-
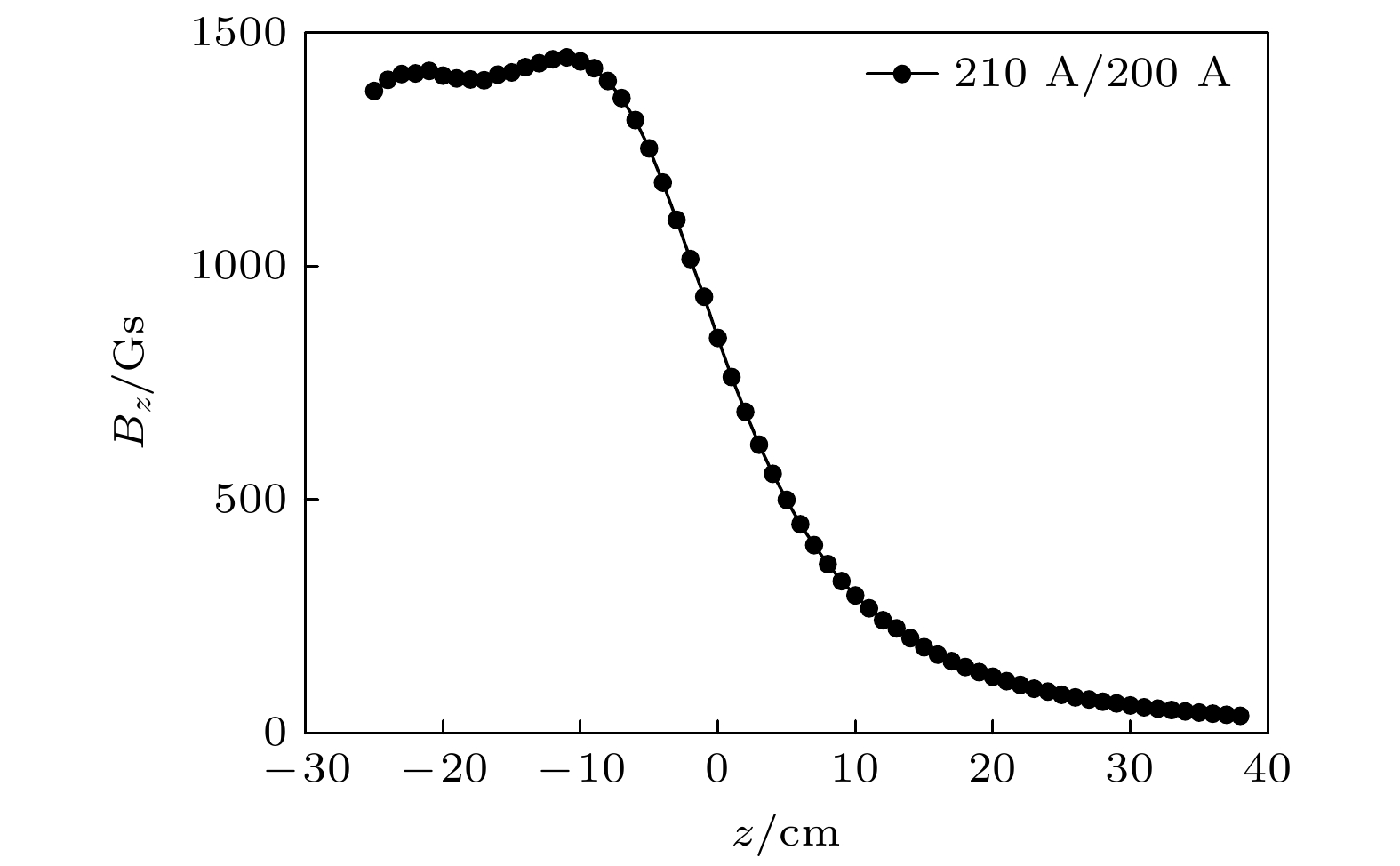
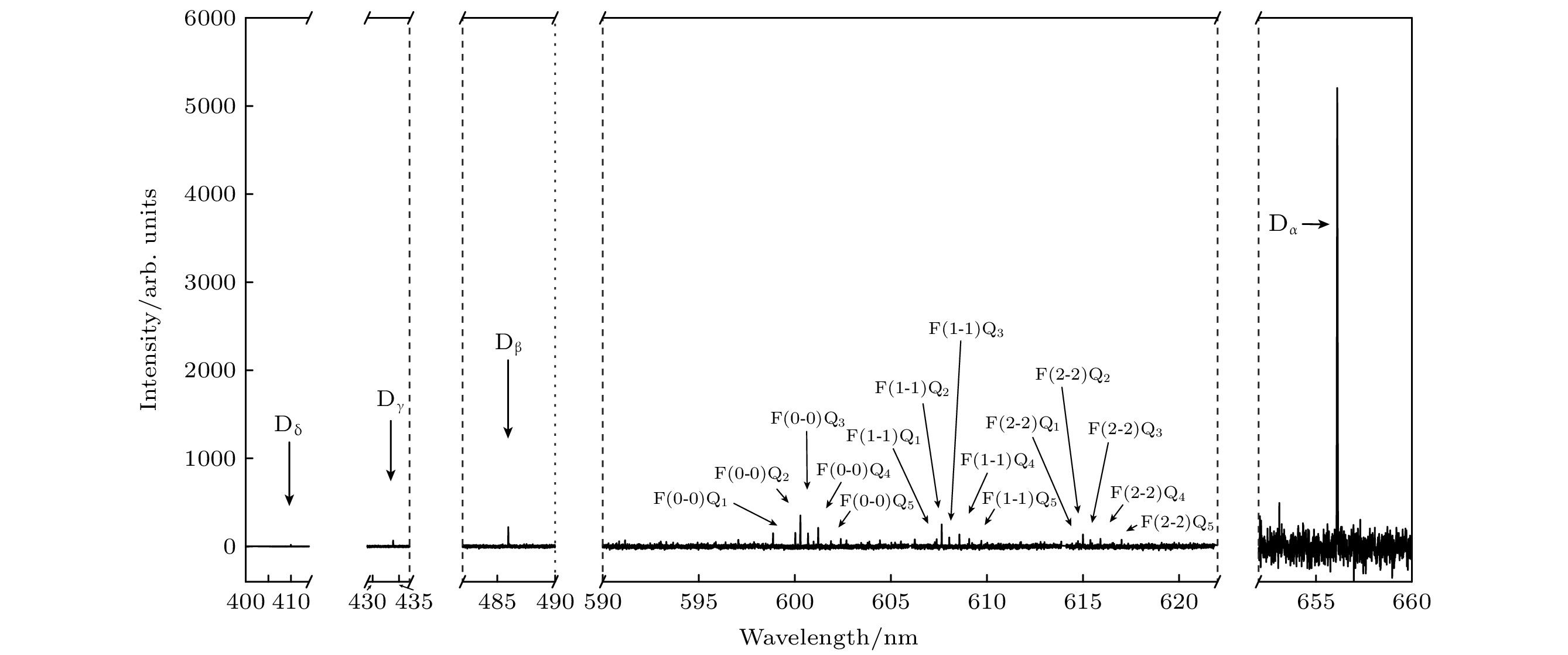
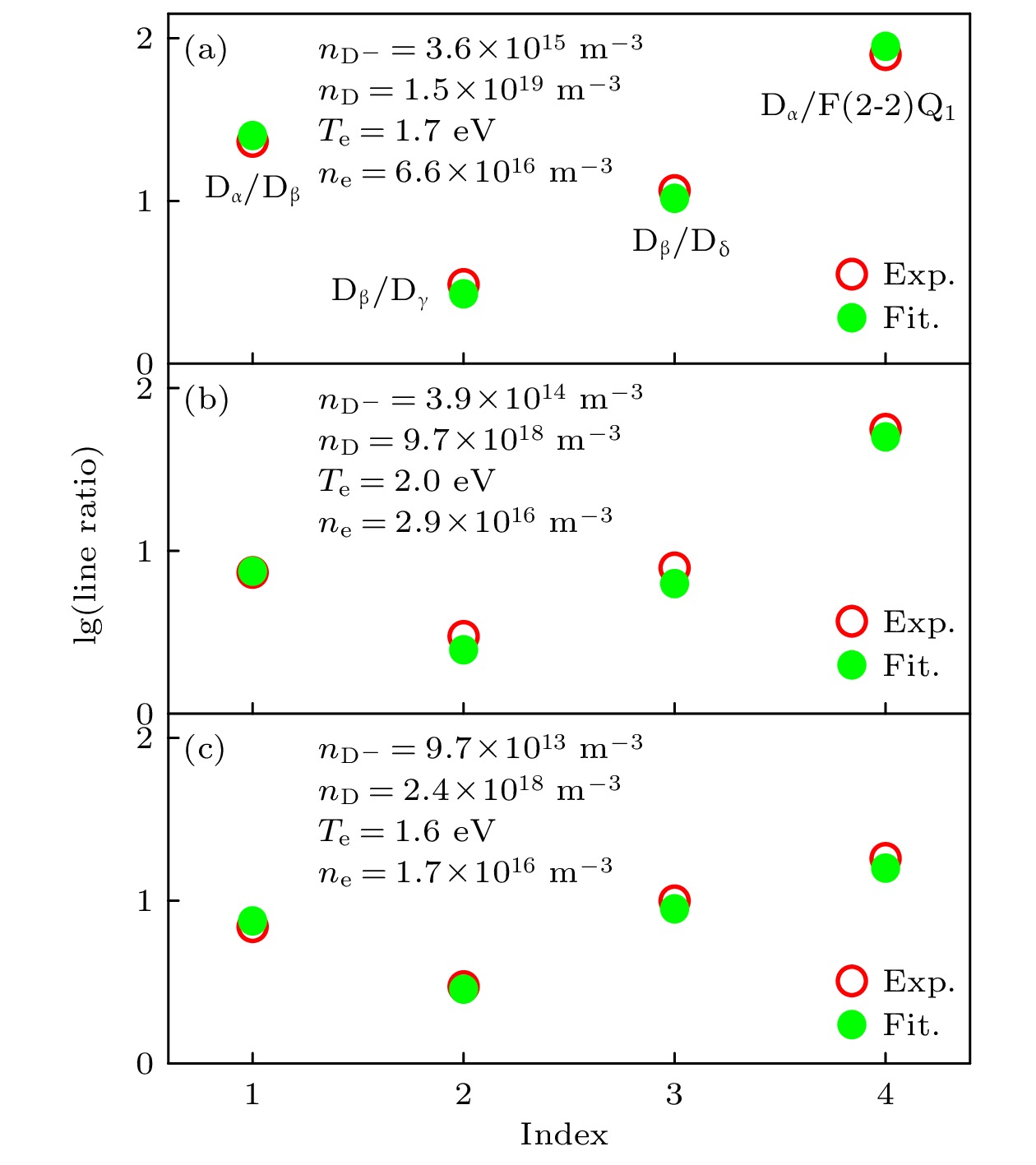
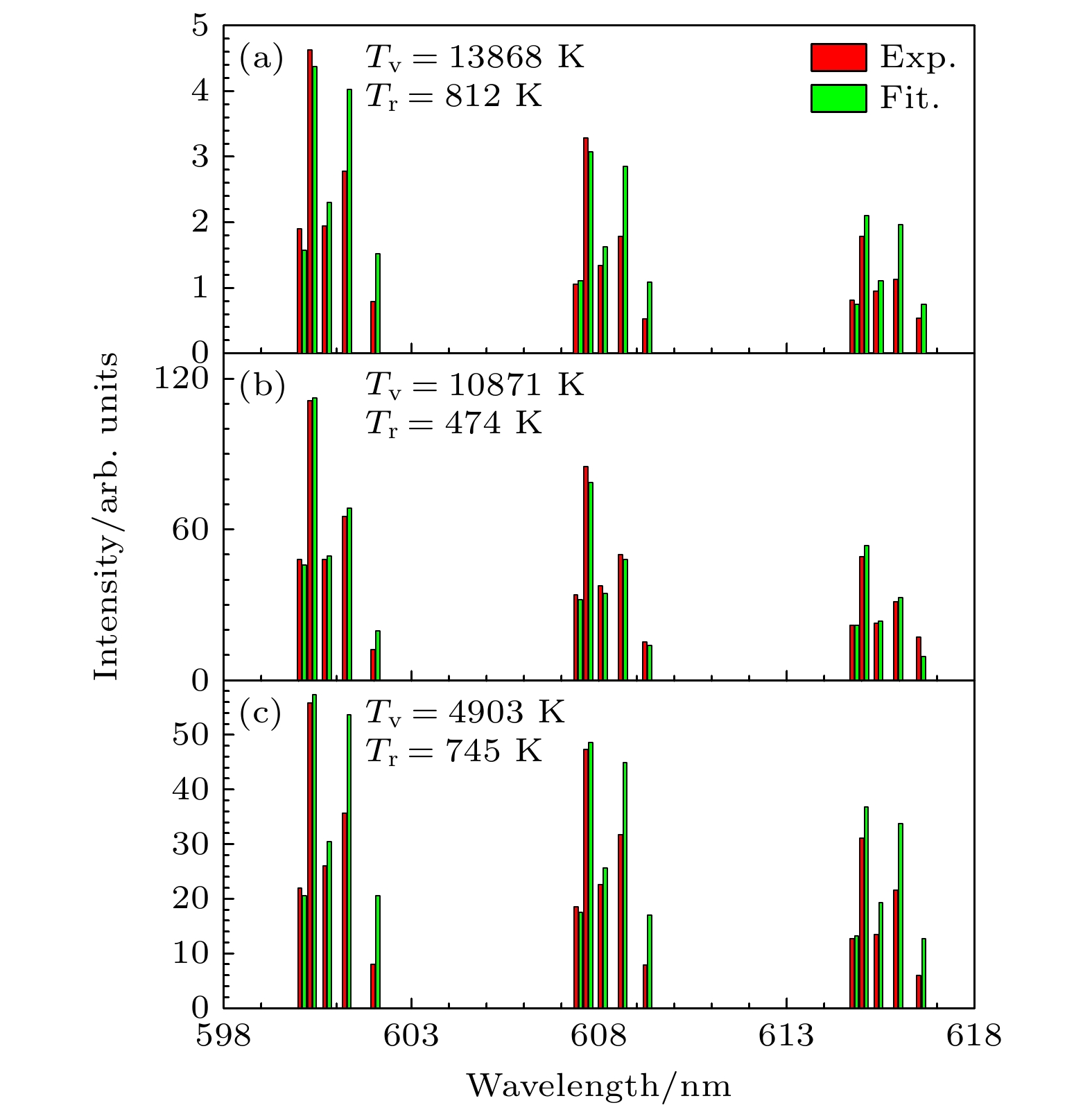
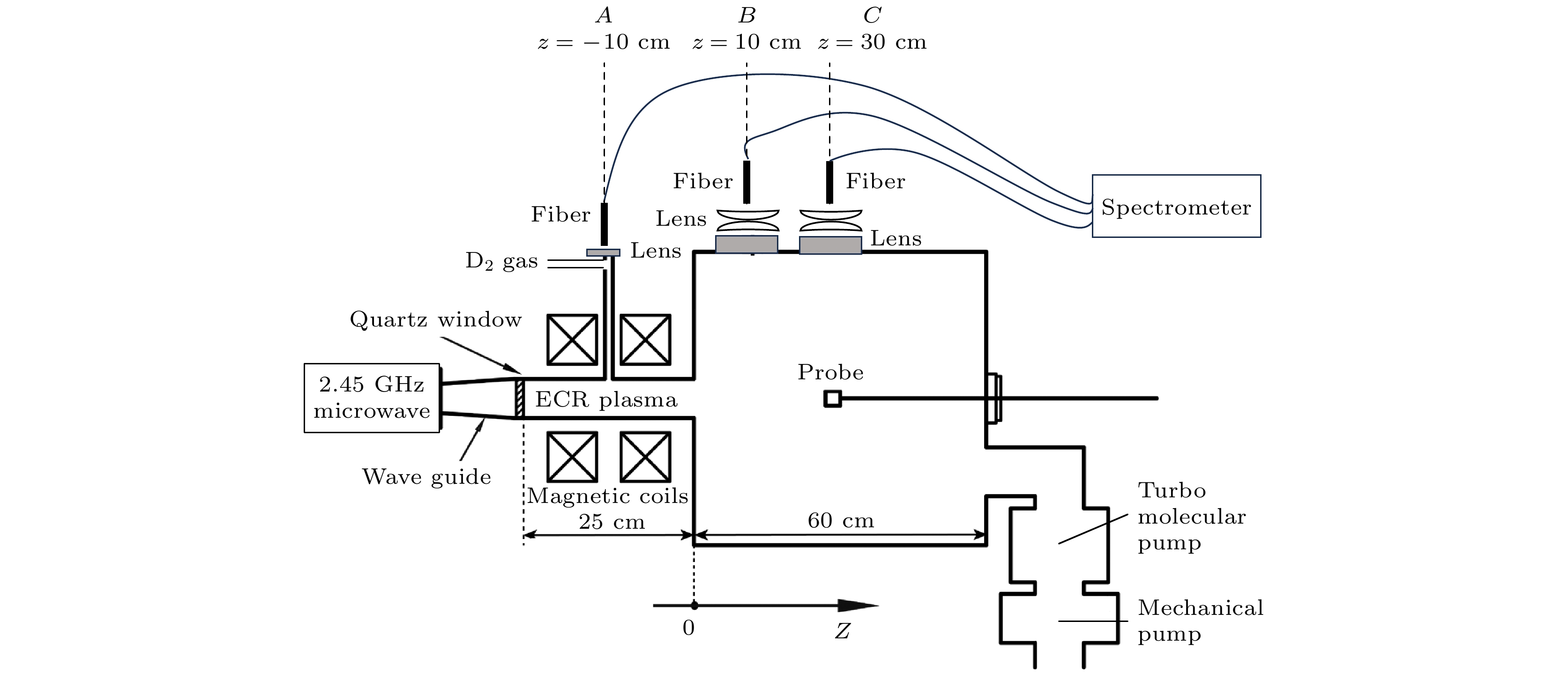
The electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) plasma is characterized by low working pressure and high dissociation rate, and it has important applications in the deuterium negative ion $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ source technology. In this paper, the Yacora collisional-radiative model is applied to the emission spectrum diagnosis of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ in ECR deuterium plasma. The $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ density is estimated by using the $ {I}_{{{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\alpha }}}}/{I}_{{{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\beta }}}} $ ratio and the relative intensity of other deuterium molecular lines, thereby avoiding complex calibration procedure of absolute intensity. The spatial structure of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ is studied by the multichannel emission spectrum measured in the source region and diffusion region. The experiments are conducted on a 2.45-GHz ECR plasma source at a deuterium gas pressure of 1 Pa and microwave power of 660 W. The Balmer series of atomic deuterium ($ {{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\alpha }}} $, $ {{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\beta }}} $, $ {{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\gamma }}} $, $ {{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\delta }}} $) and the Fulcher band Q-branches of molecular deuterium are measured in the source region and expanding region of the ECR plasma. It is found that the intensity of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\alpha }}} $ in the source region is much higher than that of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\beta }}} $, specifically, the $ {I}_{{{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\alpha }}}}/{I}_{{{\mathrm{D}}}_{{\mathrm{\beta }}}} $ ratio reaches as high as 23, indicating a selective enhancement of Balmer lines due to the mutual neutralization process of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $. Furthermore, $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ density in the source region is estimated to be about $ 3.6\times {10}^{15}\;{{\mathrm{m}}}^{-3} $, and the $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ density in the expanding region decreases significantly. In the ECR plasma source region, the plasma-wall interaction is strong due to the small volume of the cavity. The recombination desorption process produces more vibrationally excited molecules, thereby further enhancing the dissociation attachment reaction, which is beneficial to the generation of deuterium negative ions. On the other hand, the axial electric field within the ECR plasma inhibits the axial transport of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $, suggesting that the production and loss of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ are both localized. These characteristics of the ECR plasma source contribute to the formation of a large gradient of $ {{\mathrm{D}}}^{-} $ density between the source region and the expanding region. -
Keywords:
- negative deuterium ion sources /
- optical emission spectroscopy /
- electron cyclotron resonance plasma
[1] Bentounes J, Béchu S, Biggins F, Michau A, Gavilan L, Menu J, Bonny L, Fombaron D, Bès A, Lebedev Y A, Shakhatov V A, Svarnas P, Hassaine T, Lemaire J L, Lacoste A 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 055015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fantz U, Heger B 1998 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 40 2023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Averkin S N, Gatsonis N A, Olson L 2015 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 43 1926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Fantz U, Franzen P, Kraus W, Falter H D, Berger M, Christ K S, Froschle M, Gutser R, Heinemann B, Martens C, McNeely P, Riedl R, Speth E, Wunderlich D 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 02A511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Marini C, Agnello R, Duval B P, Furno I, Howling A A, Jacquier R, Karpushov A N, Plyushchev G, Verhaegh K, Guittienne P, Fantz U, Wünderlich D, Béchu S, Simonin A 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 036024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sharma S, Sahu D, Narayanan R, Kar S, Bandyopadhyay M, Chakraborty A, Singh M J, Tarey R D, Ganguli A 2022 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2244 012055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Alton G, Smithe D 1994 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 65 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhao H, Sun L, Guo J, Lu W, Xie D, Hitz D, Zhang X, Yang Y 2017 Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 20 094801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ren H T, Peng S X, Xu Y, Zhao J, Lu P N, Chen J, Zhang A L, Zhang T, Guo Z Y, Chen J E 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 02A927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Torii H, Matsui S 2024 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 42 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Seker Z, Ozdamar H, Esen M, Esen R, Kavak H 2014 Appl. Surf. Sci. 314 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ke Y J, Sun X F, Chen X K, Tian L C, Zhang T P, Zheng M F, Jia Y H, Jiang H C 2017 Plasma Sci. Technol 19 095503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 李鑫, 曾明, 刘辉, 宁中喜, 于达仁 2023 72 225202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X, Zeng M, Liu H, Ning Z X, Yu D R 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 225202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kurutz U, Friedl R, Fantz U 2017 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 59 075008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Svarnas P, Breton J, Bacal M, Mosbach T 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 532
[16] Aleiferis S, Tarvainen O, Svarnas P, Bacal M, Béchu S 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 095203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hill R N 1977 Phys. Rev. Lett. 38 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bacal M, Hamilton G W, Bruneteau A M, Doucet H J, Taillet J 1979 Rev Sci Instrum 50 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] O’Keefe A, Deacon D A G 1988 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59 2544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lee H, Kim W, Lee J, Park K S, Yoo J J, Atala A, Kim G H, Lee S J 2021 Appl Phys Rev 8 021405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fantz U, Wünderlich D 2006 New J. Phys. 8 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Heinemann B, Fantz U, Kraus W, Schiesko L, Wimmer C, Wünderlich D, Bonomo F, Fröschle M, Nocentini R, Riedl R 2017 New J. Phys. 19 015001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Furno I, Agnello R, Guittienne P, Howling A, Jacquier R, Plyushchev G, Stollberg C, Bechu S, Barbisan M, Fadone M 2020 EURO Fusion Consortium
[24] Berger M, Fantz U, Christ K S, Team N 2009 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18 025004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhu B L, Yi K Y, Yang K, Ke W, Ma J X, Zhu X D 2019 Phys. Plasma 26 082107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Schulz-Von D G V, Dbele H F 1996 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 16 461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhou H Y, Wang L, Zhu X D, Ke B, Ding F, Wen X H, Wang Y N 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81 033501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Aleiferis S, Svarnas P, Béchu S, Tarvainen O, Bacal M 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 075015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wünderlich D, Dietrich S, Fantz U 2009 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 110 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wünderlich D, Fantz U 2016 Atoms 4 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hollmann E M, Brezinsek S, Brooks N H, Groth M, McLean A G, Pigarov A Y, Rudakov D L 2006 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 48 1165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lavrov B P, Pipa A V, Röpcke J 2006 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Rayar M, Le Quoc H, Lacoste A, Latrasse L, Pelletier J 2009 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18 025013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] McNeely P, Wünderlich D 2011 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20 045005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Dang J J, Chung K J, Hwang Y S 2016 Rev Sci Instrum 87 053503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yoon J S, Kim Y W, Kwon D C, Song M Y, Chang W S, Kim C G, Kumar V, Lee B 2010 Rep. Prog. Phys. 73 116401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Méndez I, Gordillo-Vázquez F J, Herrero V J, Tanarro I 2006 J. Phys. Chem. A 110 6060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Wu H M, Graves D B, Porteous R K 1995 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 4 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Fu S L, Chen J F, Hu S J, Wu X Q, Lee Y, Fan S L 2006 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Majstorović G L, Šišović N M 2015 J. Res. Phys. 38–39 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Bentounes J, Béchu S, Biggins F, Michau A, Gavilan L, Menu J, Bonny L, Fombaron D, Bès A, Lebedev Y A, Shakhatov V A, Svarnas P, Hassaine T, Lemaire J L, Lacoste A 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 055015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fantz U, Heger B 1998 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 40 2023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Averkin S N, Gatsonis N A, Olson L 2015 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 43 1926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Fantz U, Franzen P, Kraus W, Falter H D, Berger M, Christ K S, Froschle M, Gutser R, Heinemann B, Martens C, McNeely P, Riedl R, Speth E, Wunderlich D 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 02A511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Marini C, Agnello R, Duval B P, Furno I, Howling A A, Jacquier R, Karpushov A N, Plyushchev G, Verhaegh K, Guittienne P, Fantz U, Wünderlich D, Béchu S, Simonin A 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 036024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sharma S, Sahu D, Narayanan R, Kar S, Bandyopadhyay M, Chakraborty A, Singh M J, Tarey R D, Ganguli A 2022 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2244 012055
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Alton G, Smithe D 1994 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 65 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhao H, Sun L, Guo J, Lu W, Xie D, Hitz D, Zhang X, Yang Y 2017 Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 20 094801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ren H T, Peng S X, Xu Y, Zhao J, Lu P N, Chen J, Zhang A L, Zhang T, Guo Z Y, Chen J E 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 02A927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Torii H, Matsui S 2024 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 42 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Seker Z, Ozdamar H, Esen M, Esen R, Kavak H 2014 Appl. Surf. Sci. 314 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ke Y J, Sun X F, Chen X K, Tian L C, Zhang T P, Zheng M F, Jia Y H, Jiang H C 2017 Plasma Sci. Technol 19 095503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 李鑫, 曾明, 刘辉, 宁中喜, 于达仁 2023 72 225202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X, Zeng M, Liu H, Ning Z X, Yu D R 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 225202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kurutz U, Friedl R, Fantz U 2017 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 59 075008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Svarnas P, Breton J, Bacal M, Mosbach T 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 532
[16] Aleiferis S, Tarvainen O, Svarnas P, Bacal M, Béchu S 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 095203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hill R N 1977 Phys. Rev. Lett. 38 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bacal M, Hamilton G W, Bruneteau A M, Doucet H J, Taillet J 1979 Rev Sci Instrum 50 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] O’Keefe A, Deacon D A G 1988 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59 2544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lee H, Kim W, Lee J, Park K S, Yoo J J, Atala A, Kim G H, Lee S J 2021 Appl Phys Rev 8 021405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fantz U, Wünderlich D 2006 New J. Phys. 8 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Heinemann B, Fantz U, Kraus W, Schiesko L, Wimmer C, Wünderlich D, Bonomo F, Fröschle M, Nocentini R, Riedl R 2017 New J. Phys. 19 015001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Furno I, Agnello R, Guittienne P, Howling A, Jacquier R, Plyushchev G, Stollberg C, Bechu S, Barbisan M, Fadone M 2020 EURO Fusion Consortium
[24] Berger M, Fantz U, Christ K S, Team N 2009 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18 025004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhu B L, Yi K Y, Yang K, Ke W, Ma J X, Zhu X D 2019 Phys. Plasma 26 082107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Schulz-Von D G V, Dbele H F 1996 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 16 461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhou H Y, Wang L, Zhu X D, Ke B, Ding F, Wen X H, Wang Y N 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81 033501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Aleiferis S, Svarnas P, Béchu S, Tarvainen O, Bacal M 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 075015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wünderlich D, Dietrich S, Fantz U 2009 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 110 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wünderlich D, Fantz U 2016 Atoms 4 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hollmann E M, Brezinsek S, Brooks N H, Groth M, McLean A G, Pigarov A Y, Rudakov D L 2006 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 48 1165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lavrov B P, Pipa A V, Röpcke J 2006 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Rayar M, Le Quoc H, Lacoste A, Latrasse L, Pelletier J 2009 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18 025013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] McNeely P, Wünderlich D 2011 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20 045005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Dang J J, Chung K J, Hwang Y S 2016 Rev Sci Instrum 87 053503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yoon J S, Kim Y W, Kwon D C, Song M Y, Chang W S, Kim C G, Kumar V, Lee B 2010 Rep. Prog. Phys. 73 116401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Méndez I, Gordillo-Vázquez F J, Herrero V J, Tanarro I 2006 J. Phys. Chem. A 110 6060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Wu H M, Graves D B, Porteous R K 1995 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 4 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Fu S L, Chen J F, Hu S J, Wu X Q, Lee Y, Fan S L 2006 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Majstorović G L, Šišović N M 2015 J. Res. Phys. 38–39 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2289
- PDF Downloads: 49
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: