-
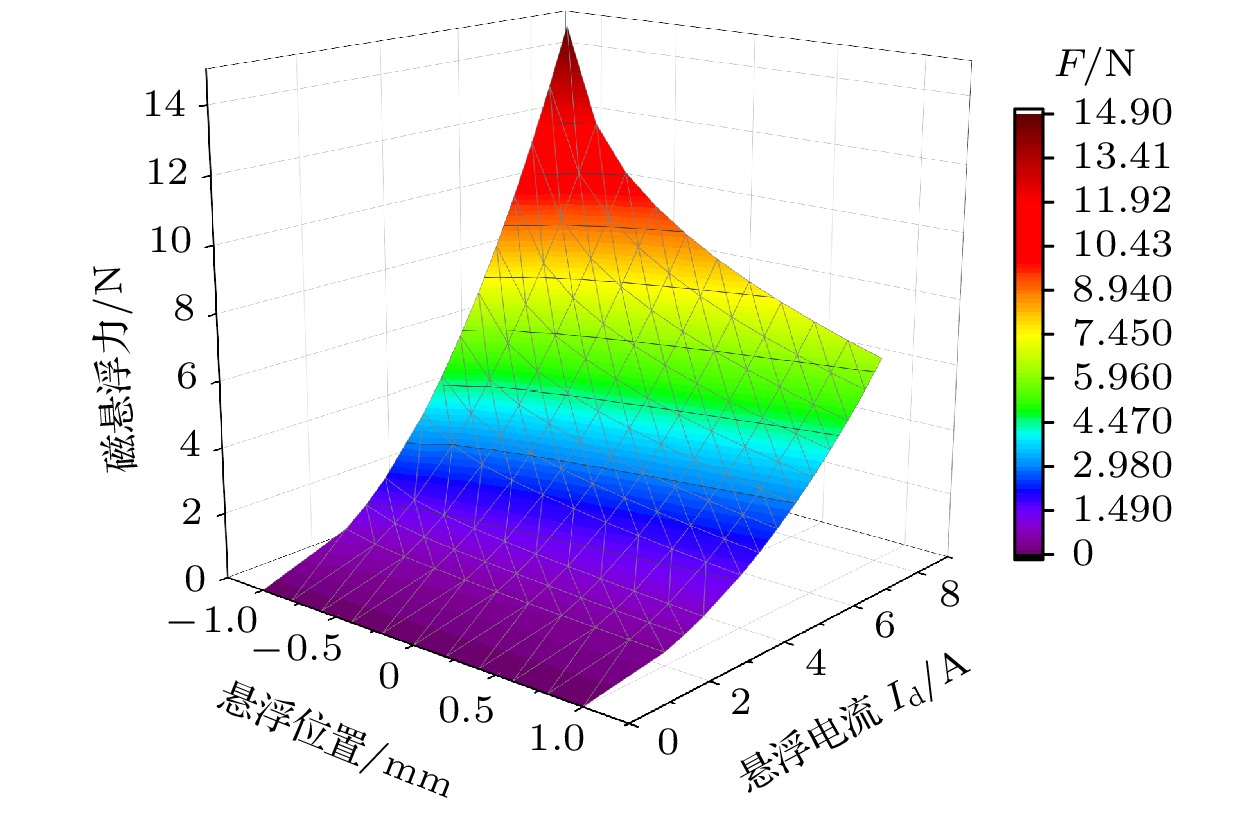
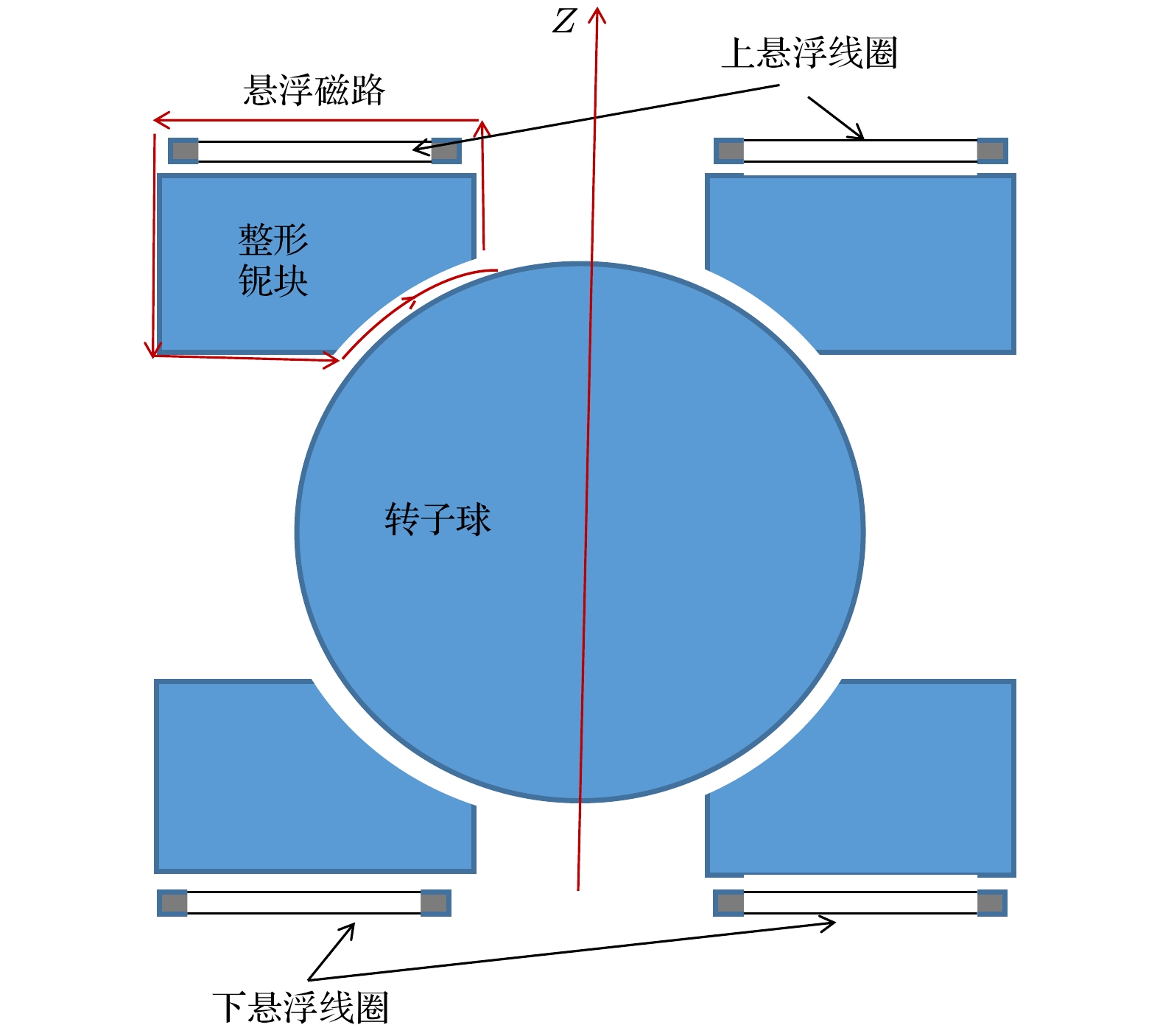
The high-speed rotating superconducting rotor can be used as a sensor to measure angular speed or angular position. Mass unbalance and oblateness of superconducting rotor are the main error sources to measure angular speed or angular position. General Electric company has developed an superconducting rotor magnetic suspension device with an accuracy of 0.005° per hour, but its rotor structure is very complex. So it is difficult to process and assemble with extremely small mass-unbalance and small oblateness, which limits the further improvement of its accuracy. According to this, in this paper we introduce a magnetic support structure with a simple superconducting rotor compared with rotor made by General Electric company. The rotor sphere is a closed structure with no theoretical mass eccentricity. Its electromagnetic structure is simpler than General Electric company’s, and the stator coil is the torquer coil at the same time. The stator coil is used to accelerate the rotor, while the torquer is used to make the rotor erect. Based on the theory of superconducting electrodynamics and the finite element method, the characteristics of the magnetic suspension structure are analyzed. The magnetic field coupling effect of the stator and the suspension coils on the surface of the superconducting rotor are studied, and their influence on magnetic supporting force is also analyzed. The current direction of the two suspension coils should be opposite, otherwise the rotor will produce forced vibration, which will make it difficult to accelerate the superconducting rotor. Then the magnetic circuit theory and the finite element method are used to model the magnetic circuit of the magnetic levitation structure, and the critical carrying capacity of the magnetic suspension structure is calculated and the optimal suspension conditions are given. Finally, a method to optimize its carrying capacity is designed. Therefore, the currents of the suspension coils are controlled by the acceleration of superconducting cavity. Through this method, the maximum bearing capacity of the magnetic levitation structure can be increased by 78% compared with that of fixed optimal suspension current support. The analysis results provide a reference for the structural design and optimization of the superconducting rotor magnetic levitation system.
-
Keywords:
- superconducting magnetic levitation /
- superconducting rotor /
- magnetic field coupling /
- carrying capacity of magnetic levitation structure
[1] 胡新宁, 王厚生, 王晖, 王秋良 2010 光学精密工程 18 169
Hu X N, Wang H S, Wang H, Wang Q L 2010 Opt. Precis. Eng. 18 169
[2] 江磊, 钟智勇, 仪德英, 张怀武 2008 仪器仪表学报 29 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang L, Zhong Z Y, Yi D Y, Zhang H W 2008 Chin. J. Sci. Instru. 29 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 崔春艳, 胡新宁, 程军胜, 王晖, 王秋良 2015 64 018403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui C Y, Hu X N, Chen J S, Wang H, Wang Q L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu X N, Wang Q L, Cui C Y 2010 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20 892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang H, Hu X N, Cui C Y, Wang L, Wang Q L 2018 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 28 5207905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schoch K F, Darrel B 1967 Proceedings of the 1966 Cryogenic Engineering Conference Colorado, America, June 13–15, 1967 p657
[7] 汤继强 2005 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Tang J Q 2005 Ph. D. Dissertation ( Harbin: Harbin Engineering University ) (in Chinese)
[8] Harding T H, Lawson D W 1968 AIAA J. 6 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Schoch K F, Darrel B 1967 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 12 657
[10] 胡新宁, 赵尚武, 王厚生, 王晖, 王秋良 2008 稀有金属材料与工程 37 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu X N, Zhao S W, Wang H S, Wang H, Wang Q L 2008 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 37 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 汤继强, 赵琳, 罗俊燕 2004 弹箭与制导学报 24 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J Q, Zhao L, Luo J Y 2004 J. Projectiles Rockets Missiles Guidance 24 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 汤继强, 孙枫, 赵玉新, 郭秋芬 2005 哈尔滨工程大学学报 26 462
Tang J Q, Sun F, Zhao Y X, Guo Q F 2005 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 26 462
[13] 赵尚武, 胡新宁, 崔春燕, 王秋良 2008 稀有金属材料与工程 37 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao S W, Hu X N, Cui C Y, Wang Q L 2008 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 37 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王浩, 王秋良, 胡新宁, 崔春燕, 苏华俊, 何忠名 2018 低温与超导 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Wang Q L, Hu X N, Cui C Y, Su H J, He Z M 2018 Cyro. Supercond. 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Buchhold T A 1961 Cryogenics 1 203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张裕恒 1997 超导物理 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社) 第11, 12页
Zhang Y H 1997 Superconducting Physics (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press) pp11, 12 (in Chinese)
[17] 蔡圣善, 朱耕 1985 经典电动力学 (上海: 复旦大学出版社) 第229—254页
Cai S S, Zh G 1985 Classical Electrodynamics (Shanghai: Fudan University Press) pp229–254 (in Chinese)
[18] 管惟炎, 李宏成, 蔡建华, 吴杭生 1981 超导电性物理基础 (北京: 科学出版社) 第47—51页
Guan W Y, Li H C, Cai J H, Wu H S 1981 The Physical Basis of Superconductivity (Beijing: Science Press) pp47–51 (in Chinese)
[19] 林其壬, 赵佑民 1987 磁路设计原理 (北京: 科学出版社) 第87, 88页
Lin Q R, Zhao Y M 1987 Magnetic Circuit Design Principle (Beijing: Machinery Industry Press) pp87, 88 (in Chinese)
[20] 邹继斌, 刘宝庭, 崔淑海, 郑萍 1998 磁路与磁场 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社) 第43—47页)
Zou J B, Liu B T, Cui S H, Zhen P 1998 Magnetic Circuit and Magnetic Field (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press) pp43–47 (in Chinese)
[21] 刘建华, 王秋良, 严陆光, 李献 2010 电工技术学报 25 1
Liu J H, Wang Q L, Yan L G, Li X 2010 Tran. China Electrotech. Soc. 25 1
-
图 2 超导转子悬浮在不同位置时的表面磁场分布 (a)平分子午线位置; (b)超导球腔底部位置; (c)超导球腔中心位置; (d)超导球腔侧偏1 mm位置
Figure 2. Distribution of the surface magnetic field at different positions of the superconducting rotor suspension: (a) Meridian position; (b) the bottom position of the superconducting cavity; (c) the center of the superconducting cavity; (d) 1 mm off the side of the superconducting cavity.
图 13 超导转子磁浮结构承载力及刚度 (a)不同悬浮电流对允许的竖直偏移位置; (b)不同悬浮电流对对应的最大承载力; (c)不同电流对的支承刚度
Figure 13. Bearing capacity and stiffness of superconducting rotor maglev structure: (a) Allowable vertical offset position of different suspension current pairs; (b) maximum bearing capacity of different suspension current pairs; (c) support stiffness of different current pairs.
图 16 优化后超导转子的临界悬浮位置与对应的临界承载力 (a)临界悬浮位置随壳体加速度的变化; (b)临界承载力随壳体加速度的变化
Figure 16. Critical suspension position and the corresponding critical bearing capacity of the optimized superconducting rotor: (a) The change of the critical suspension position with the shell acceleration; (b) the change of the critical bearing capacity with the shell acceleration.
-
[1] 胡新宁, 王厚生, 王晖, 王秋良 2010 光学精密工程 18 169
Hu X N, Wang H S, Wang H, Wang Q L 2010 Opt. Precis. Eng. 18 169
[2] 江磊, 钟智勇, 仪德英, 张怀武 2008 仪器仪表学报 29 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang L, Zhong Z Y, Yi D Y, Zhang H W 2008 Chin. J. Sci. Instru. 29 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 崔春艳, 胡新宁, 程军胜, 王晖, 王秋良 2015 64 018403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui C Y, Hu X N, Chen J S, Wang H, Wang Q L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu X N, Wang Q L, Cui C Y 2010 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20 892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang H, Hu X N, Cui C Y, Wang L, Wang Q L 2018 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 28 5207905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schoch K F, Darrel B 1967 Proceedings of the 1966 Cryogenic Engineering Conference Colorado, America, June 13–15, 1967 p657
[7] 汤继强 2005 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Tang J Q 2005 Ph. D. Dissertation ( Harbin: Harbin Engineering University ) (in Chinese)
[8] Harding T H, Lawson D W 1968 AIAA J. 6 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Schoch K F, Darrel B 1967 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 12 657
[10] 胡新宁, 赵尚武, 王厚生, 王晖, 王秋良 2008 稀有金属材料与工程 37 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu X N, Zhao S W, Wang H S, Wang H, Wang Q L 2008 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 37 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 汤继强, 赵琳, 罗俊燕 2004 弹箭与制导学报 24 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J Q, Zhao L, Luo J Y 2004 J. Projectiles Rockets Missiles Guidance 24 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 汤继强, 孙枫, 赵玉新, 郭秋芬 2005 哈尔滨工程大学学报 26 462
Tang J Q, Sun F, Zhao Y X, Guo Q F 2005 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 26 462
[13] 赵尚武, 胡新宁, 崔春燕, 王秋良 2008 稀有金属材料与工程 37 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao S W, Hu X N, Cui C Y, Wang Q L 2008 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 37 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王浩, 王秋良, 胡新宁, 崔春燕, 苏华俊, 何忠名 2018 低温与超导 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Wang Q L, Hu X N, Cui C Y, Su H J, He Z M 2018 Cyro. Supercond. 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Buchhold T A 1961 Cryogenics 1 203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张裕恒 1997 超导物理 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社) 第11, 12页
Zhang Y H 1997 Superconducting Physics (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press) pp11, 12 (in Chinese)
[17] 蔡圣善, 朱耕 1985 经典电动力学 (上海: 复旦大学出版社) 第229—254页
Cai S S, Zh G 1985 Classical Electrodynamics (Shanghai: Fudan University Press) pp229–254 (in Chinese)
[18] 管惟炎, 李宏成, 蔡建华, 吴杭生 1981 超导电性物理基础 (北京: 科学出版社) 第47—51页
Guan W Y, Li H C, Cai J H, Wu H S 1981 The Physical Basis of Superconductivity (Beijing: Science Press) pp47–51 (in Chinese)
[19] 林其壬, 赵佑民 1987 磁路设计原理 (北京: 科学出版社) 第87, 88页
Lin Q R, Zhao Y M 1987 Magnetic Circuit Design Principle (Beijing: Machinery Industry Press) pp87, 88 (in Chinese)
[20] 邹继斌, 刘宝庭, 崔淑海, 郑萍 1998 磁路与磁场 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社) 第43—47页)
Zou J B, Liu B T, Cui S H, Zhen P 1998 Magnetic Circuit and Magnetic Field (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press) pp43–47 (in Chinese)
[21] 刘建华, 王秋良, 严陆光, 李献 2010 电工技术学报 25 1
Liu J H, Wang Q L, Yan L G, Li X 2010 Tran. China Electrotech. Soc. 25 1
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6024
- PDF Downloads: 76
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: