-
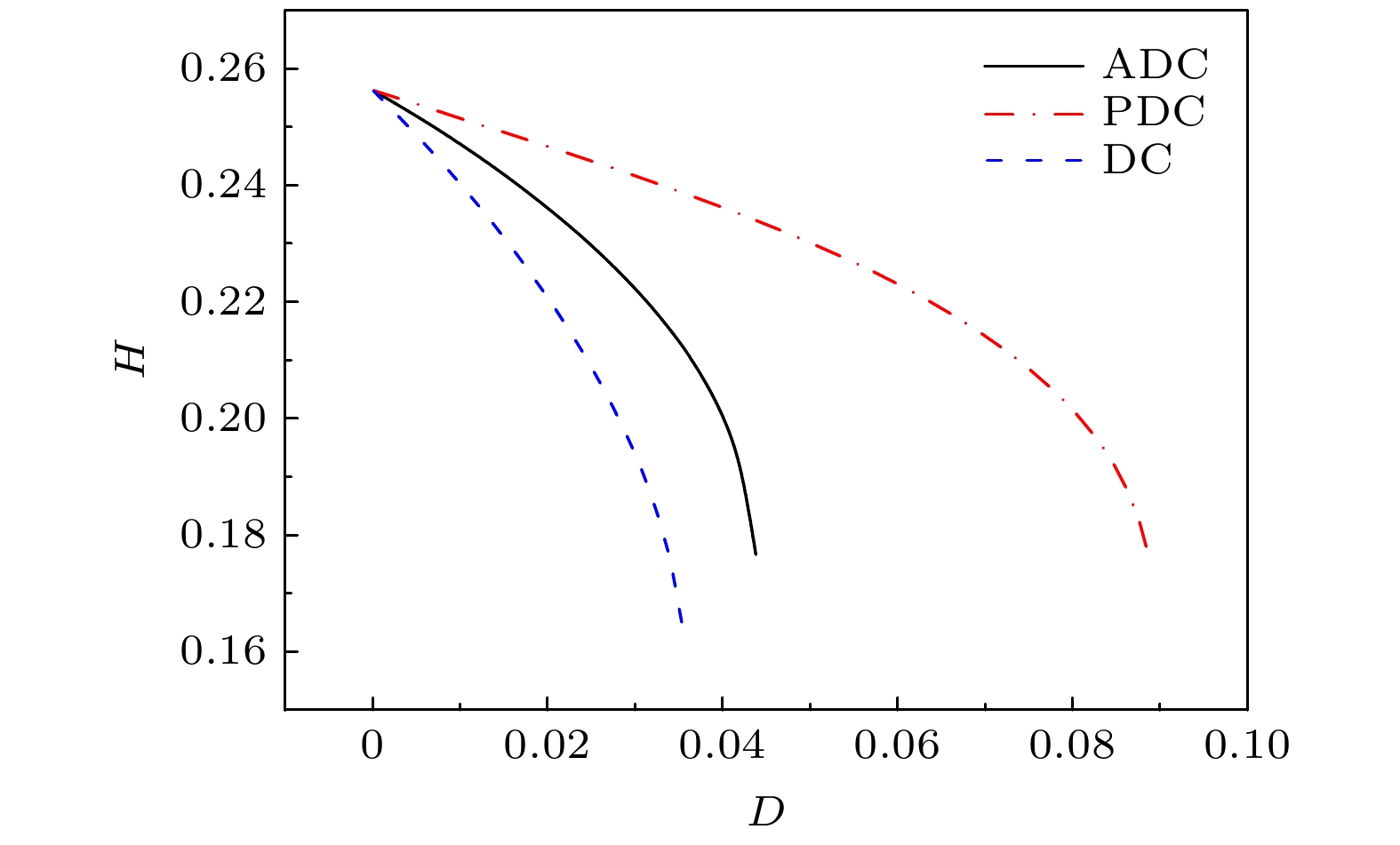
The quantum nonlocal correlation of quantum states plays an important role in the quantum information and quantum computing protocols. However, during the transmission of entangled states in the quantum channel, they will inevitably interact with the environment, resulting in the degradation of the coherence and then weakening the quantum nonlocal correlation. Using a high probability quantum nonlocal correlation testing scheme based on Hardy-type paradox, in this paper we investigate the quantum nonlocal correlation testing of two-qubit polarization entangled states when they transmit through amplitude damping channel (ADC), phase damping channel (PDC) and depolarization damping channel (DC). The results show that DC has a great influence on the quantum nonlocal correlation testing, while PDC has little influence on the quantum nonlocal correlation testing of quantum states. Finally, this paper also gives condition for the successful quantum nonlocal correlation testing of ADC under weak measurement and quantum weak measurement reversal operation. The results show that when the intensity of weak measurement increases, the influence of ADC decoherence effect on quantum nonlocal correlation testing can be effectively reduced.
-
Keywords:
- quantum nonlocal correlation /
- amplitude damping /
- phase damping /
- depolarization damping /
- weak measurement /
- quantum weak measurement reversal
[1] Einstein A, Podolsky B, Rosen N 1935 Phys. Rev. 47 777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bennett C H, Brassard G, Crepeau C, Jozsa R, Peres A, Wootters W K 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 1895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nielsen M A, Chuang I L 2000 Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp17–60
[4] Masanes L, Pironio S, Acin A 2011 Nat. Commun. 2 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gisin N, Ribordy G, Tittel W, Zbinden H 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bennett C H, Brassard G 2014 Theor. Comput. Sci. 560 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王剑, 陈皇卿, 张权, 唐朝京 2007 56 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Chen H Q, Zhang Q, Tang C J 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bennett C H, Brassard G, Ekert A K 1992 Sci. Am. 267 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Q, Tan M Y, Liu Y, Zeng H S 2009 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 42 125503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王美姣, 夏云杰 2015 64 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M J, Xia Y J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hu M L 2011 Phys. Lett. A 375 2140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xu K, Zhang G F, Liu W M 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 052305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang Q, Xu L 2020 Laser Phys. 30 045203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dodd P J, Halliwell J J 2004 Phys. Rev. A 69 052105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hu M L, Hu X, Wang J, Peng Y, Zhang Y R, Fan H 2018 Phys. Rep. 762 1
[16] Horodecki R, Horodecki P, Horodecki M, Horodecki K 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Salles A, de Melo F, Almeida M P, Hor-Meyll M, Walborn S P, Souto Ribeiro P H, Davidovich L 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 022322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kim Y S, Lee J C, Kwon O, Kim Y H 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu M L, Fan H 2020 Sci. Chin. :Phys. Mech. Astron. 63 230322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bell J S 1964 Physics 1 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Clauser J F, Horne M A, Shimony A, Holt R A 1969 Phys. Rev. Lett. 23 880
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hardy L 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] White A G, James D F V, Eberhard P H, Kwiat P G 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 3103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang M, Meng H X, Zhou J, Xu Z P, Xiao Y, Sun K, Chen J L, Xu J S, Li C F, Guo G C 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 032103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mermin N 1995 Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 755 616
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 刘晋, 缪波, 贾欣燕, 樊代和 2019 68 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Miao B, Jia XY, Fan D H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Goldstein S 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen L, Romero J 2012 Opt. Express 20 21687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fan D H, Dai M C, Guo W J, Wei L F 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 040302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Li W J, He Z, Wang Q 2017 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56 2813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xiao X, Yao Y, Xie Y M, Wang X H, Li Y L 2016 Quantum Inf. Process. 15 3881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 Alice制备的信号光子(s)和闲置光子(i)通过不同阻尼类型信道D后传输给Bob, 传输后的量子态表示为
$ {\boldsymbol{\rho }} _d^{\rm{A, P, D}} $ Figure 1. Signal photon (s) and idle photon (i) prepared by Alice are transmitted to Bob through quantum channel D with different damping types. The final quantum state after transmission can be expressed as
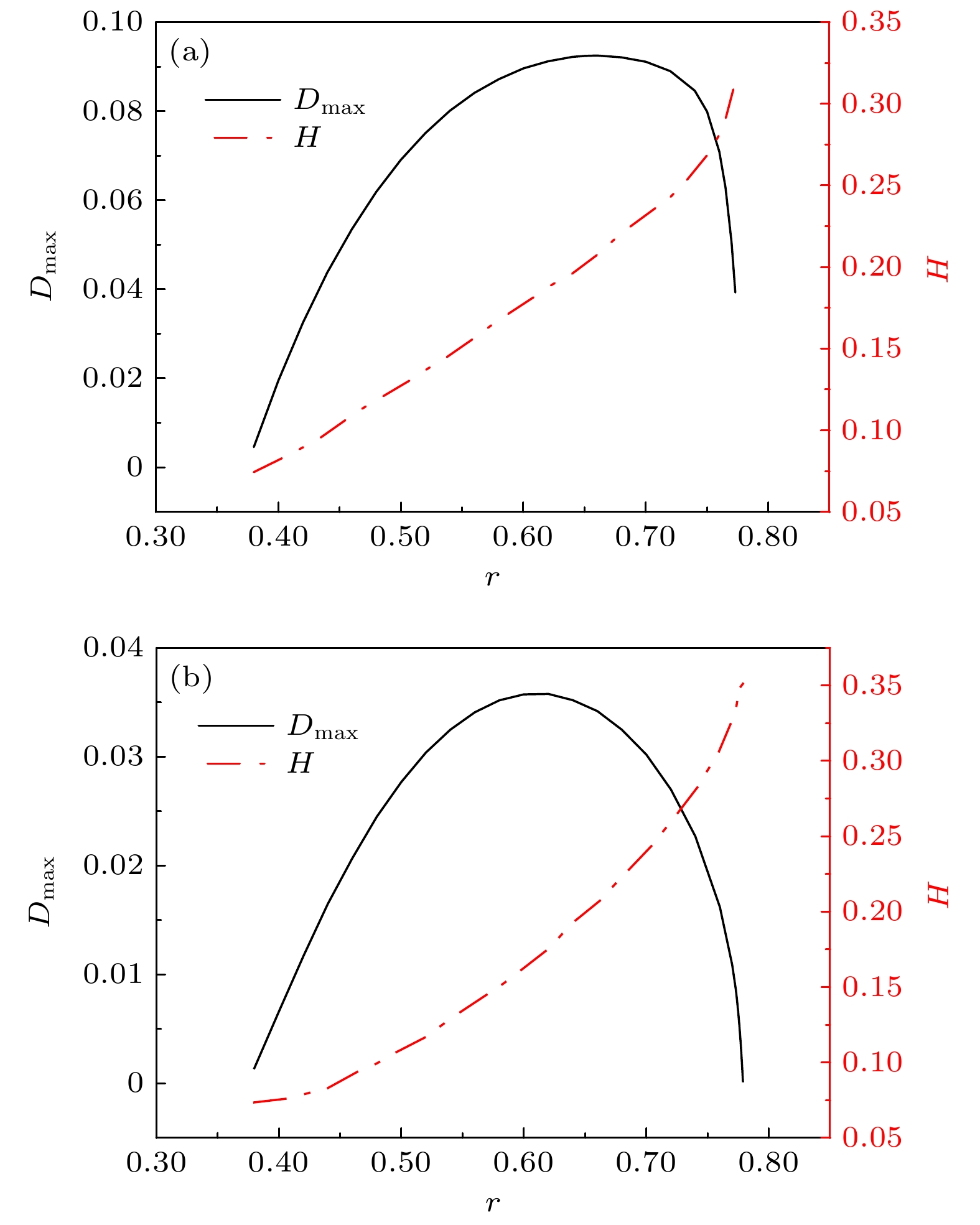
$ {\boldsymbol{\rho }}_d^{\rm{A, P, D}} $ .图 3 量子态经过PDC和DC阻尼信道时, 进行量子非局域关联检验的情况 (a) 量子态经过PDC后,
${D_{\max}}$ 和H随r的变化关系曲线; (b) 量子态经过DC后,${D_{\max}}$ 和H随r的变化关系曲线Figure 3. Quantum nonlocal correlation test when the quantum state transmitted through PDC and DC: (a) The relationship
${D_{\max}}$ and H vs r when the quantum state transmitted through PDC. (b) the relationship${D_{\max}}$ and H vs r when the quantum state transmitted through DC. -
[1] Einstein A, Podolsky B, Rosen N 1935 Phys. Rev. 47 777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bennett C H, Brassard G, Crepeau C, Jozsa R, Peres A, Wootters W K 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 1895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nielsen M A, Chuang I L 2000 Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp17–60
[4] Masanes L, Pironio S, Acin A 2011 Nat. Commun. 2 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gisin N, Ribordy G, Tittel W, Zbinden H 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bennett C H, Brassard G 2014 Theor. Comput. Sci. 560 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王剑, 陈皇卿, 张权, 唐朝京 2007 56 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Chen H Q, Zhang Q, Tang C J 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bennett C H, Brassard G, Ekert A K 1992 Sci. Am. 267 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Q, Tan M Y, Liu Y, Zeng H S 2009 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 42 125503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王美姣, 夏云杰 2015 64 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M J, Xia Y J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hu M L 2011 Phys. Lett. A 375 2140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xu K, Zhang G F, Liu W M 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 052305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang Q, Xu L 2020 Laser Phys. 30 045203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dodd P J, Halliwell J J 2004 Phys. Rev. A 69 052105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hu M L, Hu X, Wang J, Peng Y, Zhang Y R, Fan H 2018 Phys. Rep. 762 1
[16] Horodecki R, Horodecki P, Horodecki M, Horodecki K 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Salles A, de Melo F, Almeida M P, Hor-Meyll M, Walborn S P, Souto Ribeiro P H, Davidovich L 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 022322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kim Y S, Lee J C, Kwon O, Kim Y H 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu M L, Fan H 2020 Sci. Chin. :Phys. Mech. Astron. 63 230322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bell J S 1964 Physics 1 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Clauser J F, Horne M A, Shimony A, Holt R A 1969 Phys. Rev. Lett. 23 880
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hardy L 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] White A G, James D F V, Eberhard P H, Kwiat P G 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 3103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang M, Meng H X, Zhou J, Xu Z P, Xiao Y, Sun K, Chen J L, Xu J S, Li C F, Guo G C 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 032103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mermin N 1995 Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 755 616
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 刘晋, 缪波, 贾欣燕, 樊代和 2019 68 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Miao B, Jia XY, Fan D H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Goldstein S 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen L, Romero J 2012 Opt. Express 20 21687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fan D H, Dai M C, Guo W J, Wei L F 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 040302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Li W J, He Z, Wang Q 2017 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56 2813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xiao X, Yao Y, Xie Y M, Wang X H, Li Y L 2016 Quantum Inf. Process. 15 3881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7240
- PDF Downloads: 113
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: