-
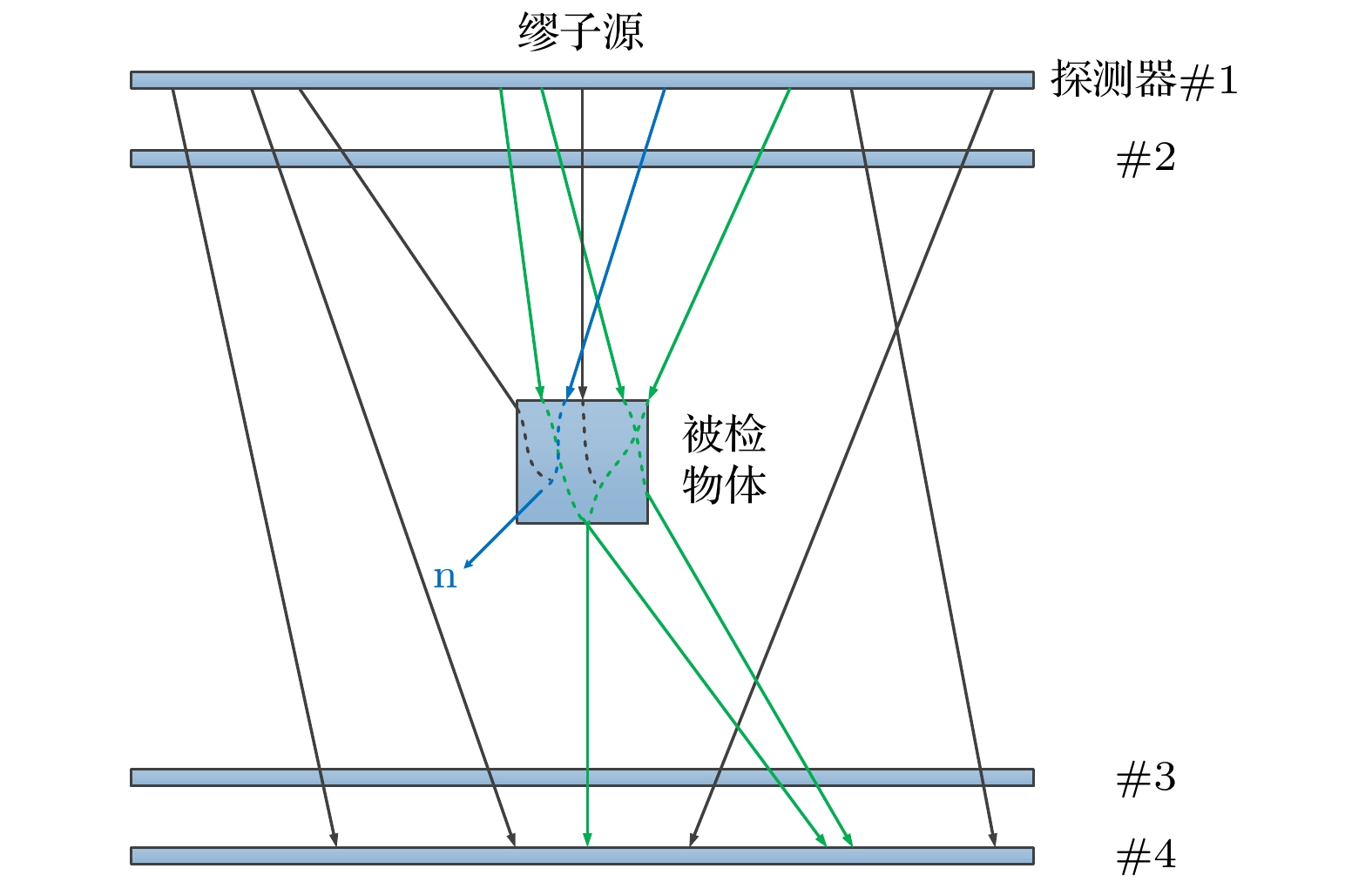
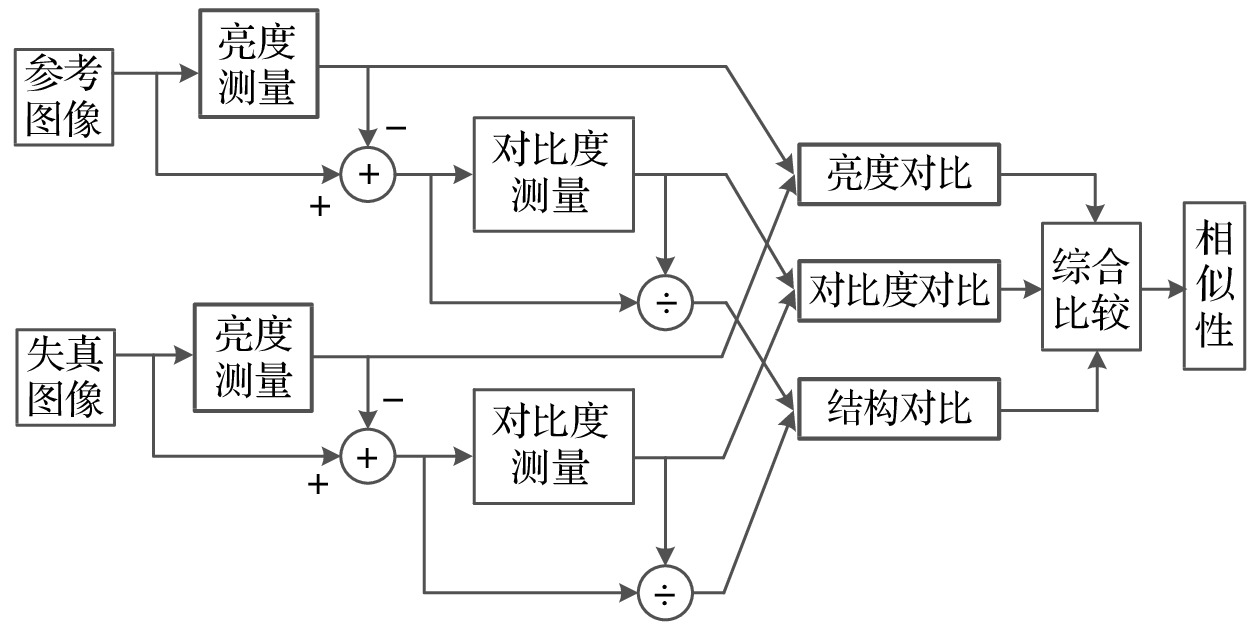
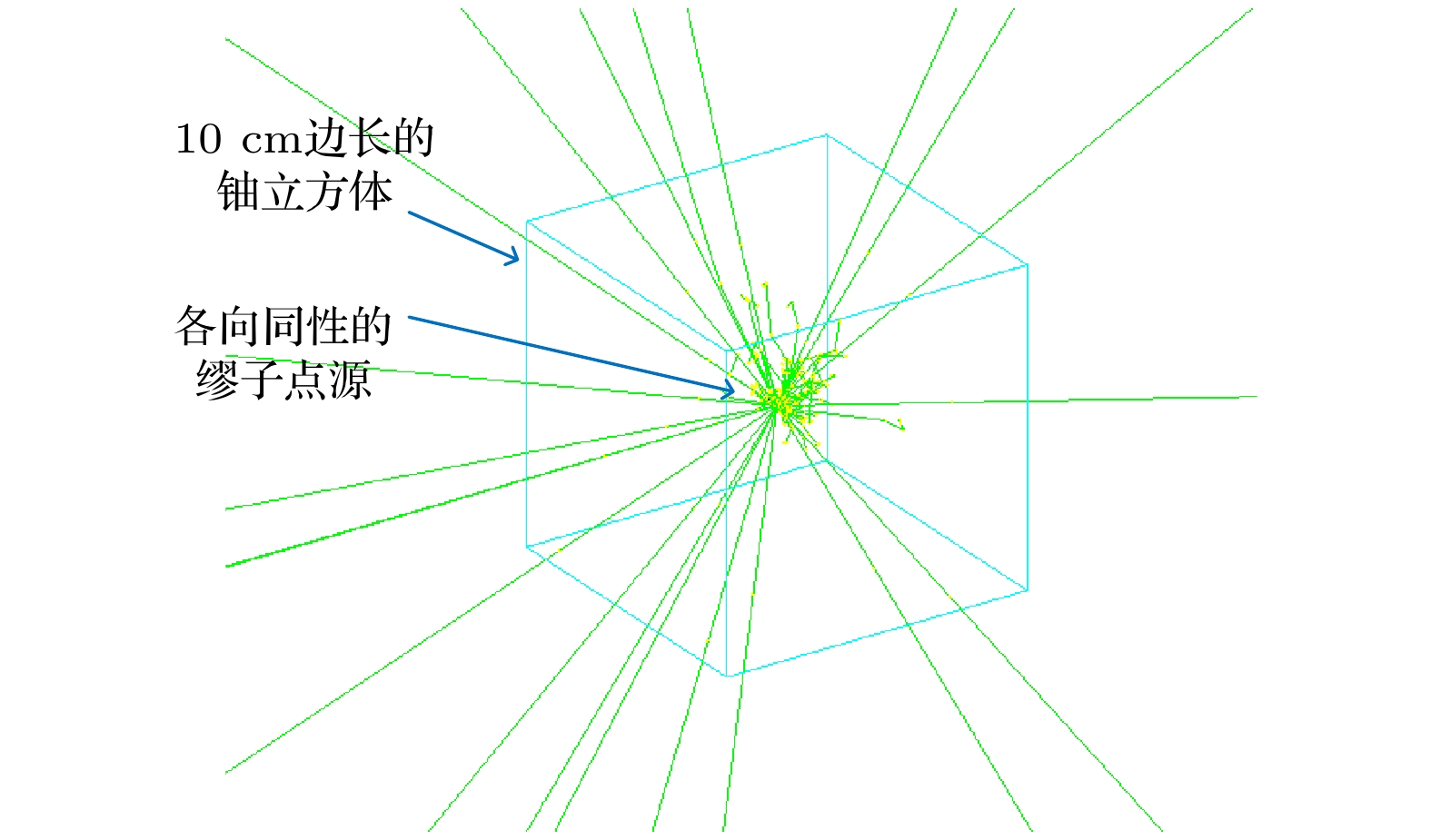
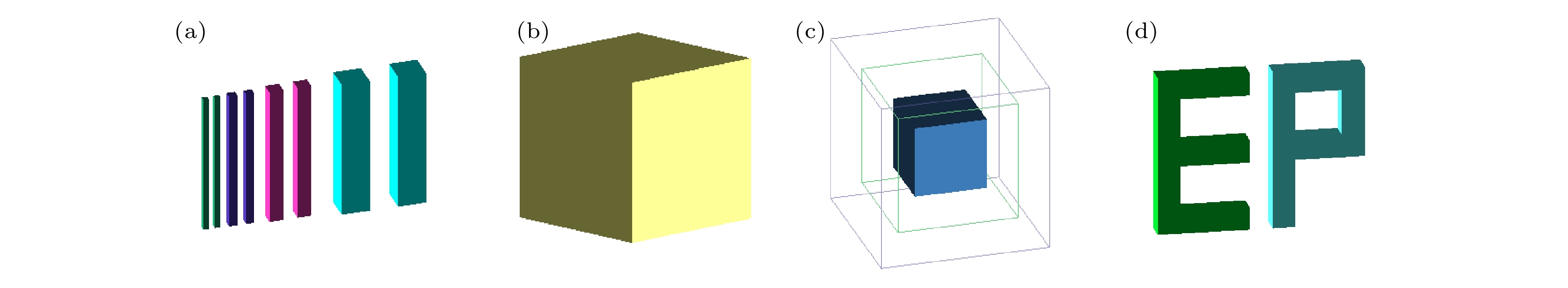
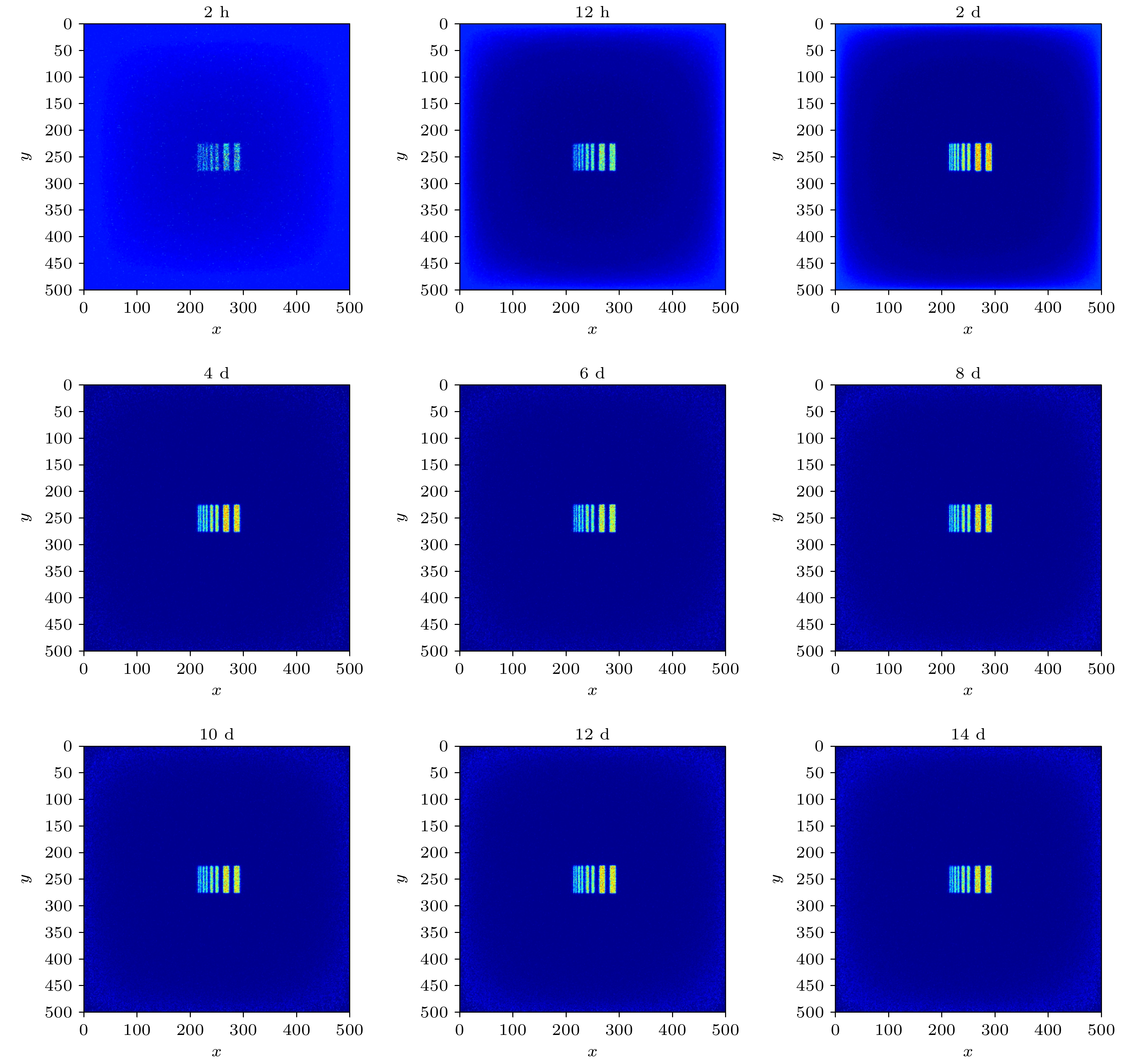
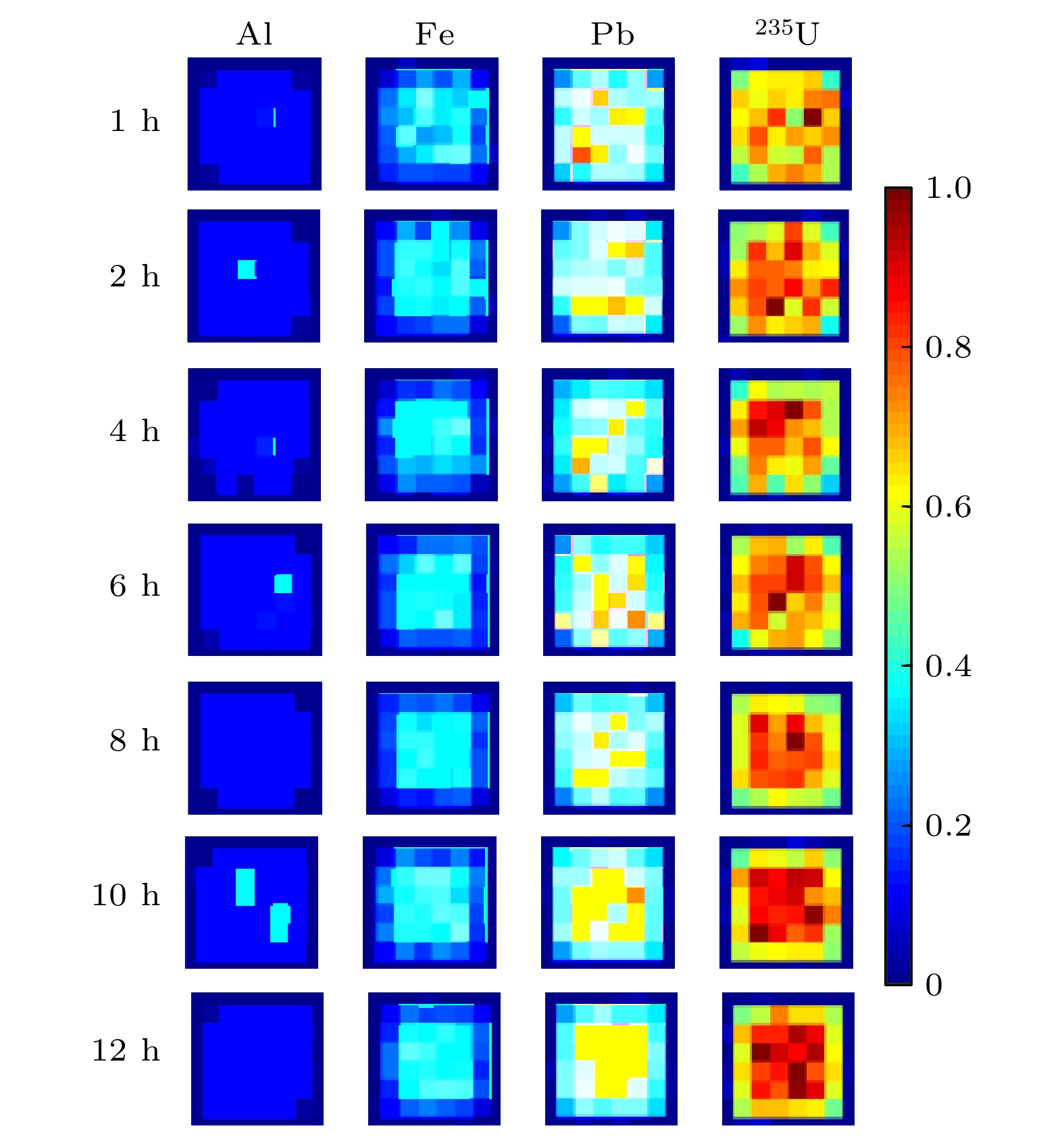
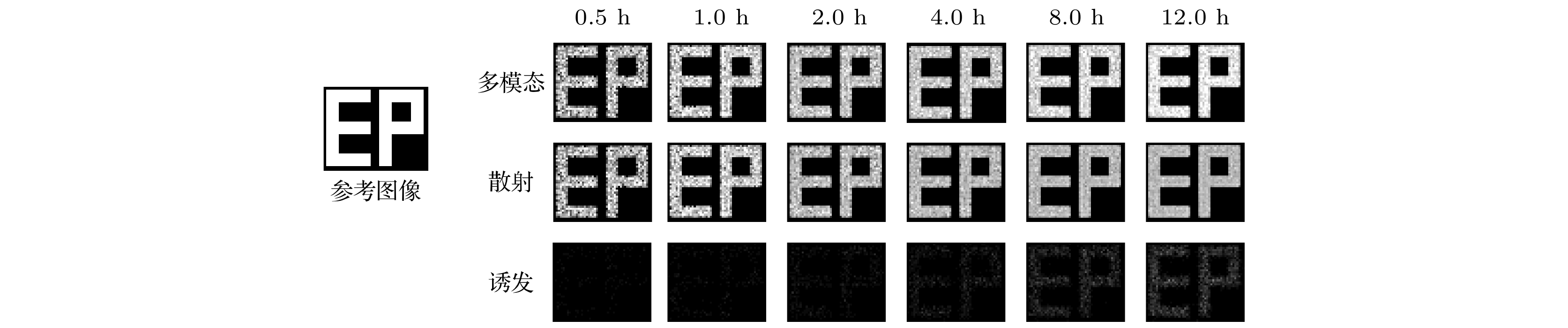
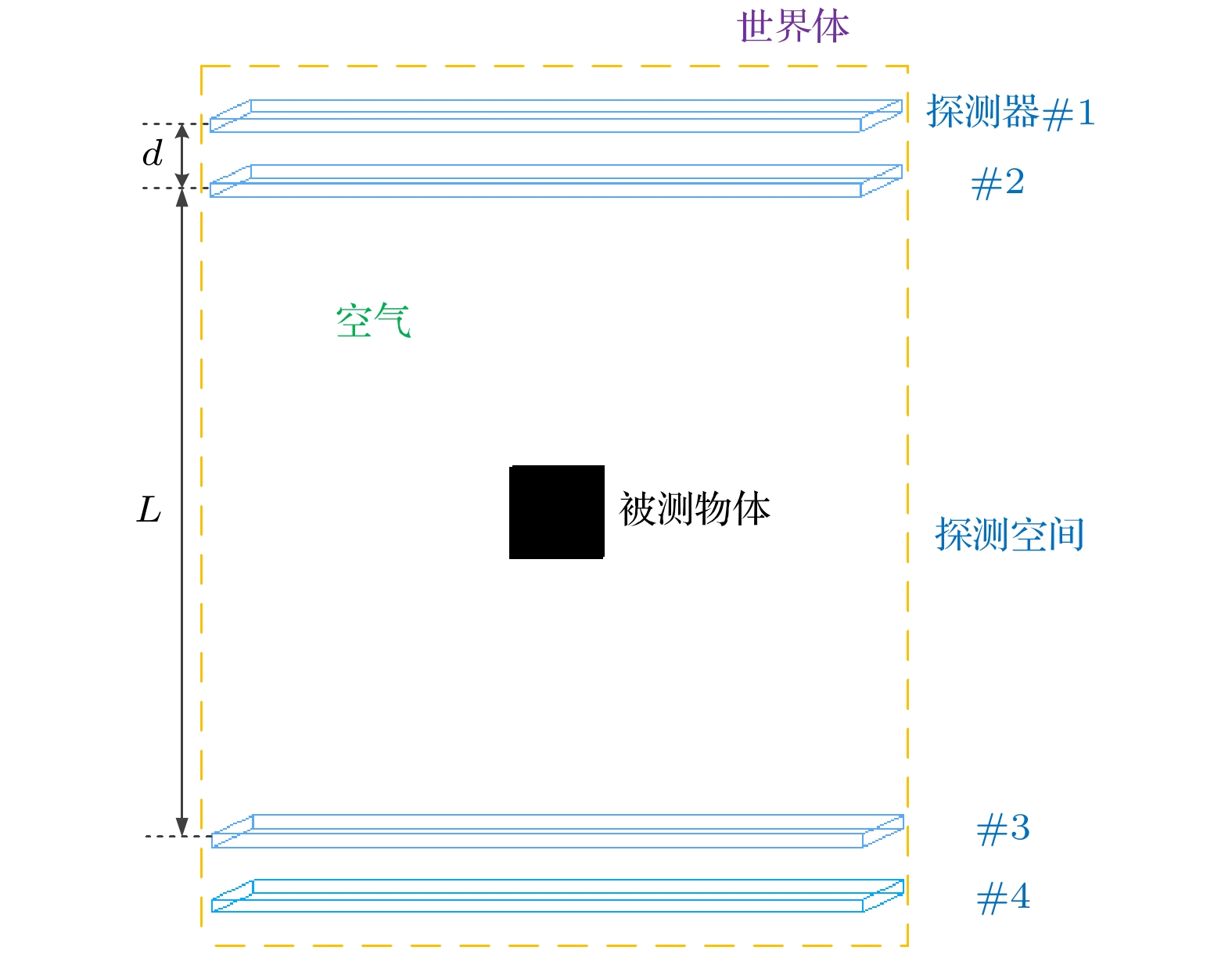
Both the information about the scattering of muons due to their interaction with material and the information about the material-stopped muons generating secondary induced neutrons effectively are used for multimodal imaging of muon. In order to evaluate the image quality of multimodal imaging of muon, the detection model is established based on Geant4 and the reliability of the detection model is verified. Both the multiple Coulomb scattering module and the muon induced neutron module prove to be reliable. The multimodal imaging simulation program is developed, and the images are reconstructed on the basis of the simulated data. Four imaging models are developed. The first model is a line pair model used to study the spatial resolution of reconstructed images with imaging time ranging from two hours to two weeks. The line pair model is composed of 235U and the length of each line pair is set to be 100 mm. The cross sections are set to be 42, 42, 62, 62, 102, 102, 202, and 202 mm2, respectively. The second model is a cube model used to study the material resolution of reconstructed images with imaging time ranging from one hour to twelve hours. The side length of each cube is 100 mm. The third model is the cladding model used to test the reliability of multimodal imaging images in complex shielding situations. The outermost layer is of lead, with the side length being 140 mm and the thickness 40 mm. The middle layer is of iron, with the side length being 100 mm and the thickness 40 mm. The innermost layer of 235U, with the side length being 60 mm. The last letter model is used to calculate the structural similarity of reconstructed images, with imaging time ranging from half an hour to twelve hours. The letter model is made of 235U and consists of cubes with side length of 50 mm. The letters “E” and “P” are made up of 16 cubes and 15 cubes respectively. The spatial resolution reaches 4 mm when imaging time is within 12 hours. The 235U and other common high-z, medium-z, and low-z material can be distinguished when imaging time is on the order of hours. Muon scattering imaging image of the cladding model will cause misjudgment. However, the multimodal imaging image can correctly reflect the existence of 235U. The structure similarity between the reconstructed image and the reference image in different imaging times proves that multimodal imaging has higher quality than single imaging method. The study indicates that the multimodal imaging of muon has better imaging quality, can adapt to more complex imaging scenes and has more advantages in the detection and recognition of special nuclear material than muon imaging method with single interaction information.
-
Keywords:
- cosmic ray muon /
- multimodal imaging of muon /
- image quality
[1] Mollerach S, Roulet E 2018 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 98 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 罗小为, 杨燕兴, 李样, 鲍煜, 殳蕾 2020 原子能科学技术 54 2296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo X W, Yang Y X, Li Y, Bao Y, Shu L 2020 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 54 2296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shukla P, Sankrith S 2018 Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33 1850175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 于百蕙 2016 博士学位论文 (北京: 清华大学)
Yu B H 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Tsinghua University) (in Chinese)
[5] Lorenzo B, Raffaello D A, Andrea G 2020 Rev. Phys. 5 100038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Erlandson A, Anghel V N P, Godin D, Jewett C, Thompson M 2021 J. Instrum. 16 02024
[7] Chatzidakis S, Liu Z Z, Hayward J P, Scaglione J 2018 Appl. Phys. 123 124903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ayuso S, Blanco J J, Tejedor J, Herrero R J, Vrublevskyy I, Población O G, Medina J 2021 J. Space Weather Space Clim. 11 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Durham J M, Poulson D, Plaud-Ramos K, Bacon J, Chichester D L, Guardincerri E, Morris C L, Plaud-Ramos K, Schwendiman W, Tolman J D, Winston P 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 9 044013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Procureur S 2018 Nucl. Instru. and Meth. A 878 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Borozdin K N, Hogan G E, Morris C, Priedhorsky W C, Saunders A, Schultz L J, Teasdale M E 2003 Nature 422 277
[12] 智宇, 周静, 陈雷, 李沛玉, 赵明锐, 刘雯迪, 贾世海, 张昀昱, 胡守扬 2020 原子能科学技术 54 990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhi Y, Zhou J, Chen L, Li P Y, Zhao M R, Liu W D, Jia S H, Zhang Y Y, Hu S Y 2020 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 54 990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Schultz L J, Borozdin K N, Gomez J J, Hogan G E, Mcgill J A, Morris C L, Priedhorsky W C, Saunders A, Teasdale M E 2004 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 519 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Baesso P, Cussans D, Glaysher P, Thomay C, Vassallo C, Velthuis J, Quillin S, Robertson S, Steer C 2012 J. Instrum. 7 P11018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gnanvo K, Grasso L, Hohlmann M, Locke J B, Quintero A, Mitra D 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 652 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen X L, Wang Y, Chen G, Han D, Guo B, Yu Y, Zhang Q, Lyu P, Wang F 2020 J. Instrum. 15 C03012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Schultz L J, Borozdin K N, Gomez J J, Hogan G E, Mc Gill J A, Morris C L, Priedhorsky W C, Saunders A, Teasdale M E 2003 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 519 687
[18] Schultz L J, Blanpied G S, Borozdin K N, Fraser A M, Hengartner N W, Klimenko A V, Morris C L, Orum C, Sossong M J 2007 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16 1985
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hou L J, Huo Y G, Zuo W M, Yao Q X, Yang J Q, Zhang Q H 2020 Nucl. Eng. Technol. 53 208
[20] Warren G A, Caggiano J A, Bertozzi W, Korbly S, Ledoux R J, Park W H 2010 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 57 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Guardincerri E, Bacon J, Borozdin K, Matthew D J, Fabritius J, Hecht A, Milner E C, Miyadera H, Morris C L, Perry J, Poulson D 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 789 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bacon J D, Borozdin K N, Fabritius II J M, Morris C, Perry J O 2013 Muon Induced Fission Neutrons in Coincidence with Muon Tomography (Los Alamos, Los Alamos National Lab, LA-UR-13-28292 [R])
[23] Volker E, Oberacker, Umar A S, Karpeshin F F 2004 arXiv: nucl-th/0403087 [nucl-th]
[24] Morris C, Durham J M, Guardincerri E, Bacon J D, Wang Z H, Fellows S, Poulson D C, Plaud-Ramos K O, Daughton T M, Johnson O R 2015 A new method of passive counting of nuclear missile warheads -a white paper for the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Lab, LA-UR-15-26068 [R])
[25] Blackwell T B, Kudryavtsev V A 2015 J. Instrum. 10 05006
[26] 何伟波 2019 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
He W B 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[27] Yan J Y, Zhang Q H, Huo Y G http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1958.O4.20210529.1750.002.html [2021-06-08]
[28] Wang Z, Bovik A, Sheikh H R, Simoncelli E P 2004 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13 600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ide K, Becchetti M F, Flaska M, Poitrasson-Riviere A, Hamel M C, Polack J K, Lawrence C C, Clarke S D, Pozzi S A 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 694 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 李凯文, 徐琳, 陈强 2020 计算机科学 47 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li K W, Xu L, Chen Q 2020 Comput. Sci. 47 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 何凯, 牛俊慧, 沈成南, 卢雯霞 2018 天津大学学报 51 763
He K, Niu J H, Shen C N, Lu W X 2018 J. Tianjin Univ. 51 763
[32] 肖洒 2018 博士学位论文(绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院)
Xiao S 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics) (in Chinese)
[33] Malyshkina Y, Pshenichnova I, Mishustina I, Hughesd T, Heidd O, Greiner W 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 289 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kasztelan M, Jedrzejczak K, Szabelski J 2019 Mod. Phys. Lett. A 6 1950046
-
表 1 4 GeV缪子穿过10 cm厚不同材料的散射角
Table 1. Multiple scattering for 4 GeV muons passing through 10 cm of various materials.
材料 L0/cm 实验值θ/rad 理论值θ/mrad 相对误差/% U 0.32 21.58 21.49 0.42 Pb 0.56 15.92 15.94 0.13 Fe 1.76 8.67 8.64 0.35 Al 8.89 3.74 3.62 3.31 表 2 铀立方体的中子出射率
Table 2. Rate of neutrons that are emitted from bare cubes of uranium.
出射中子数/入射缪子数 HEU LEU DU 1 MeV负缪子 30.8 11.7 9.35 1 MeV正缪子 0.0538 0.0193 0.0164 2 GeV负缪子 0.0291 0.0152 0.0116 2 GeV正缪子 0.0286 0.0130 0.0124 -
[1] Mollerach S, Roulet E 2018 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 98 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 罗小为, 杨燕兴, 李样, 鲍煜, 殳蕾 2020 原子能科学技术 54 2296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo X W, Yang Y X, Li Y, Bao Y, Shu L 2020 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 54 2296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shukla P, Sankrith S 2018 Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33 1850175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 于百蕙 2016 博士学位论文 (北京: 清华大学)
Yu B H 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Tsinghua University) (in Chinese)
[5] Lorenzo B, Raffaello D A, Andrea G 2020 Rev. Phys. 5 100038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Erlandson A, Anghel V N P, Godin D, Jewett C, Thompson M 2021 J. Instrum. 16 02024
[7] Chatzidakis S, Liu Z Z, Hayward J P, Scaglione J 2018 Appl. Phys. 123 124903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ayuso S, Blanco J J, Tejedor J, Herrero R J, Vrublevskyy I, Población O G, Medina J 2021 J. Space Weather Space Clim. 11 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Durham J M, Poulson D, Plaud-Ramos K, Bacon J, Chichester D L, Guardincerri E, Morris C L, Plaud-Ramos K, Schwendiman W, Tolman J D, Winston P 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 9 044013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Procureur S 2018 Nucl. Instru. and Meth. A 878 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Borozdin K N, Hogan G E, Morris C, Priedhorsky W C, Saunders A, Schultz L J, Teasdale M E 2003 Nature 422 277
[12] 智宇, 周静, 陈雷, 李沛玉, 赵明锐, 刘雯迪, 贾世海, 张昀昱, 胡守扬 2020 原子能科学技术 54 990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhi Y, Zhou J, Chen L, Li P Y, Zhao M R, Liu W D, Jia S H, Zhang Y Y, Hu S Y 2020 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 54 990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Schultz L J, Borozdin K N, Gomez J J, Hogan G E, Mcgill J A, Morris C L, Priedhorsky W C, Saunders A, Teasdale M E 2004 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 519 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Baesso P, Cussans D, Glaysher P, Thomay C, Vassallo C, Velthuis J, Quillin S, Robertson S, Steer C 2012 J. Instrum. 7 P11018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gnanvo K, Grasso L, Hohlmann M, Locke J B, Quintero A, Mitra D 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 652 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen X L, Wang Y, Chen G, Han D, Guo B, Yu Y, Zhang Q, Lyu P, Wang F 2020 J. Instrum. 15 C03012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Schultz L J, Borozdin K N, Gomez J J, Hogan G E, Mc Gill J A, Morris C L, Priedhorsky W C, Saunders A, Teasdale M E 2003 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 519 687
[18] Schultz L J, Blanpied G S, Borozdin K N, Fraser A M, Hengartner N W, Klimenko A V, Morris C L, Orum C, Sossong M J 2007 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16 1985
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hou L J, Huo Y G, Zuo W M, Yao Q X, Yang J Q, Zhang Q H 2020 Nucl. Eng. Technol. 53 208
[20] Warren G A, Caggiano J A, Bertozzi W, Korbly S, Ledoux R J, Park W H 2010 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 57 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Guardincerri E, Bacon J, Borozdin K, Matthew D J, Fabritius J, Hecht A, Milner E C, Miyadera H, Morris C L, Perry J, Poulson D 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 789 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bacon J D, Borozdin K N, Fabritius II J M, Morris C, Perry J O 2013 Muon Induced Fission Neutrons in Coincidence with Muon Tomography (Los Alamos, Los Alamos National Lab, LA-UR-13-28292 [R])
[23] Volker E, Oberacker, Umar A S, Karpeshin F F 2004 arXiv: nucl-th/0403087 [nucl-th]
[24] Morris C, Durham J M, Guardincerri E, Bacon J D, Wang Z H, Fellows S, Poulson D C, Plaud-Ramos K O, Daughton T M, Johnson O R 2015 A new method of passive counting of nuclear missile warheads -a white paper for the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Lab, LA-UR-15-26068 [R])
[25] Blackwell T B, Kudryavtsev V A 2015 J. Instrum. 10 05006
[26] 何伟波 2019 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
He W B 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[27] Yan J Y, Zhang Q H, Huo Y G http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1958.O4.20210529.1750.002.html [2021-06-08]
[28] Wang Z, Bovik A, Sheikh H R, Simoncelli E P 2004 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13 600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ide K, Becchetti M F, Flaska M, Poitrasson-Riviere A, Hamel M C, Polack J K, Lawrence C C, Clarke S D, Pozzi S A 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 694 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 李凯文, 徐琳, 陈强 2020 计算机科学 47 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li K W, Xu L, Chen Q 2020 Comput. Sci. 47 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 何凯, 牛俊慧, 沈成南, 卢雯霞 2018 天津大学学报 51 763
He K, Niu J H, Shen C N, Lu W X 2018 J. Tianjin Univ. 51 763
[32] 肖洒 2018 博士学位论文(绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院)
Xiao S 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics) (in Chinese)
[33] Malyshkina Y, Pshenichnova I, Mishustina I, Hughesd T, Heidd O, Greiner W 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 289 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kasztelan M, Jedrzejczak K, Szabelski J 2019 Mod. Phys. Lett. A 6 1950046
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8874
- PDF Downloads: 143
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: