-
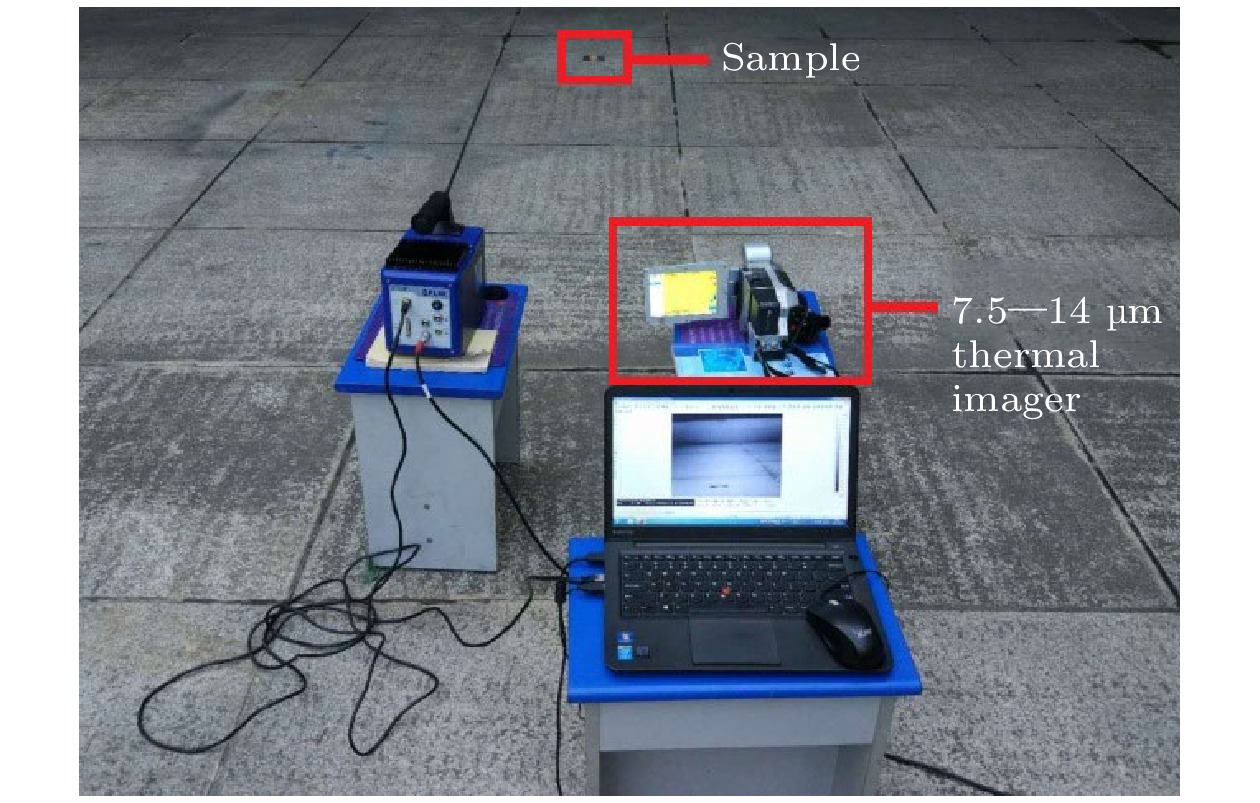
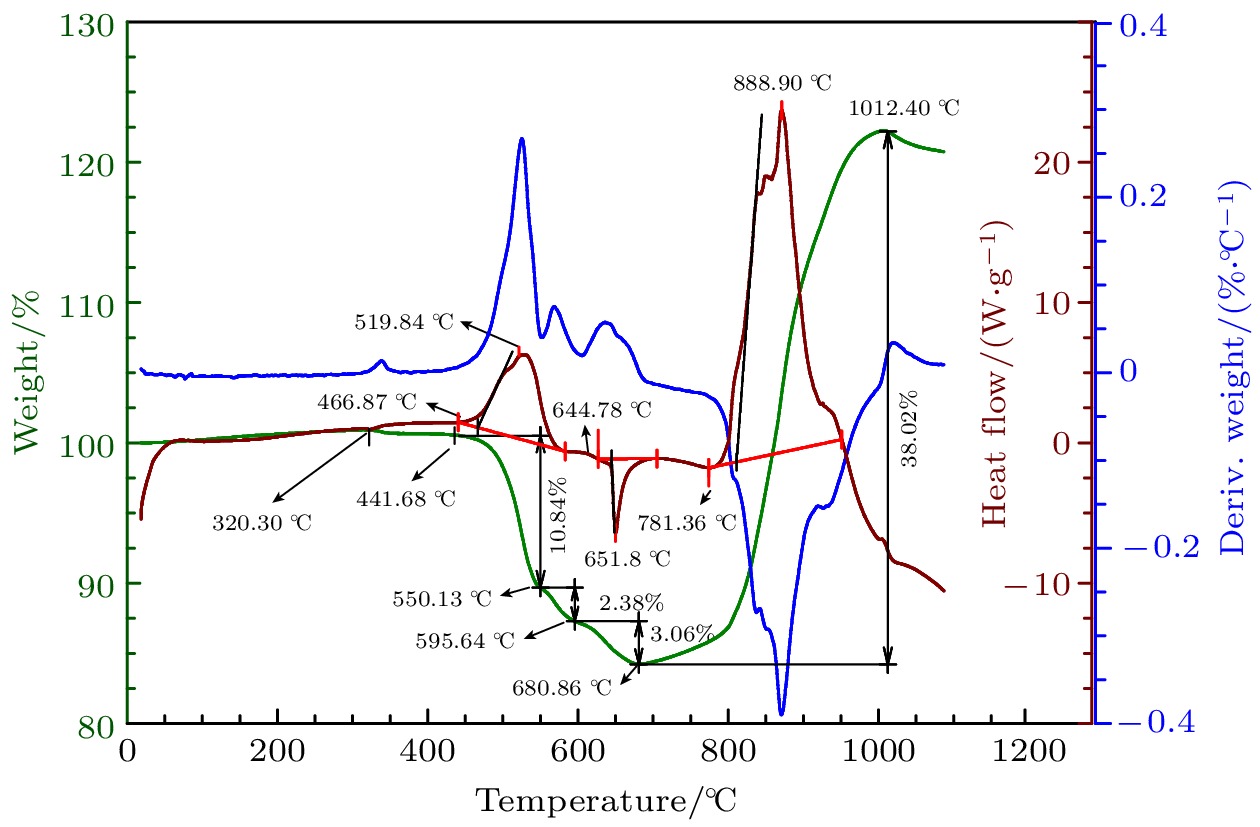
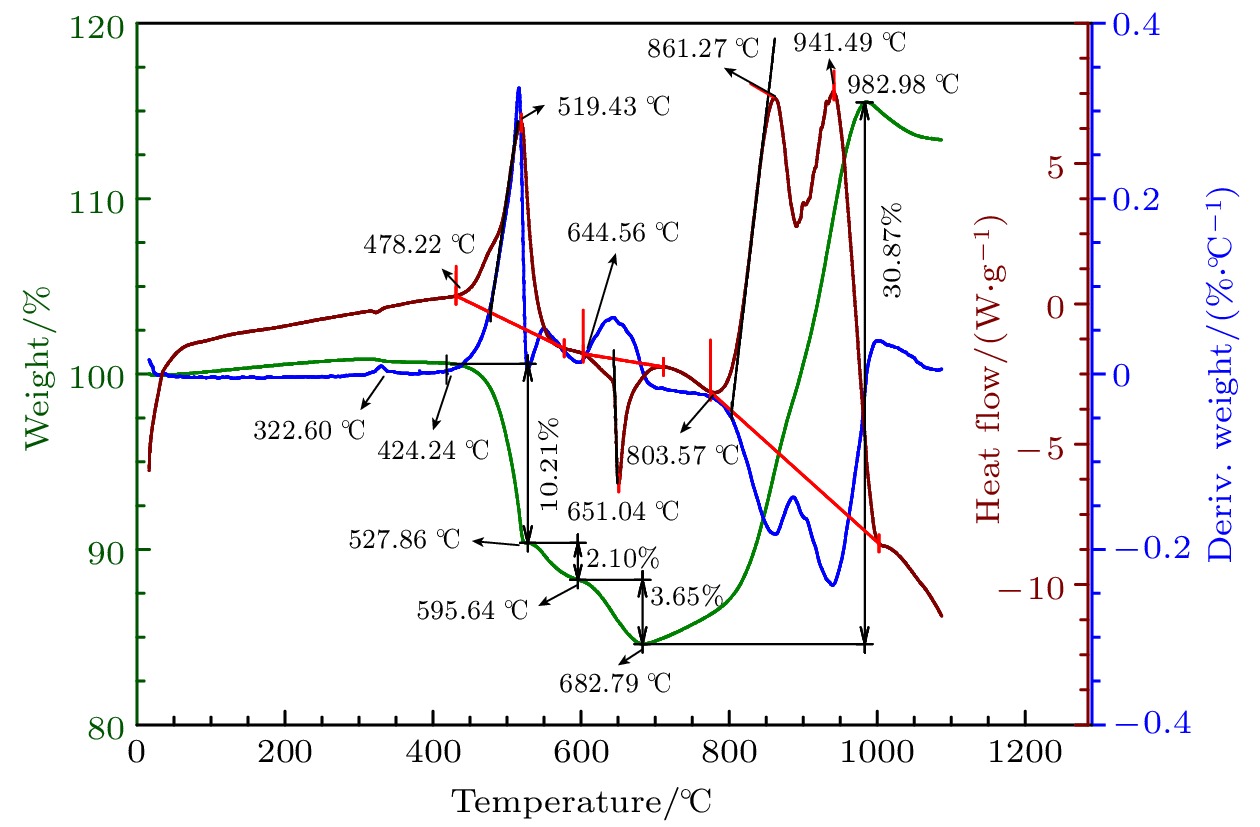
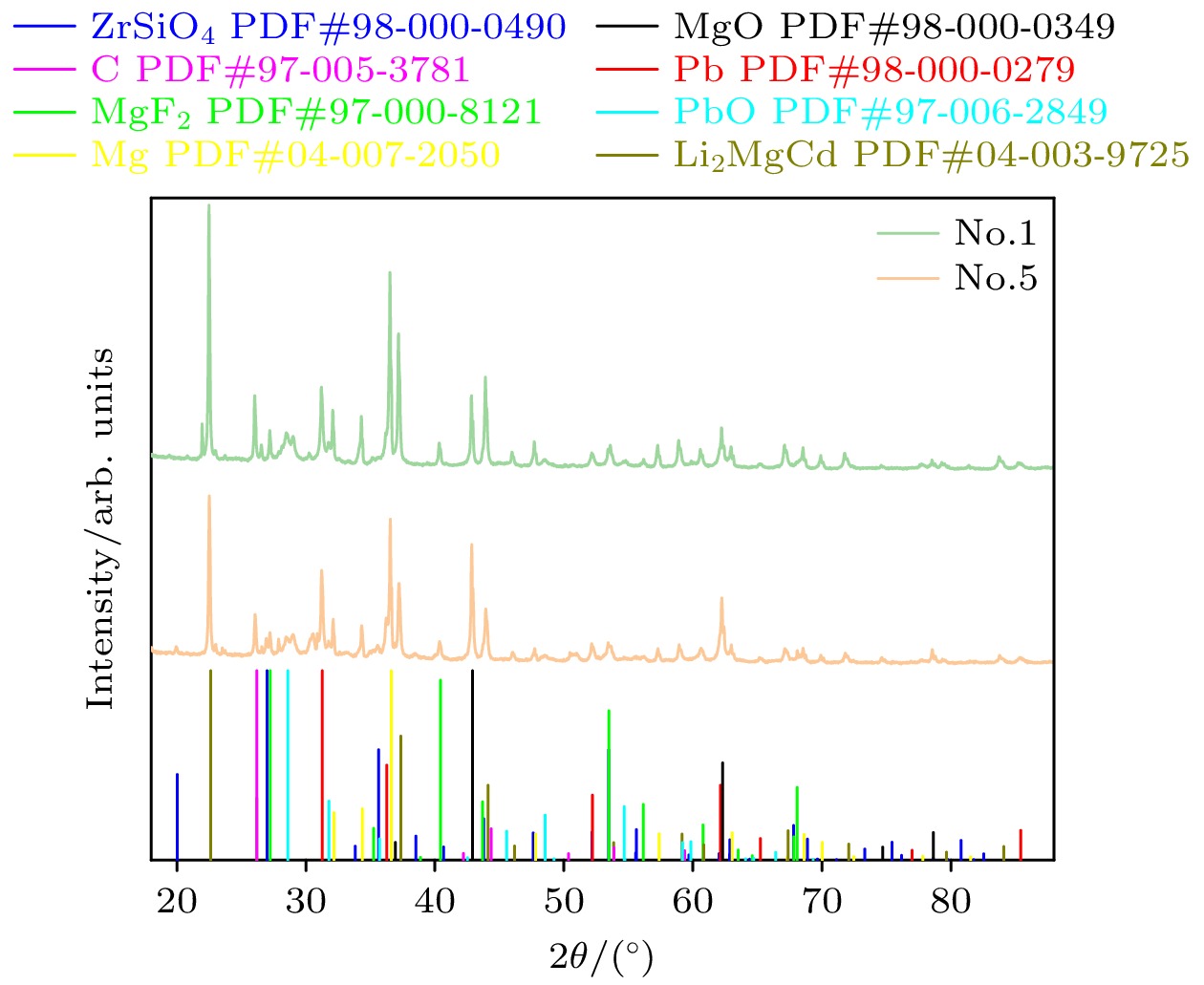
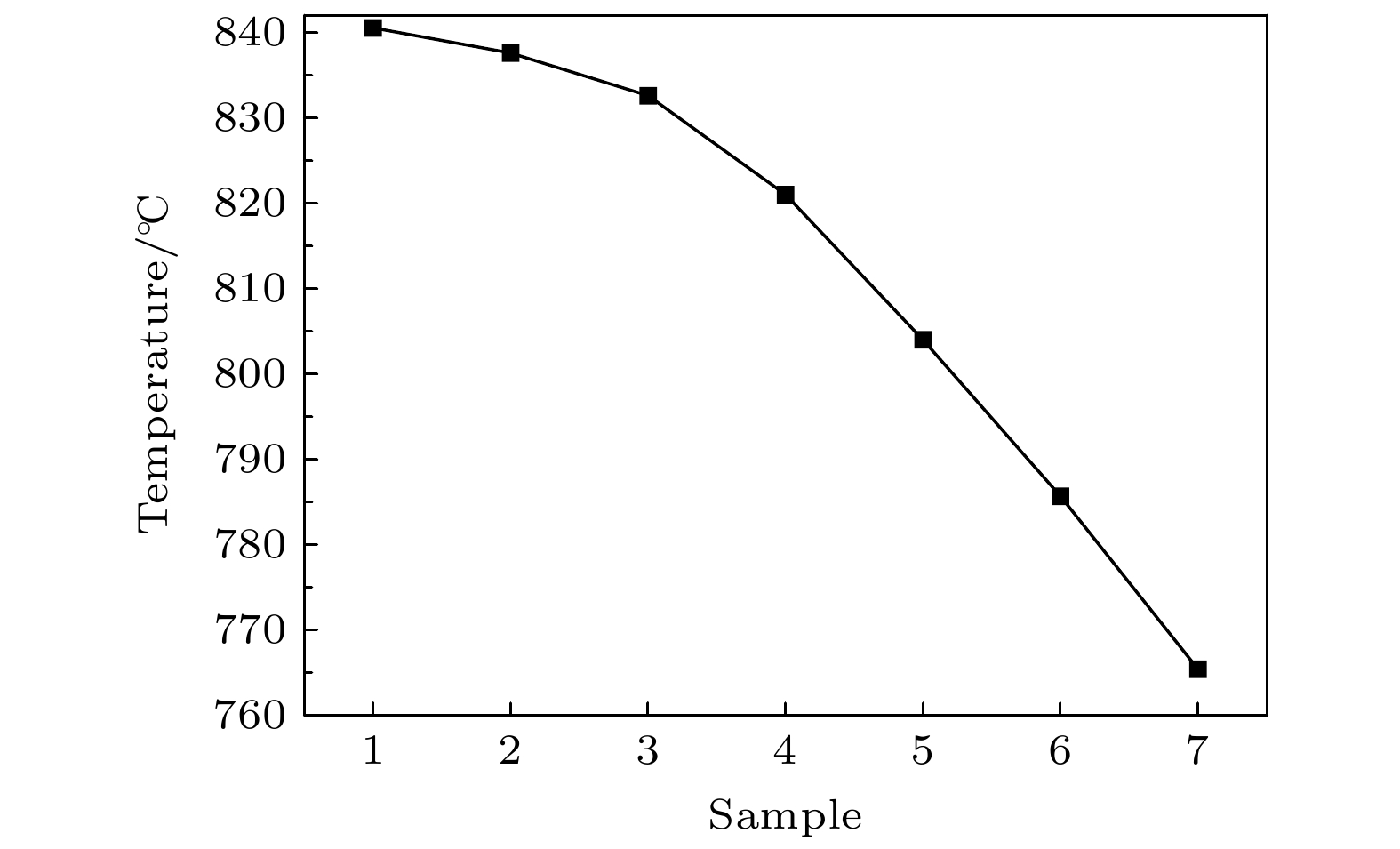
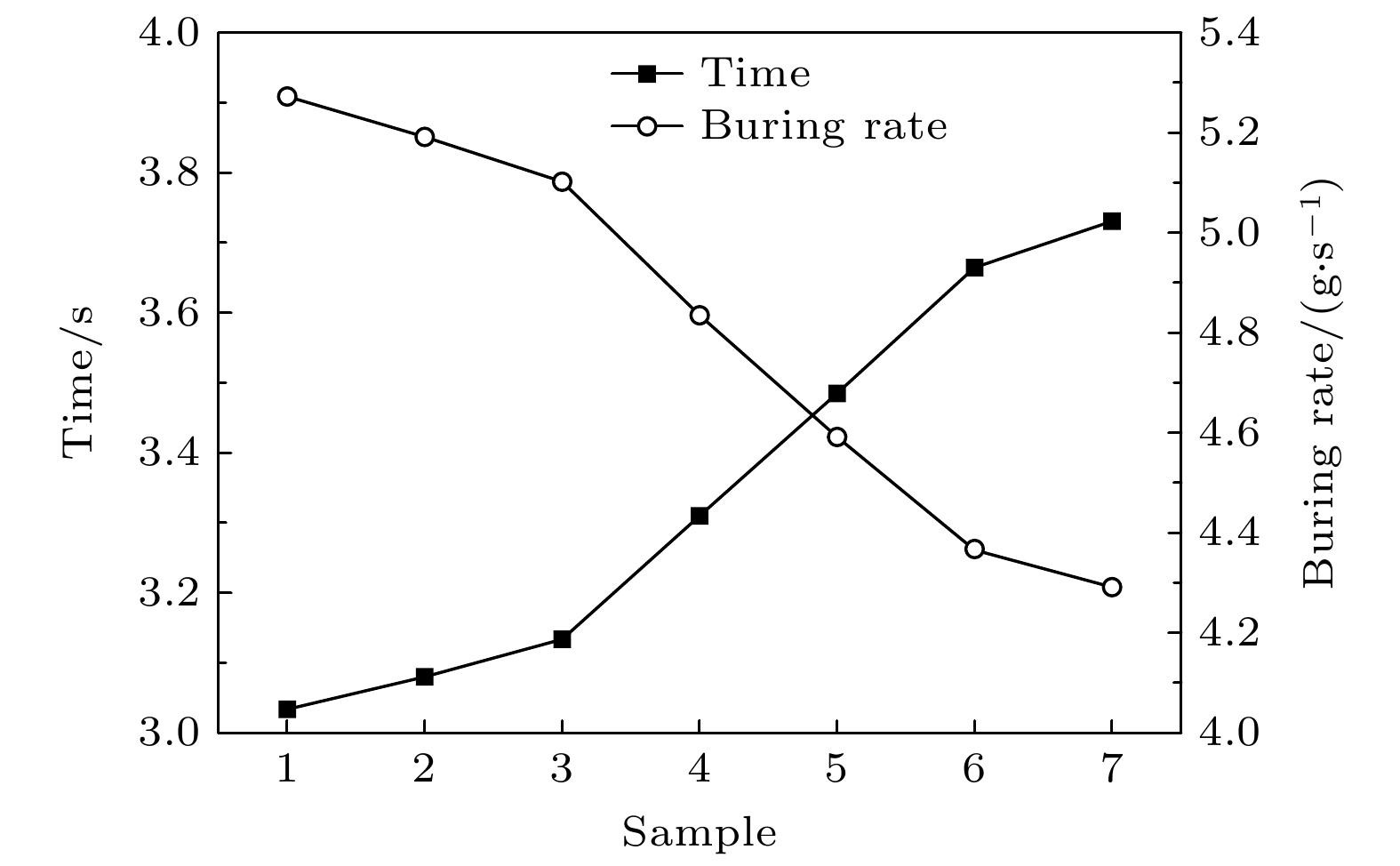
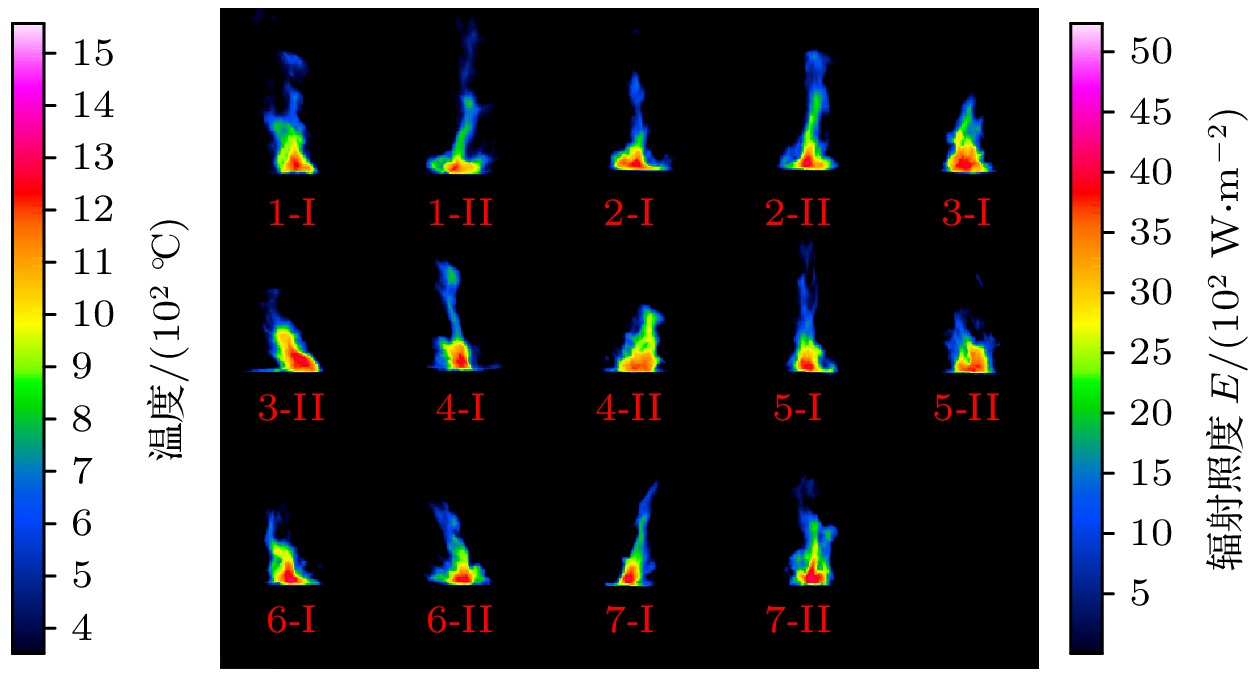
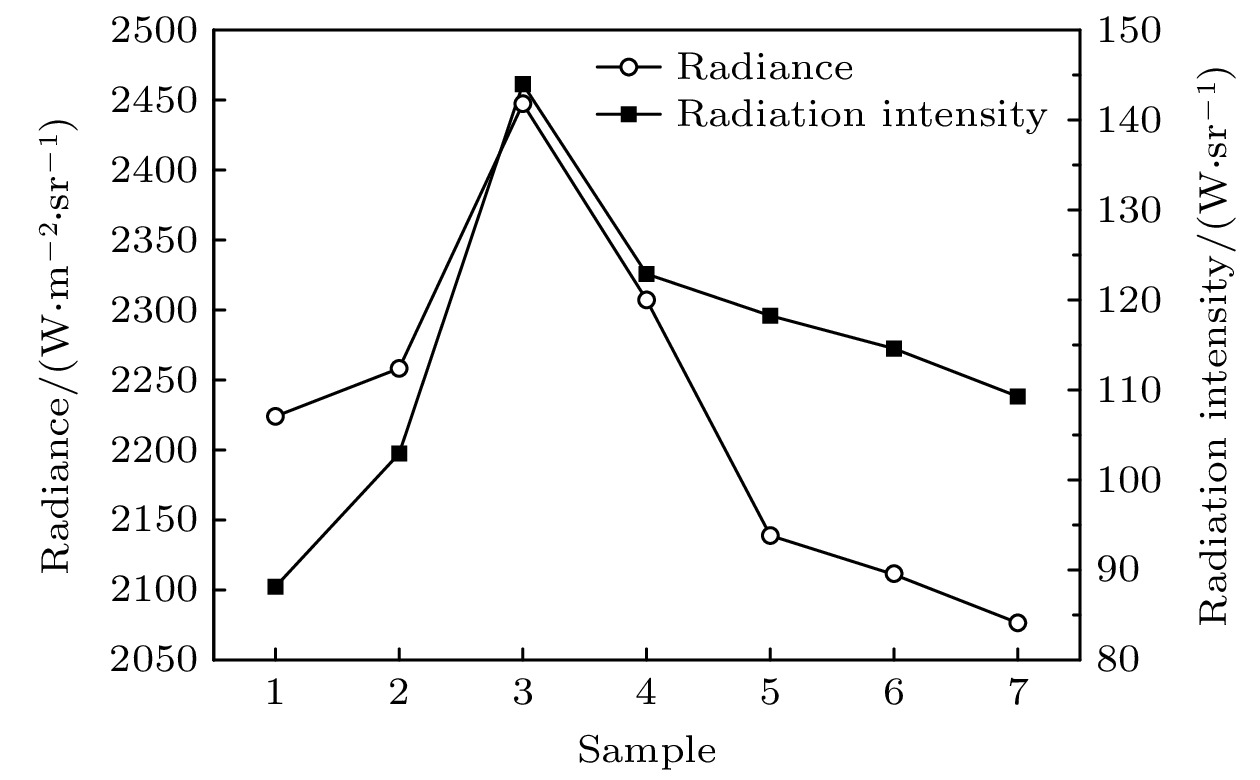
Traditional composite infrared decoy, magnesium/teflon (Mg/PTFE), has been widely used in countering infrared guided weapons since its advent. However, with the development of infrared guidance technology, its drawbacks such as insufficient far-infrared radiation and high combustion temperature emerge, making it difficult to counter novel infrared guided weapons. To address this issue, a strategy of utilizing zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4) as an additive is proposed to improve the infrared radiation of infrared decoy. Therein, seven formulations with different ratios of ZrSiO4 are designed based on the basic formula of trilead tetraoxide/ magnesium/teflon (Pb3O4/Mg/PTFE) mixed powder. And the effect of ZrSiO4 serving as an additive on the performance of Pb3O4/Mg/PTFE infrared decoy is analyzed through experiments. First, initial experiments are conducted on the thermal decomposition characteristics of the basic formula (ZrSiO4 addition ratio is 0%) and its variant counterpart with 12% ZrSiO4. Subsequently, the combustion behaviors of the compacted formulation samples are examined using an infrared thermal imager operating within the 7.5–14 μm range, subsequently, the combution time, combution temperature, burning rate, radiation area, radiance, and radiation intensity of individual samples are computed. These results show that incorporation of ZrSiO4 reduces the intensity of the primary exothermic peak during the reactions with a mixed infrared decoy agent, yielding suboptimal thermal efficiencies. Furthermore, the combustion durations of the samples progressively increase with ZrSiO4 addition increasing, accompanied by consistent reductions in their combustion temperatures. Specifically, the sample reaction time peaks at 3.73 s at a ZrSiO4 addition ratio of 18%, while the combution temperature drops to a minimum value of 765.46 ℃. Moreover, the far-infrared radiance and radiation intensity demonstrate an initial-increase-then-decrease trend with ZrSiO4 addition increasing, thereby achieving the maximum values of 2461 W/(m2·sr) and 142 W/sr, respectively at a ZrSiO4 addition ratio of 6%. Furthermore, the far-infrared radiance and radiation intensity of the base formulation are enhanced when ZrSiO4 addition ratios are kept within 18% and 9% respectively. Based on the comprehensive analysis of the experimental data and considering the requirements for the infrared decoy in practical applications, a formulation with a ZrSiO4 addition ratio of 6% is adopted as an improved formulation for the Pb3O4/Mg/PTFE infrared decoy.
-
Keywords:
- infrared decoy /
- thermal decomposition /
- thermal diffusivity /
- radiation intensity
[1] 邵晓光 2019 制导与引信 40 020012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao X G 2019 Guidance Fuze 40 020012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 卢晓, 梁晓庚, 贾晓洪 2021 红外与激光工程 50 29
Lu X, Liang X G, Jia X H 2021 Infrared Laser Eng. 50 29
[3] 周遵宁 2017 光电对抗材料基础(北京: 北京理工大学出版社
Zhou Z N 2017 Fundermentals of Electro-optical Countermeasure Materials (Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press
[4] 李泽军, 李志勇, 占明明, 张波, 姚鲲, 李秋怡, 张定宏 2024 固体火箭技术 47 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z J, Li Z Y, Zhan M M, Zhang B, Yao K, Li Q Y, Zhang D H 2024 J. Solid Rocket Technol. 47 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 赵亮, 巨秀芝 2019 航天电子对抗 35 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao L, Ju X Z 2019 Aerospace Electron. Warfare 35 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 叶淑琴, 朱晨光, 林红雪, 欧阳的华, 潘功配 2017 红外与激光工程 46 90
Ye S Q, Zhu C G, Lin H X, Ouyang D H, Pan G P 2017 Infrared Laser Eng. 46 90
[7] Elbasuney S, Elmotaz A A, Sadek M A 2020 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El. 31 6130
[8] 金青君, 吴昱, 史红星, 任秀娟, 赵建锋 2020 火工品 3 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin Q J, Wu Y, Shi H X, Ren X J, Zhao J F 2020 Initiators Pyrotechn. 3 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 胡亚鹏, 王虎, 聂学辉, 孙宏涛, 姜建增, 郭鹏宏, 强文学 2023 火工品 5 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y P, Wang H, Nie X H, Sun H T, Jiang J Z, Guo P H, Qiang W X 2023 Initiators Pyrotechn. 5 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 杨谦 2021 硕士学位论文(南京: 南京理工大学)
Yang Q 2021 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology
[11] 张建奇, 方小平 2011 红外物理(西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社)
Zhang J Q, Fang X P 2011 Infrared Physics (Xian: Xidian University Press
[12] 于志良 1994 光电技术应用 2 12
Yu Z L 1994 Electro-Opt. Technol. Appl. 2 12
[13] 卢为开 1983 远红外辐射加热技术(上海: 上海科学技术出版社)
Lu K W 1983 Infrared Radiation Heating Technology (Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers
[14] 王冰, 陈宗胜, 刘洋, 汪家春, 时家明 2018 火工品 3 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B, Chen Z S, Liu Y, Wang J C, Shi J M 2018 Initiators Pyrotechn. 3 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Griffiths T T, Robertson J, Hall P G 1985 16th International Annual ICT Conference, Germany, 1985 p19
[16] 希洛夫著 (马永利译) 1959 烟火药火焰的发光 (北京: 国防工业出版社)
Shilov (translated by Ma Y L) 1959 Flame Radiation of Fire Works Composition (Beijing: National Defence Industry Press
[17] 王伯羲, 冯增国 1997 火药燃烧理论(北京: 北京理工大学出版社)
Wang B X, Feng Z G 1997 Theory of Gunpowder Combustion (Beijing: BeiJing Institute Of Technology Press
[18] 屠传经 1992 热传导(北京: 高等教育出版社)
Tu C J 1992 Infrared Physics (Beijing: Higher Education Press
[19] 刘光启, 马连湘, 项曙光 2013 化学化工物性数据手册·无机卷 (北京:化学工业出版社)
Liu G Q, Ma L X, Xiang S G 2013 Chemical and Chemical Data Sheet (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press
[20] James G Speight 2005 Lange′s Handbook of Chemistry (16th Ed.) (New York: Mc Graw-Hill, Inc
-
表 1 7种不同ZrSiO4添加量混合红外诱饵剂配方成分比例
Table 1. Compositional ratios of 7 types of composite infrared decoys with varied ZrSiO4.
Formula m (Pb3O4)/% m (Mg)/% m (PTFE)/% m (ZrSiO4)/% 1 35 50 15 0 2 33.95 48.5 14.55 3 3 32.9 47 14.1 6 4 31.85 45.5 13.65 9 5 30.8 44 13.2 12 6 29.75 42.5 12.75 15 7 28.7 41 12.3 18 表 2 14个不同ZrSiO4添加量混合红外诱饵剂药柱样品质量和高度
Table 2. Weight and height of 14 samples of composite infrared decoys with varied ZrSiO4.
Formula I II Average Weight/g Height/mm Weight/g Height/mm Weight/g Height/mm 1 15.99 12.97 15.98 13.01 15.99 12.99 2 15.99 12.96 15.98 12.90 15.99 12.93 3 15.99 12.95 15.99 12.85 15.99 12.90 4 15.96 12.84 15.96 12.83 15.96 12.84 5 15.97 12.61 15.97 12.75 15.97 12.68 6 15.99 12.53 15.95 12.74 15.97 12.64 7 15.98 12.45 15.98 12.41 15.98 12.43 表 3 7种不同ZrSiO4添加量混合红外诱饵剂配方燃烧时间、温度和燃速
Table 3. Combution time, temperature, and burning rate of 7 types of composite infrared decoys with varied ZrSiO4.
Formula I II Average T/℃ Combustion
time/sBurning
rate/(g·s–1)T/℃ Combustion
time/sBurning
rate/(g·s–1)T/℃ Combustion
time/sBurning
rate/(g·s–1)1 857.00 3.01 5.32 823.90 3.06 5.23 840.50 3.03 5.27 2 822.58 3.09 5.18 852.19 3.07 5.21 837.39 3.08 5.19 3 830.89 3.16 5.06 834.05 3.11 5.14 832.47 3.14 5.10 4 817.44 3.37 4.75 824.39 3.25 4.92 820.91 3.31 4.84 5 809.42 3.44 4.65 798.71 3.53 4.53 804.06 3.49 4.59 6 782.70 3.71 4.31 788.54 3.62 4.42 785.62 3.67 4.37 7 761.32 3.77 4.24 769.59 3.69 4.34 765.46 3.73 4.29 表 4 Pb3O4, Mg, PTFE和ZrSiO4物理性质
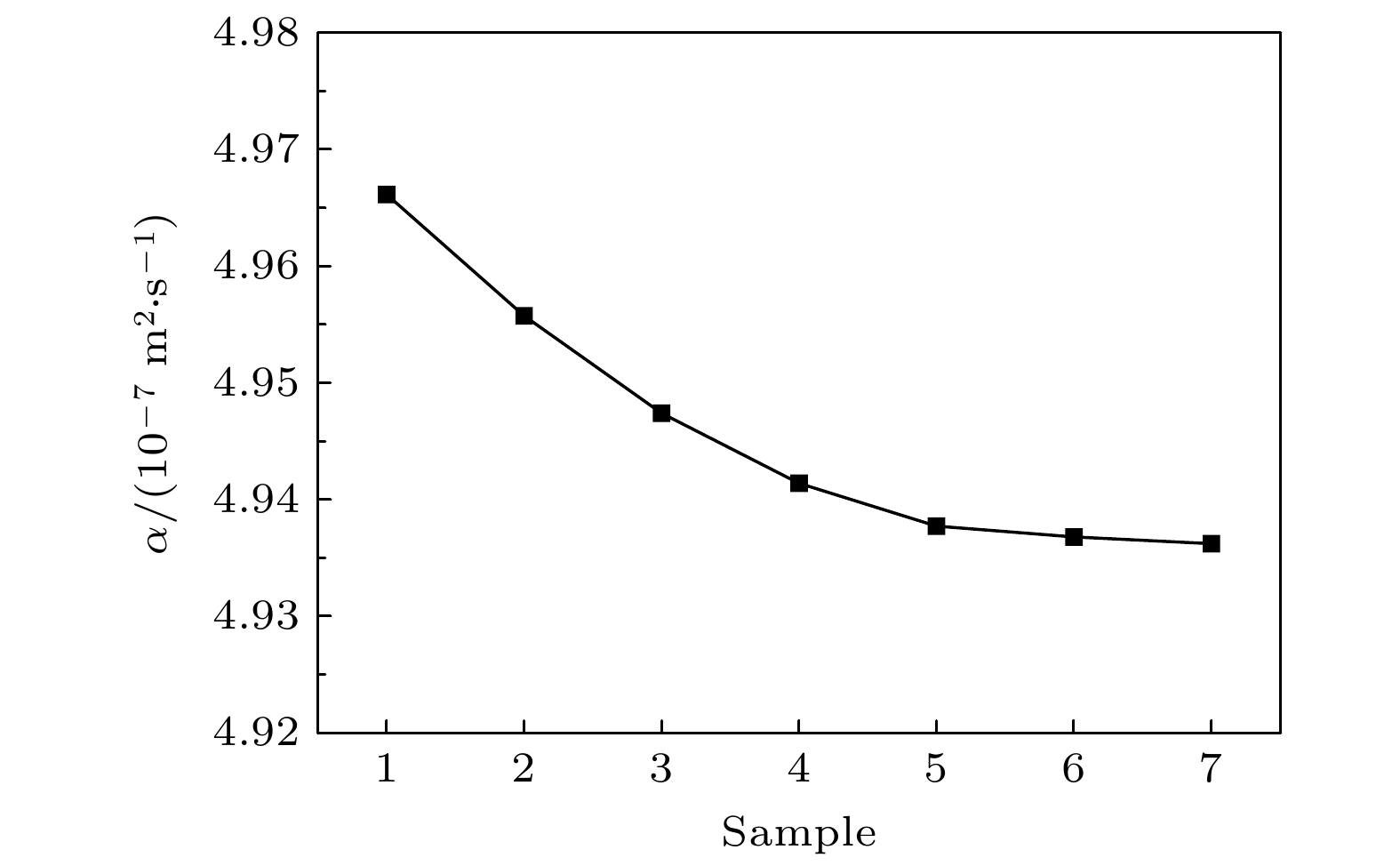
Table 4. Physical properties of Pb3O4, Mg, PTFE, and ZrSiO4.
Material λ/(J·m–1·s–1·K–1) c/(J·kg–1·K–1) ρ/(kg–1·m–3) Mg 165.1 1000 1745 PTFE 0.24 1050 2150 Pb3O4 0.288 226 9100 ZrSiO4 5.1 800 4560 表 5 7种不同ZrSiO4添加量混合红外诱饵剂配方辐射特性
Table 5. Radiation characteristics of 7 types of composite infrared decoys with varied ZrSiO4
Formula I II Average Radiance/
(W·m–2·sr–1)Radiation
area/mm2Radiation intensity/
(W·sr–1)Radiance/
(W·m–2·sr–1)Radiation
area/mm2Radiation intensity/
(W·sr–1)Radiance/
(W·m–2·sr–1)Radiation
area/mm2Radiation intensity/
(W·sr–1)1 2134 54957 117 2071 46744 97 2103 50851 107 2 2067 50508 104 2329 51714 120 2198 51111 112 3 2452 59449 146 2470 55706 138 2461 57577 142 4 2240 43043 96 2410 59574 144 2325 51308 120 5 2317 41358 96 2277 40256 92 2297 40807 94 6 2256 39882 90 2290 39050 89 2273 39466 90 7 2228 38302 85 2248 36888 82 2238 37595 84 -
[1] 邵晓光 2019 制导与引信 40 020012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao X G 2019 Guidance Fuze 40 020012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 卢晓, 梁晓庚, 贾晓洪 2021 红外与激光工程 50 29
Lu X, Liang X G, Jia X H 2021 Infrared Laser Eng. 50 29
[3] 周遵宁 2017 光电对抗材料基础(北京: 北京理工大学出版社
Zhou Z N 2017 Fundermentals of Electro-optical Countermeasure Materials (Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press
[4] 李泽军, 李志勇, 占明明, 张波, 姚鲲, 李秋怡, 张定宏 2024 固体火箭技术 47 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z J, Li Z Y, Zhan M M, Zhang B, Yao K, Li Q Y, Zhang D H 2024 J. Solid Rocket Technol. 47 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 赵亮, 巨秀芝 2019 航天电子对抗 35 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao L, Ju X Z 2019 Aerospace Electron. Warfare 35 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 叶淑琴, 朱晨光, 林红雪, 欧阳的华, 潘功配 2017 红外与激光工程 46 90
Ye S Q, Zhu C G, Lin H X, Ouyang D H, Pan G P 2017 Infrared Laser Eng. 46 90
[7] Elbasuney S, Elmotaz A A, Sadek M A 2020 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El. 31 6130
[8] 金青君, 吴昱, 史红星, 任秀娟, 赵建锋 2020 火工品 3 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin Q J, Wu Y, Shi H X, Ren X J, Zhao J F 2020 Initiators Pyrotechn. 3 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 胡亚鹏, 王虎, 聂学辉, 孙宏涛, 姜建增, 郭鹏宏, 强文学 2023 火工品 5 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y P, Wang H, Nie X H, Sun H T, Jiang J Z, Guo P H, Qiang W X 2023 Initiators Pyrotechn. 5 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 杨谦 2021 硕士学位论文(南京: 南京理工大学)
Yang Q 2021 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology
[11] 张建奇, 方小平 2011 红外物理(西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社)
Zhang J Q, Fang X P 2011 Infrared Physics (Xian: Xidian University Press
[12] 于志良 1994 光电技术应用 2 12
Yu Z L 1994 Electro-Opt. Technol. Appl. 2 12
[13] 卢为开 1983 远红外辐射加热技术(上海: 上海科学技术出版社)
Lu K W 1983 Infrared Radiation Heating Technology (Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers
[14] 王冰, 陈宗胜, 刘洋, 汪家春, 时家明 2018 火工品 3 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B, Chen Z S, Liu Y, Wang J C, Shi J M 2018 Initiators Pyrotechn. 3 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Griffiths T T, Robertson J, Hall P G 1985 16th International Annual ICT Conference, Germany, 1985 p19
[16] 希洛夫著 (马永利译) 1959 烟火药火焰的发光 (北京: 国防工业出版社)
Shilov (translated by Ma Y L) 1959 Flame Radiation of Fire Works Composition (Beijing: National Defence Industry Press
[17] 王伯羲, 冯增国 1997 火药燃烧理论(北京: 北京理工大学出版社)
Wang B X, Feng Z G 1997 Theory of Gunpowder Combustion (Beijing: BeiJing Institute Of Technology Press
[18] 屠传经 1992 热传导(北京: 高等教育出版社)
Tu C J 1992 Infrared Physics (Beijing: Higher Education Press
[19] 刘光启, 马连湘, 项曙光 2013 化学化工物性数据手册·无机卷 (北京:化学工业出版社)
Liu G Q, Ma L X, Xiang S G 2013 Chemical and Chemical Data Sheet (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press
[20] James G Speight 2005 Lange′s Handbook of Chemistry (16th Ed.) (New York: Mc Graw-Hill, Inc
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 867
- PDF Downloads: 24
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: