-
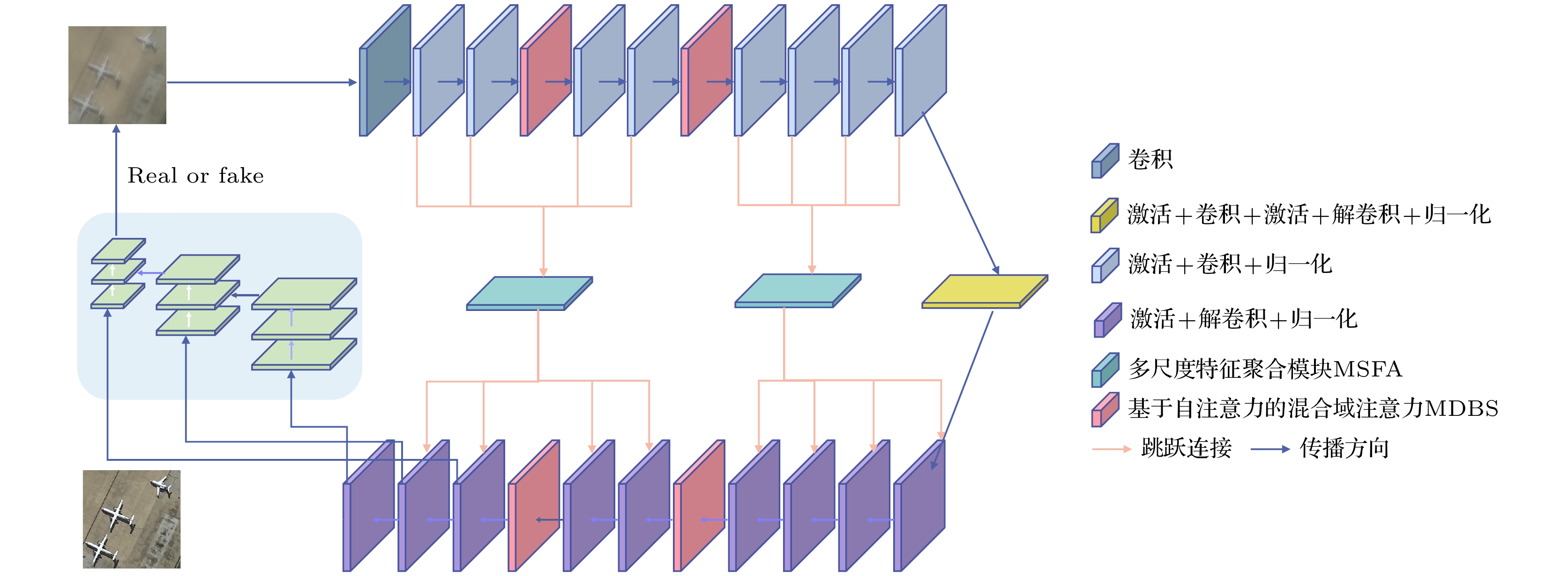
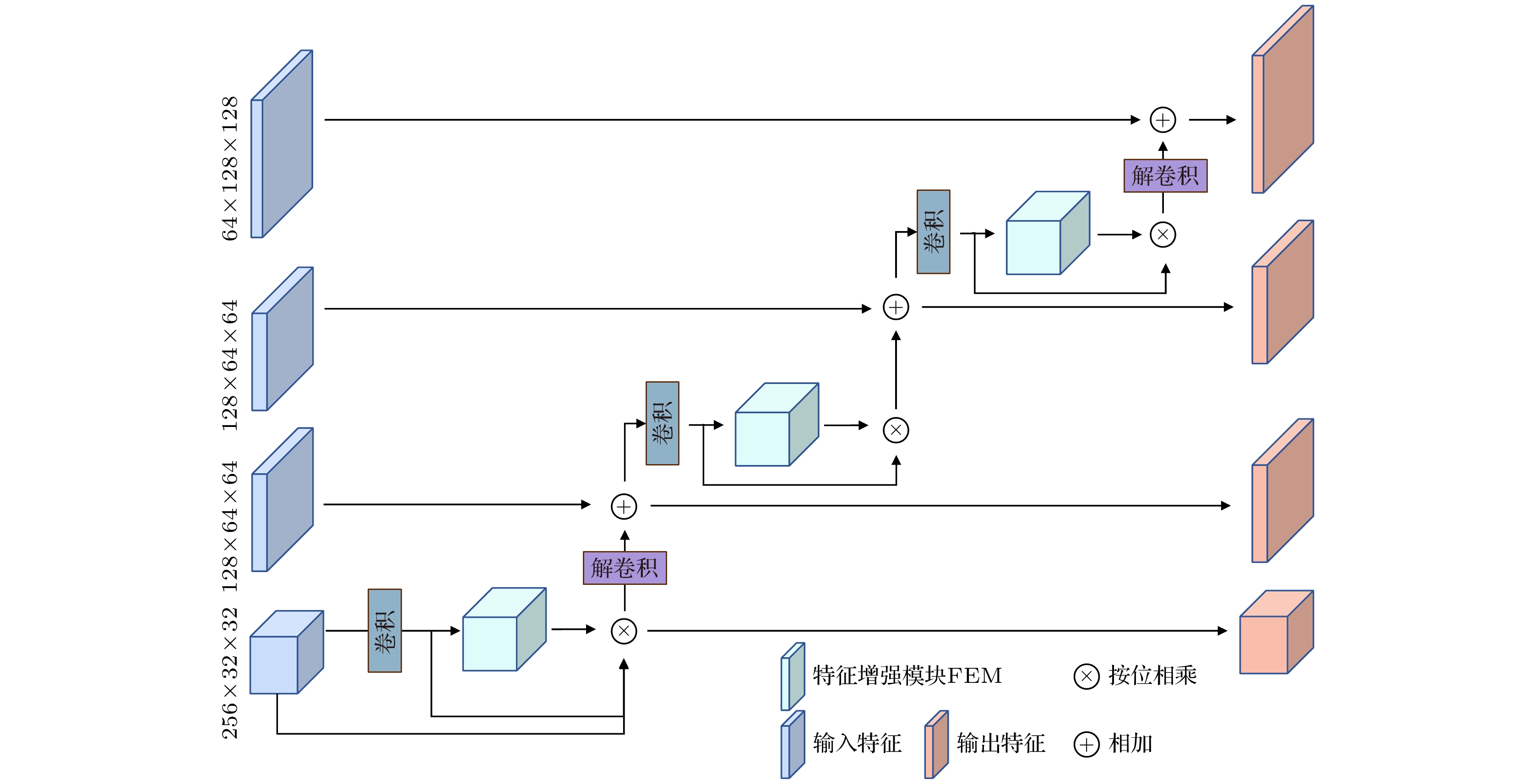
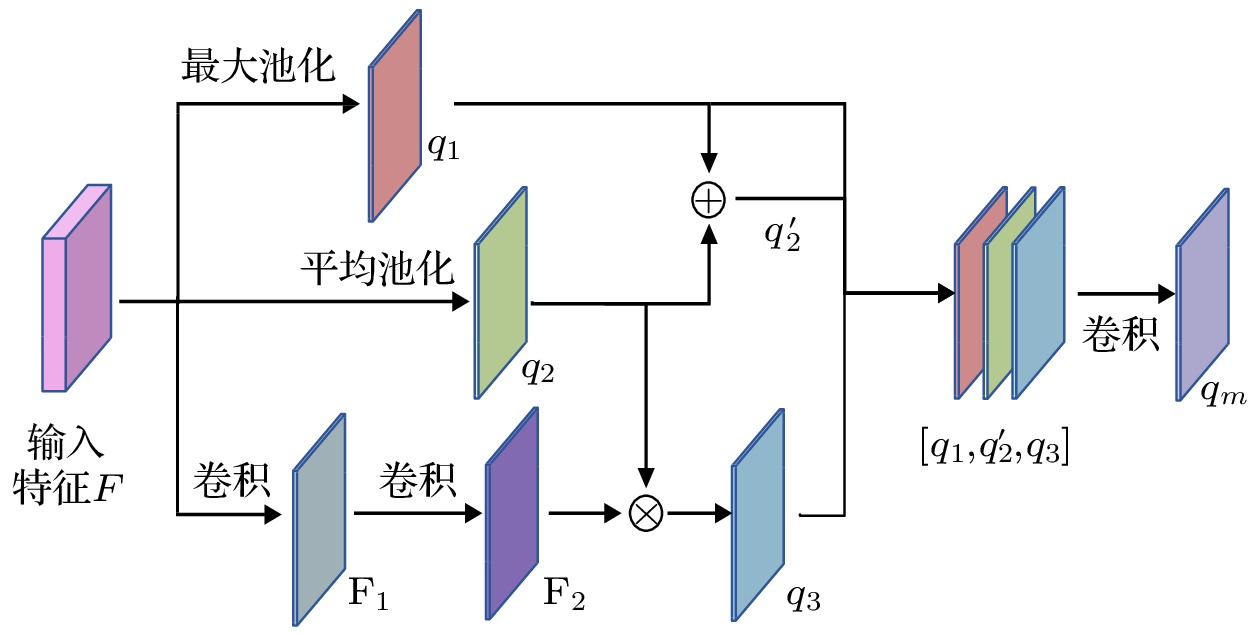
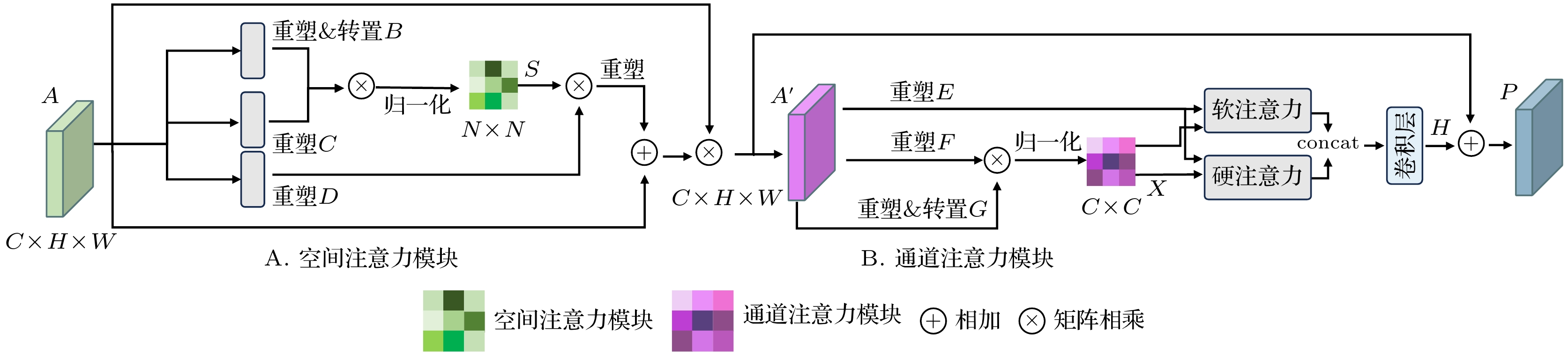
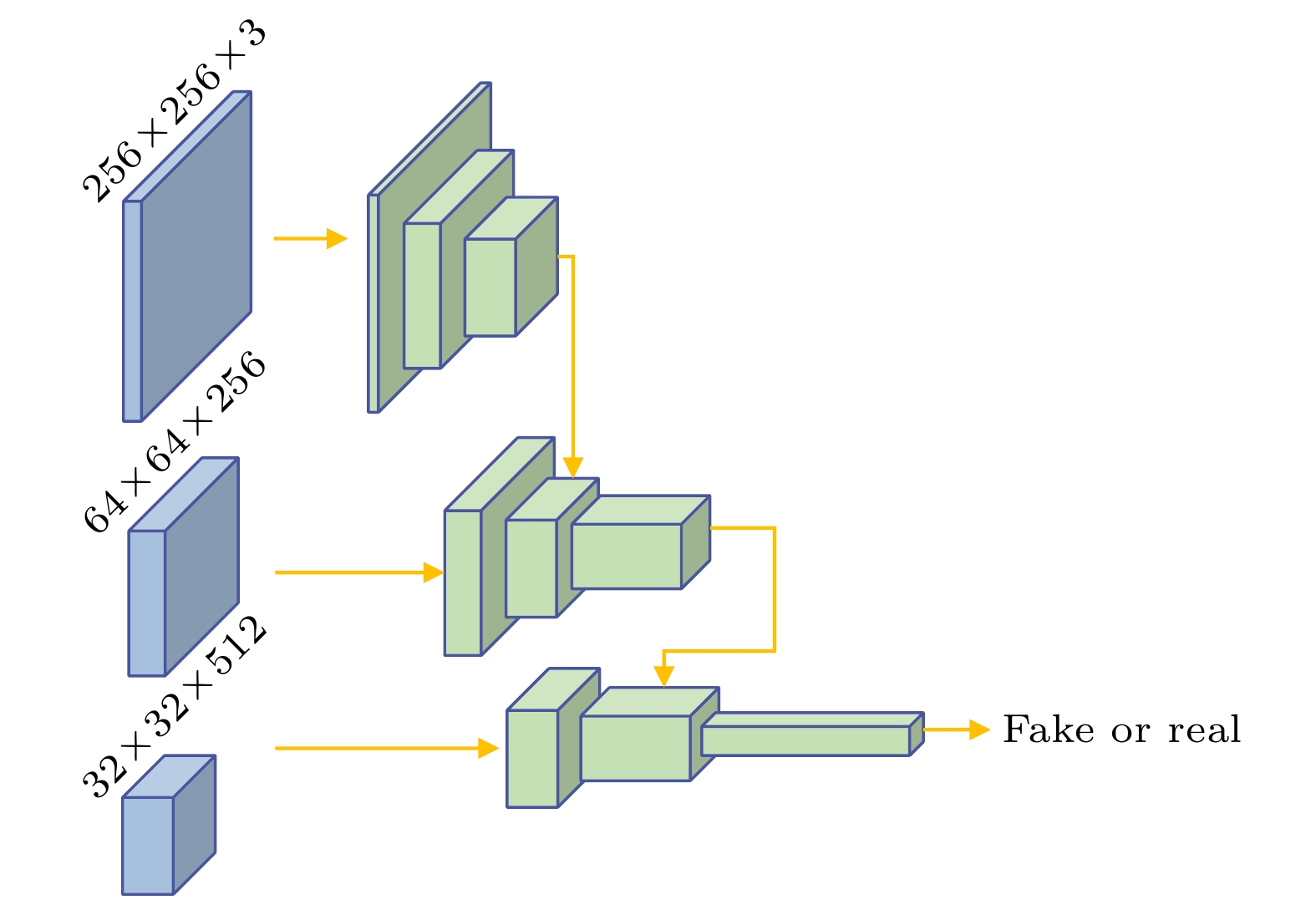
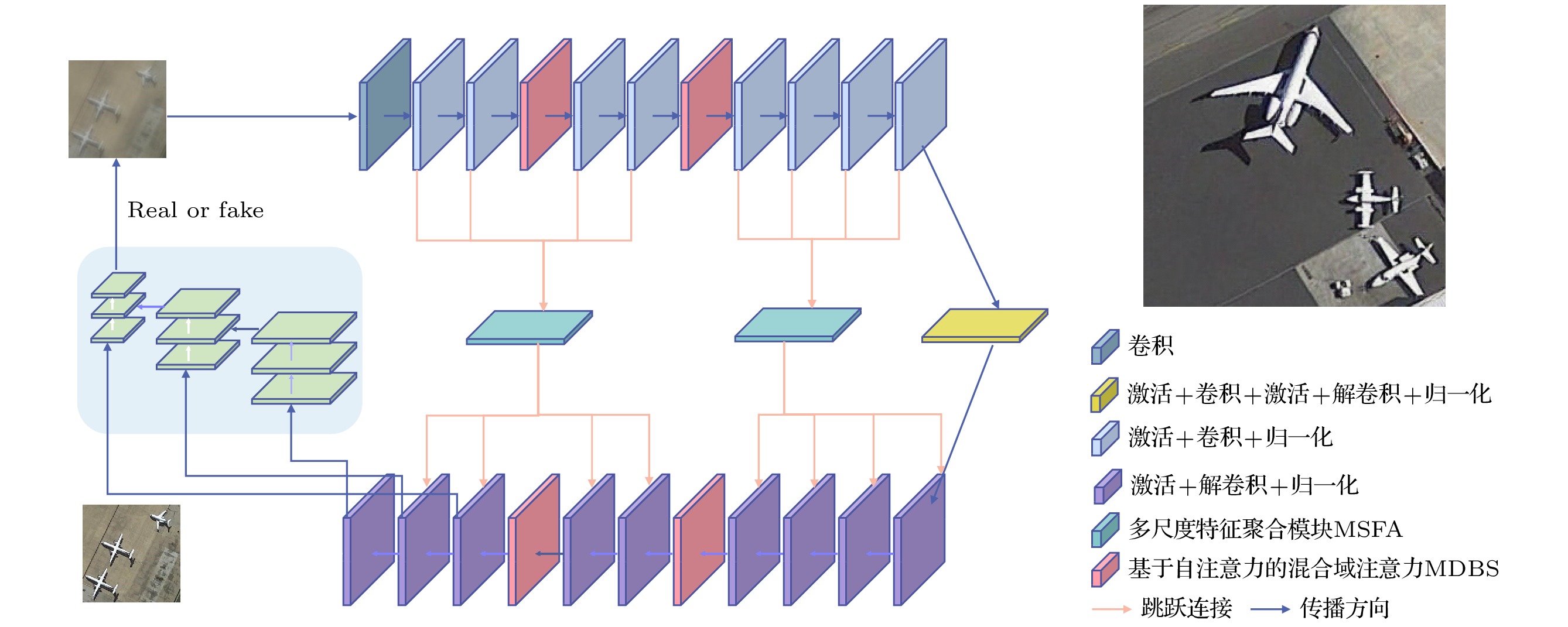
With the wide applications of high-resolution imaging technology in topographic mapping, astronomical observation, and military reconnaissance and other fields, the requirements for imaging resolution of optical system are becoming higher and higher . According to the diffraction limit and Rayleigh criterion, the imaging resolution of the optical system is proportional to the size of the aperture of the system, but affected by the material and the processing of the optical component: the single aperture of the optical system cannot be infinitely enlarged. Therefore the synthetic aperture technology is proposed to replace the single large aperture optical system. Owing to the effect of sub-aperture arrangement and light scattering, the imaging of synthetic aperture optical system will be degraded because of insufficient light area and phase distortion. The traditional imaging restoration algorithm of synthetic aperture optical system is sensitive to noise, overly relies on degraded model, requires a lot of manually designed models, and has poor adaptability. To solve this problem, a multi-scale feature enhancement method of restoring the synthetic aperture optical image is proposed in this work. U-Net is used to obtain multi-scale feature, and self-attention in mixed domain is used to improve the ability of of the network to extract the features in space and channel. Multi-scale feature fusion module and feature enhancement module are constructed to fuse the information between features on different scales. The information interaction mode of the codec layer is optimized, the attention of the whole network to the real structure of the original image is enhanced, and the artifact interference caused by ringing is avoided in the process of restoration. The final experimental results are 1.51%, 4.42% and 5.22% higher than those from the advanced deep learning algorithms in the evaluation indexes of peak signal-to-noise ratio, structural similarity and perceived similarity, respectively. In addition, the method presented in this work has a good restoration effect on the degraded images to different degrees of synthetic aperture, and can effectively restore the degraded images and the images with abnormal light, so as to solve the problem of imaging degradation of synthetic aperture optical system. The feasibility of deep learning method in synthetic aperture optical image restoration is proved.
-
Keywords:
- image processing /
- synthetic aperture /
- multi-scale /
- feature fusion
[1] Li J J, Zhou N, Sun J S, Zhou S, Bai Z D, Lu L P, Chen Q, Zuo C 2022 Light Sci. Appl. 11 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李道京, 高敬涵, 崔岸婧, 周凯, 吴疆 2022 中国激光 49 0310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li D J, Gao J H, Cui H J, Zhou K, Wu J 2022 Chin. J. Lasers 49 0310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shinwook K, Youngchun Y 2023 Opt. Express 31 4942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 刘政, 王胜千, 饶长辉 2012 61 039501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z, Wang S Q, Rao C H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin 61 039501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sun J, Cao W F, Xu Z B, Ponce J 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Viion and Pattern Recognition Boston, MA, USA, June 7–12, 2015 p769
[6] Tao X, Gao H Y, Shen X Y, Wang J, Jia J Y 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18–23, 2018 p8174
[7] Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, Hayat M, Khan F S, Yang M H, Shao L 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Nashville, TN, USA, June 20–25, 2021 p14816
[8] Chong M, Wang Q, Zhang J 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition New Orleans, LA, USA, June 18–24, 2022 p17378
[9] Li, D S, Zhang Y, Cheung K, Wang X G, Qin H W, Li H S 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision ( ECCV) Tel Aviv, Israel October 23–27, 2022 p736
[10] Kupyn O, Budzan V, Mykhailych M, Mishkin D, Matas J 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18–23, 2018 p8183
[11] Kupyn O, Martyniuk T, Wu J R, Wang Z Y 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Seoul, Korea (South), Oct. 27–Nov. 2, 2019 p8877
[12] 江泽涛, 覃露露 2020 电子学报 48 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang Z T, Qin L L 2020 J. Electron. 48 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 陈炳权, 朱熙, 汪政阳, 梁寅聪 2022 湖南大学学报(自然科学版) 49 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B Q, Zhu X, Wang Z Y, Liang Y C 2022 J. Hunan Univ. (Nat. Sci. ) 49 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王山豹, 梁栋, 沈玲 2023 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报 35 1109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S B, Liang D, Shen 2023 J. Comput. Aided Design Comput. Graphics 35 1109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘杰, 祁箬, 韩轲 2023 光学精密工程 31 2080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Qi R, Han K 2023 Opt. Precis. Eng. 31 2080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Woo S H, Park J, Lee J Y, Kweon I S 2018 Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Munich, Germany, September 8–14, 2018 p3
[17] 王向军, 欧阳文森 2022 红外与激光工程 51 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X J, Ouyang W S 2022 Infrared Laser Eng. 51 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, Hayat M, Khan F S, Yang M H 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition New Orleans, LA, USA, June 18–24, 2022 p5718
[19] Li Y W, Fan Y C, Xiang X Y, Demandolx D, Ranjan R, Timofte R, Gool L V 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Vancouver, BC, Canada, June 17–24, 2023 p18278
[20] Tsai F J, Peng Y T, Lin Y Y , Tsai C C, Lin C W 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022 p146
[21] Chen L Y, Chu X J, Zhang X, Sun J 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022 p17
[22] Tang J, Wang K Q, Ren Z R, Zhang W, Wu X Y, Di J L, Liu G D, Zhao J L 2020 Opt. Lasers Eng. 139 106463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tang J, Wu J, Wang K Q, Ren Z B, Wu X Y, Hu L S, Di J L, Liu G D, Zhao J L 2021 Opt. Lasers Eng. 146 106707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
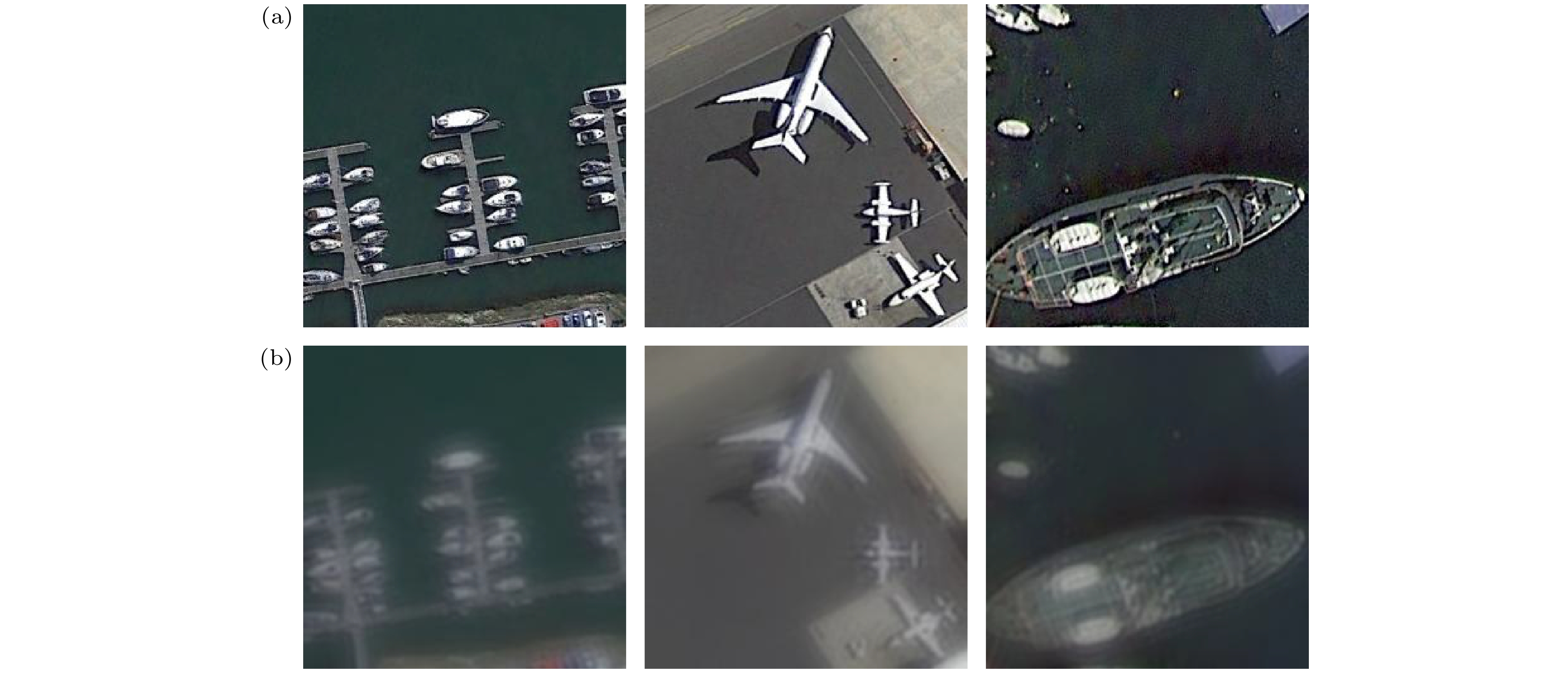
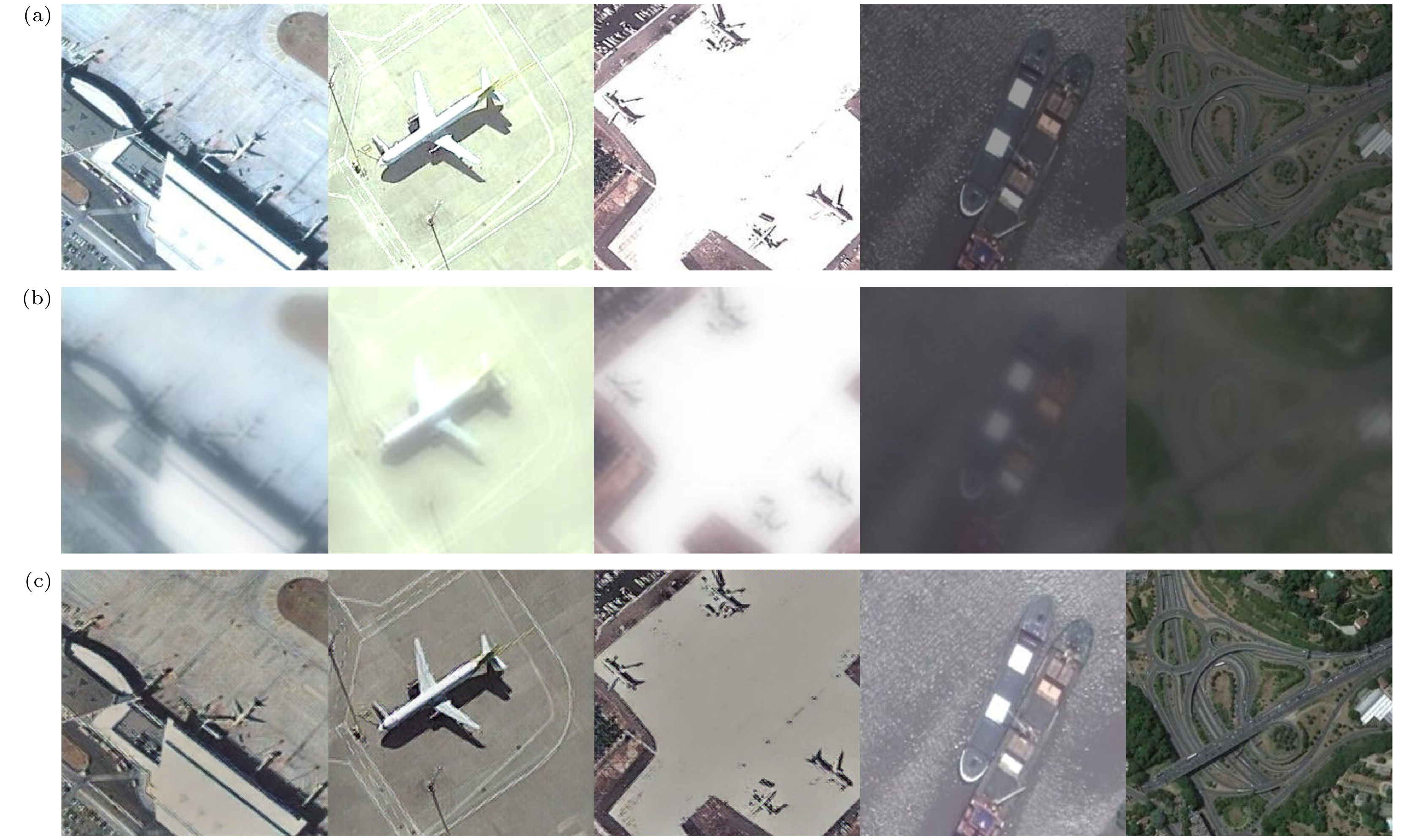
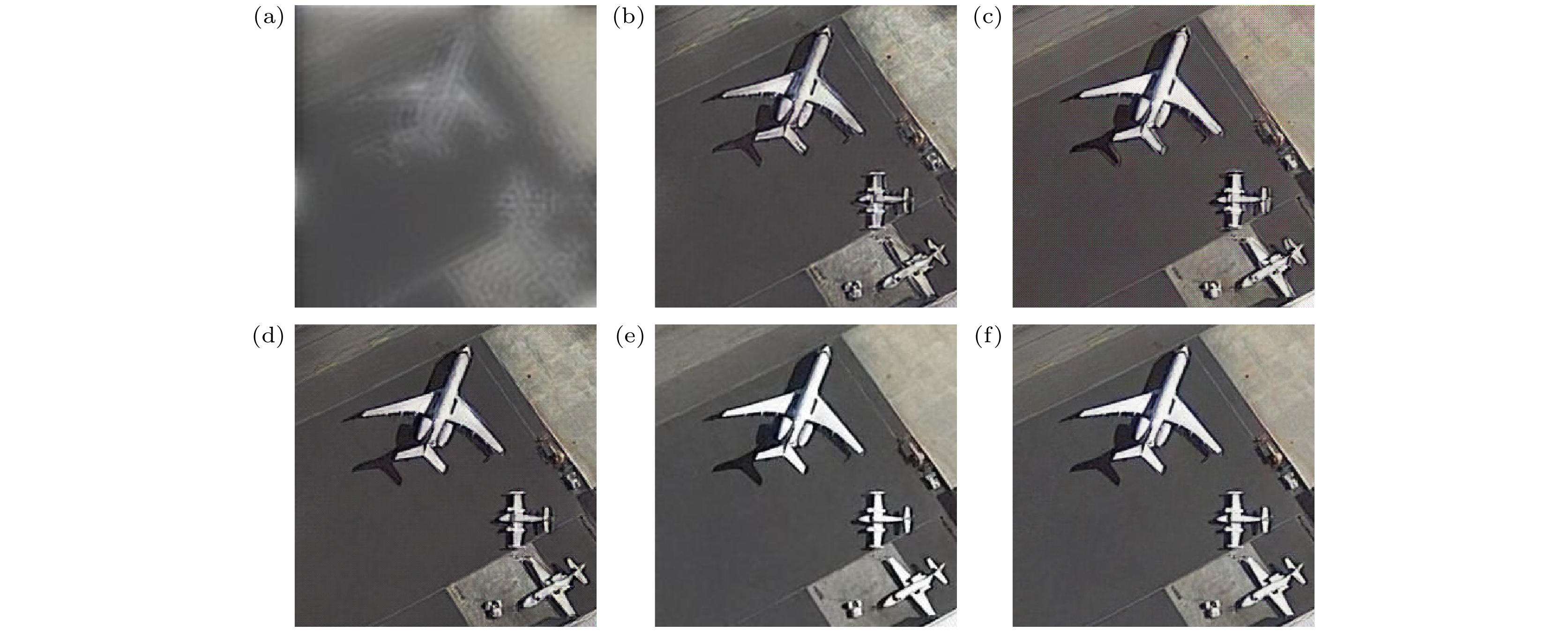
图 8 对比试验可视化结果 (a)原始清晰图像; (b) 退化图像; (c) 维纳滤波算法; (d) Deblur GAN算法; (e) SRN算法; (f) MPR-Net算法; (g) Stripformer算法; (h)本文算法
Figure 8. Visualization results of comparison experiment: (a) Clear image; (b) degraded image; (c) Wiener filtering; (d) Deblur GAN; (e) SRN; (f) MPR-Net; (g) Stripformer; (h) our proposed method.
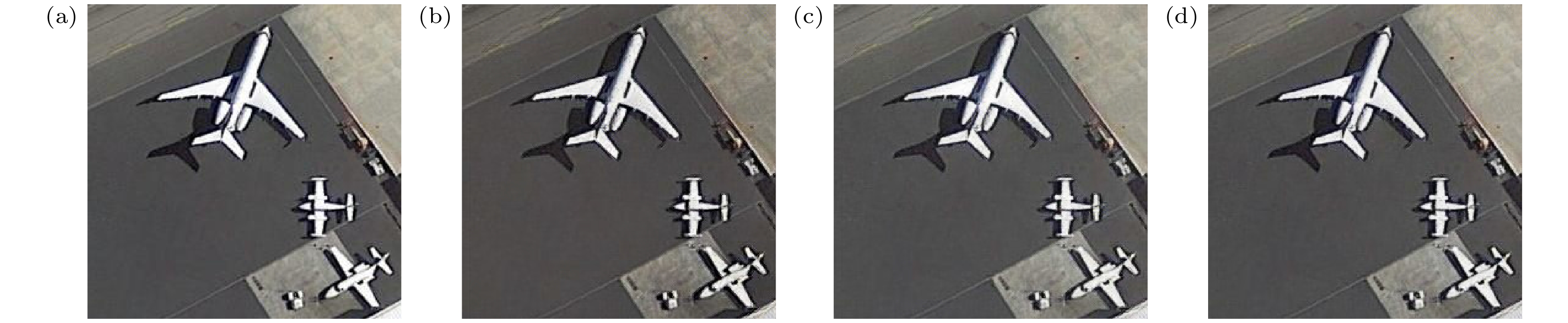
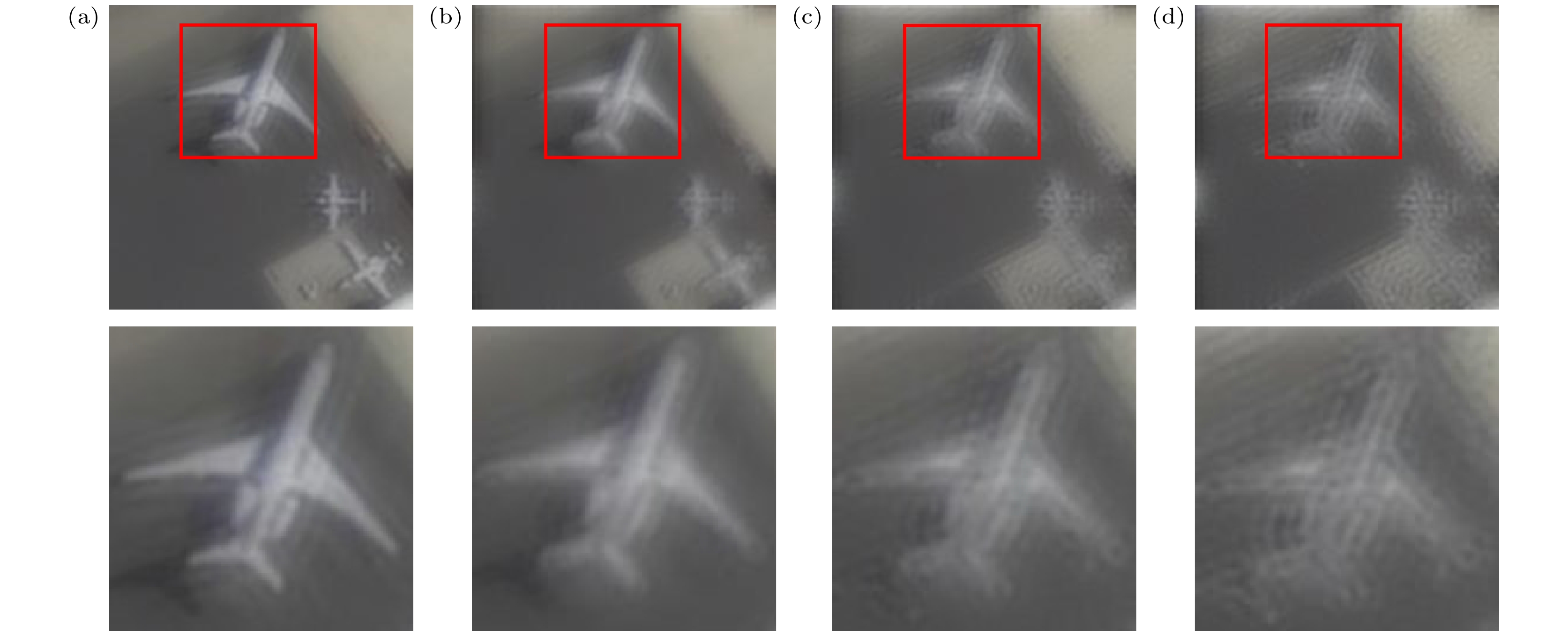
图 11 振铃增益n = 10时, 本文方法与其他方法对图像的复原结果对比 (a)受损图像; (b) Deblur GAN 算法; (c) SRN算法; (d) MPR-Net 算法; (e) Stripformer算法; (f)本文方法
Figure 11. Comparison of image restoration results between the proposed method and other methods under the influence of ringing gain (n = 10): (a) Damaged image; (b) Deblur GAN; (c) SRN; (d) MPR-Net; (e) Stripformer; (f) our proposed method.
表 1 实验环境
Table 1. Experimental environment.
Hardware and software Configuration Operating system
programming languageWindows10 Programming framework Pytorch2.0.0+ python3.9.16 CPU 12th Gen Intel(R)
Core(TM) i9-12900 KFGPU Nvidia GeForce RTX3090 Memory 32G Video memory 24G 表 2 不同算法定量实验结果
Table 2. Quantitative experiment results of different algorithms.
对比算法 PSNR/dB SSIM LPIPS FID Wiener filtering 15.227 0.5452 0.0896 3.9776 Deblur GAN 22.379 0.7011 0.0383 1.2534 SRN 17.639 0.6588 0.0697 2.1246 MPR-Net 24.725 0.7364 0.0515 0.5728 Stripformer 26.013 0.7556 0.0384 0.7138 Ours 26.408 0.7890 0.0363 0.8979 表 3 在 $ n=10 $振铃增益影响下不同算法的定量实验结果
Table 3. Quantitative experimental results of different algorithms under the influence of ringing gain ( $ n=10 $).
对比算法 PSNR/dB SSIM LPIPS Deblur GAN 16.867 0.6278 0.1006 SRN 19.369 0.7454 0.0545 MPR-Net 20.166 0.7624 0.0437 Stripformer 22.023 0.7472 0.0483 Ours 22.162 0.7702 0.0426 表 4 消融实验数据对比
Table 4. Comparison of G1 ablation data of coarse repair network.
消融策略 U-Net 多尺度特征聚合模块 特征增强模块 混合域注意力 多尺度判别器 PSNR/dB SSIM LPIPS FID 策略1 √ 19.306 0.5865 0.0841 1.2976 策略2 √ √ 21.904 0.6714 0.0833 1.0742 策略3 √ √ √ 23.872 0.6927 0.0579 0.9103 策略4 √ √ √ √ 25.425 0.7563 0.0515 0.9157 策略5 √ √ √ √ 23.261 0.7401 0.0604 0.9247 策略6 √ √ √ √ 22.558 0.7342 0.0739 0.9508 策略7 √ √ √ √ 23.074 0.7095 0.0637 0.9460 策略8 √ √ √ 20.839 0.6584 0.0799 0.9882 策略9 √ √ √ 22.944 0.6627 0.0682 0.9763 本文策略 √ √ √ √ √ 26.408 0.7890 0.0363 0.8979 -
[1] Li J J, Zhou N, Sun J S, Zhou S, Bai Z D, Lu L P, Chen Q, Zuo C 2022 Light Sci. Appl. 11 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李道京, 高敬涵, 崔岸婧, 周凯, 吴疆 2022 中国激光 49 0310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li D J, Gao J H, Cui H J, Zhou K, Wu J 2022 Chin. J. Lasers 49 0310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shinwook K, Youngchun Y 2023 Opt. Express 31 4942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 刘政, 王胜千, 饶长辉 2012 61 039501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z, Wang S Q, Rao C H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin 61 039501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sun J, Cao W F, Xu Z B, Ponce J 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Viion and Pattern Recognition Boston, MA, USA, June 7–12, 2015 p769
[6] Tao X, Gao H Y, Shen X Y, Wang J, Jia J Y 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18–23, 2018 p8174
[7] Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, Hayat M, Khan F S, Yang M H, Shao L 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Nashville, TN, USA, June 20–25, 2021 p14816
[8] Chong M, Wang Q, Zhang J 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition New Orleans, LA, USA, June 18–24, 2022 p17378
[9] Li, D S, Zhang Y, Cheung K, Wang X G, Qin H W, Li H S 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision ( ECCV) Tel Aviv, Israel October 23–27, 2022 p736
[10] Kupyn O, Budzan V, Mykhailych M, Mishkin D, Matas J 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18–23, 2018 p8183
[11] Kupyn O, Martyniuk T, Wu J R, Wang Z Y 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Seoul, Korea (South), Oct. 27–Nov. 2, 2019 p8877
[12] 江泽涛, 覃露露 2020 电子学报 48 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang Z T, Qin L L 2020 J. Electron. 48 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 陈炳权, 朱熙, 汪政阳, 梁寅聪 2022 湖南大学学报(自然科学版) 49 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B Q, Zhu X, Wang Z Y, Liang Y C 2022 J. Hunan Univ. (Nat. Sci. ) 49 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王山豹, 梁栋, 沈玲 2023 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报 35 1109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S B, Liang D, Shen 2023 J. Comput. Aided Design Comput. Graphics 35 1109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘杰, 祁箬, 韩轲 2023 光学精密工程 31 2080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Qi R, Han K 2023 Opt. Precis. Eng. 31 2080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Woo S H, Park J, Lee J Y, Kweon I S 2018 Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Munich, Germany, September 8–14, 2018 p3
[17] 王向军, 欧阳文森 2022 红外与激光工程 51 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X J, Ouyang W S 2022 Infrared Laser Eng. 51 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, Hayat M, Khan F S, Yang M H 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition New Orleans, LA, USA, June 18–24, 2022 p5718
[19] Li Y W, Fan Y C, Xiang X Y, Demandolx D, Ranjan R, Timofte R, Gool L V 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Vancouver, BC, Canada, June 17–24, 2023 p18278
[20] Tsai F J, Peng Y T, Lin Y Y , Tsai C C, Lin C W 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022 p146
[21] Chen L Y, Chu X J, Zhang X, Sun J 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022 p17
[22] Tang J, Wang K Q, Ren Z R, Zhang W, Wu X Y, Di J L, Liu G D, Zhao J L 2020 Opt. Lasers Eng. 139 106463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tang J, Wu J, Wang K Q, Ren Z B, Wu X Y, Hu L S, Di J L, Liu G D, Zhao J L 2021 Opt. Lasers Eng. 146 106707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3551
- PDF Downloads: 181
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: