-
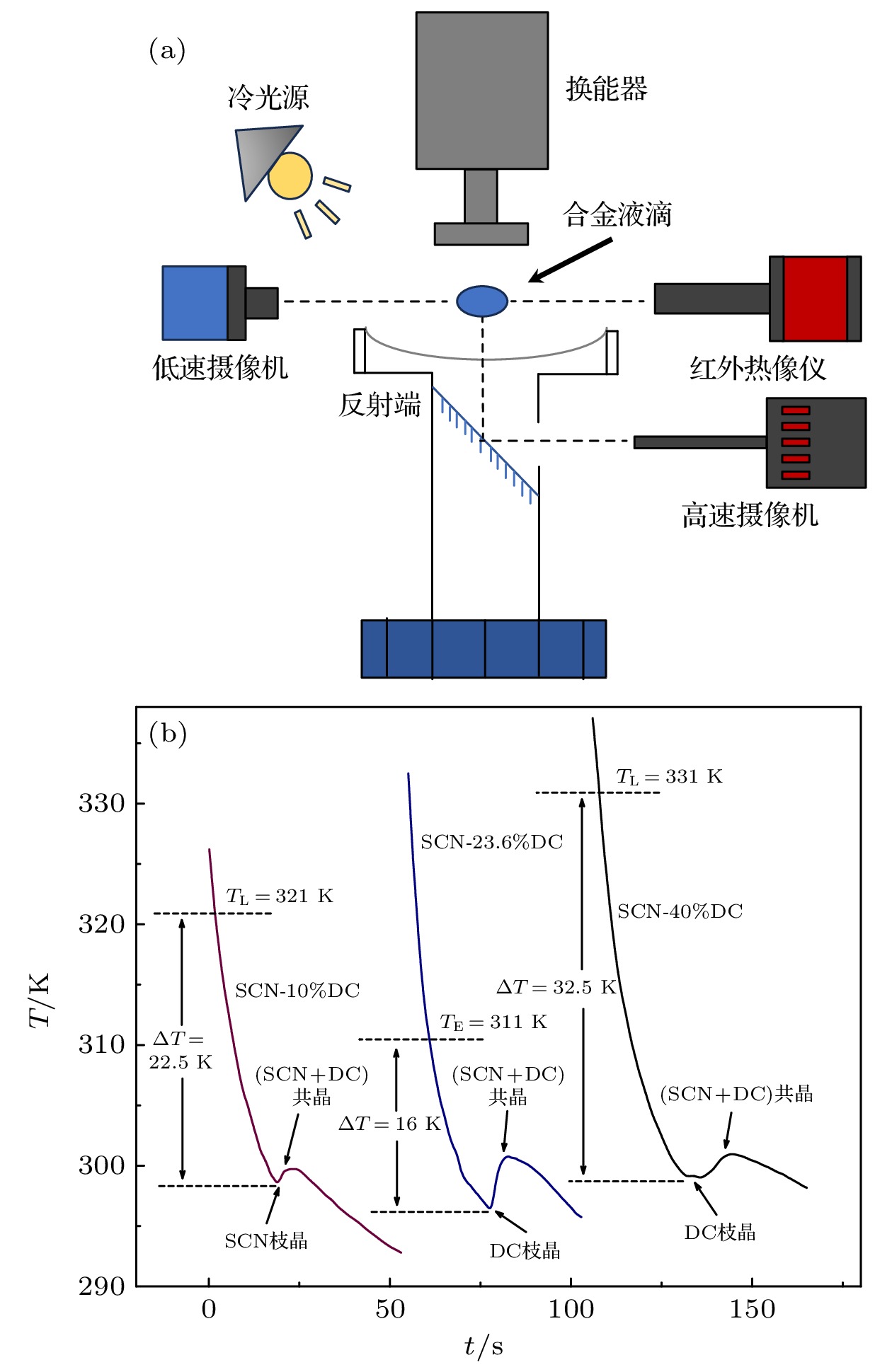
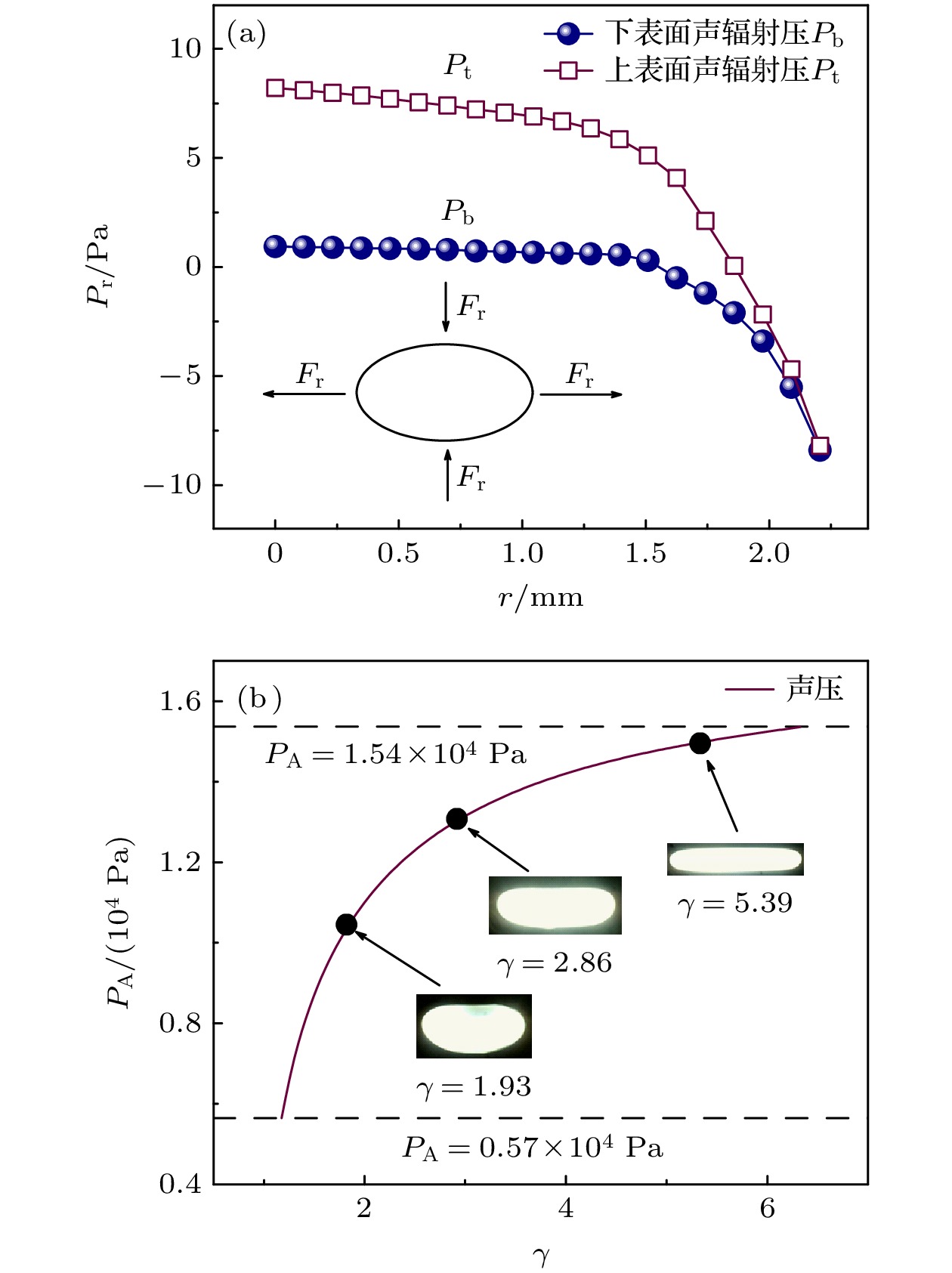
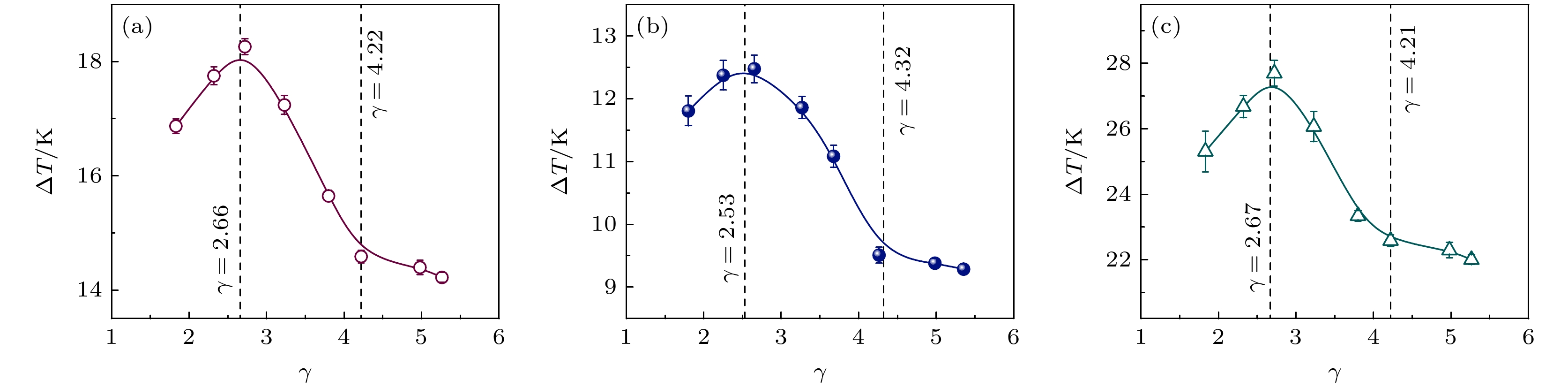
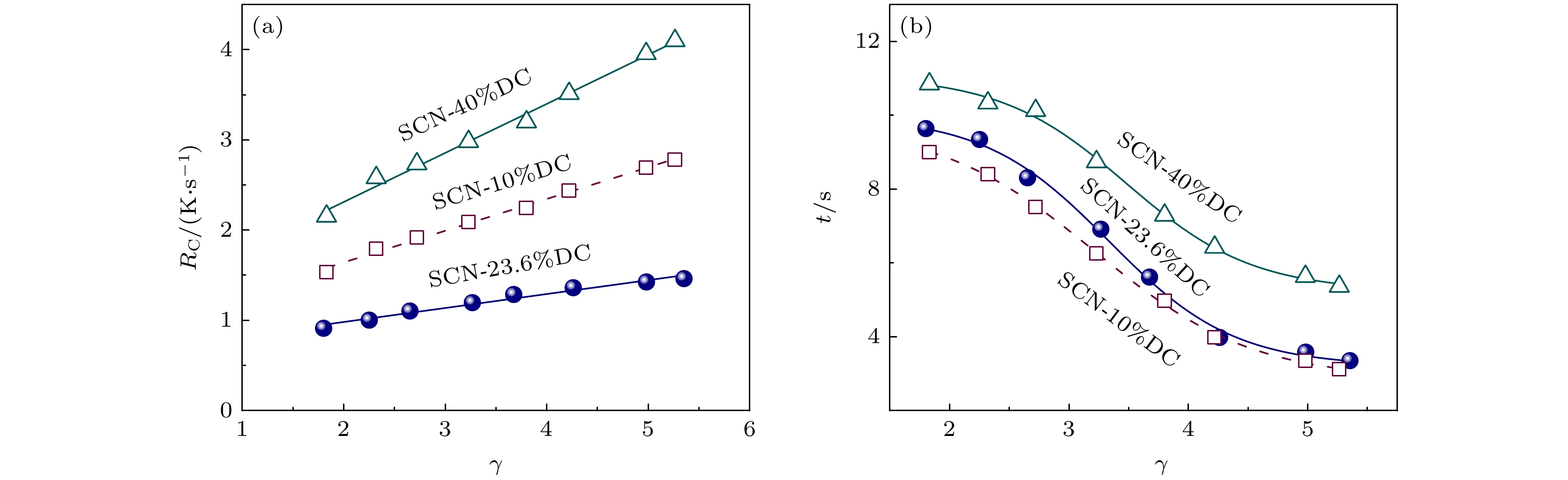
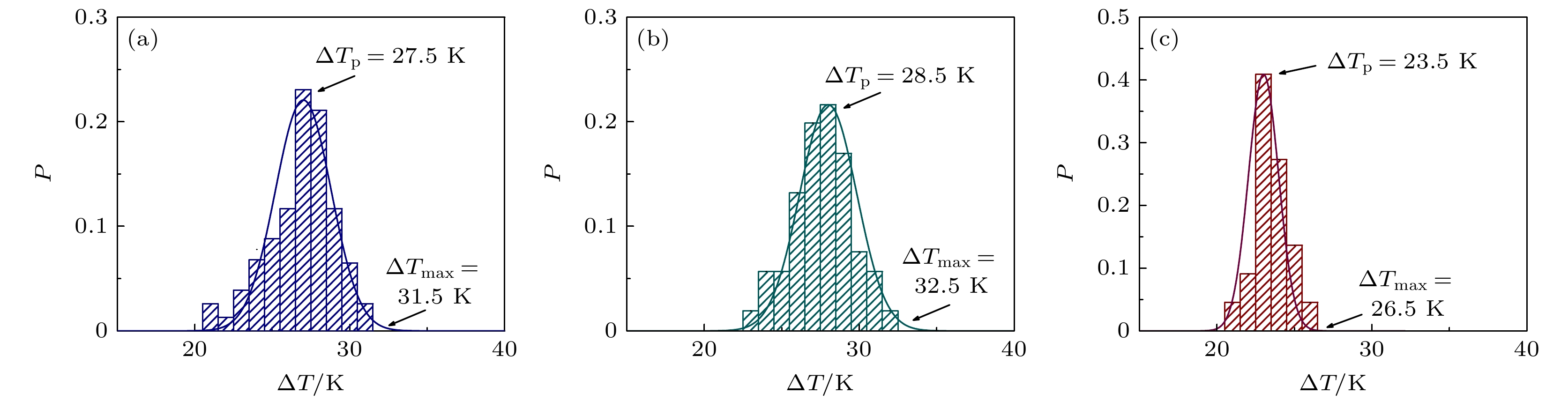
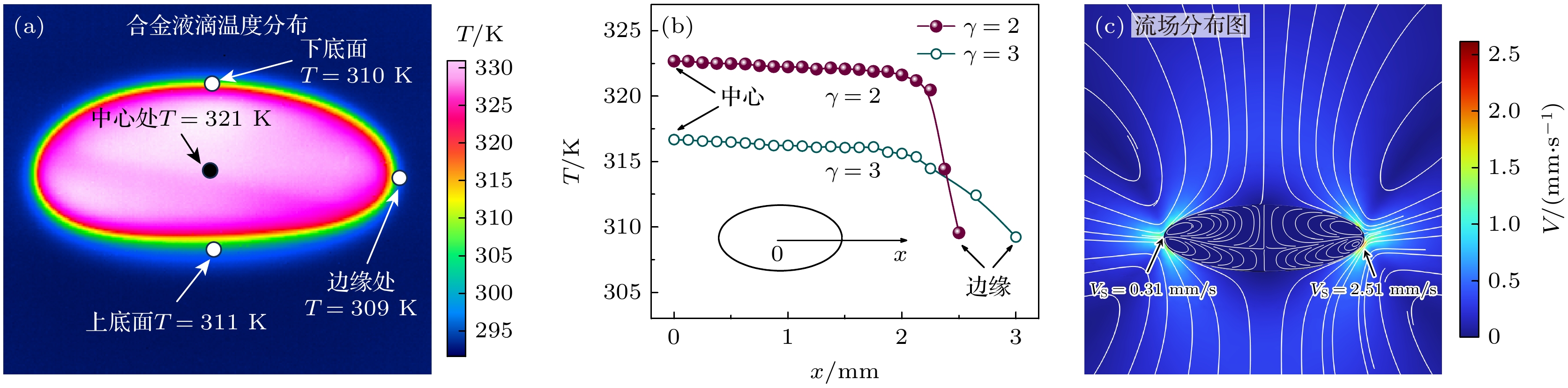
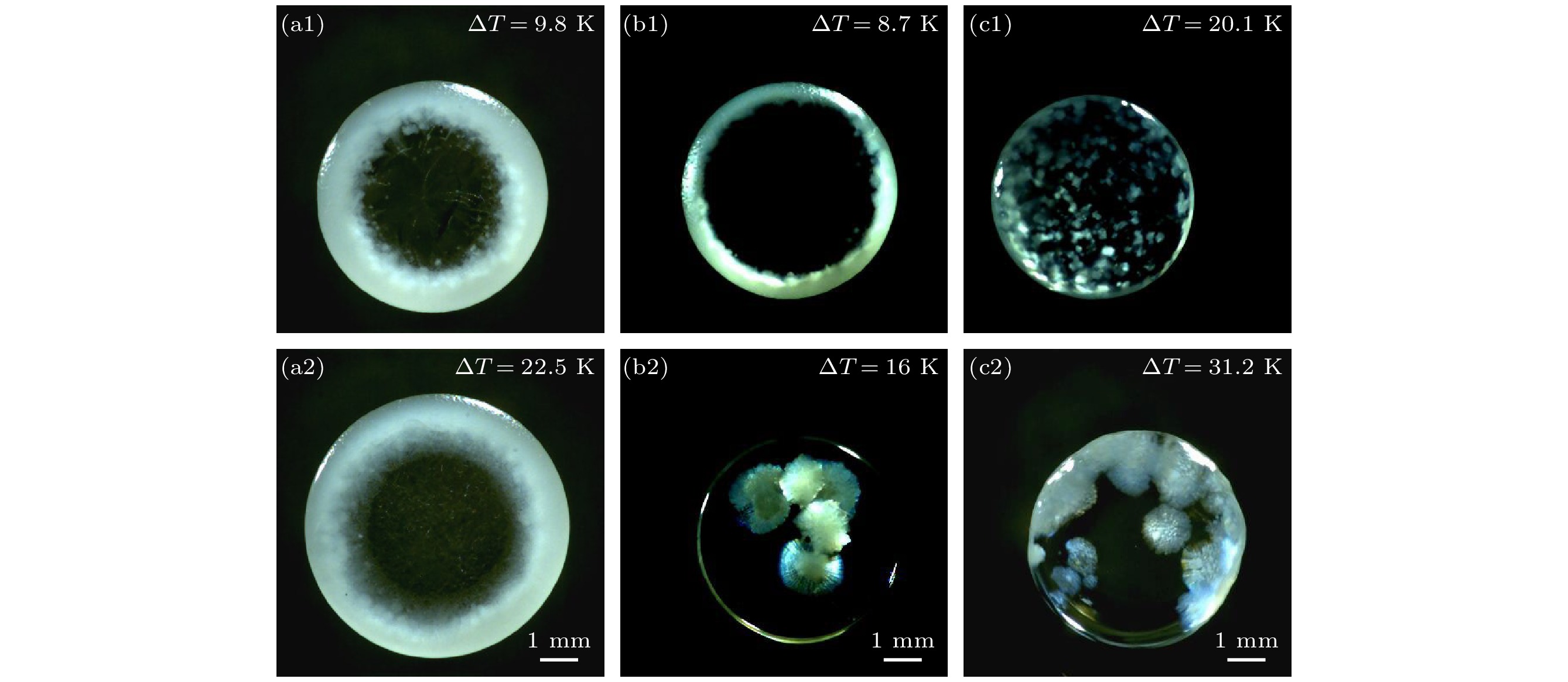
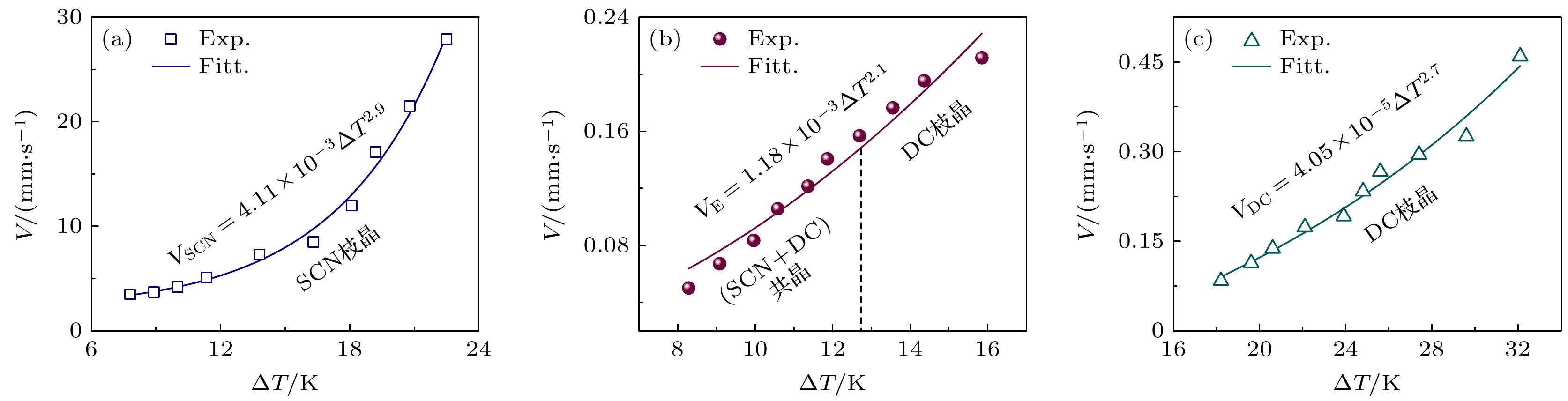
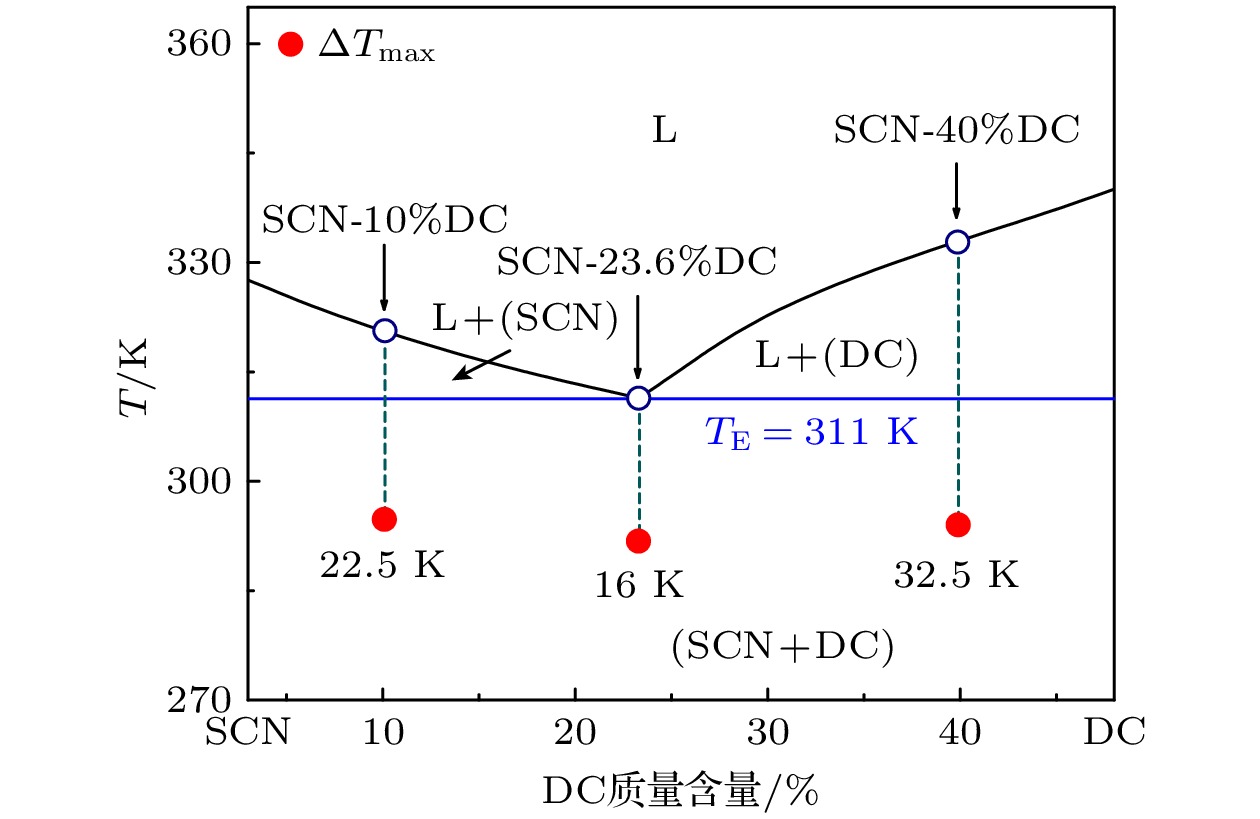
As an important and promising experimental method of simulating the containerless state in outer space, acoustic levitation provides excellent contact-free condition for investigating solidification process. Meanwhile, the radiation pressure and acoustic streaming caused by nonlinear effects bring various kinds of novel phenomena to crystallization kinetics. In this work, high-speed charge coupled device (CCD), low-speed camera and infrared thermal imager are used simultaneously to observe the crystallization process of acoustically levitated SCN-DC transparent alloys. The undercooling ability and solidification process of alloy droplets with different aspect ratios are explored in acoustic levitation state. For hypoeutectic SCN-10%DC, eutectic SCN-23.6%DC and hypereutectic SCN-40%DC alloys, the experimental maximum undercoolings reach 22.5 K (0.07TL), 16 K (0.05TE) and 32.5 K (0.1TL) and the corresponding crystal growth velocities are 27.91, 0.21 and 0.45 mm/s, respectively. In SCN-10%DC hypoeutectic alloy, the nucleation mode of SCN dendrite changes from edge nucleation into random nucleation with the increase of undercooling. For SCN-23.6%DC eutectic alloy, when the undercooling exceeds 12.6 K, DC dendrites preferentially nucleate and grow, and then the (SCN+DC) eutectic adheres to and grows on DC dendrites. Moreover, the growth interface of DC dendrites gradually changes from sharp into smooth within SCN-40%DC hypereutectic alloy as the undercooling degree rises. The undercooling distribution curve and nucleation probability variation trend versus aspect ratio are analyzed. It is found that as the aspect ratio increases, undercooling of alloy droplet first increases, then decreases, and finally remains almost unchanged. Further analysis shows that with the increase of aspect ratio, the cooling rate will rise and thus enhance the undercooling. However, the increase in surface nucleation rate and the droplet oscillation inhibits deep undercooling of alloy droplet. Therefore, the coupled effects of cooling rate, surface nucleation rate, and droplet oscillation determine the undercooling of the alloy. In the case of SCN-40% DC hypereutectic alloy, the acoustic streaming and surface oscillation arising from acoustic field are the main factors intensifying surface nucleation.
-
Keywords:
- acoustic levitation /
- SCN-DC alloy /
- nucleation /
- crystal growth
[1] Foresti D, Nabavi M, Klingauf M, Ferrari A, Poulikakos D 2013 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110 12549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xie W J, Cao C D, Lü Y J, Wei B 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 104304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Doss M, Bänsch E 2022 Chem. Eng. Sci. 248 117149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zehnter S, Andrade M A B, Ament C 2021 J. Appl. Phys. 129 134901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 秦修培, 耿德路, 洪振宇, 魏炳波 2017 66 124301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qin X P, Geng D L, Hong Z Y, Wei B B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 124301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Vieira S L, Andrade M A B 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 224901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Andrade M A B, Bernassau A L, Adamowski J C 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 044101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nada B, Daniele F, Marko D, Majid N, Dimos P 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 161904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 陈聪, 张若钦, 李锋, 李志远 2023 72 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen C, Zhang R Q, Li F, Li Z Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu B, Vansaders B, Lim M X, Jaeger H M 2023 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 e2301625120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hosseinzadeh V A, Holt R G 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 174502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kremer J, Kilzer A, Petermann M 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 015109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Brillo J, Pommrich A I, Meyer A 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 165902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Su Y, Mohr M, Wunderlich R K, Wang X D, Cao Q P, Zhang D X, Yang Y, Fecht H J, Jiang J Z 2020 J. Mol. Liq. 298 111992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mark P, Taketoshi H, Minoru E, Ivan E 1995 J. Cryst. 151 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lü Y J, Wei B 2006 J. Chem. Phys. 125 144503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Andrade M A B, Marzo A, Adamowski J C 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 250501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杜人君, 解文军 2011 60 114302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du R J, Xie W J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 114302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王哲, 王发展, 王欣, 何银花, 马姗, 吴振 2014 63 076101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z, Wang F Z, Wang X, He Y H, Ma S, Wu Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 076101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lü Y J, Xie W J, Wei B 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 184107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mauro N A, Vogt A J, Johnson M L, Bendert J C, Kelton K F 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 021904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Mauro N A, Vogt A J, Johnson M L, Bendert J C, Soklaski R, Yang L, Kelton K F 2013 Acta Mater. 61 7411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wolfgang R, Joseph P, Allen C, Daniel D 2023 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 154 1339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Loops J H, Lima E B, Leão-Neto J P, Silva G T 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 043102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] O’Connell R A, Sharratt W N, Cabral J T 2023 Phys. Rev. Lett. 131 218101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zsolt V, Arnold R, Jenő K, András R 2019 J. Cryst. 506 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Rodriguez J E, Kreischer C, Volkmann T, Matson D M 2017 Acta Mater. 122 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ohsaka K, Trinh E H 1990 J. Cryst. 106 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Witusiewicz V T, Hecht U, Rex S 2013 J. Cryst. 375 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lee C P, Wang T G 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 94 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xie W J, Wei B 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 3016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 声场计算所需物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters used for calculation
参数 单位 数值 超声频率 f kHz 22 发射端振幅 A μm 15 等效半径 $ {{R}}_{\text{s}} $ mm 4.15 重力加速度 g m/s2 9.8 介质密度 $ {\rho }_{0} $ kg/m3 1.29 介质黏度 $ {\eta}_{0} $ $ {10}^{-5}\text{ }\text{Pa∙s} $ 1.81 声速 $ {{c}}_{0} $ m/s 340 合金密度 $ {\rho }_{\text{s}} $ 103 kg/m3 1.02 合金表面张力 $ \sigma $ $ {10}^{-2}\text{\;}\text{N/m} $ 3.75 合金黏度 $ {\eta}_{\text{L}} $ $ {10}^{-3}\text{\;}\text{Pa∙s} $ 3.22 温度T K 293 -
[1] Foresti D, Nabavi M, Klingauf M, Ferrari A, Poulikakos D 2013 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110 12549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xie W J, Cao C D, Lü Y J, Wei B 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 104304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Doss M, Bänsch E 2022 Chem. Eng. Sci. 248 117149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zehnter S, Andrade M A B, Ament C 2021 J. Appl. Phys. 129 134901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 秦修培, 耿德路, 洪振宇, 魏炳波 2017 66 124301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qin X P, Geng D L, Hong Z Y, Wei B B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 124301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Vieira S L, Andrade M A B 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 224901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Andrade M A B, Bernassau A L, Adamowski J C 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 044101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nada B, Daniele F, Marko D, Majid N, Dimos P 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 161904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 陈聪, 张若钦, 李锋, 李志远 2023 72 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen C, Zhang R Q, Li F, Li Z Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu B, Vansaders B, Lim M X, Jaeger H M 2023 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 e2301625120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hosseinzadeh V A, Holt R G 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 174502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kremer J, Kilzer A, Petermann M 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 015109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Brillo J, Pommrich A I, Meyer A 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 165902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Su Y, Mohr M, Wunderlich R K, Wang X D, Cao Q P, Zhang D X, Yang Y, Fecht H J, Jiang J Z 2020 J. Mol. Liq. 298 111992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mark P, Taketoshi H, Minoru E, Ivan E 1995 J. Cryst. 151 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lü Y J, Wei B 2006 J. Chem. Phys. 125 144503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Andrade M A B, Marzo A, Adamowski J C 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 250501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杜人君, 解文军 2011 60 114302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du R J, Xie W J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 114302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王哲, 王发展, 王欣, 何银花, 马姗, 吴振 2014 63 076101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z, Wang F Z, Wang X, He Y H, Ma S, Wu Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 076101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lü Y J, Xie W J, Wei B 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 184107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mauro N A, Vogt A J, Johnson M L, Bendert J C, Kelton K F 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 021904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Mauro N A, Vogt A J, Johnson M L, Bendert J C, Soklaski R, Yang L, Kelton K F 2013 Acta Mater. 61 7411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wolfgang R, Joseph P, Allen C, Daniel D 2023 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 154 1339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Loops J H, Lima E B, Leão-Neto J P, Silva G T 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 043102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] O’Connell R A, Sharratt W N, Cabral J T 2023 Phys. Rev. Lett. 131 218101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zsolt V, Arnold R, Jenő K, András R 2019 J. Cryst. 506 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Rodriguez J E, Kreischer C, Volkmann T, Matson D M 2017 Acta Mater. 122 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ohsaka K, Trinh E H 1990 J. Cryst. 106 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Witusiewicz V T, Hecht U, Rex S 2013 J. Cryst. 375 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lee C P, Wang T G 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 94 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xie W J, Wei B 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 3016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 1886
- PDF Downloads: 53
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: