-
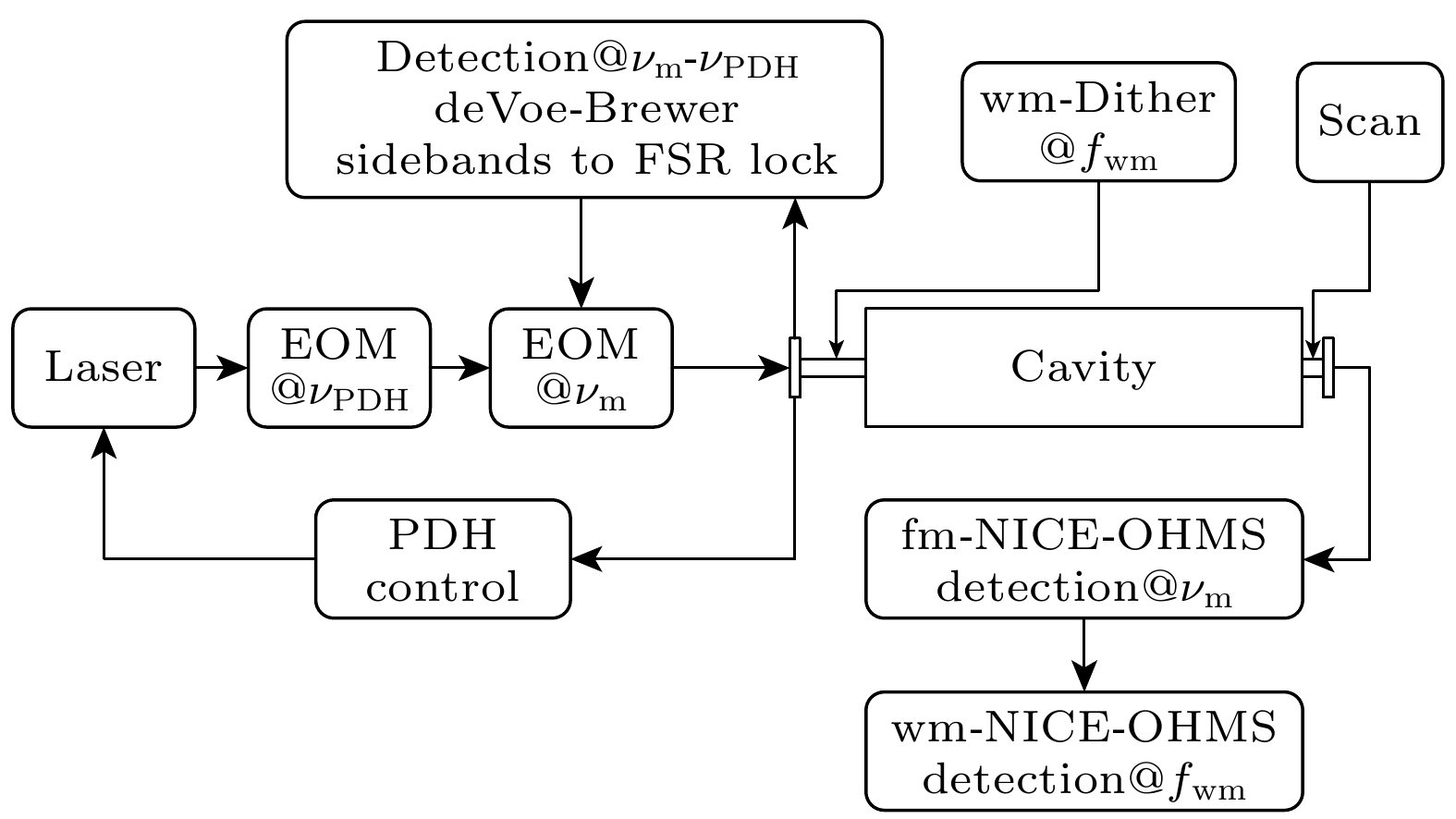
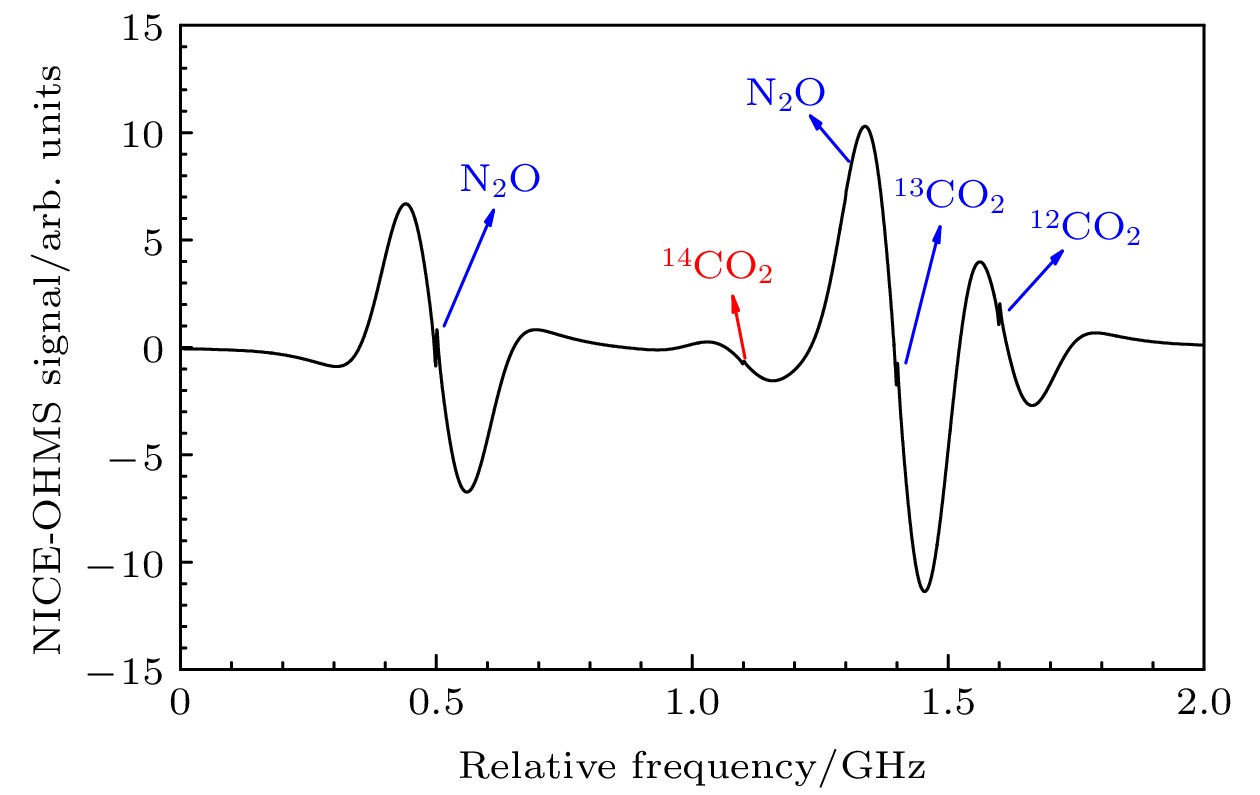
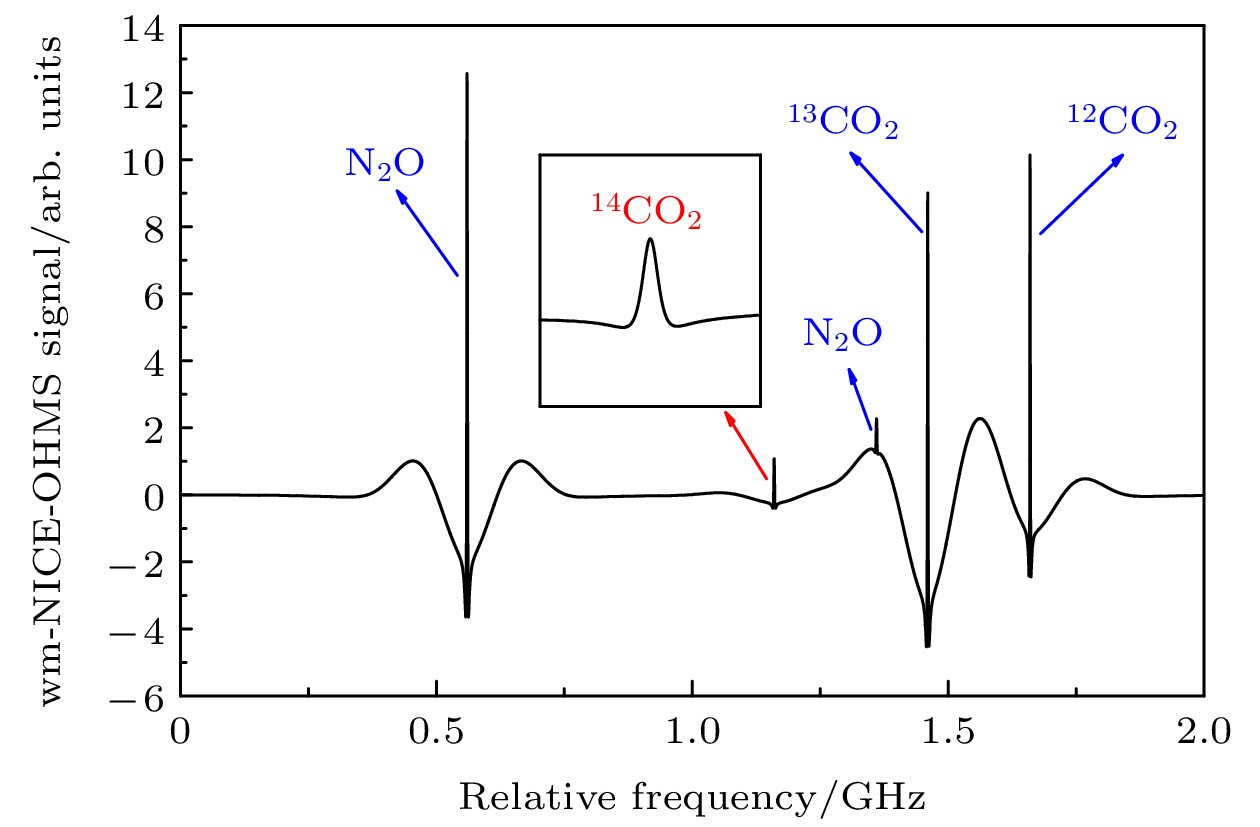
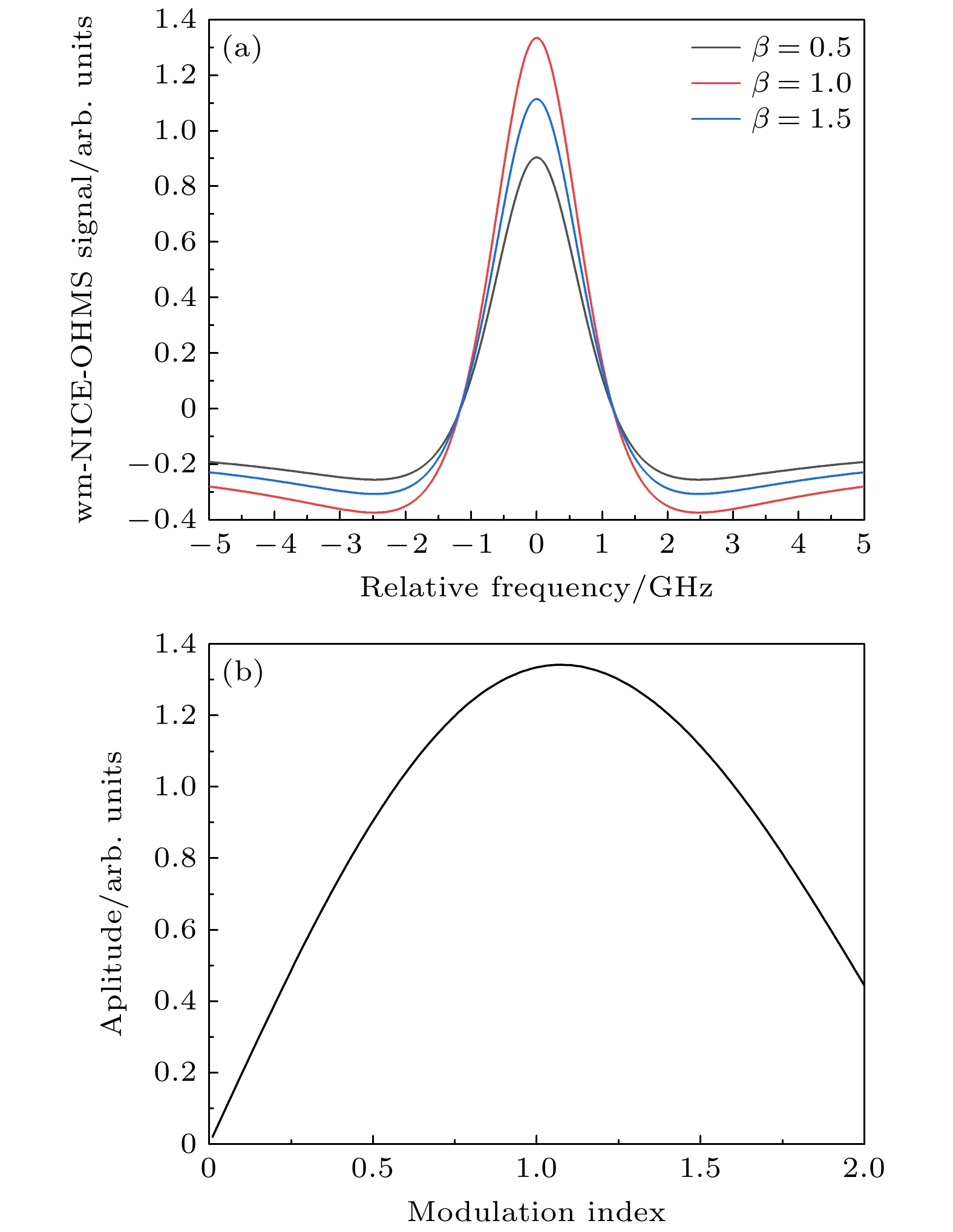
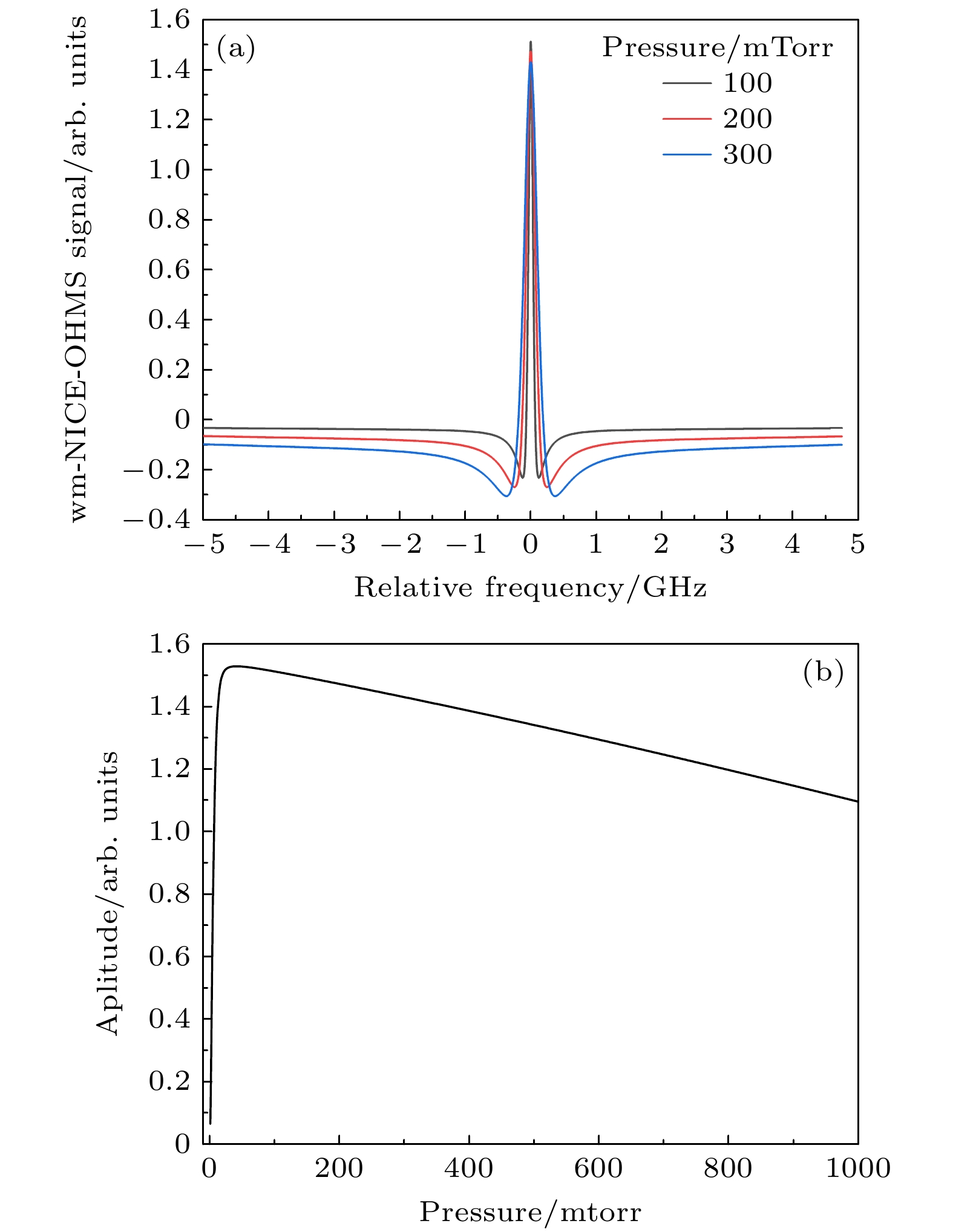
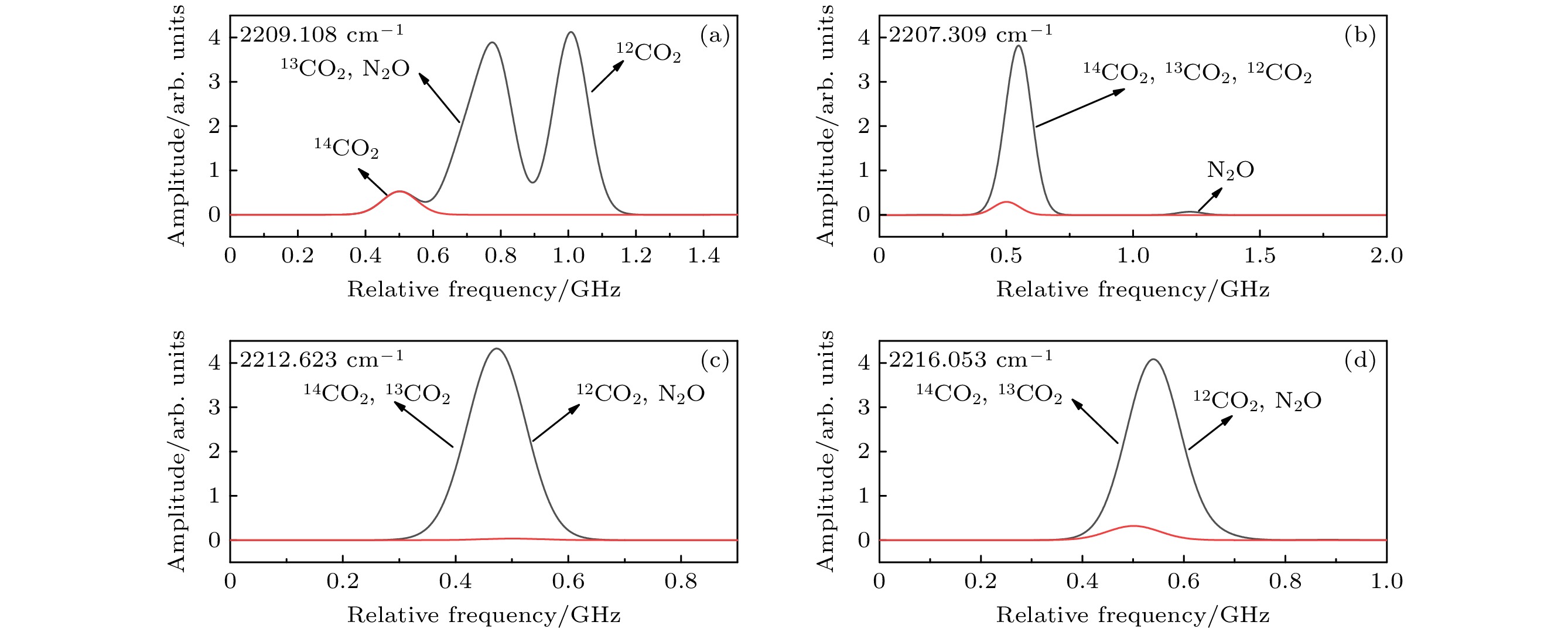
The massive emission of greenhouse gases, particularly CO2, has led to severe damage to the Earth’s ecological environment and poses a threat to human health. Many countries have therefore proposed policies to curb the greenhouse effect. Carbon monitoring is a critical prerequisite for realizing these goals, and tracking carbon emission sources can support the precise implementation and advancement of related policies more effectively. The contribution of fossil fuel combustion to greenhouse gas emissions can be inferred by detecting the abundance of 14C in carbon dioxide in a specific region. Conventional 14CO2 detection methods have significant drawbacks, including complicated operation, high cost and large equipment size. Laser absorption spectroscopy (LAS) offers advantages such as real-time, online in-situ measurement and simple operation, making it suitable for the online detection of isotopes. Among the various LAS techniques, noise immunity cavity enhanced optical heterodyne molecular spectroscopy (NICE-OHMS) is the most sensitive. This method integrates frequency modulation spectroscopy (FMS) into cavity enhanced spectroscopy (CES) to suppress the low-frequency noise while increasing the absorption paths, providing a minimum detectable absorption coefficient as low as 10–13. Additionally, the accumulation of high intracavity laser power in NICE-OHMS can stimulate saturation absorption, which has a narrow spectral width that can mitigate spectral overlap. In this work, we model the spectral signals of 14CO2 at different locations and select the transition line of 14CO2 at 2209.108 cm–1 as an optimal measurement target based on the principles of high-intensity and well-resolution. The theoretical analysis of the NICE-OHMS technique is then carried out, and theoretical simulations of a mixed sample of 14CO2 and its nearby interfering gases (13CO2, 12CO2, and N2O), are performed under the simulated experimental conditions. The results of the simulation show that the Doppler broadened spectral signal of 14CO2 is covered by the other gases’ signals with a very low amplitude, which is adverse to the detection of 14CO2. To eliminate the linear slope of the Doppler broadened signal and to further improve the signal-to-noise ratio, we perform 14CO2 spectral measurements by using wavelength-modulated NICE-OHMS (wm-NICE-OHMS). The results of the simulation show that the spectral lines are effectively separated, and the detection accuracy of the 14CO2 ratio is greatly improved. Finally, the effects of pressure and modulation index on the 14CO2 wm-NICE-OHMS signal are analyzed. The results show that when the pressure is 42 mTorr and the modulation index is 1.07, the signal amplitude of wm-NICE-OHMS reaches its maximum. This work lays a theoretical foundation for the high precision detection of 14CO2 in real-time environmental monitoring. The potential for large-scale application of wm-NICE-OHMS in carbon emission tracking is highlighted, providing a more cost-effective alternative to traditional detection methods. Furthermore, the technology is able to suppress spectral interference from other gases and achieve high resolution in 14CO2 measurements, which will greatly help monitor and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Keywords:
- noise-immune cavity-enhanced optical heterodyne molecular spectroscopy /
- theoretical simulation /
- radiocarbon isotope detection
[1] Zhao X, Ma X, Chen B, Shang Y, Song M 2022 Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 176 105959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kong W, Wan F, Lei Y, Wang C, Sun H, Wang R, Chen W G 2024 Anal. Chem. 96 15313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ge H, Kong W P, Wang R, Zhao G, Ma W G, Chen W G, Wan F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 2186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hou X L 2018 J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 318 1597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hua Q 2009 Quat. Geochronol. 4 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Levin I, Naegler T, Kromer B, Diehl M, Francey R, Gomez-Pelaez A J, Steele P, Wagenbach D, Weller R, Worthy D 2010 Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 62 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Povinec P 2018 J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 318 1573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Maity A, Maithani S, Pradhan M 2021 Anal. Chem. 93 388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lehmann B, Wahlen M, Zumbrunn R, Oeschger H, Schnell W 1977 Appl. Phys. 13 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Labrie D, Reid J 1981 Appl. Phys. A 24 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] McCartt A, Jiang J 2022 ACS Sensors 7 3258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Z, Peng T, Nie X Y, Agarwal G S, Scully M O 2022 Light Sci. Appl. 11 274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen W P, Qiao S D, Lang Z, Jiang J C, He Y, Shi Y W, Ma Y F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 3989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hashimoto K, Nakamura T, Kageyama T, Badarla V R, Shimada H, Horisaki R, Ideguchi T 2023 Light Sci. Appl. 12 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ma Y F, Liang T T, Qiao S D, Liu X N, Lang Z T 2023 Ultrafast Sci. 3 0024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Qiao S D, Ma P Z, Tsepelin V, Han G W, Liang J X, Ren W, Zheng H D, Ma Y F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang C, Qiao S D, He Y, Zhou S, Qi L, Ma Y F 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 241003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lang Z T, Qian S D, Ma Y F 2023 Light Adv. Manuf. 4 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Galli I, Pastor P C, Di Lonardo G, Fusina L, Giusfredi G, Mazzotti D, Tamassia F, De Natale P 2011 Mol. Phys. 109 2267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Terabayashi R, Saito K, Sonnenschein V, Okuyama Y, Iwamoto K, Mano K, Kawashima Y, Furumiya T, Tojo K, Ninomiya S, Yoshida K, Tomita H 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 132 083102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jiao K, Gao J, Yang J Q, Zhao G, Shi Z, Wang X P, Zhu D, He H Y, Qing J, Yan X J, Ma W G, Jia S T 2024 Microwaves Opt. Technol. Lett. 66 33946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Galli I, Bartalini S, Ballerini R, Barucci M, Cancio P, De Pas M, Giusfredi G, Mazzotti D, Akikusa N, De Natale P 2016 Optica 3 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 齐汝宾, 赫树开, 李新田, 汪献忠 2015 光谱学与光谱分析 35 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi R B, He S K, Li X T, Wang X Z 2015 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 35 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jiang J, McCartt A D 2022 International Symposium on Molecular Spectroscopy Champaign-Urbana, Illinois, USA, June 20-24, 2022 p1
[25] Zhou X B, Zhao G, Li Y, Cheng Z W, Jiao K, Zhang B F, Zhang Z H, Li Y K, Yan X J, Ma W G, Jia S T 2024 Opt. Lett. 49 202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zak E J, Tennyson J, Polyansky O L, Lodi L, Zobov N F, Tashkun S A, Perevalov V I 2017 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 189 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gagliardi G, Loock H-P 2014 Cavity-Enhanced Spectro- scopyand Sensing (Vol. 179) (Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg) p231
[28] Foltynowicz A, Ma W, Schmidt F M, Axner O 2009 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 26 1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ma W G, Foltynowicz A, Axner O 2008 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 25 1144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Foltynowicz A 2009 Ph. D. Dissertation (Sweden: Umeå University
[31] Šimečková M, Jacquemart D, Rothman L, Gamache R, Goldman A 2006 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 98 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 14CO2, N2O, 12CO2和13CO2光谱的其他参数
Table 1. Other parameters of 14CO2, N2O, 12CO2 and 13CO2 spectra.
波数/cm–1 线强$ /({\rm cm}^{-1}{\cdot}{\rm molecule}^{-1}{\cdot}{\rm cm}^{-2}) $ 跃迁底态能量/cm–1 总配分函数 14CO2 2209.107679 2.83×10–18 163.8828 2033.395 12CO2 2209.124896 1.802×10–29 5785.2772 286.09 13CO2 2209.115876 4.23×10–27 3394.9427 576.64 13CO2 2209.11747 1.54×10–27 3648.8668 576.64 N2O 2209.08543 3.41×10–21 1282.3324 4984.9 N2O 2209.11444 6.61×10–22 654.1553 4984.9 -
[1] Zhao X, Ma X, Chen B, Shang Y, Song M 2022 Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 176 105959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kong W, Wan F, Lei Y, Wang C, Sun H, Wang R, Chen W G 2024 Anal. Chem. 96 15313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ge H, Kong W P, Wang R, Zhao G, Ma W G, Chen W G, Wan F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 2186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hou X L 2018 J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 318 1597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hua Q 2009 Quat. Geochronol. 4 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Levin I, Naegler T, Kromer B, Diehl M, Francey R, Gomez-Pelaez A J, Steele P, Wagenbach D, Weller R, Worthy D 2010 Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 62 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Povinec P 2018 J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 318 1573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Maity A, Maithani S, Pradhan M 2021 Anal. Chem. 93 388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lehmann B, Wahlen M, Zumbrunn R, Oeschger H, Schnell W 1977 Appl. Phys. 13 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Labrie D, Reid J 1981 Appl. Phys. A 24 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] McCartt A, Jiang J 2022 ACS Sensors 7 3258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Z, Peng T, Nie X Y, Agarwal G S, Scully M O 2022 Light Sci. Appl. 11 274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen W P, Qiao S D, Lang Z, Jiang J C, He Y, Shi Y W, Ma Y F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 3989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hashimoto K, Nakamura T, Kageyama T, Badarla V R, Shimada H, Horisaki R, Ideguchi T 2023 Light Sci. Appl. 12 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ma Y F, Liang T T, Qiao S D, Liu X N, Lang Z T 2023 Ultrafast Sci. 3 0024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Qiao S D, Ma P Z, Tsepelin V, Han G W, Liang J X, Ren W, Zheng H D, Ma Y F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang C, Qiao S D, He Y, Zhou S, Qi L, Ma Y F 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 241003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lang Z T, Qian S D, Ma Y F 2023 Light Adv. Manuf. 4 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Galli I, Pastor P C, Di Lonardo G, Fusina L, Giusfredi G, Mazzotti D, Tamassia F, De Natale P 2011 Mol. Phys. 109 2267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Terabayashi R, Saito K, Sonnenschein V, Okuyama Y, Iwamoto K, Mano K, Kawashima Y, Furumiya T, Tojo K, Ninomiya S, Yoshida K, Tomita H 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 132 083102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jiao K, Gao J, Yang J Q, Zhao G, Shi Z, Wang X P, Zhu D, He H Y, Qing J, Yan X J, Ma W G, Jia S T 2024 Microwaves Opt. Technol. Lett. 66 33946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Galli I, Bartalini S, Ballerini R, Barucci M, Cancio P, De Pas M, Giusfredi G, Mazzotti D, Akikusa N, De Natale P 2016 Optica 3 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 齐汝宾, 赫树开, 李新田, 汪献忠 2015 光谱学与光谱分析 35 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi R B, He S K, Li X T, Wang X Z 2015 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 35 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jiang J, McCartt A D 2022 International Symposium on Molecular Spectroscopy Champaign-Urbana, Illinois, USA, June 20-24, 2022 p1
[25] Zhou X B, Zhao G, Li Y, Cheng Z W, Jiao K, Zhang B F, Zhang Z H, Li Y K, Yan X J, Ma W G, Jia S T 2024 Opt. Lett. 49 202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zak E J, Tennyson J, Polyansky O L, Lodi L, Zobov N F, Tashkun S A, Perevalov V I 2017 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 189 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gagliardi G, Loock H-P 2014 Cavity-Enhanced Spectro- scopyand Sensing (Vol. 179) (Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg) p231
[28] Foltynowicz A, Ma W, Schmidt F M, Axner O 2009 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 26 1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ma W G, Foltynowicz A, Axner O 2008 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 25 1144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Foltynowicz A 2009 Ph. D. Dissertation (Sweden: Umeå University
[31] Šimečková M, Jacquemart D, Rothman L, Gamache R, Goldman A 2006 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 98 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2807
- PDF Downloads: 75
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: