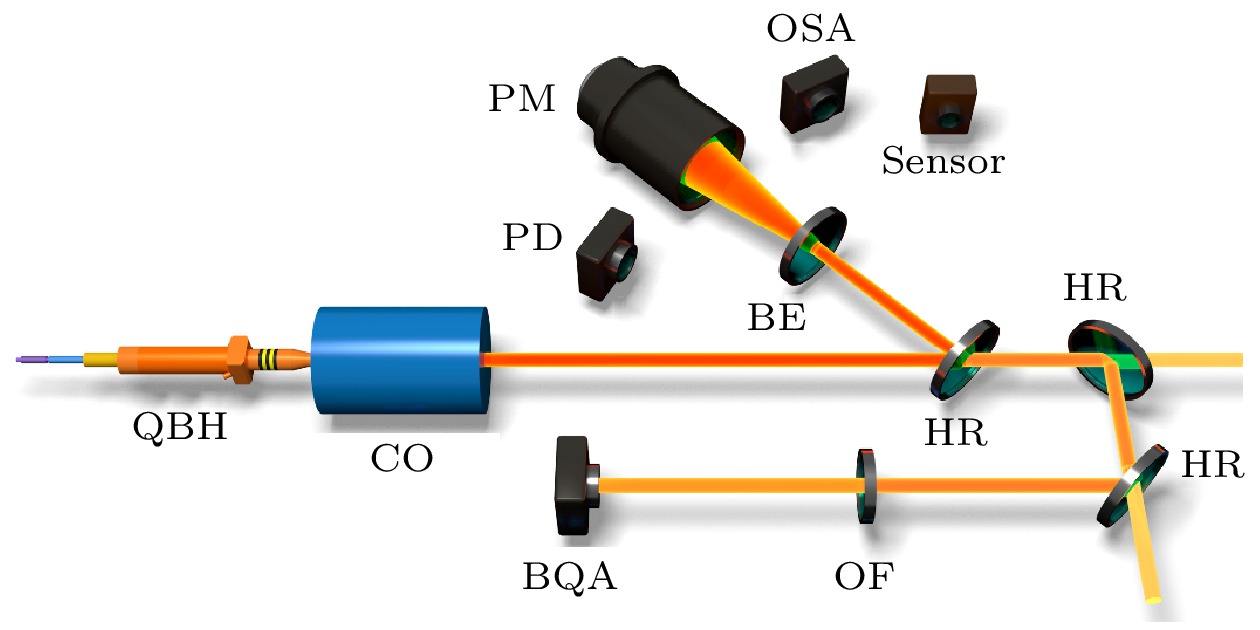
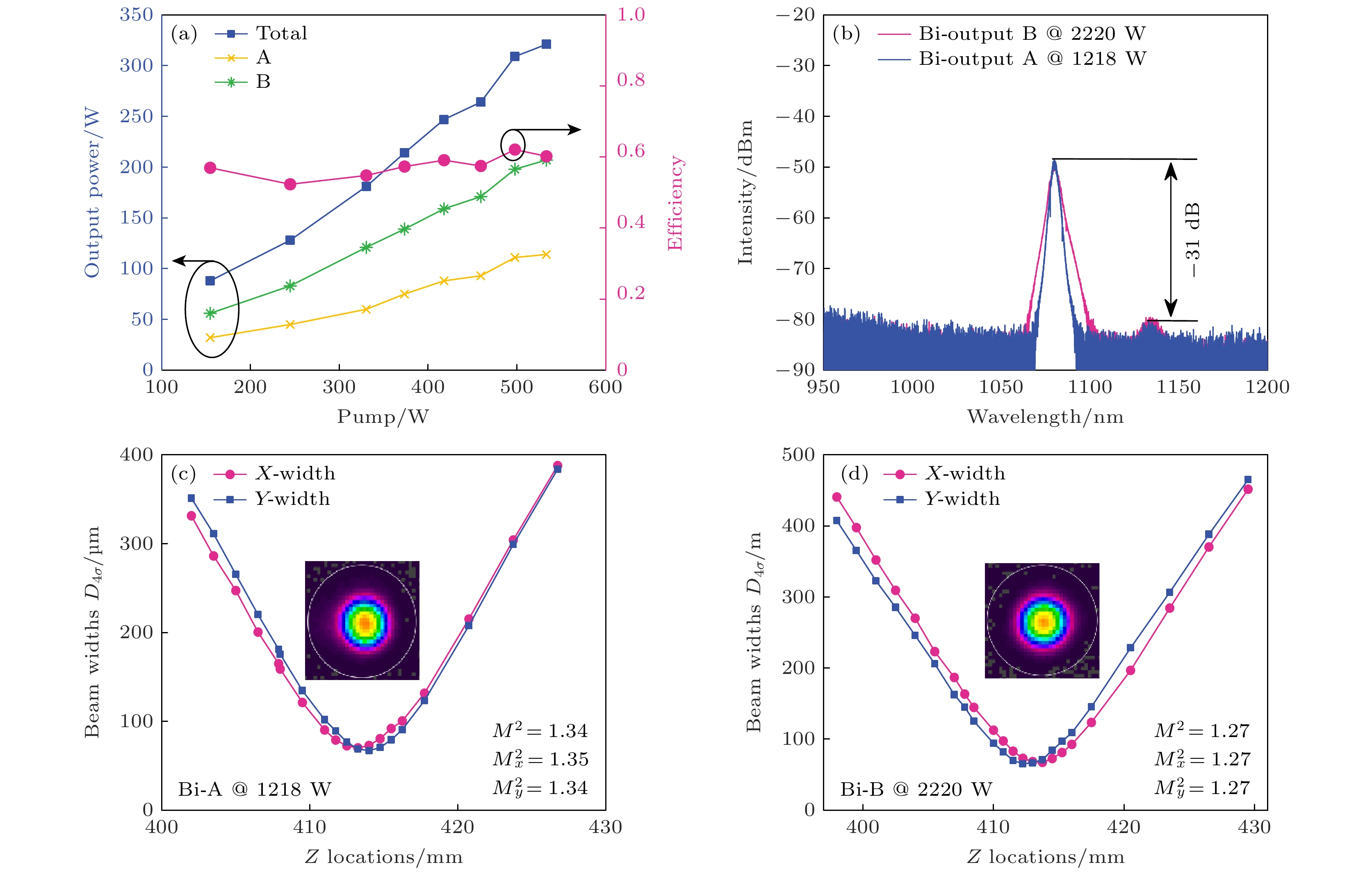
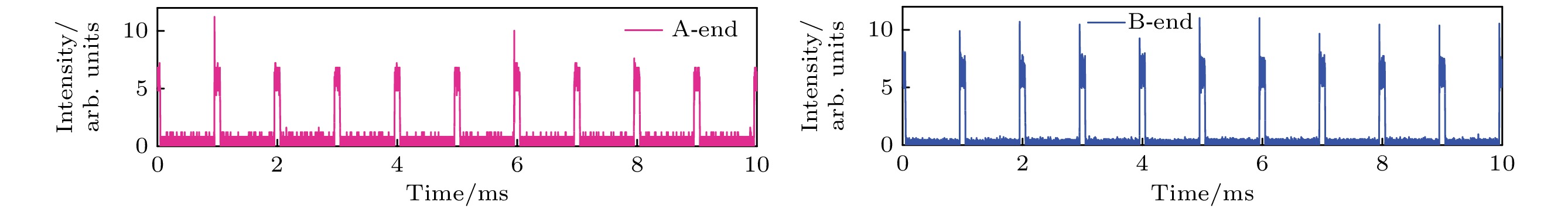
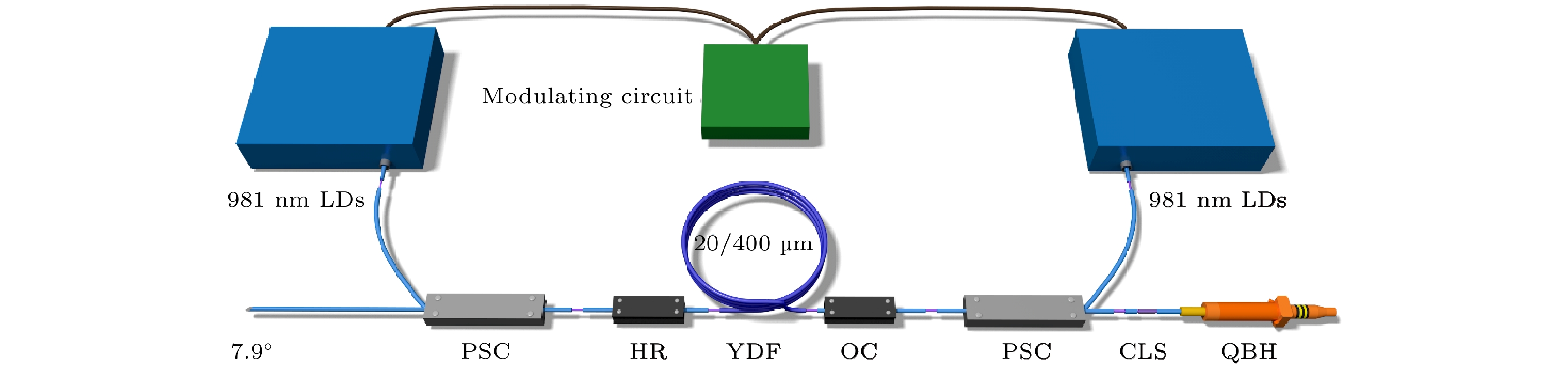
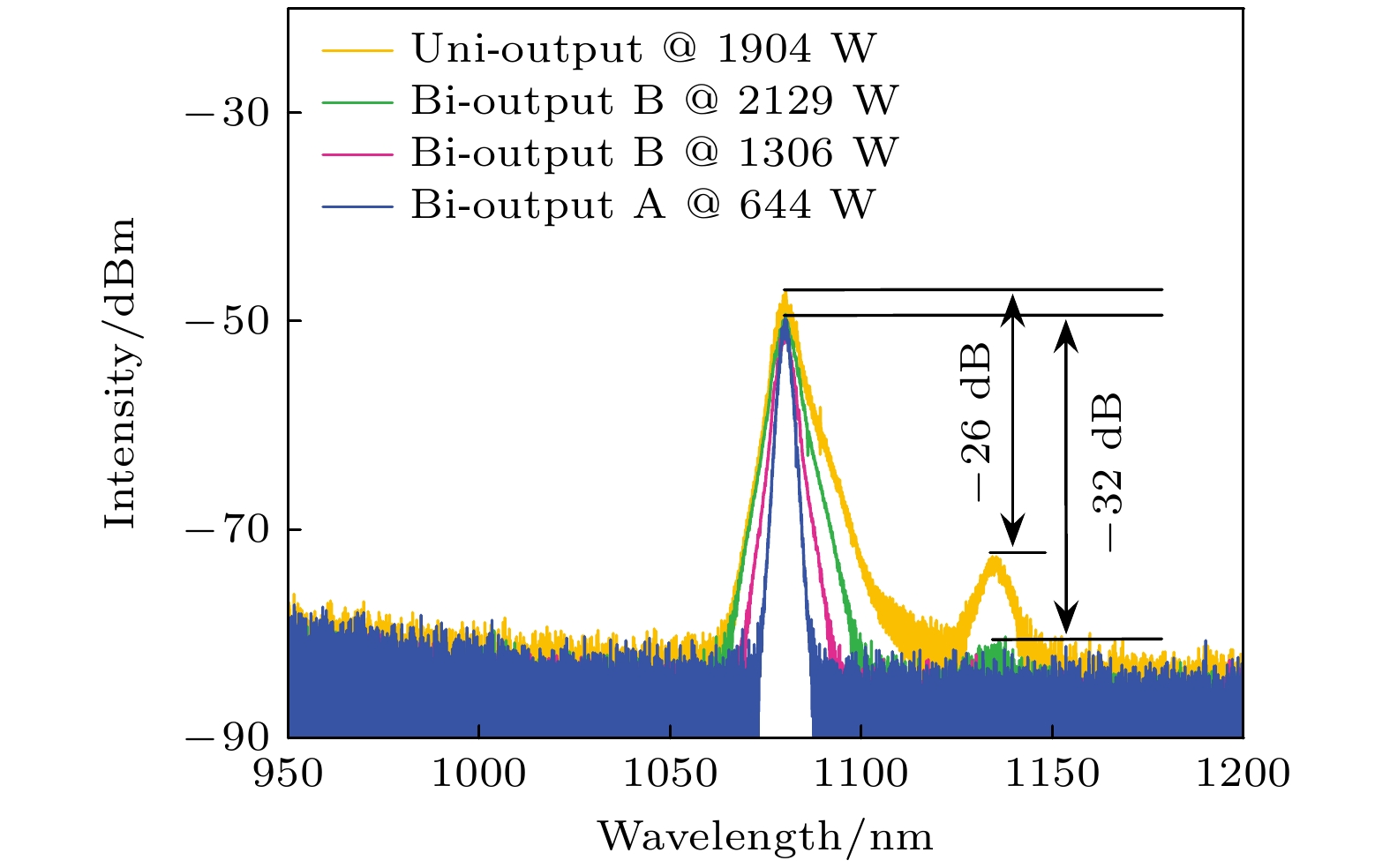
-
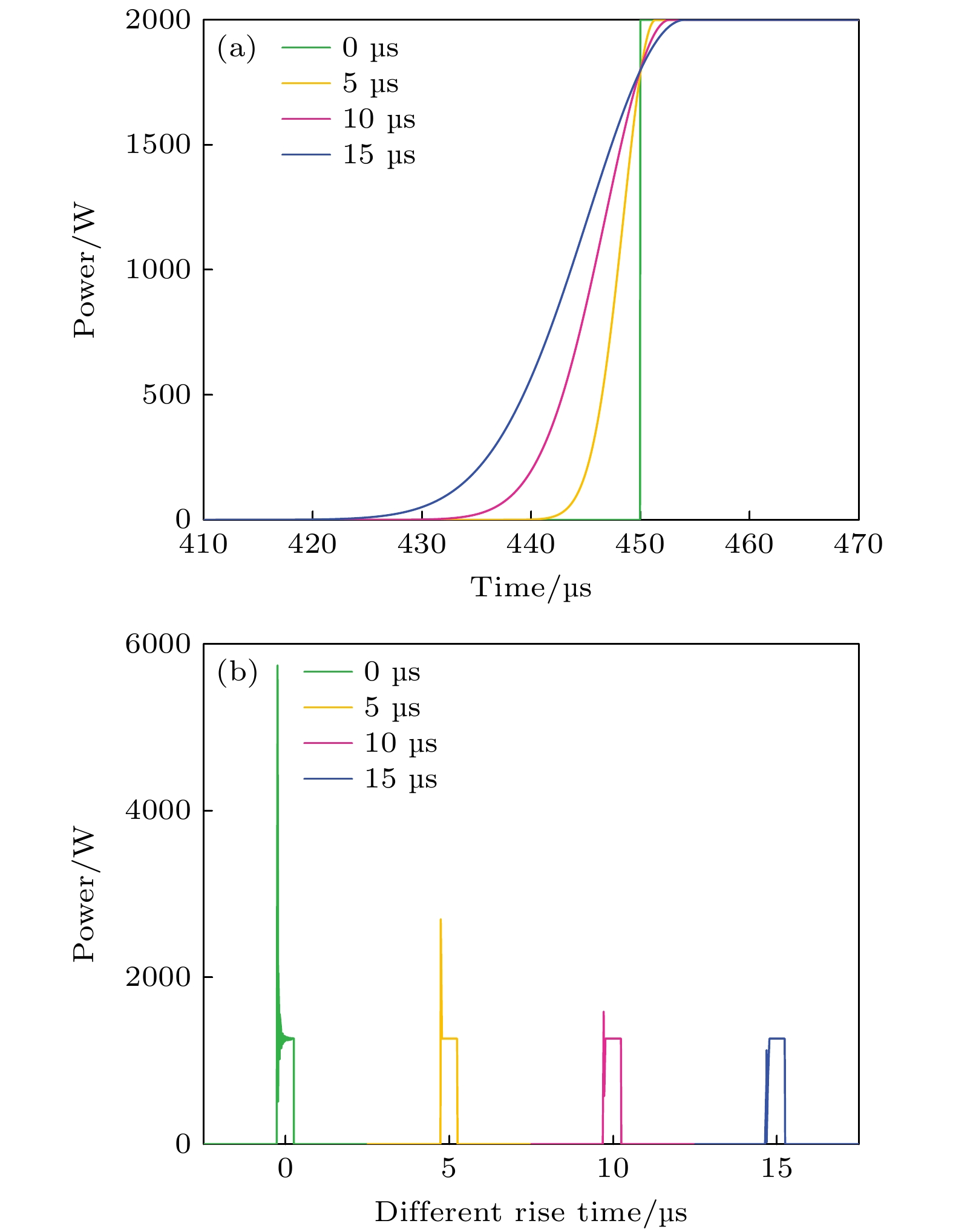
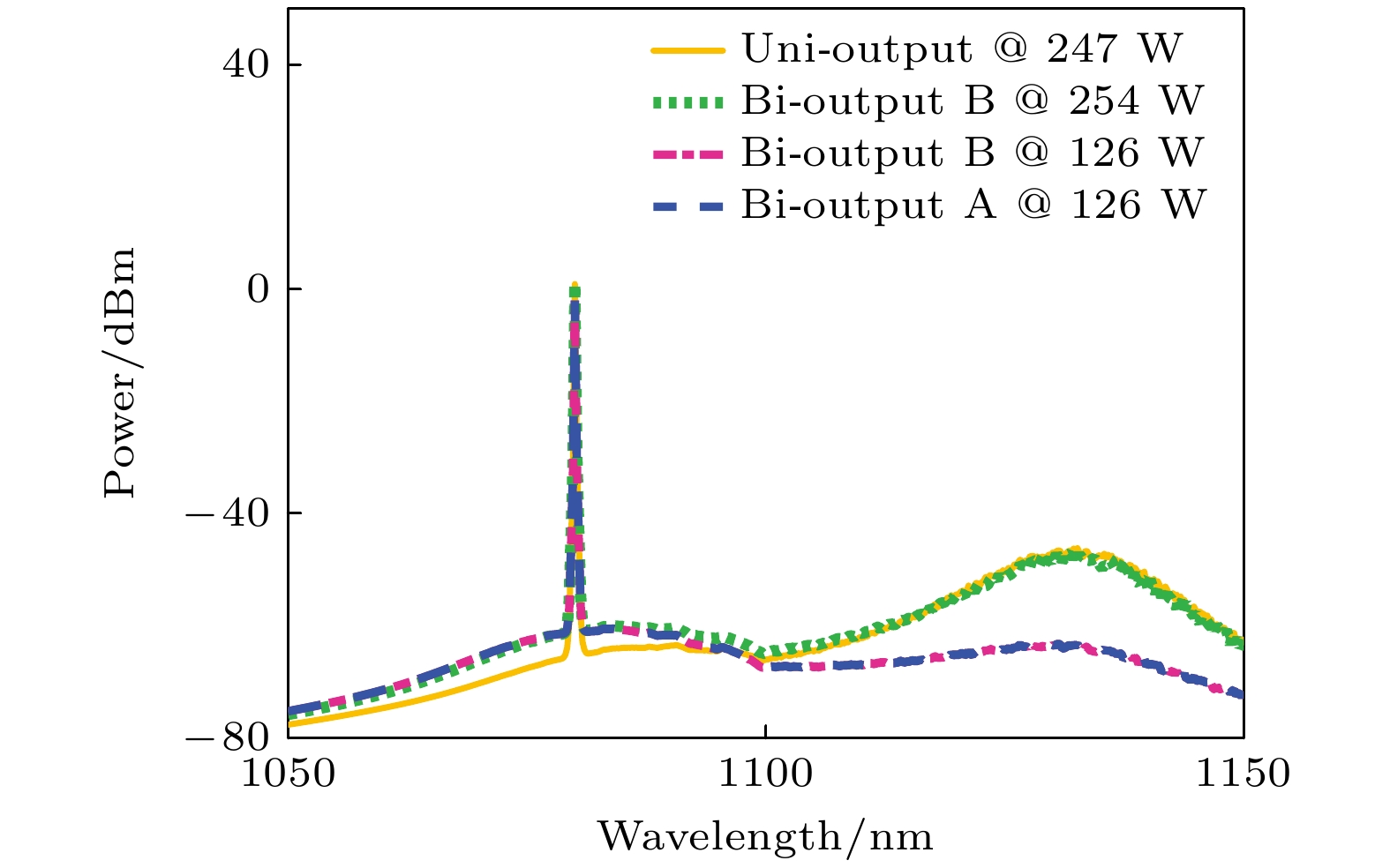
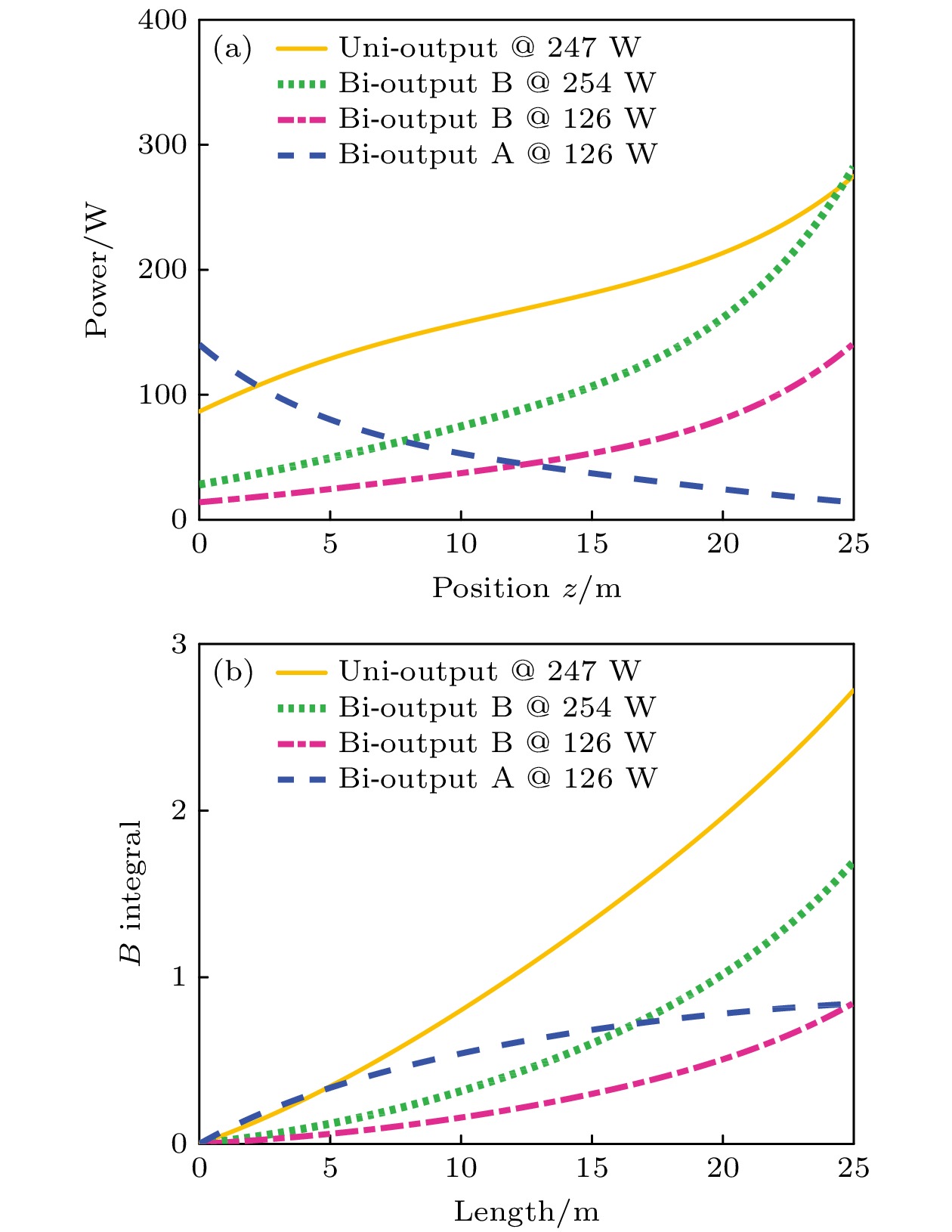
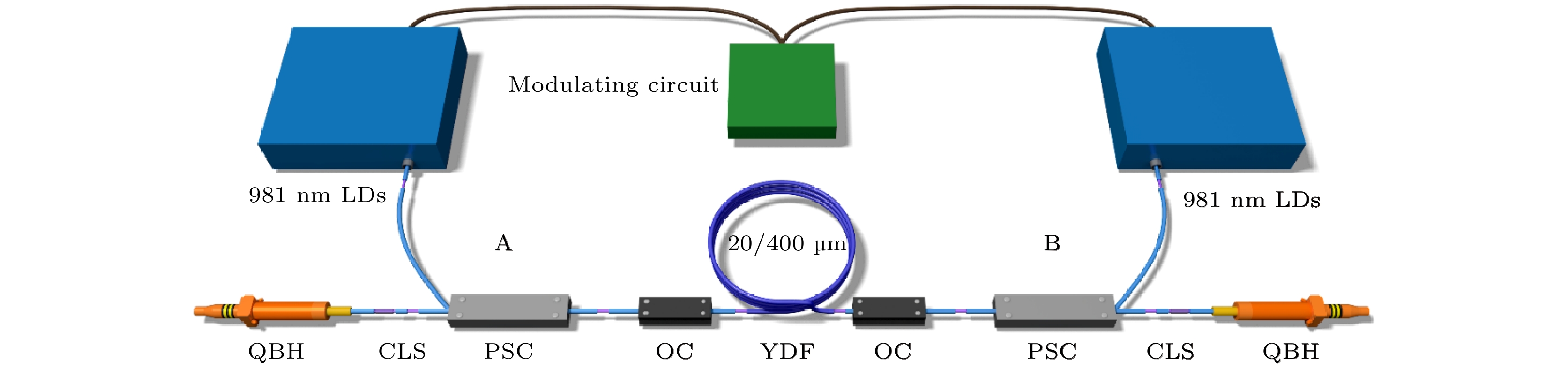
Quasi-continuous fiber lasers have a broad application prospect in the industrial field. However, in the current research on quasi-continuous wave (QCW) fiber lasers only the single-ended output structure is used. A double-ended output fiber laser oscillator needs only one resonator to realize two laser outputs. Compared with single-ended output laser, it has a low cost, small volume and high work efficiency. It is expected to achieve higher power laser output through double-ended output beam combining. Therefore, the double-ended output QCW fiber laser is proposed and studied in this paper. The steady-state rate equation establishes a theoretical model of a QCW fiber laser oscillator with two ends, considering the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and amplified spontaneous emission (ASE). The output power, time domain and nonlinear effects of this type of laser are simulated. The results show that the overshoot effect caused by relaxation oscillation will produce a large amount of thermal deposition and ultra-high peak power in the fiber. It will reduce the nonlinear threshold and limit the increase of power of the QCW fiber laser. Prolonging the rise time of the pump can effectively suppress the relaxation oscillation and obtain a stable pulse output during the pulse duration. In addition, compared with the single-ended QCW laser, the double-ended output structure changes the energy distribution in the fiber and reduces the accumulation of nonlinear effects in the gain fiber, thus inhibiting SRS. Then, the ytterbium-doped fiber with a core/cladding diameter of 20/400 μm is used to achieve the first double-ended QCW laser output with a peak power of 3 kW. The peak power values at both ends are 1218 and 2220 W, respectively. The values of corresponding beam quality factor M2 are 1.34 and 1.27. The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency is about 60%. The pulse width is 100 μs, and the repetition frequency is 1 kHz. This research verifies the feasibility of high power and high beam quality output by double-ended output QCW fiber laser, which provides support for small volume, low cost, high power and high brightness QCW fiber laser. Further breakthroughs in the research and application of high-power fiber lasers are expected to be made by continually optimizing experiments, increasing pump power, and improving the laser’s output power and conversion efficiency.
-
Keywords:
- fiber laser /
- quasi-continuous wave /
- double-ended output /
- near-single-mode
[1] 黄婷, 杜伟哲, 苏坤, 张建超, 李敬洋, 祁俊峰, 雷永平, 武强, 肖荣诗 2022 中国激光 49 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang T, Du W Z, Su K, Zhang J C, Li J Y, Qi J F, Lei Y P, Wu Q, Xiao R S 2022 Chin. J. Lasers 49 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Marimuthu S, Smith B 2021 Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 113 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen Z Z, Xu Y T, Guo Y D, Wang B S, Xu J, Xu J L, Gao H W, Yuan L, Yuan H T, Lin Y Y, Xiao Y S, Bo Y, Peng Q J, Lei W Q, Cui D F, Xu Z Y 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 5011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bian Q, Bo Y, Zuo J W, Yuan L, Chen H B, Peng Q J, Xu Z Y 2020 Opt. Express 28 13895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hong Z J, Wan Y C, Xi X M, Zhang H W, Wang X L, Xu X J 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 1826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang L, Zhang H W, Wang P, Yang B L, Wang X L, Ning Y, Xu X J 2022 Opt. Laser Technol. 154 108338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang L, Zhang H W, Wang P, Yang B L, Wang X L, Ning Y, Xu X J 2022 IEEE Photonics J. 14 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 王力, 张汉伟, 王鹏, 王小林, 宁禹, 韩凯, 许晓军 2023 中国激光 50 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L, Zhang H W, Wang P, Wang X L, Ning Y, Han K, Xu X J 2023 Chin. J. Lasers 50 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zheng J K, Bo Y, Xie S Y, Zuo J W, Wang P Y, Guo Y D, Liu B L, Peng Q J, Cui D F, Lei W Q, Xu Z Y 2013 Chin. Phys. Lett. 30 074202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/en/229/FileAttachment/YLM-QCW+and+YLR-QCW+Single-mode+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[11] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/cn/101/FileAttachment/YLM-QCW+Series+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[12] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/ru/86/FileAttachment/YLS-2000_20000-QCW+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[13] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/ru/126/FileAttachment/YLS-2300_23000-QCW+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[14] 武汉锐科 https://www.raycuslaser.com/upload/old_file/201808/5b6168071a474.pdf [2023-03-30]
[15] 武汉锐科 https://www.raycuslaser.com/upload/20210507/1f52nmd6in812mko.pdf [2023-03-30]
[16] 武汉锐科 https://www.jyothishya.com/view/2636.html [2023-03-30]
[17] 创鑫激光 http://www.maxphotonics.com/vancheerfile/files/2020/4/20200416155923674.pdf [2023-03-30]
[18] 创鑫激光 http://www.maxphotonics.com/vancheerfile/files/2020/4/20200416155938936.pdf [2023-03-30]
[19] Zhong P L, Wang L, Yang B L, Zhang H W, Xi X M, Wang P, Wang X L 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 2806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu J Q, Zeng L F, Wang P, Yang B L, Xi X M, Shi C, Zhang H W, Wang X L, Xi F J 2023 IEEE Photonics J. 15 1500209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王小林, 叶云, 奚小明, 史尘, 张汉伟, 韩凯, 王泽锋, 许晓军, 周朴, 司磊, 陈金宝 2018 中国专利 201821644646.3
Wang X L, Ye Y, Xi X M, Shi C, Zhang H W, Han K, Wang Z F, Xu X J, Zhou P, Si L, Chen J B 2018 CN Patent 201821644646.3 (in Chinese)
[22] 王小林, 张汉伟, 史尘, 段磊, 奚小明 2021 基于SeeFiberLaser的光纤激光建模与仿真 (北京: 科学出版社) 第19, 22, 40, 44页
Wang X L, Zhang H W, Shi C, Duan L, Xi X M 2021 Fiber Laser Modeling and Simulation Based on SeeFiberLaser (Beijing: Science Press) pp19, 22, 40, 44 (in Chinese)
[23] 阿戈沃著(贾东方, 葛春风 译) 2014 非线性光纤光学(第五版) (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第25, 205页
Agrawal G P (translated by Jia D F, Ge C F) 2014 Nonlinear Fiber Optics (5th Ed.) (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp25, 205 (in Chinese)
[24] 住村和彦日, 西浦匡则日著(宋鑫 译) 2013 图解光纤激光器入门 (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第62页
Zhu C H Y R, Xi P K Z R(translated by Song X) 2013 Illustrative Introduction to Fiber Lasers (Beijing: China Machine Press) p62 (in Chinese)
[25] Lv X G, Liao T Q, Yi Y 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1213 42053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 高俊峰, 闫明鉴, 梁慧生, 詹涌, 韩志刚, 朱日宏, 刘明 2021 激光与红外 51 1013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J F, Yan M J, Liang H S, Zhan Y, Han Z G, Zhu R H, Liu M 2021 Laser & Infrared 51 1013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Villate D, Blanchot N, Rouyer C 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 QCW激光器科研与产业现状
Table 1. QCW laser research and industry status.
年份 科研单位 结构/型号 峰值功率/kW 平均功率
/kW光束质量
因子M 2脉宽/ms 频率/kHz 2013 中国科学院理化技术研究所[9] 空间MOPA结构(Nd:YAG平板放大器) 0.564# 0.0423 1.56 0.075 1 2015 中国科学院理化技术研究所[3] 空间MOPA结构(Nd:YAG平板放大器) 102.5# 8.2 >3.5 0.2 0.4 2020 中国科学院理化技术研究所[4] 空间MOPA结构(Nd:YAG平板放大器) 2.2# 0.0861 1.37 0.1 0.4 2022 国防科技大学[5] 全光纤振荡器 9.7 0.898 ~2.4 0.1 1 2022 国防科技大学[6] 全光纤振荡器 6.5 0.501 1.38 0.1 1 2022 国防科技大学[7] 全光纤振荡器 7.3 0.5689 1.43 0.1 1 2023 国防科技大学[8] 全光纤振荡器 10.75 0.973 ~1.61 0.09 1 2015 IPG[10] YLM-150/1500-QCW 1.5 0.150 1.05 0.05—50 0—50 2015 IPG[11] YLM-250/2500-QCW 2.5 0.250 1.05 0.05—50 0—50 2015 IPG[12] YLS-2000/20000-QCW 20 2 12.33#, 44# 0.2—10 2 2016 IPG[13] YLS-2300/23000-QCW 23 2.3 12.33#, 44# 0.2—10 2 2018 武汉锐科[14] RFL-QCW450/1500FS 1.5 0.450 <1.45#, <5.82# 0.1—75 0.050—5 2018 武汉锐科[15] RFL-QCW150/1500 1.5 0.150 <1.45#, <5.82# 0.05—50 0—5 2021 武汉锐科[16] RFL-QCW1500/15000 15 1.5 <11.64# 0.05—50 0—5 2019 创鑫激光[17] MFSQ-150/1500W 1.5 0.150 1.3, 2.8 0.1—50 0.001—5 2019 创鑫激光[18] MFSQ-500/2500W 2.5 0.500 2.5 0.1—50 0.001—5 注: 标#数据根据已知数据计算得出. 表 2 仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameter.
物理量 物理意义 上下标
符号物理意义 $P$ 功率 $ + $ 正向 ${N_0}$ 掺杂离子浓度 $ - $ 反向 ${N_1}$ 基态粒子数密度 p 泵浦光 ${N_2}$ 激发态粒子数密度 s 信号光 Acore 纤芯面积 $m$ 泵浦光波长序数 Aeff 纤芯有效面积[24] $n$ 信号光波长序数 $\lambda $ 波长 $N$ 信号光波长
离散数$z$ 增益光纤的轴向坐标 e 发射截面 $\varGamma $ 填充因子 a 吸收截面 $\sigma $ 吸收发射截面 $ {\text{OC1}} $ 输出耦合光栅1 $R$ 反射率 ${\text{OC2}}$ 输出耦合光栅2 $a$ 损耗系数 gR 拉曼增益系数 $\tau $ 激发态粒子寿命 $\nu $ 光波频率 $\omega $ 光波角频率 Beff 斯托克斯辐射的
有效带宽Δλ 实际增益光谱带宽 L 增益光纤长度 h 普朗克常量 $\hbar $ 约化普朗克常量 c 光速 -
[1] 黄婷, 杜伟哲, 苏坤, 张建超, 李敬洋, 祁俊峰, 雷永平, 武强, 肖荣诗 2022 中国激光 49 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang T, Du W Z, Su K, Zhang J C, Li J Y, Qi J F, Lei Y P, Wu Q, Xiao R S 2022 Chin. J. Lasers 49 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Marimuthu S, Smith B 2021 Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 113 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen Z Z, Xu Y T, Guo Y D, Wang B S, Xu J, Xu J L, Gao H W, Yuan L, Yuan H T, Lin Y Y, Xiao Y S, Bo Y, Peng Q J, Lei W Q, Cui D F, Xu Z Y 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 5011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bian Q, Bo Y, Zuo J W, Yuan L, Chen H B, Peng Q J, Xu Z Y 2020 Opt. Express 28 13895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hong Z J, Wan Y C, Xi X M, Zhang H W, Wang X L, Xu X J 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 1826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang L, Zhang H W, Wang P, Yang B L, Wang X L, Ning Y, Xu X J 2022 Opt. Laser Technol. 154 108338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang L, Zhang H W, Wang P, Yang B L, Wang X L, Ning Y, Xu X J 2022 IEEE Photonics J. 14 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 王力, 张汉伟, 王鹏, 王小林, 宁禹, 韩凯, 许晓军 2023 中国激光 50 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L, Zhang H W, Wang P, Wang X L, Ning Y, Han K, Xu X J 2023 Chin. J. Lasers 50 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zheng J K, Bo Y, Xie S Y, Zuo J W, Wang P Y, Guo Y D, Liu B L, Peng Q J, Cui D F, Lei W Q, Xu Z Y 2013 Chin. Phys. Lett. 30 074202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/en/229/FileAttachment/YLM-QCW+and+YLR-QCW+Single-mode+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[11] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/cn/101/FileAttachment/YLM-QCW+Series+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[12] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/ru/86/FileAttachment/YLS-2000_20000-QCW+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[13] IPG https://www.ipgphotonics.com/ru/126/FileAttachment/YLS-2300_23000-QCW+Datasheet.pdf [2023-03-30]
[14] 武汉锐科 https://www.raycuslaser.com/upload/old_file/201808/5b6168071a474.pdf [2023-03-30]
[15] 武汉锐科 https://www.raycuslaser.com/upload/20210507/1f52nmd6in812mko.pdf [2023-03-30]
[16] 武汉锐科 https://www.jyothishya.com/view/2636.html [2023-03-30]
[17] 创鑫激光 http://www.maxphotonics.com/vancheerfile/files/2020/4/20200416155923674.pdf [2023-03-30]
[18] 创鑫激光 http://www.maxphotonics.com/vancheerfile/files/2020/4/20200416155938936.pdf [2023-03-30]
[19] Zhong P L, Wang L, Yang B L, Zhang H W, Xi X M, Wang P, Wang X L 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 2806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu J Q, Zeng L F, Wang P, Yang B L, Xi X M, Shi C, Zhang H W, Wang X L, Xi F J 2023 IEEE Photonics J. 15 1500209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王小林, 叶云, 奚小明, 史尘, 张汉伟, 韩凯, 王泽锋, 许晓军, 周朴, 司磊, 陈金宝 2018 中国专利 201821644646.3
Wang X L, Ye Y, Xi X M, Shi C, Zhang H W, Han K, Wang Z F, Xu X J, Zhou P, Si L, Chen J B 2018 CN Patent 201821644646.3 (in Chinese)
[22] 王小林, 张汉伟, 史尘, 段磊, 奚小明 2021 基于SeeFiberLaser的光纤激光建模与仿真 (北京: 科学出版社) 第19, 22, 40, 44页
Wang X L, Zhang H W, Shi C, Duan L, Xi X M 2021 Fiber Laser Modeling and Simulation Based on SeeFiberLaser (Beijing: Science Press) pp19, 22, 40, 44 (in Chinese)
[23] 阿戈沃著(贾东方, 葛春风 译) 2014 非线性光纤光学(第五版) (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第25, 205页
Agrawal G P (translated by Jia D F, Ge C F) 2014 Nonlinear Fiber Optics (5th Ed.) (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp25, 205 (in Chinese)
[24] 住村和彦日, 西浦匡则日著(宋鑫 译) 2013 图解光纤激光器入门 (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第62页
Zhu C H Y R, Xi P K Z R(translated by Song X) 2013 Illustrative Introduction to Fiber Lasers (Beijing: China Machine Press) p62 (in Chinese)
[25] Lv X G, Liao T Q, Yi Y 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1213 42053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 高俊峰, 闫明鉴, 梁慧生, 詹涌, 韩志刚, 朱日宏, 刘明 2021 激光与红外 51 1013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J F, Yan M J, Liang H S, Zhan Y, Han Z G, Zhu R H, Liu M 2021 Laser & Infrared 51 1013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Villate D, Blanchot N, Rouyer C 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8749
- PDF Downloads: 127
- Cited By: 0














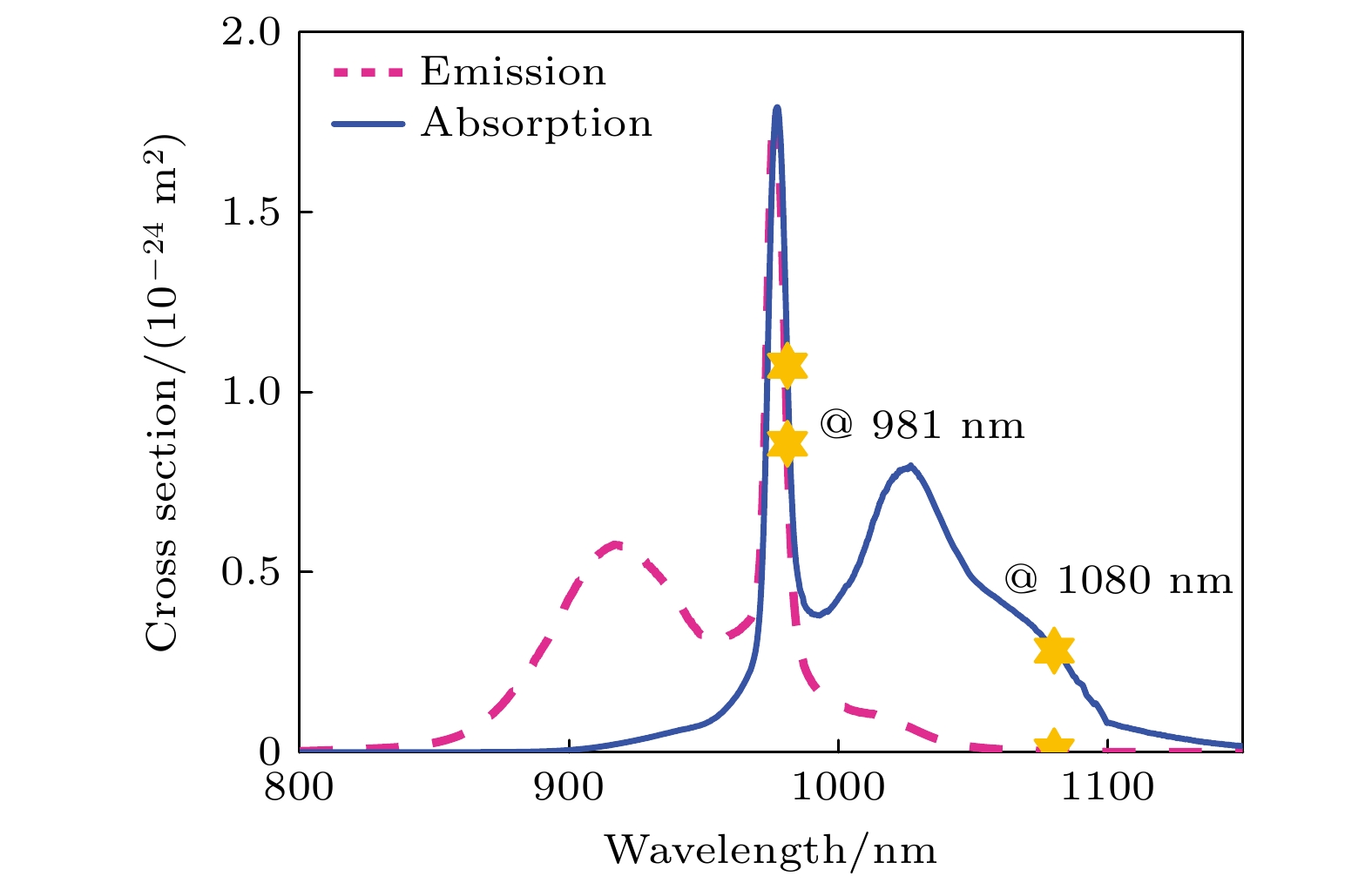
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: