-
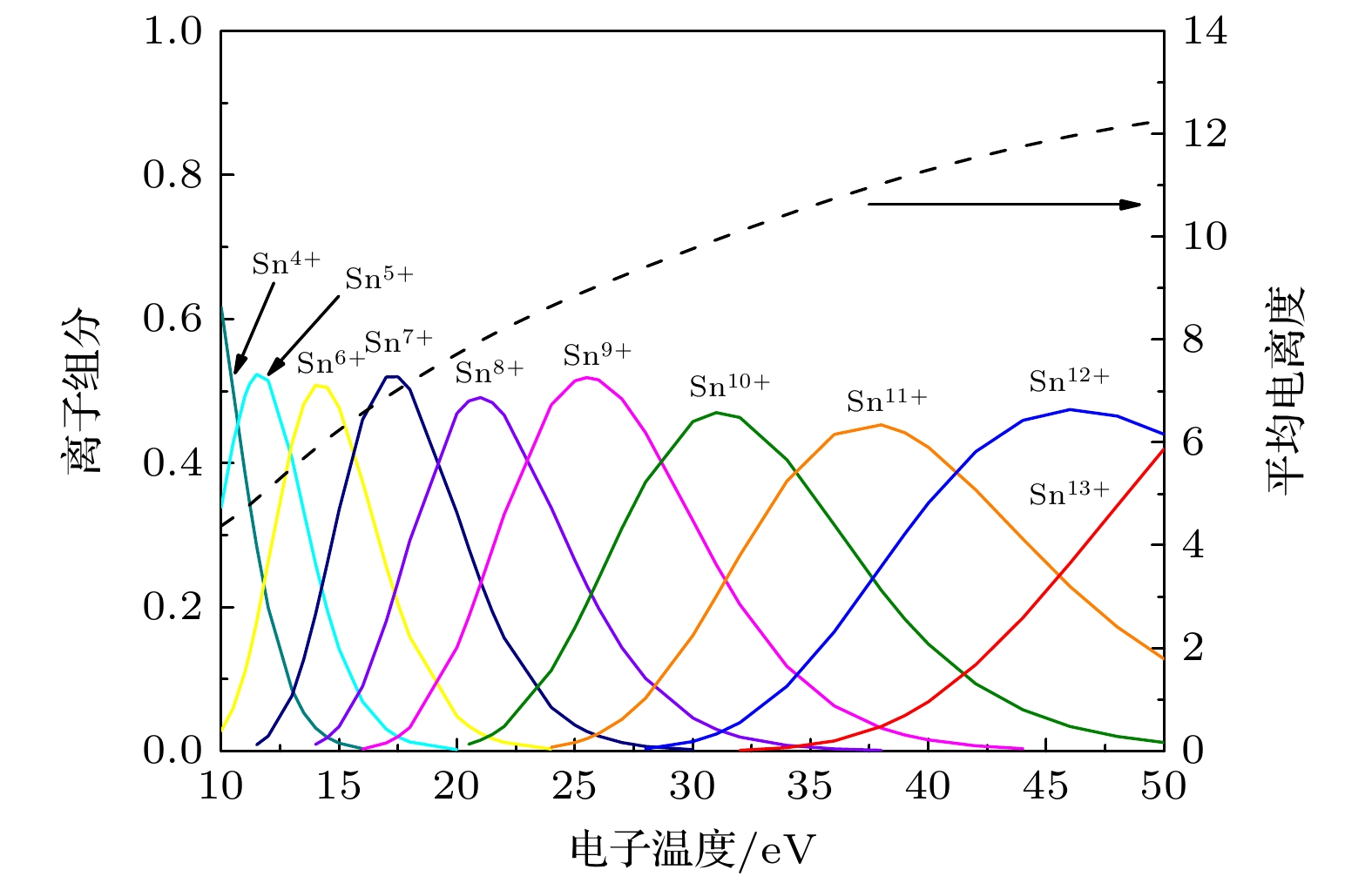
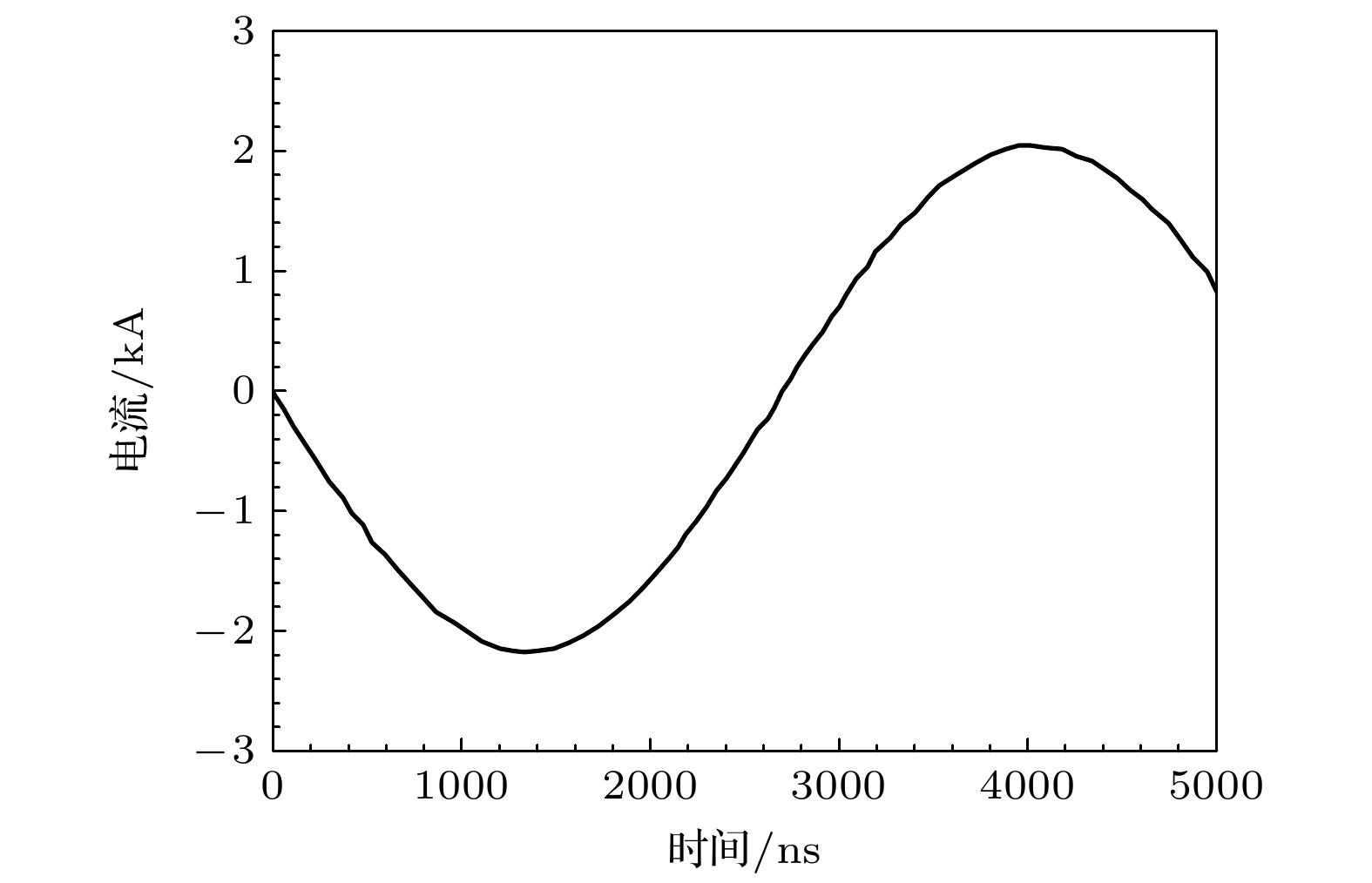
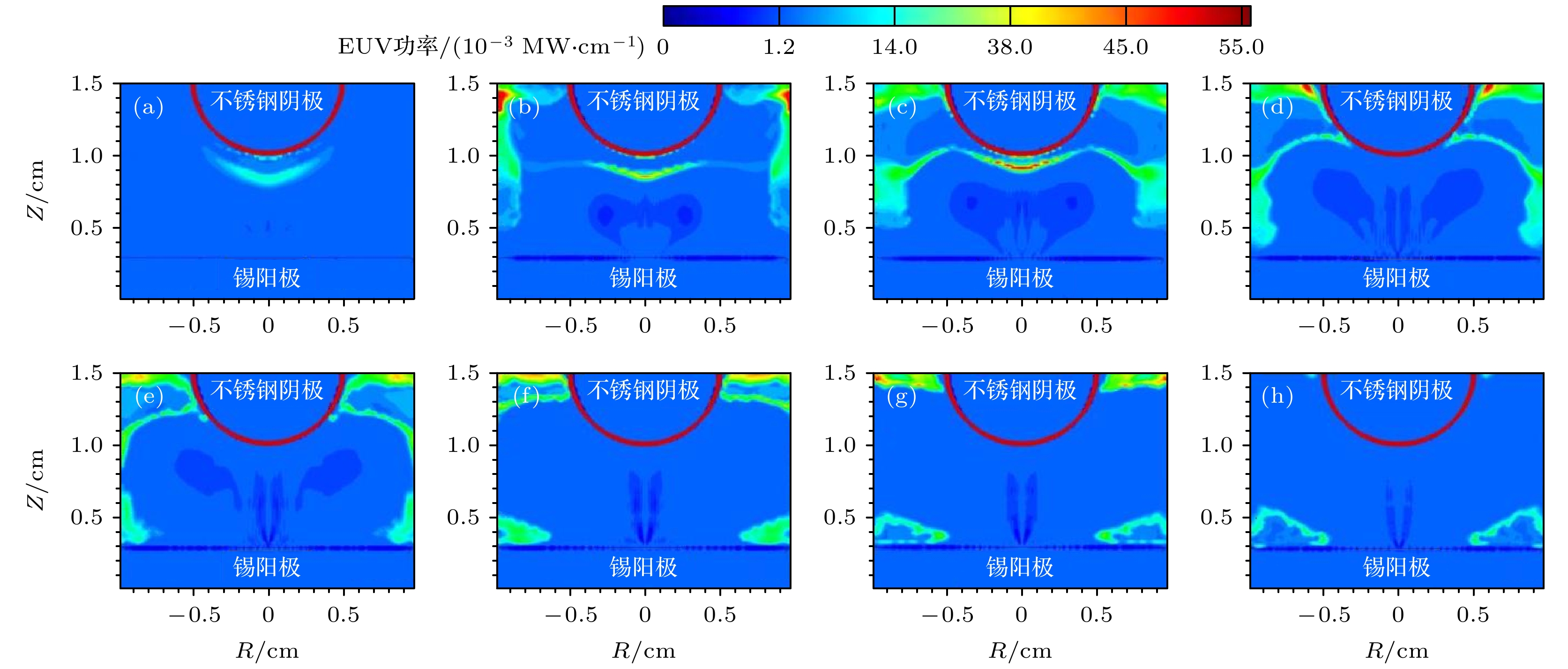
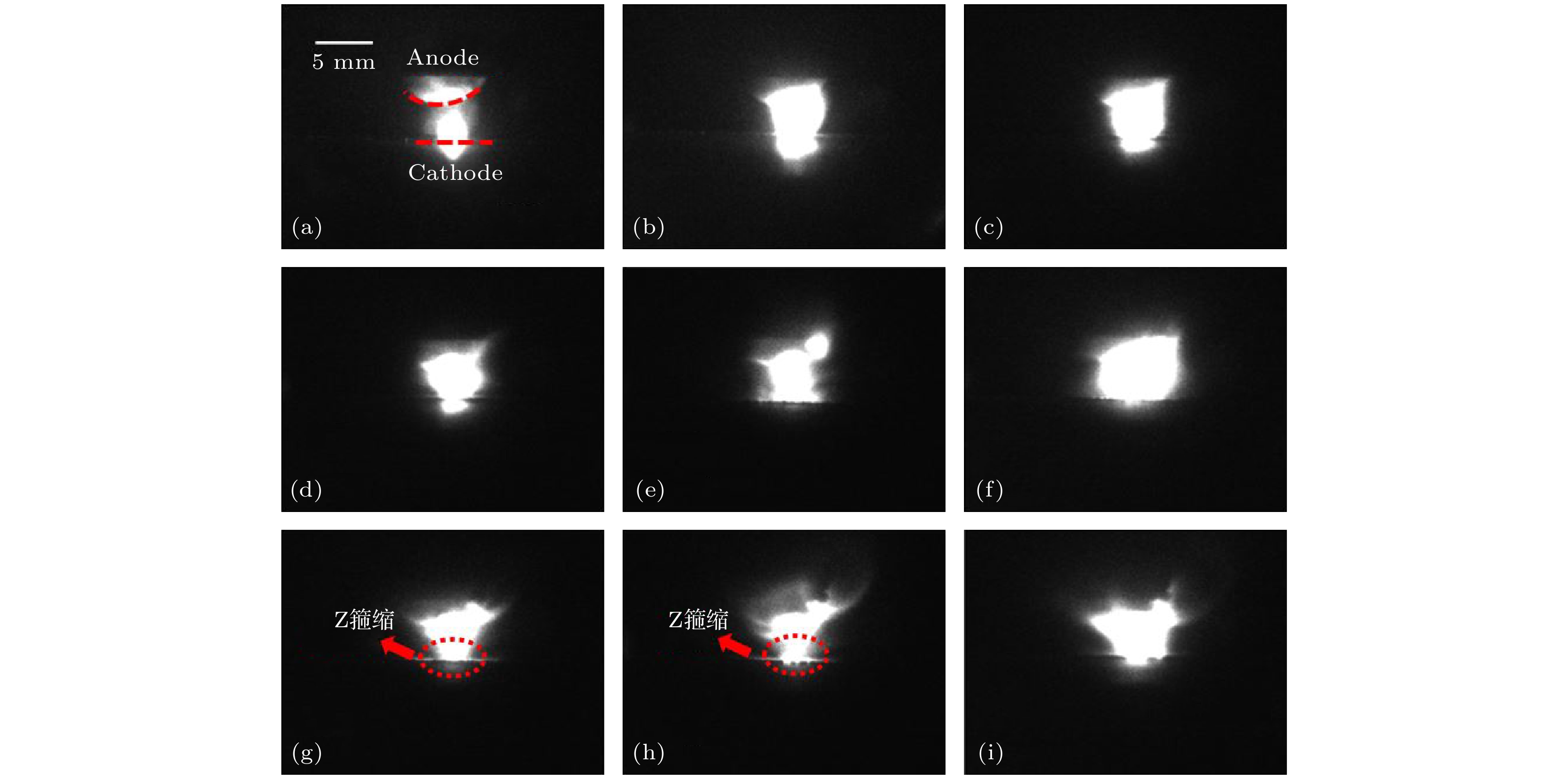
Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source is an important part of EUV lithography system in semiconductor manufacturing. The EUV light source requires that the 4p64dn-4p54dn+1 + 4dn–14f transitions of Sn8+~13+ ions emit thousands of lines which form unresolved transition arrays near 13.5 nm. Laser-induced discharge plasma is one of the important technical means to excite target into an appropriate plasma condition. Laser-induced discharge plasma has a simple structure and a low cost. It also has important applications in mask inspection, microscopic imaging, and spectral metrology. In the design and production process, there are many factors that can influence the conversion efficiency, such as current, electrode shape, and laser power density. The simulation method is a convenient way to provide guidance for optimizing the parameters. In this paper, a completed radiation magneto-hydrodynamic model is used to explore the dynamic characteristics of laser-induced discharge plasma and its EUV radiation characteristics. To improve the accuracy, a more detailed global equation of state model, an atomic structure calculation model including relativistic effect and a collision radiation model are proposed simultaneously. The simulation reconstructs the discharge process effectively, which is divided into five stages in the first half cycle of current, including expansion of laser plasma, column formation of discharge plasma, diffusion of discharge plasma, contraction of discharge plasma, and re-diffusion of discharge plasma. It is revealed that the pinch effect during the current rising time exerts a significant influence on the generation of EUV radiation. The conversion efficiency of EUV radiation is still low under our existing conditions, and hopefully a higher rising rate of current can improve the conversion efficiency in the future work.
-
Keywords:
- radiation magneto-hydrodynamic /
- laser induced discharge plasma /
- collisional-radiative model /
- extreme ultraviolet
[1] Wagner C, Harned N 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tallents G, Wagenaars E, Pert G 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Schriever G, Semprez O R, Jonkers J, Yoshioka M, Apetz R 2012 J. Microlithogr. Microfabr. Microsyst. 11 021104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Pankert J, Bergmann K, Klein J, Neff W, Rosier O, Seiwert S, Smith C, Probst S, Vaudrevange D, Siemons G, et al. 2004 Emerging Lithographic Technologies VIII Santa Clara, California, May 20, 2004 p152
[5] Sayan S, Chakravorty K, Teramoto Y, Shirai T, Morimoto S, Watanabe H, Sato Y, Aoki K, Liang T, Tezuka Y, et al. 2021 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography XII San Jose, California, United States, March 23, 2021 p116090L
[6] Teramoto Y, Santos B, et al. 2014 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography V San Jose, California, United States, April 17, 2014 p904813
[7] Sayan S, Chakravorty K, Teramoto Y, Santos B, Nagano A, Ashizawa N, Shirai T, Morimoto S, Watanabe H, Aoki K, Sato Y 2023 Optical and EUV Nanolithography XXXVI San Jose, California, United States, May 26, 2023 pPC124940E
[8] Kruecken T 2007 AIP Conf. Proc. 901 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hassanein A, Sizyuk V A, Tolkach V I, Morozov V A, Rice B J 2004 J. Micro/Nanolithgr. MEMS MOEMS 3 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hassanein A, Sizyuk V, Sizyuk T 2008 Emerging Lithographic Technologies XII, San Jose, California, United States, March 20, 2008 p692113
[11] Zakharov V S, Juschkin L, Zakharov S V, O’Sullivan G, Sokel E, Tobin I 2012 International Workshop on EUV and Soft X-Ray Sources Dublin, Ireland, October 8–11, 2012 pS26
[12] Sasaki A, Nishihara K, Sunahara A, Furukawa H, Nishikawa T, Koike F 2010 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography San Jose, California, United States, March 22, 2010 p76363D
[13] Masnavi M, Nakajima M, Hotta E, Horioka K, Niimi G, Sasaki A 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 033306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tsygvintsev I P, Krukovskiy A Y, Gasilov V A, Novikov V G, Romanov I V, Paperny V L, Rupasov A A 2016 Mathematical Models and Computer Simulations 8 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Beyene G A, Tobin I, Juschkin L, Hayden P, O’Sullivan G, Sokell E, Zakharov V S, Zakharov S V, O’Reilly F 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 225201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吴福源, 禇衍运, 叶繁, 李正宏, 杨建伦, Ramis R, 王真, 祁建敏, 周林, 梁川 2017 66 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu F Y, Chu Y Y, Ye F, Li Z H, Yang J L, Ramis R, Wang Z, Qi J M, Zhou L, Liang C 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 陈忠旺, 宁成 2017 66 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng Z W, Ning C 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zakharov S V, Zakharov V S, Choi P, Krukovskiy A Y, Novikov V G, Solomyannaya A D, Berezin A V, Vorontsov A S, Markov M B, Parot’kin S V 2011 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography II San Jose, California, United States, April 8, 2011 p796932
[19] Zakharov V S 2017 The International Photonics and Optoelectronics Meeting, Wuhan, China, November 3–5, 2017 pASu4A.1
[20] Sasaki A, Sunahara A, Furukawa H, Nishihara K, Nishikawa T, Koike F 2016 J. Phys. Conf. 688 012099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang L J, Qian Z H, Huang X L, Jia S L 2013 IEEE T. Plasma Sci. 41 2015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vovchenko E D, Melekhov A P V 2016 International Conference of Photonics and Information Optics Moscow, Russia, February 3–5, 2016 p012013
[23] More R M, Warren K H, Young D A, Zimmerman G B 1988 Phys. Fluids 31 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sasaki A 2013 High Energ. Dens. Phys. 9 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 汤文辉, 徐彬彬, 冉宪文, 徐志宏 2017 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W H, Xu B B, Ran X W, Xu Z H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 段耀勇, 郭永辉, 邱爱慈 2011 核聚变与等离子体物理 31 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan Y Y, Guo Y H, Qiu A C 2011 Nucl. Fusion Plasma Phys. 31 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 段耀勇, 郭永辉, 邱爱慈, 吴刚 2010 59 5588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan Y Y, Guo Y H, Qiu A C, Wu G 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 5588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Dunning F B, Hulet R G 1997 Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics: Charged Particles (San Diego: Academic Press) p169
[29] 韩小英, 李凌霄, 戴振生, 郑无敌, 谷培俊, 吴泽清 2021 70 115202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han X Y, Li L X, Dai Z S, Zheng W D, Gu P J, Wu Z Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 115202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Vichev I Y, Solomyannaya A D, Grushin A S, Kim D A 2019 High Energ. Dens. Phys. 33 100713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gu M F 2004 AIP Conf. Proc. 730 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Han B, Wang F, Salzmann D, Zhao G 2015 Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 67 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zeng J L, Gao C, Yuan J M 2010 Phys. Rev. E 82 026409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 王均武, 王新兵, 左都罗 2020 激光技术 44 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J W, Wang X B, Zuo D L 2020 Laser Technology 44 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Xie Z, Wu J, Dou Y P, Lin J Q, Tomie T 2019 AIP Adv. 9 085029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wang J W, Wang X B, Zuo D L, Zakharov V S 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 095207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Wagner C, Harned N 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tallents G, Wagenaars E, Pert G 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Schriever G, Semprez O R, Jonkers J, Yoshioka M, Apetz R 2012 J. Microlithogr. Microfabr. Microsyst. 11 021104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Pankert J, Bergmann K, Klein J, Neff W, Rosier O, Seiwert S, Smith C, Probst S, Vaudrevange D, Siemons G, et al. 2004 Emerging Lithographic Technologies VIII Santa Clara, California, May 20, 2004 p152
[5] Sayan S, Chakravorty K, Teramoto Y, Shirai T, Morimoto S, Watanabe H, Sato Y, Aoki K, Liang T, Tezuka Y, et al. 2021 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography XII San Jose, California, United States, March 23, 2021 p116090L
[6] Teramoto Y, Santos B, et al. 2014 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography V San Jose, California, United States, April 17, 2014 p904813
[7] Sayan S, Chakravorty K, Teramoto Y, Santos B, Nagano A, Ashizawa N, Shirai T, Morimoto S, Watanabe H, Aoki K, Sato Y 2023 Optical and EUV Nanolithography XXXVI San Jose, California, United States, May 26, 2023 pPC124940E
[8] Kruecken T 2007 AIP Conf. Proc. 901 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hassanein A, Sizyuk V A, Tolkach V I, Morozov V A, Rice B J 2004 J. Micro/Nanolithgr. MEMS MOEMS 3 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hassanein A, Sizyuk V, Sizyuk T 2008 Emerging Lithographic Technologies XII, San Jose, California, United States, March 20, 2008 p692113
[11] Zakharov V S, Juschkin L, Zakharov S V, O’Sullivan G, Sokel E, Tobin I 2012 International Workshop on EUV and Soft X-Ray Sources Dublin, Ireland, October 8–11, 2012 pS26
[12] Sasaki A, Nishihara K, Sunahara A, Furukawa H, Nishikawa T, Koike F 2010 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography San Jose, California, United States, March 22, 2010 p76363D
[13] Masnavi M, Nakajima M, Hotta E, Horioka K, Niimi G, Sasaki A 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 033306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tsygvintsev I P, Krukovskiy A Y, Gasilov V A, Novikov V G, Romanov I V, Paperny V L, Rupasov A A 2016 Mathematical Models and Computer Simulations 8 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Beyene G A, Tobin I, Juschkin L, Hayden P, O’Sullivan G, Sokell E, Zakharov V S, Zakharov S V, O’Reilly F 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 225201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吴福源, 禇衍运, 叶繁, 李正宏, 杨建伦, Ramis R, 王真, 祁建敏, 周林, 梁川 2017 66 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu F Y, Chu Y Y, Ye F, Li Z H, Yang J L, Ramis R, Wang Z, Qi J M, Zhou L, Liang C 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 陈忠旺, 宁成 2017 66 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng Z W, Ning C 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zakharov S V, Zakharov V S, Choi P, Krukovskiy A Y, Novikov V G, Solomyannaya A D, Berezin A V, Vorontsov A S, Markov M B, Parot’kin S V 2011 Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography II San Jose, California, United States, April 8, 2011 p796932
[19] Zakharov V S 2017 The International Photonics and Optoelectronics Meeting, Wuhan, China, November 3–5, 2017 pASu4A.1
[20] Sasaki A, Sunahara A, Furukawa H, Nishihara K, Nishikawa T, Koike F 2016 J. Phys. Conf. 688 012099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang L J, Qian Z H, Huang X L, Jia S L 2013 IEEE T. Plasma Sci. 41 2015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vovchenko E D, Melekhov A P V 2016 International Conference of Photonics and Information Optics Moscow, Russia, February 3–5, 2016 p012013
[23] More R M, Warren K H, Young D A, Zimmerman G B 1988 Phys. Fluids 31 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sasaki A 2013 High Energ. Dens. Phys. 9 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 汤文辉, 徐彬彬, 冉宪文, 徐志宏 2017 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W H, Xu B B, Ran X W, Xu Z H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 段耀勇, 郭永辉, 邱爱慈 2011 核聚变与等离子体物理 31 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan Y Y, Guo Y H, Qiu A C 2011 Nucl. Fusion Plasma Phys. 31 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 段耀勇, 郭永辉, 邱爱慈, 吴刚 2010 59 5588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan Y Y, Guo Y H, Qiu A C, Wu G 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 5588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Dunning F B, Hulet R G 1997 Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics: Charged Particles (San Diego: Academic Press) p169
[29] 韩小英, 李凌霄, 戴振生, 郑无敌, 谷培俊, 吴泽清 2021 70 115202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han X Y, Li L X, Dai Z S, Zheng W D, Gu P J, Wu Z Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 115202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Vichev I Y, Solomyannaya A D, Grushin A S, Kim D A 2019 High Energ. Dens. Phys. 33 100713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gu M F 2004 AIP Conf. Proc. 730 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Han B, Wang F, Salzmann D, Zhao G 2015 Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 67 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zeng J L, Gao C, Yuan J M 2010 Phys. Rev. E 82 026409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 王均武, 王新兵, 左都罗 2020 激光技术 44 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J W, Wang X B, Zuo D L 2020 Laser Technology 44 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Xie Z, Wu J, Dou Y P, Lin J Q, Tomie T 2019 AIP Adv. 9 085029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wang J W, Wang X B, Zuo D L, Zakharov V S 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 095207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7242
- PDF Downloads: 263
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: