-
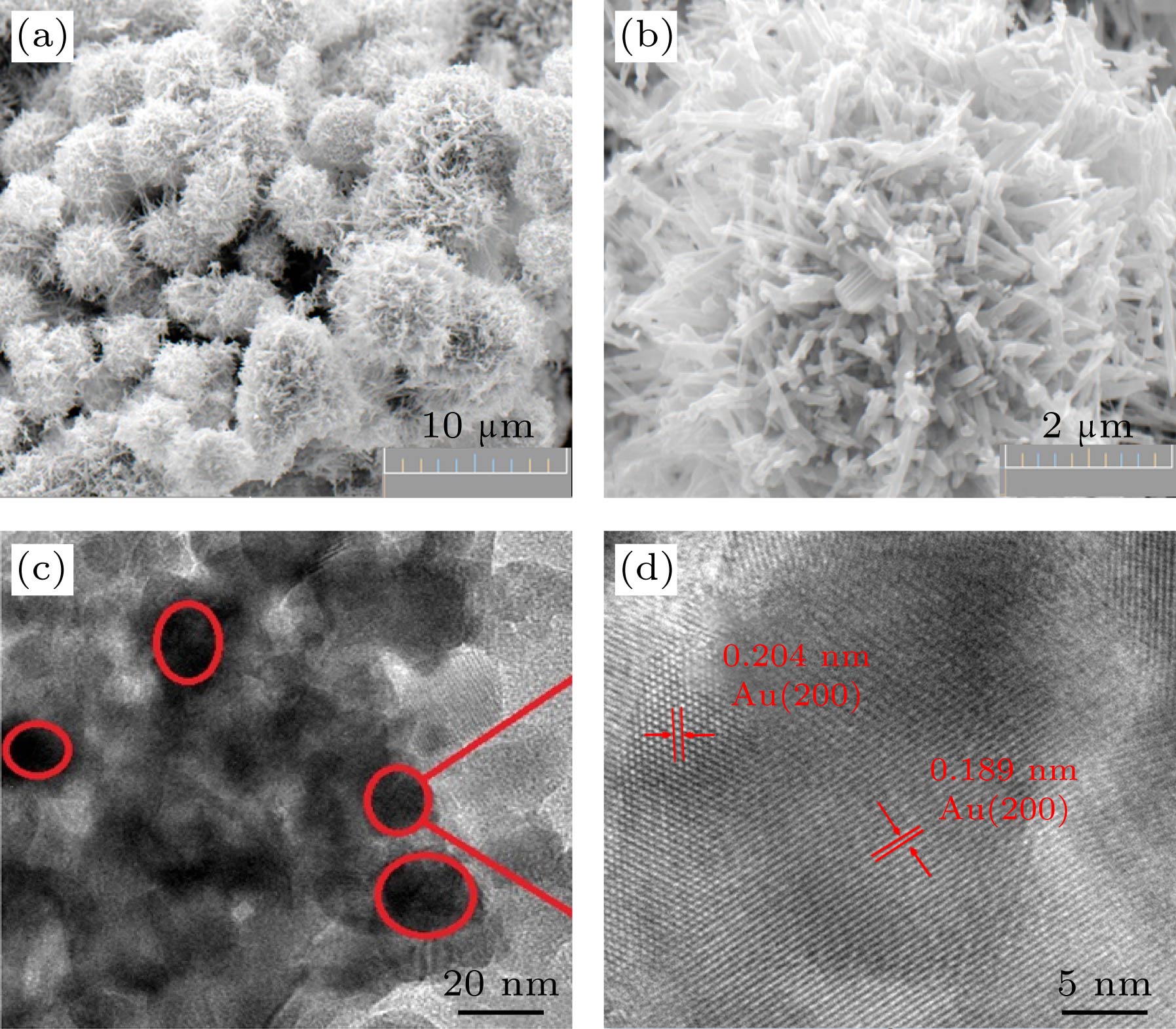
Pure and Au nanoparticles loaded WO3 nanoflowers are synthesized by the hydrothermal method.The structures and morphologies of the as-prepared products are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD),scanning electron microswcope (SEM), and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The gas sensing performance of the Au/WO3 sensor to xylene is investigated. The Au content and the operating temperature are first optimized. It is found that WO3 with 0.4 μL Au nanoparticles shows the highest sensitivity at an operating temperature of 250 ℃. Compared with pure WO3, Au(0.4)/WO3 possesses fast response/recovery speed and high target gas selectivity. Its sensitivity to 100 ppm xylene is 29.5. Meanwhile, the practical detection limitation is as low as 0.5 ppm. Finally, the mechanism of Au/WO3 gas sensing is also proposed and discussed. Au nanoparticles loaded WO3 nanoflowers are considered to be a promising sensing material for detecting xylene pollutants.
-
Keywords:
- WO3 /
- Au nanoparticles /
- xylene /
- gas sensing properties
[1] Zhang Y M, Zhao J H, Du T F, Zhu Z Q, Zhang J, Liu Q J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang F J, Qu G, Mohammadi E, Mei J G, Diao Y 2017 Adv. Funct. Mater. 27 1701117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang S, Li Q W, Yu H M, Li J Z 2018 Non-Ferrous Min. Metall. 34 39
[4] Gui Y H, Yang L L, Wang H Y, Li X M, Zhang H Z 2018 J. Synth. Cryst. 47 2115
[5] Li F, Guo S J, Shen J L, Shen L, Sun D M, Wang B, Chen Y 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 238 364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Rong X R, Chen D L, Qu G P, Li T, Zhang R, Sun J 2018 Sens. Actuators, B 269 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li Y X, Chen N, Deng D Y, Xing X X, Xiao X C, Wang Y D 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 238 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yildiz A, Crisan D, Dragan N, Iftimie N, Florea D, Mardare D 2011 J. Mater. Sci.- Mater. Electron. 22 1420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Su P G, Liao W H 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 252 854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao S K, Shen Y B, Zhou P F, Zhong X X, Han C, Zhao Q, Wei D Z 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 282 917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Su X T, Li Y N, Jian J K, Wang J D 2010 Mater. Res. Bull. 45 1960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shi J C, Hu G J, Sun Y, Geng M, Wu J, Liu Y F, Ge M Y, Tao J C, Cao M, Dai N 2011 Sens. Actuators, B 156 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Righettoni M, Tricoli A, Gass S, Schmid A, Amann A, Pratsinis S E 2012 Anal. Chim. Acta 738 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C, Sun R, Li X, Sun Y F, Sun P, Liu F M, Lu G Y 2014 Sens. Actuators, B 204 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lv C, Wang M H, Liu Z Q, Liu Y K, Shen X Q 2018 J. Synth. Cryst. 47 1237
[16] Zhang H W, Wang Y Y, Zhu X G, Li Y, Cai W P 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 280 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kabcum S, Kotchasak N, Channei D, Tuantranont A, Wisitsoraat A, Phanichphant S, Liewhiran C 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 252 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ma J H, Ren Y, Zhou X R, Liu L L, Zhu Y H, Cheng X W, Xu P C, Li X X, Deng Y H, Zhao D Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1705268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Comini E, Faglia G, Sberveglieri G, Pan Z W, Wang Z L 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 1869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu X H, Zhang J, Yang T L, Guo X Z, Wu S H, Wang S R 2011 Sens. Actuators, B 156 918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vallejos S, Stoycheva T, Umek P, Navio C, Snyders R, Bittencourt C, Llobet E, Blackman C, Moniz S, Correig X 2011 Chem. Commun. 47 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 5 (a)在不同操作温度下各个气体传感器对50 ppm二甲苯的的响应曲线; (b)在最佳操作温度时, 各个气体传感器对不同浓度二甲苯的响应曲线
Figure 5. (a) Response curves of various gas sensors exposed to 50 ppm xylene at different operating temperatures; (b) response curves of various gas sensors to different concentrations of xylene at optimal operating temperatures.
-
[1] Zhang Y M, Zhao J H, Du T F, Zhu Z Q, Zhang J, Liu Q J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang F J, Qu G, Mohammadi E, Mei J G, Diao Y 2017 Adv. Funct. Mater. 27 1701117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang S, Li Q W, Yu H M, Li J Z 2018 Non-Ferrous Min. Metall. 34 39
[4] Gui Y H, Yang L L, Wang H Y, Li X M, Zhang H Z 2018 J. Synth. Cryst. 47 2115
[5] Li F, Guo S J, Shen J L, Shen L, Sun D M, Wang B, Chen Y 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 238 364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Rong X R, Chen D L, Qu G P, Li T, Zhang R, Sun J 2018 Sens. Actuators, B 269 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li Y X, Chen N, Deng D Y, Xing X X, Xiao X C, Wang Y D 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 238 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yildiz A, Crisan D, Dragan N, Iftimie N, Florea D, Mardare D 2011 J. Mater. Sci.- Mater. Electron. 22 1420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Su P G, Liao W H 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 252 854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao S K, Shen Y B, Zhou P F, Zhong X X, Han C, Zhao Q, Wei D Z 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 282 917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Su X T, Li Y N, Jian J K, Wang J D 2010 Mater. Res. Bull. 45 1960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shi J C, Hu G J, Sun Y, Geng M, Wu J, Liu Y F, Ge M Y, Tao J C, Cao M, Dai N 2011 Sens. Actuators, B 156 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Righettoni M, Tricoli A, Gass S, Schmid A, Amann A, Pratsinis S E 2012 Anal. Chim. Acta 738 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C, Sun R, Li X, Sun Y F, Sun P, Liu F M, Lu G Y 2014 Sens. Actuators, B 204 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lv C, Wang M H, Liu Z Q, Liu Y K, Shen X Q 2018 J. Synth. Cryst. 47 1237
[16] Zhang H W, Wang Y Y, Zhu X G, Li Y, Cai W P 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 280 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kabcum S, Kotchasak N, Channei D, Tuantranont A, Wisitsoraat A, Phanichphant S, Liewhiran C 2017 Sens. Actuators, B 252 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ma J H, Ren Y, Zhou X R, Liu L L, Zhu Y H, Cheng X W, Xu P C, Li X X, Deng Y H, Zhao D Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1705268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Comini E, Faglia G, Sberveglieri G, Pan Z W, Wang Z L 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 1869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu X H, Zhang J, Yang T L, Guo X Z, Wu S H, Wang S R 2011 Sens. Actuators, B 156 918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vallejos S, Stoycheva T, Umek P, Navio C, Snyders R, Bittencourt C, Llobet E, Blackman C, Moniz S, Correig X 2011 Chem. Commun. 47 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12246
- PDF Downloads: 143
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad:







