-
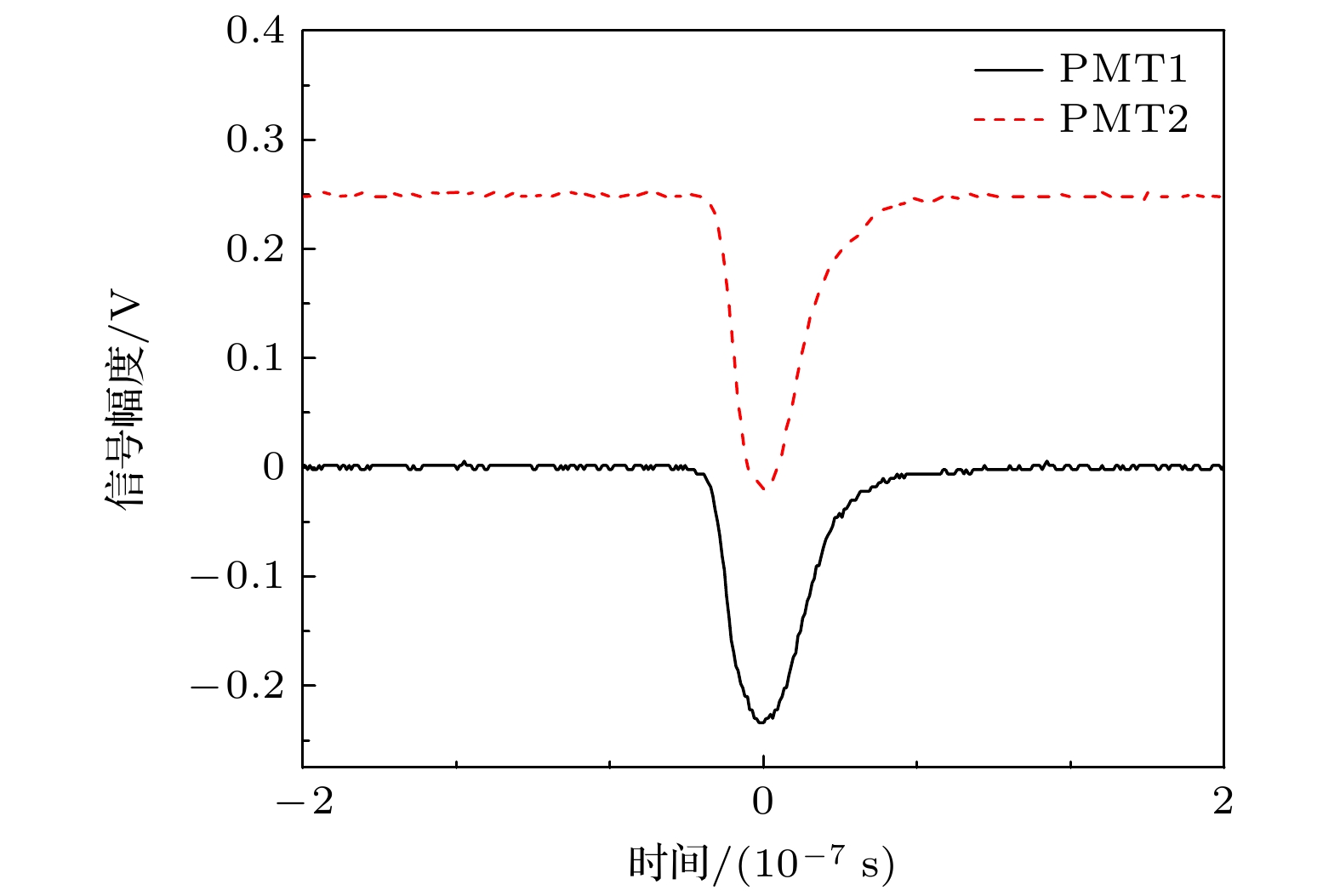
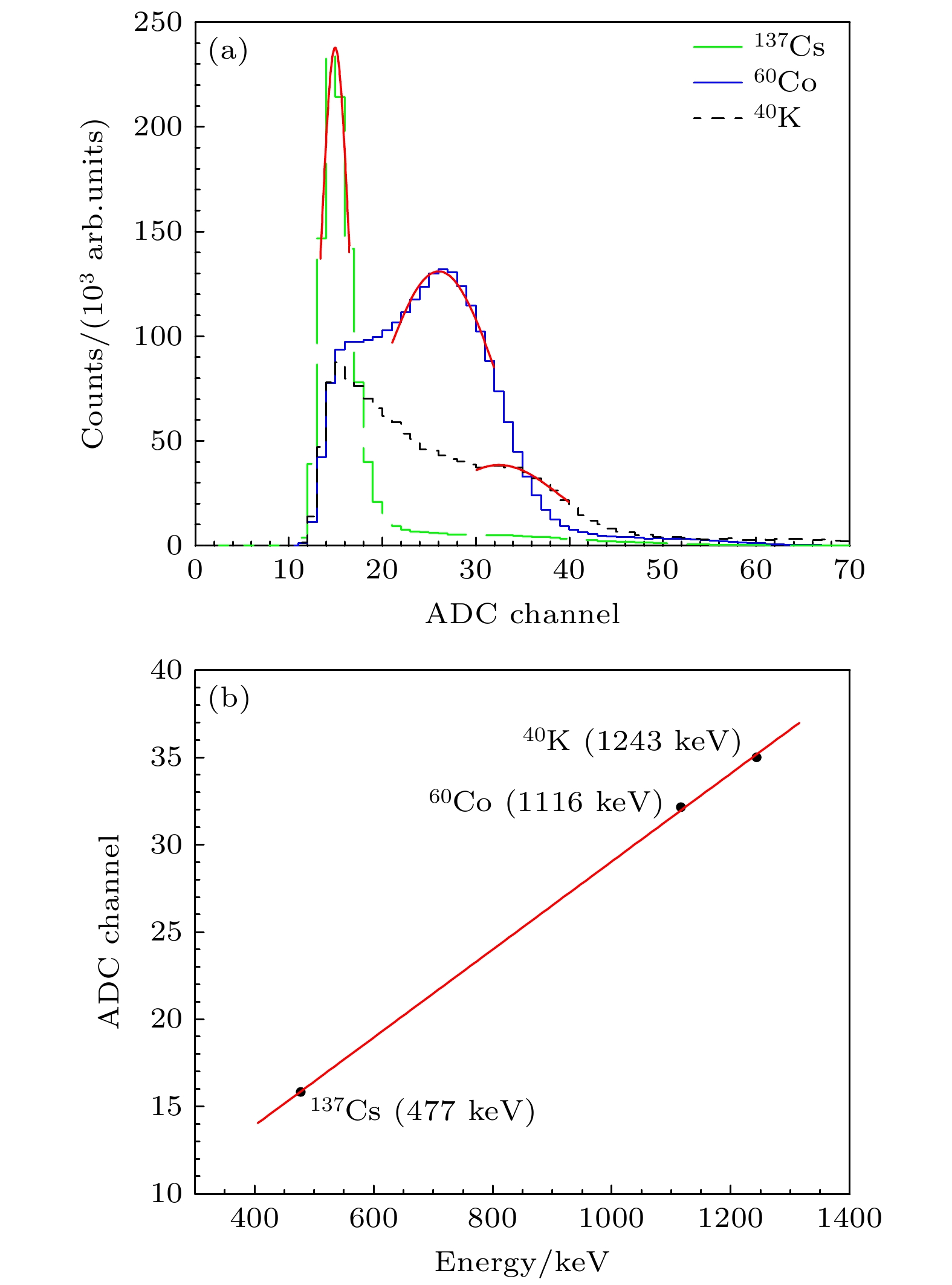
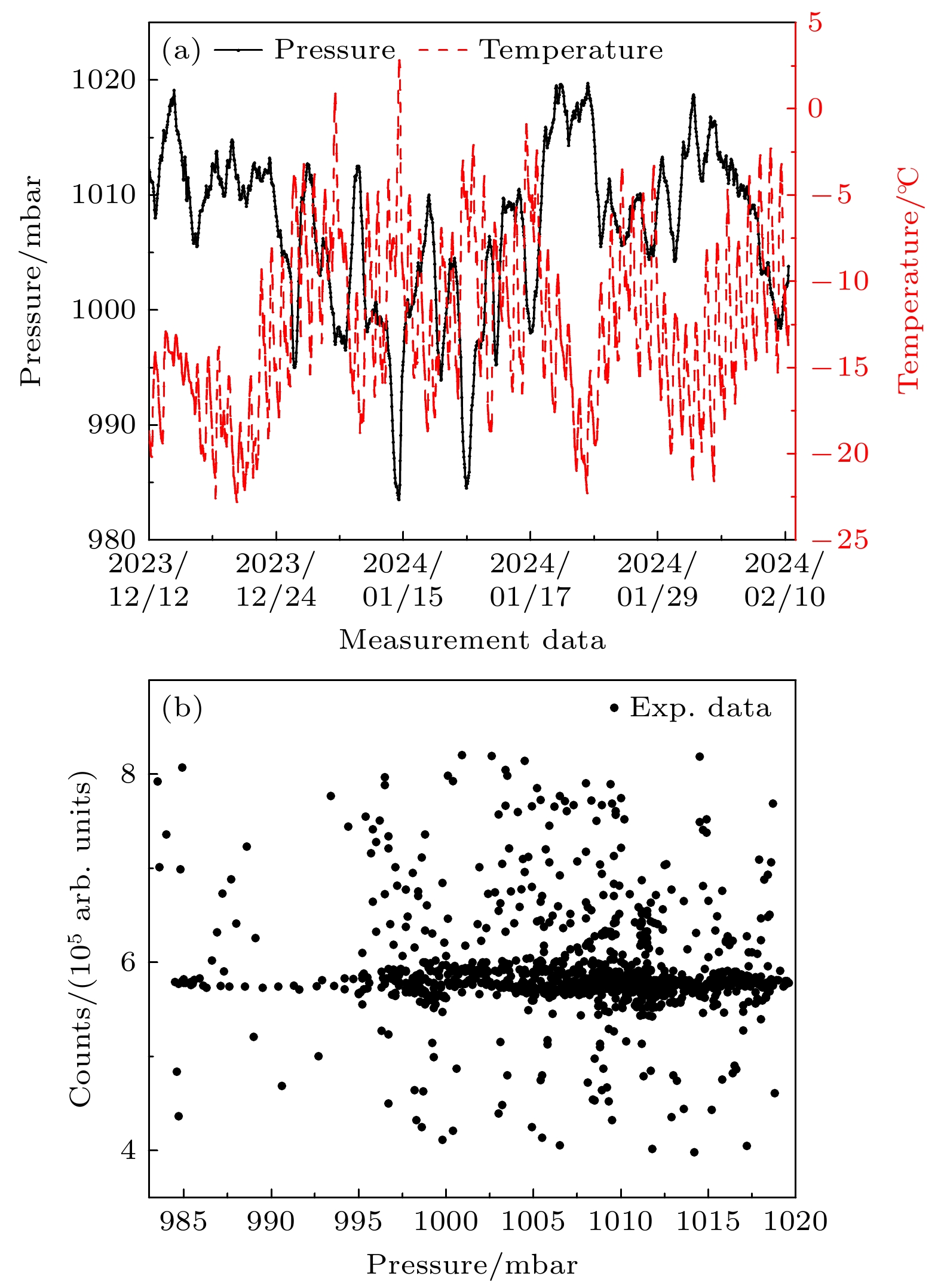
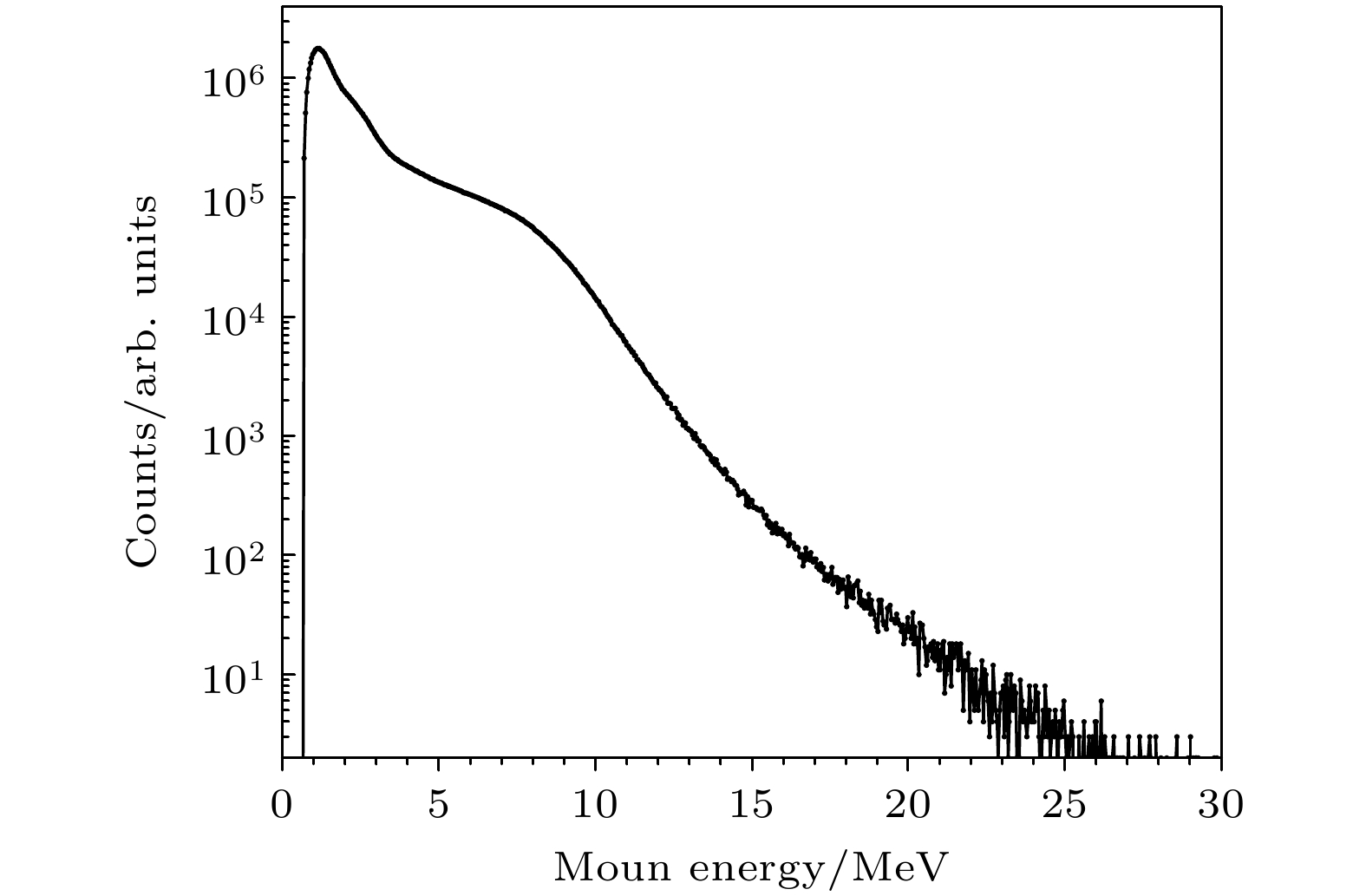
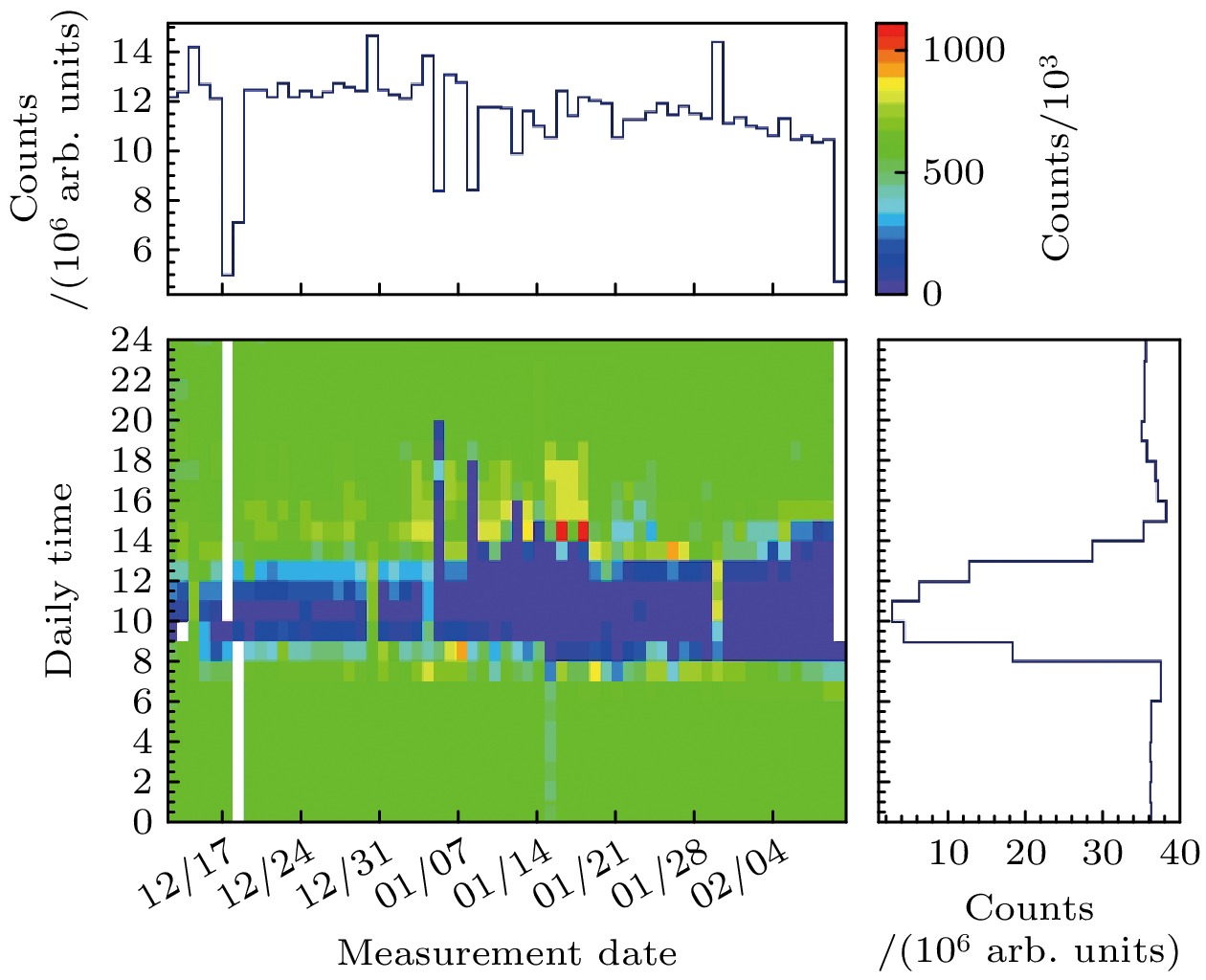
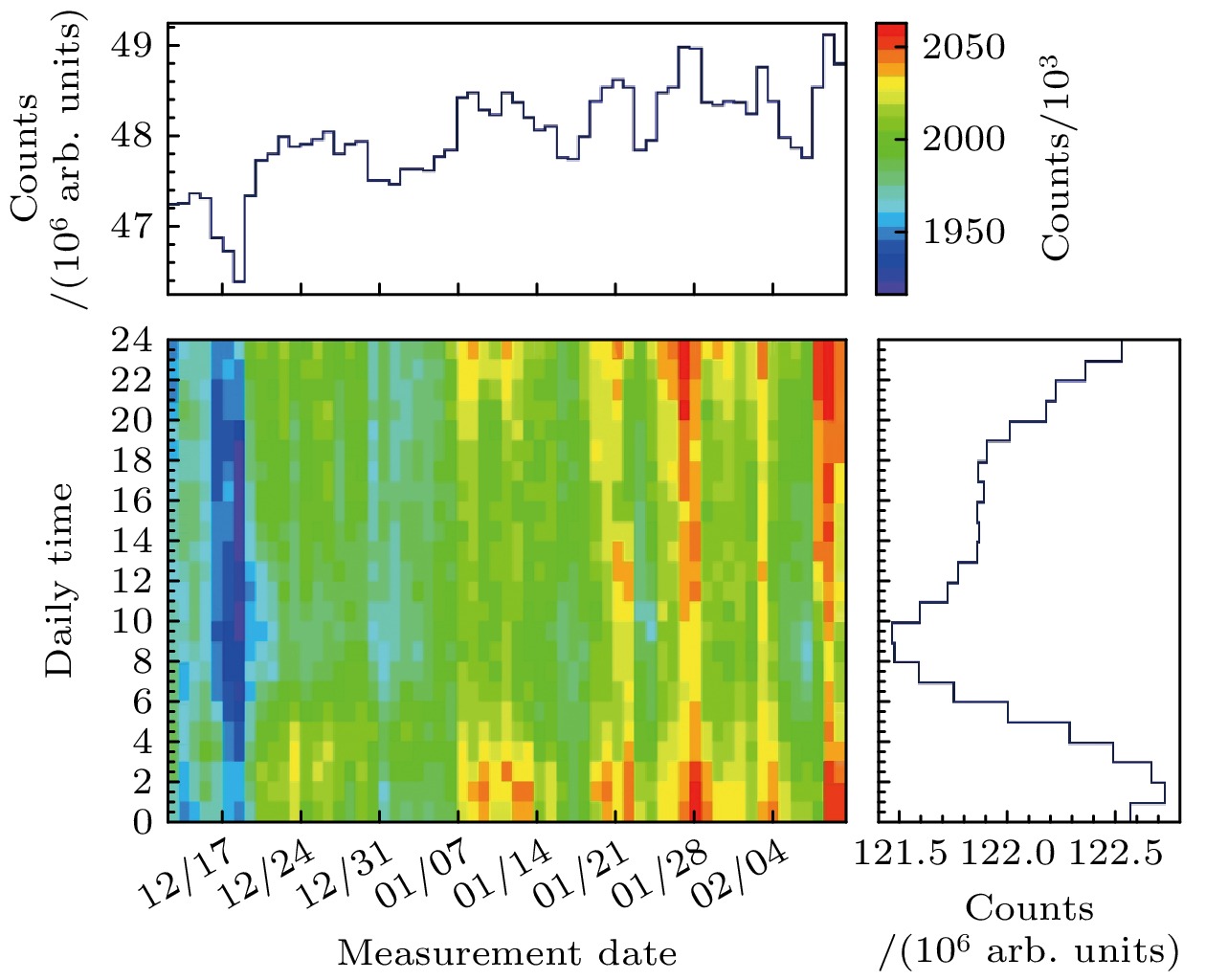
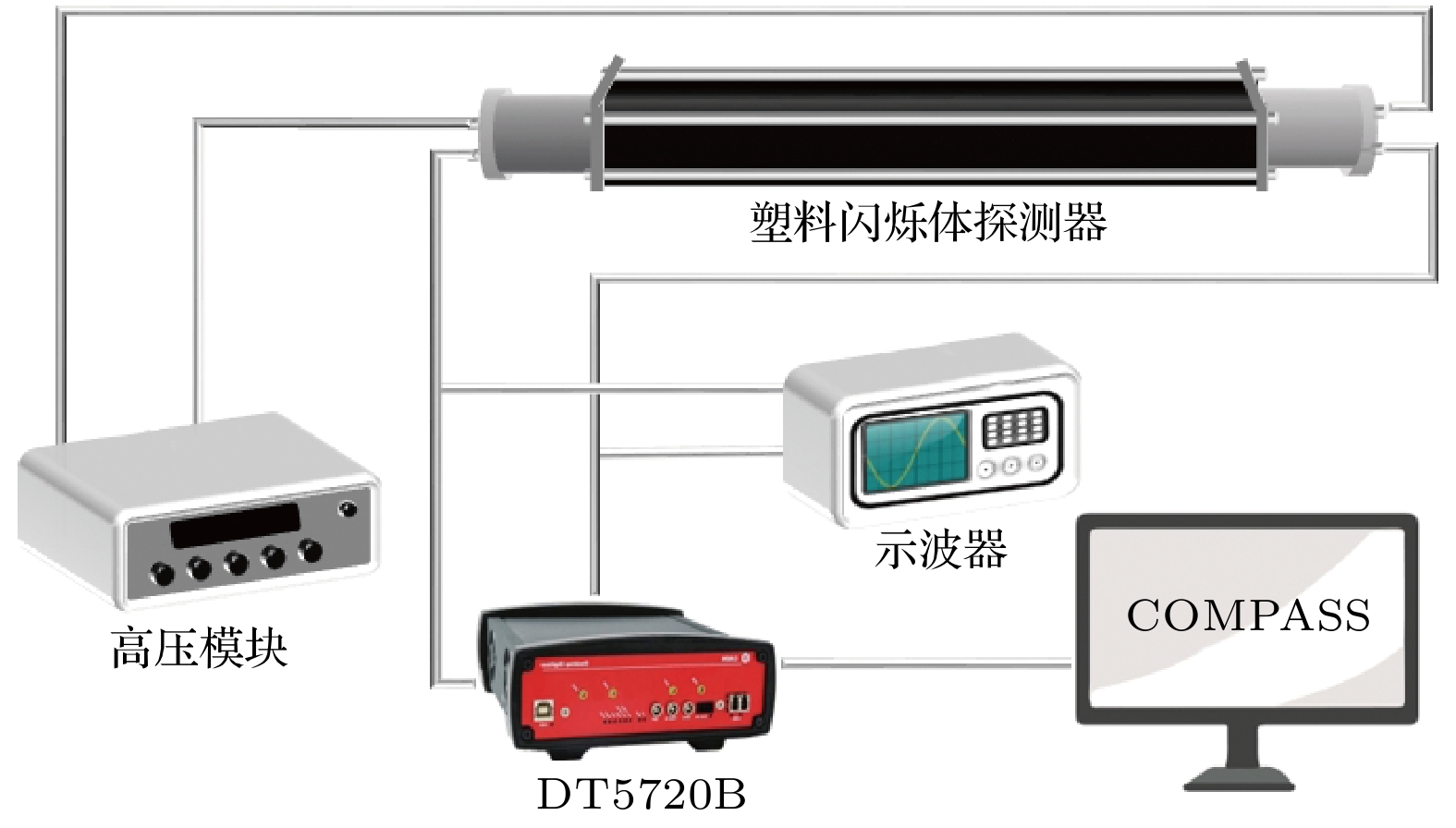
利用塑料闪烁体探测器进行了宇宙线缪子计数谱及各向异性特性的观测实验. 实验采用双端符合测量和标准γ源进行能量刻度, 显著减小了探测器的噪声干扰, 提高了测量数据的可靠性. 通过引入温度与气压修正函数, 对计数结果进行了气象效应校正. 实验结果显示, 缪子在塑料闪烁体探测器中的能量损失呈现出随时间和太阳活动变化的周期性特征, 反映出太阳对宇宙线各向异性的调制效应. 此外, 实验数据与羊八井观测站中子-缪子望远镜的观测结果在缪子计数的日周期变化趋势上表现出较高的一致性. 本研究为深入探索宇宙线缪子的能量分布及太阳调制效应提供了可靠的实验依据, 同时为宇宙线探测技术的应用与发展提供了重要参考.Cosmic rays, originating from stars, supernovae, and other astrophysical sources, are composed of high-energy particles that enter Earth’s atmosphere. Upon interaction with atmospheric nuclei, these primary cosmic rays generate secondary particles, including neutrons, electrons, and muons, with muons constituting a dominant component at ground level. Muons, due to their relative abundance, stability, and well-characterized energy loss mechanisms, serve as critical probes for investigating the fundamental properties of cosmic rays. Studies of muon energy distribution, diurnal anisotropy, and their modulation by solar activity provide critical insights into the mechanism of particle acceleration in cosmic ray sources and the effects of solar and atmospheric.This study aims to characterize the counting spectra and anisotropic properties of cosmic ray muons by using a plastic scintillator detector system. The experiment was conducted over a three-month period, from December 2023 to February 2024, leveraging long-bar plastic scintillator detectors equipped with dual-end photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) and a high-resolution digital data acquisition system. A dual-end coincidence measurement technique was used to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio by suppressing thermal noise and other background interferences. Comprehensive calibration of the detection system was performed using standard gamma-ray sources, including 137Cs, 60Co, and 40K, thereby ensuring precise energy scaling and reliable performance.The observed energy spectra of cosmic ray muons are in excellent agreement with theoretical predictions, which explains the energy losses caused by muons passing through the detector. Diurnal variations in muon count rates exhibit a pronounced pattern, with a systematic reduction occurring between 8:00 AM and 1:00 PM. This phenomenon is attributed to the solar shielding effects, where enhanced solar activity during daytime hours modulates the flux of galactic cosmic rays reaching Earth’s surface. To account for atmospheric influences, meteorological corrections are performed using temperature and pressure adjustment functions derived from regression analysis. These corrections indicate that atmospheric pressure and temperature are significant factors affecting muon count rates, and a clear linear relationship is observed.The study further corroborates these findings through cross-comparisons with data from the Yangbajing Cosmic Ray Observatory. Minor discrepancies, primarily in low-energy muon count rates, are attributed to variations in detector sensitivities and local atmospheric conditions. These observations underscore the robustness of the plastic scintillator detector system for capturing detailed muon spectra and anisotropic patterns.This research establishes a reliable experimental framework for analyzing cosmic ray muons and their modulation by solar and atmospheric phenomena. The results contribute to a more in-depth understanding of anisotropy of cosmic rays and the interaction between astrophysical and geophysical processes. Furthermore, these findings provide valuable insights for optimizing detection technologies and enhancing the accuracy of cosmic ray studies.
-
Keywords:
- cosmic rays /
- muons /
- anisotropy /
- plastic scintillator /
- solar modulation
[1] 刘佳, 曹臻 2024 物理 53 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Cao Z 2024 Physics 53 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李骢, 杨睿智, 曹臻 2024 科学通报 69 2698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Yang R Z, Cao Z 2024 Chin. Sci. Bull. 69 2698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 阿西克古, 周勋秀, 张云峰 2024 73 129201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Axi Kugu, Zhou X X, Zhang Y F 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 129201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Compton A H, Getting I A 1935 Phys. Rev. 47 817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 宋小健, 罗熙 2022 年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集-1 (北京: 北京伯通电子出版社) 第9页
Song X J, Luo X 2022 Proc. of the Joint Annual Meeting of Chinese Earth Sciences-1 (Beijing: Beijing Botong Press) p9
[6] 仝帆, 贾焕玉, 周勋秀等 2015 原子核物理评论 32 286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tong F, Jia H Y, Zhou X X, et al. 2015 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 32 286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘珺, 周德文 2007 郑州大学学报 (理学版) 01 75
Liu J, Zhou D W 2007 J. Zhengzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 01 75
[8] 刘珺, 贾焕玉, 黄庆 2004 原子核物理评论 01 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Jia H Y, Huang Q 2004 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 01 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 贾焕玉, 曹臻, 张慧敏 1994 高能物理与核物理 09 788
Jia H Y, Cao Z, Zhang H M 1994 High Energy Phys. Nucl. Phys. 09 788
[10] 刘烨, 牛赫然, 李兵兵等 2023 72 140202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Niu H R, Li B B, et al. 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 140202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aemnomori M, Ayabe S, Cui S, et al. 2005 The Asrophysical Journal 626 L29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 王启奇, 张湘, 田立朝等 2023 核技术 46 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Q, Zhang X, Tian L C, et al. 2023 J.Nucl.Tech. 46 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘新铭, 宋小健, 耿泽坤等 2024 地球 67 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X M, Song X J, Geng Z K, et al. 2024 Chin. J. Geophys. 67 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 肖政耀, 王梓丞, 黄新等 2022 广西物理 43 8
Xiao Z Y, Wang Z C, Huang X, et al. 2022 Guangxi Phys. 43 8
[15] 何韦杰, 李波 2024 大学物理 43 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He W J, Li B 2024 College Phys. 43 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 尹俊, 张亚鹏, 倪发福等 2017 核电子学与探测技术 37 929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin J, Zhang Y P, Ni F F, et al. 2017 Nuclear Electronics Detection Technology 37 929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 皮本松, 魏志勇, 王振等 2017 核技术 40 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pi B S, Wei Z Y, Wang Z, et al. 2017 J.Nucl.Tech. 40 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Han J X, Ye Y L, Lou J L, et al. 2023 Commun. Phys. 6 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 耿朋, 段利敏, 马朋等 2010 原子核物理评论 27 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng P, Duan L M, Ma Peng, et al. 2010 Nuclear Phys. Rev. 27 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 郝佳欣, 郭戈, 孙保华 2024 大学物理 43 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao J X, Guo G, Sun B H 2024 College Phys. 43 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 常乐, 刘应都, 杜龙等 2015 核技术 38 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang L, Liu Y D, Du L, et al. 2015 J. Nucl. Tech. 38 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang S Y L T, Chen Z Q, Han Rui, et al. 2013 Chin. Phys. C 37 71
[23] 唐云秋, 卢红, 乐贵明等 2004 空间科学学报 24 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Q Y, Lu H, Le G M, et al. 2004 Chinese Journal of Space Science 24 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu C L, Wang Y, Qin G, et al. 2023 Res. Astron. Astrophys. 23 025010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Adamson P, Andreopoulos1 C, Arms K E, et al. 2010 Phys. Rev. D 81 012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dorman L I 1974 Cosmic Rays, Variation and Space Exploration North-Holland
[27] Erhart A, Wagner V, Wex A, et al. 2024 Eur. Phys. J. C 84 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 周勋秀, 王新建, 黄代绘等 2015 64 149202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou X X, Wang X J, Huang D H, et al. 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 149202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang J L, Tan Y H, Wang H, et al. 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 623 1030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Institute of High Energy Physics (ihep.ac.cn) http://ybjnm.ihep.ac.cn/.
-
-
[1] 刘佳, 曹臻 2024 物理 53 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Cao Z 2024 Physics 53 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李骢, 杨睿智, 曹臻 2024 科学通报 69 2698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Yang R Z, Cao Z 2024 Chin. Sci. Bull. 69 2698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 阿西克古, 周勋秀, 张云峰 2024 73 129201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Axi Kugu, Zhou X X, Zhang Y F 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 129201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Compton A H, Getting I A 1935 Phys. Rev. 47 817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 宋小健, 罗熙 2022 年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集-1 (北京: 北京伯通电子出版社) 第9页
Song X J, Luo X 2022 Proc. of the Joint Annual Meeting of Chinese Earth Sciences-1 (Beijing: Beijing Botong Press) p9
[6] 仝帆, 贾焕玉, 周勋秀等 2015 原子核物理评论 32 286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tong F, Jia H Y, Zhou X X, et al. 2015 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 32 286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘珺, 周德文 2007 郑州大学学报 (理学版) 01 75
Liu J, Zhou D W 2007 J. Zhengzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 01 75
[8] 刘珺, 贾焕玉, 黄庆 2004 原子核物理评论 01 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Jia H Y, Huang Q 2004 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 01 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 贾焕玉, 曹臻, 张慧敏 1994 高能物理与核物理 09 788
Jia H Y, Cao Z, Zhang H M 1994 High Energy Phys. Nucl. Phys. 09 788
[10] 刘烨, 牛赫然, 李兵兵等 2023 72 140202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Niu H R, Li B B, et al. 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 140202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aemnomori M, Ayabe S, Cui S, et al. 2005 The Asrophysical Journal 626 L29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 王启奇, 张湘, 田立朝等 2023 核技术 46 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Q, Zhang X, Tian L C, et al. 2023 J.Nucl.Tech. 46 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘新铭, 宋小健, 耿泽坤等 2024 地球 67 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X M, Song X J, Geng Z K, et al. 2024 Chin. J. Geophys. 67 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 肖政耀, 王梓丞, 黄新等 2022 广西物理 43 8
Xiao Z Y, Wang Z C, Huang X, et al. 2022 Guangxi Phys. 43 8
[15] 何韦杰, 李波 2024 大学物理 43 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He W J, Li B 2024 College Phys. 43 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 尹俊, 张亚鹏, 倪发福等 2017 核电子学与探测技术 37 929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin J, Zhang Y P, Ni F F, et al. 2017 Nuclear Electronics Detection Technology 37 929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 皮本松, 魏志勇, 王振等 2017 核技术 40 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pi B S, Wei Z Y, Wang Z, et al. 2017 J.Nucl.Tech. 40 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Han J X, Ye Y L, Lou J L, et al. 2023 Commun. Phys. 6 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 耿朋, 段利敏, 马朋等 2010 原子核物理评论 27 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng P, Duan L M, Ma Peng, et al. 2010 Nuclear Phys. Rev. 27 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 郝佳欣, 郭戈, 孙保华 2024 大学物理 43 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao J X, Guo G, Sun B H 2024 College Phys. 43 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 常乐, 刘应都, 杜龙等 2015 核技术 38 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang L, Liu Y D, Du L, et al. 2015 J. Nucl. Tech. 38 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang S Y L T, Chen Z Q, Han Rui, et al. 2013 Chin. Phys. C 37 71
[23] 唐云秋, 卢红, 乐贵明等 2004 空间科学学报 24 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Q Y, Lu H, Le G M, et al. 2004 Chinese Journal of Space Science 24 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu C L, Wang Y, Qin G, et al. 2023 Res. Astron. Astrophys. 23 025010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Adamson P, Andreopoulos1 C, Arms K E, et al. 2010 Phys. Rev. D 81 012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dorman L I 1974 Cosmic Rays, Variation and Space Exploration North-Holland
[27] Erhart A, Wagner V, Wex A, et al. 2024 Eur. Phys. J. C 84 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 周勋秀, 王新建, 黄代绘等 2015 64 149202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou X X, Wang X J, Huang D H, et al. 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 149202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang J L, Tan Y H, Wang H, et al. 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 623 1030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Institute of High Energy Physics (ihep.ac.cn) http://ybjnm.ihep.ac.cn/.
计量
- 文章访问数: 1825
- PDF下载量: 80
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: