-
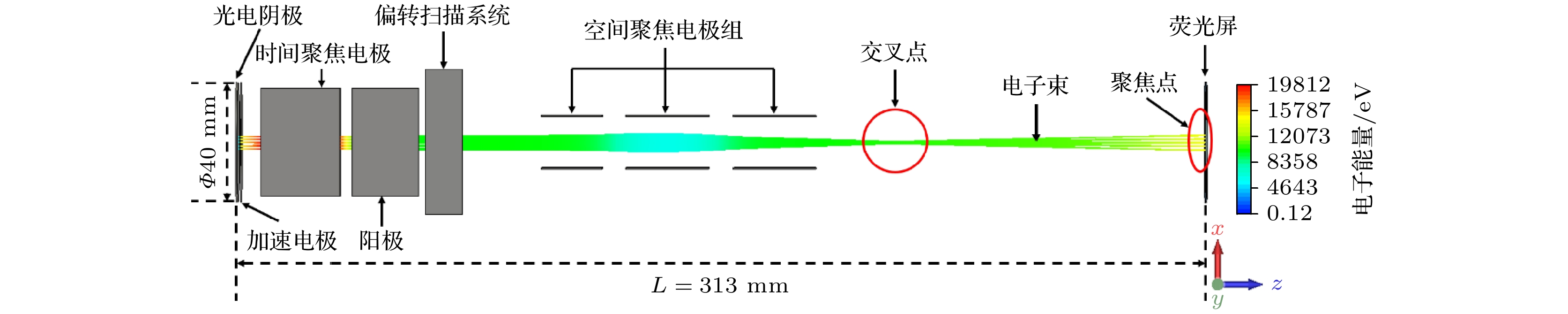
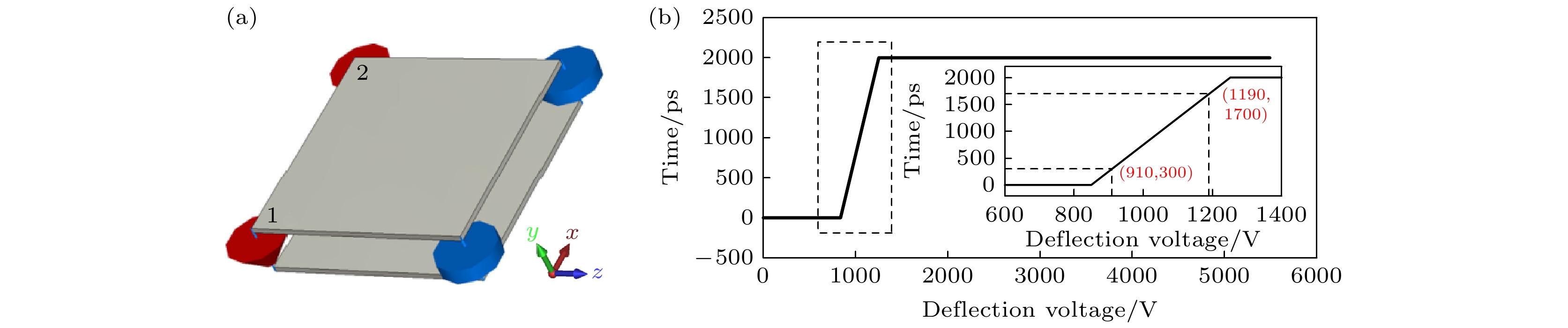
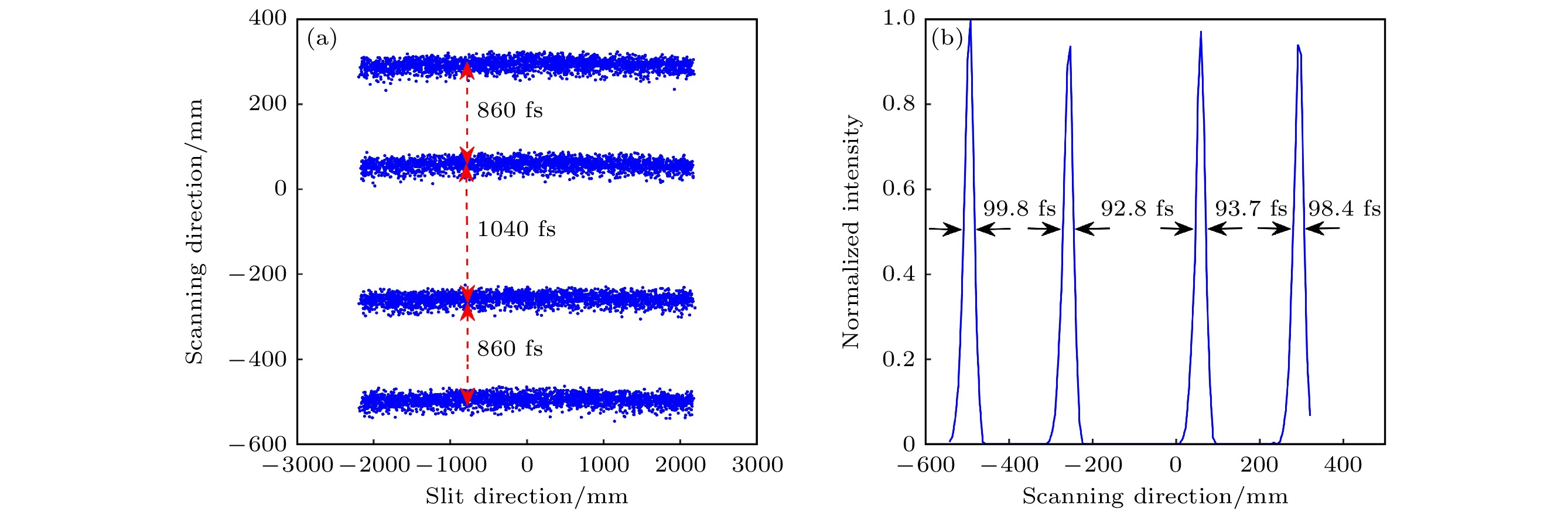
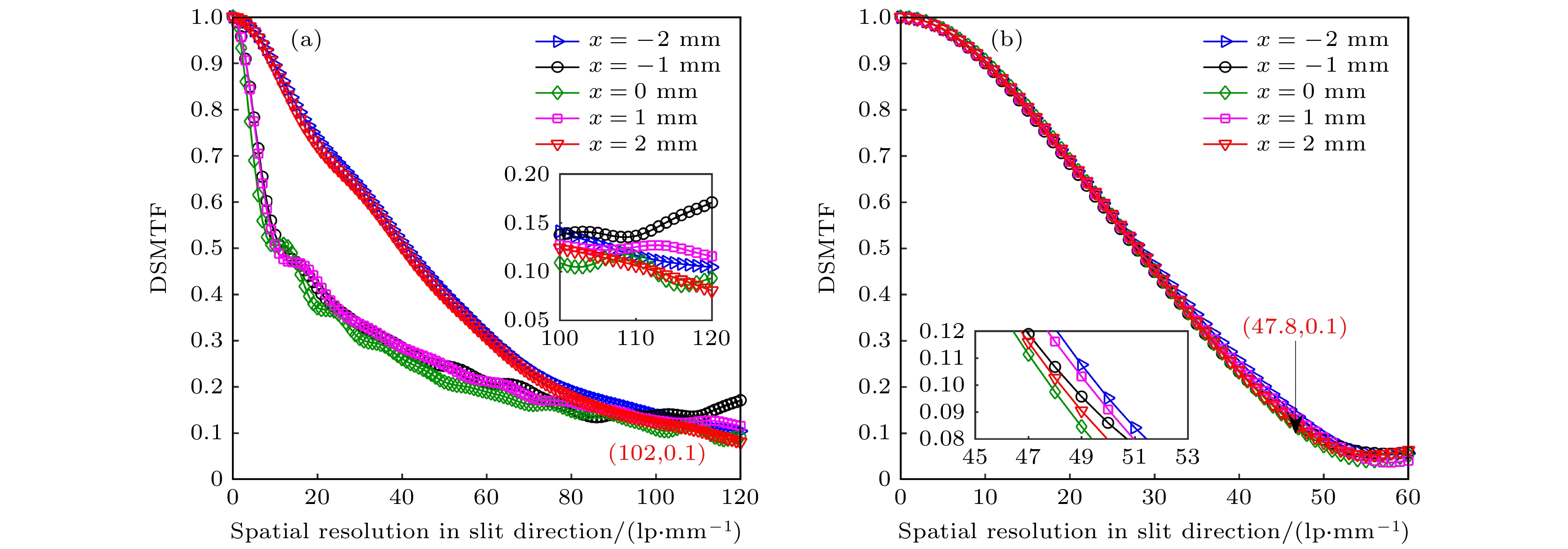
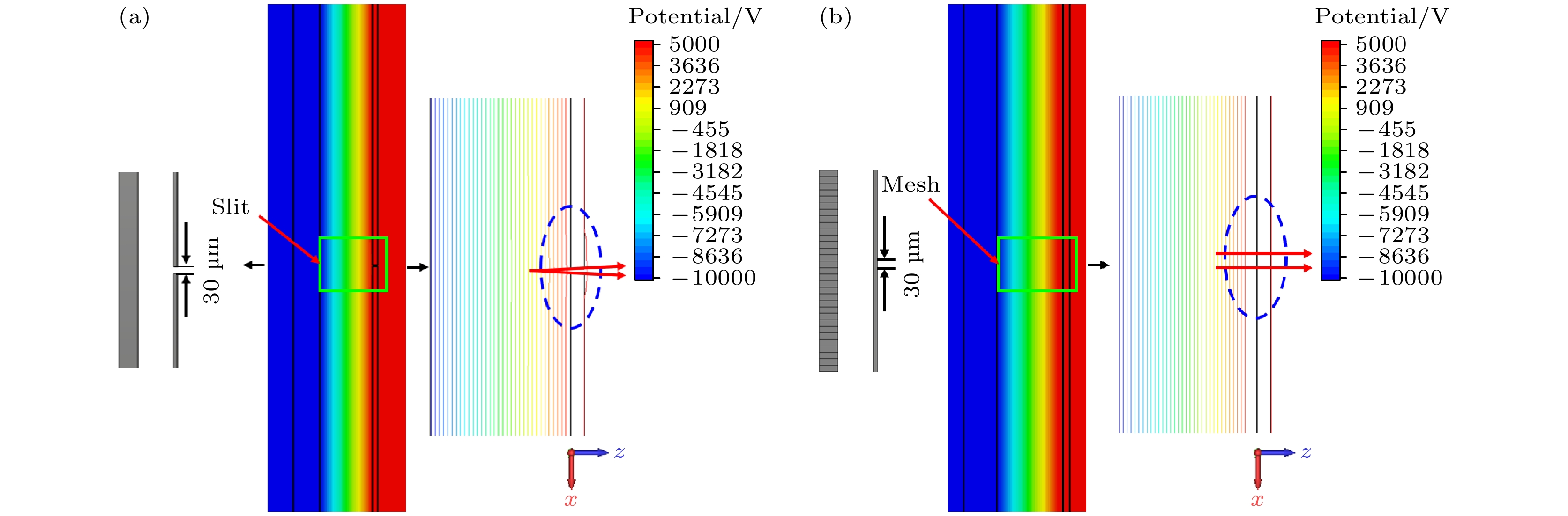
Reducing the space charge effect and the time dispersion caused by the edge field effect of the scanning deflection system is the key to realizing a 100-fs streak tube. In this paper, a novel fs streak tube is proposed and designed. The factors affecting its temporal resolution are analyzed theoretically and the specifications are given. Parameters including the electric field distribution and electron transmittance of the two common acceleration systems (planar cathode-mesh accelerating electrode and planar cathode-slit accelerating electrode) are compared with each other and analyzed theoretically. The results show that although the electric field distribution formed by the planar cathode (mesh accelerating electrode) can form uniform electric field, the electron transmittance is very low; planar cathode-slit accelerating structure will defocus the photoelectron beam along the scanning direction, but the electron transmittance in the effective detection range of the cathode is as high as 100%. The defocusing of the photoelectron beam can be removed by setting a narrow slit in front of the anode. The focusing electrode adopts two sets of plate-like structures which are vertically positioned in front and back to form a one-dimensional focusing electric fields along the scanning direction and the slit direction, respectively. The spatial focusing electrode is arranged close to the phosphor screen, which is beneficial to pushing back the cross-point of the electron beam along the spatial direction. Thus, the electron transit time dispersion in the condition of large electron density will decrease. At the same time, the anode can provide a post-accelerating voltage of +5000 V, which is beneficial to shortening the transit time and dispersion of the photoelectrons, thereby improving the temporal resolution. Based on the above theoretical analysis, a novel femtosecond streak tube is designed by using the planar cathode-slit accelerating electrode, anisotropic focusing system and post-accelerating method. The influence of the anode slit width on the spatial and temporal resolution is simulated. The results show that the temporal resolution deteriorates with the increase of the anode slot width (10-50 μm), due to the fact that the increase of the anode slit width will lead to the gradual increase of the size of the electron spot along the scanning direction, which will lead to the increase of the technical time dispersion. In addition, this study gives the simulation results of the femtosecond streak tube when the anode slit width is in a range of 10-50 μm. The results show that the static spatial resolution is higher than 100 lp/mm at MTF = 10%, dynamic spatial resolution is higher than 29 lp/mm at MTF = 10%, the temporal resolution is better than 122 fs in the range of 4-mm cathode effective detection length. When the effective detection length of the cathode is increased to 8 mm, the dynamic spatial resolution of the streak tube is higher than 22 lp/mm at MTF = 10%, and the temporal resolution is better than 191 fs.
-
Keywords:
- anisotropy focusing technology /
- post-accelerating technology /
- temporal resolution /
- femtosecond streak tube
[1] Kassier G H, Haupt K, Erasmus N, Rohwer E G, Bergmann H M, Schwoerer H, Coelho S M M, Auret F D 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81 105103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Musumeci P, Moody J T, Scoby C M, Gutierrez M S, Tran T 2009 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80 013302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pei C Q, Wu S L, Luo D, Wen W L, Xun J K, Tian J S, Zhang M R, Chen P, Chen J Z, Liu R 2017 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 855 148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Courtney-Pratt J S 1949 J. Research: A Journal of Science and its Applications. 2 287
[5] 罗端, 惠丹丹, 温文龙, 李立立, 辛丽伟, 钟梓源, 吉超, 陈萍, 何凯, 王兴, 田进寿 2020 69 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo D, Hui D D, Wen W L, Li L L, Xin L W, Zhong Z Y, Ji C, Chen P, He K, Wang X, Tian J S 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 田进寿 2020 强激光与粒子束 32 112003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian J 2020 High Power Laser Part. Beams 32 112003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gallant P, Forget P, Dorchies F, Jiang Z, Kieffer J C 2000 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71 3627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Feng J, Shin H J, Nasiatka J R, et al. 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 134102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shakya M M, Chang Z H 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 041103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kinoshita K, Ishihara Y, Ai T, Hino S, Inagaki Y, Mori K, Goto M, Niikura F, Takahashi A, Uchiyama K, Abe S 2016 Proceedings of the 31st International Congress on High-speed Imaging and Photonic Osaka, Japan, November 7–10, 2016 p305
[11] 柳雪玲, 田进寿, 田丽萍, 陈萍, 张敏睿, 薛彦华, 李亚晖, 方玉熳, 徐向晏, 刘百玉, 缑永胜 2021 70 218502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X L, Tian J S, Tian L P, Chen P, Zhang M R, Xue Y H, Li Y H, Fang Y M, Xue X Y, Liu B Y, Gou Y S 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 218502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tian L P, Shen L B, Li L L, Wang X, Chen P, Wang J F, Chen L, Zhao W, Tian J S 2021 Optik 242 166791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Macphee A G, Dymoke-Bradshaw A K, Hares J D, Gassett J, Hatch B W, Meadowcroft A L, Bell P M, Bradley D K, Datte P S, Landen O L, Palmer N E, Piston K W, Rekow V V, Hilsabeck T J, Kilkenny J D 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 11E202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tian L P, Shen L B, Chen L, Li L L, Tian J S, Chen P, Zhao W 2021 Meas. Sci. Rev. 21 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 惠丹丹, 田进寿, 王俊锋, 卢裕, 温文龙, 徐向晏 2016 65 018502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hui D D, Tian J S, Wang J F, Lu Y, Wen W L, Xu X Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 018502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 田丽萍, 李立立, 温文龙, 王兴, 陈萍, 卢裕, 王俊锋, 赵卫, 田进寿 2018 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian L P, Li L L, Wen W L, Wang X, Chen P, Lu Y, Wang J F, Zhao W, Tian J S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 狭缝宽度对电子斑的影响, 蓝色拟合曲线表示电子转移效率, 红色拟合曲线表示屏幕上沿扫描方向的电子斑点宽度
Figure 3. Variation of electron transfer efficiency and width of electron spot along scanning direction on screen with width of anode. The blue fitted curve represents the electron transfer effiency, and the red fitted curve represents the width electron spot along scanning direction on screen.
表 1 不同阳极狭缝宽度下飞秒管的时空分辨率
Table 1. Spatio-temporal resolution versus different width of anode slit.
阳极狭缝宽度dAnode/μm 狭缝方向动态空间
分辨率/(lp·mm–1)扫描方向动态空间
分辨率/(lp·mm–1)动态时间分辨率
(点源发射)/fs动态时间分辨率
(狭缝发射)/fs10 245 97 47 82 20 155 71 76 86 30 112 47 84 93 40 92 37 93 103 50 71 29 116 122 表 2 不同阴极有效长度及阳极狭缝宽度下飞秒管的时空分辨率
Table 2. Spatio-temporal resolution versus different effective cathode length and anode slit width.
类别 性能指标 阳极狭缝宽度 dAnode/μm 10 20 30 40 50 阴极有效长度4 mm 狭缝方向动态空间分辨率/(lp·mm–1) 245 155 112 92 71 扫描方向动态空间分辨率/(lp·mm–1) 97 71 47 37 29 动态时间分辨率(狭缝发射)/fs 82 86 93 103 122 阴极有效长度8 mm 狭缝方向动态空间分辨率/(lp·mm–1) 72 48 33 26 22 扫描方向动态空间分辨率/(lp·mm–1) 97 71 47 36 29 动态时间分辨率(狭缝发射)/fs 166 170 175 184 191 -
[1] Kassier G H, Haupt K, Erasmus N, Rohwer E G, Bergmann H M, Schwoerer H, Coelho S M M, Auret F D 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81 105103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Musumeci P, Moody J T, Scoby C M, Gutierrez M S, Tran T 2009 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80 013302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pei C Q, Wu S L, Luo D, Wen W L, Xun J K, Tian J S, Zhang M R, Chen P, Chen J Z, Liu R 2017 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 855 148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Courtney-Pratt J S 1949 J. Research: A Journal of Science and its Applications. 2 287
[5] 罗端, 惠丹丹, 温文龙, 李立立, 辛丽伟, 钟梓源, 吉超, 陈萍, 何凯, 王兴, 田进寿 2020 69 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo D, Hui D D, Wen W L, Li L L, Xin L W, Zhong Z Y, Ji C, Chen P, He K, Wang X, Tian J S 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 052901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 田进寿 2020 强激光与粒子束 32 112003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian J 2020 High Power Laser Part. Beams 32 112003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gallant P, Forget P, Dorchies F, Jiang Z, Kieffer J C 2000 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71 3627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Feng J, Shin H J, Nasiatka J R, et al. 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 134102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shakya M M, Chang Z H 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 041103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kinoshita K, Ishihara Y, Ai T, Hino S, Inagaki Y, Mori K, Goto M, Niikura F, Takahashi A, Uchiyama K, Abe S 2016 Proceedings of the 31st International Congress on High-speed Imaging and Photonic Osaka, Japan, November 7–10, 2016 p305
[11] 柳雪玲, 田进寿, 田丽萍, 陈萍, 张敏睿, 薛彦华, 李亚晖, 方玉熳, 徐向晏, 刘百玉, 缑永胜 2021 70 218502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X L, Tian J S, Tian L P, Chen P, Zhang M R, Xue Y H, Li Y H, Fang Y M, Xue X Y, Liu B Y, Gou Y S 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 218502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tian L P, Shen L B, Li L L, Wang X, Chen P, Wang J F, Chen L, Zhao W, Tian J S 2021 Optik 242 166791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Macphee A G, Dymoke-Bradshaw A K, Hares J D, Gassett J, Hatch B W, Meadowcroft A L, Bell P M, Bradley D K, Datte P S, Landen O L, Palmer N E, Piston K W, Rekow V V, Hilsabeck T J, Kilkenny J D 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 11E202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tian L P, Shen L B, Chen L, Li L L, Tian J S, Chen P, Zhao W 2021 Meas. Sci. Rev. 21 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 惠丹丹, 田进寿, 王俊锋, 卢裕, 温文龙, 徐向晏 2016 65 018502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hui D D, Tian J S, Wang J F, Lu Y, Wen W L, Xu X Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 018502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 田丽萍, 李立立, 温文龙, 王兴, 陈萍, 卢裕, 王俊锋, 赵卫, 田进寿 2018 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian L P, Li L L, Wen W L, Wang X, Chen P, Lu Y, Wang J F, Zhao W, Tian J S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4098
- PDF Downloads: 90
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: