-
The Field transformation (FT) is a novel theory for controlling the polarization and impedance of electromagnetic waves, which is independent on the angle of incidence. Thus, the FT method is superior for wide-angle devices design. In this paper, we propose a wide-angle method for generating vortex beam based on the FT theory. According to this method, an artificial media for vortex beam generation is designed and simulated, which demonstrates the proposed method. The designed artificial media is a multi-layered structure, which can generate vortex beam of order 2 with an incident angle stability up to 60°.
-
Keywords:
- orbital angular momentum /
- field transformation /
- wide-angle /
- vortex beam
[1] Bliokh K Y, Bekshaev A Y, Nori F 2013 New J. Phys. 15 33026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Menglin C, Li J, Wei S 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang J, Yang J Y, Fazal I M 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 苏志锟, 王发强, 路轶群, 金锐博, 梁瑞生, 刘颂豪 2008 57 3016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su Z K, Wang F Q, Lu Y Q, Jin R B, Liang R B, Liu S H 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lemaitre-Auger P, Abielmona S, Caloz C 2013 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61 1838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] David G 2003 Nature 424 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘义东, 高春清, 高明伟, 李丰 2007 56 854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y D, Gao C Q, Gao M W, Li F 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Oemrawsingh S S R, Houwelingen J A W, Eliel E R, Woerdman J P, Verstegen E J K, Kloosterboer J G 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Beijersbergen M W, Coerwinkel R P C, Kristensen M, Woerdman J P 1994 Opt. Commun. 112 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Turnbull G A, Robertson D A, Smith G M, Allen L, Padgett M J 1996 Opt. Commun. 127 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Marrucci L, Manzo C, Paparo D 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 163905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Paterson C, Smith R 1996 Opt. Commun. 124 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Mohammadi S M, Daldorff L K S, Bergman J E S, Karlsson R L, Thide B, Forozesh K 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2 565
[14] Genevet P, Y u, N, Aieta F, Lin J, Kats M A, Blanchard R 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 1
[15] Pu M, Li X, Ma X, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Wang C 2015 Sci. Adv. 1 e1500396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang L, Chen X, Holger Mühlenbernd, Li G, Zhang S 2012 Nano Lett. 12 5750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Arbabi A, Horie Y, Bagheri M 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 937
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yue F, Wen D, Xin J, Gerardot B D, Li J, Chen X 2016 ACS Photonics acsphotonics 6 b00392
[19] Yang H, Niu J, Zhang K, Ding X, Wu Q 2016 IEEE International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT) Harbin, China, August 20–22, 2016 p552
[20] Tamburini F, Mari E, Thideì Bo, Barbieri C, Romanato F 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vaishnavi V, Priya V G, Sharmila Devi A, Manoj Kumar M, Venkatesh S, Sundaram G A 2014 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing Melmaruvathur, India, April 3–5, 2014 p1414
[22] Liu F, Liang Z, Li J 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 033901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu F, Li J S 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 103902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhao J M, Zhang L H, Li J S, Feng Y J, Dyke A, Haq S, Hao Y 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 17532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shi H Y, Hao Y 2013 Opt. Express 26 20132
[26] Shi H, Giddens H, Hao Y 2019 IET Microwaves Antennas Propag. 13 1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shi H Y, Giddens H, Hao Y 2017 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 2869
[28] Chen M L N, Jiang L J, Sha W E I 2019 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Schurig D, Mock J J, Justice B J, Cummer S A, Pendry J B, Starr A F, Smith D R 2016 Science 314 977
[30] Born M, Wolf E, Bhatia A B 2002 Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light 7th (expanded) (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp220–225
[31] Chen M L N, Jiang L J, Sha W E I 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 119 064506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kang M, Chen J, Wang X, Wang H 2012 J.Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 29 572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
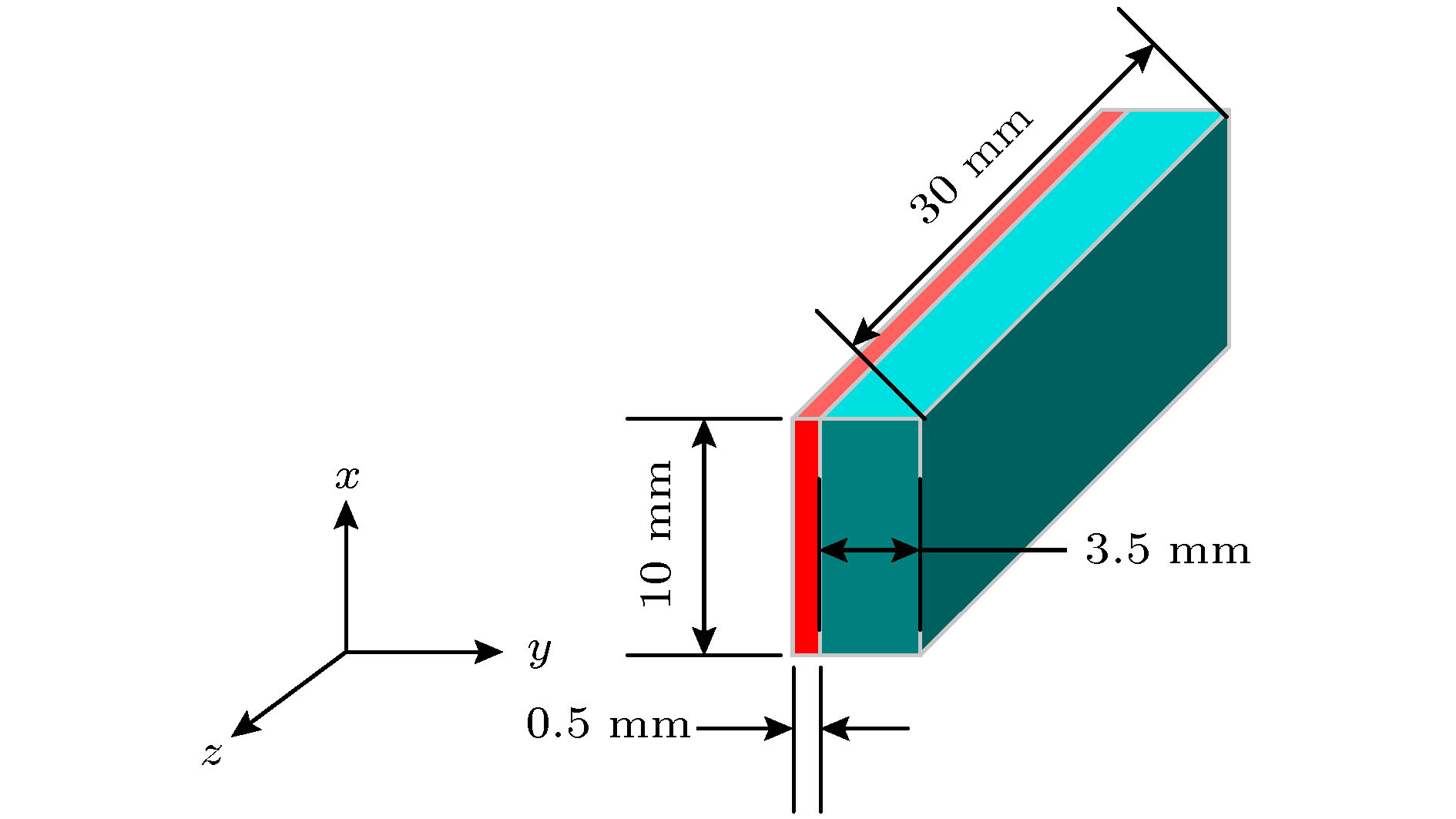
图 2 人工双折射材料:
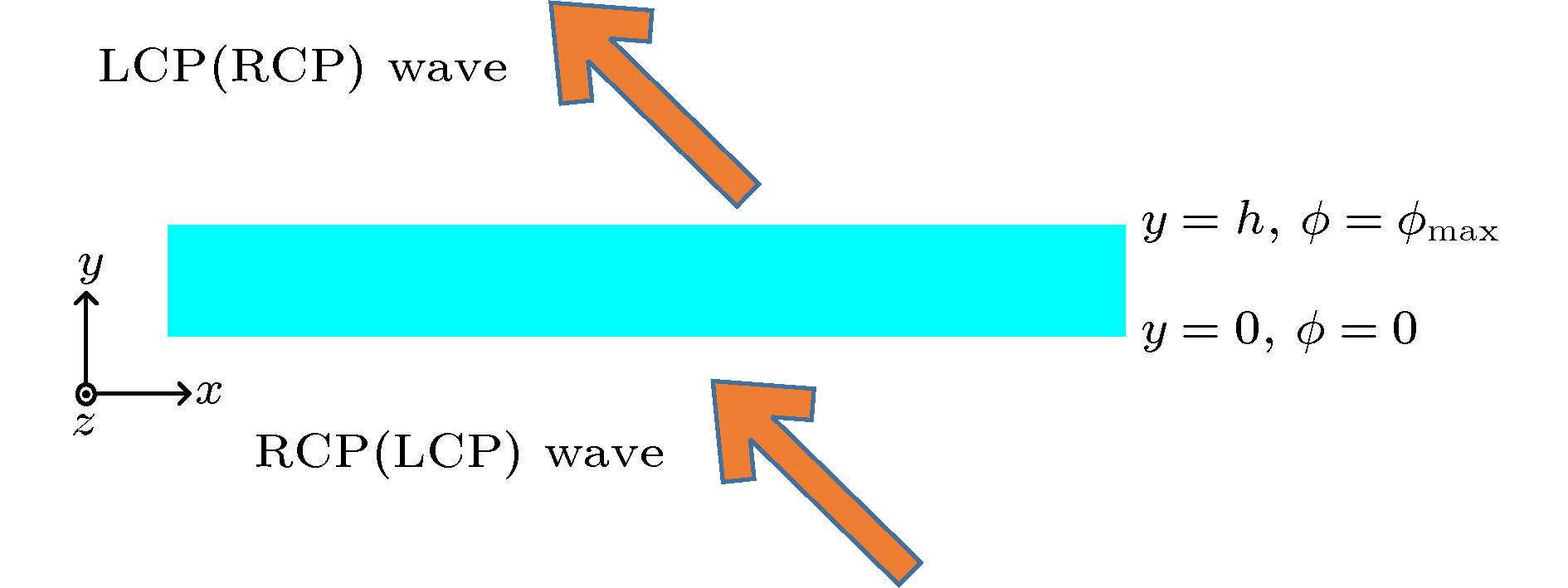
$xyz$ 轴绕y轴旋转45°变成${x'}y{z'}$ , 入射波在$xy$ 平面内,$\theta $ 为入射角,${k_0}$ 是入射波的波数Figure 2. Artificial birefringence medium: The
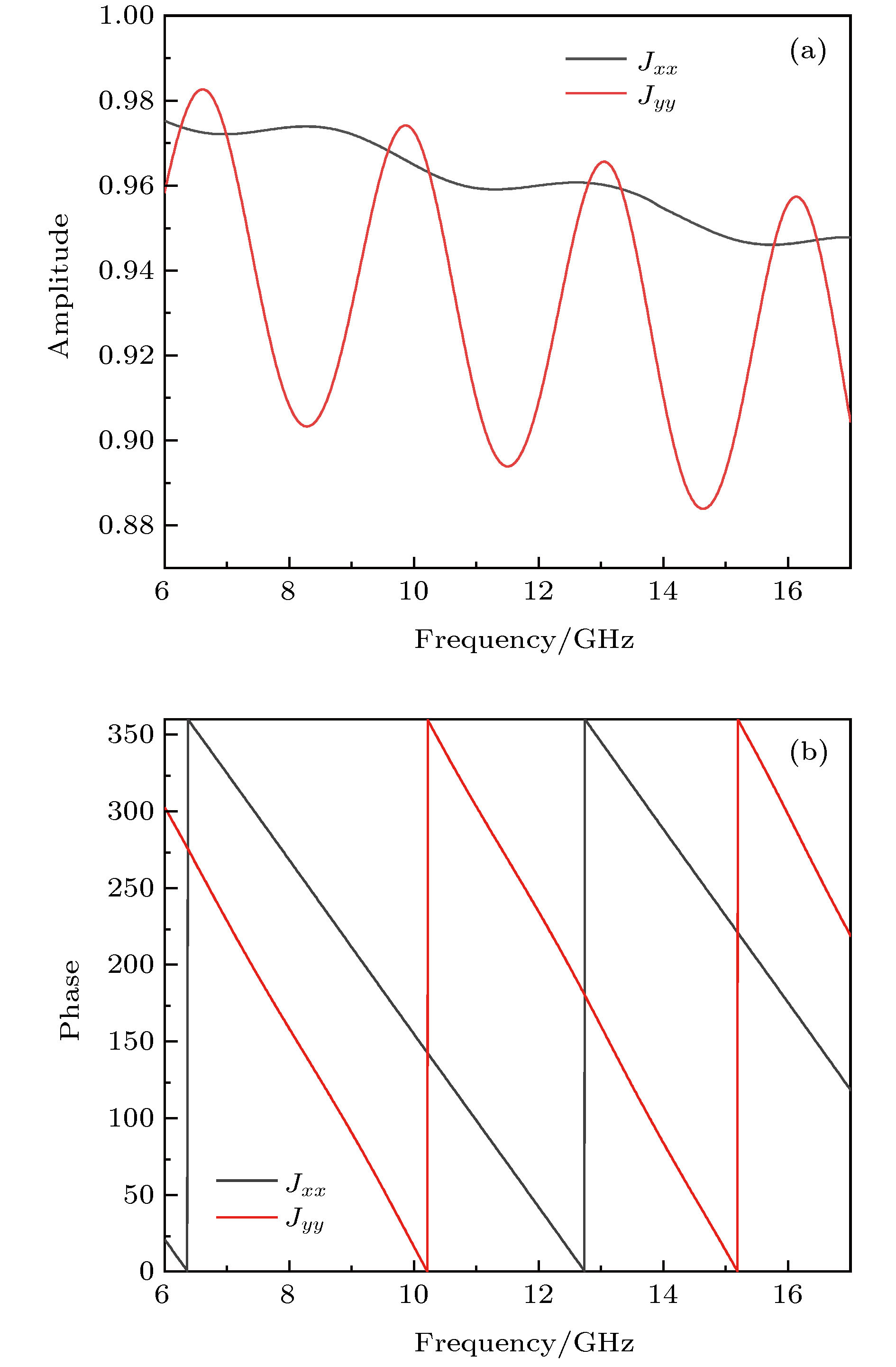
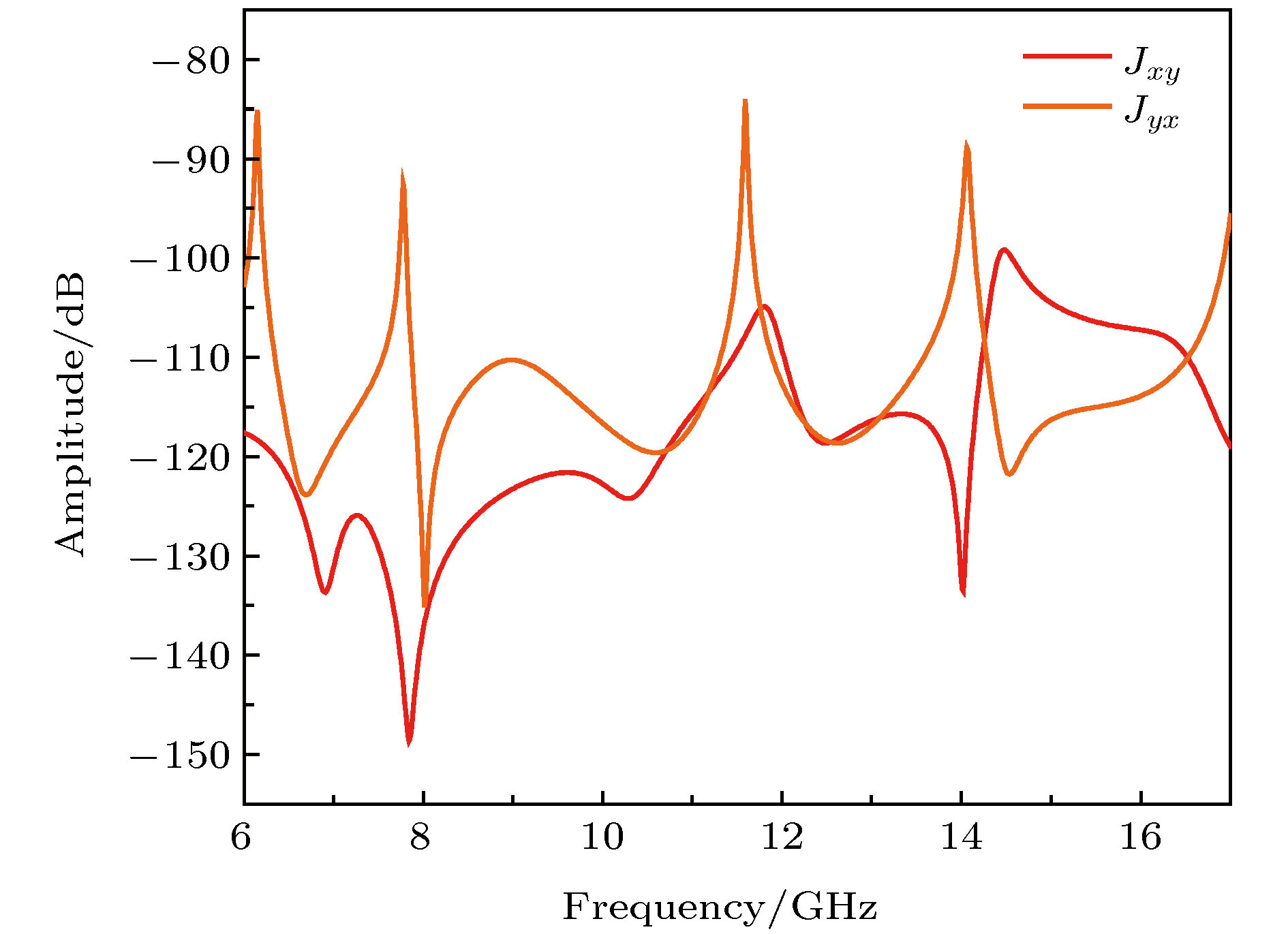
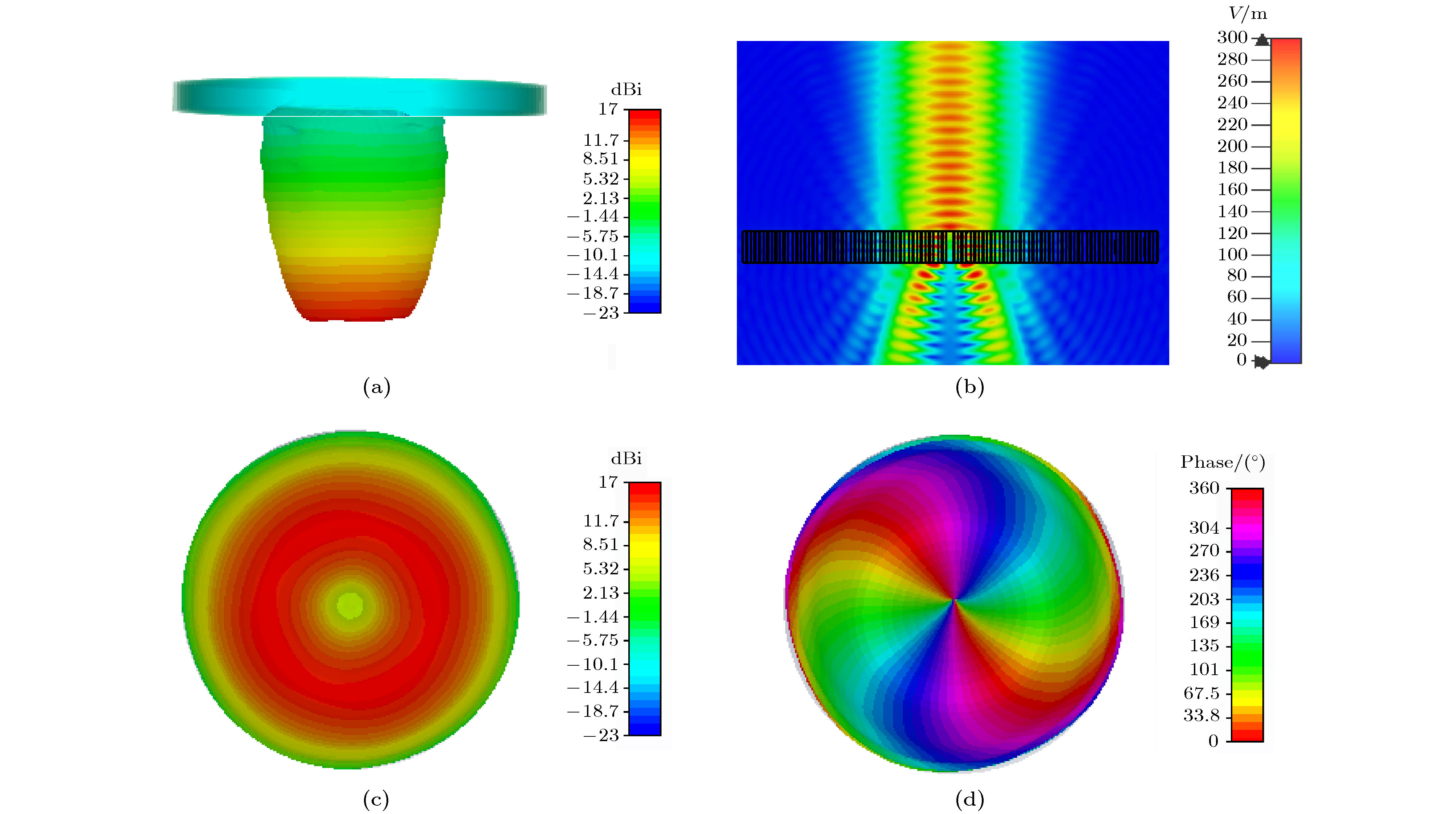
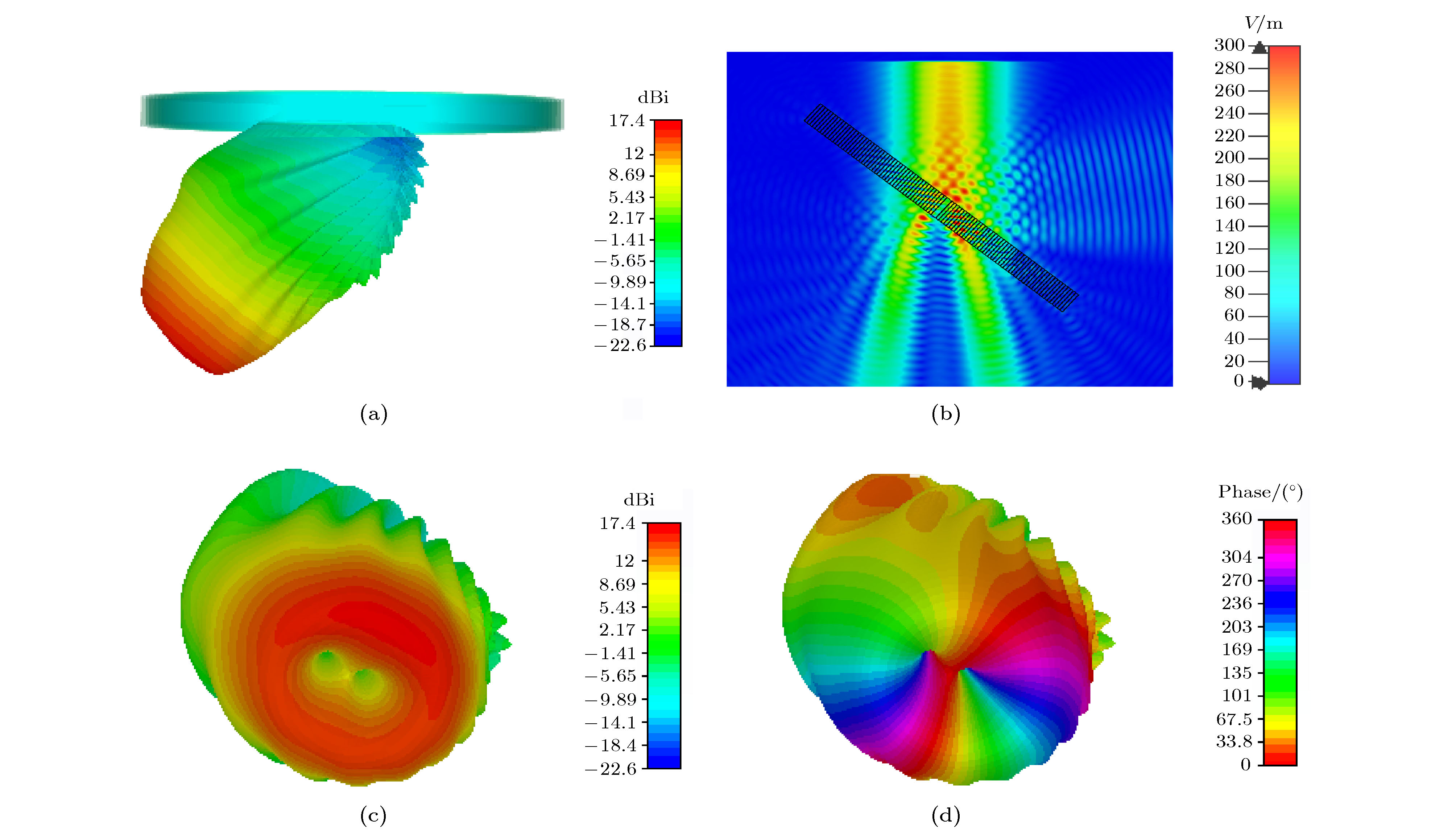
$xyz$ coordinate is twisted along the y -axis by 45° to the${x'}y{z'}$ coordinate. The incident plane is x-y plane,$\theta $ is the incident angle,${k_0}$ is the wave vector of the incident wave.图 9 (a) 20°斜入射时的透射波; (b)介质圆环周围空间的电场分布; (c) 20°斜入射时13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的幅度; (c) 20°斜入射时在13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的相位
Figure 9. (a) The transmission wave while incident angle is 20°; (b) E-field distribution around dielectric rings; (c) amplitude of RCP wave at 20° oblique incidence; (d) phase of RCP wave at 20° oblique incidence.
图 10 (a) 40°斜入射时的透射波; (b)介质圆环周围空间的电场分布; (c) 40°斜入射时13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的幅度; (d) 40°斜入射时13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的相位
Figure 10. (a) The transmission wave while incident angle is 40°; (b) E-field distribution around dielectric rings; (c) amplitude of RCP wave at 40° oblique incidence; (d) phase of RCP wave at 40° oblique incidence.
图 11 (a) 50°斜入射时的透射波; (b)介质圆环周围空间的电场分布; (c) 50°斜入射时13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的幅度; (d) 50°斜入射时在13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的相位
Figure 11. (a) The transmission wave while incident angle is 50°; (b) E-field distribution around dielectric rings; (c) amplitude of RCP wave at 50° oblique incidence; (d) phase of RCP wave at 50° oblique incidence.
图 12 (a) 60°斜入射时的透射波; (b) 60°入射时介质圆环周围的电场分布; (c) 60°斜入射时13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的幅度; (d) 60°斜入射时13 GHz的右旋圆极化波的相位
Figure 12. (a) The transmission wave while incident angle is 60°; (b) E-field distribution around dielectric rings at 60° oblique incidence; (c) amplitude of RCP wave at 60° oblique incidence; (d) phase of RCP wave at 60° oblique incidence.
表 1 垂直入射时不同频点的右旋分量的最大值
Table 1. Maximum values of RCP at different frequencies when normal incidence.
频率/GHz 右旋圆极化分量最大值/dBi 11 14.70 12 15.80 13 16.90 14 17.30 15 17.50 表 2 20°斜入射时不同频点的右旋分量的最大值
Table 2. Maximum values of RCP at different frequencies when incident angle is 20°.
频率/GHz 右旋圆极化分量最大值/dBi 11 15.30 12 16.10 13 17.20 14 17.70 15 17.40 表 3 40°斜入射时不同频点右旋分量的最大值
Table 3. Maximum values of RCP at different frequencies when incident angle is 40°.
频率/GHz 右旋圆极化分量最大值/dBi 11 16.0 12 16.7 13 17.4 14 18.6 15 18.5 表 4 50°斜入射时不同频点的左旋和右旋分量的最大值
Table 4. Maximum values of RCP at different frequencies when incident angle is 50°.
频率/GHz 右旋圆极化分量最大值/dBi 11 16.8 12 17.2 13 17.6 14 18.6 15 19.6 表 5 60°斜入射时不同频点的左旋和右旋分量的最大值
Table 5. Maximum values of RCP at different frequencies when incident angle is 60°.
频率/GHz 右旋圆极化分量最大值/dBi 11 16.1 12 16.9 13 17.9 14 18.5 15 19.6 -
[1] Bliokh K Y, Bekshaev A Y, Nori F 2013 New J. Phys. 15 33026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Menglin C, Li J, Wei S 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang J, Yang J Y, Fazal I M 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 苏志锟, 王发强, 路轶群, 金锐博, 梁瑞生, 刘颂豪 2008 57 3016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su Z K, Wang F Q, Lu Y Q, Jin R B, Liang R B, Liu S H 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lemaitre-Auger P, Abielmona S, Caloz C 2013 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61 1838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] David G 2003 Nature 424 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘义东, 高春清, 高明伟, 李丰 2007 56 854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y D, Gao C Q, Gao M W, Li F 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Oemrawsingh S S R, Houwelingen J A W, Eliel E R, Woerdman J P, Verstegen E J K, Kloosterboer J G 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Beijersbergen M W, Coerwinkel R P C, Kristensen M, Woerdman J P 1994 Opt. Commun. 112 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Turnbull G A, Robertson D A, Smith G M, Allen L, Padgett M J 1996 Opt. Commun. 127 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Marrucci L, Manzo C, Paparo D 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 163905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Paterson C, Smith R 1996 Opt. Commun. 124 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Mohammadi S M, Daldorff L K S, Bergman J E S, Karlsson R L, Thide B, Forozesh K 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2 565
[14] Genevet P, Y u, N, Aieta F, Lin J, Kats M A, Blanchard R 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 1
[15] Pu M, Li X, Ma X, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Wang C 2015 Sci. Adv. 1 e1500396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang L, Chen X, Holger Mühlenbernd, Li G, Zhang S 2012 Nano Lett. 12 5750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Arbabi A, Horie Y, Bagheri M 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 937
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yue F, Wen D, Xin J, Gerardot B D, Li J, Chen X 2016 ACS Photonics acsphotonics 6 b00392
[19] Yang H, Niu J, Zhang K, Ding X, Wu Q 2016 IEEE International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT) Harbin, China, August 20–22, 2016 p552
[20] Tamburini F, Mari E, Thideì Bo, Barbieri C, Romanato F 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vaishnavi V, Priya V G, Sharmila Devi A, Manoj Kumar M, Venkatesh S, Sundaram G A 2014 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing Melmaruvathur, India, April 3–5, 2014 p1414
[22] Liu F, Liang Z, Li J 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 033901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu F, Li J S 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 103902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhao J M, Zhang L H, Li J S, Feng Y J, Dyke A, Haq S, Hao Y 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 17532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shi H Y, Hao Y 2013 Opt. Express 26 20132
[26] Shi H, Giddens H, Hao Y 2019 IET Microwaves Antennas Propag. 13 1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shi H Y, Giddens H, Hao Y 2017 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 2869
[28] Chen M L N, Jiang L J, Sha W E I 2019 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Schurig D, Mock J J, Justice B J, Cummer S A, Pendry J B, Starr A F, Smith D R 2016 Science 314 977
[30] Born M, Wolf E, Bhatia A B 2002 Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light 7th (expanded) (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp220–225
[31] Chen M L N, Jiang L J, Sha W E I 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 119 064506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kang M, Chen J, Wang X, Wang H 2012 J.Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 29 572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10137
- PDF Downloads: 228
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: