zhang X 2011 Nano Lett. 11 4357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tanemura T, Balram K C, Dany-Sebastien L G, Pierre W, White J S, Brongersma M L, Miller D A B 2011 Nano Lett. 11 2693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lee S Y, Kim K, Lee G Y, Lee B 2015 Opt. Express 23 15598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lee B, Park H, Kim K Y, Kim K, Lee S Y, Kim S J 2015 Optica 2 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wintz D, Genevet P, Ambrosio A, Woolf A, Capasso F 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kim H, Park J, Cho S W, Lee S Y, Kang M, Lee B 2010 Nano Lett. 10 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang Y J, Thirunavukkarasu G, Babiker M, Yuan J 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 094802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu J L, Gao Y, Ran L L, Guo K, Lu Z W, Liu S T 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 013116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen C F, Ku C T, Tai Y H, Wei P K, Lin H N, Huang C B 2015 Nano Lett. 15 2746
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rui G H, Abeysinghe D C, Nelson R L, Zhan Q W 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 2237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhou H L, Dong J J, Zhou Y F, Zhang J H, Liu M, Zhang X L 2015 IEEE Photonics J. 7 1
[26] Ren H R, Li X P, Zhang Q M, Gu M 2016 Science 352 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Garoli D, Ongarello T, Zilio P, Carli M, Romanato F 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 1161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Garoli D, Romanato F, Carli M, Zilio P, Giorgis V 2014 Opt. Express 22 26302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hu C B, Xu J, Ding J 2017 J. Mod. Opt. 64 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 王帅, 邓子岚, 王发强, 王晓雷, 李向平 2019 68 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S, Deng Z L, Wang F Q, Wang X L, Li X P 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Lin J, Mueller J P B, Wang Q, Yuan G H, Antoniou N, Yuan X C, Capasso F 2013 Science 340 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lee S Y, Kim S J, Kwon H, Lee B 2015 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27 705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Chen Y G, Li Z Y 2016 Plasmonics 11 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Li X, Zhang R R, Zhang Y Q, Ma L, He C W, Ren X R, Liu C X, Cheng C F 2018 New J. Phys. 20 063037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang S, Wang S, Zhang Y 2018 Opt. Express 26 5461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wang J, Zhang J 2018 Opt. Express 26 14626
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Jiang Q, Bao Y J, Lin F, Zhu X, Zhang S, Fang Z Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1705503
[38] 祁云平, 周培阳, 张雪伟, 严春满, 王向贤 2018 67 107104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y P, Zhou P Y, Zhang X W, Yan C M, Wang X X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 107104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Maier S A 2007 Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications (Berlin: Springer Berlin) pp13−34
[40] Fu Y Q, Zhou W, Lim L E N, Du C L, Luo X G 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 061124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Shi H, Dong X, Lv Y, Du C 2009 Appl. Phys. B 95 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
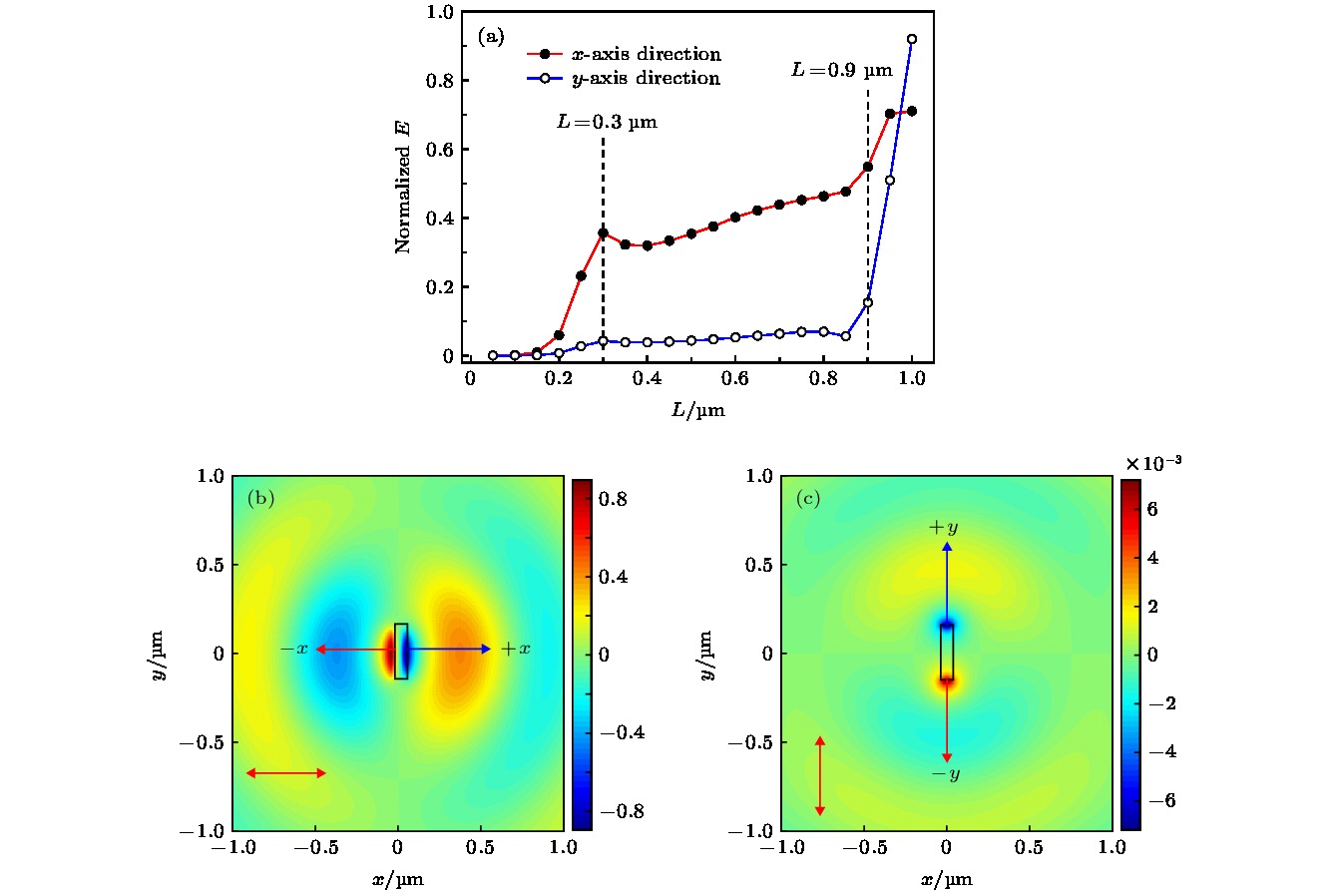
图 1 矩形纳米狭缝激发的SPPs场 (a) x方向线偏振光入射下x和y方向电场强度随L的变化; (b) x方向线偏振光入射激发的场; (c) y方向线偏振光入射激发的场
Fig. 1. SPPs field excited by rectangular nanoslit: (a) Electric field intensity along the L curves in the x and y direction with the x-direction linearly polarized light incident; (b) electric field excited by the incident light in the x direction; (c) electric field excited by the incident light in the y direction.
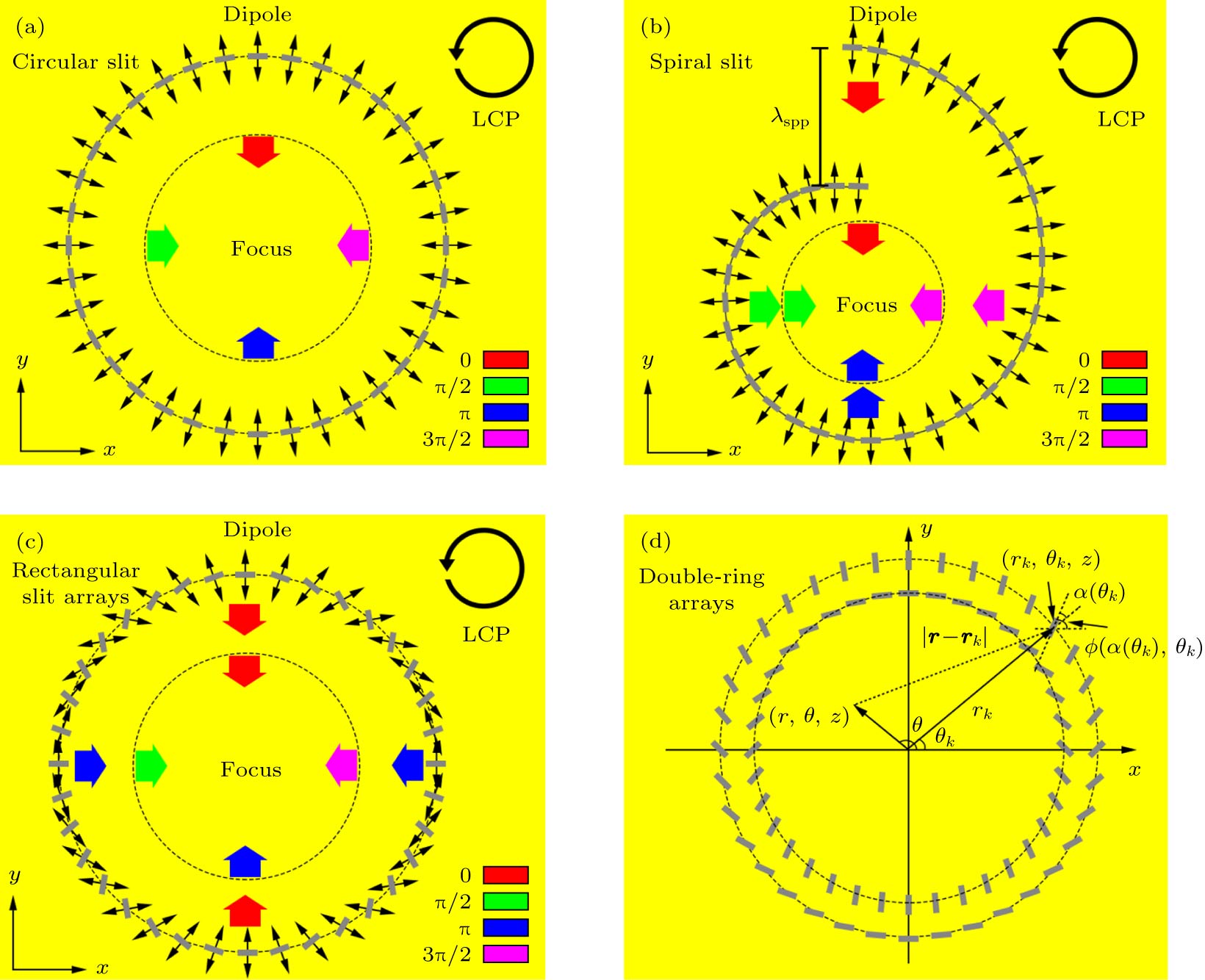
图 2 左旋圆偏振光入射下, (a) 圆狭缝、(b) 螺旋线狭缝、(c) 旋转排列的矩形纳米狭缝阵列激发SPPs原理示意图; (d) 矩形纳米狭缝双圆环阵列结构示意图
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of excitation of SPPs by (a) circular slit, (b) spiral slit, (c) rotating rectangular nanoslit arrays under the incidence of left-handed circularly polarized light; (d) schematic diagram of double-ring rectangular nanoslit arrays.
图 6 不同偏振方向线偏振光激发的电场分布 (a)
$\psi = {0^\circ }$ ; (b)$\psi = +{45^\circ }$ ; (c)$\psi = {90^\circ }$ ; (d)$\psi = -{45^\circ }$ Fig. 6. Electric field distribution excited by linearly polarized light in different polarization directions: (a)
$\psi = {0^\circ }$ ; (b)$\psi = +{45^\circ }$ ; (c)$\psi = {90^\circ }$ ; (d)$\psi = -{45^\circ }$ . -
[1] Barnes W L, Dereux A, Ebbesen T W 2003 Nature 424 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fang N, Lee H, Sun C, Zhang X 2005 Science 308 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lieven V, Catrysse P B, Yu Z F, Fan S H 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 033902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yin L, Vlasko-Vlasov V K, Pearson J, Hiller J M, Hua J, Welp U, Brown D E, Kimball C W 2005 Nano Lett. 5 1399
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shen Z, Hu Z J, Yuan G H, Min C J, Fang H, Yuan X C 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 4627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang J J, Duan G T, Liu G Q, Yue L, Chen Z X, Lei X, Cai W P 2016 J. Hazard. Mater. 303 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Coluccio M L, Francardi M, Gentile F, Candeloro P, Ferrara L, Perozziello G, Fabrizio E D 2014 Sensors 14 6056
[8] Song W T, Fang Z Y, Huang S, Lin F, Zhu X 2010 Opt. Express 18 14762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Holmgaard T, Gosciniak J, Bozhevolnyi S I 2010 Opt. Express 18 23009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Raghunathan S B, Gan C H, Dijk T V, Kim B E, Schouten H F, Ubachs W, Lalanne P, Visser T D 2012 Opt. Express 20 15326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Song E Y, Lee Y L, Hong J, Lee K, Lee Y, Lee G Y, Kim H, Lee B 2016 Laser Photon. Rev. 10 299
[12] López-Tejeira F, Rodrigo S G, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J, Devaux E, Ebbesen T W, Krenn J R, Radko I P, Bozhevolnyi S I, González M U 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Radko I P, Bozhevolnyi S I, Brucoli G, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J, Boltasseva A 2009 Opt. Express 17 7228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li X W, Huang L L, Tan Q F, Bai B F, Jin G F 2011 Opt. Express 19 6541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li L, Li T, Wang S, Zhu S, Zhang X 2011 Nano Lett. 11 4357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tanemura T, Balram K C, Dany-Sebastien L G, Pierre W, White J S, Brongersma M L, Miller D A B 2011 Nano Lett. 11 2693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lee S Y, Kim K, Lee G Y, Lee B 2015 Opt. Express 23 15598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lee B, Park H, Kim K Y, Kim K, Lee S Y, Kim S J 2015 Optica 2 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wintz D, Genevet P, Ambrosio A, Woolf A, Capasso F 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kim H, Park J, Cho S W, Lee S Y, Kang M, Lee B 2010 Nano Lett. 10 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang Y J, Thirunavukkarasu G, Babiker M, Yuan J 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 094802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu J L, Gao Y, Ran L L, Guo K, Lu Z W, Liu S T 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 013116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen C F, Ku C T, Tai Y H, Wei P K, Lin H N, Huang C B 2015 Nano Lett. 15 2746
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rui G H, Abeysinghe D C, Nelson R L, Zhan Q W 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 2237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhou H L, Dong J J, Zhou Y F, Zhang J H, Liu M, Zhang X L 2015 IEEE Photonics J. 7 1
[26] Ren H R, Li X P, Zhang Q M, Gu M 2016 Science 352 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Garoli D, Ongarello T, Zilio P, Carli M, Romanato F 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 1161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Garoli D, Romanato F, Carli M, Zilio P, Giorgis V 2014 Opt. Express 22 26302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hu C B, Xu J, Ding J 2017 J. Mod. Opt. 64 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 王帅, 邓子岚, 王发强, 王晓雷, 李向平 2019 68 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S, Deng Z L, Wang F Q, Wang X L, Li X P 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Lin J, Mueller J P B, Wang Q, Yuan G H, Antoniou N, Yuan X C, Capasso F 2013 Science 340 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lee S Y, Kim S J, Kwon H, Lee B 2015 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27 705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Chen Y G, Li Z Y 2016 Plasmonics 11 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Li X, Zhang R R, Zhang Y Q, Ma L, He C W, Ren X R, Liu C X, Cheng C F 2018 New J. Phys. 20 063037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang S, Wang S, Zhang Y 2018 Opt. Express 26 5461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wang J, Zhang J 2018 Opt. Express 26 14626
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Jiang Q, Bao Y J, Lin F, Zhu X, Zhang S, Fang Z Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1705503
[38] 祁云平, 周培阳, 张雪伟, 严春满, 王向贤 2018 67 107104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y P, Zhou P Y, Zhang X W, Yan C M, Wang X X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 107104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Maier S A 2007 Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications (Berlin: Springer Berlin) pp13−34
[40] Fu Y Q, Zhou W, Lim L E N, Du C L, Luo X G 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 061124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Shi H, Dong X, Lv Y, Du C 2009 Appl. Phys. B 95 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11407
- PDF下载量: 191
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: